

Logos Definition
What is logos? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Logos , along with ethos and pathos , is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic or reason. For example, when a speaker cites scientific data, methodically walks through the line of reasoning behind their argument, or precisely recounts historical events relevant to their argument, he or she is using logos.
Some additional key details about logos:
- Aristotle defined logos as the "proof, or apparent proof, provided by the words of the speech itself." In other words, logos rests in the actual written content of an argument.
- The three "modes of persuasion"— pathos , logos , and ethos —were originally defined by Aristotle.
- In contrast to logos's appeal to reason, ethos is an appeal to the audience based on the speaker's authority, while pathos is an appeal to the audience 's emotions.
- Data, facts, statistics, test results, and surveys can all strengthen the logos of a presentation.
How to Pronounce Logos
Here's how to pronounce logos: loh -gos
Logos and Different Types of Proof
While it's easy to spot a speaker using logos when he or she presents statistics or research results, numerical data is only one form that logos can take. Logos is any statement, sentence, or argument that attempts to persuade using facts, and these facts need not be the result of long research. "The facts" of an argument can also be drawn from the speaker's own life or from the world at large, and presenting these examples to support one's view is also a form of logos. Take this example from Sojourner Truth's "Ain't I a Woman?" speech in support of women's rights:
That man over there says that women need to be helped into carriages, and lifted over ditches, and to have the best place everywhere. Nobody ever helps me into carriages, or over mud-puddles, or gives me any best place! And ain't I a woman? Look at me! Look at my arm! I have ploughed and planted, and gathered into barns, and no man could head me! And ain't I a woman?
Truth points to her own strength, as well as to the fact that she can perform physically tiring tasks just as well as a man, as proof of equality between the sexes: she's still appealing to the audience's reason, but instead of presenting abstract truths about reality or numerical evidence, she's presenting the facts of her own experience as evidence. In this case, the logic of the argument is anecdotal (meaning it's derived from a handful of personal experiences) rather than purely theoretical, but it goes to show that logos doesn't have to be dry and clinical just because it's concerned with proving something logically.
Logos: Proof vs. Apparent Proof
Not all speakers who use logos can be blindly trusted. As Aristotle specifies in his definition of the term, logos can be "proof, or apparent proof." A speaker may present facts, figures, and research data simply to show that he or she has "done their homework," in an effort to attain the degree of credibility that is often automatically attributed to scientific studies and evidence-driven arguments. Or a speaker might present facts in a way that is wholly or partially misrepresentative, using those facts (and, by extension, logos ) to make a claim that feels credible while actually arguing something that is untrue. Yet another factor that can cause a speech or text to have the appearance of providing proof is the use of overlong words and technical language—but just because someone sounds smart doesn't mean their argument stands to reason.
Even if the facts have been manipulated, any argument that relies on or even just claims to rely on "facts" to appeal to a listener's reason is still an example of logos. Put another way: logos is not about using facts correctly or accurately , it's about using facts in any way to influence an audience.
Logos Examples
Examples of logos in literature.
While Aristotle defined the term logos with public speaking in mind, there are many examples of logos in literature. Generally, logos appears in literature when characters argue or attempt to convince one another that something is true. The degree to which characters use logos -driven arguments can also provide important insight into their personalities and motives.
Logos in Shakespeare's Othello
In Othello , Iago plots to bring about the downfall of his captain, Othello. Iago engineers a series of events that makes it look like Othello’s wife, Desdemona, is cheating on him. Suspicion of his wife’s infidelity tortures Othello, who only recently eloped with Desdemona against her father’s wishes. In this passage from Act 3, Scene 3, Iago manipulates Othello by means of logos . Iago "warns" Othello not to succumb to paranoia even as he fans the flames of that paranoia:
Oh, beware, my lord, of jealousy! It is the green-eyed monster which doth mock The meat it feeds on….. Who, certain of his fate, loves not his wronger, But, oh, what damnèd minutes tells he o’er Who dotes, yet doubts— suspects, yet soundly loves… She did deceive her father, marrying you… She loved them most…. I humbly do beseech you of your pardon For too much loving you….
Iago here lectures Othello on the abstract dangers of jealousy, but then goes on to use reason and deduction to suggest that, because Desdemona deceived her beloved father by marrying Othello, she'd probably be willing to deceive Othello, too.
Logos in Don DeLillo's White Noise
In this passage from Part 2 of Don Delillo’s novel White Noise, Jack Gladney and his son Heinrich gaze through binoculars at an Airborne Toxic Event—or cloud of poison gas—that has just hit their town. Jack , in denial, tries to reassure his son that the cloud won’t blow in their direction and that there’s no cause for alarm. Heinrich disagrees:
"What do you think?" he said. "It's still hanging there. Looks rooted to the spot." "So you're saying you don't think it'll come this way." "I can tell by your voice that you know something I don't know." "Do you think it'll come this way or not?" "You want me to say it won't come this way in a million years. Then you'll attack with your little fistful of data. Come on, tell me what they said on the radio while I was out there." "It doesn't cause nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, like they said before." "What does it cause?" "Heart palpitations and a sense of deja vu." "Deja vu?" "It affects the false part of the human memory or whatever. That's not all. They're not calling it the black billowing cloud anymore." "What are they calling it?" He looked at me carefully. "The airborne toxic event." ... "These things are not important. The important thing is location. It's there, we're here." "A large air mass is moving down from Canada," he said evenly. "I already knew that." "That doesn't mean it's not important." "Maybe it is, maybe it isn't. Depends."
Jack tries to reassure himself and his family that the situation isn’t serious. Heinrich tries to counter his father’s irrational, fear-driven response to the catastrophe with his "fistful of data": information he's learned in school from a science video on toxic waste, as well as reports about the disaster that he heard on the radio. He presents the facts so that his father can’t ignore them, thereby strengthening the logos of his argument that the situation is serious and the cloud will come their way. In this particular example, the lack of logos in Jack's argument reveals a lot about his character—even though Jack is a tenured college professor, strong emotions and fear for his own mortality often drive his behavior and speech.
Logos in Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird
In this example from To Kill a Mockingbird , lawyer Atticus Finch uses logos to argue on behalf of a black defendant, Tom Robinson, who stands accused of raping a white woman.
"The state has not produced one iota of medical evidence to the effect that the crime Tom Robinson is charged with ever took place. It has relied instead upon the testimony of two witnesses whose evidence has not only been called into serious question on cross-examination, but has been flatly contradicted by the defendant. The defendant is not guilty, but somebody in this courtroom is."
The logos in this case lies in Atticus' emphasis on the facts of the case, or rather, the fact that there are no facts in the case against Tom. He temporarily ignores questions of racial justice and emotional trauma so that the jury can look clearly at the body of evidence available to them. In short, he appeals to the jury's reason .
Logos in Robert M. Pirsig's Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance
In Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance , the narrator takes a cross-country motorcycle trip with his son Chris, and their two friends John and Sylvia. When Chris tells the group in Chapter 3 that his friend Tom White Bear believes in ghosts, the narrator tries to explain that scientific principles only exist in our heads, and therefore are actually modern man's equivalent of ghosts:
"Modern man has his ghosts and spirits too, you know." "What?" "Oh, the laws of physics and of logic...the number system...the principle of algebraic substitution. These are ghosts. We just believe in them so thoroughly they seem real." "They seem real to me," John says. "I don't get it," says Chris. So I go on. "For example, it seems completely natural to presume that gravitation and the law of gravitation existed before Isaac Newton. It would sound nutty to think that until the seventeenth century there was no gravity." "Of course" "So when did this law start? Has it always existed?...What I'm driving at is the notion that before the beginning of the earth, before the sun and the stars were formed, before the primal generation of anything, the law of gravity existed." "Sure." "Sitting there, having no mass of its own, no energy of its own, not in anyone's mind because there wasn't anyone, not in space because there was no space either, not anywhere—this law of gravity still existed?" Now John seems not so sure. "If the law of gravity existed," I say, "I honestly don't know what a thing has to do to be non existent. It seems to me that law of gravity has passed every test of nonexistence there is...And yet it is still 'common sense' to believe that it existed." "I guess I'd have to think about it." "Well, I predict that if you think about it long enough you will find yourself going round and round and round and round until you finally reach only one possible, rational, intelligent conclusion. The law of gravity and gravity itself did not exist before Isaac Newton. No other conclusion makes sense. And what that means... is that that law of gravity exists nowhere except in people's heads! It's a ghost!"
The narrator uses logos in his discourse on scientific concepts by presenting his audience with an example—gravity—and asking them to consider their own experience of gravity as empirical evidence in support of his argument. He urges his friends to come to a "rational, intelligent conclusion" about the concept of gravity, instead of relying on conventional wisdom and unexamined assumptions.
Logos in Political Speeches
Politicians frequently use logos, often by citing statistics or examples, to persuade their listeners of the success or failure of policies, politicians, and ideologies.
Logos in Barack Obama's 2015 State of the Union Address
In this example, Obama cites historical precedent and economic data from past years to strengthen his argument that recent progress has been substantial and that the nation's economy is in good health:
But tonight, we turn the page. Tonight, after a breakthrough year for America, our economy is growing and creating jobs at the fastest pace since 1999. Our unemployment rate is now lower than it was before the financial crisis. More of our kids are graduating than ever before. More of our people are insured than ever before. And we are as free from the grip of foreign oil as we’ve been in almost 30 years.
Logos in Ronald Reagan's 1987 "Tear Down this Wall" Speech
In this speech, Reagan intends for his comparison between the poverty of East Berlin—controlled by the Communists—and the prosperity of Democratic West Berlin to serve as hard evidence supporting the economic superiority of Western capitalism. The way he uses specific details about the physical landscape of West Berlin as proof of Western capitalist economic superiority is a form of logos:
Where four decades ago there was rubble, today in West Berlin there is the greatest industrial output of any city in Germany--busy office blocks, fine homes and apartments, proud avenues, and the spreading lawns of parkland. Where a city's culture seemed to have been destroyed, today there are two great universities, orchestras and an opera, countless theaters, and museums. Where there was want, today there's abundance--food, clothing, automobiles--the wonderful goods of the Ku'damm. From devastation, from utter ruin, you Berliners have, in freedom, rebuilt a city that once again ranks as one of the greatest on earth...In the 1950s, Khrushchev [leader of the communist Soviet Union] predicted: "We will bury you." But in the West today, we see a free world that has achieved a level of prosperity and well-being unprecedented in all human history. In the Communist world, we see failure, technological backwardness, declining standards of health, even want of the most basic kind—too little food. Even today, the Soviet Union still cannot feed itself. After these four decades, then, there stands before the entire world one great and inescapable conclusion: Freedom leads to prosperity. Freedom replaces the ancient hatreds among the nations with comity and peace. Freedom is the victor.
Why Do Writers Use Logos?
It's important to note that the three modes of persuasion often mutually reinforce one another. They don't have to be used in isolation from one other, and the same sentence may even include examples of all three. While logos is different from both ethos (an appeal to the audience based on the speaker's authority) and pathos (an appeal to the audience's emotions), the use of logos can serve as a strong complement to the use of ethos and/or pathos —and vice versa.
For instance, if a politician lists the number of casualties in a war, or rattles off statistics relating to a national issue, these facts may well appeal to the audience's emotions as well as their intellect, thereby strengthening pathos as well as logos as elements in the speech. Consider this passage from Michelle Obama's 2015 speech at The Partnership for a Healthier America Summit, in which she updates listeners on the success of her Let's Move! project for improving children's nutrition:
I mean, just think about what our work together means for a child born today. Maybe that child will be one of the 1.6 million kids attending healthier daycare centers where fruits and vegetables have replaced cookies and juice. And when that child starts school, maybe she’ll be one of the over 30 million kids eating the healthier school lunches that we fought for. Maybe she’ll be one of the 2 million kids with a Let’s Move! salad bar in her school, or one of the nearly 9 million kids in Let’s Move! Active Schools who are getting 60 minutes of physical activity a day, or one of the 5 million kids soon attending healthier after-school programs.
While Obama includes statistics to persuade her audience that Let's Move! has been a success ( logos) , she's also using those facts and figures to stir up enthusiasm for her cause ( pathos).
Other Helpful Logos Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Logos: A detailed explanation and history of the term.
- The Dictionary Definition of Logos: A definition encompassing the different meanings of the word logos.
- Logos on Youtube: A video from TED-Ed about the three modes of persuasion.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1956 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 41,253 quotes across 1956 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Blank Verse
- Antanaclasis
- Extended Metaphor
- Tragic Hero
- Rhetorical Question
- Polysyndeton
- Figurative Language
- Rhyme Scheme
- End-Stopped Line


