- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Apple Is Organized for Innovation
- Joel M. Podolny
- Morten T. Hansen

When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. Believing that conventional management had stifled innovation, Jobs laid off the general managers of all the business units (in a single day), put the entire company under one P&L, and combined the disparate functional departments of the business units into one functional organization. Although such a structure is common for small entrepreneurial firms, Apple—remarkably—retains it today, even though the company is nearly 40 times as large in terms of revenue and far more complex than it was in 1997. In this article the authors discuss the innovation benefits and leadership challenges of Apple’s distinctive and ever-evolving organizational model in the belief that it may be useful for other companies competing in rapidly changing environments.
It’s about experts leading experts.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Major companies competing in many industries struggle to stay abreast of rapidly changing technologies.
One Major Cause
They are typically organized into business units, each with its own set of functions. Thus the key decision makers—the unit leaders—lack a deep understanding of all the domains that answer to them.
The Apple Model
The company is organized around functions, and expertise aligns with decision rights. Leaders are cross-functionally collaborative and deeply knowledgeable about details.
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to 137,000 employees and $260 billion in revenue in 2019. Much less well-known are the organizational design and the associated leadership model that have played a crucial role in the company’s innovation success.
- Joel M. Podolny is the dean and vice president of Apple University in Cupertino, California. The former dean of the Yale School of Management, Podolny was a professor at Harvard Business School and the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
- MH Morten T. Hansen is a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a faculty member at Apple University, Apple. He is the author of Great at Work and Collaboration and coauthor of Great by Choice . He was named one of the top management thinkers in the world by the Thinkers50 in 2019. MortentHansen
Partner Center
Apple Business Strategy: Plans that made it a Multi-Trillion dollar Company