What is Logos? Definition, Examples of Logos in Literature
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is Logos? Definition, Examples of Logos in Literature
Logos definition: Logos is a rhetorical device that includes any content in an argument that is meant to appeal to logic.
What is Logos?
What does logos mean in literature? Logos is a rhetorical device that includes any content in an argument that is meant to appeal to logic.
Logos is one of the three Aristotelian appeals. A writer utilizes the three appeals in order to convince his audience of his argument. The other two appeals are ethos (ethics) and pathos (emotion).
Appeals to logos are those that involve or influence the logical reasons an audience should believe an argument.

Examples of logos in an argument for tax reform might include:
- The United States has the highest corporate income tax in the world.
- Our own small businesses cannot compete with such a relatively high tax burden.
- Therefore, the government should lower corporate income tax rates.
The first statement is a fact; the second and third statements create a syllogism. Both are appeals to logos.
Modern Examples of Logos

Whether it’s Mom explaining why you need to do your homework before bedtime, a newspaper columnist commenting on the day’s events, or an engineer explaining a need for new equipment, logical appeals are evident in everyday speech and argument.
However, be mindful that simply stating facts is not an appeal to logos. Writers use appeals to logos when they have an argument they are trying to prove . Yet, just about anything could be an argument.
Look at the above examples—each speaker is trying to convince someone of something. This is where logos might come into play.
The Function of Logos

It is very difficult to believe or support an argument if it does not make logical sense. This is why a writer should include appeals to logos in his argument. The purpose of writing is to convince someone of something. Logos is a tool that helps writers do this.
Not all arguments will have the same “amount” of logical appeals. Some arguments might call for more emotional appeals. It is the writer’s responsibility to evaluate his audience to determine the best appeals for his argument.
Examples of Logos in Literature

Let me start with the economy, and a basic fact: The United States of America, right now, has the strongest, most durable economy in the world. We’re in the middle of the longest streak of private sector job creation in history. More than 14 million new jobs, the strongest two years of job growth since the ‘90s, an unemployment rate cut in half. Our auto industry just had its best year ever. That’s just part of a manufacturing surge that’s created nearly 900,000 new jobs in the past six years. And we’ve done all this while cutting our deficits by almost three-quarters.
With these words, Obama is utilizing facts, numbers, and statistics to logically prove to his audience that American’s economy is on the rise. Here, Obama is appealing to logos to convince his audience that, as President, he has positively made change to affect America’s growth and development.
This is an example of logos.
Summary: Logos Definition Literature
Define logos in literature: the definition of logos in literature is a rhetorical device that appeals to logic and reason.
In summary, logos is:
- an appeal to logic
- one of the three Aristotelian appeals
- usually evident as facts, numbers, or statistics
- used to convince an audience of an argument
What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
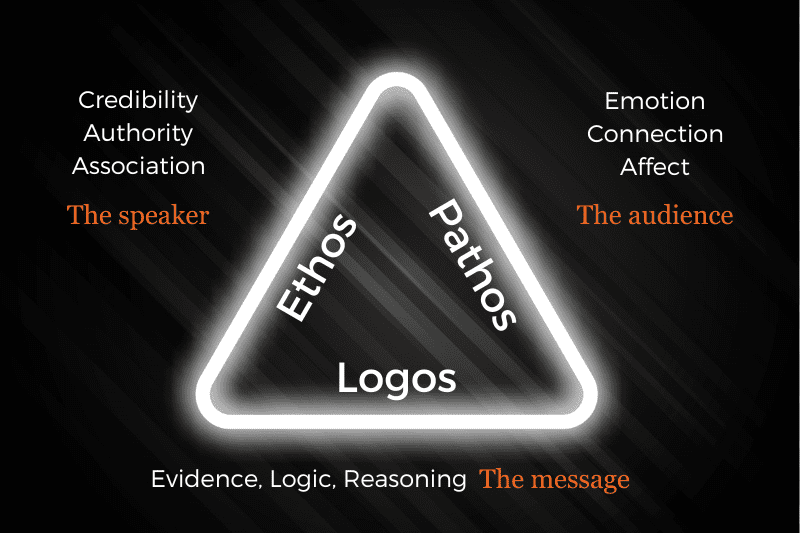
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, logos – logos definition.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Emily Lane

What is Logos?
Logos refers to an appeal to logic as opposed to an appeal to pathos or ethos .
Here, logos does not refer to formal logic such as that practiced in mathematics, philosophy, or computer science. Rather, logos refers to the consistency and clarity of an argument as well as the logic of evidence and reasons. It plays a role as one of the main three modes of persuasion:
Utilizing these appeals to reason within our writing and daily life allows us to create more convincing arguments targeted to our audience .
Related Concepts: Evidence ; Inductive Order, Inductive Reasoning, Inductive Writing ; Deductive Order, Deductive Reasoning, Deductive Writing ; Reasoning – Guide to Reasoning with Evidence