The study was first published on September 27, 2021, and then updated on September 18, 2023.
This strategy teardown compiles the ideas, innovations, technological research, partnerships, and, most importantly, the strategies responsible for Apple’s growth to such heights.
However, before we move forward, here is a small intro about Apple.
On Friday, June 30, 2023, Apple became the first company in history to reach a $3 trillion market valuation. It stays ahead by half a trillion dollars from the second most-valued company on the planet- Microsoft. Apple is now the most profitable technology corporation in the world.
Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne founded Apple on the 1st of April 1976, bringing creativity to the table through their rendition of a personal computer. Apple is one of the world’s most popular and recognized labels. The company has experienced unparalleled revenue growth, from just $8 billion in 2004 to over $274B last year . This is more when compared to other technology giants out there today, such as Google ($181B) and Microsoft ($143B).
Apple’s growth could primarily be attributed to its business strategy. By combining its designing capabilities, hardware expertise, software prowess, and strategic acquisitions , the company has built an ecosystem that a user doesn’t want to leave.
Vertical integration is another main reason that distinguishes Apple from the competition. It has reaped enormous benefits from the vertical model. It has always built, controlled, and manufactured all of its hardware and software. This inherent benefit assists the corporation in achieving a higher degree of synergy between its hardware and applications. Even the apps are tightly controlled to follow Apple policies. The company also increased its spending on the cost of sales and product R&D to $26,251 billion, which was less than 18% of its total expenditure.
“We have fierce competition at the developer side and the customer side. It’s so competitive, I would describe it as a street fight for market share in the smartphone business.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple Inc.
Apple’s business strategy consists of the following four elements:
- Focus on product design and functionality
- Strengthening Apple’s ecosystem
- Improving consumer service experience
- Reducing the business’s reliance on iPhone sales
As for the product and service categories, Apple Inc. includes iPhone, Mac, iPad, Wearables, Home and Accessories, and Services like iMessage, FaceTime, Apple Maps, etc.
This study explores Apple’s business strategy that will help you acquire some basic principles that could be applied to any kind of business, even yours. So, if you’d like the entire analysis in PDF form that you can download and save for later reading (or sharing with your friends), just fill out the form below, and we’ll deliver it right to your inbox.
Now, let’s dive deep into the reasons behind Apple’s success.
Table of Contents
History of Apple
These products and strategies helped apple win before the launch of the iphone..
While the iMac sparked Apple’s rebirth in 1998, the introduction of the iPod in Oct 2001 sent the company to the top of the world’s most valuable companies list.
“With the iPod, Apple has invented a whole new category of digital music player that lets you put your entire music collection in your pocket and listen to it wherever you go,” said Steve Jobs, Apple’s CEO. “With iPod, listening to music will never be the same again.” We all know digital music players used to exist before the iPod, but as we know, Apple’s marketing is phenomenal at positioning its products.
The iPod was introduced as a part of Apple’s digital hub strategy . The iPod had unparalleled marketing and promotional exposure. Apple introduced a new kind of digital music player with the iPod, allowing users to carry their complete music library in their pocket and listen to it on the move.
The device’s original edition was released with 5GB and 10GB capacities , beginning at just under £300. The iPod was a spectacular success, increasing Apple’s overall revenue from $1.9 billion in Q1 of 2000 to $3.2 billion in the same quarter of 2001.
After dropping the price of the 5GB iPod to $299 in July 2002 and expanding compatibility to Windows, the iPod became the best-selling digital music player in history until smartphones came along.
By 2004, it had established a strong market leadership position in the worldwide digital music player sector. Apple spent a lot of money advertising the iPod . The advertising, which featured shadows dancing to the rhythms of their iPods, could be found in print, on television, and on billboards. In a relatively short period, Apple established an iconic image for the iPod that drew both young and old people. The iPod period, which began in 2001, ended in 2014.
With the introduction of iTunes in 2001, Apple opened up a vast new market sector in digital music, which it has now controlled for more than a decade. Customers worldwide flocked to iTunes because of the incredible value it provided, and music companies and artists benefited as well. Furthermore, Apple safeguarded recording companies by developing copyright protection that was not inconvenient for customers. While the company has dominated this blue ocean for more than a decade, as new online businesses entered the market, the issue for Apple has been to maintain its sights on the expanding mainstream market rather than competitive benchmarking or high-end niche marketing.
As iTunes’ success developed, so did its content offerings – one of the most important aspects of Apple’s digital domination was how it adapted what it learned from selling music to TV shows, movies, and, eventually, applications. The company created and employed a distribution strategy as well as a usage model to continue adding media to the three prongs of its ecosystem.
Steve Jobs introduced the initial 15-inch MacBook Pro , Apple’s thinnest, quickest, and lightest notebook to date, in 2006. The MacBook was a tremendous hit with buyers, and it was one of the reasons that Mac sales were rising three times faster than PC sales.
The Apple TV , which debuted in March 2007, was praised for its attractive interface, painless setup, and overall ease of use – all of which marked a significant shift from prior network-based home entertainment systems. Almost a year later, the hardware remained the same, but a free software upgrade essentially gave the device a makeover. Apple subsequently reduced the price of the 40GB model to $229, while the 160GB model was reduced to $329.
Apple’s award-winning computers, OS X operating system, and iLife, and professional apps continued to set the industry standard for innovation. It was also at the forefront of the digital media revolution with its iPod portable music and video players and iTunes online store, as well as its innovative iPhone entry into the mobile phone industry.
In 2007, Apple entered the mobile market with the iPhone , which was widely praised for its unique design, touch-screen capabilities, and lack of a conventional keyboard.
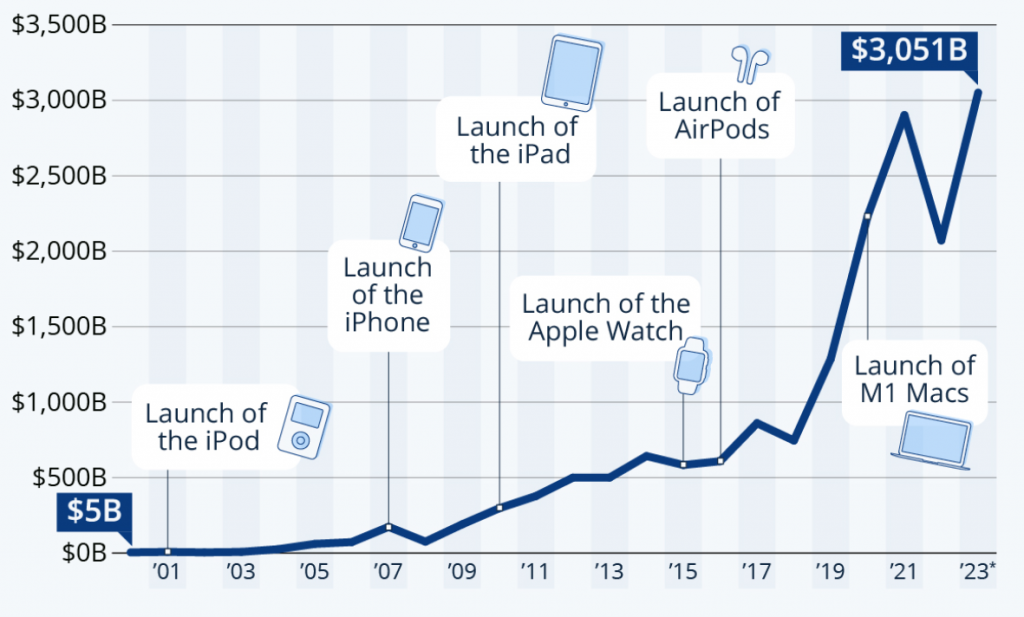
Apple Market Cap as of June 2023 – source
Apple’s Product Strategies After the Launch of the iPhone
After the launch of the first-generation iPhone, the company’s product strategy was very clear, i.e., ‘ Design a high-end smartphone in which the user experience is more important than making a slew of features available.’
The iPhone was not the first smartphone to have a mobile Web, email, and touch-screen user interface, but it was intended to have a better experience than most smartphones. Another strategy was to have superior technology, which included the mobile operating system and the thousands of mobile applications available via the App Store.
Before the launch of the iPhone, the annual revenue of Apple — in the year 2006 — was $19.3 billion, which increased to $24.4 billion in 2007 and $37.4 billion in 2008. And since 2008, iPhones have been Apple’s main source of revenue.
The launch became one of the most anticipated technological product launches in Apple’s history, owing to the company’s masterful media build-up. After the launch of the iPhone on January 9, 2007, the share price of Apple’s stock boosted and doubled to a value of $179.40 on January 9, 2008. The iPhone was described as a mix between its iconic iPod music player and a mobile phone programmed to browse the Internet.
Apple Inc. used the strong reputation of the Apple brand and the success of the iPod to penetrate the competitive cell phone market, a move that may have posed a possible challenge to the company as other firms launched smartphones with strong music storage and playback capabilities.
During the iPhone’s two-year growth phase, Jobs launched a campaign to secure a wireless company as the iPhone’s exclusive carrier. Customers who purchased an iPhone were forced to sign a two-year wireless deal with AT&T Inc. to make calls or access the phone’s other capabilities. Apple had even struck agreements with Viacom, Disney, Google, and Yahoo, all of which were carefully chosen to add internet applications to the iPhone.
Apple chose a promotion and delivery policy in European countries that were similar to its strategy in the United States. In France, it offered France Telecom’s smartphone affiliate, Orange, to be the sole carrier. Even in the United Kingdom, Telefonica’s telecom division, O2, was chosen as the sole cellular provider for iPhone customers with a two-year contract.
Apple developed a clear overall marketing strategy for the iPhone and successfully managed every aspect of the iPhone’s launch. Despite some shortcomings and pitfalls, the company was able to create a one-of-a-kind package for tech-savvy buyers interested in a hybrid mobile phone-music player and make those customers aware of the device through well-managed marketing campaigns and positive advertising. Both of these efforts significantly increased Apple’s stock price and solidified its status as a pioneer in consumer electronic gadgetry.
After the launch of the iPhone, the company adopted the strategy of patenting everything it does. The vigorous patenting helped shield Apple from competitors working on related technologies. It also provided Apple with a legal arm for the future.
One of Apple’s attorneys explained, “We basically tried to patent everything … And we tried to patent it as many different ways as we could, even the stuff we weren’t 100% sure would go in a product.”
Apple, too, has been chasing and implementing its design patents, endangering the whole technology industry. It has adopted a policy of patenting any tiny recognizable bit of its merchandise, including design patents, which protect a product’s ornamental appearance rather than its usable components.
Presently, out of the total revenue of Apple Inc., the maximum revenue is generated from the sales of the iPhone. The iPhone sales continue to be the most significant contributor to their total revenue, routinely averaging over 50%! We’ll discuss their annual revenue breakdown further down in this article.
Now that we have covered the strategic aspects, let’s examine the company’s financial information, growth and revenue numbers for the last few years, and projected growth going forward.
What does Apple’s Financial Growth look like?
Growth projection and market-related factors.
Under a realistic growth profile, Apple’s revenue is expected to grow by 9.66% over 10 years. Capital expenditures are estimated to be valued at $11 billion from 2024 to 2026 and $9 billion from 2027 to 2031. Also, over the 10-year forecast period, Apple’s earnings per share (EPS) are expected to increase by 10.68% .
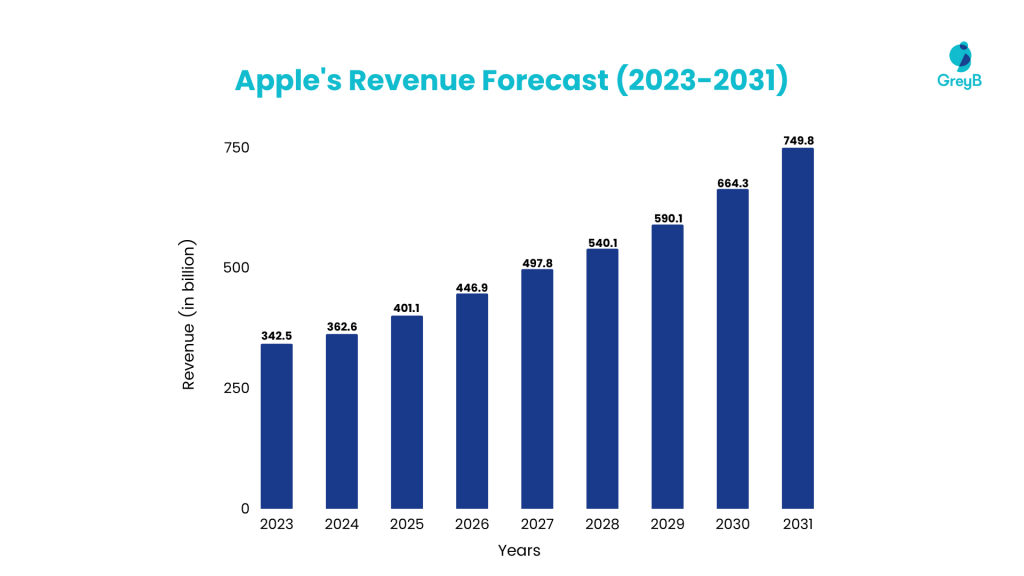
Apple’s growth would continue over the next 10 years, and while substantial risks do exist, early warnings and evaluations may efficiently monitor them.
The following are some of the market-related factors that influence Apple’s growth projections:
- Due to increased demand, the Mac and iPad will flourish in the coming decade.
- High customer satisfaction scores with Apple’s products, 82/100 (2020 survey by MBLM).
- The App Store gives several benefits to users, such as privacy, curated quality applications, protection from malware and malicious scams, etc.
- Home and Accessories, Wearables, and Services provide opportunities for several decades.
- The future launch of new products, namely the Apple Car, AR/VR headset, and AR smart glasses.
- Increased anticipation for future iPhone models.
Revenue of the Last 5 Years (in $ Billion)
Apple’s annual revenue in fiscal year 2022 was $394.32 Billion, an 8% growth over the previous year. It’s less impressive than the 33% jump from 2020 to 2021, but it’s a positive trend nonetheless. Here’s the breakdown of Apple’s revenue in the last five years across its most notable business lines.
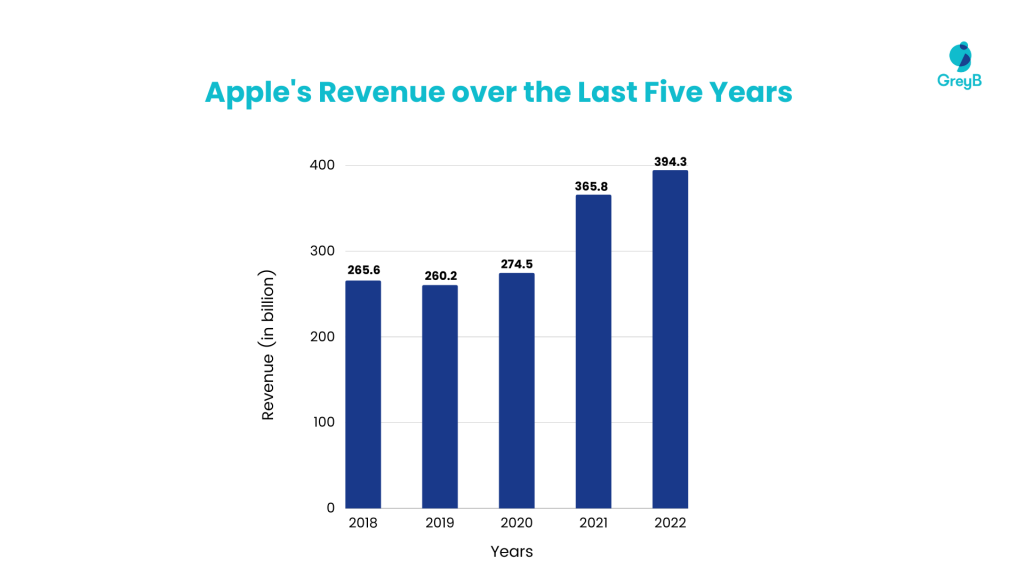
Apple’s iPhone sales revenue grew by 7% from 2021 and approximately 40% compared to 2020. Mac and services, like Apple Music and Apple TV, saw higher growth in 2021-2022, up nearly 14% year-over-year.
Between September 2021 and 2022, iPhone sales accounted for 52% of the company’s total revenue! The 3-year revenue breakdown below provides more details .
Revenue Breakdown (Section-Wise) of the Last 3 Years
The last three annual reports of Apple suggest that the iPhone category had the highest revenue amongst all the categories of Apple. The breakdown of revenue for the last 3 years is listed below:
| 205,489 | 7% | 191,973 | 39% | 137,781 | |
| 40,177 | 14% | 35,190 | 23% | 28,622 | |
| 29,292 | (8)% | 31,862 | 34% | 23,724 | |
| 41,241 | 7% | 38,367 | 25% | 30,620 | |
| 78,129 | 14% | 68,425 | 27% | 53,768 | |
- Apple currently has 2 billion active devices globally.
- Apple’s net expenditures in 2022 were $295.5 billion, leaving them a hefty $99.8 billion profit.
- The company’s new iPhone models released during the fourth quarter of 2021 were a massive success.
- Mac sales netted approximately $5 billion more than fiscal year 2021. Their new Mac Studio with the Apple M1 Max chip may have attracted people looking for powerful desk workstation upgrades.
- iPad Pro sales decreased from 2021 to 2022, leading to a relatively small reduction in revenue. This is likely because no other iPad lineup was noticeably refreshed during this period with notable features, except for integrating the M1 chip. In addition, Apple had said during this period that it had faced supply issues with the iPad, which may have impacted sales.
The corporation has been vigorously investing in research and development to ensure an increased revenue stream. Let’s now look at Apple’s R&D strategy and the tech areas in which the company is increasingly investing.
What does Apple’s R&D investment strategy look like?
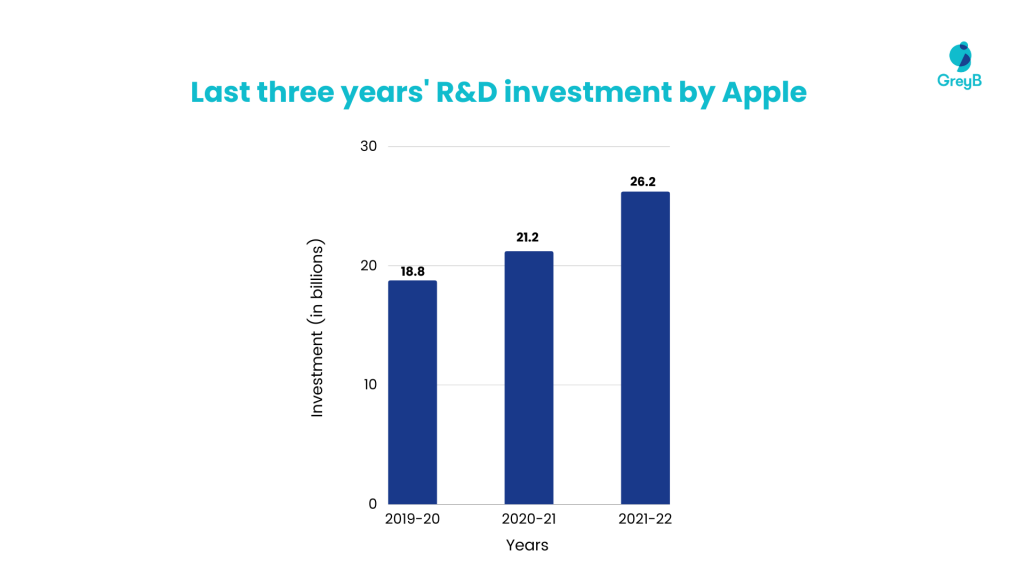
The tech giant has vigorously invested in research and development to ensure an increased revenue stream. We observed that Apple continuously increases its R&D budget each year, with 2022 closing in at $26.2 billion, increasing by about $4 billion from 2021.
How much has Apple invested in R&D in the Past 3 Years (in $ Billion)?
- In 2020, several patents revealed that Apple focuses on wearables, fitness, and health innovations. Various wearable patents indicated that the company could target AirPods with biometric sensors, Apple Watch with UV tracking, motion recognition for AR/VR applications, machine learning experiments to allow autonomous driving, and incorporation of various existing devices with a vehicle.
- In 2021, they launched several noteworthy products. Perhaps the most disruptive of them was AirTag. These item trackers have quickly become so popular that Apple sold 20 million units within eight months of launch! Now, analysts claim Apple is projected to sell 55 million AirTags by the end of this year.
- In 2022, they introduced the Apple Watch Ultra to their product line. It’s their flagship wearable device with several top-tier features like a titanium build, two times brighter display, and a dual-frequency GPS system, among other things. Driven by this model, the Apple Watch accounted for 34.1% of total smartwatch shipments in 2022 and 60% of the revenue for the global market.
Which Tech Areas is Apple focusing its R&D on?
Apple Inc. had invested in further expanding its research and development centers globally. The company had invested over half a billion dollars in research development centers in China alone. The company also concentrated on R&D centers in the United Kingdom, owing to their increasing emphasis on creating unique innovations to underpin its product designs, including A-series processors, W-series wireless chips, unique manufacturing, materials experience, speech recognition, machine intelligence, and many more.
These are the key areas where the company focuses its innovation efforts the most.
Apple invests heavily in developing new hardware for its products. Their most recent and notable advancement has been with their M-series processors for computers to supplement their excellent A-series mobile chips. These have smashed benchmarks worldwide, delivering chart-topping performance and power efficiencies never seen before. They make some of the best pro-grade displays , too.
Apple’s software development efforts include creating new operating systems for their products, new applications, and services. All their software products are designed and optimized for their ecosystem, allowing seamless inter-device connectivity. This interconnected approach to innovation can be seen throughout their designs, like on this expansive 358-page patent they filed for the first iPhone’s multi-touch capability .
Artificial Intelligence
Apple also invests in artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve its products and services. They’ve made numerous acquisitions to enhance their in-house AI capabilities, which we will discuss further in this article. Their advanced machine learning algorithms enable many features, ranging from FaceID’s fundamental security to fun AR Animojis on Facetime calls.
Healthcare Technology
Apple has been expanding its focus on healthcare , developing health-related features for its devices, such as the Apple Watch. Alongside regular customers, Apple wishes to be the go-to choice among doctors and healthcare professionals as well. They’ve partnered with healthcare providers like Geisinger and Ochsner to provide a seamless way for doctors and patients to connect. Their CEO, Tim Cook, has often made it clear that healthcare is one of Apple’s top priorities as a business sector.
Augmented/Virtual Reality
Spatial computing is one of Apple’s lesser-known yet rapidly developing departments. Our research suggests that Apple has been working on an AR and VR-capable wearable device for nearly 16 years!
“The products that are in R&D, there is quite a bit of investment in there for products and services that are not currently shipping or derivations of what is currently shipping…You can look at the growth rate and conclude that there’s a lot of stuff that we’re doing beyond the current products.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple Inc.
Which Core Innovation Areas Is Apple Majorly Focusing on?
For the tenth year in a row, Forbes magazine ranked the company as the most valuable brand in the world in 2020. Apple took second place in 2023, around $2 billion shy of Amazon in brand value. Nonetheless, Apple has risen to become the world’s largest company by market capitalization, not by attempting to become the largest smartphone provider but by becoming the most beloved. Apple, more than any other tech company, has always prioritized the end-user experience over anything else, not just the speed, storage capacity, or other technical specifications of its products.
Apple’s innovations are often incremental, with the company adapting its design expertise to the most recent consumer tech trends. Apple did not invent the MP3 player or the smartphone, but it went on to dominate both devices by emphasizing design, user experience, and brand cachet. The company has aggressively increased the domains where the Apple experience is part of daily life during the last ten years.
Apple guarantees that the universe of Apple-mediated behaviors continues to grow by encouraging app developers while strictly enforcing rules. By reinventing product form factor and function, from computing in a user’s pocket to managing home electronics to reminding the calorie count or parking spot — all of these experiences are connected, integrated, and packaged in a single accessible ecosystem of complimentary items.
Moreover, Apple has focused on innovation outside the core by developing the infrastructure required to support this ecosystem safely and frictionlessly (Apple Pay secure payments or biometric facial recognition since the iPhone X).
We have mentioned before that Apple vigorously patented everything it did. After looking at the wide array of domains on which Apple works, it becomes important to examine the kind of patent portfolio Apple has accumulated over the years.
What does Apple Patent Portfolio look like?
A company’s patent portfolio provides us with another set of lenses to find the core areas it has been focusing on for quite some time and what it plans to launch next. Let’s take a deep dive.
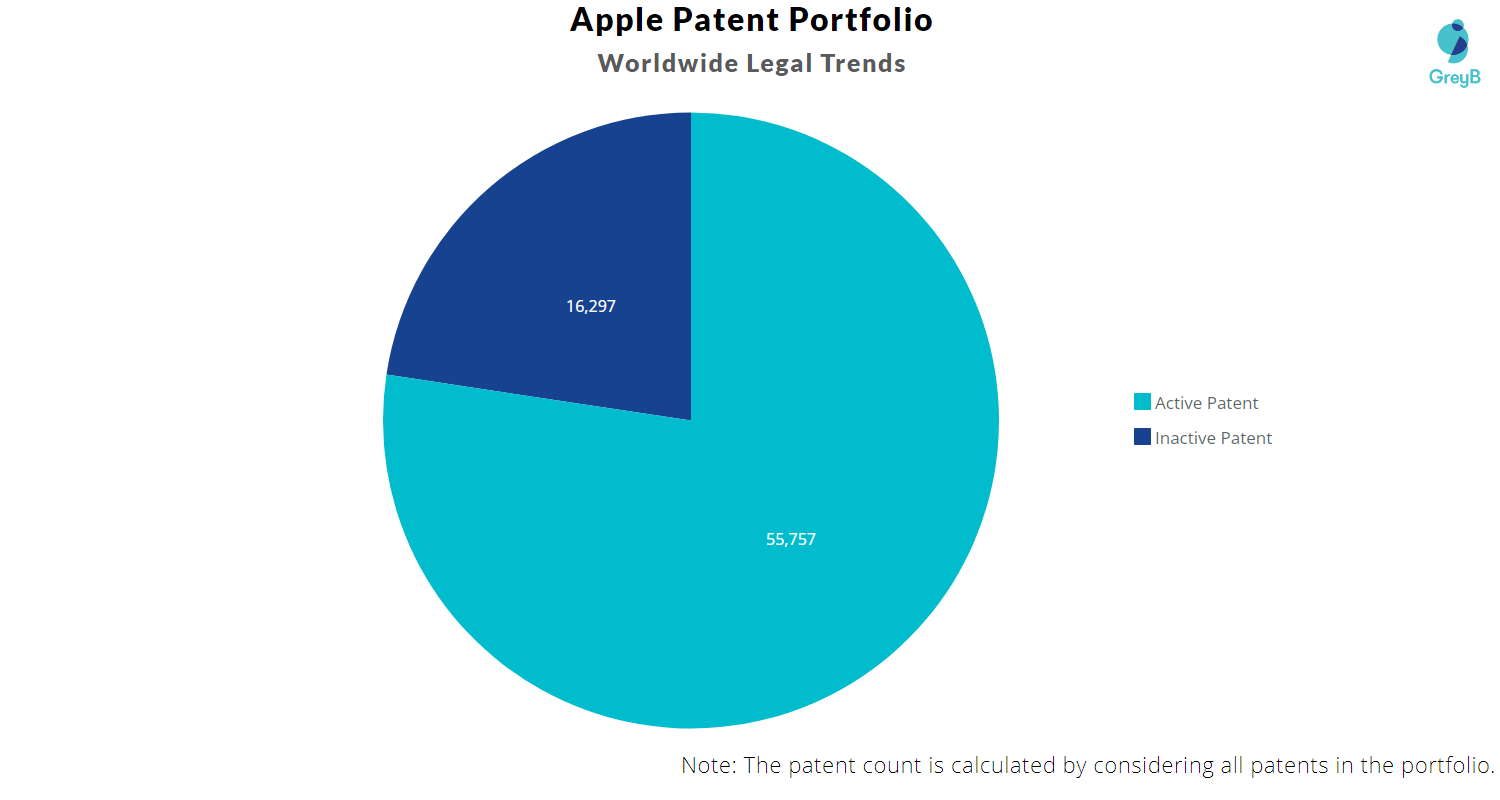
Source: Insights;Gate by GreyB
With 72000+ patents (24000+ patent families) in its entire portfolio, Apple is one of the top patent filing companies in the world. It has more than 55000 patents that are still active.
Looking at the filing trend, you can see the year 2007 saw a sharp increase. It was the same year they launched the iPhone. One can conclude that the iPhone is one of the reasons Apple invested heavily in securing its technologies.
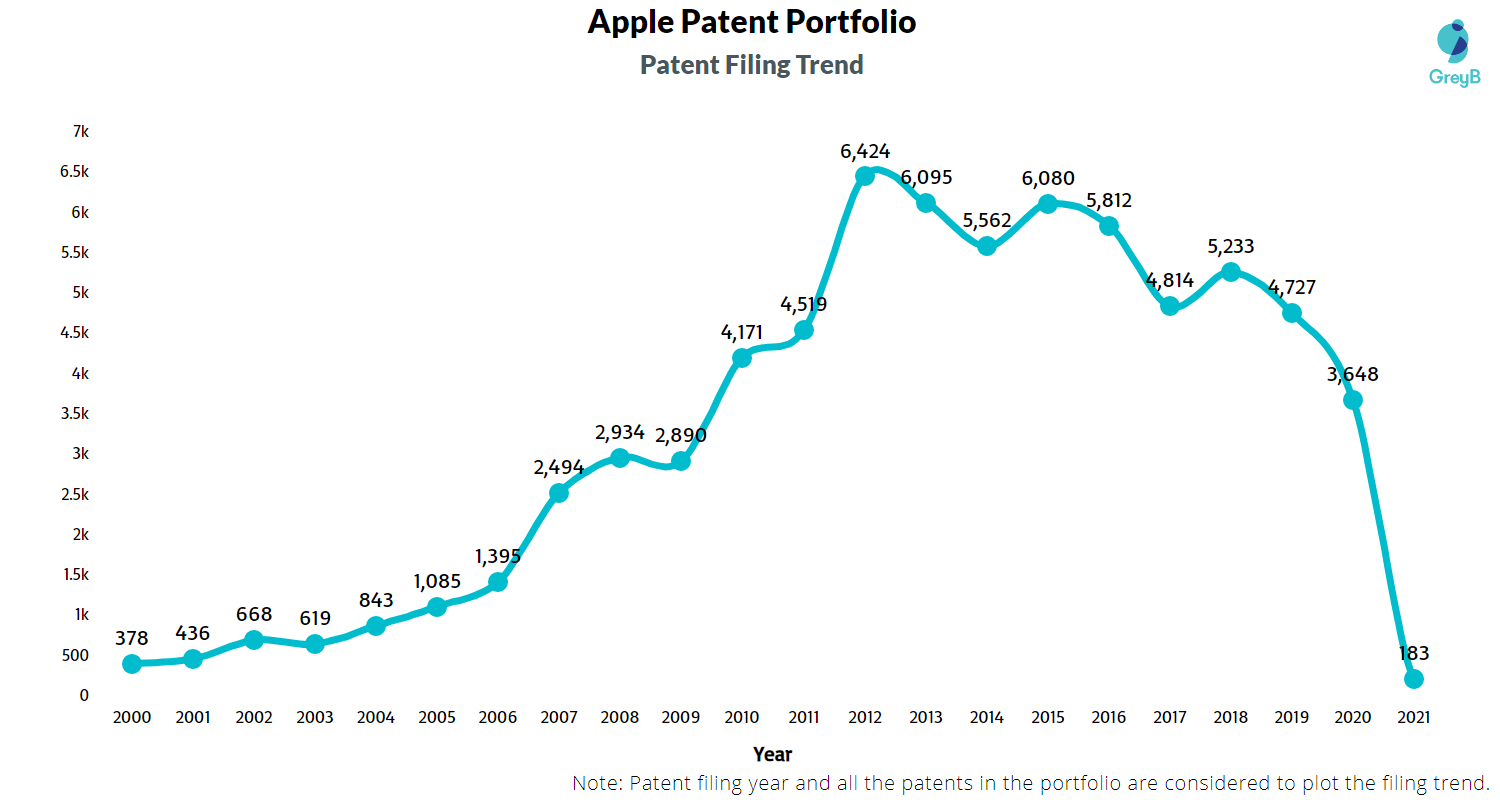
The Apple vs Samsung lawsuit is still one of the largest patent infringement lawsuits that happened in the tech industry. And that further pushed the consumer electronic gadgetry pioneer to invest more in patents. (See the growth in 2012)
One of the reasons for this growth is Apple’s consideration to secure its tech in more countries. As Apple is gaining more and more global markets, it is securing its patents in more and more jurisdictions.
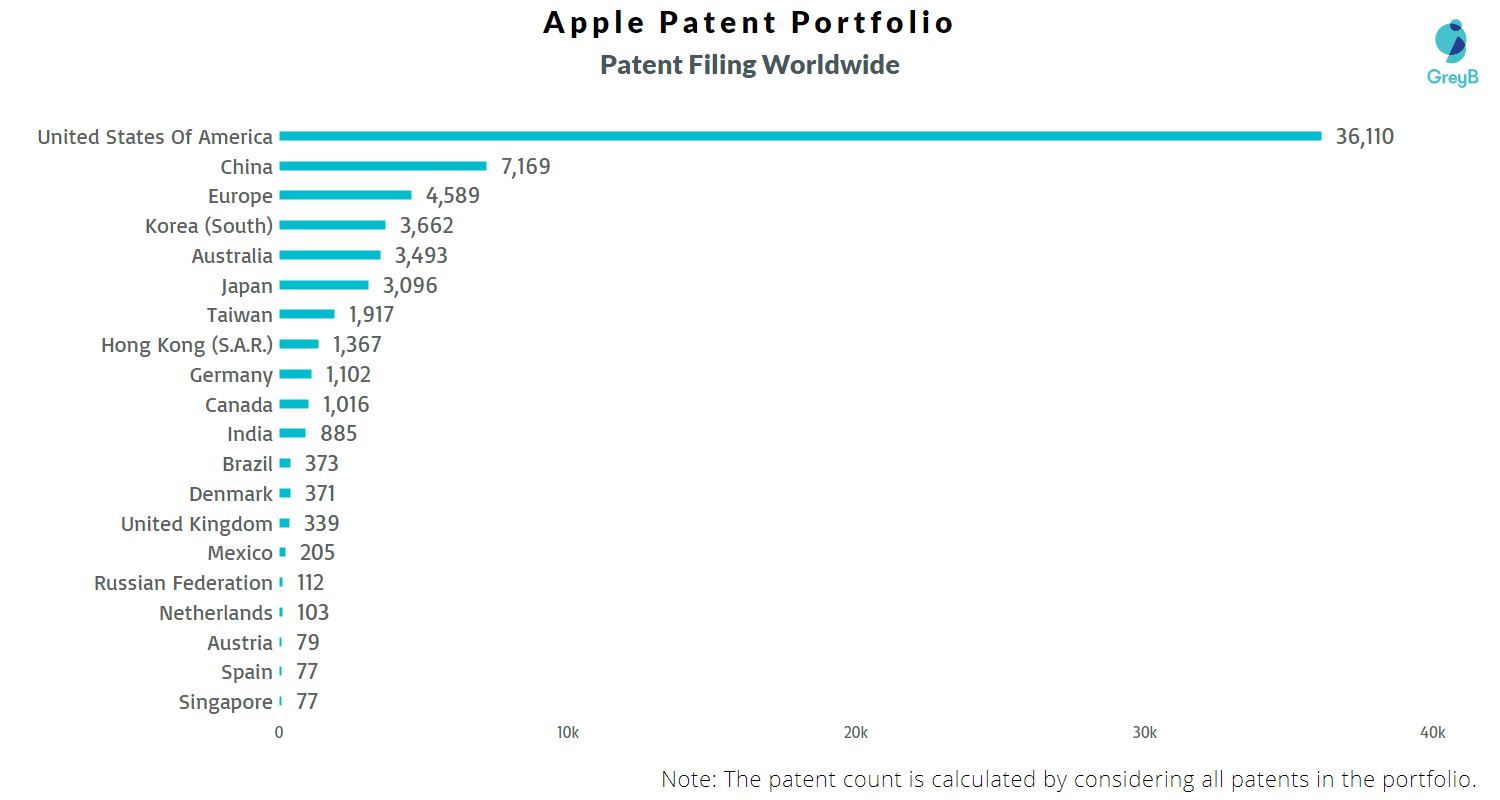
The US is the home market for Apple, so, naturally, the company has the most patents in the US. China is a crucial market for smartphone makers now more than ever. China has become more patent aware thus most of the big companies are trying to secure more and more technologies/patents in the country. Apple being one of the biggest technology companies, it makes sense that it has secured thousands of patents in China.
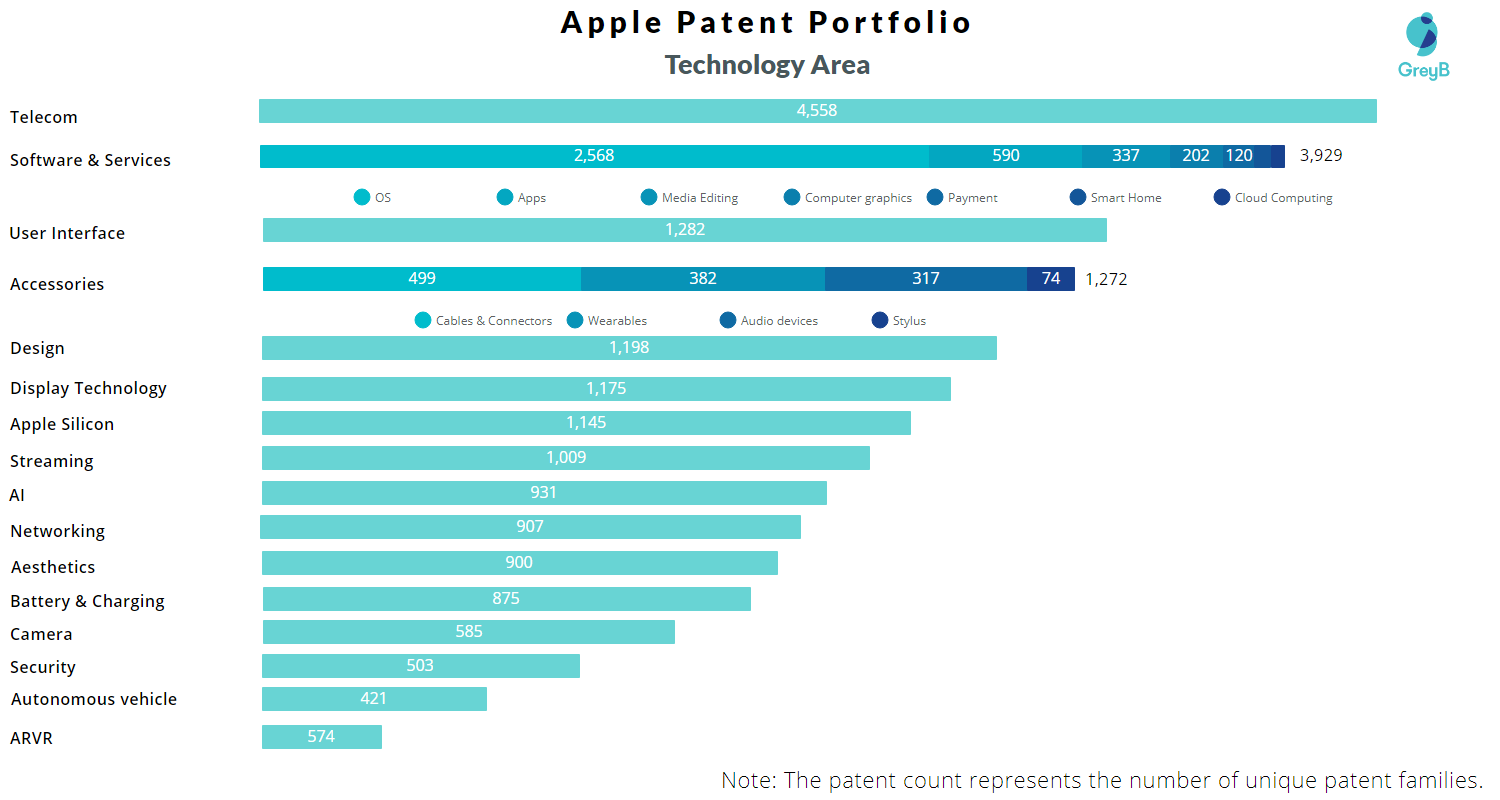
The huge portfolio of Apple is categorized into 16 different technologies that the company uses for its products/services or future products.
Being a smartphone manufacturer makes Apple research heavily in the Telecom sector, which is also crucial for companies, especially when 5G is on the doorstep.
Another interesting figure is of Apple’s design patents. The company focuses greatly on the design part, and the patent count is proof of how valuable product designs are for Apple.
Apple hasn’t made any public announcements yet on their Autonomous Vehicle front, but the AR/VR space is where we had a long-awaited announcement in June 2023 – their Vision Pro headset. We’ll discuss this in more detail in the upcoming sections.
Moving forward, let’s go through Apple’s expertise in various sections.
What are the products and services responsible for Apple’s growth?
Design and functionality.
Apple’s competitive advantages include software control, hardware control, retail strategy, product differentiation, and, most importantly, Steve Jobs’ strategic decision-making. Since its foundation, the company has introduced simple-to-use computers to the market so that people would not face any issues while using Apple goods. Apple used both horizontal and vertical integration. It depended on its designs and refused to let third-party access to its hardware. Apple employed superior software, which aided it in increasing its market share. The company also provided a comprehensive desktop solution with hardware, software, and other components. Apple has always used typical designs for its products.
Apple has over 4,000 design patents in its portfolio, which is a big number.
Consumer Electronics
Apple Inc., a computing and consumer electronics giant, is one of the world’s most recognizable and famous brands, with hundreds of its retail shops. A globally leading consumer electronics developer with key products including the iPhone, which runs Apple’s IOS operating system, personal computers (Macs), and tablet computers (iPads), all of which utilize Apple’s exclusive operating systems. Other notable products include the Apple Watch, AirPod, Homepod smart speakers, Apple TV streaming device, Beats headphones, and iPod Touch music player.
The company’s product strategy results in extremely high-quality products. It’s known as the “great product” strategy.
Apple refuses to join the bandwagon other gadget makers employ by maintaining high-quality standards. The “great product” strategy emphasizes quality over quantity as well.
While other manufacturers’ strategies include releasing items one after the other quickly and having such a diverse product mix, Apple opted to stick to what it does well.
Smartphones (iPhones)
Since 2008, the iPhone has been Apple’s most valuable product and its primary source of income. Although Apple has expanded its product range with the Watch, AirPods, and services, the iPhone still accounts for 50% of its income. The company’s extensive relations with China, particularly in the manufacturing sector, are one of the key bear arguments.
Most of Apple’s products are manufactured in China. While Apple has been expanding production into other countries, recent estimates suggest that 95% of the total iPhone supply still comes from China. Apple also has manufacturing facilities and assembly lines in other countries, such as the United States, Ireland, and Brazil.
Three of the company’s aforementioned contract partners, all of whom are situated in Taiwan, made relocation news in the summer of 2020:
- Foxconn began producing the iPhone 11 in India in July 2020 and had invested $1 billion in the nation.
- Pegatron established a subsidiary in India.
The demographic of iPhone users changes a little each year. Here are some of the latest statistics on iPhone users:
- 51% of iPhone users are female, while males make up the remaining 49%
- The 16 – 34 age group has the highest number of iPhone users
- 35% of iPhone owners also have an Apple Watch
- The average income of iPhone users in the US is 85,000 USD
Its main competitors in the worldwide smartphone industry are Samsung and Huawei, with the business following the other two with a share of 13.5 % in the most recent quarter.
In the second quarter of 2023, Apple’s global market share for the iPhone was 17%, while Samsung’s, Xiaomi’s, and Oppo’s market shares were 20%, 12%, and 10%, respectively. The company sold 845.3 million smartphones in the second quarter of 2023, while Samsung sold 53.5 million handsets. Xiaomi and Oppo, respectively, sold 33.2 million and 28 million units.
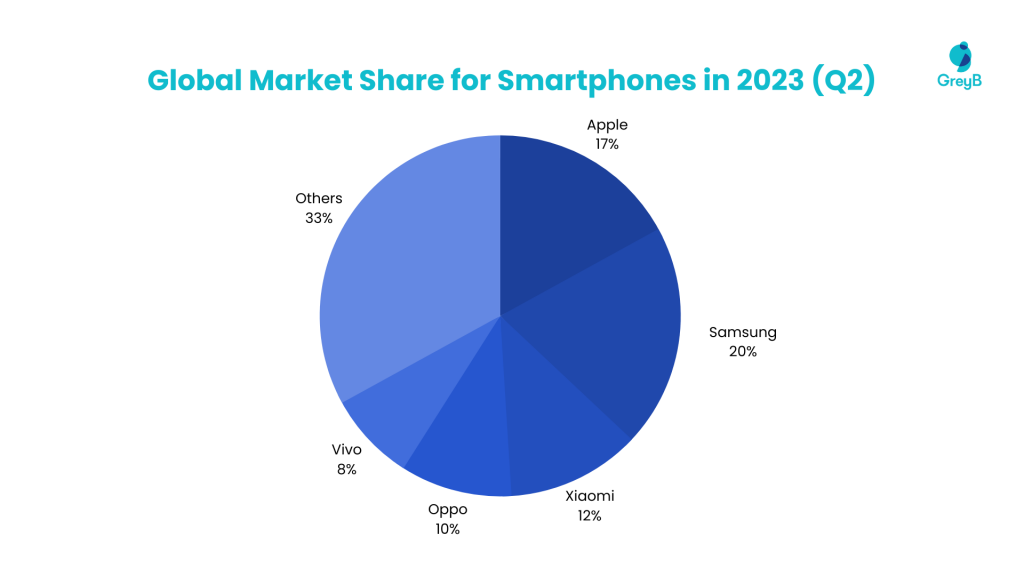
Apple’s iPhone is the market leader due to excellent hardware and software integration and control over both sides of the equation. Any Android app will lag in terms of speed and performance when compared to an iPhone app.
In 2021, Apple spent an additional $45 million on Corning, which manufactures the glass used in the iPhone, Apple Watch, and iPad. In May 2021, the company announced a $410 million grant to II-VI, which develops the technology for the iPhone’s Face ID and Portrait mode.
With over 1 billion iPhones in use, Apple is the doorway to the most valuable clients in the mobile industry. In 2021, Apple has updated its iPhone software and allows consumers to choose whether they want to be followed for targeted adverts.
Even though both iOS and Android have millions of apps in their app stores, developers still prefer the iPhone as the launch platform of choice for the latest new apps. Mario Run, for example, was released for iOS in December 2016 and Android in March 2017. Instagram for Android was released two years later for the iPhone.
The iPhone 15 lineup in 2023 builds upon the foundations set by the 14 series with additional features like USB-C replacing the lightning port, the dynamic island-inspired design on the 15 and 15 Plus, and the newer A17 Pro chip on the “Pro” models. Apple says the A17 Pro is the industry’s first chip to feature a 3-nanometer fabrication process.
And thankfully, the rumors about the USB ports being locked behind the MFi authentication layer were false.
Smart Speakers (HomePod)
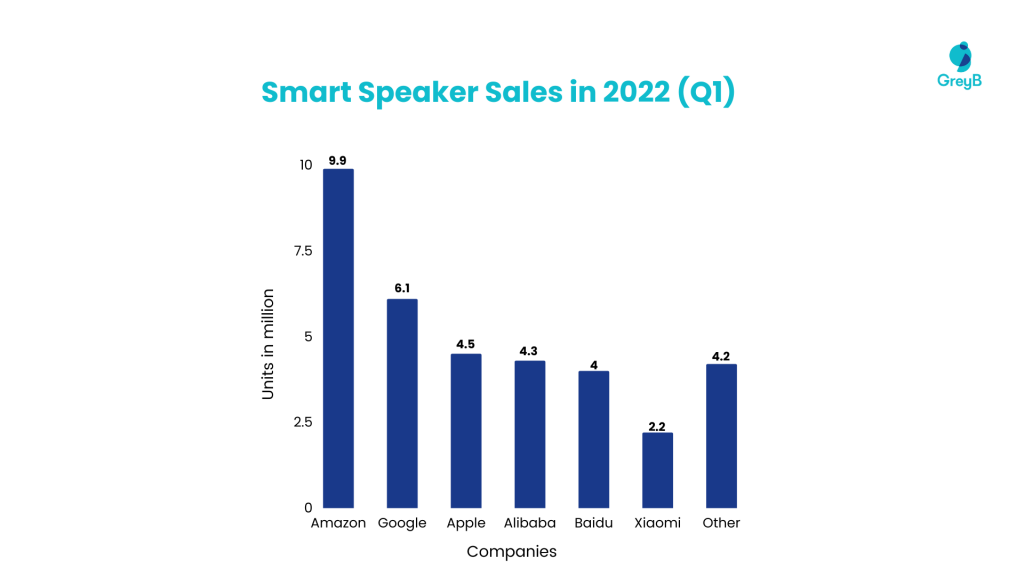
HomePod has experienced limited success in the Smart Speakers market. Apple trailed Amazon and Google in terms of unit sales . However , the release of the HomePod Mini has made significant advances, enabling Apple to double its share in the smart speaker market in 2021. According to survey results from Statista Consumer Insights, Amazon remains the clear market leader in the smart speaker segment in the United States. Apple took third place among the global smart speaker sellers as of Q1 2022.
Apple’s HomePod is the best-sounding wireless smart speaker today, and it can be operated by speech using the in-house virtual assistant, Siri. However, the HomePod is only worth considering if the owner possesses an iPhone and subscribes to Apple Music. In March 2021, Apple announced the discontinuation of the original Homepod after 4 years and indicated its focus on the mini Homepod it released last year.
Laptop & PC (MacBook and Mac)
Despite Apple’s shift in priority from PC to mobile, the Mac has remained a key component of the company’s product lineup. The company has maintained a core group of devices throughout the decade: the MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, Mac Pro, and iMac. Even after modifications and new models, its core has remained popular among many professional clients.
In 2022, Apple had a 9.8% market share, following market leaders Lenovo, which had a 24.1% market share, HP Inc., which had a 19.4% market share, and Dell, which had a 17.5% market share.
When a customer purchases a Mac, that purchase is a philosophy as much as it is a piece of computer technology. The hardware and software are produced by the same corporation, and the laptops share an aesthetic sensibility with Apple phones and tablets.
Macs are popular among music producers due to Apple’s high-end Logic Pro software and the user-friendly GarageBand program, both of which are free. Apple acquired Emagic, a music production software, on July 1, 2002, for $30 million as the foundation for these two apps.
In addition, other Apple-exclusive media software like Final Cut Pro and Pixelmator could convince photo and video editors to switch to Mac OS.
Apple Watch
Since its debut in 2015, Apple Watch has dominated the smartwatch industry, with a market share of 40% in Q4 2020 .
According to Counterpoint Research, Apple Watch shipments increased by 19% between 2019 and 2020, reaching 33.9 million units in 2020. In Q4 2020, Apple Watch Series 6 and SE delivered 12.9 million devices. Further, markets such as India saw strong demand for Apple Watch Series 3 and 6 in 2020, with a growth of 144.3% in overall Apple wearable devices shipments.
Apple dominated the market in 2022 with a 30% share, followed by Samsung at 10.1% and Huawei at 6.9%, among others.
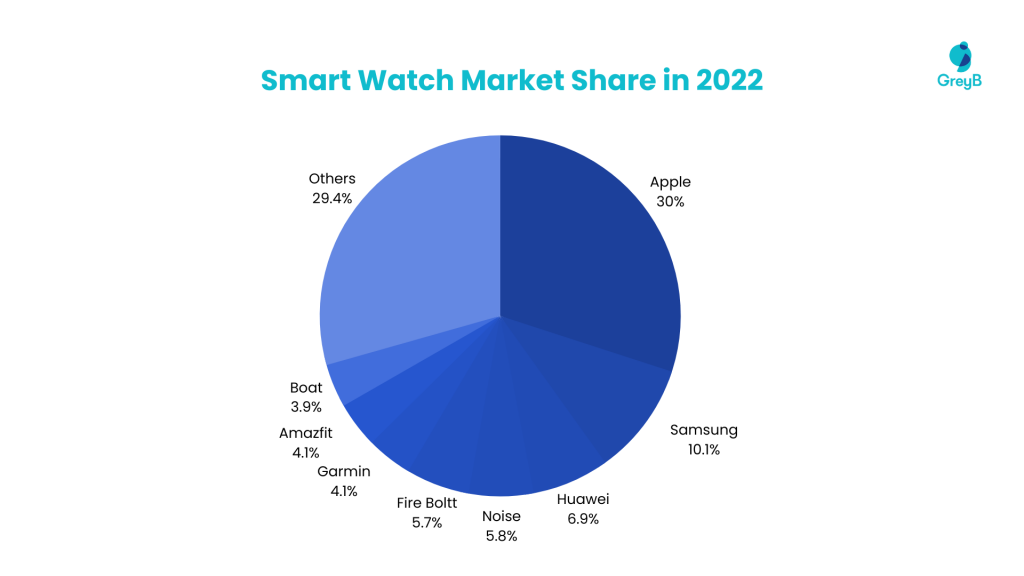
The same trends are also reflected in Q1 of 2023 , where Apple is leading the market with a 26% share and Samsung at 9%.
The Apple Watch is the greatest smartwatch on any platform in terms of appearance, message handling, activity tracking, app choices, and battery life. The Apple Watch is water resistant to 50 meters, making it ideal for swimming and surfing. The Sleep app monitors the user’s sleeping habits and assists in creating a plan and bedtime routine to accomplish sleep goals. Apple is, in fact, making strides in the Healthcare sector with its Apple watch.
Read Now: Apple in Healthcare: Top MedTech Acquisitions and How Can You Gain an Edge over it?
AirPod and AirPod Max
Apple’s AirPods have grown into a significant business for the company, with 114 million sold by 2020. A commodity that many saw as an expensive accessory has become common, with nearly every phone maker selling their own ‘hearable’ to compete with Apple. Apple was ahead of the pack in Q2 of 2022, holding 27.8% of the total market share. Samsung and Xiaomi followed up with 9.3% and 5.3% respectively.
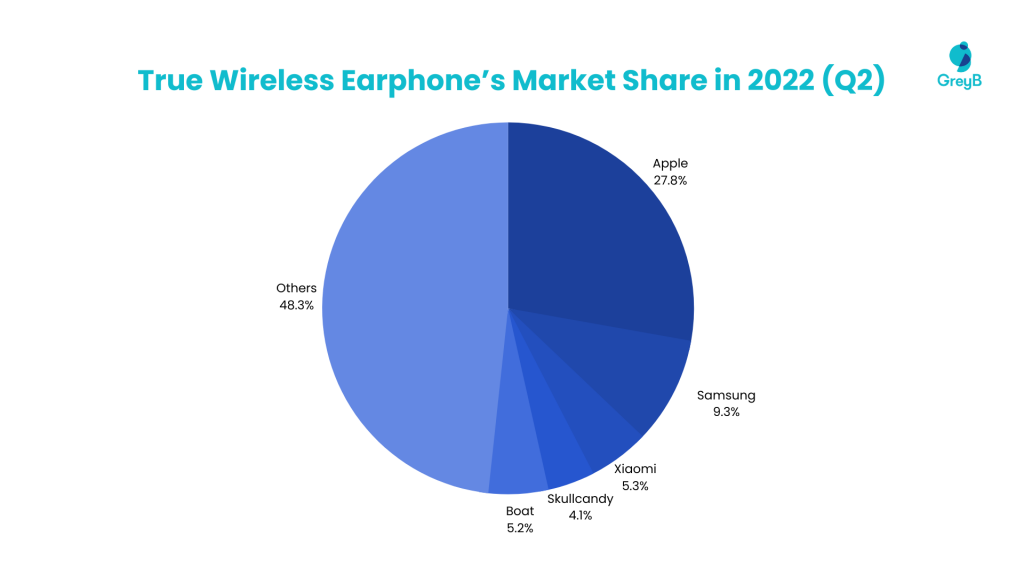
Further, Apple released AirPod Max, Bluetooth over-ear headphones, in Dec 2020 with a price tag of $549. While Analysts estimated that AirPod Max won’t boost Apple sales because of a niche market, some expect that it could boost AirPod sales because of Apple’s Goldilocks strategy.
Cybart forecasts that Apple’s wearables segment will generate $30 billion in revenue by 2021, including the Watch, AirPods, and select Beats headphones.
The five reasons why Apple built a strong wearables business are mentioned below:
- Early adopter: One of Apple’s guiding principles is to make technology more personal, and it began investing in wearables, including its silicon processors, in the early 2010s.
- Other corporations gambled on voice: Because few Large Tech businesses had Apple’s hardware competence, they bet big on voice (example: Amazon’s Echo) as the future computing paradigm. It appeared to be a bad gamble.
- Design expertise: People must desire to wear wearables, which requires design skills. Apple has a track record (and aptitude) for designing devices that consumers want to show off as much for its aesthetic as it does for its computational capabilities.
- Advantage of the supply chain: Wearable technology is built on top of smartphone components. Apple has been able to capitalize on lessons learned and partnerships formed through the iPhone production process.
- Advantage of the ecosystem: Apple’s entry-level AirPods and Watch were around $200. Because the wearables effectively share computational power with the iPhone, it achieved these pricing thresholds.
According to Cybart, Apple’s wearables segment will likely reach $50 billion in the following year if present trends continue.
Apple Silicon (Chipsets, Processors)
Apple announced that it would switch from Intel chipsets to its own Apple Silicon processors based on ARM in 2020. In keeping with this, the business released a new M1 processor as well as three products powered by it — the MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, and Mac Mini. A survey from market analysis firm TrendForce suggested that M1-powered Mac machines represented around 0.8% of overall laptop sales in 2020, months after the products became available for purchase.
In terms of operating systems, Windows was the global leader in the laptop industry. However, due to the strong expansion of Chromebooks in 2020, Windows’ market share would fall below 80% for the first time in history. Windows is unlikely to regain lost market share immediately since its fall is predicted to continue. TrendForce predicts that the market shares of Windows, Chrome OS, and macOS will each settle at around 70-75%, 20-15%, and less than 10%, respectively.
In 2020, Apple is anticipated to launch the first MacBook to utilize its silicon processor rather than Intel’s, allowing all its key product lines to run on the same architecture.
When considering Apple’s most notable purchases, two stand out:
- In 1997, NeXT Software was purchased for $404 million. The acquisition of Steve Jobs’ post-Apple venture, which featured the forerunner to iOS, returned Jobs to the firm he created.
- Beats for $3 billion in 2014: Apple’s largest acquisition was Dr. Dre and Jimmy Iovine’s headphone firm, which laid the framework for Apple Music.
- However, a third (and extremely significant) transaction set Apple’s mobile product roadmap: the $278 million acquisition of P.A. Semi in 2008.
According to tech analyst Ben Thompson, P.A., Semi gained the expertise and intellectual property (IP) “that would underpin (Apple’s) A-series of processors, which have powered every iPad and iPhone since 2010.”
Apple introduced the Apple TV in March 2007. And much to everyone’s surprise, it was not an actual TV set but rather a box to offer services using the software. It was praised for its attractive interface, painless setup, and overall ease of use – all of which marked a significant shift from prior network-based home entertainment systems.
The hardware remained the same almost a year later, but a free software upgrade essentially gave the device a makeover. Apple subsequently reduced the price of the 40GB model to $229, while the 160GB model was reduced to $329.
People still wonder why Apple never made an actual TV like Samsung or Sony. There are multiple reasons why Apple didn’t enter the TV manufacturing business even with enough expertise.
First, this industry’s margin is very thin, and Apple always focuses on making profits. Second, unlike smartphones or other consumer electronics, there isn’t much design to make it unique. You can find many identical TV designs from different companies. Third, Apple can provide a good user experience through its software, so it went for a box to provide better UX in any TV.