In formal logic, in abstraction, the following is the case: if A is true and B is true and A is an instance of B, then the repercussions of B will always be true. The problem, however, is that this kind of logic doesn’t work for real-life situations. This is where the argument comes into play.
Formal logic would say that speeding, for example, is a violation of traffic laws. A repercussion of violating a traffic law is a ticket; therefore, every person who speeds gets a ticket. However, in real life, not in abstract theory, things aren’t that cut and dried. Most people would not agree that all speeders, in every circumstance, should receive a ticket. In an argument about a real-life situation, the audience needs particulars to make their decisions. Sometimes there’s an exception. Why was that person speeding? Well, if an eighteen-year-old is speeding to show off for his friends, then yes, most people would agree that he deserves a ticket. However, if a man is driving his pregnant wife to the hospital, then maybe he does not deserve the ticket. One could, and probably would, make the argument that he should not get a ticket.
How to Appeal to Logos?
Let’s examine how the appeal to logos would work in an argument for the speeding father-to-be.
Because arguments are based on values and beliefs as well as facts and evidence, it is logical that the argument must coincide with accepted values and beliefs.
What are enthymemes?
The enthymeme is the foundation of every argument.
Enthymemes have three parts:
- the unstated assumption that is provided by the audience.
All three of these textual elements must make sense to your audience in order for your argument to be considered logical. The claim of an argument for the father-to-be could be something like, “This man should not get a speeding ticket.” That’s it. The claim is pretty simple. It is your educated opinion on the matter. The reason would be something like “because his wife is in labor in the backseat.” So the two stated parts of your enthymeme would be, “This man should not get a speeding ticket because his wife is in labor in the backseat.” Now, this seems obviously logical to us; however, what is our underlying value, our unstated assumption about this argument? Most of us would probably agree that a hospital is a better place to give birth than a backseat. That is the third part of the enthymeme. Your audience must agree that your assumption is true in order for your argument to be considered logical. If your readers don’t have the same assumption, they are not going to see your logic. You must find an enthymeme that works for your audience. The pregnant wife’s enthymeme is fairly easy to see. In more volatile claims and reasons, the unstated assumptions can be trickier to identify and work out with your audience.
How do enthymemes Relate to Logos?
Reasons like “because his wife is in labor” are motivations for the driver’s actions, not evidence. Most audiences need facts. Evidence is the facts. Both reasons and evidence are used in appeals to logos ; however, reasons cannot be your only support. Evidence as to why the man should speed might include studies about the problems with births in difficult or dangerous circumstances, interviews with women who have given birth in automobiles, and infant mortality rates for births that do not occur in hospitals. As you can see, there are many different kinds of evidence you could provide for this argument.
Consistency means not changing the unstated or stated rules governing your argument. Consistency is essential to logic. Let us continue with the speeding example. If, for instance, you are arguing that the infant mortality rate is too high for babies born outside the hospital and that the father is required to speed for the safety of his unborn child, then you may not want to include evidence of the high infant mortality rate in car crashes. Although this information may be part of the infant mortality rate, it goes against the underlying assumption that speeding is acceptable because of the high risk of harming the baby if it is born in the backseat.
Why is Logos important?
So why should you care about logos? In your own writing, logos is important because it appeals to your readers’ intellect. It makes your readers feel smart. Logos is the part of the argument where you treat your audience like purely rational, “only the facts, ma’am” kind of people. Also, gaps, leaps, and inconsistencies in logic, no matter how well developed the other appeals may be, can tear apart an argument in short order. This is the same reason you cannot ignore logos in others’ arguments either. All the appeals are linked together; for instance, if you use as evidence an article that has leaps in logic, or relies only on authority and pathos , this article could damage your own ethos as an author . It is important to remember that all three appeals must be well developed and work together to make a good argument .
Logos Examples
As you now know, logos can be defined as a writer’s or speaker’s attempt to appeal to the logic or reason of their audience. Let’s look at some examples of logos that you might commonly find when reading texts of various media:
When a writer employs data or statistics within a text, you can probably assume that he or she is attempting to appeal to the logic and reason of the reader. For example, an argument in favor of keeping abortion legal may cite the May 2011 Pew Research poll that found 54 percent of Americans in favor of legal abortion. This figure makes a logical argument: abortion should be legal because the majority of Americans support it, and in a democracy, the majority makes the decisions.
Causal Statements
When you see an “if-then” statement, with credible supporting evidence, the writer is likely appealing to your reason. Consider an argument about lowering the drinking age from 21 to 18: a writer might suggest that, if the legal drinking age were 18, then people between 18 and 21 would be less likely to drive under the influence. If the writer offers evidence that the reason that some between the ages of 18 and 21 drive drunk is that they fear calling a friend or parent because they have illegally ingested alcohol, then this causal statement would be an appeal to a reader’s sense of reason.
Relevant Examples or Other Evidence
You might begin to think about logos as evidence that doesn’t involve an appeal to your emotions. Even expert testimony, which would certainly be an example of ethos, also could be an example of logos, depending on its content. For example, in a discussion about recent cuts in education funding, a statement from the Hillsborough County, Florida, the superintendent would be an appeal to authority. But if that statement contained a discussion of the number of teachers and classes that would have to be cut if the state were to reduce the district’s funding, the statement from the superintendent could also be an appeal to logic.
Fallacies of Logos
Appeal to Nature
Suggesting a certain behavior or action is normal/right because it is “natural.” This is a fallacious argument for two reasons: first, there are multiple, and often competing, ways to define “nature” and “natural.” Because there is no one way to define these terms, a writer cannot assume his or her reader thinks of “nature” in the same way he or she does. Second, we cannot assume that “unnatural” is the same as wrong or evil. We (humans) have made lots of amendments to how we live (e.g., wearing clothes, living indoors, farming) with great benefit.
Argument from Ignorance
Assuming something is true because it has not been proven false. In a court of law, a defendant is, by law, “innocent until proven guilty.” However, judges and jurors must hear testimonies from both sides and receive all facts in order to draw conclusions about the defendant’s guilt or innocence. It would be an argument from ignorance for a judge or juror to reach a verdict without hearing all of the necessary information.
Intentionally misrepresenting your opponent’s position by over-exaggerating or offering a caricature of his or her argument. It would be fallacious to claim to dispute an opponent’s argument by creating a superficially similar position and refuting that position (the “straw man”) instead of the actual argument. For example, “Feminists want to turn men into slaves.” This statement fails to accurately represent feminist motivations—which can be very diverse. Most feminists agree in their goal to ensure women’s equality with men. Conceptions of equality can vary among feminists, but characterizing them as men-haters detracts from their true motivations.
False Dilemma
Assuming that there are only two options when there are, in fact, more. For example, “We either cut Social Security, or we have a huge deficit.” There are many ways to resolve deficit problems, but this statement suggests there is only one.
Hasty Generalization
Drawing a broad conclusion based on a small minority. For instance, if you witnessed a car accident between two women drivers, it would be a hasty generalization to conclude that all women are bad drivers.
Cum Hoc, Ergo Propter Hoc (With This, Therefore Because of This)
Confusing correlation with causation—that is, thinking that because two things happened simultaneously, then one must have caused the other. For example, “There has been an increase in both immigration and unemployment; therefore, immigrants are taking away American jobs.” This statement is fallacious because there is no evidence to suggest that immigration and unemployment are related to each other—other than that their rates increased simultaneously.
The Slippery Slope
The slippery slope argument is often a way to scare readers or listeners into taking (or not taking) a particular action (see “ Fallacious Pathos “). The slippery slope argument can also function as a false invocation of logic or reason in that it involves a causal statement that lacks evidence. For example, I might argue that if the drinking age were lowered from 21 to 18, vast numbers of college students would start drinking, which in turn would lead to alcohol poisoning, binge drinking, and even death. This conclusion requires evidence to connect the legality of drinking with overindulgence. In other words, it does not follow that college students would drink irresponsibly if given the opportunity to drink legally.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing
Logos Definition
Classification of logos, examples of logos in literature, example #1: political ideals (by bertrand russell).
“The wage system has made people believe that what a man needs is work. This, of course, is absurd. What he needs is the goods produced by work, and the less work involved in making a given amount of goods, the better … But owing to our economic system …where a better system would produce only an increase of wages or a diminution in the hours of work without any corresponding diminution of wages.”
In this paragraph, Russell is presenting arguments for the unjust distribution of wealth and its consequences. He answers through logic and states that a reason for this injustice is due to evils in institutions. He deduces that capitalism and the wage system should be abolished to improve the economic system.
Example #2: The Art of Rhetoric (By Aristotle)
“All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.”
Example #3: Of Studies (By Francis Bacon)
“Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man.”
Example #4: Of Studies (By Francis Bacon)
“Crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them; for they teach not their own use; but that is wisdom without them, and above them, won by observation.”
This is also a perfect example of logos. Here, Bacon discusses the matter of theories versus skills. There comes a clash between reading and not reading. He argues that a reader is better than those who cling to what they already know. He uses the logic that reading is necessary because it improves skills.
Example #5: Othello (By William Shakespeare)
“Oh, beware, my lord, of jealousy! It is the green-eyed monster which doth mock The meat it feeds on … Who, certain of his fate, loves not his wronger, But, oh, what damnèd minutes tells he o’er Who dotes, yet doubts — suspects, yet soundly loves … She did deceive her father, marrying you … She loved them most … I humbly do beseech you of your pardon For too much loving you …”
In this excerpt, Iago convinces Othello with logic and reasoning and makes him doubtful that there is a secret relationship between Desdemona and Cassio.
Logos Meaning and Function
Related posts:, post navigation.
What is Logos in Literature?

Before you can think about teaching argumentation and persuasion , you must understand the basics of logos, including what it is, why it’s used, and how to spot it in writing or argument. This article teaches you everything you need to know about the logical component of persuasion and argumentation.
Logos Definition
Derived from the Greek word for “word” or “reason,” logos is one of the three primary rhetorical appeals, alongside ethos and pathos. Just like you would assume based on how the word sounds, logos is the elements of an argument that appeal to an audience’s sense of logic and reasoning. Writers use several forms of logical evidence to convince the audience through a rational and well-supported argument, including:
- Test results
- Expert testimony
- Textual evidence
- Historical or literal analogies
- Cause and effect relationships
The term “logos” traces its roots to ancient Greek philosophy, particularly in the works of Aristotle. In his work “Rhetoric,” Aristotle broke down the key elements of persuasive communication, including supporting with logic (logos), appealing to emotions (pathos), and establishing trust and credibility (ethos). According to his work, these three elements work together to create a compelling and convincing argument. While logos can be found in literature, it is often used in academic writing, persuasive speeches, law, political campaigns, marketing, and advertisements.
Logos Pronunciation
Logos is a two-syllable word dating back to ancient Greek philosophy and is pronounced as low-gowz .
What are the Different Types of Logos?
All forms of logos serve the same purpose: to convince an audience using logical evidence and reasoning. However, this can be achieved through logic or perceived logic . Let’s break down the difference:
In rhetoric, logic involves using clear reasoning and concrete evidence to build a compelling argument. It adheres strictly to the principles of deductive and inductive reasoning, using facts, statistics, and logical connections to persuade the audience. Examples of this form of logic include:
- Presenting statistical data to support an argument.
- Defending a thesis with textual evidence and clear explanation.
- Citing well-established facts or scientific evidence.
- Utilizing deductive reasoning to draw a logical conclusion.
Perceived Logic
On the other hand, perceived logic focuses on creating an impression of logic when there isn’t much hard evidence. Instead, this form of logical reasoning relies on using relatable stories, comparisons, and a smooth flow of ideas to give the impression that the argument makes sense. Writers may create a sense of perceived logic using techniques such as:
- Using relatable anecdotes to make a point, even if they are not supported by statistics.
- Employing analogies to convey a sense of similarity or connection.
- Crafting a narrative that feels logically consistent, even if it lacks empirical evidence.
- Appealing to common beliefs to assert that an argument is valid.
Both approaches to logos can be effective in different contexts, catering to the diverse ways in which audiences engage with and understand logical arguments.
What it’s NOT: Logical Fallacies
When using logos, writers never want to unintentionally poking holes in their own argument. (Makes sense, right?) However, it happens all the time. Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning or flawed arguments that can weaken the validity and soundness of an argument. Understanding these fallacies is crucial for critical thinking and effective communication. Here are some common examples:
Ad Hominem: Attacking the character of the person making the argument rather than addressing the substance of the argument itself. Example: bashing someone’s environmental proposals because they are a vegan.
Straw Man: Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to attack instead of addressing the actual position. Example: Claiming that someone proposing a reduction in educational spending wants the population to be dumb.
False Cause , also called Causal Fallacy or Post Hoc: Incorrectly assuming that because one event follows another, the first caused the second. Example: “Since I started eating ice cream, I haven’t been sick. Therefore, ice cream must be keeping me healthy.”
False Dilemma: Presenting only two extreme options when there are actually more nuanced possibilities. Example: “Either you support this policy, or you don’t care about the future of our country.”
Appeal to Authority: Relying on the endorsement of an unqualified or irrelevant celebrity or authority figure rather than substantive evidence. Example: “Tom Brady uses that brand of toothpaste, so it must be the best out there.”
Red Herring: Attempting to shing the focus in a discussion or debate to divert attention away from the original topic or argument. Example: Shifting the focus to personal responsibility during a discussion on systemic issues contributing to healthcare costs.
Other logical fallacies include:
- Hasty Generalization
- Appeal to Ignorance
- Circular Reasoning
- Sunk Cost Fallacy
- Bandwagon Fallacy
- Slippery slope
- Equivocation
Why Do Writers Use Logos?
Writers employ logos as a persuasive strategy to build a rational and well-supported case, making their arguments more convincing and harder to argue against. By presenting concrete evidence and well-developed logic, authors build credibility to their argument. This not only enhances the persuasiveness of the writing but also provides a solid foundation for their claims.
Additionally, logos helps simplify complex ideas. Well-structured logical reasoning helps authors bridge the gap between their argument and the audience’s understanding or experiences, adding a compelling and convincing edge to their argument. Presenting logical connections and evidence makes the material more accessible and engaging for the audience.
How to Spot Logos in Writing
Sometimes logos is very straightforward, while other times, especially in more complex arguments or works of literature, it can be more challenging to pinpoint. However, in either case, the steps below make it easier to identify logos in writing or any form of persuasion:
1. Consider the claim, purpose, and evidence
Logos relies heavily on evidence, whether in the form of statistics, research findings, or real-life examples. Writers employing logos will support their claims with concrete data to strengthen their arguments. As yourself:
- What is the claim or argument the author is trying to make?
- Do they use concrete evidence, such as facts or statistics, to support their claim?
- Does the author reference credible sources or authorities to strengthen their points?

2. Pay attention to suture
The overall structure of the writing says a lot about logos. A well-organized piece will present ideas in a logical sequence, with each point building upon the previous one to form a coherent argument. Ask yourself:
- Is the argument presented in a clear and structured way, establishing a logical flow?
- Do the ideas progress logically, building upon each other to support the overall argument?
3. Look for clarity and precision
A clear argument is a strong argument. Writers using logos will carefully define terms, avoid ambiguity, and ensure that their arguments are presented in a straightforward manner. Ask yourself:
- Do I understand the point the author is trying to make?
- Are there any flaws in the reasoning or logical fallacies poking holes in the argument?
- Are key terms and concepts clearly defined to avoid ambiguity or confusion?
Tips for Teaching Logos
- Start with the definition: Rather than assuming your students know what logos is, begin by providing a clear and concise definition of logos to ensure a foundational understanding.
- Use real-world examples: Add relevance and context to logos by using real-world examples, such as current events and contemporary issues, demonstrating its application in a real-world context.
- Hold debates and discussions: Create an active learning experience by encouraging students to participate in class debates and discussions where students can practice and refine their logical reasoning skills. (Get things started with these engaging argumentative prompts .)
- Guide students through close readings: Analyze written texts together, identifying how authors use logos to build their arguments and discussing the effectiveness of different approaches.
- Look at advertisements: Bring logos to life by reviewing and analyzing advertisements for logical appeals. Look at advertisements such as print ads, social media ads, and commercials for a multimedia experience.
- Don’t skip logical fallacies : Discuss common logical fallacies to help students recognize and avoid them in their own writing and critical analysis of texts—and to save you stress and frustration when grading.
Examples of Logos
1. in literature: to kill a mockingbird by harper lee.
In “To Kill a Mockingbird,” logos shines through as Atticus Finch uses logical arguments and evidence to defend Tom Robinson during trial. For example, Atticus questions the lack of medical evidence to support Mayella Ewell’s claims and even proves Tom Robinson could not have caused the injuries to Mayella’s face due to his injured left arm.
Throughout the trial, Atticus emphasizes the absence of concrete proof, proving the case is rooted in hearsay versus factual reasoning. Unfortunately, despite Atticus’ strong logical reasoning, Tom Robinson is not set free, underscoring the racial injustices of the American South in the 1930s.
2. In a Famous Speech: “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a powerful example of logos as he crafts a logical and persuasive argument for civil rights. Dr. King makes several historical references, particularly to crucial American documents, including the Emancipation Proclamation, the Constitution, and the Declaration of Independence, to make his case. This tactic allows him to highlight the gap between the nation’s founding principles and promises and the reality for many citizens.
King focuses on grounding his speech in logic before moving toward more emotional appeal to resonate with his audience, using the lessons of the past to support his vision for the future. Through a mix of logos and pathos, he presents a powerful, logical argument, calling on the need for racial equality and justice.
3. In an Essay: “Civil Disobedience” by Henry David Thoreau
Thoreau’s essay, iconically written while in jail for not paying a poll tax as an act of peaceful protest, is a classic example of logos. To support his personal beliefs, he presents a logical argument supporting individual resistance against unjust laws and immoral government actions. Through the use of clear and specific examples, he advocates for the moral duty to resist policies that violate one’s personal principles.
Despite being rooted in his personal beliefs, Thoreau crafts a structurally sound argument, allowing the reader to follow along as he logically builds his case. His examples include both local references to drive his points home while drawing comparisons to broader-scale issues, such as the Mexican War, to help paint a clearer picture of reason and support for his argument.
Additional Resources for Teaching Logos
Check out my lesson plan on evaluating arguments to guide students through examining, analyzing, and evaluating arguments in nonfiction passages.
Read this post for more tips on teaching argument and persuasion .
Start here if you’re looking for more on how to teach argumentative message writing .
Looking to incorporate videos? Check these resources out:
- Dive into Ethos, Logs, and Pathos with the help of this TEDed video .
- Your students will have fun spotting the logos in these commercials .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
What Are Ethos, Logos, and Pathos?
Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of persuasion. We’ll be covering what they mean and how to include them in your writing.

Quick Summary on Using Ethos, Logos, and Pathos in Your Writing
- Ethos , logos , and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer’s credibility, logos appeals to the audience’s reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions.
- These three concepts, also known as the rhetorical triangle , three rhetorical appeals , or three modes of persuasion , were coined by Aristotle in his explanation of what makes rhetoric effective.
Ethos vs. Logos vs. Pathos
To understand what ethos, logos, and pathos are, you must first know what rhetoric is.
Rhetoric is defined by the Oxford Dictionary as “the art of effective or persuasive speaking or writing.” Aristotle defined rhetoric as “the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion.” In simpler terms, rhetoric is the effectiveness of the words (spoken or written) you choose to convey a message or change your audience’s perspective.
According to Aristotle, there are three means by which your rhetoric can be more powerful and that’s through the use of ethos, logos, and pathos. Knowing how to apply these three elements of persuasion can make your writing more compelling, so we’re going to teach you exactly what they mean and how to use them.
What Is Ethos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
Ethos establishes the writer’s credibility or authority. Imagine you’re at a climate change conference to learn how you can help planet Earth. Whose speech would you find more trustworthy—that of a CEO of a gas company that has profited millions of dollars by drilling for oil, or a speech by the CEO of a non-profit that helps clean oceans?
Ethos “appeals to the writer’s credibility, authority, or character” to get the audience to trust them.
My non-profit organization started with just one volunteer—me. I’d walk up and down the beaches collecting trash. Then, a friend joined me. The following week, that friend brought a friend. And then another. Until it grew to what it is today—an organization with more than 300 volunteers who have helped remove more than 15,000 pounds (6.8 tons) of trash from the beaches and the oceans. So, I know quite a bit on getting people together for a good cause.
Consider word choice, spelling, and grammar when incorporating ethos to your writing. It’s hard to trust a writer when their text is riddled with errors. Depending on what you’re writing, it may be a good idea to explicitly explain why you’re trustworthy and your expertise in the area you’re writing about.
To ensure your writing is error-free, try using LanguageTool as your writing assistant. This multilingual spelling and grammar checker can detect various types of mistakes in your writing and suggest stylistic improvements.
What Is Logos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The word logic is derived from the word logos. As you might have imagined, logos is the “appeal to the reader’s logic.” This means that you use facts, data, and statistics to support your reasoning.
Using logos in your writing is effective because it provides evidence that makes it difficult for your audience to disagree with you. Proper use of logos in your writing requires thorough research. The following example includes logos:
According to NASA and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), “the influence of human activity on the warming of the planet has evolved from theory to established fact.” This can be proven through data collected from ice cores, rocks, and tree rings as well as modern equipment, like satellites.
What Is Pathos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The last of the three elements of persuasion we’ll be discussing is pathos, which appeals to the audience’s emotions. In other words, writers try to persuade their audience by having them feel a certain way. Consider the following example:
Climate change is already happening all around us. But let’s pretend that we’re at the liberty of not having to worry about it because its effects won’t be evident in our lifetimes. What about your children? Or your children’s children? Imagine the life they will live as they have to endure extreme heat, catastrophic hurricanes, unprecedented rainfalls, and more. Climate change may not affect you personally, but it will affect those you love.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Makes For Effective Writing
Depending on what you’re writing and how you’re writing it, you may find yourself using more of either ethos, logos, or pathos. Truly effective writing finds a way to incorporate all three, even if one or two are used just a bit. As you read, try to recognize ethos, logos, and pathos. This will help you better incorporate it into your writing.