Source: Apple
The box design remained the same throughout the years, but they made multiple changes to its remote.
The iPod was one of the most successful products ever created by Apple. It was a little device that let users listen to music on the go. However, it is now 2021, and despite having Apple Music on iPhones and even being accessible on Android and even smart TVs, Apple continues to offer the iPod Touch . One of the main reasons is that it is not an iPhone and is suitable for children.

Further, iPod Touch uses iOS with the same inbuilt software. It’s basically an iPhone without cellular network connectivity. The user can play games, surf the internet using Wi-Fi, and can send messages using a web browser.
It is Apple’s tactic to prime the iPod users to turn into iPhone users when they choose to buy a smartphone. By using the iPod for 2 or 3 years, most users would want to choose an iPhone over other smartphone brands.
As the iPod is a part of the Apple ecosystem, it helps users remain in it even when they want to upgrade a device.
AirTag, a compact and elegantly designed device that helps keep track of and find the stuff that matters most with Apple’s Find My app, was announced in April 2021 . AirTag, whether connected to a handbag, keys, backpack, or other objects, connects to the enormous, worldwide Find My network and can assist in recovering a misplaced item, keeping location data private and anonymous using end-to-end encryption.
“We’re excited to bring this incredible new capability to iPhone users with the introduction of AirTag, leveraging the vast Find My network, to help them keep track of and find the important items in their lives.” – Kaiann Drance, Vice President of Worldwide iPhone Product Marketing of Apple
Dongles link headphones to charging connections, computers to TVs or card readers, etc. Dongles are a major business nowadays since it’s difficult to conduct many routine computer chores without them. This is owing, in large part, to Apple, which, in 2016, eliminated the headphone jack from the iPhone range and shifted nearly completely to USB-C connectors on its Macs. The newest iPhone isn’t the only Apple gadget that requires an array of dongles to function properly.
A dongle is necessary to connect a MacBook Air to an Ethernet wire. A dongle is also required if the user wants to add a second screen to the computer or import images from an SD card. A USB to USB-C adaptor is required even if users put a flash drive directly into the MacBook.
This causes users to accept the dongle as an integral part of their lives, allowing Apple to establish a sizable market for dongles. Apple, Belkin, and other accessory firms have established a massive market for these dongles, which Facts and Factors estimates will be worth more than $25 billion by 2027.
It is unknown how much Apple’s revenue is from Dongles, but considering the user base’s preferences and Apple’s dongle prices, it could be more than a billion dollars.
Now, let’s move on to the core of all these products- Software.
For over four decades, Apple has been a Silicon Valley trendsetter. Apple’s competitors have widely imitated the Apple II, Macintosh, iPod, iPhone, and iPad. Apple’s success may be attributed in large part to the company’s obsessive attention to the user experience. The iPod first debuted in 2001, followed by the iPhone in 2007, and the iPad in 2010. Consequently, Apple earned about $40 billion in earnings in its fiscal year 2014. Apple is a design-focused corporation that prefers to create all aspects of a product — hardware, software, and internet services — in-house.
Apple II computers were sold until 1993, when they were phased out in favor of Macintosh computers. Around 5 million Apple II computers were sold in total. The first Macintosh had significant limits. However, later versions were more powerful. In 1987, Apple introduced color to the Macintosh with the Macintosh II. The groundbreaking graphical interface of the Mac immediately drew several imitators. Apple debuted the iPod music player in 2001. More crucially, the iPod was compatible with iTunes, Apple’s jukebox software for the Mac, making it simple for users to transfer music from CDs to their iPods. Apple, too, capitalized on the iPhone’s popularity in 2010 by releasing the iPad, a tablet computer built on the same software.
Operating Systems
Both Mac OS X and iOS originated from Darwin, an older Apple operating system based on BSD UNIX. iOS is a proprietary mobile operating system owned by Apple that can only be loaded on Apple devices.
Apple’s iOS is a closed ecosystem, which implies that Apple creates both the operating system and the hardware, and no other corporation utilizes either of them to integrate with their services. It gives Apple an advantage over Android regarding hardware and software synchronization. In the case of Android, however, the hardware is manufactured by companies like Qualcomm and MediaTek (rather than Google), and the manufacturers create their own flavor that runs on top of Android. In addition, Apple allows users to offer 3D touch inputs with mini menu selections. The iOS devices are set up to detect pressure sensitivity on the screen and allow various input choices based on it.
As of July 2023, Android occupies 70.9% of the mobile OS market, followed by Apple’s iOS at 28.36%.
The Mac OS was released in 1984 to power Apple’s Macintosh series of personal computers (PCs). The Macintosh heralded the age of graphical user interface (GUI) systems, inspiring Microsoft Corporation to create its own GUI, the Windows operating system.
The interface is the most noticeable variation between Windows and Mac operating systems. macOS is perceived to be more basic, streamlined, and elegant, but Windows is considered to be more sophisticated and feature-rich, with more customization choices.
The design styles for Mac and PC are vastly different. Whereas macOS has smooth edges and a consistent application across all apps, Windows has jagged edges and a UI that frequently changes across programs. As Apple has complete control over hardware and software, new security enhancements can be implemented on macOS. Similarly, Apple has a simple and comprehensive AppleCare service in place to assist consumers with any hardware issues. Newer Apple products have Touch ID functionality by default for system access, further protecting devices from fraudulent logins.
Microsoft Windows has a 77.74% market share for desktop operating systems (OS) as of July 2020. Apple’s macOS has grown in popularity over the years but is still a minor player in the desktop OS industry. Linux, the third most popular desktop operating system, has a tiny but constant market share. As of May 2021, OS X had a market share of 15.87% , while Windows had a market share of 73.54%, and Linux had a market share of 2.38%.
The WatchOS app experience differs from app experiences on other platforms in several ways. For example, because the Apple Watch is meant to be worn, the UI is tailored to wearers and provides a lightweight, responsive, and highly personalized experience. People commonly utilize the related experiences of a WatchOS app such as Apple complications, notifications, and Siri interactions — more than they use the app itself.
The latest WatchOS 9 update reflects Apple’s goals in healthcare and personalization. Users can now see more information about their workouts on the screen. Turning the Digital Crown reveals metrics like Activity rings, Heart Rate Zones, Power, and Elevation.
In healthcare, Apple has been at work for years, acquiring medtech startups and using its patented technology to strengthen its WatchOS ecosystem. For instance, most of the sleep-tracking technology on Apple Watch likely came from startups like Beddit, which Apple acquired in 2017. Through the acquisition, Apple also got rights to Beddit’s patents on crucial health features, such as a system for determining sleep quality and applying a pressure sensor .
Read More Here: Apple in Healthcare: top MedTech acquisitions and how can you gain an edge over it?
Apple devices are well-known for linking users to content. This sense of connection is anticipated from Apple TV, although it is not a product that the user can physically grasp or touch. Apple TV is a one-of-a-kind platform with unique specifications . TvOS apps can provide incredible experiences with great visual quality thanks to 4K resolution, Dolby Vision, and HDR10, as well as immersive sound thanks to Dolby Atmos. Furthermore, the Siri Remote provides access to three-axis gyro data, allowing users to build even more immersive gaming and interactive experiences.
Tizen is the largest TV streaming platform globally among smart TVs in use, with a market share of around 13% as of the end of 2020, followed by LG’s WebOS with 6.4% market shares, Sony PlayStation, Roku TV OS, and Amazon’s Fire OS tied for third place. Apple TvOS had a market share of 2.7% as of 2020.
Smart TV Streaming Device Market Share Worldwide As Of 2020 (%)