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
15 Logos Examples

Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch)
Tio Gabunia is an academic writer and architect based in Tbilisi. He has studied architecture, design, and urban planning at the Georgian Technical University and the University of Lisbon. He has worked in these fields in Georgia, Portugal, and France. Most of Tio’s writings concern philosophy. Other writings include architecture, sociology, urban planning, and economics.
Learn about our Editorial Process

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.

Logos is a rhetorical device that uses logic, reasoning, and factual evidence to support an argument or persuade an audience.
Logos refers to one of the three main technical means of persuasion in rhetoric. According to Aristotle, it is the means that has to do with the arguments themselves.
Aristotle claims that there are three technical means of persuasion:
“Now the proofs furnished by the speech are of three kinds. The first depends upon the moral character of the speaker, the second upon putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind, the third upon the speech itself, in so far as it proves or seems to prove” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 3).
Each of these corresponds to the three means of persuasion:
- Ethos (Appeal to credibility) : Persuasion through establishing the character of the speaker.
- Pathos (Appeal to emotion) : Persuasion through putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind.
- Logos (Appeal to logic): Persuasion through proof or seeming proof.
For Aristotle, speech consists of three things: the speaker, the hearer, and the speech. These correspond to ethos, pathos, and logos , respectively. The latter is the subject of this article.
Definition of Logos
At its core, logos refers to the use of logic (or perceived logic) to persuade.
However, logos may be the most confusing of the three means of persuasion because the word has been used by different philosophers to mean different but related things.
- Heraclitus of Ephesus used the word logos to refer to something like the message that the world gives us (Graham, 2021).
- The sophists used the term to refer to discourse in general.
- Pyrrhonist skeptics used the term to refer to dogmatic accounts of debatable matters.
- The Stoics meant by it the generative principle of the universe.
I could list further examples, but for this article, Aristotle’s definition will suffice.
Logos, in rhetoric, refers to persuasion through logical argumentation or its simulation (Keith & Lundberg, 2017).
As Aristotle writes,
“… persuasion is produced by the speech itself, when we establish the true or apparently true from the means of persuasion applicable to each individual subject.” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 6).
Syllogisms, enthymemes, examples, and other arguments use logos to influence people’s thinking . Due to the structure of this persuasion tool, it is the only one that can directly argue for the speaker’s point of view. What Aristotle stresses over and over again is that deceptive or fallacious arguments can have a persuasive effect if the fallacy is concealed well enough.
Persuasion through logos requires only that the hearers think that something has been proven, whether it actually has been is a different matter.
Logos Examples
- Scientific Research: Any form of scientific research is fundamentally grounded in logos, as it relies on empirical data, statistical analysis, and logical reasoning to draw conclusions. For example, if you were to present the scientific evidence to a consumer about why your product is the best, it may convince them to switch brand loyalty over to you.
- Legal Arguments: In court, attorneys use logos extensively when presenting evidence, citing precedents, or constructing logical arguments to persuade the judge or jury. Generally, it is expected that the jury be presented the best objective evidence in order for them to make an objective decision. However, at times, they will rely on pathos, and the judge’s job is often to curtail this if needed.
- Newspaper Editorials: Newspaper editorials often use logos to make a persuasive point, presenting facts, statistics, and logical analysis to support the writer’s viewpoint. Without facts and data, the readers my close the newspaper and dismiss the writer as simply engaging in hearsay.
- Referencing in Essays: In essays, we are often required to cite our sources. This is, in part, relying on ethos (appeal to credibility), but at the same time, it’s also allowing the reader to go ahead and check the primary data to ensure it’s correct.
- Financial Reports: Financial analysts use logos when they analyze data, financial statements, and market trends to provide investment advice. They know an investor wants to make the most evidence-based decision as possible with the data, so they need to present this evidence as clearly as possible.
- Medical Diagnosis: Doctors use logos when they diagnose patients by interpreting symptoms, medical histories, and test results to arrive at a logical conclusion. Without evidence, customers may distrust the doctor and refuse to follow the doctor’s advice.
- Speeches and Presentations: Speakers and debaters often use logos in their speeches or presentations to make their points more persuasive, providing evidence, statistics, and logical analysis to back up their arguments, with the intent of convincing the audience and winning the debate over the competitors (although, pathos is highly convincing in speeches as well).
- Instruction Manuals: Logos is used in instruction manuals for constructing furniture where a logical sequence of steps is provided to guide users in assembling a product or operating a piece of software. An instruction manual won’t say “if you feel like it,…” because this won’t get the job done – constructing the item!
- Funding Proposals: In making a funding pitch, proposals are often supported by logos in the form of cost-benefit analyses, case studies, and logical reasoning to convince others that their money will be in good hands.
- Problem-Solving: In a group’s blue skies brainstorming session or a problem-solving meeting, logos is used when the participants identify the problem, analyze the factors contributing to the problem, and propose logical solutions based on evidence and reasoning.
- Technological Innovations: When developing a new product or technology, engineers and designers use logos to analyze the needs of the market, create a logical design to meet those needs, and justify their decisions with reasoning and evidence. In fact, engineers need strong analytical skills and have to rely extensively on logos (rather than pathos or ethos) in their daily job roles.
Logos as Perceived Logic
Aristotle writes that even fallacious arguments are examples of logos, because they seem to prove something. In other words, logos isn’t just being logical , rather it’s attempting to appear logical .
Here are some examples:
- Straw Man Fallacy : This happens when an individual distorts, exaggerates, or misrepresents someone’s argument in order to make it easier to attack. For example, “My opponent believes in healthcare reform, he must want to give free healthcare to everyone.” Here, they are attempting to construct some logic that isn’t really there – they’re actually creating false facts to put forward a point of view!
- Slippery Slope Fallacy : This is an argument that suggests taking a minor action will lead to major and often ludicrous consequences. For example, “If we allow students to redo tests, they’ll want to redo homework, quizzes, and even final exams!” Here, the argument sounds like it could be logical, but draws a long bow and makes claims that something will happen, even though it may not (and probably won’t) actually come to pass.
- False Dichotomy Fallacy : This fallacy occurs when an argument presents only two options or sides when there may be more. For example, “You’re either with us, or against us.” Once the false dichotomy is constructed, logos can be used to convince people one perspective is better than the other, as if only the two exist.
- Hasty Generalization Fallacy : This happens when someone makes a broad conclusion based on a small or unrepresentative sample size. For example, “I met a rude person from City X, therefore everyone from City X must be rude.” Here, they are attempting to use logic – and their argument is ostensibly logical – but in reality, it (like the slippery slope) draws a long bow and is unlikely to actually be true.
Logos Strengths
- Appeal to rationality: For many people, the apparent rationality of a speech is its most important and persuasive part. Especially in academic settings where the orator cannot make themselves stand out through appeals to ethos and pathos, logos is often the most important part of the rhetorical triangle.
- Trustworthiness : While pathos and ethos are often viewed with suspicion, there is no such negative stigma attached to logos. Appeals to emotion or personal authority may seem dishonest and manipulative, but arguments, unless fallacious, rarely seem so.
- Counter arguments: Logos is the only mode of persuasion that can directly address objections because the evaluation of opposing views is itself a rational activity.
Logos Weaknesses
- Subjective matters: In certain settings, logos can be far less persuasive than pathos and ethos. This is particularly evident in settings where there are no objective criteria for deciding if the speaker is right or wrong.
See Also: The 5 Types of Rhetorical Situations
Aristotle. (1926). Rhetoric. In Aristotle in 23 Volumes, Vol. 22, translated by J. H. Freese. Harvard University Press. (Original work published ca. 367-322 B.C.E.)
Hansen, H. (2020). Fallacies. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2020). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2020/entries/fallacies/
Rapp, C. (2022). Aristotle’s Rhetoric. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2022). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2022/entries/aristotle-rhetoric/

- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 6 Types of Societies (With 21 Examples)
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Public Health Policy Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cultural Differences Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link Social Interaction Types & Examples (Sociology)

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 23 Achieved Status Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Ableism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Defense Mechanisms Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- All Insights
- Top-Rated Articles
- How-to Guides
- For Parents
Understanding Logos in Literature
Delve into the power of logos in literature and how it influences persuasion and rhetoric in writing.
The Definition and Significance of Logos
Logos, in literature, refers to the use of logic and reason to persuade the audience. Derived from the Greek word for 'word', logos plays a crucial role in creating a strong argument or presenting information in a clear and logical manner. It appeals to the audience's rationality and intellect, making it an effective tool in communication and persuasion.
The significance of logos lies in its ability to provide evidence, facts, and logical reasoning to support the writer's claims or arguments. It adds credibility to the writer's message and helps establish a sense of trust with the audience. Logos is particularly important in academic and analytical writing, where logical reasoning and evidence-based arguments are highly valued.
Moreover, logos helps writers establish a logical structure in their writing, enabling them to present their ideas in a coherent and organized manner. It guides the audience through a logical progression of thoughts, making it easier for them to follow and understand the writer's message.
The Role of Logos in Persuasion
Logos plays a pivotal role in persuasion by appealing to the audience's logic and reason. It provides a rational basis for the writer's arguments, making them more convincing and compelling. By presenting evidence, facts, and logical reasoning, logos helps build a strong and coherent argument that is difficult to refute.
In persuasion, logos works hand in hand with ethos and pathos. While ethos appeals to the audience's credibility and trust in the writer, and pathos appeals to their emotions, logos appeals to their intellect and rationality. By employing logos, writers can provide logical explanations, statistics, expert opinions, and examples to support their claims and persuade the audience to accept their viewpoint.
Moreover, logos helps writers anticipate and address counterarguments or objections. By presenting a logical and well-supported argument, writers can effectively refute opposing viewpoints and strengthen their own position. Logos, therefore, plays a critical role in shaping and influencing the audience's perception and understanding of a particular issue or topic.
Examples of Logos in Literature
Logos can be found in various forms of literature, including essays, speeches, and academic papers. One example of logos in literature is the use of statistics and research findings to support a claim. For instance, a writer may present data on the rising global temperatures to argue for the urgency of addressing climate change.
Another example of logos in literature is the use of logical reasoning and deductive arguments. A writer may use a series of logical steps to arrive at a conclusion or support a thesis statement. This can be seen in many philosophical texts, where authors use logical arguments to explore complex ideas and concepts.
Additionally, logos can be found in the use of expert opinions and quotations. Writers may cite authoritative figures or experts in a particular field to lend credibility and support to their arguments. This can be seen in academic papers, where scholars often reference other scholarly works to strengthen their own arguments.
These examples demonstrate how logos is employed in literature to persuade the audience through logic, reason, and evidence-based arguments.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Logos in Writing
When analyzing the effectiveness of logos in writing, it is important to consider how well the writer presents logical reasoning and evidence to support their claims. A strong use of logos involves providing clear and relevant evidence, using logical and coherent arguments, and anticipating and addressing counterarguments.
One way to assess the effectiveness of logos is to evaluate the quality and relevance of the evidence presented. Is the evidence credible and reliable? Does it come from reputable sources? Additionally, one can analyze the logical progression of the writer's arguments. Are the arguments logically sound? Do they follow a clear and coherent structure?
Furthermore, the effectiveness of logos can be evaluated based on how well the writer addresses counterarguments. Does the writer acknowledge opposing viewpoints and provide logical refutations? Are any potential weaknesses or limitations in the argument addressed?
By critically analyzing the effectiveness of logos in writing, readers can better understand the strength of the writer's arguments and the persuasive impact they may have on the audience.
Expanding the Use of Logos in Contemporary Literature
While logos has long been utilized in literature, its use can be expanded and adapted in contemporary writing. In today's digital age, where information is readily available and opinions are easily shared, the use of logos becomes even more important.
Contemporary literature can benefit from incorporating logos by providing accurate and up-to-date data, statistics, and research findings. With the abundance of information online, writers can use logos to separate reliable sources from unreliable ones and present well-supported arguments.
Moreover, the use of visuals, such as graphs, charts, and infographics, can enhance the impact of logos in contemporary literature. Visual representations of data and statistics can make complex information more accessible and compelling to the audience.
Furthermore, the expansion of logos in contemporary literature can involve incorporating interdisciplinary approaches. By drawing on multiple disciplines and fields of study, writers can strengthen their arguments and provide a more comprehensive perspective on a particular topic.
By expanding the use of logos in contemporary literature, writers can harness the power of logic and reason to engage and persuade readers in an increasingly information-rich world.
Related Insights
Slippery slope arguments - a logical fallacy to look out for, why add laughter in serious contexts, learn to create a persuasive speech: how to apply these tools to investigate your topic (part 2).

- 5 Prep Tips for BP
- Top Speech Introductions
- Public Speaking and Debate Competitions
- Incorporating Humor
- Logical Fallacies
- How-To: Prepare for Debate Tournaments
- How-To: Judge a Debate
- How-To: Win a BP Debate
- How-To: Win An Argument
- How-To: Improve at Home
- Team China Wins World Championship
- Ariel Wins Tournament
- Jaxon Speaks Up
- Tina Improves

The Essential AP Guide to Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
The goal of argumentative writing is to persuade your audience that your ideas are convincing. Basically, there are three ways of doing this:
- You can convince your reader that your authority is indisputable (ethos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his emotions (pathos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his sense of logic and reason (logos)
Think of these different modes of persuasion, ethos, pathos, and logos, as tactics or strategies. Tactics you’ve used all your life when you use words to try to persuade someone to do something, be that agree with your opinion or buy you a new bike.
Yes, you use ethos, pathos, and logos every day.
To succeed in AP English, you need to know how to identify ethos, pathos, and logos quickly. Below is our quick guide that gives you everything you need to know to identify ethos, pathos, and logos and ace AP English.

Pathos, Logos, and Ethos
Most people are able to drive a car without fully understanding how the car operates. Making an argument is the same way. Most of us attempt to persuade people every day without understanding how persuasion works. Learning how a strong argument is crafted empowers us to better communicate and persuade others to understand our viewpoints.
What Are Pathos, Logos, and Ethos?
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader.
Pathos , or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and stories that evoke emotion. Authors can desire a range of emotional responses, including sympathy, anger, frustration, or even amusement.
Logos , or the appeal to logic, means to appeal to the audiences’ sense of reason or logic. To use logos, the author makes clear, logical connections between ideas, and includes the use of facts and statistics. Using historical and literal analogies to make a logical argument is another strategy. There should be no holes in the argument, also known as logical fallacies, which are unclear or wrong assumptions or connections between ideas.
Ethos is used to convey the writer’s credibility and authority. When evaluating a piece of writing, the reader must know if the writer is qualified to comment on this issue. The writer can communicate their authority by using credible sources; choosing appropriate language; demonstrating that they have fairly examined the issue (by considering the counterargument); introducing their own professional, academic or authorial credentials; introducing their own personal experience with the issue; and using correct grammar and syntax.
Sample Paragraph
Imagine this: a small dog sits in a dark, cold garage. His hair is matted and dirty; he is skinny and weak from going days without food. There is no water for him to drink, no person to give him love and no blanket to keep him warm at night. 1 While this might be a hard scenario to imagine, it is not an uncommon one in America today. According to the Humane Society of the United States, nearly 1,000,000 animals are abused or die from abuse every year. 2 As a veterinarian with 30 years of experience, I have seen how even one incident of abuse can affect an animal for the rest of its life. 3 As a society, we need to be more aware of this terrible problem and address this issue before it gets worse.
1 Pathos: the author paints a vivid picture to evoke a feeling from the reader—sadness and pity for the abused animal.
2 Logos: the author uses a startling statistic to appeal to our intellect. Keep in mind that these three strategies can often overlap. This sentence qualifies as both Logos and Ethos because it cites a reputable organization, so we know the author is using credible sources.
3 Ethos: the author establishes their own credibility by stating their occupation and experience.>
How Do I Know if the Author is Using Pathos, Logos or Ethos?
Pathos—does the writer appeal to the emotions of their reader.
- Do they use individuals’ stories to “put a face” on the problem you’re exploring? For example, using an individual’s story about losing their home during the mortgage crisis of the 2008 Recession may be more powerful than using only statistics.
- Do they use charged language or words that carry appropriate connotations? For example, if a writer describes a gun as a “sleek, silver piece of sophisticated weaponry,” they are delivering a much different image than if she writes, “a cold hunk of metal, dark and barbaric and ready to kill.”
Logos—does the writer appeal to the rational mind by using logic and evidence?
- Do they include facts and statistics that support their point? It’s more convincing to tell the reader that “80% of students have committed some form of plagiarism,” than simply saying that “Lots of students have plagiarized.”
- Do they walk us through the logical quality of their argument? Do they show us how ideas connect in a rational way? For example: “English students have been able to raise their overall grade by meeting with peer tutors, so it’s safe to assume that math students could also benefit from frequent tutoring sessions.” This example points out that logically, if the result has been seen in one situation, then it should be seen in a different but similar situation.
- Hasty generalizations: “Even though the movie just started, I know it’s going to be boring.”
- Slippery Slope: “If the government legalizes marijuana, eventually they’ll legalize all drugs.”
- Circular Argument: “Barack Obama is a good communicator because he speaks effectively.”
Ethos—is this writer trustworthy?
- What are their credentials? Are they an expert in the field? Have they written past essays, articles or books about this topic?
- Do they use reputable sources? Do they support her statements with sources from established publications like The New York Times or a government census report? Do they fail to mention any sources?
- Are they a fair-minded person who has considered all sides of this issue? Have they acknowledged any common ground they share with the opposite side? Do they include a counterargument and refutation?
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer .
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay .
Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