Apple’s machine learning teams are conducting cutting-edge research in machine learning and artificial intelligence. The team employs machine learning to educate their devices to comprehend the environment in the same way that humans do. Apple did a research study to investigate the feasibility of inferring accessibility for mobile apps from their display pixels.
Using a dataset of manually collected and annotated iPhone app screens, they trained a robust, quick, memory-efficient on-device model to recognize UI components. Due to this research, Apple launched the Screen Recognition function, which combines machine learning and computer vision to recognize and present material readable by VoiceOver for apps that would otherwise be inaccessible.
Even in May 2021, Apple Inc. hired Samy Bengio , a former prominent Google AI scientist. The hiring will lead to the establishment of a new AI research team within Apple, led by John Giannandrea. Bengio pioneered the “deep learning” methods that underpin today’s AI systems for processing photos, audio, and other data types.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are now present in almost every aspect of the iPhone.
“I think that Apple has always stood for that intersection of creativity and technology. And I think that when you’re thinking about building smart experiences, having vertical integration, all the way down from the applications, to the frameworks, to the silicon, is really essential… I think it’s a journey, and I think that this is the future of the computing devices that we have, is that they are smart, and that, that smart sort of disappears.” – John Giannandrea, Senior Vice President for Machine Learning and AI Strategy at Apple
Apple has made a practice of crediting machine learning with boosting specific functions in the iPhone, Apple Watch, or iPad, but it seldom goes into much detail.
Apple has taken a more subtle and astute approach to AI. Apple hinted at various AI and ML-powered improvements and enhancements in its June 2020 announcements for iOS, iPadOS, and macOS.
- The Apple Watch utilizes machine learning to identify motions and detect sleep. Users only need to wear the Apple Watch to bed, and it will track their sleep.
- The new handwashing functionality on the Apple Watch, which utilizes AI to detect when one is scrubbing the mitts and starts a countdown, is one of the greatest examples of Apple’s approach.
- One of the features in iOS that allow the iPhone to listen for things like doorbells, sirens, dogs barking, or babies crying is sound alerts. AI excels at picture recognition tasks, and recognizing both Chinese and English characters is an accurate model.
- Apple HomeKit, a smart home solution, allows customers to use their smartphones to control and interact with connected gadgets. Users can utilize the HomeKit framework to provide a means for users to configure accessories and define actions to control them. Users may even bundle actions together and use Siri to initiate them.
- In iOS 14, Apple included a translation app. The app’s purpose is to provide translations from one language to another. Because of the inbuilt on-device machine learning, the Translate app works offline. The program includes various beneficial features while learning a new language and seeking to communicate with someone who speaks an anonymous language.
- Handwriting recognition is a difficult challenge for AI because the more natural a task is for humans, the more difficult it is for AI. In the most recent iPadOS update, when users draw anything with the Apple Pencil, the iPad can recognize their handwriting and, using Scribble, transform it into written text. It works in the same way that most machine learning does.
Artificial intelligence and its subset, machine learning, are being employed to improve the user experience in various Apple gadgets.
Comparison with Google, Amazon, Microsoft
Google paid $400 million for a DeepMind startup in 2014. This company provides various AI-powered solutions, ranging from picture and speech recognition to human simulation in video games. Google employs AI in various mundane tasks, including Gmail reply suggestions and sophisticated search algorithms. In addition, the business just released TensorFlow, a machine learning technology that is open to use by any developer.
Google also has Google Assistant, which assists users in doing daily chores more effectively and timely. It is supported by a wide range of devices (Sonos speakers, Samsung smart TVs, and Philips Hue) and is one of the most extensively used AI solutions today. Duplex is an AI-powered voice that assists users in scheduling business appointments using Google Assistant. The most recent PAIR initiative from Google in AI is worth mentioning. PAIR is an acronym that stands for People + AI Research and attempts to make working with AI as pleasurable and helpful as possible.
When consumers think about Amazon in AI, the first thing that comes to mind is Alexa. This is another virtual assistant that can set alarms, send alerts, and communicate by speech and is supported by Amazon Echo Dot speakers.
Amazon has lately launched the Alexa Shopping functionality. Customers may now use Alexa to place orders on Amazon. The assistant may add things to the basket, delete them, track their progress, and alert customers when they are delivered. Voice shopping reached $40 million by 2020; Amazon made a very smart move.
Microsoft Research AI is a Microsoft-founded organization dedicated to AI research and development. Since the corporation currently uses AI in its processes (Skype chatbots, data analysis, interaction with Cortana, and so on), it’s no surprise that it further intends to increase the usage of AI.
Aside from that, Microsoft has been releasing AI-powered products through its Azure cloud computing service and working on AI integration into Office 365. By 2018, Microsoft bought five artificial intelligence (AI) technology firms. Microsoft’s most recent purchase was XOXCO, a software product design and development firm.
Apple has Siri, one of the world’s most popular virtual assistants. Siri was initially developed as an app and released on the Apple app store by Nuance Communications, Inc. in February 2010. Apple acquired it two months later, on April 27, 2010, for approximately $200 million. Siri was then introduced with the launch of iPhone 4S on October 4, 2011.
It offers face recognition, which is entertaining to experiment with and improves security. Furthermore, Apple employs AI to identify fraud and improve battery usage, appearing to be an equal competitor.
Apple does not spend as heavily on AI as Google or Amazon. Second, it takes a fairly local approach, with its CreateML framework only operating on iOS devices, whereas most businesses train their ML models in the cloud.
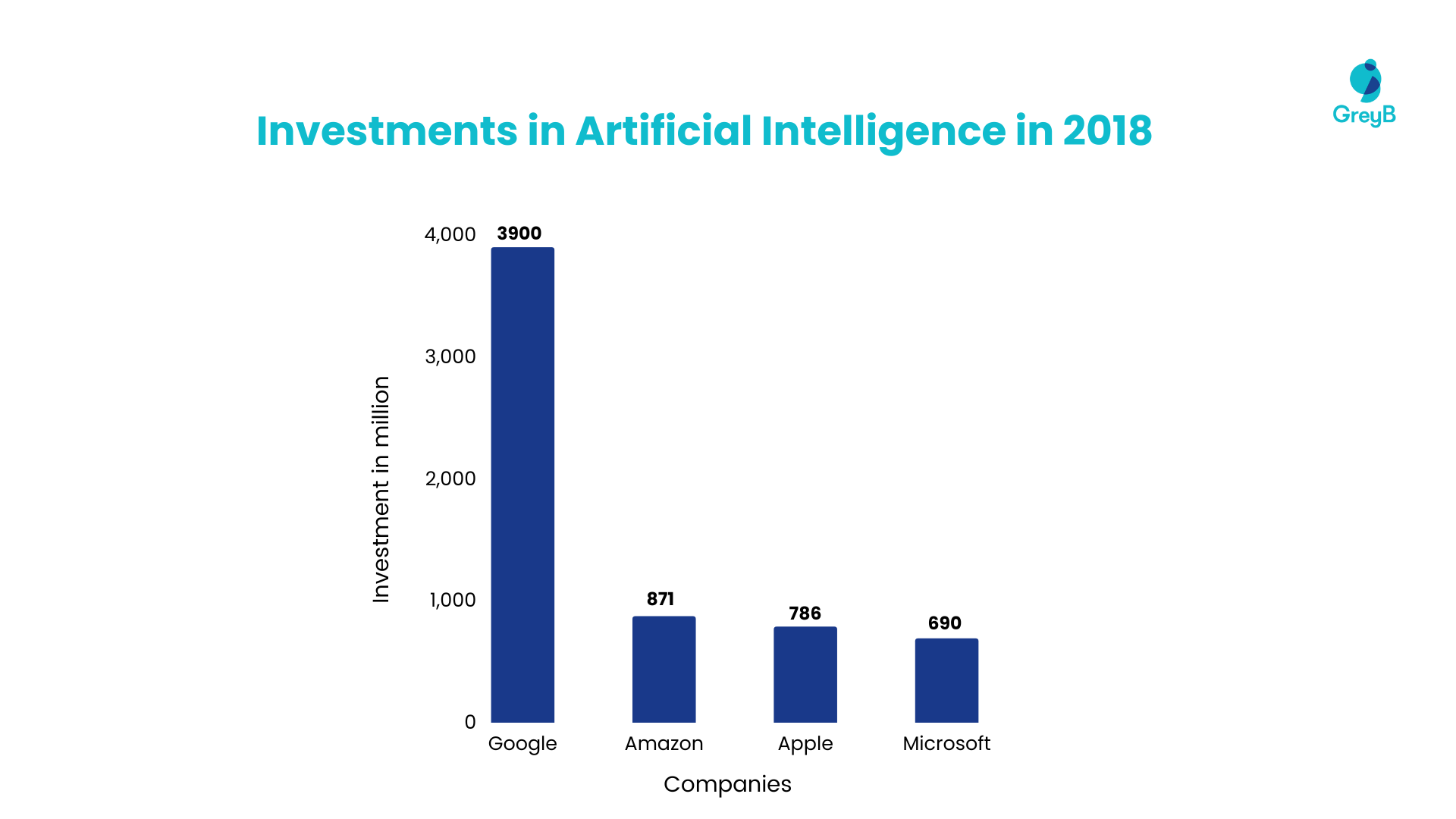
Since 2006, Google has invested over $3.9 billion in AI in disclosed transactions. There have been several organizations that have invested money in acquiring AI startups up till 2018. Some of these businesses are Amazon ($871 M), Apple ($786 M), and Microsoft ($690 M).
Acquisitions Related to AI
According to a report from GlobalData, Apple acquired around 25 artificial intelligence firms between 2016 to 2020. The various acquisitions that Apple made include:
- Emotient (Jan 2016)
Emotient, a San Diego business developing artificial intelligence technology that scans facial expressions to determine emotions, was bought by Apple. Apple did not specify the details of the acquisition in the report.
- Flyby Media (Jan 2016)
Apple acquired Flyby Media, an augmented reality business that created technology that lets mobile phones “see” the world around them. Apple has been interested in virtual reality for several years. The purchase occurred shortly after Apple announced the hiring of a prominent AR/VR specialist, Doug Bowman. Apple may have been working on technology that will someday find its way to the iPhone, similar to Google’s Project Tango, which delivers computer vision to mobile devices.
- Gliimpse (August 2016)
Gliimpse, a health data firm, was purchased by Apple for around $200 million. Gliimpse allowed users to import their medical information into a single virtual environment. Apple’s incorporation of Gliimpse into its existing products appeared to be more evident, given that the business has been working on health-related software for some years now. It was simple to see how Gliimpse, with its structured data centered on individuals, would be useful in products such as HealthKit, ResearchKit, and CareKit. Thus opening a gateway for Apple in the healthcare sector .
- Turi (August 2016)
Turi, a machine learning and artificial intelligence business, was purchased by Apple for more than $200 million. The acquisition is part of Apple’s bigger push into artificial intelligence and machine learning. Apple’s ambitions for Turi’s technology are unknown, but the corporation has been expanding its Siri personal assistant and associated technologies to make a larger push into artificial intelligence.
- Tuplejump (September 2016)
Tuplejump, a machine learning team based in India and the United States, was bought by Apple. The acquisition was motivated by Apple’s interest in “FiloDB,” an open-source project developed by Tuplejump to quickly apply machine learning ideas and analytics to enormous volumes of complicated data as it came in.
- RealFace (February 2017)
Apple has spent $2 million acquiring the Israeli company RealFace, a cybersecurity and machine learning business focusing on face recognition technologies. RealFace’s software employs exclusive IP in the realm of “frictionless face recognition,” which enables quick learning from facial traits.
- DeskConnect (March 2017)
DeskConnect, the start-up behind Workflow, was acquired by Apple. Workflow is similar to Automator, an Apple utility tool that comes with macOS Sierra but has no iOS counterpart. DeskConnect’s namesake cross-platform file-transfer tool was discontinued last month. Apple’s AirDrop, Handoff, and Universal Clipboard, among other services, were recommended by the firm.
- Lattice Data (May 2017)
Apple invested $200 million in acquiring Lattice Data, an AI firm. By acquiring Lattice Data, Apple was prepared to expand into machine learning and artificial intelligence. Around 20 engineers also joined Apple.
- SensoMotoric Instruments (June 2017)
SensoMotoric Instruments, a German provider of eye-tracking eyewear and systems, was acquired by Apple. SensoMotoric has created eye-tracking technology for virtual reality headsets such as the Oculus Rift, which monitors the wearer’s gaze and aids in the reduction of motion sickness, a major side effect of VR. Apple revealed a prototype set of “smart glasses” that would link to an iPhone and show the wearer “pictures and other information.”
- Regaind (September 2017)
Regaind, a French firm, was bought by Apple. Regaind had been working on a machine vision API for analyzing photo content. Apple used this technique to improve the Memories tab in the Photos app. iOS builds albums depending on events, location, and other factors. Using Regaind, iOS may search for aesthetically similar photographs, display the best image as cover art, and generate a recap movie with the finest photographs. Apple has integrated Regaind technology with the new Face ID sensor in the iPhone X, for example, to enhance animoji facial expressions.
- Pop Up Archive (December 2017)
Pop Up Archive, an Oakland-based online platform focused on developing tools to transcribe, organize, and search audio recordings, was bought by Apple. Apple, the long-dominating hands-off curator of the podcast world, has bought a technology aimed at boosting the knowability and sortability of the hundreds of thousands of broadcasts delivered via its Apple Podcast platform.
- Spektral (October 2018)
Apple invested over $30 million in Spektral, a computer vision business in Denmark that has worked on segmentation technology. Spektral’s initial application may have been the rather outdated world of school photos and the most prominent contribution Spektral might make to Apple’s photographic industry.
- Asaii (October 2018)
Apple invested less than $100 million in Asaii, a music analytics start-up focused on discovering new and rising musicians. The acquisition comes as Spotify, Apple Songs’s major competitor, expands its reach beyond conventional popular performers and supports unsigned musicians, who may now submit their music straight to the service.
- Silk Labs (November 2018)
Silk Labs, a firm focused on developing on-device machine learning software, had been acquired by Apple. The purchase perfectly fit Apple’s privacy-focused approach to artificial intelligence. Apple followed a similar approach to AI development, distinguishing itself from competitors such as Google, which collects large volumes of user data and analyses it on the cloud.
- PullString (February 2019)
PullString was acquired by Apple for around $30 million. It is a big indication of Apple’s plan to make Siri creation easier for iOS developers. The acquisition also provides Apple with extensive domain experience in the areas of voice app development, voice app designer and developer requirements, and the complexities of both Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant.
- Laserlike (March 2019)
Laserlike, a machine learning start-up, has been bought by Apple. Laserlike uses machine learning to collect massive amounts of data from the web and then give user-specific findings via an eponymous app. The transaction was made for an unknown purpose, according to Apple. Laserlike’s team may be trying to improve Siri’s long-struggling capacity to retrieve relevant information from the web.
- Lighthouse AI (March 2019)
Apple purchased Lighthouse’s patents for AI-powered home security cameras (eight patents and patent applications). Even the Lighthouse’s Co-Founders, along with about 20 employees, had joined Apple. Apple’s current emphasis on AI-driven home security systems is part of a broader tech industry embrace of so-called smart or connected homes, which include a large number of AI-driven and machine-to-machine gadgets.
- Drive.ai (June 2019)
Apple bought Drive.ai in June 2019. As a consequence of the agreement, hundreds of Drive.ai developers joined the tech giant’s top-secret Project Titan. Apple bought the company’s assets, including its self-driving vehicles.
- Spectral Edge (December 2019)
Apple invested an unknown sum in another UK start-up, Spectral Edge, in an apparent move to strengthen the iPhone camera. Spectral Edge created Phusion, a computer photography approach that employs infrared light that is invisible to the human eye to sharpen and restore color in smartphone images.
- Xnor.ai (January 2020)
Apple acquired Xnor.ai, a Seattle business specializing in low-power, edge-based artificial intelligence solutions. The transaction was completed for around $200 million. According to the agreement, Xnor’s AI-enabled picture identification technologies might become standard capabilities in future iPhones and cameras.
- Voysis (April 2020)
Apple Inc. acquired Voysis, an Irish artificial intelligence firm, in April 2020 for an undisclosed amount. Voysis’ technology, which includes a platform that adds vocal interactions to digital shops, might be used to improve the understanding of what consumers say by Apple’s Siri speech assistant.
- Inductiv Inc. (May 2020)
Apple Inc. acquired Inductiv Inc., a machine-learning firm situated in Ontario, Canada. Inductiv created technology that employs artificial intelligence to automate the job of detecting and repairing data problems. This technology will be used by Apple in a variety of products and improve Siri data.
- Subverse Corp.(Scout FM) (September 2020)
Apple Inc. acquired Subverse Corp. (Scout FM), a start-up that makes listening to podcasts more like tuning into radio stations, to strengthen its service in the face of increasing competition from Spotify. While other podcast applications, such as Apple’s, allow users to select an individual podcast to listen to, Scout FM established podcast stations on various themes. Scout FM was popular among Apple device owners and could be linked with CarPlay. This interface shows on compatible car screens when an iPhone is connected, and Apple’s Siri digital assistant.
- Vilynx (October 2020)
Apple Inc. invested $50 million in acquiring the artificial intelligence and vision firm Vilynx Inc. Vilynx technology might be adapted to Siri and Apple’s general search operations.
Apple Services
Apple has been working on different services to increase revenue, especially when iPhone sales are declining since 2018. Apple knew that it was bound to happen, so the company made several tactics to boost its revenue. One is simply to increase the price.
Apple iPhone, iPad, Watch, and Macbook average prices have seen growth that helped Apple consistently increase its revenue. But that tactic was a short-term plan and Apple Couldn’t rely on it for the long term. That’s where Apple services come into the picture.
Apple has introduced several services in the past 6 to 7 years, such as Apple Pay, App Store, Apple News+, Apple Music, Apple TV+, Apple Podcasts, Apple Fitness+, etc.
Apple generated $53.7 Billion in 2020 through its services, which accounted for 19% of total revenue. Surely, the number will keep growing in the coming years as Apple has a solid user base and is making the services a part of their ecosystem, which will help in user experience.
iMessage is Apple’s instant messaging service for iPhone, iPad, and Mac devices. iMessage, which debuted with iOS 5 in 2011, allows users to share messages, photographs, stickers, and other content between any Apple devices through the Internet. iMessage is exclusively available on Apple devices. That implies users won’t be able to send an iMessage to their Android contacts. Apple prioritizes privacy, which is why everything users transmit as an iMessage is encrypted from beginning to end. This implies that no one can intercept or read it except the person to whom it was sent, even Apple. In reality, even if they have a smartphone, they cannot force their way into a user’s iMessages. No, not without a user passcode. Apple has been chastised by the US government for this same reason, since it cannot, even if it wanted to, expose iMessages.
Apple’s FaceTime is a video chat application. FaceTime was built by Apple on an open standard, which implies that it may be utilized across a variety of platforms and that other manufacturers may exploit FaceTime’s protocol. But instead, FaceTime was only available to customers of Apple products until recently. With the release of iOS 15, FaceTime is coming out of the Apple closet. The software giant is making it possible for people who have Android phones and Windows laptops to hop on FaceTime calls — no iPhone required (well not really tho).
Before you jump to search the FaceTime app on the play store, here’s the catch- you won’t find it. Users will be able to join a FaceTime call on their Android and Windows devices using a link, so long as the person scheduling or starting the call has an Apple device and an Apple account. It now has a market share of less than 0.01%. Zoom is the market leader in this industry, with a 39.66% market share followed by GoToWebinar with a 20.64% market share, and Cisco Webex with a 16.48% market share.
Apple Maps and Google Maps have transformed the way we locate destinations, discover local businesses, and share directions with friends. Both serve the same objective, although their navigation tools and interfaces differ slightly . Google Maps, which debuted in 2005, has been the leading mobile mapping service since the smartphone’s inception. Apple acquired Placebase on July 7, 2009, to build its own Maps application for iPhone and iPad. This app didn’t come until 2012 and was stuck with technical challenges for years.
With the introduction of iOS 13 and iPadOS 13, Apple gained a foothold. Apple Maps was upgraded to exclude third-party navigation data in favor of new data obtained exclusively by Apple. The new maps are significantly more precise and accurate, thanks to millions of miles driven in camera- and LiDAR-equipped automobiles, new high-resolution satellite photos, Apple staffers canvassing areas on foot with radar modules strapped to their backs, and plenty of aerial photography.
Apple included routes for bicycles, routing for electric cars, congestion zones, and Guides for discovering the finest locations to visit in cities around the world in iOS 14 and iPadOS 14. Apple Maps is only available on Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. It’s incorporated into all Apple-branded products, including Macs. It is not available on devices that are not part of the Apple ecosystem.
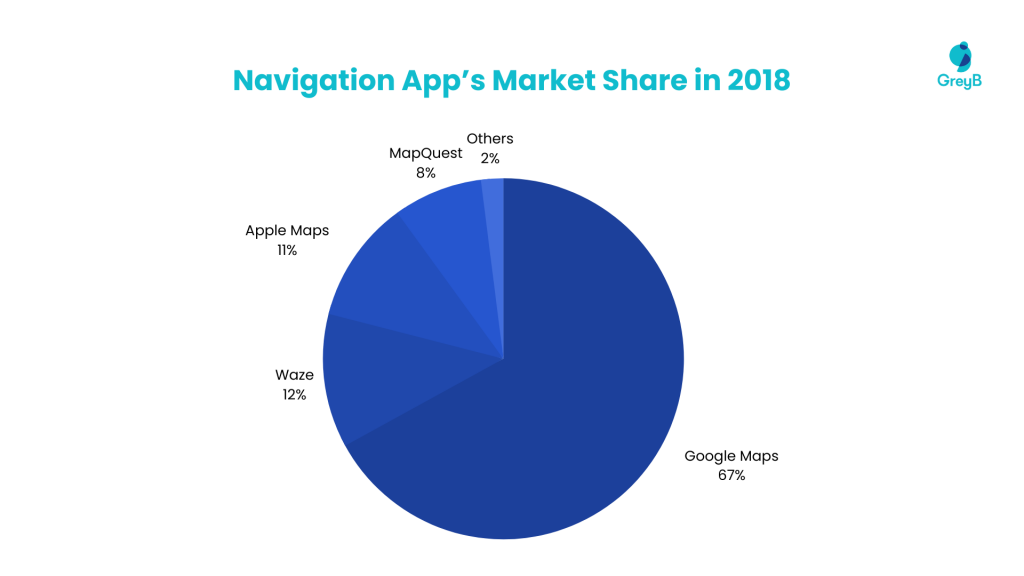
According to the latest survey data from The Manifest in 2018, the majority of smartphone owners use navigation applications, with the majority preferring Google Maps. It has a market share of 67% compared to 12% for Waze, 11% for Apple Maps, and 8% for MapQuest.
Apple’s digital software distribution platform for iOS devices is known as the App Store. The App Store, which debuted in 2008, allows software developers to publish content designed exclusively for the iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch. Apps may also be downloaded for the Apple Watch through the iOS App Store.
The App Store is more than just a shop; it is an innovative place dedicated to delivering incredible experiences. A large part of it is ensuring that the applications the firm provides adhere to the highest privacy, security, and content standards.
Android users have a choice of 3.48 million apps as of the first quarter of 2021, making Google Play the app store with the most available apps . With about 2.22 million iOS apps available, the Apple App Store stands second in the ranking.
While the actual number of applications may vary since Apple and Google constantly delete low-quality material from their app stores, the number of applications has continuously increased over the years.
Since 2008, the App Store has paid out more than $200 billion to developers.
According to mobile expert Horace Dediu, who provided even more current data which are as follows:
- $1.8 billion in App Store sales over the week between Christmas Eve and New Year’s Eve (+27% year on year)
- $540 million in App Store sales on January 1, 2021 (+40% year on year)
- 600 million: The number of iPhone users with an active subscription.
According to Apple, the App Store saw $643 billion in total commercial transactions in 2020, a 24% increase compared to 2019. At the present rate of growth, the indicated economic value might exceed $1 trillion within two years.
Apple TV+ is Apple’s own TV and movie streaming service. It features award-winning shows, captivating dramas, ground-breaking documentaries, children’s entertainment, comedy, and more. Every month, new Apple Originals are added. The service is positioned as Apple’s direct competitor to Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+, and will exclusively offer original programming via the existing Apple TV app, which is available on various platforms.
It is available on a monthly subscription basis and is accessible across several devices via the most recent version of the Apple TV app. Apple TV+ provides ad-free, unique programming that has either been green-lit or created in-house by Apple.
A family membership to Apple TV+ costs £4.99 / $4.99 per month. Apple’s services package, which includes Apple Music, Apple TV+, Apple Arcade, Apple News+, and Fitness+, was launched in October 2020. Apple TV+ is accessible on iOS/iPadOS devices and the Mac via the Apple TV app.
A survey was conducted in May 2020, with Apple’s reader at Android Authority, ‘Which streaming service would they pick if they could only pick one?’ From this survey, it was seen that Apple TV+ captured less than 1% of the total vote. The majority of consumers complained that the library was just too small, while it would work better as a second or third membership for people who can’t get enough content.
Position in the Market Compared To Others
Apple TV+ was marketed as a unique curated stream of entertainment available exclusively through the Apple TV app. Despite Apple’s investments in new movies and programming for its streaming service Apple TV+, the platform is still considered to gain a large success. During the fourth quarter of 2020, it was reported that Apple TV+ has only a 3% market share in the United States, trailing competitors such as Netflix, Disney+, and even Peacock.
Apple TV+ was not the most popular streaming service in the fourth quarter of 2020. Apple TV+ trailed Peacock, NBCUniversal’s streaming service launched in July 2019, which had a 6% market share during the same period. Netflix maintained its 31% market share of streaming platforms in the United States, while Amazon Prime Video grew and drew close to 22%. Hulu came in second with 14%, followed by Disney+ with 13%, and HBO Max with 9%.
In 2020, Apple had a terrible year because most productions were halted due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Apple TV+’s catalog is extremely modest in comparison to its competitors because it only includes original movies and series. Apple extended the Apple TV+ trial term to members who had previously completed the one-year free trial in January 2021.
Apple is in a unique position since it both creates original video content and distributes third-party video bundles. Apple’s aim to become the “bundler of bundles” looks to profit when power shifts from one or two corporations to a lot of others. Apple TV+, Apple’s streaming video service, was priced at $4.99 per month, which was less than any other major provider.
As additional competitors plan to launch their services with larger video libraries consisting of famous series and movies, the firm was obliged to keep the pricing low . Within a few months of its inception, the one-year free trial had propelled Apple TV+ to the top of the streaming services.
Apple’s Plan to Increase Its Streaming Business
Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO, announced the debut of video streaming, news subscriptions, and a credit card in 2019. Apple took a calculated move to join the video streaming sector. The choice to enter the video streaming market is a little departure from the company’s core business, which has garnered its brand recognition.
Furthermore, since Apple has broadened its horizons in the services category, the launch of a video streaming service appeared to be an opportune decision, since this sector has a lot of untapped development potential.
- Online video streaming might be thought of as a replacement for television. In the United States, video streaming services have already surpassed television in terms of household penetration, with 69% of homes using a video streaming service.
- Apple has the economies of scale to enter this market with relative ease. It has significant client loyalty and may be able to gain clients more readily as a result of its loyal client base. Furthermore, with the aid of its existing products, the firm may be able to effortlessly pull in its existing consumers on video streaming services.
Apple TV+ is less expensive than the majority of its competitors. It costs $4.99 per month, which is less than half the price of a standard Netflix membership, and it is free for the first year for customers who buy Apple gadgets. Even now, Apple has been collecting older movies and episodes for its TV+ streaming service, intending to build a back library of material that can compete with the massive libraries offered on Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+. According to sources familiar with the topic, the company’s video-programming executives have received presentations from Hollywood studios about licensing older content for TV+ and have purchased several episodes and movies.
It is predicted that in the future the company might acquire Disney . If Apple is serious about becoming a large SVOD player, which they may not be, abandoning Apple TV+ and redirecting its programming to Disney’s established streaming portfolio makes sense. Disney is the only studio large enough to propel Apple into streaming dominance, and it just so happens to fit Apple’s family-friendly image and public values.
“Apple can easily push the Disney streaming apps onto every phone and make certain offerings free for everyone in markets that are underserved.” – David Offenberg, Associate Professor of Entertainment Finance in LMU’s College of Business Administration
Apple had planned to introduce augmented reality material to Apple TV+ , as it sought new methods to attract and keep members, as well as generate interest in AR technology. Even the ‘Bonus content’ has been one of the numerous ways in which Apple has attempted to increase the value of TV+ and keep consumers enrolled. Apple is planning to launch podcasts based on existing TV+ series. Apple is planning to release a headgear that combines augmented and virtual reality in 2022, with an emphasis on gaming, media consumption, and virtual meetings.
Apple Music
Apple Music was launched in 2015 and is a music streaming service that offers access to over 70 million songs. Its fantastic features include the option to download favorite tracks and play them offline, real-time lyrics, listening across all of your favorite devices, new music customized specifically for its users, curated playlists from their editors, and many more. All of this is in addition to exclusive and unique material.
Apple Music also includes live radio stations and connectivity with Siri, allowing users to operate most of their devices with voice commands. The Apple Music service not only allows one to stream any tune from the iTunes collection on demand, but it also allows one to access all of the music in one location on all of the devices, whether purchased from iTunes, copied from a CD, or downloaded from the web. Individual plans cost £9.99 (US$9.99) per month. A Family subscription, which can accommodate up to six people, costs £14.99 or $14.99 per month, which is less than Spotify’s equivalent. The University Student plan, which costs £4.99/$4.99 a month, is the final option.
This streaming service now supports lossless streaming quality up to 24-bit/192 kHz! This app is available even for Android OS users to download and get a subscription, starting at only $1.19 or ₹99 per month. University students can get it even cheaper with free Apple TV+, making it one of the world’s best and surprisingly affordable lossless music streaming services. It’s unlike Apple to open up its ecosystem to other players, but audiophiles certainly appreciate this move.
Acquisitions and Collaborations
- On August 1, 2014, Apple acquired Beats Music & Beats Electronics for $3 billion.
“Music is such an important part of all of our lives and holds a special place within our hearts at Apple. That’s why we have kept investing in music and are bringing together these extraordinary teams so we can continue to create the most innovative music products and services in the world.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
Beats Electronics began to employ Apple’s patented technology in various products following the acquisition, such as the W1 chip in select Bluetooth headphones. Apple shut down Beats Music at the end of the year in anticipation of the 2015 launch of Apple Music.
- In Jan 2015, Apple purchased Semetric , a business that analyzes music data online. This agreement was reached to revitalize the development of iTunes and Beats Music. Apple’s interest in Semetric is most likely limited to the Musicmetric product, which might be used to reliably compute record label royalties for a music streaming service like Apple Music. After purchasing Beats for $3 billion last year, Apple expressed a desire to extend its online music services with the acquisition.
- Apple purchased technologies from cloud-based music platform Omnifone in November 2016 and employed at least a dozen (at least 16) former Omnifone workers. Omnifone provided “white-label” music services, which allowed businesses to provide their personalized music services to clients and subscribers. Many former Omnifone employees have gone on to work as software developers at Apple, presumably in areas such as iTunes and Apple Music.
- In April 2021, Pinna, an on-demand audio entertainment service provider, announced collaborations with Apple . “Pinna is thrilled to be on the forefront of this exciting launch in collaboration with Apple.”, said Maggie McGuire, CEO of Pinna. Apple Podcasts Subscriptions will let them expand their worldwide reach even further, providing them with a unique ability to personalize channels to certain demographics and interests.
Apple has joined a crowded, competitive field populated by banks and upstart fintech companies. Tim Cook provided some insight into the company’s progress toward becoming a financial player during the company’s quarterly earnings call in 2018.
Apple Pay transactions increased from the previous year to over 1 billion in 2018. Apple had been working on a credit card with Goldman Sachs and MasterCard. In 2019, Apple launched its Apple credit card in collaboration with Goldman Sachs and MasterCard.
According to the firm, Apple customers were able to sign up for the new card using their iPhones in the summer of 2019. It revolves around Apple Pay, the company’s mobile payment and digital wallet service, which debuted in 2014.
Even though Apple was late to the credit card industry, its marketing prowess and dedicated client base allowed the business to expand very swiftly. Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO, indicated that more than 70% of U.S. shops accept Apple Pay and that around 40 countries had joined by the end of 2019.
- The Apple Card is more likely to put branded credit card issuers under competitive pressure than Goldman’s rival banks. Apple may continue to provide additional financial products to its customers, notably bank accounts, which are a good complement to credit accounts.
- According to Gene Munster of Loup Ventures, Apple Pay is still active on around 25% of all iPhones in the United States. This would hasten the adoption of Apple’s payment method since, unlike Apple Pay, the card could be used everywhere.
- Apple also paid around $100 million for acquiring Mobeewave, a payments start-up. The payment startup provides near-field communications (NFC) technology, which allows smartphones to be used as payment terminals. The technology enables mobile payment options such as Apple Pay and Google Pay.
Apple Pay was launched in October 2014 and is an Apple Inc. mobile payment and digital wallet service that allows users to make payments in person, in iOS applications, and on the web using Safari. It is compatible with the iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, and Mac.
Apple introduced person-to-person Apple Pay payments using the Messages app on the iPhone and Apple Watch in 2017. Apple Pay has surpassed Starbucks to become the most used mobile payment platform in the United States as of 2019.
In 2020, the Apple Card had around 3.1 million users in the United States. Apple Pay also allows customers to make one-tap purchases within applications that have implemented the Apple Pay API, and it is available on the web on iOS 10 or macOS Sierra or later devices.
Presently, Apple Pay is accepted by more than 85% of retailers in the U.S. Apple Pay is also available at a variety of locations other than regular retail outlets, such as colleges, ballparks, non-profit organizations, Bitcoin payment providers, and ATMs from Bank of America, Chase, and Wells Fargo.
Apple Inc. announced Apple Card in August 2019 in collaboration with Goldman Sachs and MasterCard. It is a credit card with Apple Pay branding that gives 2% cashback on Apple Pay transactions. In addition to cash benefits for Apple Pay transactions, the card provides financing alternatives for Apple devices.
Apple Card functions similarly to a traditional credit card, but it is deeply integrated into the Wallet app, providing real-time views of the most recent transactions as well as a comprehensive overview of spending organized by category, as well as payment options optimized to encourage minimal interest.
Apple also provides 3% cashback when using the Apple Card with Apple Pay to make purchases at Uber, Uber Eats, T-Mobile, Walgreens, Nike, and Duane Reade. Apple also intends to offer 3% cashback rewards to additional shops and applications in the future.
What are the Potential Future Products of Apple?
Ar/vr/mr devices.
Apple is developing a range of augmented and virtual reality products that will be powered by a new 3D sensor technology. They announced Vision Pro , a new extended reality headset, on June 5, 2023. Interestingly, they never used the terms “virtual reality” or “augmented reality” throughout their presentation and marketing material. Instead, they’re calling this their first “Spatial Computer.” We’re well familiar with Apple’s tendency to create unique names for everything in their catalog.
Interestingly, we noticed one of their recently granted patents on this technology was filed back on May 4, 2007. It indicates that Apple has been working on this headset idea since the same year they launched the first iPhone! Say what you will about their walled-garden ecosystem approach; their vision (no pun intended) and relentless spirit of innovation are truly commendable.
This headset won’t need any external controllers whatsoever. You just use eye movement, voice, and hand gestures! The product even supports 3D video capture, allowing users to record and store memories like never before.
Through the VisionOS interface on its immersive dual 4K displays, Apple may be positioning this headset as a future replacement for smartphones and other handheld computing devices. Looking at the company’s track record of delivering seamless tech integrations into its ecosystem, we believe that the Vision Pro would be a natural extension of everyday tech for an Apple user.
Apple acquired SensoMotoric Instruments in 2017. They were a German provider of dedicated computer vision applications. Their tech was used in ARKit and likely made its way to the Vision Pro. In the same year, they acquired VRvana, an augmented reality headset startup, for $30 million. A number of the startup’s employees had joined Apple in California. Their work and expertise would have made its way to the Vision Pro.
The product isn’t set to launch until early 2024 in the US, but their featured claims seem revolutionary in this niche. Its asking price of $3499 is undoubtedly a steep jump for most consumers, and Apple is aware of that. Financial Times reports that Apple has reduced its production supply goal from 1 Million in 2024 to 400,000. This product may take some time to pick up speed for all but the most tech-savvy of consumers and early adopters.
Apple Glass
Apple Glass is expected to operate on Starboard (or perhaps glassOS), a proprietary operating system revealed in iOS 13’s final version. The augmented reality framework appears several times in code and text documents, implying that Apple is testing activation and application. According to Bloomberg, Apple Glass will be available in 2023 at the earliest. Apple is getting closer to releasing a VR headset that will compete with the Oculus Rift 2.
According to Scoble, Apple will most certainly release AR glasses next year , giving it a 2-3 year head start on all competitors.
Apple’s objective is to personalize computers. The Cupertino firm has everything in place to launch an AR product to the masses:
- Hardware manufacturing competence and a stable supply chain allow for seamless integration with an iPhone, AirPods, and Apple Watch.
- It comes with its operating system, chip, and App Store.
Because every buyer of these AR glasses will almost certainly have an iPhone, Apple can provide a lightweight product at a reasonable price.
Apple’s foray into personal mobility appeared to have begun in 2014 , with the announcement of something named Project Titan. This project is about the company’s efforts to bring a Tesla-style electric vehicle to market before the end of the decade.
The Apple Car project has had many lead changes and hundreds of layoffs during its development, but it is presently led by John Giannandrea, Apple’s Chief of AI and machine learning, who took over from Bob Mansfield after Mansfield departed in 2020.
It was verified in December 2020 that Apple is still working on a car and now aims to produce a vehicle in three to six years. According to Ming-Chi Kuo, an Analyst at Apple, a car would not be launched until 2025 to 2027. Ming-Chi Kuo, an Apple analyst, believes the automobile will be the company’s “next star product,” with Apple able to offer greater integration of hardware, software, and services than prospective competitors in the automotive business, thanks to Apple-designed processors made by TSMC.
“We’re focusing on autonomous systems. It’s a core technology that we view as very important. We are sort of seeing it as the mother of all AI projects. It’s probably one of the most difficult AI projects to actually work on.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
The first car chassis of Apple might be built on Hyundai’s E-GMP electric vehicle (BEV) platform. The Apple Car will almost certainly be sold as an “extremely high-end” or “substantially higher” model than a regular electric car. Apple has been aiming for a game-changing design that might be employed in a future driverless car.
Apple is also working on a novel battery architecture that has the potential to “radically” lower battery costs while increasing vehicle range. The battery technology has been compared to “the first iPhone” and hailed as “next level.” Apple intends to use a novel “mono cell” design that bulks out the individual cells in the battery while freeing up room inside the battery pack by removing pouches and modules that carry battery components.
Apple is also developing a self-driving shuttle service known as ‘PAIL’ (Palo Alto to Infinite Loop). The shuttle service will transport staff between Apple’s Silicon Valley headquarters. Apple is collaborating with Volkswagen and will put self-driving software in Volkswagen T6 Transporter vehicles that will act as staff shuttles.
In 2019 and 2020, speculations circulated that the project had shifted once again and that Apple was still pursuing an Apple-branded car. However, many speculations in late 2020 indicated that Apple is still working on a full-fledged Apple-branded automobile. This is primarily aimed towards customers, with ambitions to collaborate with an established vehicle manufacturer.
Under the secret name “Project Titan,” Apple had hundreds of people working on the design of a minivan electric car. This project is being led by Steve Zadesky, Apple VP of Product Design.
Apple bought Drive.ai , a self-driving car startup, in June 2019. For its self-driving vehicle project, Apple engaged many Drive.ai professionals in engineering and product design. According to Axios, Apple bought the company’s assets, including its self-driving cars.
Drive.ai vans are customized Nissan NV200s that operate in a restricted region near major sites and sports venues. This acquisition was made primarily to improve the company’s autonomous vehicle development effort.
According to Morgan Stanley analysts, Apple spent approximately $19 billion on research and development in 2020, which equates to almost one-fifth of the overall R&D investment across the automotive sector (about $100 billion).
By May 2020, 700 employees were working on Apple AV Tech in the Bay Area.
What does Apple M&A Landscape look like?
Apple is well-known for its strict secrecy, especially when it comes to new iPhone releases. Apple has completed around 100 mergers and acquisitions in the last six years, the majority of which was done in secret. Apple has rigorous nondisclosure agreements in place and urges acquired staff not to update their LinkedIn pages.
The top 10 major acquisitions that Apple has made are mentioned below:
Apple’s Top 10 Acquisitions
Acquisition of beats.
The highest amount at which Apple did an acquisition on August 1, 2014, was at $3 billion, for Beats Music & Beats Electronics. This acquisition includes buying both Beats Audio hardware and Beats Music. One of the main reasons for this acquisition was the talent and reputation that Apple looks for when creating new products and services. Another relevant reason is Apple wanted to modify and uplift its iTunes. Therefore, Apple began acquisition negotiations with Beats just four months after their Beats Music service first debuted. Even Apple was impressed by the amount of revenue that Beats generated from their headphones.
Acquisition of Intel Smartphone Modem Business
In July 2019, the acquisition of Intel Smartphone Modem Business for $1 billion was Apple’s 2nd largest acquisition ever. In this deal, Apple had acquired the majority of Intel’s smartphone modem business. This deal also included the transactions of intellectual property, equipment, and approximately 2,200 Intel employees joining Apple. The agreement aided Apple in acquiring a large portfolio of wireless patents from Intel. More than 17,000 wireless technology patents have been held by Apple, ranging from cellular network protocols to modem architecture and modem service. According to multiple reports, Apple intends to produce its modems for iPhones by 2022-2023, and this Intel contract will undoubtedly aid those efforts.
Acquisition of Dialog Semiconductor
On October 11, 2018, Apple went under a deal to license IP, acquire assets and talent from Dialog Semiconductor to expand chipmaking in Europe at a deal of $600 million. The deal also involved more than 300 Dialog staff transitioning to Apple employees, becoming part of Apple’s hardware technologies team under Johny Srouji. In some cases, Apple will take over whole buildings formerly occupied by Dialog, and in others, they will co-locate in buildings where Dialog will continue to grow its own business.
Acquisition of Anobit Technologies
In December 2011, Apple went under an acquisition with Anobit Technologies , an Israeli semiconductor startup. The deal was completed at approximately $500 million. The main two reasons for which this acquisition was made include the flash memory controllers of Anobit made a key component of all Apple’s leading products (from iPads and iPhones to MacBook Airs) and finally the acquisition added a large team of chip engineers to payroll. Flash memory has been a crucial piece of Apple’s technology puzzle.
Acquisition of Texture
In March 2018, Apple acquired Texture , a digital magazine service by Next Issue Media LLC. The deal was done for $485 million, and it provided subscribers with unrestricted access to their favorite titles with a single monthly subscription fee.
“We’re excited Texture will join Apple, along with an impressive catalog of magazines from many of the world’s leading publishers. We are committed to quality journalism from trusted sources and allowing magazines to keep producing beautifully designed and engaging stories for users.” – Eddy Cue, Apple’s Senior Vice President of Internet Software and Services
Acquisition of Shazam
On September 24, 2018, Apple acquired Shazam to have more opportunities to explore and experience music. The deal was finalized at $400 million.
“Apple and Shazam have a long history together. Shazam was one of the first apps available when we launched the App Store and has become a favorite app for music fans everywhere. With a shared love of music and innovation, we are thrilled to bring our teams together to provide users even more great ways to discover, experience, and enjoy music.” – Oliver Schusser, Apple’s Vice President of Apple Music
In May 2018, Apple revealed that Apple Music had reached 50 million users.
Acquisition of Next Software
Back in 1996, Apple had acquired Next Software at a deal of $400 million. Apple paid approximately $350 million in cash and stock for the privately held Next to purchase that company’s shares and an additional $50 million to cover its debts.
Since its technology was agile, Apple hoped that Next’s object-oriented, Java-enabled open software platform would greatly boost its Internet and intranet status. It also aimed to capitalize on Next’s enterprise role.
“This is a complementary arrangement, and the pieces fit together better than any other alternative we looked at, and it will launch a new round of technology.” – Gilbert Amelio, Former Chairman and CEO at Apple
Acquisition of PrimeSense
In 2013, Apple acquired PrimeSense , an Israeli-based pioneer in 3D sensor technology. The deal was completed at approximately $360 million. PrimeSense’s system could potentially be used in a variety of Cupertino devices. This acquisition was Apple’s second purchase of an Israeli company, as it bought Anobit in January 2012. Apple did not disclose the intentions behind the purchase of PrimeSense.
Acquisition of AuthenTec
In 2012, Apple bought AuthenTec , a fingerprint sensor technology developer for approximately $356 million. The fingerprint technology, used in mobile phones in Japan for authentication of mobile payments, would help Apple bring those services to markets such as the United States.
Apple had also acquired the right to pay the company to license certain patents totaling as much as $115 million. AuthenTec’s authentication features would be integrated into Apple’s iPads, iPhones, and potentially as security measures for other features, such as non-mobile computer systems or cloud-based networks or services.
Acquisition of PA Semi
In 2008, Apple acquired PA Semi , a chip designer for approximately $278 million. This acquisition was a strategic move by Apple, as it aimed to continue to differentiate its next-generation handheld products amongst a growing fleet of competitors. Even the power savings offered by P.A. Semi’s designs may have been amongst the firm’s most compelling assets in Apple’s eyes.
| 1 | August 1, 2014 | Beats Music & Beats Electronics | $3 billion |
| 2 | July 25, 2019 | Intel’s smartphone modem business | $1 billion |
| 3 | October 11, 2018 | Dialog Semiconductor | $600 million |
| 4 | December 2011 | Anobit Technologies | $500 million |
| 5 | March 2018 | Texture | $485 million |
| 6 | September 24, 2018 | Shazam | $400 million |
| 7 | 1996 | Next Software | $400 million |
| 8 | 2013 | PrimeSense | $360 million |
| 9 | 2012 | AuthenTec | $356 million |
| 10 | 2008 | PA Semi | $278 million |
Now, let’s move forward to Apple’s top 5 Market regions besides the US.
What are Apple’s Top 5 Markets besides the US by Revenue?
Apple’s top markets besides the US by revenue include the regions from Europe, Greater China, Japan, and the rest of Asia Pacific. America’s high income is partly attributable to Apple’s good performance in its home market, the United States. Apple has by far the greatest market share among smartphone suppliers in the United States.
Even though overseas sales account for a greater portion of Apple’s overall income, the United States still accounts for around 40% of Apple’s net sales.
During the years 2020 and Q1 2021, the annual revenue of Apple is divided into several regions, such as the U.S., Europe, Greater China, Japan, and the rest of Asia Pacific. The new iPhone 12 Pro and 12 Pro Max, now in their 14th iteration, continue to contribute to the success of Apple’s trademark product, helping push for year-on-year iPhone sales increase despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
Apple gained 28% of the European market in the first quarter of 2020, making it the company’s greatest first quarter of the fiscal period. Even in China during the year 2020, Apple captured a market share of approximately 10.5% . In Q4 2020, Apple was the only brand that showed positive year-on-year growth in the China market that year.
The following table shows the annual revenue:
|
| ||||||
| 51.5 | 27.75 | 25.78 | 7.12 | 9.81 | ||
| 40.88 | 23.28 | 18.34 | 7.72 | 7.04 | ||
| 37.47 | 19.29 | 14.6 | 5.45 | 6.15 | ||
| 39.81 | 22.76 | 15.47 | 5.7 | 6.37 | ||
| 49.28 | 27.68 | 23.91 | 6.76 | 9.54 | ||
| 37.78 | 23.95 | 17.81 | 7.18 | 8.12 | ||
|
| 35.38 | 20.21 | 15.76 | 4.82 | 5.63 | |
Source: Statista
What does Apple’s Investment Landscape look like?
With the accelerating pace of technological change, investing in startups has become a key part of Apple’s corporate strategies. By doing so, they also tend to closely monitor their smaller brethren. Given below are the top 5 investments made by Apple.
Top 5 Investments Made by Apple
Apple has made several investments in startup companies globally. Amongst them, the top 5 investments include:
- In May 2016, Apple announced it had invested in a Chinese ride-hailing service, Didi Chuxing . Apple invested around $1 billion to help Apple to understand the critical Chinese market. The investment gave Apple a stake in two burgeoning waves of technology, i.e., the sharing economy and car technology. Even Apple has been trying to reinvigorate sales in China, where it has come under greater pressure from regulators.
“From a Didi point of view, we see that one, it is a great investment. Two, we think that there are some strategic things that the companies can do together over time. And three, we think that we’ll learn a lot about the business and the Chinese market beyond what we currently know.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
- Even in June 2016, Apple and other firms backed unicorn Didi Chuxing Technology , which raised $4.5 billion in a fundraising drive to oppose Uber’s assault on the Chinese market.
- On March 31, 2021, Apple invested an amount of $50 million in UnitedMasters, a music distribution, and data analytics company. The platform aims to democratize the music industry by allowing budding musicians to earn money and get distribution across a variety of music platforms, including Spotify and Apple Music. This agreement marks the beginning of a strategic engagement with Apple, which will open up a plethora of new prospects for UnitedMasters artists.
“Steve Stoute and UnitedMasters provide creators with more opportunities to advance their careers and bring their music to the world.” – Eddy Cue, Apple Executive
- In March 2016, Apple, together with Blackboard, Dropbox, Udemy, and other companies invested around $2.3 million in Volley Labs , a learning technology firm. Volley’s primary goal is to provide technology that assists students, particularly those enrolled in advanced high school or college curricula, in understanding the content they are learning by surfacing relevant, machine-curated explanations from the web via their mobile devices. The Volley’s funders’ ultimate goal is to spare students from spending too much time “processing” material and redirect their time and energy on meaningful learning.
- On November 21, 2015, Apple invested in God-i , a startup that specialized in wearable devices in the seed round. But afterward, Apple exited from further investments in God-i.
- On February 25, 2019, Apple along with other investors invested an amount of $21 million in FreightWaves during a Series B funding. FreightWaves is a data and content forum that delivers near-real-time statistics to industry players.
Apart from investing in smaller companies and startups, collaboration is another strategy opted by Industry giants such as Apple. Let’s look at the top 10 partnerships and collaborations Apple has made over the past years.
Top 10 Partnerships/Collaborations Made by Apple
The various top partnerships and collaborations that were made by Apple are mentioned below:
- In September 2020, Singapore’s government and Apple announced a collaboration on the health initiative LumiHealth, which would use Apple Watch. LumiHealth, developed in partnership with a team of physicians and public health professionals, encourages the use of technology and behavioral insights. Singaporeans might use their Apple Watch and iPhone to stay healthy and complete wellness challenges.
“Singapore has one of the world’s leading healthcare systems, and we are thrilled to be partnering with them to incorporate Apple Watch and LumiHealth into their holistic approach to well-being” – Jeff Williams, COO of Apple
- In April 2020, Google and Apple announced a partnership initiative to use Bluetooth technology to help governments and health organizations in reducing the transmission of the COVID-19 virus, with user privacy and security at the forefront of the design. Both organizations would offer APIs in May that would allow Android and iOS devices to communicate with public health applications. Users would be able to download these official apps from their respective app stores.
- In October 2017, Apple and GE launched a collaboration to deliver powerful industrial applications that would provide predictive data and analytics from Predix, GE’s industrial Internet of Things (IoT) platform, to iPhone and iPad. The corporations announced the release of a new Predix software development kit (SDK) for iOS, which would provide developers with the tools they require to build their own powerful industrial IoT apps.
“Together, Apple and GE are fundamentally changing how the industrial world works by combining GE’s Predix platform with the power and simplicity of iPhone and iPad.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
- In August 2017, Apple and Accenture announced a collaboration to help businesses revolutionize the way employees interact with consumers by developing new business solutions for iOS. Accenture Digital Studios would establish a dedicated iOS practice in key locations across the world. The two firms would provide a new set of tools and services, including IoT, to assist businesses in unlocking new income sources, increasing efficiency, improving customer experience, and lowering expenses.
- In September 2016, Apple and Nike unveiled the Apple Watch Nike+, the latest product of their long-standing collaboration. Apple Watch Nike+ has been the ideal running tool, combining exclusive Nike Sport Bands with the Apple Watch Series 2, including GPS, a two-times brighter display, 50-meter water resistance, a strong dual-core CPU, and watchOS 3.
“Apple Watch Nike+ takes performance tracking to a whole new level and we can’t wait to bring it to the world’s largest community of runners.” – Jeff Williams, COO of Apple
- In May 2016, Apple and SAP announced a collaboration to reimagine the mobile work experience for corporate clients of all sizes by combining powerful native apps for the iPhone and iPad with the better capabilities of the SAP HANA platform.
“As the leader in enterprise software and with 76% of business transactions touching an SAP system, SAP is the ideal partner to help us truly transform how businesses around the world are run on iPhone and iPad. Through the new SDK, we’re empowering SAP’s more than 2.5 million developers to build powerful native apps that fully leverage SAP HANA Cloud Platform and tap into the incredible capabilities that only iOS devices can deliver.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
- In 2016, Apple and Deloitte announced a collaboration to assist organizations to accelerate business transformation on iPhone and iPad. They would also collaborate on the creation of EnterpriseNext, a new service offering from Deloitte Consulting designed to help clients fully leverage the iOS ecosystem of hardware, software, and services in the workplace.
“Our dedicated Apple practice will give global businesses the expertise and resources they need to empower their mobile workforce to take advantage of the powerful ecosystem iOS, iPhone, and iPad offer, and help them achieve their ambitions while driving efficiency and productivity.” – Punit Renjen, CEO of Deloitte Global
- In August 2015, Apple announced a partnership with Cisco to build a fast lane for iOS business customers by optimizing Cisco networks for iOS devices and apps with the integration of iPhone with Cisco corporate settings to offer unique collaboration on iPhone and iPad.
“iPhone and iPad have become essential tools for the modern workforce and are changing the way work gets done. Together with Cisco, we believe we can give businesses the tools to maximize the potential of iOS and help employees become even more productive using the devices they already love.” – Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
- In July 2014, Apple and IBM announced an exclusive collaboration that would combine each company’s strengths to improve workplace mobility by integrating IBM’s big data and analytics capabilities to iPhone and iPad. The collaboration would improve in the integration of Apple’s machine learning framework, Core ML, with IBM Watson, resulting in strong insights that become deeper with time and use. The alliance would include exclusive IBM cloud services optimized for iOS, such as device management, security, analytics, and mobile integration.
- In 2013, Square partnered with Apple to offer the new Square Stand, a point-of-sale system through Apple’s extensive retail network. The Square Stand is an iPad accessory with the capacity to connect to a variety of devices including cash registers, barcode scanners, and printers. In addition, the gadget has a built-in credit card reader. In 2016, the company announced a new collaboration that would allow consumers to connect money saved on Square’s virtual card, Square Cash, to their Apple Wallet.
Future Outlook
Apple has been doing more than good for a long time and say since the company launched the iPhone.
For the 10th consecutive year, Forbes magazine ranked Apple as the most valuable brand in the world in 2020. Apple’s great track record should continue as long as future management takes care of the brand and pushes it into new sectors. Apple’s breakthroughs are often incremental, with the company adapting its design prowess to the most recent consumer tech trends.
Looking ahead ten years, the Apple of 2030 should continue to progressively enhance its hardware products while also introducing new ones such as Apple automobiles, AR/VR headsets, AR smart glasses, and so on. Apple will also broaden its brand to provide a suite of packaged consumer offerings.
In 2020, Apple executed an AR-related acquisition, acquiring NEXTVR for around $100 million, considering the future growth and vast applications of AR and how Apple can take advantage of it.
“When I think about that in different fields, whether it’s health, whether it’s education, whether it’s gaming, whether it’s retail, I’m already seeing AR take off in some of these areas with the use of the phone,” said Tim Cook on a podcast . “And I think the promise is even greater in the future.”
Aside from possible smart eyewear, Apple is said to be working on self-driving automobiles. Besides these new, futuristic initiatives, Apple is projected to continue selling a large number of iPhones, Apple Watches, iPad tablets, laptops, and desktops even ten years from now. By 2030, it’s feasible that Apple will have a version of almost every form of entertainment, financial, or other consumer service.
Apple announced an acceleration of its US investments, with plans to make additional contributions totaling more than $430 billion and create 20,000 new jobs throughout the country over the next five years, beginning in April 2021. Apple has increased its investment by 20% over the next five years, boosting American innovation and delivering economic benefits in every state. Tens of billions of dollars will be invested in next-generation semiconductor research and 5G innovation throughout nine US states.
“At this moment of recovery and rebuilding, Apple is doubling down on our commitment to US innovation and manufacturing with a generational investment reaching communities across all 50 states.” – Tim Cook , Apple CEO.
It is becoming undebatable that Apple has amassed enormous status and reputation across the world. The capacity of Apple to retain and satisfy users inside its ecosystem is at the heart of its sustained success. In a realistic scenario, the future growth of Apple from 2022 to 2031 is depicted below:
- In this scenario, iPhone revenue will be moderately higher at the end of the 10 years than in 2021.
- By 2031, the Mac will grow only by 5%, the iPad by 8%, Wearables, Home and Accessories by 20%, and Services by 15%. One new product introduction, Product X, will generate $10 billion in revenue by 2031.
| 151,904 | 144,308 | 137,093 | 143,948 | 151,145 | 158,702 | 150,767 | 143,229 | 150,390 | 157,910 | |
| 31,556 | 33,134 | 34,790 | 36,530 | 38,356 | 40,274 | 42,288 | 44,402 | 46,622 | 48,953 | |
| 27,672 | 29,885 | 32,276 | 34,858 | 37,647 | 40,659 | 43,911 | 47,424 | 51,218 | 55,316 | |
| 44,093 | 52,911 | 63,494 | 76,192 | 91,431 | 109,717 | 131,660 | 157,992 | 189,591 | 227,509 | |
| 71,108 | 81,774 | 94,041 | 108,147 | 124,369 | 143,024 | 164,478 | 189,149 | 217,522 | 250,150 | |
| – | 500 | 1,000 | 2,500 | 4,000 | 5,500 | 7,000 | 8,000 | 9,000 | 10,000 | |
Over 10 years, sales growth is 9.66%, a reasonable rate for a company of this size. The iPhone growth narrative is far from done, and a couple more upgrade cycles may drive a revival in growth over the following two decades. Even if App Store fees are reduced to 0%, Apple’s management will find another way to monetize service offerings.
Authored By: Vipin Singh, Market Research
Next Read: Amazon Business Strategy: Insights of its operation and investment plan to become the top Fortune 500 company
Also Read: Airbnb expanding into social media? A peek into Airbnb’s expansion plan
[…] What is Apple Business Strategy?; […]
[…] instance, Apple’s strategic plan in the early 2000s centered on designing groundbreaking products like the iPhone, which set clear […]
[…] 1. GreyB: Apple Business Strategy: A Detailed Company Analysis 2. EdrawMind: Apple Segmentation, Targeting, and […]
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

- Deepak Syal (Director)
- +91-8297806050
- Chakshu Kalra (Director)
- +91-9878481471
- UNITED STATES
- +1-202-455-5058
- +65 84306322

- Pooja Sehgal (HR)
- +91 8427102546
- Vaishali Shorey (Talent Lead)
- +91 7589465756
- hr@greyb.com
Become a part of GreyB’s insider list
Get our distilled learning delivered to you.
Get the Sample Report
Fill out the form and get the report.

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Apple’s Competitive Strategy & Growth Strategies

Apple’s generic competitive strategies and intensive growth strategies relate to the company’s strategies in pricing, marketing, and other areas of the business. Michael E. Porter’s model for generic competitive strategies defines strategic options that the company can use to develop its competitive advantages in the consumer electronics and information technology and services industries. Apple’s generic competitive strategy determines competitive advantages over other companies that provide information technology, consumer electronics, and online services. On the other hand, Igor Ansoff’s Matrix of growth strategies presents ways for the technology business to intensively grow in current or new markets and industries. In this case, Apple’s intensive growth strategies support the ability to maintain a strong position in the global market. With a high rate of innovation and emphasis on excellence in product design, the enterprise succeeds with its premium selling prices. This successful positioning indicates Apple’s effectiveness in using its generic strategy for competitive advantage, and intensive strategies for business growth.
Apple’s generic competitive strategy aligns with the company’s intensive growth strategies, especially in maximizing the use of the organization’s competitive advantages. In particular, the intensive growth strategy of product development is key to fulfilling this generic competitive strategy and supporting the long-term growth and success of the company’s technological goods and services. This alignment between the generic competitive strategy and the intensive growth strategies provides support for fulfilling Apple’s mission statement and vision statement .
Apple’s Competitive Strategy (Porter’s Model)
Apple’s generic competitive strategy is differentiation . This generic strategy focuses on competitive advantages based on key features that differentiate the company and its products from competitors, including IT and consumer electronics companies, like Samsung , Google (Alphabet) , Microsoft , and Sony . These competitive advantages also apply to Apple TV Plus, which competes with the video-streaming services of Netflix , Disney , Amazon , and Facebook (Meta) . Through differentiation as its generic competitive strategy, Apple stands out in the market. For example, elegant design and user-friendliness of products, combined with high-end branding, effectively differentiate the technology business.
The generic competitive strategy of differentiation means that Apple always aims to set itself apart from competitors not by price but by competitive advantages based on product design that attracts customers. Such design includes seamless connectivity among devices and cutting-edge aesthetics. Even though this generic competitive strategy makes Apple different, the company still broadly reaches various segments of the market. The firm’s products are designed for everyone, thereby supporting a broad market reach. For example, the company targets individuals and business organizations through the Mac product line. In this way, the generic competitive strategy of differentiation supports the company in maintaining its competitive advantage, leadership, and position as a high-end and high-value technology business.
The generic competitive strategy of differentiation has significant implications on Apple’s strategic objectives. For example, to apply this competitive strategy, the company must continue emphasizing innovation through research and development. Apple must keep developing innovative products so that the business maintains its competitive advantages. Competitors eventually catch up with new technologies and new products, so the generic competitive strategy of differentiation compels the company to continuously innovate to keep itself always ahead of the competition. Thus, continuous innovation is one of Apple’s strategic objectives based on differentiation as the generic competitive strategy.
To maintain business growth, the company must keep growing its market reach, such as in the global consumer electronics market. In its generic strategy for competitive advantage, Apple does not focus on specific market segments. Instead, the company competes by selling various goods and services that suit the various segments of the consumer electronics and information technology services industries. Thus, another of Apple’s strategic objectives based on its generic competitive strategy is to penetrate markets to ensure a more expansive market reach. This expansion and business growth are achieved through intensive strategies for growth.
Apple’s Growth Strategies (Ansoff Matrix)
Product Development . Apple uses product development as its main intensive strategy for growth. Product development requires that the company develop attractive and profitable technology products to grow its market share and business performance. Apple implements this intensive growth strategy through innovation in its research and development processes. Through product development, the company uses innovation as a critical success factor and competitive advantage. For example, the business continues to innovate and enhance MacBooks and the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. In this intensive growth strategy, the company grows because new products allow the business to generate more revenues, such as through the sale of new iPhone models. The company’s generic strategy agrees with this intensive growth strategy by focusing on technological innovation to increase competitive advantages and profits. Apple’s organizational structure (corporate structure) supports this growth strategy. The structure’s product-based divisions enable strategic management specific to product development. Also, Apple’s company culture (business culture) emphasizes innovation that supports product development.
Market Penetration . Apple Inc. uses market penetration as its second most significant intensive strategy for growth. Market penetration involves gaining a larger share of the current market by selling more of the company’s current products. For example, the company applies this growth strategy by selling more iPhones and iPads to its current markets in North America. Also, the company achieves more sales by adding more authorized sellers to boost its distribution network’s competitive advantages in its current markets. This approach penetrates markets where Apple has not yet achieved a significant position. Moreover, with market penetration as an intensive growth strategy, the company uses promotion through various websites and media outlets. Advertisements encourage more people to buy Apple products. This intensive growth strategy agrees with the company’s generic competitive strategy of differentiation by addressing the need to broadly capture the market through the sale of more technological products to more customers. The distribution strategy and promotional strategies and tactics in Apple’s marketing mix (4P) influence the effectiveness of the organization’s competitive advantages and this intensive growth strategy.
Market Development . Apple uses market development as a low-priority intensive strategy for growth. Using the company’s competitive advantages, market development involves selling existing products in new markets or market segments. For example, Apple Inc. applies this intensive growth strategy by authorizing new sellers in markets or market segments where the company does not have any presence yet. This growth strategy agrees with the generic competitive strategy of differentiation by expanding the company’s market reach, such as by introducing its current consumer electronics to new overseas markets or market segments. Differentiation as a generic strategy for competitive advantage also requires offering products to different market segments, which Apple satisfies via market development. Through its various product models of consumer electronics and other goods and services, the company fulfills this strategic requirement. The business strengths discussed in the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc. facilitate the implementation of market development as a growth strategy.
Strategic Analysis and Recommendations for Apple Inc.
Apple’s generic competitive strategy of differentiation adds competitive advantage by making the business stand out. Differentiation in product function and design supports the firm’s goal of leading the market through technological innovation. Innovation is at the heart of Apple’s business. However, to improve its application of this generic strategy for competitive advantage, the company must aggressively penetrate markets. This recommendation is especially applicable in developing countries where the corporation has limited market reach for its information technology goods and services.
Apple’s main intensive growth strategy is product development. Market penetration and market development have lower priority in this technology enterprise. These intensive growth strategies agree with and support Apple’s generic competitive strategy. The company is strong in product development through innovation. However, to improve performance, Apple needs to focus more on market penetration and market development. These two intensive growth strategies can improve the company’s resilience against aggressive competitors, like Samsung. Also, adjustments to Apple’s operations management can optimize the effectiveness of these growth strategies and the differentiation generic strategy for competitive advantage.
- Ali, B. J., & Anwar, G. (2021). Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies and its influence on the Competitive Advantage. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, Management and Science, 7 (6), 42-51.
- Apple Developer – Design – Human Interface Guidelines .
- Apple Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Apple Store Online .
- Doan, T. N. T., & Nguyen, H. H. (2022). Value creation and value capture: Analysis of Apple company. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 5 (4), 1089-1095.
- Li, Z. (2023). Strategic Marketing – Marketing Analysis of Apple Company. International Journal of Management Science Research, 6 (4), 19-26.
- Liang, X., Luo, Y., Shao, X., & Shi, X. (2022). Managing complementors in innovation ecosystems: A typology for generic strategies. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 122 (9), 2072-2090.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

Steve Jobs Summed Up Apple's Entire Strategy Using Just 6 Bullet Points. Each Teaches an Amazing Lesson
In a recently published meeting agenda, apple co-founder steve jobs teaches a master class in how to write a strategic plan..

On October 24, 2010, Apple CEO Steve Jobs sent a very important email .
It contained the agenda for the company's upcoming "Top 100" retreat, a top secret and super exclusive offsite management meeting that was reserved for 100 of Apple's most influential employees.
The agenda, part of an email which was recently published in connection with the ongoing Epic v. Apple lawsuit, is long and detailed, with tons of lessons for business leaders. But it's the first point on the agenda, entitled "2011 Strategy" and assigned to Jobs himself, that stands out most.
Jobs's agenda point consists of only six major bullet points, but each one teaches an amazing lesson.
The six points are as follows:
- Who are we?
- What do we do?
- Post PC era
2011: Holy War with Google
- 2011: Year of the Cloud
2015: New Campus
Let's break each of them down.
Be intentional
Jobs begins with two very important questions:
Upon first glance, these questions might surprise you. After all, Jobs had been back as CEO of Apple for over a decade at this point, and had conducted one of the greatest turnarounds ever.
But Jobs knew well how easy it is to fall from the top. Apple had experienced huge success in the past, only to lose itself in a flurry of products and initiatives.
To keep history from repeating itself, Jobs knew Apple needed to continually question who it was and what it did. It had to clearly identify company leadership, values, and focus -- and make sure to align its goals with its desired culture and purpose.
Takeaway: Your company will change as time goes on. Keep questioning yourself, and make those changes intentional, not accidental.
Identify your strengths
The next bullet point, "Post PC era," did two important things. First, it early identified the consumer shift of purchasing more mobile devices.
Just as important, though, it highlighted Apple's strength in this nascent market.
"Apple is the first company to get here," Jobs wrote -- which was entirely true, as the iPhone and iPad had proven revolutionary. Mobile products now accounted for 66 percent of the company's revenues, with the iPad alone having outsold the Mac within six months.
The key for future success, as Jobs outlined, would be to leverage this shift through continued improvement of mobile devices, communication, apps, and cloud services -- a strategy that Apple is continuing to follow over a decade later and that has transformed it into a trillion-dollar company.
Takeaway: Identify what your company does well in the context of the overall market. Then, double down on doing those things better.
Learn from competitors
The next bullet point encapsulated Jobs's view of the competition:
While it was true that the iPhone and iPad were revolutionary, Google had begun to surpass Apple in some ways -- and Jobs knew it. Later in the agenda, he highlighted how Google's Android operating system excelled at deeply integrating Google's cloud services, admitting that Android was "way ahead of Apple" in cloud services for contacts, calendar, and mail.
The goal, then?
"Catch up to Android where we are behind...and leapfrog them."
Takeaway: Focus on your strengths, but ignore your weaknesses at your own peril.
Focus on one big thing
Jobs next clearly establishes the single most important priority for 2011, which he terms "the year of the cloud."
Apple "invented" the digital hub concept, writes Jobs, by using the PC as a hub for digital assets like contacts, calendars, photos, music, and videos. But the digital hub was shifting from the PC to the cloud, and Apple had to move fast.
"Google and Microsoft are further along on the technology," he wrote, "but [they] haven't quite figured it out yet.... [We need to] tie all of our products together, so we further lock customers into our ecosystem."
Identifying and executing on this priority was pivotal in helping shape Apple's strategy for years to come, and in helping the company keep up with -- and, in some ways, surpass -- its competitors.
Takeaway: There are countless things you could be working on, a few things you should be working on, and only one thing that should be your top priority.
Figure it out, and make sure everyone is working to support it.
Look to the future
Jobs's final bullet point is only three words:
Of course, this was a reference to what eventually became "Apple Park," the company's 175-acre campus and futuristic office complex that now serves as the its corporate headquarters. This was one of the final projects pitched by Jobs, a workplace that would embody the spirit of Apple and inspire employees to continue to "think different."
Sadly, Jobs didn't live to see construction on Apple's new campus begin. However, he set the plans in motion and was heavily involved in the design of the campus, reportedly specifying even small details about building materials and other features.
And in April 2017, two years later than originally planned, Apple Park was opened to employees.
Takeaway: Focus on the here and now. But always, always plan for the future.
There it is.
A single agenda topic. Six major bullet points. Just enough words to form a few paragraphs, at most.
Yet, those few words contain a master class in business strategy:
1. Be intentional
2. Identify your strengths
3. Learn from competitors
4. Focus on one big thing
5. Look to the future
Take a page out of Steve Jobs's playbook and use those five steps to help plan your business strategy.
Sign up for our weekly roundup on the latest in tech
Privacy Policy
More From Forbes
Apple's key to success goes beyond products and services and includes world class operations.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Steve Jobs legacy looms large, but Tim Cook's business acumen secured continued success for Apple. ... [+] (Photo by Justin Sullivan/Getty Images)
When Steve Jobs returned to Apple in 1997, he started to turn Apple from a company that was $1 billion in the red to one of the most valuable companies in the world. In August 2018, the iPhone maker became the first company to cross $1 trillion . It hit the $2 trillion mark on August 20, 2020. Apple became a $3 trillion company briefly on January 3, 2022, and today its valuation is about $2.6 trillion.
By focusing on creating breakthrough products like the iPod, iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch, along with a rich set of services that have recurring revenues, Apple's growth, especially since Steve Jobs's death in 2011, has been no less than spectacular.
While Steve Jobs will always be known as the visionary behind all of their products and software, he should be recognized for his choices in hiring world-class leaders to execute his vision. And his best hire has been Tim Cook, the current CEO of Apple today. His decision to have Tim work on their supply chain and operations when he returned to Apple goes down as a visionary move by Jobs. He had a clear vision for product designs by 1998 but needed a top-notch person to salvage a broken supply chain crippled by the last two CEOs at Apple from 1992-1997.
Tim Cook not only corrected the supply chain and operational deficiencies but created a world-class version of each that Apple has built on to become a multi-trillion dollar company.
Another thing that Jobs did was mentor and help prepare Tim Cook to take over his role at some point.
Indeed, once Jobs got his cancer diagnosis in 2003, he sped up the process of tutoring Mr. Cook to take over someday. As a result, Cook became CEO in 2010, a year before Steve Jobs died. Here again, Jobs' foresight has served the company well, as Apple's most significant growth has come under Cook over the last 12 years.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Of course, the tech industry and just about all sectors have been hit hard due to Covid, supply chain issues, inflation, and operational challenges. And Apple was not immune to these obstacles.
Apple CFO Luca Maestri made an important point and clear distinction about why Apple has fared better than most during the last earnings call. He stated, " Our June quarter results continued to demonstrate our ability to manage our business effectively despite the challenging operating environment.”
Apple continues to be a growth stock as most buy-side analysts forecast that Apple's stock range will be between $170 to $200 in the future. At this writing, Apple's stock was $164.48 and up close to $35 from earlier this year.
Apple's upside, besides growing sales and demand from the current line of products and services, is framed by the fact that Apple has two other big things in the works. First, in the nearest future will be some AR-MR headsets that could debut as early as 2023. And it is well known that Apple has a significant research project on autonomous vehicles in the process. However, that release date is anyone's guess as Apple has been very mum on this project.
Another big thing in the works will take all of Mr. Cook's operational skills to execute to achieve its potential. According to Needham analyst Laura Martin , "Apple is trying to step in and solve the ad-revenue problem for its app developers that are ad-driven." Ms. Martin made these comments during a CNBC interview with Jon Fortt.
In this interview, Mr. Fortt and Ms. Martin discuss the $450 billion total addressable market for mobile ads that Apple could tap into with a suitable business model and execution.
This potentially large market for ads that Apple could address will need Mr. Cook to bring all of his business acumen and operational experience to this opportunity. As Ms. Martin of Needham points out, it could be one of Apple's more extensive service opportunities. Success with mobile ads and the upcoming entries in AR-MR and perhaps someday autonomous cars suggests that Apple's upside could be substantial during the rest of this decade.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Consumer & Retail
- Enterprise Tech
- Financial Services
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Industrials
- Media & Entertainment
- Climate Tech
- Information Security
- Quantum Tech
- Big Tech Reports
- Future Of Reports
- Investment Thesis Maps
- Market Maps
- Market Reports & ESPs
- MVP Technology Frameworks
- State Of Reports
- Strategy Maps
- Top Company Lists
- Valuations Reports
- Yardstiq Vendor Reports
- The CB Insights Newsletter
- Upcoming Webinars
Join 500,000+ CB Insights newsletter readers
Analyzing Apple’s growth strategy: The business moves hinting at the secretive $2T+ giant’s strategic future
- July 20, 2022
- Artificial Intelligence
- Augmented & Virtual Reality
- Hardware Tech
- Semiconductors & HPC
- Strategy Map
- Wellness Tech
- Share Analyzing Apple’s growth strategy: The business moves hinting at the secretive $2T+ giant’s strategic future on Facebook
- Share Analyzing Apple’s growth strategy: The business moves hinting at the secretive $2T+ giant’s strategic future on Twitter
- Share Analyzing Apple’s growth strategy: The business moves hinting at the secretive $2T+ giant’s strategic future on LinkedIn
- Share Analyzing Apple’s growth strategy: The business moves hinting at the secretive $2T+ giant’s strategic future via Email
We mined Apple's acquisitions, investments, and partnerships to discern the company's emerging strategic priorities.
Apple is looking for the next big thing.
As the world’s most valuable company, with a $2T+ market cap and over $100B in annual profit, Apple has long been known for its cell phones, laptops, tablets, and watches. Today, the company is investing aggressively in high-tech areas like AR/VR, AI, and semiconductors to lay the groundwork for products and features that affect health & wellness, mobility, digital connections, and more.
download the 12 Tech Trends To Watch Closely In 2022 report
Download our full report to find out the top trends poised to reshape industries in 2022.
Although Apple is famously secretive, its acquisitions, partnerships, and investment activity provide a window into where it’s headed next. The company has acquired more than 25 companies since 2018, from edge-based AI startup Xnor.ai to VR streaming platform NextVR . Apple has also committed $430B for new investments and 20,000 new jobs in the US over 5 years — in addition to further investments in Europe and India — across silicon engineering, AI, and 5G tech.
Using CB Insights data, we uncovered 4 of Apple’s emerging strategic priorities highlighted by its recent acquisitions, investments, and partnerships. We then categorized companies by their business relationships with Apple across these priorities.
Digital health
Machine learning & ai, semiconductors & advanced materials.
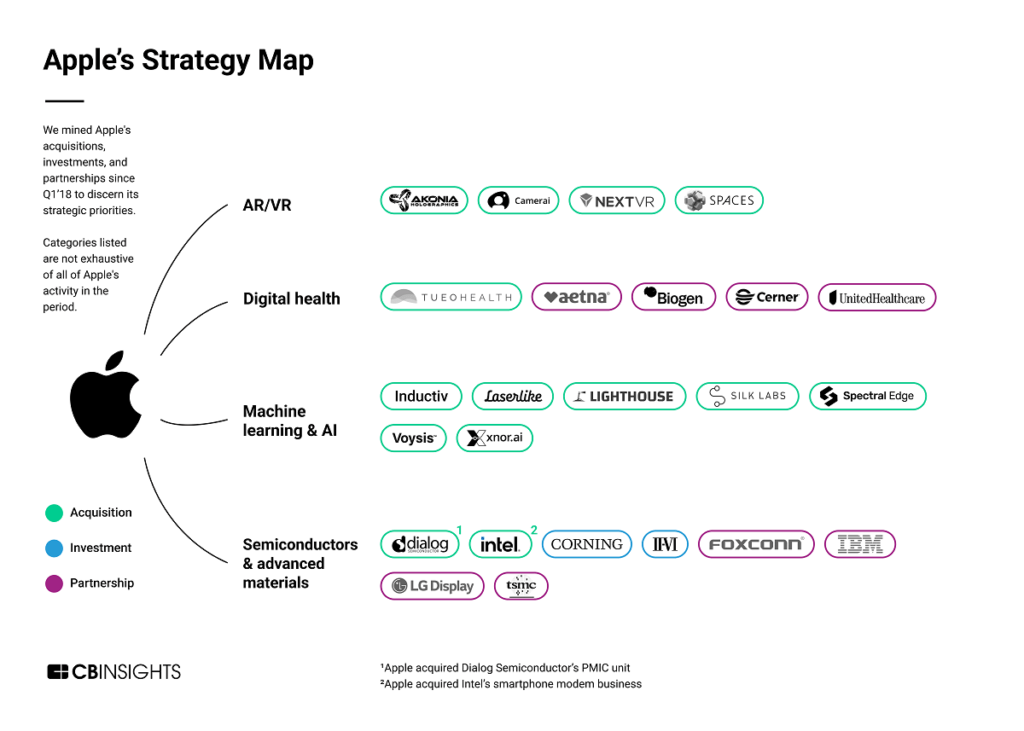
These designations are not exhaustive of Apple’s investment and partnership activity in the analyzed period.
Apple started investigating augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) applications over a decade ago, as evidenced by its patent activity . For example, its ARKit framework (launched in 2017) — which enables developers to build AR experiences into their apps — is now used in over 14,000 apps with over 13M total downloads.
In recent years, companies in the AR/VR space have become serious M&A targets for Apple, coinciding with rumors about its internal development of a mixed reality headset that is expected to release in 2023 (eventually followed by a sleeker pair of glasses ).
In 2018, Apple acquired 2 companies in the space: Camerai , an Israel-based computer vision and AR tech company, and Akonia Holographics , an AR optics developer . These purchases helped grow Apple’s patent portfolio and talent, setting the foundation for its future AR products.
Then in 2020, Apple acquired two VR companies. First was NextVR for a reported $100M , which developed solutions for the capture and delivery of sports and entertainment virtual reality content. A few months later, Apple purchased Spaces , which created location-based and themed virtual environments.
While Apple has not been explicit about its metaverse ambitions like fellow big tech giant Meta , its continued investment in AR/VR sets it up for more immersive digital environments of the future — and the hardware they may need.
Apple is continuing to cement its focus in health as part of a wider strategic priority, as we’ve previously examined here and here . Apple is also working with companies, universities, app developers, and others to move this priority forward.
Central to this strategy are Apple devices, such as the Apple Watch and iPhone, which enable users to track, aggregate, and share their health data.
The company’s research teams are actively exploring new health indicators the Apple Watch could help monitor. Last year, Apple announced a collaboration with Biogen IDEC to investigate how the device can detect declines in cognitive health. Apple has also teamed up with several university and government partners — such as the NIH, the White House, Harvard , UCLA , and the University of Michigan — to conduct studies that use Apple devices to address issues ranging from Covid-19 to noise exposure to women’s health.
Meanwhile, Apple has landed agreements with major health plans like UnitedHealthcare and Aetna to offer subsidized Apple Watches and other wellness services to members.
In 2019, the company purchased Tueo Health , which developed a system to help parents monitor asthma symptoms in sleeping children. This acquisition is further indication of Apple’s intention to engage consumers on health & wellness.
Apple has aggressively acquired companies across the machine learning (a type of AI that leverages past data to understand future scenarios) and AI space — outpacing fellow tech giants like Google and Microsoft — to shore up its AI efforts .
Apple’s AI acquisition spree has been essential to the development of new iPhone features. Many of its purchases are positioned to enhance its virtual assistant, Siri, but they also have applications across many other parts of its software.
For example, Apple acquired in 2019 and 2020:
- Laserlike , an ML platform that could better personalize Siri, news feeds, and video apps for individual users.
- Voysis , to improve Siri’s language understanding.
- Inductiv , which developed an AI platform to automatically identify and correct errors in datasets, helping software to improve with less human intervention.
- Spectral Edge , a company with infrared tech that could enhance iPhone photos.
In January 2020, Apple also acquired Xnor.ai for a reported $200M , which specialized in developing highly efficient ML models deployed at the edge. The edge computing startup could enhance a number of Apple’s device ML models, including those related to capturing and processing images, natural language processing, and object recognition.
Other AI acquisitions include Lighthouse AI , a developer of AI-powered home security cameras, and Silk Labs , which developed on-device ML software. These possibly point to Apple strengthening its smart speaker, the HomePod, with a focus on privacy by keeping data on the device.
Apple is considered by some as the most advanced semiconductor design firm in the world. It’s also partnered with TSMC — the most advanced semiconductor production firm in the world — to produce chips. Semiconductor production is an extremely complex manufacturing process, making this partnership critical.
Apple’s design history started in 2008, when the company made the prescient purchase of PA Semi , a semiconductor design firm. Apple understood that if it wanted the best consumer experience possible, it needed to design its own chips, tailored to its own devices.
In the years since, Apple has remained aggressive in semiconductor design. The company purchased Intel ‘s smartphone modem business in 2019 for $1B, giving it a significant patent portfolio and 2,200 former Intel employees. This followed the acquisition of Dialog Semiconductor ‘s power management division in 2018 for $600M .
Apple has built out its semiconductor capabilities further with investments in critical suppliers, including Corning and II-VI . Corning is the manufacturer of Gorilla Glass, a durable glass used for iPhone screens. On top of the $450M it’s already given to Corning, Apple invested $45M in the company in 2021 — coinciding with the rise of bendable iPhone rumors, though no official purpose for the funding was given.
Meanwhile, Apple invested $410M in II-VI in 2021, building on its $390M investment in II-VI-owned Finisar in 2017. II-VI makes the optical technologies that power features like Face ID and Portrait mode, as well as the lasers used in Apple’s LiDAR Scanner, which is used to create AR experiences.
In addition to these investments, Apple has developed partnerships with leading firms such as Foxconn , one of its main partners in iPhone production, and LG Display , a producer of its OLED displays.
Other categories
Beyond these 4 strategic areas, Apple has made noteworthy acquisitions, investments, and partnerships across a number of other categories.
Rumors of an Apple car have existed since 2014, further materializing in 2018 when the company partnered with Volkswagen to turn some of the carmaker’s vans into autonomous employee shuttles.
Over the past few years, Apple has also filed a number of car patents. Using CB Insights patents search tool , we can see that the company is focusing on traditional car technologies, such as thermal management systems and vehicle seating .
Beyond patents, Apple has made one acquisition in the space, purchasing autonomous driving startup Drive.ai in 2019. Apple has also reportedly held talks with Hyundai , Toyota , and Porsche — focusing on car and battery production in the US with Hyundai and Toyota, and car production with Porsche.
DIGITAL MEDIA & Services
Apple has grown its services segment — which includes Apple Music, Apple TV+, cloud services, and others — to nearly $20B in quarterly revenue, with 825M paid subscriptions as of the second quarter.
Alongside this growth, Apple has made multiple acquisitions of digital media companies over the last 2 years, including Scout FM , Vilnyx , Primephonic , and AI Music . These purchases are aimed at enhancing its music and podcasting capabilities, while the Vilynx purchase — for a reported $50M — provides AI tools that help analyze and understand videos.
Apple’s 2018 acquisition of digital magazine service Texture laid the foundation for its subscription service Apple News+, launched in 2019.
More recently, Apple notably invested in independent music distribution platform UnitedMasters , participating in the company’s 2021 Series B alongside Alphabet and Andreessen Horowitz. The company also partnered with Verizon to offer the telecom’s Unlimited customers a free trial of Apple Music, and with Comcast on a cross-platform distribution deal for their streaming apps.
Apple first released Apple Pay — a digital wallet and mobile payment system — in 2014. Since then, Apple has continued to invest in payments and beyond .
In July 2020, the company acquired Mobeewave , which developed a solution to turn any NFC phone into a mobile payment terminal. Most recently, Apple purchased UK-based fintech Credit Kudos , which uses consumer banking data for better informed credit checks.
Apple has also developed partnerships to grow its services, including with PayHawk and Isracard to expand Apple Pay , and with Goldman Sachs to launch the Apple credit card.

Apple Business Strategy: a brief overview
Apple business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. Specifically, the multinational technology company differentiates its products and services on the basis of simple, yet attractive design and advanced functionality.

Apple business strategy consists of the following four elements:
1. Focus on design and functionality of products . According to its business strategy, Apple has adapted advanced features and capabilities of its products and services as bases of its competitive advantage. The list of innovations introduced by Apple include, but not limited to the introduction of iPad, the first device of its kind that stored thousands of songs with a simple shuffle capabilities through songs, development Macintosh, the first computer to use a graphical user interface and the launch of iMac that “ripped up the computer design rule book, doing away with dull beige boxes and instead replacing them with fun, translucent machines in shades such as “Bondi Blue” that hinted at the aesthetic Apple would become so well-known for.” [1]
The first company ever to be valued at $1 trillion systematically improves features and capabilities of its products, setting new standards for the industry at the same time. Take photos for example. Apple single-handedly advanced global photography industry with a range of innovations illustrated in table below.
| High dynamic range imaging | 2010 |
| Panorama photos | 2012 |
| True Tone flash | 2013 |
| Optical image stabilization | 2015 |
| Dual-lens camera | 2016 |
| portrait mode | 2016 |
| portrait lighting | 2017 |
| night mode | 2019 |
| LiDar scanning | 2020 |
Photography innovations by Apple Inc.
First mover advantage is another element of Apple competitive advantage. It has to be stated that Apple competitive advantage may be challenging to be sustained for long-term perspective. Specifically, the management may fail in terms of ensuring the addition of innovative features and capabilities in new versions of its products, thus compromising its competitive advantage.
2. Enhancing customer experience. Focusing on customer experience is one of the pillars of Apple business strategy. It is not rare for Apple fans to create videos of themselves unwrapping their new Apple products and uploading the video on YouTube. This happens because the company has succeeded in creating a customer experience that extends beyond the purchasing process of a product.
For example, starting using any Apple product is extremely easy. Customers open the box, plug to electricity, turn on and start using products. There is no need to install or download anything. More than 518 Apple Stores in 25 countries and regions, where people can try products and ask helpful staff questions effectively also contribute to customer experience.
3. Strengthening Apple ecosystem . Apple business strategy can be characterised as vertical integration in a way that the company has advanced expertise in software, hardware, and services at the same time. Apple’s vertical integration is one of the major factors that set it apart from the competition. The company has been benefiting from its vertical integration immensely. Specifically, an important source of Apple competitive advantage relates to its ecosystem, which is enabled by such integration.
Apple devices and software sync easily and work well with each other. Applications work on multiple Apple devices at the same time and there is no much difference in user interfaces. However the same items do not pair with products of other companies, thus creating the likes of a closed ecosystem. Apple’s ecosystem creates switching costs for its customers to the competition. The ecosystem also provides the opportunities to leverage relationships with existing customers to offer other products and services.
4. Decreasing dependence of the business on the sales of iPhones . Apple business strategy is transitioning from relying on iPhone sales to prioritizing its services business and other divisions. John Giannandrea has been promoted to a machine learning and AI role, retail chief Angela Ahrendts left the company and Bill Stasior has been removed as a head of Siri. [2] These high-profile changes that took place within the timeframe of less than three months are clear indication of company’s focus on services and other business divisions in order decrease dependence of the business on the sales of iPhones.
It is important to note that these and other efforts are showing positive results. Specifically, Apple’s services business division generated record revenues of USD 53,77 billion in 2020, an increase of 16% compared to the previous year. [3]
Apple Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Apple business strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Apple. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Apple leadership, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Apple marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

[1] Apple’s Greatest Innovations (2016) The Telegraph, Available at: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/picture-galleries/6099399/Top-10-Apple-innovations.html
[2] Broussard, M. (2019) Apple’s Recent Leadership Changes Suggest Transition From iPhone Reliance to Focus on Services, Mac Rumors, Available at: https://www.macrumors.com/2019/02/18/apples-leadership-changes-services/
[3] Annual Report (2020) Apple Inc.
Understanding Apple Business Strategy

Based in Cupertino, California, Apple is an American multinational company that designs and sells consumer electronics, software, and services. Apple’s iPhones helped spark the dawn of the smartphone-era and have revolutionized the way the world sees phones.
Apple’s business strategy, though simple, holds up to date and has played a major role in helping Apple become the first-ever company to reach the trillion-dollar valuation .
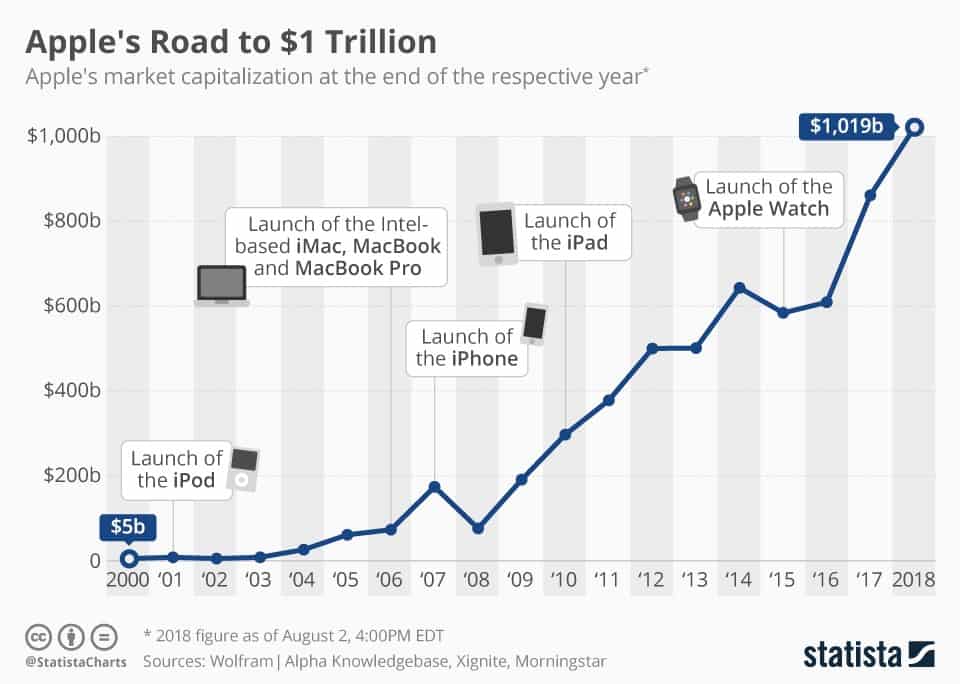
Apple’s business strategy can be easily understood by knowing the type of products and services they provide.
Let’s find out.
The Business of Apple
Apple was founded on 1 April 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, and bought innovation to the table in form of their rendition of what a personal computer should look like with the Apple I.
Apple continued producing quality and perfectly engineered products, with an emphasis on design and aesthetics. Apple primarily made desktop systems and hardware accessories related to it for a while and soon diversified into making other consumer electronics such as laptops, PDAs, music players and such.
Their first major success of the new millennium was the iPod – which wholly embraced all of Apple’s design philosophy and set stage for its future products. The revolutionary iPhone was launched in 2007. With resounding success, Apple once again redefined the public’s perception of the smartphone.
To put it in short, Apple has brought about –
- The revolution of the PC industry
- Introduced mouse and graphical user interface to consumer products
- Innovated the music player
- Launched the smartphone revolution
- Bringing innovating technologies that set trends for the rest of the industry
Here are all the products and online services that Apple currently provides –

Apple is among the leading electronics manufacturers in the world with profit margins and revenues that put most major businesses to shame. Apple became the first “tech” company to reach a trillion-dollar market capitalization value in August 2017.
There are only five other companies to have made it to the trillion-dollar list, which brings us to –
What is Apple’s business strategy that has led them to become such a successful company?
Let’s find out the operational tactics of Apple which have helped them list as one of the market leaders in the technology and electronics industry.
Apple Business Strategy
Apple ecosystem.
Apple has always designed, developed and manufactured its hardware and software in-house. This innate advantage helps them create a deeper level of integration between its hardware and software – between for all of its devices.
Here’s an example –
Say, you buy an iPhone. You soon start using a few of its online services such as iCloud for storage. Herein lies its brilliance – the hardware, software, and services on the iPhone are so well designed and intuitive to use that you soon fully embrace it. Once you do, it leads you to create a good image and also only the rest of Apple devices can use the services.
This makes you buy their laptops and other hardware that plays well with one another. This extends to their accessories as well – the recent line of iPhones have removed the headphone jack which makes people buy more of Apple’s wireless AirPods earphones.
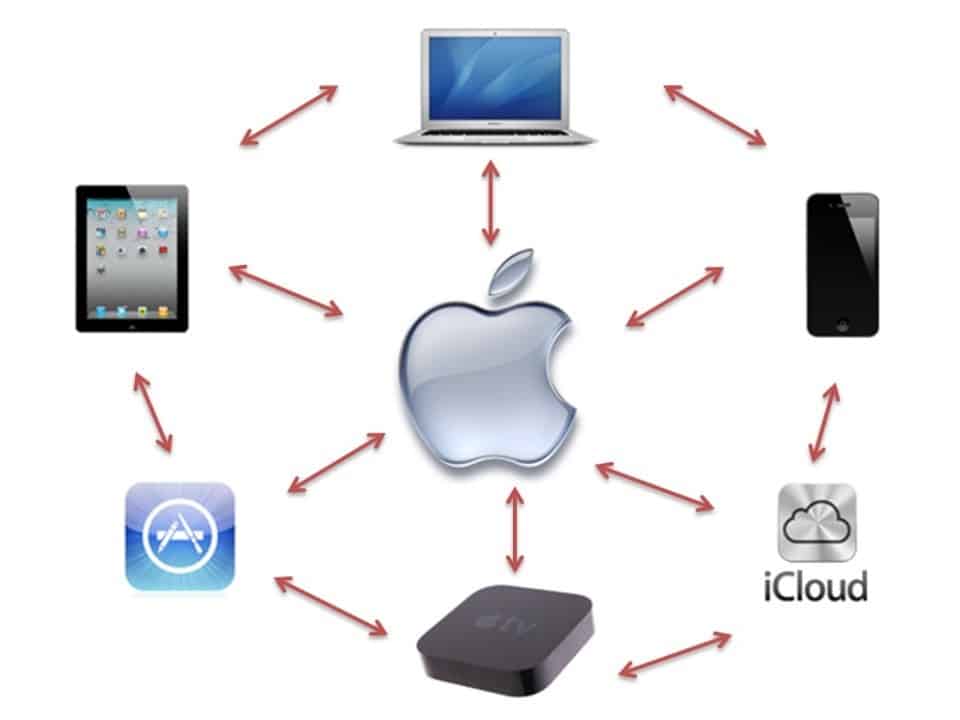
This strategy has helped Apple create an environment or “ecosystem” that offers a consistent and great experience to its users.
Customer Relation
Apple has always made a major point in providing stellar customer service and has been able to facilitate this with its AppleCare service and by employing knowledgeable sales and service personnel to cater to the customers in need.

This has helped Apple set itself apart from the rest of the competition in terms of customer relations and support, increasing its brand loyalty . Apple has made it a point to focus on providing the best quality of service to its consumers and this has been reflected in the increased chance of customers sticking with Apple.
Apple also builds upon this with their purpose-built Apple Stores, which are mostly situated at prime locations, allowing customers to experience Apple products before making the purchase.

The Apple Stores also help have much finer control over the customer experience and apart from showcasing Apple products and devices, Apple Stores double up as service centres.

Form Over Function
One of Apple’s main strategies when it comes to product development lies in its ability to provide well-designed products and services – with emphasis on minimalism, clean lines, and solid tones.

But it can also be said that Apple has made it a point to focus on design and aesthetics over performance when possible.
The recent Macbook (laptop) lineup is a great example of this. Apple has sacrificed heat dissipation capabilities and has included a thinner keyboard – which is riddled with issues such as not working in case the slightest of dust getting in between the keys – all in the pursuit of maintaining a thin and sleek design.
But this strategy has still worked out fine and in favour of Apple. The average consumer mostly prefers thinner and quieter laptops.
Brand Differentiation
Apple’s brand strategy and marketing strategy have always made it a point to promote itself as a luxury brand while focusing on differentiating itself from its competitors. Apple makes sure that it puts forth the following brand image – Apple competes against itself and not against others. This helps Apple in achieving its desired brand image and recognition.
Consumers anyway tend to presume this is because Apple has built its reputation as a manufacturer of well-built premium products.
Customer Privacy
Apple has always made it clear that it values customer privacy and has shown to handle its customer’s data much better than the rest of its competitors.

During CES 2020, Apple’s senior director for global privacy mentioned Apple’s take on privacy as –
- Minimize the amount of personal data collected from its users.
- Providing highly secured cloud storage (iCloud)
- Providing tools for users to be able to maintain their privacy
Final Thoughts
Apple’s main strategies are as follows –
Apple uses product development and market penetration as its main intensive strategy for growth.
Apple’s product development revolves around creating clean and premium products that are quite timeless and appeal to a wider audience while their market penetration strategy can be summed up as distinguishing themselves from the rest of the competition, providing an air of distinction and recognition for their products.
Their exceptional customer support and the seamless integration between their products are icing on the cake which helps Apple firmly hold its place as one of the market leaders in the technology and consumer electronics industry.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Apple Business Strategy in the comments section.

Started out to become a developer but felt at home in the home of startups. The journey started from a single novel. Been an entrepreneur since schooling days. Interested in coding, reading and movies.
Related Posts:


- Innovative Prompts
- Strategies Packs
- Skills Packs
- SOPs Toolkits
- Business Ideas
- Super Guides
- Innovation Report
- Canvas Examples
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Discounted Bundles
- Search for:
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
Apple Business Model
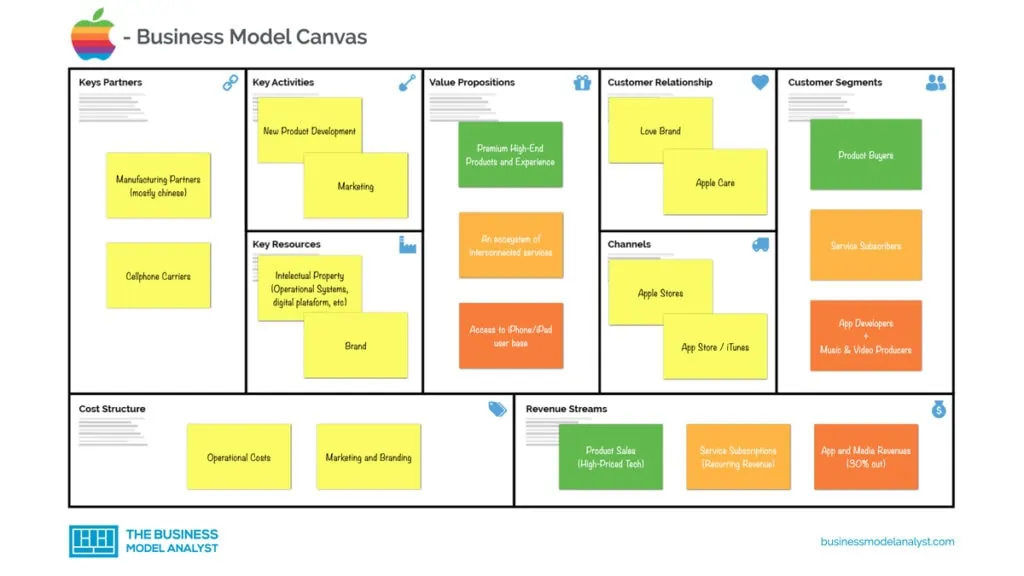
Apple Business Model focuses primarily on selling its products and offering services through subscriptions. Sales of Apple products like the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and MacBook make up a large percentage of Apple’s revenue, while its services include Apple TV+, Apple Fitness+, Apple Music, iCloud+, and Apple Arcade, although a small percentage of its revenue, net them a whopping average of $13 billion per quarter.
Apple has surpassed the trillion-dollar market cap mark through its business model, making it the first company to ever manage such a feat.
A brief history of Apple:
Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, two college dropouts, founded Apple on April 1, 1976, using Jobs’ garage as their main office. They aimed to revolutionize the way people saw computers. They wanted to make computers small enough to fit in people’s homes and offices. In effect, their first product, the Apple 1 — a hand-built computer —, included only functional hardware modules like CPU, RAM, and basic textual-video chips , and excluded features like monitors, keyboards, and other Human Interface Devices.
On their second product, the Apple II, expansion slots were included for attaching floppy disk drives and other components and Human Interface Devices. This second product increased their sales from $7.8 million in 1978 to $118 million in 1980 (when they went public).
A few years later, in 1983, Wozniak left the company, and Jobs followed suit in 1985, after hiring PepsiCo’s John Sculley as president . He was ousted after the growing friction between him and Sculley resulted in him organizing a ‘coup’ to remove Sculley. This coup backfired, however.
Steve Jobs founded his NeXT software company soon afterward, after buying Pixar from George Lucas. However, his departure was short-lived, and in 1997 Apple bought his company. This was done to bring him back to the company in order to save their declining market shares. The changes he implemented after coming back saved the company from impending doom, and in 2007, they launched one of their most successful product, the iPhone.
They have launched other successful products and services since then, which helped them become the first company ever to cross the trillion-dollar mark, this was in 2018. In 2020, they doubled their market cap by doubling down on their highly successful business model .
Who Owns Apple:
According to 2021 shareholder data, Apple’s major shareholders included corporations like The Vanguard Group (7.68%), BlackRock, Inc. (6.47%), Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (5.56%), and private investors like Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO, Artur Levinson, Jeff Williams, Al Gore, Dave Adams, and Andrea Jung.
Apple’s mission statement:
Apple’s Mission Statement is: “To bring the best user experience to customers through innovative hardware, software, and services.” – Bstrategyhub
How Apple makes money
Apple leverages its unique ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software, and services to provide its customers with products and solutions with innovative design, superior ease of use, and seamless integration — 10-K 2017 .
Apple makes money by designing, manufacturing, and selling smartphones, tablets, personal computers, wearables, and accessories. Their main products include iPhones, MacBooks, iPads, Apple Watch, AirPods, and the Apple TV. They also generate revenue by offering subscription services like their iCloud cloud services, Apple TV+ subscriptions, Apple Arcade, and iTunes. The company recently announced its plans to start hardware subscription services for its products.
Furthermore, Apple makes money when the users of its products pay fees for the extension of their warranties. In addition to their products, they also sell compatible third-party accessories and apps.
As a passive revenue source, Apple also makes money through in-app purchases on iPhones, and app sales on their App Store — they take a 30% cut from every transaction.
Their largest and most profitable revenue source is the sales of their products, however, their subscription services generate the highest gross margins in comparison to product sales.
Apple’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Apple Business Model Canvas below:

Download FREE!
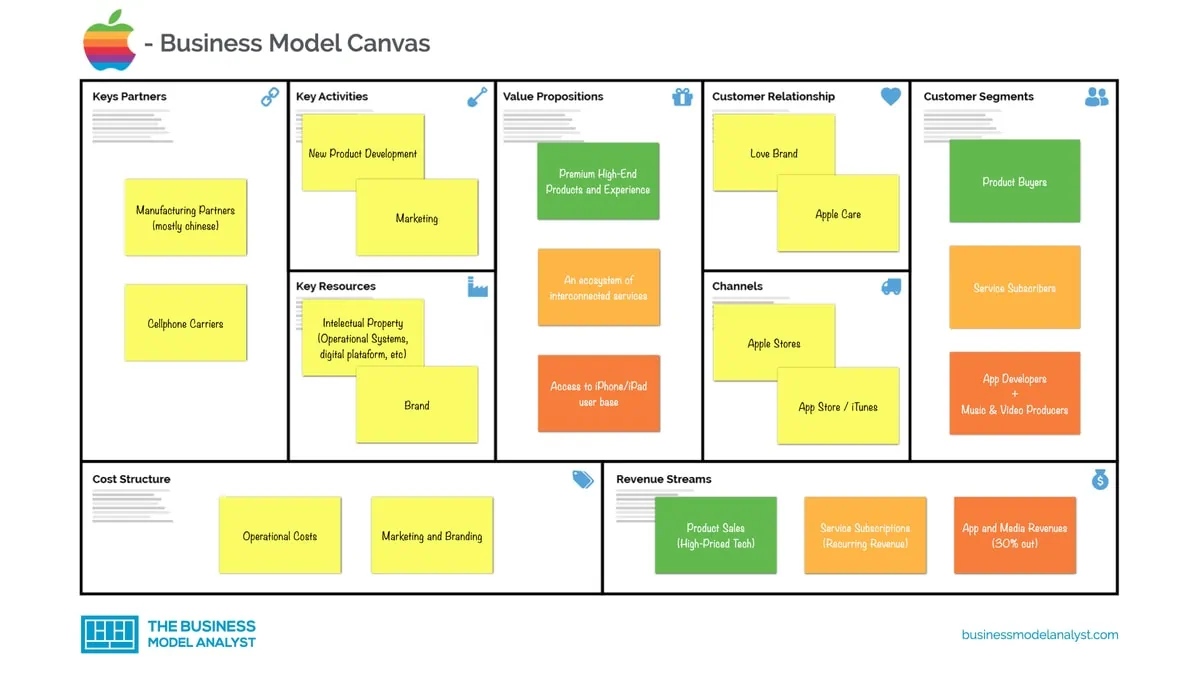
To download Apple Business Model Canvas today just enter your email address!
Apple’s Customer Segments
Apple’s customer segments consist of:
- Product Buyers: These include people that buy their products for their high-end performances and people who use them as their primary devices regardless of performance. A section of their customers also buys their products because of the brand name;
- Service Subscribers (most service subscribers overlap as product buyers): These include subscribers of Apple Arcade — their games’ subscription service —, Apple TV+, iCloud+, and their warranty extension services.
- App Developers (and music producers) : Anyone that would like to sell their apps and music to the Apple user base and monetize through app store or iTunes.
Apple’s Value Propositions
Apple’s value propositions consist of:
- Premium High-end Products (with a focus on privacy): Apple offers its customers carefully crafted products with a focus on performance, stability, and privacy, a number of its customers have stayed around because of this.
- An ecosystem of interconnected services : Apple’s line-up of services (and products) are well integrated with each other, offering users hassle-free inter-use of their products and services.
- Access to iPhone/iPad user base : one of the richest user bases in the world that are willing to spend much more than Google Android user base.
Apple’s Channels
Apple’s channels consist of:
- Apple Stores
- Third-party Stores
- Telecom Companies (Apple’s iPhones are typically bundled with a mobile plan to reduce costs by offering monthly repayment packages)
Apple’s Customer Relationships
Apple’s customer relationships consist of:
- Social Media
- Customer Service
- Operating Systems
- Loyal Community
Apple’s Revenue Streams
Apple’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sale of Products
- Subscription Services
- App Store and in-app purchase percentage cuts
- Licensing Fees
- Cloud Services
Apple’s Key Resources
Apple’s key resources consist of:
- Brand Name and Recognition
- Management Team
Apple’s Key Activities
Apple’s key activities consist of:
- Design & Manufacturing
- Marketing & Sales
Apple’s Key Partners
Apple’s key partners consist of:
- Hardware Suppliers , such as Qualcomm, Samsung, Cisco, etc.;
- Software Providers : cloud service providers, such as Google and Amazon;
- Investors/Shareholders
- Telecom Companies
Apple’s Cost Structure
Apple’s cost structure consists of:
- Manufacturing & Distribution
- Platforms Maintenance Fees
- Payment Processing Fees
- Management & Administration
Apple’s Competitors
- Samsung : One of Apple’s main competitors in the smartphone space, Samsung holds a whopping 20% share of the global smartphone market. Samsung’s entrance into the market with its Samsung Galaxy and Note series has negatively influenced the sales of iPhones globally, however, they are not the only company that has contributed to this, others include Xiaomi, Vivo, and Oppo.
- Dell : Dell Technologies (DVMT) is a company that makes desktop and mobile computing devices, including laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. Dell’s biggest competitor is Apple; the two companies have a long history of competing against one another. In fact, in 2004 Dell released a product to compete with Apple’s iPod music player: Dell DJ.
- HP : Hewlett-Packard Co. (HPQ), established in 1939, is known as the founding company of Silicon Valley as well as for making affordable consumer computers. HP has expanded its presence in recent years to include computers for a broader range of consumers around the globe. Apple Inc. is a leading competitor for HP outside the United States.
Apple’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT Analysis of Apple:

Apple’s Strengths
- Pricing Strategy : Apple’s high prices makes it possible for the company to sell a small number of products and still rake in a large amount of revenue;
- Subscription Services : The company’s subscription services and the principles of the subscription business model enables Apple to have a predictable chunk of revenue;
- Performance : Apple’s insistence on rolling out its products with high-performance processors has cemented its name as a go-to company for high-quality products;
- Brand Recognition : Their popularity and fame as a goto company for quality products and services has helped them increase and maintain their market cap;
- Loyal Community : Apple’s community of loyal customers allows them to have customer feedback aimed at improving the quality of their products and services. This community also enables Apple to have a somewhat stable revenue proposition.
Apple’s Weaknesses
- Pricing Strategy : Apple’s prices make it a luxury company in developing countries, thus driving away most middle-class and lower-class potential customers;
Apple’s Opportunities
- Products and Pricing Strategy : Although being partially implemented, the design and manufacturing of products aimed at middle-class and lower-class consumers will enable Apple to increase its already high revenue and market cap.
Apple’s Threats
- Market Trends : As a result of Apple’s yearly release of products, the market trend is a big factor that determines the revenue yield of its new line-up of devices. Because most customers already have recent versions of their products or do not have plans of purchasing new ones, Apple’s yearly revenue yield at new product launches seems to be reducing year by year, and will most likely continue;
- Competition : Competitors like Samsung are already affecting Apple’s customer base via their offering of flexible and customizable OS in their products. The arrival of better competitors aimed at the high and middle classes of developed countries will most likely affect Apple’s user base.
-> Read More About Apple’s SWOT Analysis .
Through the success of its application, Apple’s business model is worth considering for new entrants into the tech space. However, do not expect overnight success since Apple experienced its fair share of challenges even with its implementation of its business model. Apple’s combination of the subscription business model and their product sales was a major factor that determined their huge revenue growth and as such, if you are to adopt the Apple business model, do not overlook the subscription business model .
Daniel Pereira
Receive our updates.
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- HBS Case Collection
Apple Inc. in 2020
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 31
About The Author
David B. Yoffie
Related work.
- December 2020
- Faculty Research
- January 2022
Apple Inc. in 2020 – Select Market Data
- Apple Inc. in 2020 By: David B. Yoffie
- Apple Inc. in 2020 – Select Market Data By: David B. Yoffie
Tim Cook Reveals Apple's 10-Year Plan For Future Tech
The company's vision for the future is already being etched into its products. just look closely; it's right in front of you..

Vision of the Future
Apple revealed its 10-year plan for the future this week.
If you don't remember that slide from the hours of presentations Apple executives made onstage during the company's developer conference on Monday, you're not alone.
Apple didn't explicitly call it a 10-year plan. And the company was very subtle about how it showed this road map.
But look closely, and it's easy to see.
Instead of introducing flashy new products that will change your life today, this year's WWDC conference was all about putting the pieces in place for what comes next.
It's a Trojan-horse strategy — sneak the seeds for the next breed of technology products into the stuff that we're already using.
A new augmented reality platform, virtual reality development tools, the HomePod speaker, and improvements to iOS 11 on the iPad may not feel revolutionary or even particularly useful right now, but they are the building blocks for the technologies Apple is betting will power our future.
Let's break it down:
Augmented Reality
Ask most tech companies which product will replace the smartphone and the answer will probably revolve around a wearable device for "augmented reality," the tech that overlays digital images on the real world.
Microsoft has the HoloLens headset. Google has Project Tango for Android devices and, one day, headgear like Google Glass. Facebook announced its AR ambitions a few months ago, and Mark Zuckerberg even said AR glasses would replace the need for most screens in your life one day.
Apple's approach is different.
There weren't any AR goggle demos or TED-talk-esque prophecies about how a pair of glasses will soon be the only computer you need. Instead, Apple is starting with something already very familiar: the iPhone and a new way for developers to build AR apps for the phone. When iOS 11 becomes available on tens of millions of Apple devices this fall, Apple will immediately have the largest AR platform. Even better, it'll be on the devices that people already use — not futuristic glasses or headsets. Apple will get a major advantage over its AR competitors with one simple software update.
That won't be a game changer right away of course, and it certainly won't deliver the kind of jaw-dropping experience being developed by companies like Magic Leap. AR-enabled iPhones will mostly mean some cool games and entertainment apps at first. Pikachu will look more realistic in "Pokémon Go." You'll be able to build virtual Lego models on your coffee table. The rainbow puke in your Snapchat selfies will look even better.
But AR on the iPhone sets Apple up for the long run by building a base of developers already dedicated to the platform who want to make stuff for the largest number of users they can. If and when Apple decides to take AR to the next level with a pair of smart glasses or something else, it'll be in a better position than companies trying to win over developers.
Virtual Reality
Apple has been hesitant to get involved with virtual reality, even as the rest of the tech industry seemed to be hyperventilating over its prospects. But now the time feels right for Apple, and it's offering a new set of tools in the coming macOS Sierra software that it says will let developers connect VR headsets and create 3D and VR content.
This isn't about attracting gamers and VR enthusiasts to the Mac. This is about making sure Apple's most dedicated class of users has the tools it needs to create the content of the future. Apple has historically been the platform of choice for digital artists, filmmakers, and other professionals, and adding VR development tools will make sure those users have what they need and don't abandon Apple.
HomePod and Ambient Computing
HomePod, the new Amazon Echo competitor, is Apple's biggest new Trojan horse of all.
Even though Apple focused on HomePod's music capabilities and pitched it as a new kind of home stereo, it undersold the rest of the real potential. HomePod is also Apple putting Siri in your home in a new way and making a long-term play for the concept of ambient computing, in which everything you own is connected and powered by an underlying artificial intelligence.
HomePod is a way to put Siri everywhere else when you're not looking at your iPhone, typing on your Mac, listening to your AirPods, or tracking your workout on your Apple Watch. HomePod is Apple creeping into the rest of your life under the guise of a really nice Wi-Fi stereo. Apple may be focusing on music now with HomePod, but it's also sneaking in a lot of Amazon Echo-like features like controlling your connected appliances and getting updates from Siri.
That said, it's pretty clear why Apple would want to bury the AI features of HomePod. Pitching it as a digital assistant instead of a music player will only open up Apple to more criticism about how it is falling behind in AI compared with Google and Amazon. Apple's Siri is still much less capable as a virtual assistant than the offerings from Amazon and Google, and Apple has a lot more work to do to catch up. But there's no question that AI is a big area of investment for Apple, and HomePod will play an important role in this strategy as Apple makes progress.
iOS 11 on iPad
The biggest news with iOS 11 wasn't on the iPhone. It was on the iPad.
Apple has finally started making improvements to the software that help turn the iPad into the laptop replacement the company has been promising for years. There's a new file-storage system, an app dock similar to the one on Mac, the ability to drag and drop content in between apps, and apps that float in separate windows. The iPad is starting to feel less like a giant iPhone and more like a touch-screen Mac.
There's still a lot of work to do. The iPad Pro's keyboard isn't as good as the one on a normal laptop, and it's now up to developers to build compelling apps that take advantage of all the new iOS 11 features and give people a better reason to ditch their laptop for an iPad. The new 10.5-inch iPad is a small move in the right direction because its larger size allows for a full-size keyboard, but it's still not enough.
But Apple is inching closer toward its ultimate goal of creating a super thin and portable laptop replacement, and iOS 11 feels like a huge milestone.
What's Next
A lot of this stuff may not work out. We're in a period of relatively flat innovation across most of the tech industry, where new gizmos improve only incrementally each year. It's impossible to tell which wild idea will actually end up taking off and which will fizzle. (Two years ago everyone thought smartwatches were going to revolutionize the tech industry, after all. Now that's barely part of the conversation.)
In some sense, Apple's latest batch of WWDC announcements feels underwhelming, as if Apple is dabbling in various areas rather than making a bold move in any one direction. But the company's vision for the future is already being etched into its products. Just look closely; it's right in front of you.
Share This Article

Apple Business Manager Support

Apple Business Manager
A simple, web-based portal that provides a fast, streamlined way to deploy Apple devices.

Apple Business Essentials
Keep track of and manage every aspect of your organization’s Apple devices with one complete subscription.

Check availability
Find out if Apple Business Manager is available for your region, and what payment methods are accepted.
- Find availability for your region

Training for IT professionals
Explore tutorials and exercises that cover everything you need to support Apple devices in organizations.
- Get started

Apple Configurator
Apple Configurator integrates with the Device Enrollment Program to automate MDM enrollment to seamlessly configure devices and distribute apps.
- Learn about Apple Configurator
Enrollment and deployment

Automated Device Enrollment
Simplify initial device setup with Automated Device Enrollment.

Manage device suppliers
Find out how to add devices to Apple Business Manager at the time of purchase.

Apple Platform Deployment
Easily deploy and manage your Apple hardware, software, and services.
- Manage your devices
Manage content and users

Distribute content with Apps and Books
You can distribute content purchased in Apps and Books directly to your users for your school or business.
- Learn how to distribute content

Understand Managed Apple IDs
Apple Business Manager makes it easy to create and manage Apple IDs owned by your organization.

Whether your organization has ten devices or ten thousand, Apple fits easily into your existing infrastructure.
- Learn more about Apple at Work
Your guide to Apple Business

Apple Business Manager User Guide
Learn about features and discover all that Apple Business Manager can do.
- Browse the guide
- Review the release notes

Apple Business Essentials User Guide
Learn about features and discover all that Apple Business Essentials can do.

AppleCare Professional Support
Get personalized assistance from experts who can keep your IT operations running smoothly.
- Learn more about AppleCare for Enterprise
Search for more topics

Apple Communities
Find iPhone , iPad , or Mac business solutions from users around the world.
Contact Support
Get help using Managed Apple IDs, deploying apps, or managing devices.
- Find the phone number for your country or region
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Advertisement
Supported by
Welcome to the Era of the A.I. Smartphone
Apple and Google are getting up close and personal with user data to craft memos, summarize documents and generate images.
- Share full article

By Brian X. Chen
Every year, Apple and Google announce major software updates that bring new features to our smartphones, like cosmetic overhauls to the home screen, stronger privacy protections and fun messaging tools. This year, the changes will feel more radical because the companies are focusing on reinventing our phones with artificial intelligence.
At its annual software developer conference on Monday, Apple showed a host of enhancements coming this fall to iOS 18, its operating system powering iPhones. The new tools include a revamped version of its voice assistant, Siri , that is easier to talk to and an A.I. system that will generate images, create summaries of web articles and craft responses to text messages and emails.
Apple’s news followed Google’s Android announcements last month, which included an A.I. system that automatically summarizes audio transcripts, detects whether a phone conversation is likely a scam and helps students with homework.
Because A.I. tech is still new, it’s unclear whether these improvements will resonate with the masses. The change that will have a more immediate effect has to do with old-school text messages — also known as the green bubble . Apple said its new software would adopt a messaging standard that would let iPhone users send higher-quality messages to Androids, addressing an issue that has made it more difficult for people to communicate for more than a decade.
Apple and Google are set to release their free software updates for iOS and Android this fall. Here’s what to know about how our smartphones will change.
Siri Is Getting an A.I. Brain Transplant
Apple said it had completely reworked Siri, its 13-year-old virtual assistant.
The assistant will soon be powered by Apple Intelligence, the company’s version of a “large language model.” That type of A.I. technology uses statistics and complex algorithms to guess what words belong together, similar to the autocomplete feature on your phone. It’s the same type of underlying technology we’ve seen powering chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini . Apple said its system was more private than others’ because people’s data would remain on their iPhones.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Apple doubles down on artificial intelligence, announcing partnership with OpenAI

OPEN AI TECH ON APPLE DEVICES

Apple software chief Craig Federighi, right, pictured with exec John Giannandrea, announced a partnership with OpenAI to bring AI features to its products. (AP Photo/Jeff Chiu) Jeff Chiu/AP hide caption
Apple is going all-in with artificial intelligence, announcing several new AI features and a partnership with ChatGPT-maker OpenAI. The company announced the deal at its Worldwide Developers Conference on Monday afternoon.
The highly anticipated AI partnership is the first of its kind for Apple, which has been regarded by analysts as slower to adopt artificial intelligence than other technology companies such as Microsoft and Google.
The deal allows Apple’s millions of users to access technology from OpenAI, one of the highest-profile artificial intelligence companies of recent years. OpenAI has already established partnerships with a variety of technology and publishing companies, including a multibillion-dollar deal with Microsoft.
OpenAI will be integrated into Apple’s digital assistant Siri, Apple software chief Craig Federighi said during the conference. That would allow people to ask for help with things like recipe ideas, room decorations or composing a story, Federighi said.
“Suppose you want to create a custom bedtime story for your six-year-old who loves butterflies and solving riddles,” Federighi said. “Put in your initial idea, and send to ChatGPT.”
The announcement comes as AI has experienced explosive growth, and some embarrassing setbacks. Chatbots and AI assistants have been beset with issues including hallucinations, plagiarism and incorrect or biased results . OpenAI itself has been embroiled in allegations of copying actor Scartlett Johansson’s voice without her permission.
Apple is also at the center of an antitrust lawsuit filed by the Justice Department and 15 states. The government accuses Apple of abusing its power as a monopoly to push out rivals and keep customers using its products. It’s unclear how Apple’s new partnership with OpenAI could play into this case.
Shortly after Apple’s announcement, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman posted on X, formerly known as Twitter, “very happy to be partnering with apple to integrate chatgpt into their devices later this year! think you will really like it.”
Apple is also rolling out what it calls Apple Intelligence, its term for Apple's own new generative AI software.
Apple Intelligence will enable transcription for phone calls, AI photo retouching and improvements in the natural conversation flow with Siri, the company said. The software can also be used to summarize notifications and text messages, as well as articles, documents and open web pages.
Federighi placed an emphasis on privacy, with a new system called Private Cloud Compute that he said will ensure data security for users.
Apple says the new features will be released later this year.
- artificial intelligence
Apple's genius AI plan
The company's new AI features for the iPhone actually work
On Monday, as part of its Worldwide Developers Conference, Apple unveiled software features for its various products, including the iPhone and the iPad. The most anticipated part of the show was getting details on how the company would integrate artificial intelligence into its phones and operating systems.
During the presentation, Apple executives showed off how the tech giant's AI system — which they pointedly referred to as Apple Intelligence instead of artificial intelligence — could help with searching texts and photos, creating images, fixing grammar and spelling, summarizing text, and editing photos.
After the announcement, tech pundits , extremely online billionaires, and cheap seats the world over complained that the features were small potatoes . CNET's Katie Collins wrote that Apple's most interesting new features were long overdue, summing up her reaction as "finally." Bloomberg's Mark Gurman called them " minor upgrades ." My colleague Jordan Hart said they weren't the silver bullet Apple needed to reinvigorate the company. And Elon Musk registered his disappointment by sharing a stupid meme . In sum, many people are underwhelmed by Apple's practical integration of AI. Sure, maybe summarizing long emails and making transcripts of calls sounds boring compared with conjectures that AI could be used to detect cancer earlier , but guess what? Apple's scale and specificity of vision also make it the first Big Tech company to get AI integration right.
Apple is using AI to do what the technology has proved it can do: be an assistant. Yes, the virality of OpenAI's ChatGPT-3 put AI's potential on display. But using AI to power a robot that does your chores or to answer open-ended questions is still extremely imperfect. Chatbots lie, they hallucinate, they tell my colleagues to eat glue . Google's rollout and subsequent rollback of offering AI answers to people's search queries is just one sign that the current iteration of the tech isn't ready for all the use cases Silicon Valley is dreaming about — to say nothing of the venture capitalist Marc Andreessen's claims that AI will be able to "save the world," "improve warfare," and become our therapists, tutors, confidants, and collaborators, ushering in a "golden age" of art.
Related stories
Apple's updates are an appeal for everyone to get a grip. They are a clarion call for other tech companies to be practical with what they promise consumers and to deliver AI products that make our lives incrementally easier instead of confusing us with overpromises. Apple's use of the best of AI is also the best way for normal people to develop an understanding of what it can do. This is a way to build trust. Sure, maybe one day AI will figure out how to destroy civilization or whatever, but right now it's best at finding that photo of your dog dressed as a pickle you took back in 2019. And for the vast majority of people, that's perfectly fine.
What does AI do?
The fact that people are disappointed in Apple says more about the hype around AI's capabilities than it does about Apple . Musk has since 2019 been promising that Tesla will make a self-driving robocar, and for even long he's been overselling his driver-assistance technology as "autopilot." OpenAI's internal arguments turned palace intrigue turned media fodder are mostly centered on concern for the speed at which AI's supposedly fearsome power will reshape humanity, not the limitations of its current practical application. The biggest models, the most powerful Nvidia chips, the most talented teams poached from the hottest startups — that is the drumbeat of AI news from Silicon Valley and Wall Street. We've seen tech hype cycles before; they're mostly about raising money and selling stock. Only time will tell if the investments Wall Street and Silicon Valley are making in AI infrastructure will actually produce commensurate returns. That's how this game goes.
Apple's updates are an appeal for everyone to get a grip.
But in all that noise, the reality of what AI is good (and bad) at right now has gotten lost — especially when it comes to the large language models that undergird most of the new AI tools consumers will use, like virtual assistants and chatbots. The tech is based on pattern recognition: Rather than make value judgments, LLMs simply scan a vast library of information they've hoovered — books, webpages, speech transcripts — and guess which word most logically comes next in the chain. There is an inherent limitation in that design. Sometimes facts are improbable, but what makes them facts is that they are provable. It might not make sense that Albany, not New York City, is the capital of the state of New York, but it's a fact. It might make sense to use glue, an adhesive, to stick cheese on pizza, if you're a robot with no context for what "food" is. But that's definitely not how it's done. Such as they are, large language models can't make this value judgment between pattern and fact. It's unclear whether they'll ever be able to. Yann LeCun , Meta's lead AI scientist and one of the " godfathers of AI ," has said that LLMs have a "very limited understanding of logic" and that they "do not understand the physical world, do not have persistent memory, cannot reason in any reasonable definition of the term and cannot plan." He has also said they cannot learn anything beyond the data they're trained on — anything new or original — which makes them mentally inferior to a house cat .
In other words, they're not perfect.
Enter Apple, a company known for a culture of perfection. It was slow to embrace the hype surrounding AI, and, as I mentioned, for a while it refused to use the term "artificial intelligence," instead preferring the long dethroned, snoozefest name " machine learning ." Apple started developing its own generative AI after ChatGPT-3 launched in 2022 , but it revealed the new features only when it felt they were good and ready. This tech is what will power features like Genmoji, which allows you to describe a custom emoji to fit whatever's going on and then creates it — say, one of you crying while eating an entire pizza. It will also power more-practical applications, like writing an email to your boss when you're sick or pulling up that link your mom sent you in a text message. Right now, these basic call-and-response applications are the things at which LLMs excel.
Apple's rigorous standards serve as a way to firmly establish AI's present capabilities — or limitations, depending on how you see the glass.
If you want to use the latest Apple products to get into the freakier and more fungible world of talking to a chatbot, Siri will call up ChatGPT for you and let you run wild. This is Apple making a clear delineation between where its reliability ends and where a world of technological inconsistency begins. For Apple, this distinction makes sense. It wants its products to be associated with cutting-edge technology but also efficacy and productivity.
The distinction, however, does not serve the rest of Silicon Valley or their venture-capital investors. Anyone fundraising or investing in this technology would prefer you see the capabilities and value of AI as a moving target — specifically moving up, to the right, and fast. Apple's rigorous standards serve as a way to firmly establish AI's present capabilities — or limitations, depending on how you see the glass. The alternative is what we're seeing at other companies, where users are guinea pigs, used to working with tech that makes them question what they see. Societies around the world are already grappling with a crisis of faith in institutions; faulty AI just spreads that mistrust wider and faster. It's another stone in the wall between people's faith and what they read on the internet. In that way, Apple's cautious approach may be a service for the rest of the tech industry. By slowly acclimatizing its constellation of users to AI that makes their lives better instead of frustrating them, Apple makes the tech feel like a natural upgrade instead of an unreliable, scary intrusion.
Sure, Apple's AI may not be sexy or scary, but at least it doesn't seem stupid. Ideally, that means it won't make our world any stupider either.
Linette Lopez is a senior correspondent at Business Insider.
About Discourse Stories
Through our Discourse journalism, Business Insider seeks to explore and illuminate the day’s most fascinating issues and ideas. Our writers provide thought-provoking perspectives, informed by analysis, reporting, and expertise. Read more Discourse stories here .

More from Tech
Most popular
- Main content
'Best WWDC Ever': Wall Street is pumped up over Apple's AI game plan
- Wall Street was definitely impressed by Apple's WWDC event on Monday.
- The integration of OpenAI, a more conversational Siri, and an emphasis on privacy were key highlights.
- Analysts predict AI features will drive significant upgrade cycles for the iPhone 16 and iPhone 17.

Apple's unveiling of its artificial intelligence capabilities at WWDC on Monday failed to impress investors as the stock fell 2%, but it did impress Wall Street in a big way.
A more conversational Siri, the integration of OpenAI, and an emphasis on privacy should help boost Apple device sales for the long-term, according to several Wall Street analysts.
"Best WWDC ever," analysts at Citi said, concisely summarizing Wall Street's view that the integration of AI into Apple's hardware lineup could supercharge the company's growth after nearly two years of flat revenue growth.
Here's what Wall Street is saying about Apple's WWDC event.
Goldman Sachs: 'Should help to drive upgrade demand'
Analysts at Goldman Sachs said the software announcements at WWDC on Monday should drive hardware sales as the new AI capabilities are only compatible with the iPhone 15 and Macs with M1 chips or better.
"We're encouraged by the financial implication of today's announcements, with product features that should help to drive upgrade demand for products, leaves an opportunity for more direct AI monetization in the future, and potentially mitigate compute costs by allowing users with paid ChatGPT accounts to link to Apple accounts," Goldman Sachs analyst Michael Ng said.
Goldman Sachs rates Apple at "Buy" with a $238 price target.
Citi: 'Best WWDC ever'
"We believe Apple's WWDC was the best WWDC conference in a long time as it introduced 'AI for the rest of the people," analysts at Citi said.
The firm said as AI features become available in the fall, combined with an iPhone 16 launch, a supercycle in iPhone upgrades should begin to materialize and cap off with the iPhone 17 in 2025.
"We expect all IP16 models to be AI capable with IP17 to drive the super cycle refresh as developers will have a whole year to develop apps," Citi analyst Atif Malik said.
Citi rates Apple at "Buy" with a $210 price target.
JPMorgan: AI to drive emerging market upgrade cycle
With Apple's new AI features being compatible only with the iPhone 15 Pro models and future iPhones, JPMorgan analysts believe that that will spur a big upgrade cycle in emerging markets.
"While the availability of the AI features on iPhone 15 Pro models might appear on the headline as offering backward compatibility in some sense, we believe it will serve to accelerate the AI-related upgrade cycle in multiple emerging markets where local market demographics lead Apple to focus marketing on the last generation of the iPhone line up with affordability for the consumer in mind," JPMorgan analyst Samik Chatterjee said.
Chatterjee echoed Citi's thoughts that the AI features should drive a massive upgrade cycle for the iPhone over the next two years.
"We continue to expect the start of a device upgrade cycle for iPhones later this fall with the upgrade cycle likely peaking with the launch of the iPhone 17 in 2025," Chatterjee said.
JPMorgan rates Apple at "Overweight" with a $225 price target.
Wedbush: 'Changes the game for Apple'
Wedbush analyst Dan Ives said Apple Intelligence "changes the game" for the company as it leverages its massive installed base to roll out and refine its AI technology.
"For developers, Apple is looking to tap into customer data then monetize on top of that so this technology stays within the ecosystem while developers have to tap into this," Ives said.
"This was a historical day for Apple and Cook and Co. did not disappoint," Ives said.
Wedbush rates Apple at "Outperform" with a $275 price target.
- Main content
Introducing Apple Intelligence, the personal intelligence system that puts powerful generative models at the core of iPhone, iPad, and Mac
New Capabilities for Understanding and Creating Language
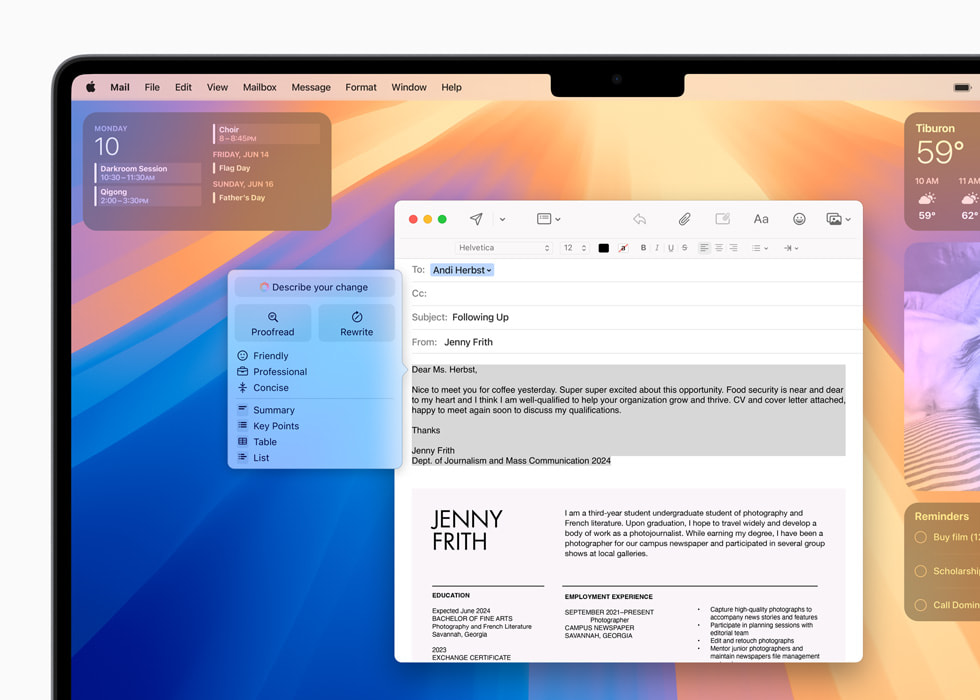
Image Playground Makes Communication and Self‑Expression Even More Fun
Genmoji Creation to Fit Any Moment
New Features in Photos Give Users More Control

Siri Enters a New Era

A New Standard for Privacy in AI
ChatGPT Gets Integrated Across Apple Platforms
Text of this article
June 10, 2024
PRESS RELEASE
Setting a new standard for privacy in AI, Apple Intelligence understands personal context to deliver intelligence that is helpful and relevant
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA Apple today introduced Apple Intelligence , the personal intelligence system for iPhone, iPad, and Mac that combines the power of generative models with personal context to deliver intelligence that’s incredibly useful and relevant. Apple Intelligence is deeply integrated into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia. It harnesses the power of Apple silicon to understand and create language and images, take action across apps, and draw from personal context to simplify and accelerate everyday tasks. With Private Cloud Compute, Apple sets a new standard for privacy in AI, with the ability to flex and scale computational capacity between on-device processing and larger, server-based models that run on dedicated Apple silicon servers.
“We’re thrilled to introduce a new chapter in Apple innovation. Apple Intelligence will transform what users can do with our products — and what our products can do for our users,” said Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO. “Our unique approach combines generative AI with a user’s personal context to deliver truly helpful intelligence. And it can access that information in a completely private and secure way to help users do the things that matter most to them. This is AI as only Apple can deliver it, and we can’t wait for users to experience what it can do.”
Apple Intelligence unlocks new ways for users to enhance their writing and communicate more effectively. With brand-new systemwide Writing Tools built into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia, users can rewrite, proofread, and summarize text nearly everywhere they write, including Mail, Notes, Pages, and third-party apps.
Whether tidying up class notes, ensuring a blog post reads just right, or making sure an email is perfectly crafted, Writing Tools help users feel more confident in their writing. With Rewrite, Apple Intelligence allows users to choose from different versions of what they have written, adjusting the tone to suit the audience and task at hand. From finessing a cover letter, to adding humor and creativity to a party invitation, Rewrite helps deliver the right words to meet the occasion. Proofread checks grammar, word choice, and sentence structure while also suggesting edits — along with explanations of the edits — that users can review or quickly accept. With Summarize, users can select text and have it recapped in the form of a digestible paragraph, bulleted key points, a table, or a list.
In Mail, staying on top of emails has never been easier. With Priority Messages, a new section at the top of the inbox shows the most urgent emails, like a same-day dinner invitation or boarding pass. Across a user’s inbox, instead of previewing the first few lines of each email, they can see summaries without needing to open a message. For long threads, users can view pertinent details with just a tap. Smart Reply provides suggestions for a quick response, and will identify questions in an email to ensure everything is answered.
Deep understanding of language also extends to Notifications. Priority Notifications appear at the top of the stack to surface what’s most important, and summaries help users scan long or stacked notifications to show key details right on the Lock Screen, such as when a group chat is particularly active. And to help users stay present in what they’re doing, Reduce Interruptions is a new Focus that surfaces only the notifications that might need immediate attention, like a text about an early pickup from daycare.
In the Notes and Phone apps, users can now record, transcribe, and summarize audio. When a recording is initiated while on a call, participants are automatically notified, and once the call ends, Apple Intelligence generates a summary to help recall key points.
Apple Intelligence powers exciting image creation capabilities to help users communicate and express themselves in new ways. With Image Playground, users can create fun images in seconds, choosing from three styles: Animation, Illustration, or Sketch. Image Playground is easy to use and built right into apps including Messages. It’s also available in a dedicated app, perfect for experimenting with different concepts and styles. All images are created on device, giving users the freedom to experiment with as many images as they want.
With Image Playground, users can choose from a range of concepts from categories like themes, costumes, accessories, and places; type a description to define an image; choose someone from their personal photo library to include in their image; and pick their favorite style.
With the Image Playground experience in Messages, users can quickly create fun images for their friends, and even see personalized suggested concepts related to their conversations. For example, if a user is messaging a group about going hiking, they’ll see suggested concepts related to their friends, their destination, and their activity, making image creation even faster and more relevant.
In Notes, users can access Image Playground through the new Image Wand in the Apple Pencil tool palette, making notes more visually engaging. Rough sketches can be turned into delightful images, and users can even select empty space to create an image using context from the surrounding area. Image Playground is also available in apps like Keynote, Freeform, and Pages, as well as in third-party apps that adopt the new Image Playground API.
Taking emoji to an entirely new level, users can create an original Genmoji to express themselves. By simply typing a description, their Genmoji appears, along with additional options. Users can even create Genmoji of friends and family based on their photos. Just like emoji, Genmoji can be added inline to messages, or shared as a sticker or reaction in a Tapback.
Searching for photos and videos becomes even more convenient with Apple Intelligence. Natural language can be used to search for specific photos, such as “Maya skateboarding in a tie-dye shirt,” or “Katie with stickers on her face.” Search in videos also becomes more powerful with the ability to find specific moments in clips so users can go right to the relevant segment. Additionally, the new Clean Up tool can identify and remove distracting objects in the background of a photo — without accidentally altering the subject.
With Memories, users can create the story they want to see by simply typing a description. Using language and image understanding, Apple Intelligence will pick out the best photos and videos based on the description, craft a storyline with chapters based on themes identified from the photos, and arrange them into a movie with its own narrative arc. Users will even get song suggestions to match their memory from Apple Music. As with all Apple Intelligence features, user photos and videos are kept private on device and are not shared with Apple or anyone else.
Powered by Apple Intelligence, Siri becomes more deeply integrated into the system experience. With richer language-understanding capabilities, Siri is more natural, more contextually relevant, and more personal, with the ability to simplify and accelerate everyday tasks. It can follow along if users stumble over words and maintain context from one request to the next. Additionally, users can type to Siri, and switch between text and voice to communicate with Siri in whatever way feels right for the moment. Siri also has a brand-new design with an elegant glowing light that wraps around the edge of the screen when Siri is active.
Siri can now give users device support everywhere they go, and answer thousands of questions about how to do something on iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Users can learn everything from how to schedule an email in the Mail app, to how to switch from Light to Dark Mode.
With onscreen awareness, Siri will be able to understand and take action with users’ content in more apps over time. For example, if a friend texts a user their new address in Messages, the receiver can say, “Add this address to his contact card.”
With Apple Intelligence, Siri will be able to take hundreds of new actions in and across Apple and third-party apps. For example, a user could say, “Bring up that article about cicadas from my Reading List,” or “Send the photos from the barbecue on Saturday to Malia,” and Siri will take care of it.
Siri will be able to deliver intelligence that’s tailored to the user and their on-device information. For example, a user can say, “Play that podcast that Jamie recommended,” and Siri will locate and play the episode, without the user having to remember whether it was mentioned in a text or an email. Or they could ask, “When is Mom’s flight landing?” and Siri will find the flight details and cross-reference them with real-time flight tracking to give an arrival time.
To be truly helpful, Apple Intelligence relies on understanding deep personal context while also protecting user privacy. A cornerstone of Apple Intelligence is on-device processing, and many of the models that power it run entirely on device. To run more complex requests that require more processing power, Private Cloud Compute extends the privacy and security of Apple devices into the cloud to unlock even more intelligence.
With Private Cloud Compute, Apple Intelligence can flex and scale its computational capacity and draw on larger, server-based models for more complex requests. These models run on servers powered by Apple silicon, providing a foundation that allows Apple to ensure that data is never retained or exposed.
Independent experts can inspect the code that runs on Apple silicon servers to verify privacy, and Private Cloud Compute cryptographically ensures that iPhone, iPad, and Mac do not talk to a server unless its software has been publicly logged for inspection. Apple Intelligence with Private Cloud Compute sets a new standard for privacy in AI, unlocking intelligence users can trust.
Apple is integrating ChatGPT access into experiences within iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia, allowing users to access its expertise — as well as its image- and document-understanding capabilities — without needing to jump between tools.
Siri can tap into ChatGPT’s expertise when helpful. Users are asked before any questions are sent to ChatGPT, along with any documents or photos, and Siri then presents the answer directly.
Additionally, ChatGPT will be available in Apple’s systemwide Writing Tools, which help users generate content for anything they are writing about. With Compose, users can also access ChatGPT image tools to generate images in a wide variety of styles to complement what they are writing.
Privacy protections are built in for users who access ChatGPT — their IP addresses are obscured, and OpenAI won’t store requests. ChatGPT’s data-use policies apply for users who choose to connect their account.
ChatGPT will come to iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia later this year, powered by GPT-4o. Users can access it for free without creating an account, and ChatGPT subscribers can connect their accounts and access paid features right from these experiences.
Availability
Apple Intelligence is free for users, and will be available in beta as part of iOS 18 , iPadOS 18 , and macOS Sequoia this fall in U.S. English. Some features, software platforms, and additional languages will come over the course of the next year. Apple Intelligence will be available on iPhone 15 Pro, iPhone 15 Pro Max, and iPad and Mac with M1 and later, with Siri and device language set to U.S. English. For more information, visit apple.com/apple-intelligence .
Press Contacts
Cat Franklin
Jacqueline Roy
Apple Media Helpline
Images in this article

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to ...
Apple business strategy consists of using its designing capabilities, hardware expertise, and software prowess to build an ecosystem for its consumers. June 19, 2024 +1-202-455-5058 [email protected]. Open Innovation; ... Apple is planning to launch podcasts based on existing TV+ series. Apple is planning to release a headgear that combines ...
at have played a crucial role in the company's innovation success.When Jobs arrived back at Apple, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was. divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. General managers ran the Macintosh products group, the information.
The billions of people who use Facebook are affected by Apple's strategy to squeeze more cash from apps. Companies have also said that they felt forced to charge people money in their iPhone ...
Apple's generic competitive strategy determines competitive advantages over other companies that provide information technology, consumer electronics, and online services. On the other hand, Igor Ansoff's Matrix of growth strategies presents ways for the technology business to intensively grow in current or new markets and industries.
Apple lawsuit, is long and detailed, with tons of lessons for business leaders. But it's the first point on the agenda, entitled "2011 Strategy" and assigned to Jobs himself, that stands out most.
Apple Business account Shop in person at an Apple Store. Call us at 1-800-854-3680. Connect with an enterprise expert. Tell us about your business. Apple Footer
Strategic Planning at Apple Inc. By: Fabrizio Di Muro, Kyle Murray, Miranda Goode. Apple Inc. is one of the world's most successful and most recognizable companies. Over its 30 year existence, the company had seen a lot of changes in the computer industry. What would the future….
A set of three simple Apple Business Essentials plans enable businesses to cover every employee and device in their organization. Plans can be customized to support each user with up to three devices and up to 2TB of secure storage in iCloud, starting at $2.99 per month, with optional AppleCare+ for Apple Business Essentials. 1. Availability.
It hit the $2 trillion mark on August 20, 2020. Apple became a $3 trillion company briefly on January 3, 2022, and today its valuation is about $2.6 trillion. By focusing on creating breakthrough ...
Apple has also committed $430B for new investments and 20,000 new jobs in the US over 5 years — in addition to further investments in Europe and India — across silicon engineering, AI, and 5G tech. Using CB Insights data, we uncovered 4 of Apple's emerging strategic priorities highlighted by its recent acquisitions, investments, and ...
Apple has a business model that is divided into products and services. Apple generated over $394 billion in revenues in 2022, of which $205.5 came from iPhone sales, $40 billion came from Mac sales, over $41 billion came from accessories and wearables (AirPods, Apple TV, Apple Watch, Beats products, HomePod, iPod touch, and accessories), $29.3 billion came from iPad sales, and $78.13 billion ...
Apple business strategy can be characterised as vertical integration in a way that the company has advanced expertise in software, hardware, and services at the same time. Apple's vertical integration is one of the major factors that set it apart from the competition. The company has been benefiting from its vertical integration immensely.
Understanding Apple Business Strategy. Based in Cupertino, California, Apple is an American multinational company that designs and sells consumer electronics, software, and services. Apple's iPhones helped spark the dawn of the smartphone-era and have revolutionized the way the world sees phones. Apple's business strategy, though simple ...
Posted on May 28, 2024 by Daniel Pereira. Apple Business Model focuses primarily on selling its products and offering services through subscriptions. Sales of Apple products like the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and MacBook make up a large percentage of Apple's revenue, while its services include Apple TV+, Apple Fitness+, Apple Music, iCloud+ ...
Abstract. After a decade as CEO, Tim Cook is facing one of his biggest strategic transitions of his tenure. While Apple had performed spectacularly well under Cook, Apple's core business was maturing. Sales of iPhones, iPads, and Macs were flat or down. However, Apple's new hardware—Apple Watch and Airpods—as well as services were growing ...
A Look At Apple's Business Strategy For The Coming Years. Business / By Gennaro Cuofano / December 28, 2018. Back in 1985, Steve Jobs was ousted from Apple. The company would still benefit from a few years of continuing growth until it hit a roadblock and sales started to fall. By 1996 Apple brought in a new CEO which was supposed to turn it ...
Apple Business Essentials is now available as a subscription for all small businesses in the US. Flexible plans can be customized to support each user and device in an organization with up to 2TB of secure storage in iCloud, starting at $2.99 (US) per month after a two-month free trial. Plans that include AppleCare+ for Apple Business ...
Updated 6.9.17, 11:15 AM EDT by Business Insider. Image by Apple. Vision of the Future. Apple revealed its 10-year plan for the future this week.
With Apple Business Essentials, you can add plans and assign them to users or devices, providing them with device management, iCloud storage, and AppleCare support. You can start using Apple Business Essentials, including a two month free trial, by selecting from employee or device plans, and mix and match plans based on the services you need ...
Get help using Managed Apple IDs, deploying apps, or managing devices. Find the phone number for your country or region. Learn more about Apple Business Support. Get access to top topics, resources and all of the contact options you might need for business support.
Apple just kicked off a brand new era for the company with the introduction of its first generative AI features for the iPhone. At its annual Worldwide Developers Conference on Monday, the company ...
Apple's $430 billion US investments include working with more than 9,000 suppliers and companies large and small in all 50 states, supporting American job creation across dozens of sectors, including silicon engineering, 5G, and manufacturing. To foster innovation and growth in the sector, Apple launched its $5 billion Advanced Manufacturing ...
Apple Inc. shares rose to a record after it took the wraps off long-awaited new artificial intelligence features, betting that a personalized and understated approach to the technology will win ...
Apple said it had completely reworked Siri, its 13-year-old virtual assistant. The assistant will soon be powered by Apple Intelligence, the company's version of a "large language model."
Apple has announced a much-anticipated partnership with OpenAI, the maker of ChatGPT. The deal to bring AI features to iPhones and other devices is a major move for Apple, which has been slower ...
Business Essentials. One complete subscription that seamlessly brings together device management, 24/7 support, and cloud storage. With Apple Business Essentials, your small business can easily manage every iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple TV — every step of the way. Try it free Watch the film. Try it free.
Apple's genius AI plan. The company's new AI features for the iPhone actually work ... Business Insider seeks to explore and illuminate the day's most fascinating issues and ideas. Our writers ...
Apple's unveiling of its artificial intelligence capabilities at WWDC on Monday failed to impress investors as the stock fell 2%, but it did impress Wall Street in a big way. A more conversational ...
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA Apple today introduced Apple Intelligence, the personal intelligence system for iPhone, iPad, and Mac that combines the power of generative models with personal context to deliver intelligence that's incredibly useful and relevant.Apple Intelligence is deeply integrated into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia. It harnesses the power of Apple silicon to understand and ...