Ethos, Logos, and Pathos

When being introduced to rhetorical concepts, among the first appeals students learn about are the rhetorical appeals. There are three main appeals that can be used: ethos, pathos, and logos. Although this handout does provide examples of each appeal below, it is important to note that a piece of media or text might actually contain more than one appeal. For example, one sentence might contain elements of two separate appeals, and that’s ok! We’ve only separated them out to help you better identify how these parts work on their own.
Ethos is all about credibility—is the source coming from research that is reliable and has a good reputation? A writer can use ethos to show readers why they are the best person to be writing or talking about a particular topic or issue. Sometimes, ethos can be established through a writer’s experiences, education, work, or research.
Take this biography that was posted in the article “What They Take with Them: Findings from the Peer Writing Tutor Alumni Research Project” published in the Writing Center Journal . Since the Writing Center Journal is a peer-reviewed, academic source, the name of the journal also has a positive ethos appeal. However, this biography gives the reader an understanding why Dr. Hughes is the right person to write about this particular topic.
At the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Bradley Hughes has been director of the writing center since 1984 and director of writing across the curriculum since 1990. He co-chaired the IWCA Summer Institutes in 2003, 2008, and 2009. His most recent publication, co-authored with colleagues, focuses on writing center podcasts (Writing Lab Newsletter, 2009). Together with colleagues at UW-Madison, he’s currently developing an authoring program for creating computer simulations to use in tutor education, which will be distributed as open-source software starting in 2011.
- Hughes’ current projects immerse him in writing center scholarship.
- Hughes’ job title and location indicates his prominence in the writing center field.
- Professional tone and language subtly add to the ethos appeal.
- The publications named are relevant to the topic and field.
- The extracurricular activities listed relate to the article’s topic.
Although many people will associate using numbers and statistics with logos, logos also includes logic and reasoning. In this way, logos appeals can be more subtly communicated. Note that logos appeals are different from logical fallacies, which contain flawed reasoning or logic and should be avoided.
The survey itself is deliberately open-ended and flexible because we wanted to give alumni room to respond in ways we could never anticipate, and because we want colleagues who participate in the PWTARP to replicate or adapt our survey design to their own institutions and to their own research goals. We tried to design open-ended questions that would elicit full responses, not too scripted, we hoped, by the questions.
- There is plenty of justification provided as to why this research method was selected.
- The reasons listed are practical rather than emotional.
Unlike logos, pathos appeals rely heavily on emotional manipulation. Pathos can trigger any kind of emotions in the reader ranging from sadness to anger. These appeals are particularly effective in terms of connecting with the audience, and giving the message a personal and relatable touch.
- Her eyes are expressive and clear—the way the ad is designed has you look at her face as you read the text.
- Her mouth covered as if she is being spoken over by the search results, which evokes an emotional response.
- Putting the women’s face directly behind the text increases emotional impact since we can see directly who is being discussed.
- The Google search bar is familiar and widely used. The idea that this is on a common search engine increases its emotional appeal.
Tips for Incorporating Rhetorical Appeals in Your Writing
- Consider your audience and rhetorical situation to make smart choices.
- Be mindful of your tone and word choices—small word choices can have big consequences!
- Use appeals together– just because you are presenting a logical argument doesn’t mean you have to avoid emotional appeals as well. The best arguments blend appeals together for a multi-layered effect.
- Sometimes you can drive audiences away if you use too much of a certain appeal. For example, if using too much pathos, your audience may have a less sympathetic response or may feel manipulated.
Hughes, Bradley, et al. “What They Take with Them: Findings from the Peer Writing Tutor Alumni Research Project.” The Writing Center Journal , vol. 30, no. 2, 2010, pp. 12–46, www.jstor.org/stable/43442343.
UN Women . “UN Women Ad Series Reveals Widespread Sexism.” 21 Oct. 2013, http://www.unwomen.org/en/news/stories/2013/10/women-should-ads.

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
Project Types We Cover
- Admissions Essay
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Research Paper
- Book Reviews
- Personal Statement
- Ph.D Dissertation
- Proofreading
Academic Fields & Subjects
- Programming
- Computer Science
- Other projects we help with
- Our Experts
- Plagiarism Checker
- Writing Tips
- Ethos Pathos and Logos
Persuasive Essay Using Ethos Pathos and Logos
By: Henrique Bertulino

You may not know it but you need logos, ethos, pathos, and even kairos to come up with a good essay. Basically, these things, also called modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals, can help you convince your audience and support your arguments. These four elements of persuasion were even described by Aristotle in his Rhetoric, and he definitely knew how to be persuasive. Now you can get a short summary of the ancient philosopher's research and use his knowledge in your favor!
Understanding Logos, Ethos, and Pathos
Examples of logos, examples of ethos , examples of pathos , bonus: what is kairos.
So, what are logos, ethos, and pathos? You can see them as three elements of an effective persuasive message, which can come in handy for your argumentative essay. You're using them already, there's no doubt, but you're just doing it unknowingly for now. But by knowing them well and using them purposefully you can get as convincing and confident as by using a professional rhetorical approach. Also, knowing the structure of your persuasion will improve the structure of your speech overall, both written and spoken. So get to know logos, ethos, pathos, and kairos better.
What Is Logos?
Logos is the persuasive technique appealing to the rational part. It's related to the facts you use to support your argument and make your idea look more attractive to the audience. Logos is usually called a "logical appeal", and it comes in the form of the citation of statistics, facts, charts, graphs, etc. It makes your statement more reliable and legit by using undoubtful things that can be checked and measured.
There are different rational modes of thinking to use, here are some examples:
- Deductive reasoning — going from a broad, general claim to a specific point.
- Inductive reasoning — using some specific examples to support a broad generalization.
- Comparison — highlighting the strength of your claim by comparing your case with a similar one in which the fairness of your position is clearer.
- Cause/effect thinking — basing your position on making assumptions about the future, making predictions that prove you're right.
- Exemplification — listing many examples of evidence to support your opinion.
- Coherent thought — structuring your thoughts properly so that they are easy to receive and understand.
Let’s pretend you need to write an argumentative essay reflecting global warming. Here are some examples of logos you can use to make your arguments stronger.
- The average surface temperature of the Earth has risen about 2.05 degrees Fahrenheit since the late 19th century.
- NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment have data showing that Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019.
- When it comes to surface ocean waters, their level of acidity has increased by about 30% since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.
What Is Ethos
Ethos is another important brick in the wall of your persuasion, it appeals to your character and evaluates your opinion in terms of your trustworthiness. It relies on your credibility as a speaker and decreases or increases the level of trust that the audience has towards you depending on how reliable you are as a source. Ethos is not only related to your own authority and achievements but also to the values or ideologies that your potential listener or reader may share.
There are several ways to show people your credibility, such as:
- Describing more than one opinion and providing counterarguments to show that you're knowledgeable and open to other positions.
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the beliefs that matter to the audience, which may also include using special language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles, to build the bond.
- Demonstrating your reputation, expertise, experience, or academic knowledge in a field.
Let’s continue with your discussion paper on global warming. Here are some examples of ethos that can support your argument.
- I have a degree in Biology and I can assure you the way this company disposes of its waste can harm the environment.
- My family has a business related to fishing and I can say that for the last 15 years, the level of water quality has been decreasing dramatically.
- As I've spent the last summer as a volunteer for a non-profit environmental organization, I know that the effect of global warming is even more dreadful than the media portray it.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos focuses your audience's attention on their emotions and how your writing corresponds with them. It appeals to such things as empathy, imagination, feelings, fears, etc. Combined with two other modes, this emotional one can help you build a strong argument that will convince any audience that you're right.
Here are some examples of what can help you:
- Describing things, people, places, events, and ideas in an expressive and relatable way.
- Creating vivid images that make readers not only understand but also feel your claim.
- Sharing personal stories to build a stronger connection with your readers.
- Using emotionally charged vocabulary to reflect a specific mindset and create a specific atmosphere.
- Appealing to the facts that may affect your audience and their lives so that they can actually relate to the things you're saying.
As we keep going with your imaginary discussion essay about global warming, let's see what pathos examples can be useful.
- Due to global warming hurricanes will become stronger and more intense, which is a life-threatening change.
- Extreme heat affects not only people's health, but also energy consumption, agricultural industry, and economics.
- Obviously, the rising of the temperature leads to declining water supplies, which means the price of just an ordinary water bottle will increase drastically in no time.
This one is way less-used but still present. Kairos stands for "right time". And it basically refers to the optimal moment to take action. You can make your claim stronger by building a connection between your position and the actual situation you and your audience are in right now. Your logos, ethos, and pathos need to be served in a perfect moment to strike effectively, and that's when kairos comes into play.
User ratings:
User ratings is 4.4 stars.
4.4 /5 ( 28 Votes)

Head of Customer Success
I'm a medical doctor and brand manager. The process of getting into Med school and studying at it made me learn and apply many strategies to keep my productivity high while spending less time and effort. As a working student, I had to figure out how to study smarter, not harder. During this period, my interest in neurology and psychiatry, as well as my aspiration to help others, intensified. At Studybay, I use my knowledge, skills, and experience to develop helpful solutions for students and make their study paths more productive and fun.
Add Your Comment
We are very interested to know your opinion
Frankly speaking, when I started reading about Ethos, Logos, Pathos, and Kairos, I could not understand what they are and how they can be used in essay writing. However, after reading your notes, everything has become clear. It will be very easier to me to teach my students how these rhetorical appeals are used in essay writing. Thank you very much.
Jean Bosco Twahirwa
This is a detailed lesson about the use of persuasive strategies in essay writing. Shout out to you; hats off! May I have another detailed example of a full written essay about inclusive education? That will be kind of you, guys.
TWAHIRWA Jean Bosco
Such an enlightening article! It not only explained the importance of ethos, pathos, and logos but also showcased how they work together to make arguments more convincing. I feel more confident in my argumentative essay writing after reading this.
I never realized how much of an impact my use of ethos, pathos, and logos made in my writing until I read this article.
I’ve used the techniques in this article for my latest essay and noticed a significant improvement in its persuasive power.
I found this extremely helpful in improving my essay writing skills. The examples provided were spot-on and helped me better grasp the importance of ethos, pathos, and logos in persuasive writing. Highly recommended!

Upgrade your writing skills!
Try our AI essay writer from Studybay today!
Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
You may be surprised to learn that much of your life consists of constructing arguments. If you ever plead a case to your parents—in order to extend your curfew or to get a new gadget, for example—you are using persuasive strategies. When you discuss music with friends and agree or disagree with them about the merits of one singer compared to another, you are also using strategies for persuasion.
Indeed, when you engage in these "arguments" with your parents and friends, you are instinctively using ancient strategies for persuasion that were identified by the Greek philosopher Aristotle a few thousand years ago. Aristotle called his ingredients for persuasion pathos , logos , and ethos .
Persuasion Tactics and Homework
When you write a research paper , write a speech , or participate in a debate , you also use the persuasion strategies mentioned above. You come up with an idea (a thesis) and then construct an argument to convince readers that your idea is sound.
You should become familiar with pathos, logos, and ethos for two reasons: First, you need to develop your own skills at crafting a good argument so that others will take you seriously. Second, you must develop the ability to identify a really weak argument, stance, claim, or position when you see or hear it.
Logos Defined
Logos refers to an appeal to reason based on logic. Logical conclusions come from assumptions and decisions derived from weighing a collection of solid facts and statistics . Academic arguments (research papers) rely on logos.
An example of an argument that relies on logos is the argument that smoking is harmful based on the evidence that, "When burned, cigarettes create more than 7,000 chemicals. At least 69 of these chemicals are known to cause cancer, and many are toxic," according to the American Lung Association. Notice that the statement above uses specific numbers. Numbers are sound and logical.
An everyday example of an appeal to logos is the argument that Lady Gaga is more popular than Justin Bieber because Gaga's fan pages collected 10 million more Facebook fans than Bieber's. As a researcher, your job is to find statistics and other facts to back up your claims. When you do this, you are appealing to your audience with logic or logos.
Ethos Defined
Trustworthiness is important in research. You must trust your sources, and your readers must trust you. The example above concerning logos contained two examples that were based on hard facts (numbers). However, one example comes from the American Lung Association. The other comes from Facebook fan pages. You should ask yourself: Which of these sources do you suppose is more credible?
Anyone can start a Facebook page. Lady Gaga may have 50 different fan pages, and each page may contain duplicate "fans." The fan page argument is probably not very sound (even though it seems logical). Ethos refers to the credibility of the person posing the argument or stating the facts.
The facts provided by the American Lung Association are probably more persuasive than those provided by fan pages since the American Lung Association has been around for more than 100 years. At first glance, you might think that your own credibility is out of your control when it comes to posing academic arguments, but that is incorrect.
Even if you write an academic paper on a topic that is outside your area of expertise, you can improve your credibility—using ethos to persuade—by coming across as a professional by citing credible sources and making your writing error-free and concise.
Pathos Defined
Pathos refers to appealing to a person by influencing his emotions. Pathos is involved in the strategy of convincing the audience by invoking feelings through their own imaginations. You appeal through pathos when you try to convince your parents of something. Consider this statement:
"Mom, there is clear evidence that cellphones save lives in emergency situations."
While that statement is true, the real power lies in the emotions that you will likely invoke in your parents. What mother wouldn't envision a broken-down automobile perched by the side of a busy highway upon hearing that statement?
Emotional appeals are extremely effective, but they can be tricky. There may or may not be a place for pathos in your research paper . For example, you may be writing an argumentative essay about the death penalty.
Ideally, your paper should contain a logical argument. You should appeal to logos by including statics to support your view such as data that suggests that the death penalty does/does not cut down on crime (there's plenty of research both ways).
Use Appeals to Emotion Sparingly
You may also use pathos by interviewing someone who witnessed an execution (on the anti-death penalty side) or someone who found closure when a criminal was executed (on the pro-death penalty side). Generally, however, academic papers should employ appeals to emotions sparingly. A long paper that is purely based on emotions is not considered very professional.
Even when you are writing about an emotionally charged, controversial issue like the death penalty, you can't write a paper that is all emotion and opinion. The teacher, in that circumstance, will likely assign a failing grade because you haven't provided a sound (logical) argument.
- “ What's In a Cigarette? ” American Lung Association,
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Use Social Media to Teach Ethos, Pathos and Logos
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- Logos (Rhetoric)
- Words, Phrases, and Arguments to Use in Persuasive Writing
- Pathos in Rhetoric
- Artistic Proofs: Definitions and Examples
- Definition and Examples of Ethos in Classical Rhetoric
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- What is an Appeal in Rhetoric?
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- Proof in Rhetoric
Frequently asked questions
What are logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
Frequently asked questions: Writing an essay
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
Let’s say you’re writing a five-paragraph essay about the environmental impacts of dietary choices. Here are three examples of topic sentences you could use for each of the three body paragraphs :
- Research has shown that the meat industry has severe environmental impacts.
- However, many plant-based foods are also produced in environmentally damaging ways.
- It’s important to consider not only what type of diet we eat, but where our food comes from and how it is produced.
Each of these sentences expresses one main idea – by listing them in order, we can see the overall structure of the essay at a glance. Each paragraph will expand on the topic sentence with relevant detail, evidence, and arguments.
The topic sentence usually comes at the very start of the paragraph .
However, sometimes you might start with a transition sentence to summarize what was discussed in previous paragraphs, followed by the topic sentence that expresses the focus of the current paragraph.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
If you have to hand in your essay outline , you may be given specific guidelines stating whether you have to use full sentences. If you’re not sure, ask your supervisor.
When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is yours. Some students find it helpful to write out their ideas in full sentences, while others prefer to summarize them in short phrases.
You will sometimes be asked to hand in an essay outline before you start writing your essay . Your supervisor wants to see that you have a clear idea of your structure so that writing will go smoothly.
Even when you do not have to hand it in, writing an essay outline is an important part of the writing process . It’s a good idea to write one (as informally as you like) to clarify your structure for yourself whenever you are working on an essay.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
If you’re not given a specific prompt for your descriptive essay , think about places and objects you know well, that you can think of interesting ways to describe, or that have strong personal significance for you.
The best kind of object for a descriptive essay is one specific enough that you can describe its particular features in detail—don’t choose something too vague or general.
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We often try to avoid conflict in our personal lives, but as a writer sometimes your job is to advance an argument and effectively persuade your audience. The term logos is used to refer to the use of logic and reasoning in crafting a piece of persuasive writing or rhetoric. Building a logical case can take time and effort, but understanding logos and being able to make effective logical ...
Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic or reason. For example, when a speaker cites scientific data, methodically walks through the line of reasoning behind their argument, or precisely ...
Define logos in literature: the definition of logos in literature is a rhetorical device that appeals to logic and reason. In summary, logos is: an appeal to logic. one of the three Aristotelian appeals. usually evident as facts, numbers, or statistics. used to convince an audience of an argument. Contents [ hide]
Logos Definition. Derived from the Greek for "logic," logos is a rhetorical device that uses reason and logic to persuade an audience. It can be implemented using facts, figures, or logical statements. Logos can be divided into two categories: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning starts with specific cases to ...
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Logos is the part of the argument where you treat your audience like purely rational, "only the facts, ma'am" kind of people. Also, gaps, leaps, and inconsistencies in logic, no matter how well developed the other appeals may be, can tear apart an argument in short order.
Logos Definition. Derived from a Greek word, Logos means "logic.". Logos is a literary device that can be described as a statement, sentence, or argument used to convince or persuade the targeted audience by employing reason or logic. In everyday life, arguments depend upon pathos and ethos besides logos.
Through a mix of logos and pathos, he presents a powerful, logical argument, calling on the need for racial equality and justice. 3. In an Essay: "Civil Disobedience" by Henry David Thoreau. Thoreau's essay, iconically written while in jail for not paying a poll tax as an act of peaceful protest, is a classic example of logos.
5.2: Logos, Ethos, and Pathos. In order to persuade a particular audience of a particular point, a writer makes decisions about how best to convince the reader. Aristotle recognized three basic appeals that a writer (or orator) should consider when presenting an argument: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
Definition of Logos. At its core, logos refers to the use of logic (or perceived logic) to persuade. However, logos may be the most confusing of the three means of persuasion because the word has been used by different philosophers to mean different but related things.. Heraclitus of Ephesus used the word logos to refer to something like the message that the world gives us (Graham, 2021).
Logos can be found in various forms of literature, including essays, speeches, and academic papers. One example of logos in literature is the use of statistics and research findings to support a claim. For instance, a writer may present data on the rising global temperatures to argue for the urgency of addressing climate change.
The Essential AP Guide to Ethos, Pathos, and Logos. The goal of argumentative writing is to persuade your audience that your ideas are convincing. Basically, there are three ways of doing this: Think of these different modes of persuasion, ethos, pathos, and logos, as tactics or strategies. Tactics you've used all your life when you use words ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader. Pathos, or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and ...
2. Major premise: To help change worker exploitation, we should use the strategy the workers in the situation are asking for. Minor premise: In this case, the workers do not want U.S. consumers to ___ the company. Conclusion: Therefore, if we want to help, we should use a different strategy besides boycotting.
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
Logos. Logos is about appealing to your audience's logical side. You have to think about what makes sense to your audience and use that as you build your argument. As writers, we appeal to logos by presenting a line of reasoning in our arguments that is logical and clear. We use evidence, such as statistics and factual information, when we ...
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos When being introduced to rhetorical concepts, among the first appeals students learn about are the rhetorical appeals. There are three main appeals that can be used: ethos, pathos, and logos. Although this handout does provide examples of each appeal below, it is important to note that a piece of media or text might actually contain more than one appeal.
In the following essay, the three writing techniques of Ethos, Logos, and Pathos are demonstrated, followed by an explanation of their relevance. Imagine this: a small dog sits in a dark, cold garage.
You may not know it but you need logos, ethos, pathos, and even kairos to come up with a good essay. Basically, these things, also called modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals, can help you convince your audience and support your arguments. These four elements of persuasion were even described by Aristotle in his ...
For example, you may be writing an argumentative essay about the death penalty. Ideally, your paper should contain a logical argument. You should appeal to logos by including statics to support your view such as data that suggests that the death penalty does/does not cut down on crime (there's plenty of research both ways).
Logos appeals to the audience's reason, building up logical arguments. Ethos appeals to the speaker's status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example. Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical ...