- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write the Rationale of the Study in Research (Examples)
What is the Rationale of the Study?
The rationale of the study is the justification for taking on a given study. It explains the reason the study was conducted or should be conducted. This means the study rationale should explain to the reader or examiner why the study is/was necessary. It is also sometimes called the “purpose” or “justification” of a study. While this is not difficult to grasp in itself, you might wonder how the rationale of the study is different from your research question or from the statement of the problem of your study, and how it fits into the rest of your thesis or research paper.
The rationale of the study links the background of the study to your specific research question and justifies the need for the latter on the basis of the former. In brief, you first provide and discuss existing data on the topic, and then you tell the reader, based on the background evidence you just presented, where you identified gaps or issues and why you think it is important to address those. The problem statement, lastly, is the formulation of the specific research question you choose to investigate, following logically from your rationale, and the approach you are planning to use to do that.
Table of Contents:
How to write a rationale for a research paper , how do you justify the need for a research study.
- Study Rationale Example: Where Does It Go In Your Paper?
The basis for writing a research rationale is preliminary data or a clear description of an observation. If you are doing basic/theoretical research, then a literature review will help you identify gaps in current knowledge. In applied/practical research, you base your rationale on an existing issue with a certain process (e.g., vaccine proof registration) or practice (e.g., patient treatment) that is well documented and needs to be addressed. By presenting the reader with earlier evidence or observations, you can (and have to) convince them that you are not just repeating what other people have already done or said and that your ideas are not coming out of thin air.
Once you have explained where you are coming from, you should justify the need for doing additional research–this is essentially the rationale of your study. Finally, when you have convinced the reader of the purpose of your work, you can end your introduction section with the statement of the problem of your research that contains clear aims and objectives and also briefly describes (and justifies) your methodological approach.
When is the Rationale for Research Written?
The author can present the study rationale both before and after the research is conducted.
- Before conducting research : The study rationale is a central component of the research proposal . It represents the plan of your work, constructed before the study is actually executed.
- Once research has been conducted : After the study is completed, the rationale is presented in a research article or PhD dissertation to explain why you focused on this specific research question. When writing the study rationale for this purpose, the author should link the rationale of the research to the aims and outcomes of the study.
What to Include in the Study Rationale
Although every study rationale is different and discusses different specific elements of a study’s method or approach, there are some elements that should be included to write a good rationale. Make sure to touch on the following:
- A summary of conclusions from your review of the relevant literature
- What is currently unknown (gaps in knowledge)
- Inconclusive or contested results from previous studies on the same or similar topic
- The necessity to improve or build on previous research, such as to improve methodology or utilize newer techniques and/or technologies
There are different types of limitations that you can use to justify the need for your study. In applied/practical research, the justification for investigating something is always that an existing process/practice has a problem or is not satisfactory. Let’s say, for example, that people in a certain country/city/community commonly complain about hospital care on weekends (not enough staff, not enough attention, no decisions being made), but you looked into it and realized that nobody ever investigated whether these perceived problems are actually based on objective shortages/non-availabilities of care or whether the lower numbers of patients who are treated during weekends are commensurate with the provided services.
In this case, “lack of data” is your justification for digging deeper into the problem. Or, if it is obvious that there is a shortage of staff and provided services on weekends, you could decide to investigate which of the usual procedures are skipped during weekends as a result and what the negative consequences are.
In basic/theoretical research, lack of knowledge is of course a common and accepted justification for additional research—but make sure that it is not your only motivation. “Nobody has ever done this” is only a convincing reason for a study if you explain to the reader why you think we should know more about this specific phenomenon. If there is earlier research but you think it has limitations, then those can usually be classified into “methodological”, “contextual”, and “conceptual” limitations. To identify such limitations, you can ask specific questions and let those questions guide you when you explain to the reader why your study was necessary:
Methodological limitations
- Did earlier studies try but failed to measure/identify a specific phenomenon?
- Was earlier research based on incorrect conceptualizations of variables?
- Were earlier studies based on questionable operationalizations of key concepts?
- Did earlier studies use questionable or inappropriate research designs?
Contextual limitations
- Have recent changes in the studied problem made previous studies irrelevant?
- Are you studying a new/particular context that previous findings do not apply to?
Conceptual limitations
- Do previous findings only make sense within a specific framework or ideology?
Study Rationale Examples
Let’s look at an example from one of our earlier articles on the statement of the problem to clarify how your rationale fits into your introduction section. This is a very short introduction for a practical research study on the challenges of online learning. Your introduction might be much longer (especially the context/background section), and this example does not contain any sources (which you will have to provide for all claims you make and all earlier studies you cite)—but please pay attention to how the background presentation , rationale, and problem statement blend into each other in a logical way so that the reader can follow and has no reason to question your motivation or the foundation of your research.
Background presentation
Since the beginning of the Covid pandemic, most educational institutions around the world have transitioned to a fully online study model, at least during peak times of infections and social distancing measures. This transition has not been easy and even two years into the pandemic, problems with online teaching and studying persist (reference needed) .
While the increasing gap between those with access to technology and equipment and those without access has been determined to be one of the main challenges (reference needed) , others claim that online learning offers more opportunities for many students by breaking down barriers of location and distance (reference needed) .
Rationale of the study
Since teachers and students cannot wait for circumstances to go back to normal, the measures that schools and universities have implemented during the last two years, their advantages and disadvantages, and the impact of those measures on students’ progress, satisfaction, and well-being need to be understood so that improvements can be made and demographics that have been left behind can receive the support they need as soon as possible.
Statement of the problem
To identify what changes in the learning environment were considered the most challenging and how those changes relate to a variety of student outcome measures, we conducted surveys and interviews among teachers and students at ten institutions of higher education in four different major cities, two in the US (New York and Chicago), one in South Korea (Seoul), and one in the UK (London). Responses were analyzed with a focus on different student demographics and how they might have been affected differently by the current situation.
How long is a study rationale?
In a research article bound for journal publication, your rationale should not be longer than a few sentences (no longer than one brief paragraph). A dissertation or thesis usually allows for a longer description; depending on the length and nature of your document, this could be up to a couple of paragraphs in length. A completely novel or unconventional approach might warrant a longer and more detailed justification than an approach that slightly deviates from well-established methods and approaches.
Consider Using Professional Academic Editing Services
Now that you know how to write the rationale of the study for a research proposal or paper, you should make use of Wordvice AI’s free AI Grammar Checker , or receive professional academic proofreading services from Wordvice, including research paper editing services and manuscript editing services to polish your submitted research documents.
You can also find many more articles, for example on writing the other parts of your research paper , on choosing a title , or on making sure you understand and adhere to the author instructions before you submit to a journal, on the Wordvice academic resources pages.
How to Write the Rationale for a Research Paper
- Research Process
- Peer Review
A research rationale answers the big SO WHAT? that every adviser, peer reviewer, and editor has in mind when they critique your work. A compelling research rationale increases the chances of your paper being published or your grant proposal being funded. In this article, we look at the purpose of a research rationale, its components and key characteristics, and how to create an effective research rationale.
Updated on September 19, 2022

The rationale for your research is the reason why you decided to conduct the study in the first place. The motivation for asking the question. The knowledge gap. This is often the most significant part of your publication. It justifies the study's purpose, novelty, and significance for science or society. It's a critical part of standard research articles as well as funding proposals.
Essentially, the research rationale answers the big SO WHAT? that every (good) adviser, peer reviewer, and editor has in mind when they critique your work.
A compelling research rationale increases the chances of your paper being published or your grant proposal being funded. In this article, we look at:
- the purpose of a research rationale
- its components and key characteristics
- how to create an effective research rationale
What is a research rationale?
Think of a research rationale as a set of reasons that explain why a study is necessary and important based on its background. It's also known as the justification of the study, rationale, or thesis statement.
Essentially, you want to convince your reader that you're not reciting what other people have already said and that your opinion hasn't appeared out of thin air. You've done the background reading and identified a knowledge gap that this rationale now explains.
A research rationale is usually written toward the end of the introduction. You'll see this section clearly in high-impact-factor international journals like Nature and Science. At the end of the introduction there's always a phrase that begins with something like, "here we show..." or "in this paper we show..." This text is part of a logical sequence of information, typically (but not necessarily) provided in this order:

Here's an example from a study by Cataldo et al. (2021) on the impact of social media on teenagers' lives.

Note how the research background, gap, rationale, and objectives logically blend into each other.
The authors chose to put the research aims before the rationale. This is not a problem though. They still achieve a logical sequence. This helps the reader follow their thinking and convinces them about their research's foundation.
Elements of a research rationale
We saw that the research rationale follows logically from the research background and literature review/observation and leads into your study's aims and objectives.
This might sound somewhat abstract. A helpful way to formulate a research rationale is to answer the question, “Why is this study necessary and important?”
Generally, that something has never been done before should not be your only motivation. Use it only If you can give the reader valid evidence why we should learn more about this specific phenomenon.
A well-written introduction covers three key elements:
- What's the background to the research?
- What has been done before (information relevant to this particular study, but NOT a literature review)?
- Research rationale
Now, let's see how you might answer the question.
1. This study complements scientific knowledge and understanding
Discuss the shortcomings of previous studies and explain how'll correct them. Your short review can identify:
- Methodological limitations . The methodology (research design, research approach or sampling) employed in previous works is somewhat flawed.
Example : Here , the authors claim that previous studies have failed to explore the role of apathy “as a predictor of functional decline in healthy older adults” (Burhan et al., 2021). At the same time, we know a lot about other age-related neuropsychiatric disorders, like depression.
Their study is necessary, then, “to increase our understanding of the cognitive, clinical, and neural correlates of apathy and deconstruct its underlying mechanisms.” (Burhan et al., 2021).
- Contextual limitations . External factors have changed and this has minimized or removed the relevance of previous research.
Example : You want to do an empirical study to evaluate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the number of tourists visiting Sicily. Previous studies might have measured tourism determinants in Sicily, but they preceded COVID-19.
- Conceptual limitations . Previous studies are too bound to a specific ideology or a theoretical framework.
Example : The work of English novelist E. M. Forster has been extensively researched for its social, political, and aesthetic dimensions. After the 1990s, younger scholars wanted to read his novels as an example of gay fiction. They justified the need to do so based on previous studies' reliance on homophobic ideology.
This kind of rationale is most common in basic/theoretical research.
2. This study can help solve a specific problem
Here, you base your rationale on a process that has a problem or is not satisfactory.
For example, patients complain about low-quality hospital care on weekends (staff shortages, inadequate attention, etc.). No one has looked into this (there is a lack of data). So, you explore if the reported problems are true and what can be done to address them. This is a knowledge gap.
Or you set out to explore a specific practice. You might want to study the pros and cons of several entry strategies into the Japanese food market.
It's vital to explain the problem in detail and stress the practical benefits of its solution. In the first example, the practical implications are recommendations to improve healthcare provision.
In the second example, the impact of your research is to inform the decision-making of businesses wanting to enter the Japanese food market.
This kind of rationale is more common in applied/practical research.
3. You're the best person to conduct this study
It's a bonus if you can show that you're uniquely positioned to deliver this study, especially if you're writing a funding proposal .
For an anthropologist wanting to explore gender norms in Ethiopia, this could be that they speak Amharic (Ethiopia's official language) and have already lived in the country for a few years (ethnographic experience).
Or if you want to conduct an interdisciplinary research project, consider partnering up with collaborators whose expertise complements your own. Scientists from different fields might bring different skills and a fresh perspective or have access to the latest tech and equipment. Teaming up with reputable collaborators justifies the need for a study by increasing its credibility and likely impact.
When is the research rationale written?
You can write your research rationale before, or after, conducting the study.
In the first case, when you might have a new research idea, and you're applying for funding to implement it.
Or you're preparing a call for papers for a journal special issue or a conference. Here , for instance, the authors seek to collect studies on the impact of apathy on age-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
In the second case, you have completed the study and are writing a research paper for publication. Looking back, you explain why you did the study in question and how it worked out.
Although the research rationale is part of the introduction, it's best to write it at the end. Stand back from your study and look at it in the big picture. At this point, it's easier to convince your reader why your study was both necessary and important.
How long should a research rationale be?
The length of the research rationale is not fixed. Ideally, this will be determined by the guidelines (of your journal, sponsor etc.).
The prestigious journal Nature , for instance, calls for articles to be no more than 6 or 8 pages, depending on the content. The introduction should be around 200 words, and, as mentioned, two to three sentences serve as a brief account of the background and rationale of the study, and come at the end of the introduction.
If you're not provided guidelines, consider these factors:
- Research document : In a thesis or book-length study, the research rationale will be longer than in a journal article. For example, the background and rationale of this book exploring the collective memory of World War I cover more than ten pages.
- Research question : Research into a new sub-field may call for a longer or more detailed justification than a study that plugs a gap in literature.
Which verb tenses to use in the research rationale?
It's best to use the present tense. Though in a research proposal, the research rationale is likely written in the future tense, as you're describing the intended or expected outcomes of the research project (the gaps it will fill, the problems it will solve).
Example of a research rationale
Research question : What are the teachers' perceptions of how a sense of European identity is developed and what underlies such perceptions?

Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3(2), 77-101.
Burhan, A.M., Yang, J., & Inagawa, T. (2021). Impact of apathy on aging and age-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Research Topic. Frontiers in Psychiatry
Cataldo, I., Lepri, B., Neoh, M. J. Y., & Esposito, G. (2021). Social media usage and development of psychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence: A review. Frontiers in Psychiatry , 11.
CiCe Jean Monnet Network (2017). Guidelines for citizenship education in school: Identities and European citizenship children's identity and citizenship in Europe.
Cohen, l, Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2018). Research methods in education . Eighth edition. London: Routledge.
de Prat, R. C. (2013). Euroscepticism, Europhobia and Eurocriticism: The radical parties of the right and left “vis-à-vis” the European Union P.I.E-Peter Lang S.A., Éditions Scientifiques Internationales.
European Commission. (2017). Eurydice Brief: Citizenship education at school in Europe.
Polyakova, A., & Fligstein, N. (2016). Is European integration causing Europe to become more nationalist? Evidence from the 2007–9 financial crisis. Journal of European Public Policy , 23(1), 60-83.
Winter, J. (2014). Sites of Memory, Sites of Mourning: The Great War in European Cultural History . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.

Rationale for the Study
It is important for you to be able to explain the importance of the research you are conducting by providing valid arguments. Rationale for the study, also referred to as justification for the study, is reason why you have conducted your study in the first place. This part in your paper needs to explain uniqueness and importance of your research. Rationale for the study needs to be specific and ideally, it should relate to the following points:
1. The research needs to contribute to the elimination of a gap in the literature. Elimination of gap in the present literature is one of the compulsory requirements for your study. In other words, you don’t need to ‘re-invent the wheel’ and your research aims and objectives need to focus on new topics. For example, you can choose to conduct an empirical study to assess the implications of COVID-19 pandemic on the numbers of tourists visitors in your city. This might be previously undressed topic, taking into account that COVID-19 pandemic is a relatively recent phenomenon.
Alternatively, if you cannot find a new topic to research, you can attempt to offer fresh perspectives on existing management, business or economic issues. For example, while thousands of studies have been previously conducted to study various aspects of leadership, this topic as far from being exhausted as a research area. Specifically, new studies can be conducted in the area of leadership to analyze the impacts of new communication mediums such as TikTok, and other social networking sites on leadership practices.
You can also discuss the shortcomings of previous works devoted to your research area. Shortcomings in previous studies can be divided into three groups:
a) Methodological limitations . Methodology employed in previous study may be flawed in terms of research design, research approach or sampling.
b) Contextual limitations . Relevance of previous works may be non-existent for the present because external factors have changed.
c) Conceptual limitations . Previous studies may be unjustifiably bound up to a particular model or an ideology.
While discussing the shortcomings of previous studies you should explain how you are going to correct them. This principle is true to almost all areas in business studies i.e. gaps or shortcomings in the literature can be found in relation to almost all areas of business and economics.
2. The research can be conducted to solve a specific problem. It helps if you can explain why you are the right person and in the right position to solve the problem. You have to explain the essence of the problem in a detailed manner and highlight practical benefits associated with the solution of the problem. Suppose, your dissertation topic is “a study into advantages and disadvantages of various entry strategies into Chinese market”. In this case, you can say that practical implications of your research relates to assisting businesses aiming to enter Chinese market to do more informed decision making.
Alternatively, if your research is devoted to the analysis of impacts of CSR programs and initiatives on brand image, practical contributions of your study would relate to contributing to the level of effectiveness of CSR programs of businesses.
Additional examples of studies that can assist to address specific practical problems may include the following:
- A study into the reasons of high employee turnover at Hanson Brick
- A critical analysis of employee motivation problems at Esporta, Finchley Road, London
- A research into effective succession planning at Microsoft
- A study into major differences between private and public primary education in the USA and implications of these differences on the quality of education
However, it is important to note that it is not an obligatory for a dissertation to be associated with the solution of a specific problem. Dissertations can be purely theory-based as well. Examples of such studies include the following:
- Born or bred: revising The Great Man theory of leadership in the 21 st century
- A critical analysis of the relevance of McClelland’s Achievement theory to the US information technology industry
- Neoliberalism as a major reason behind the emergence of the global financial and economic crisis of 2007-2009
- Analysis of Lewin’s Model of Change and its relevance to pharmaceutical sector of France
3. Your study has to contribute to the level of professional development of the researcher . That is you. You have to explain in a detailed manner in what ways your research contributes to the achievement of your long-term career aspirations.
For example, you have selected a research topic of “ A critical analysis of the relevance of McClelland’s Achievement theory in the US information technology industry ”. You may state that you associate your career aspirations with becoming an IT executive in the US, and accordingly, in-depth knowledge of employee motivation in this industry is going to contribute your chances of success in your chosen career path.
Therefore, you are in a better position if you have already identified your career objectives, so that during the research process you can get detailed knowledge about various aspects of your chosen industry.

My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.
John Dudovskiy

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
How do you Write the Rationale for Research?
- By DiscoverPhDs
- October 21, 2020

What is the Rationale of Research?
The term rationale of research means the reason for performing the research study in question. In writing your rational you should able to convey why there was a need for your study to be carried out. It’s an important part of your research paper that should explain how your research was novel and explain why it was significant; this helps the reader understand why your research question needed to be addressed in your research paper, term paper or other research report.
The rationale for research is also sometimes referred to as the justification for the study. When writing your rational, first begin by introducing and explaining what other researchers have published on within your research field.
Having explained the work of previous literature and prior research, include discussion about where the gaps in knowledge are in your field. Use these to define potential research questions that need answering and explain the importance of addressing these unanswered questions.
The rationale conveys to the reader of your publication exactly why your research topic was needed and why it was significant . Having defined your research rationale, you would then go on to define your hypothesis and your research objectives.
Final Comments
Defining the rationale research, is a key part of the research process and academic writing in any research project. You use this in your research paper to firstly explain the research problem within your dissertation topic. This gives you the research justification you need to define your research question and what the expected outcomes may be.

A science investigatory project is a science-based research project or study that is performed by school children in a classroom, exhibition or science fair.

This post explains the difference between the journal paper status of In Review and Under Review.

The Thurstone Scale is used to quantify the attitudes of people being surveyed, using a format of ‘agree-disagree’ statements.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

Thinking about applying to a PhD? Then don’t miss out on these 4 tips on how to best prepare your application.

The term monotonic relationship is a statistical definition that is used to describe the link between two variables.

Dr Roberts gained her PhD from Duke University in 2014 in the field of biomedical engineering. She now runs her own business named Personal Finance for PhDs.

Dr Norman gained his PhD in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology from the University of East Anglia in 2018. He is now the Public Engagement Officer at the Babraham Institute.
Join Thousands of Students
How to Write a Rationale for Your Research Paper
Learn how to write a compelling research rationale. Discover key elements, steps, and tips to justify your study and strengthen your academic paper.
Jun 25, 2024

A research rationale is a crucial component of any academic paper, serving as a concise explanation of why your research project is necessary and valuable.
It justifies the importance of your study and outlines its potential contributions to the field, effectively bridging the gap between your research question and the existing body of knowledge.
In academic writing , the rationale plays a vital role by providing context for your research and helping readers understand its relevance and significance. It demonstrates that you've identified a meaningful gap or problem in the current literature, justifying the time, effort, and resources required for your study.
A well-crafted rationale helps convince readers - whether they're supervisors, peers, or funding bodies - of the merit of your research. In other words, writing the rationale for research is essential. In other words, writing the rationale for research is essential.
Moreover, it sets the stage for your methodology and expected outcomes, strengthening the overall structure and coherence of your research paper.
By clearly articulating the purpose and value of your study, a strong rationale for a research paper lays the foundation for a compelling and impactful research article.
Purpose of a Rationale
The purpose of a research rationale is to justify your study and explain its contributions to your research proposal.
Essentially, the rationale for a research paper should clarify these points. Justifying the need involves answering "Why does this study matter?" Highlight the problem's significance and why current knowledge is insufficient, emphasizing this in your rationale for a research paper.
Point out gaps, contradictions, or new developments in existing research in your rationale for research.
Explaining contributions demonstrates your work's value and the impact of your research in your dissertation.
This may include new methods, challenging theories, providing evidence, or exploring overlooked aspects of your research topic. A clear rationale shows your research is the reason it is necessary and valuable to the field.
It convinces readers that your work advances collective knowledge in meaningful ways by highlighting the impact of your research.
Elements of an Effective Rationale
An effective research rationale has three key elements: clear justification, relevance to the research topic, and supporting evidence.
- Clear problem statement: Identify the specific issue or gap your research addresses. State the problem concisely and explain why it matters, emphasizing the rationale of your research .
- Relevance to existing literature: Show how your work fits into current knowledge. Highlight connections to previous studies and explain what's missing or needs further exploration, particularly when writing the rationale for the research.
- Potential impact of the research: Describe the expected outcomes and their significance. Explain how your findings could advance theory, improve practice, or benefit society, providing a strong justification for your research. This is crucial when conducting research.
Steps to write a rationale:
Identify the research problem:.
- Pinpoint the specific issue or question your study addresses in the rationale of your research.
- Ensure it's clear, focused, and significant to your specific research field.
Review relevant literature:
- Examine current research related to your topic.
- Identify gaps, contradictions, or areas needing further study in the rationale of the study.
Articulate the significance of your study:
- Explain why your research matters, stating the rationale of your research.
- Highlight potential contributions to theory or practice.
Explain your unique approach or perspective:
- Describe how your method or viewpoint differs from previous research when writing a research article.
- Show how your approach adds value to the field in your research topic proposal and conducting the study.
Tips for Crafting a Compelling Rationale:
Be concise and focused:.
- Use clear, direct language.
- Stick to essential information.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or repetition.
Use evidence to support your claims:
- Cite relevant studies or statistics in your dissertation .
- Provide concrete examples when possible.
- Show how evidence links to your arguments within the context of conducting research.
Address potential counterarguments:
- Anticipate possible objections to your research while writing the rationale for the research.
- Acknowledge the limitations of your approach in your thesis.
- Explain why your study is still valuable despite these challenges.
Conclusion
A well-written rationale for a research paper is crucial for a strong research paper, justifying your study's need, explaining its contribution, and setting the stage for your work. Remember to clearly state your research problem, show relevance to existing literature, and highlight potential impact. Be concise and focused, use evidence to support claims, and address counterarguments.
Avoid common pitfalls like vagueness, disconnection from prior research, and overstatement. A solid rationale strengthens your paper by providing context for your study, demonstrating its significance and originality, and convincing readers of its value and necessity. Writing the rationale for research is key in this process. Ultimately, a compelling rationale lays the foundation for a persuasive and impactful research paper, enhancing its credibility and relevance in your field of study as part of your research proposal.
Easily pronounces technical words in any field
Thesis Writing
Research Methodology
Research Rationale
Recent articles
9 Free AI Tools for Research
Derek Pankaew
Jun 26, 2024
Academic research
Research papers
AI-powered research
Free AI tools

5 Best Reading Programs for Dyslexia: A Parent's Guide
Glice Martineau
Orton-Gillingham

How to Choose and Develop a Research Topic: Ideas and Examples
Kate Windsor
Thesis Development
Literature Review
Academic Writing
Research Idea Generation
Research Topic Selection

Quick Guide to Getting a College Financial Aid
Jun 27, 2024
Student Loans
College Funding
Financial Aid
- [email protected]
Rationale for Research: Writing Tips & Examples
The rationale for research justifies the need for a study and its potential contributions. It highlights gaps in existing knowledge and aims to fill those gaps. A well-crafted rationale increases the chances of publication success and funding approval. The rationale typically follows a logical sequence from literature review to research objectives. Its length varies based on the type of research document, ranging from a few sentences to several pages .

📘 Guidelines for Writing the Rationale for Research
📏 length.
- Scope : The length of the rationale can vary depending on the overall length of the research proposal or paper .
- Detail : Typically, the rationale should be concise and focused, ranging from a few sentences to a page or two(typically 4-10 sentences ).
- Purpose : Aim to provide enough detail to justify the importance and relevance of the study without being overly lengthy or repetitive.
📍 Position
- Placement : The rationale is usually positioned early in the research proposal or paper, often following the introduction or background section.
- Sequence : It should come after the research question or hypothesis has been clearly stated, as the rationale aims to justify why the research question is important and worth investigating.
- Integration : In some cases, the rationale may be integrated into the introduction or background section, rather than being a separate section.
🔗 Transition Words
- Function : Transition words help to connect ideas and create a logical flow in the rationale.
- Contrast/Gaps : “However,” “Despite,” “While,” “Although”
- Logical Connection : “Therefore,” “Thus,” “Consequently,” “As a result”
- Addition of Points : “Moreover,” “Furthermore,” “In addition”
- Purposeful Action : “To address this gap,” “To fill this need,” “To bridge this gap”
📝 Example of a Well-Drafted Rationale
- “Despite the growing prevalence of obesity among children, current interventions have shown limited long-term effectiveness. [Transition: However,] recent studies suggest that family-based interventions targeting both diet and physical activity may be more promising. [Transition: Therefore,] the proposed study aims to investigate the effectiveness of a novel family-based intervention program for treating childhood obesity, which combines nutrition education, physical activity promotion, and parent-child bonding activities. [Transition: Moreover,] the study will assess the long-term maintenance of weight loss and lifestyle changes, which has been a major challenge in previous interventions. [Transition: To address this gap,] the findings of this study could inform the development of more effective and sustainable interventions for childhood obesity, ultimately improving the health and well-being of children and their families.”
In this example, the rationale is concise (one paragraph), positioned after the background information on childhood obesity, and uses transition words ( however, therefore, moreover, to address this gap ) to create a logical flow and connection between ideas.
Rationale for Research Practices: Good vs. Bad
| 🎯 “While previous studies have investigated the effects of social media on adolescent mental health, few have examined the specific role of Instagram use in this relationship.” | ❓ “Social media is a popular topic, and many studies have been conducted on it. This study will investigate social media use among adolescents.” | |
| 🌟 “Understanding the impact of Instagram use on adolescent mental health is crucial, as it can inform the development of interventions and guidelines for healthy social media use among this vulnerable population.” | ⭕ “This study will investigate the relationship between Instagram use and adolescent mental health.” | |
| 🔍 “A mixed-methods approach, combining a large-scale survey with in-depth interviews, will provide a comprehensive understanding of both the prevalence and the lived experiences of Instagram use and mental health among adolescents.” | 🧐 “This study will use a survey to collect data from adolescents.” | |
| 💡 “The findings of this study may have important implications for parents, educators, and mental health professionals in terms of promoting healthy social media habits and identifying adolescents at risk for mental health problems.” | ➡️ “This study will contribute to the existing literature on social media and adolescent mental health.” | |
| ✅ “The proposed study is feasible, as the researchers have established partnerships with local schools and have experience conducting research with adolescent populations. The study timeline and budget are realistic and aligned with the research objectives.” | ❌ “This study will recruit a large sample of adolescents from across the country and conduct extensive assessments over a five-year period.” | |
| 🌍 “The proposed study aligns with the national priorities for adolescent mental health research and the growing concern about the impact of social media on youth well-being. The findings will contribute to the development of evidence-based guidelines for healthy social media use.” | 🔗 “This study will investigate the relationship between Instagram use and adolescent mental health, which is an interesting topic.” | |
| 📝 “The proposed study aims to investigate the relationship between Instagram use and adolescent mental health, using a mixed-methods approach to provide a comprehensive understanding of this important issue.” | 🌀 “The proposed study aims to elucidate the multifaceted relationship between the utilization of the Instagram platform and the psychological well-being of adolescent populations, employing a mixed-methods approach to provide a comprehensive understanding of this important issue.” |
Rationale for Research-Good Research Practices Across Disciplines
| 🧬 Despite advancements in cancer treatment, pancreatic cancer remains one of the deadliest cancers with poor prognosis. This study aims to investigate the potential of a novel immunotherapy approach targeting specific genetic mutations found in pancreatic cancer cells, which could lead to the development of more effective and targeted treatments for this aggressive cancer. | |
| 📚 While previous studies have examined the representation of women in Victorian literature, few have focused on the portrayal of women in the works of lesser-known female authors of the period. This study aims to analyze the works of three understudied Victorian female writers to provide a more comprehensive understanding of women’s experiences and perspectives during this time, contributing to the ongoing discourse on gender and literature. | |
| 🔧 Current surgical techniques for repairing rotator cuff tears have limitations, including high re-tear rates and prolonged recovery times. This study proposes to evaluate the effectiveness of a novel surgical technique using a biodegradable scaffold to enhance tendon healing and improve patient outcomes. The findings could lead to the development of a more reliable and efficient surgical approach for treating rotator cuff injuries. | |
| 🦷 Dental anxiety is a common problem that can lead to avoidance of dental care and poor oral health outcomes. While previous studies have investigated the effectiveness of various interventions for reducing dental anxiety, few have focused on the use of virtual reality (VR) technology. This study aims to assess the feasibility and efficacy of a VR-based relaxation technique for reducing dental anxiety in patients undergoing dental procedures, which could provide a non-invasive and accessible tool for improving patient experiences and outcomes. | |
| 🔋 The development of high-performance, eco-friendly battery materials is crucial for meeting the growing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions. This study proposes to investigate the synthesis and characterization of a novel cathode material based on abundant and non-toxic elements, which could lead to the development of safer, more affordable, and longer-lasting batteries for various applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles. |
Let’s go deeper into writing a good research rationale. You’ll learn the structure, important parts, and ways to make a strong point. This guide helps both seasoned researchers and beginners. You’ll learn to make your research matter and interest your readers with its significance .
What is a Rationale for Research?
knowledge gap the study wants to fill and its possible contribution to literature .
Overview of the Research Rationale
A solid research rationale starts with careful literature review analysis. This step identifies areas where the knowledge base is incomplete. It makes sure the new research does something novel. 1 The rationale sums up key points from previous studies. It talks about what we’re still not sure about or which results are mixed. It shows how the new study will add to what’s already known.
Significance and Novelty of Research
The research rationale underlines the study’s significance and novelty . It should explain the practical and theoretical benefits the study offers. 2 Take, for example, Cataldo et al.’s (2021) research on social media and teens. This study might discuss its real-world impacts and its input to theories about teen and tech use. 2
Rationales can also show a study’s practical benefits .Like, Burhan et al. (2021) could explain how their study on apathy aids with new elderly care interventions .
When is the Rationale for Research Written?
The rationale for research is key at different times in research. It’s crucial early on or after a study ends. At each point, it has a specific role.
Before the Research: Research Proposal
Before starting a research project, the rationale for research is vital. It’s a big part of the research proposal . Here, the rationale lays out the study’s plan, goals, and significance .
After the Research: Research Paper or Dissertation
After the study is over, the rationale for research goes in the final research paper or dissertation . It explains why the research focused on certain aims and how the results fit the bigger picture.
It doesn’t matter if it’s early or late, the rationale for research is crucial. It shows why the study matters, making readers see its worth for the field.
Basis for Writing the Research Rationale
Creating a strong research rationale starts with a detailed literature review . This means deeply looking into past studies. It helps you spot where there’s not enough information in the current knowledge about your topic.By carefully checking what’s already known, a literature review ensures your study will add something new. It won’t just repeat what others have done before. 1
Literature Review
A thorough literature review is key to solid research reasoning. It lets you pull together the main points from studies that have gone before. This way, you really understand what is known about your study area. 1 This stop you from covering old ground but also shows what needs more looking into. This sets up your research to bring a fresh perspective. 3
Identifying Gaps in Knowledge
Finding where there is still knowledge to be found is one big goal of the literature review . These gaps might be due to different or unclear findings, study restrictions, or lack of research for certain groups. 1 By recognizing these knowledge gaps , your study becomes important. It tries to answer key questions and push the field forward. 3
Avoiding Duplication
Another goal is to make sure you’re not just repeating what’s already known. The literature review is crucial in this. It shows you what’s been done already and lets you check your approach to be unique. 1 This step helps avoid doing work that’s already been covered. It opens the door for new ideas, building on existing knowledge.
Length of the Research Rationale
The length of the research rationale in a research proposal or article is typically a few sentences 1 . But for a thesis or dissertation , it could be a couple of paragraphs.
How long the research rationale length is can change. It depends on the field or how new and unusual the idea is 1 . A very new idea might need more explaining than something continuing existing research 2 .
The prestigious journal Nature specifies that articles should ideally be no more than 6 to 8 pages long, with the introduction being around 200 words including a brief account of the background and rationale of the study.
In some cases like a thesis or a lengthy book study, the research rationale can be quite long. It might even be more than ten pages, depending on the details.
| Type of Publication | Typical Length of Research Rationale |
|---|---|
| Journal Article | A few sentences |
| Thesis/Dissertation | A couple of paragraphs |
| Novel/Unconventional Research | More detailed justification |
The length of the research rationale is often set by the journal or sponsor’s rules 2 .
Basic Elements of the Research Rationale
A well-crafted research rationale sets the stage for a successful study. It justifies the investigation with solid reasons. This reason should show the importance and originality of the work you want to do.
Literature Review Conclusions
It’s critical to summarize what’s already known in your field. This summary helps put your study in context. It also helps you see what needs to be researched further, known as research gaps and knowledge gaps .
Knowledge Gaps
Looking at past studies should show where we need more information. These areas without enough data give a good reason to continue researching. By finding and talking about these knowledge gaps , you can make sure your study brings something new.
Controversial or Inconclusive Findings
Sometimes, past research doesn’t give clear answers. It might even have different or uncertain results. In these cases, your study could help by clarifying or solving these issues.
Building on Previous Research
Your research should aim to add to what we already know. It can be about any new questions, updating old ideas, or using new technology for more insights. This approach shows the value in your work.
By combining these essential elements, your research’s foundation becomes strong. It makes a clear case for the study’s unique contribution and importance .
Example of a Research Rationale
Abc xyz is a new microalgae species found in fish tanks. It’s getting attention for lots of carotenoids and a special carotenoid profile . Although Abc xyz algae have worried fish farmers, some studies show they could help aquaculture .

In this genus, only a few microalgal species have been studied for carotenoid content . So far, they haven’t found great sources of these healthy compounds. 4 Studying Abc xyz’s carotenoid profile will help us find new and useful carotenoids. They could be a great natural source for aquaculture . 4
Every research rationale should mention previous findings, gaps in knowledge, and new research questions. This is to update what we know and make it better.
A research rationale can be over ten pages in a thesis . It depends on the topic’s depth. 2 Dissertations might have even longer explanations, maybe a few paragraphs.
- Preliminary data from a literature review helps make the study’s reasons clear. It also stops us from repeating things we already know.
- Research that brings together different fields can be very powerful. It makes the work more trustworthy and important.
- Working with well-known partners makes our studies more reliable. It also helps show why our research is needed.
Importance of Describing the Research Rationale
Explaining why you are doing research is key. It shows the big picture and new ideas of your project. When you tell people why you’re studying something, it makes them see how important and needed your work is. It’s important to share your research’s purpose clearly.
Why you are researching something is really important, especially in a research proposal . But, keep it short, a few sentences are enough. However, for a thesis or dissertation , you might get to talk more about it. You could use a couple of paragraphs to explain in more detail.
To build a strong research rationale , start with a deep look at the literature. Studying what’s already out there helps you find where new studies are needed. This way, your research can truly add something new and not just repeat what others have done.
A solid research rationale should talk about key findings from the literature, points not yet looked into, and areas where old studies don’t agree. It should also explain why more research in this area is needed.
Showing the need for your research makes it more important and valuable. By clearly explaining why your work is needed, you increase its chance of getting recognized by researchers.
Writing a Clear and Concise Rationale
To explain your research’s purpose and what it means, crafting a clear and short rationale is key. The problem-solution-rationale model is a good way to do this. First, point out the problem or issue. Then, suggest a solution. Finally, show why that solution is the right one.
Problem-Solution-Rationale Model
The model makes your ideas clear and logical. Start by clearly stating the problem or gap in knowledge. Then, talk about your solution. This could be a new approach or method. At the end, explain why your choice is the best to solve the problem.
Language for Signaling Rationale
Using certain phrases can show your rationale clearly. Phrases like “in order to,” “for the following reasons,” and “the reason this was done” work well. They make your argument stronger and easier to follow.
A good rationale for research is brief but persuasive. It highlights why your work matters. Using the problem-solution-rationale model and clear language can make your rationale effective. This is important for starting off your research on the right foot. 3
Justifying the Rationale
Showing a strong rationale justification is vital for your research to make an impact. It proves why your study matters and what it can offer the world. By explaining your study’s purpose clearly, you can highlight its big role in advancing what we know.
Showing Importance and Significance
To make your research’s rationale stand out, talk about its importance using phrases like “This was important because…” This shows how your study led to important results or met specific needs, making your work more valuable.
Say something like, “This was significant because it explored a topic not studied enough, which is key for moving our understanding forward. Or, “The importance was in challenging common beliefs, giving a new view on the issue we looked into.”

Linking your reasons to real results or filling knowledge gaps strengthens your work’s significance . It shows your study matters and adds real value to your field.
A well-explained rationale not just makes your research more trusted. It also opens doors for more discoveries, pushing knowledge forward.
A strong and clear rationale can help you gain support, be noticed, and create real impact in your area of study and even outside of it.
Tips for Effective Rationale Writing
Writing a good research rationale is key for academics. It helps you talk about your study’s rationale writing tips . You can show why your work matters and how it helps the field. Make sure you explain the “why” of your study clearly. This way, your rationale will catch your audience’s interest.
Getting help from academic writing pros is smart. They offer focused advice and tips on how to show your rationale well. This makes your writing more effective.
Every research rationale should include an overview of conclusions from a literature review , gaps in current knowledge, inconclusive or controversial findings from previous studies, and the need to build on previous research.
When writing your rationale, these rationale writing tips are important to remember:
- Clearly state the gaps in current knowledge that your study will fill.
- Show why your study’s results are crucial and how they can make a difference.
- Talk about how your research adds to what was already known in the field.
- Be clear and convincing to make your study’s importance clear to readers.
The rationale part should be easy to understand and to the point. It should explain the problem, your solution, and why your research matters. Using resources like guides for writing rationales can make your writing stronger.
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Literature Review | Talk about the main points from your review to set the stage for your research. |
| Show what’s missing in the research so far that your study will tackle. | |
| Mention any unclear or disputed results your research can help clarify. | |
| Explain how your work continues or improves on what has been done before. |
Use these rationale writing tips and get advice from those with experience. This way, you can create a strong rationale. It will clearly show why your study is important.
Use services of www.editverse.com to write effective Rationale
Editverse.com offers top-notch academic editing services . They help researchers and scholars globally. 5 Their experts work on the rationale section of your papers, making sure it’s clear, coherent, and persuasive.
Making a strong rationale is tough, whether you’re new or experienced. Editverse.com has professional editing just for this. They help you show why your research is important in a clear and impactful way.
Editverse.com’s expert editors will closely look at your rationale. They make sure it: Clearly identifies gaps in existing knowledge Highlights the potential contributions of your study Persuasively justifies the need for your research
Using Editverse.com’s rationale editing makes your research rationale stand out. It boosts the quality of your work, ensuring it grabs your readers’ attention.
| Editing Services | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Rationale Review | Ensuring clarity, coherence, and persuasiveness |
| Formatting Assistance | Adhering to journal guidelines and academic conventions |
| Language Polishing | Enhancing the flow and precision of your writing |
Editverse.com’s know-how helps you craft a rationale that shines. It clearly shows your research’s worth and importance.
The rationale for research is key in showing why a study is important. It explains the research’s goal, finds knowledge gaps , and shows its potential. This makes the study stand out for its innovation and value. 1
A strong, well-thought rationale can make your work more likely to be published. It needs to address what’s already known, any debates, and what’s next. By doing this, your research gains more credibility and impact.
No matter if it’s for a proposal, article, or thesis, a powerful rationale is vital. It sets the groundwork for your work’s significance and context. Spending time on this part can greatly enhance your work’s success and recognition in the academic world.
What is the rationale for research?
When is the research rationale written, what is the basis for writing the research rationale, how long should the research rationale be, what are the basic elements of the research rationale, why is it important to describe the research rationale, how can i write a clear and concise rationale, how can i justify the rationale, what are some tips for effective rationale writing, can professional editing services help with writing the research rationale, source links.
- https://www.editverse.com/write-clinical-case-report-step-by-step-guide/
- https://www.editverse.com/consort-guidelines-simplified-for-trial-reporting/
- ← How Do I Do a Review of Related Literature | Guides
- How to Write a Rebuttal Letter After Paper Rejection – Examples and Tips →
Privacy Overview

Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Knowledge and curiosity lays the foundation of scientific progress. The quest for knowledge has always been a timeless endeavor. Scholars seek reasons to explain the phenomena they observe, paving way for development of research. Every investigation should offer clarity and a well-defined rationale in research is a cornerstone upon which the entire study can be built.
Research rationale is the heartbeat of every academic pursuit as it guides the researchers to unlock the untouched areas of their field. Additionally, it illuminates the gaps in the existing knowledge, and identifies the potential contributions that the study aims to make.
Table of Contents
What Is Research Rationale and When Is It Written
Research rationale is the “why” behind every academic research. It not only frames the study but also outlines its objectives , questions, and expected outcomes. Additionally, it helps to identify the potential limitations of the study . It serves as a lighthouse for researchers that guides through data collection and analysis, ensuring their efforts remain focused and purposeful. Typically, a rationale is written at the beginning of the research proposal or research paper . It is an essential component of the introduction section and provides the foundation for the entire study. Furthermore, it provides a clear understanding of the purpose and significance of the research to the readers before delving into the specific details of the study. In some cases, the rationale is written before the methodology, data analysis, and other sections. Also, it serves as the justification for the research, and how it contributes to the field. Defining a research rationale can help a researcher in following ways:
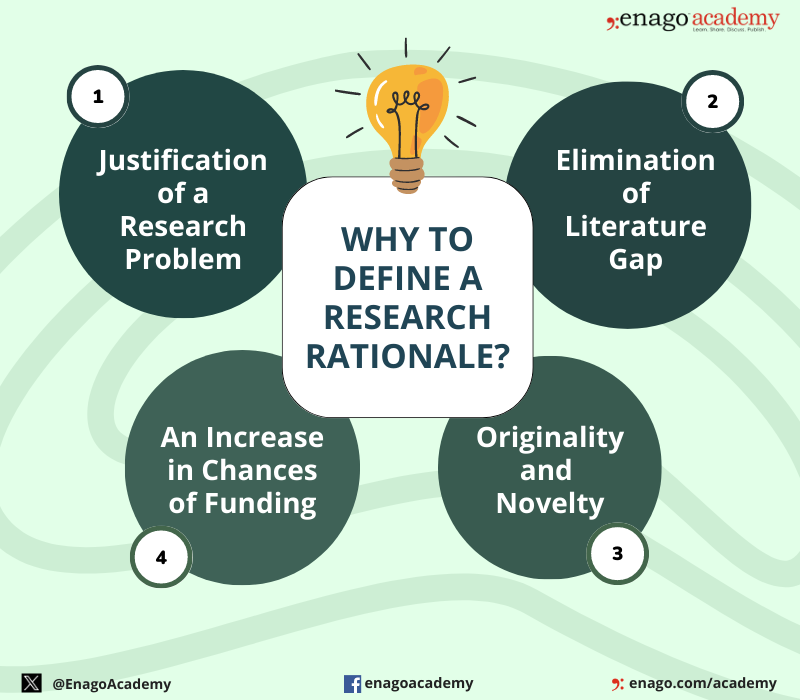
1. Justification of a Research Problem
- Research rationale helps to understand the essence of a research problem.
- It designs the right approach to solve a problem. This aspect is particularly important for applied research, where the outcomes can have real-world relevance and impact.
- Also, it explains why the study is worth conducting and why resources should be allocated to pursue it.
- Additionally, it guides a researcher to highlight the benefits and implications of a strategy.
2. Elimination of Literature Gap
- Research rationale helps to ideate new topics which are less addressed.
- Additionally, it offers fresh perspectives on existing research and discusses the shortcomings in previous studies.
- It shows that your study aims to contribute to filling these gaps and advancing the field’s understanding.
3. Originality and Novelty
- The rationale highlights the unique aspects of your research and how it differs from previous studies.
- Furthermore, it explains why your research adds something new to the field and how it expands upon existing knowledge.
- It highlights how your findings might contribute to a better understanding of a particular issue or problem and potentially lead to positive changes.
- Besides these benefits, it provides a personal motivation to the researchers. In some cases, researchers might have personal experiences or interests that drive their desire to investigate a particular topic.
4. An Increase in Chances of Funding
- It is essential to convince funding agencies , supervisors, or reviewers, that a research is worth pursuing.
- Therefore, a good rationale can get your research approved for funding and increases your chances of getting published in journals; as it addresses the potential knowledge gap in existing research.
Overall, research rationale is essential for providing a clear and convincing argument for the value and importance of your research study, setting the stage for the rest of the research proposal or manuscript. Furthermore, it helps establish the context for your work and enables others to understand the purpose and potential impact of your research.
5 Key Elements of a Research Rationale
Research rationale must include certain components which make it more impactful. Here are the key elements of a research rationale:

By incorporating these elements, you provide a strong and convincing case for the legitimacy of your research, which is essential for gaining support and approval from academic institutions, funding agencies, or other stakeholders.
How to Write a Rationale in Research
Writing a rationale requires careful consideration of the reasons for conducting the study. It is usually written in the present tense.
Here are some steps to guide you through the process of writing a research rationale:
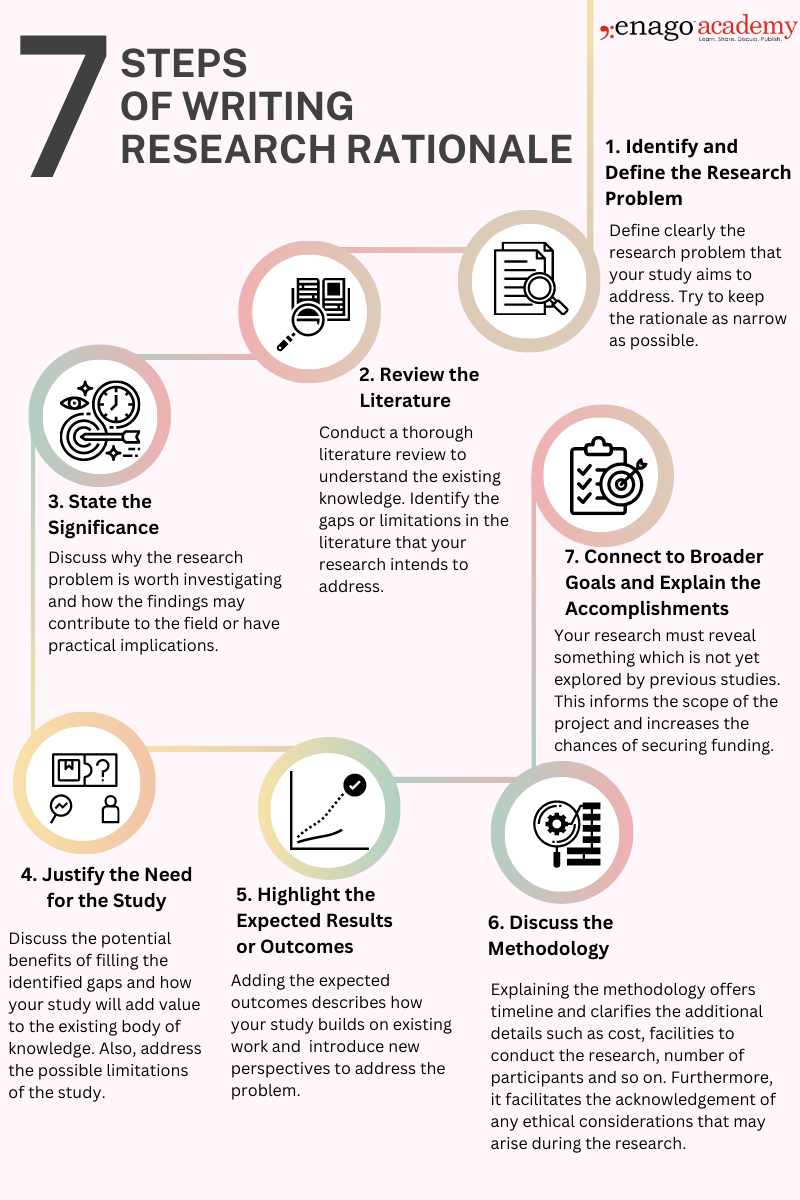
After writing the initial draft, it is essential to review and revise the research rationale to ensure that it effectively communicates the purpose of your research. The research rationale should be persuasive and compelling, convincing readers that your study is worthwhile and deserves their attention.
How Long Should a Research Rationale be?
Although there is no pre-defined length for a rationale in research, its length may vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project. It also depends on the academic institution or organization, and the guidelines set by the research advisor or funding agency. In general, a research rationale is usually a concise and focused document.
Typically, it ranges from a few paragraphs to a few pages, but it is usually recommended to keep it as crisp as possible while ensuring all the essential elements are adequately covered. The length of a research rationale can be roughly as follows:
1. For Research Proposal:
A. Around 1 to 3 pages
B. Ensure clear and comprehensive explanation of the research question, its significance, literature review , and methodological approach.
2. Thesis or Dissertation:
A. Around 3 to 5 pages
B. Ensure an extensive coverage of the literature review, theoretical framework, and research objectives to provide a robust justification for the study.
3. Journal Article:
A. Usually concise. Ranges from few paragraphs to one page
B. The research rationale is typically included as part of the introduction section
However, remember that the quality and content of the research rationale are more important than its length. The reasons for conducting the research should be well-structured, clear, and persuasive when presented. Always adhere to the specific institution or publication guidelines.
Example of a Research Rationale

In conclusion, the research rationale serves as the cornerstone of a well-designed and successful research project. It ensures that research efforts are focused, meaningful, and ethically sound. Additionally, it provides a comprehensive and logical justification for embarking on a specific investigation. Therefore, by identifying research gaps, defining clear objectives, emphasizing significance, explaining the chosen methodology, addressing ethical considerations, and recognizing potential limitations, researchers can lay the groundwork for impactful and valuable contributions to the scientific community.
So, are you ready to delve deeper into the world of research and hone your academic writing skills? Explore Enago Academy ‘s comprehensive resources and courses to elevate your research and make a lasting impact in your field. Also, share your thoughts and experiences in the form of an article or a thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Platform .
Join us on a journey of scholarly excellence today!
Frequently Asked Questions
A rationale of the study can be written by including the following points: 1. Background of the Research/ Study 2. Identifying the Knowledge Gap 3. An Overview of the Goals and Objectives of the Study 4. Methodology and its Significance 5. Relevance of the Research
Start writing a research rationale by defining the research problem and discussing the literature gap associated with it.
A research rationale can be ended by discussing the expected results and summarizing the need of the study.
A rationale for thesis can be made by covering the following points: 1. Extensive coverage of the existing literature 2. Explaining the knowledge gap 3. Provide the framework and objectives of the study 4. Provide a robust justification for the study/ research 5. Highlight the potential of the research and the expected outcomes
A rationale for dissertation can be made by covering the following points: 1. Highlight the existing reference 2. Bridge the gap and establish the context of your research 3. Describe the problem and the objectives 4. Give an overview of the methodology
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![sample of rationale of the study in research What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What would be most effective in reducing research misconduct?
- Translation
How to write the Rationale for your research
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 19 November, 2021
The rationale for one’s research is the justification for undertaking a given study. It states the reason(s) why a researcher chooses to focus on the topic in question, including what the significance is and what gaps the research intends to fill. In short, it is an explanation that rationalises the need for the study. The rationale is typically followed by a hypothesis/ research question (s) and the study objectives.
When is the rationale for research written?
The rationale of a study can be presented both before and after the research is conducted.
- Before : The rationale is a crucial part of your research proposal , representing the plan of your work as formulated before you execute your study.
- After : Once the study is completed, the rationale is presented in a research paper or dissertation to explain why you focused on the particular question. In this instance, you would link the rationale of your research project to the study aims and outcomes.
Basis for writing the research rationale
The study rationale is predominantly based on preliminary data . A literature review will help you identify gaps in the current knowledge base and also ensure that you avoid duplicating what has already been done. You can then formulate the justification for your study from the existing literature on the subject and the perceived outcomes of the proposed study.
Length of the research rationale
In a research proposal or research article, the rationale would not take up more than a few sentences . A thesis or dissertation would allow for a longer description, which could even run into a couple of paragraphs . The length might even depend on the field of study or nature of the experiment. For instance, a completely novel or unconventional approach might warrant a longer and more detailed justification.
Basic elements of the research rationale
Every research rationale should include some mention or discussion of the following:
- An overview of your conclusions from your literature review
- Gaps in current knowledge
- Inconclusive or controversial findings from previous studies
- The need to build on previous research (e.g. unanswered questions, the need to update concepts in light of new findings and/or new technical advancements).
Example of a research rationale
Note: This uses a fictional study.
Abc xyz is a newly identified microalgal species isolated from fish tanks. While Abc xyz algal blooms have been seen as a threat to pisciculture, some studies have hinted at their unusually high carotenoid content and unique carotenoid profile. Carotenoid profiling has been carried out only in a handful of microalgal species from this genus, and the search for microalgae rich in bioactive carotenoids has not yielded promising candidates so far. This in-depth examination of the carotenoid profile of Abc xyz will help identify and quantify novel and potentially useful carotenoids from an untapped aquaculture resource .
In conclusion
It is important to describe the rationale of your research in order to put the significance and novelty of your specific research project into perspective. Once you have successfully articulated the reason(s) for your research, you will have convinced readers of the importance of your work!
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services , a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.

How to Write a Rationale: A Guide for Research and Beyond
Ever found yourself scratching your head, wondering how to justify your choice of a research topic or project? You’re not alone! Writing a rationale, which essentially means explaining the ‘why’ behind your decisions, is crucial to any research process. It’s like the secret sauce that adds flavour to your research recipe. So, the only thing you need to know is how to write a rationale.

What is a Rationale?
A rationale in research is essentially the foundation of your study. It serves as the justification for undertaking a particular research project. At its core, the rationale explains why the research was conducted or needs to be conducted, thus addressing a specific knowledge gap or research question.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements involved in crafting a rationale:
Linking Background to Research Question:
The rationale should connect the background of the study to your specific research question. It involves presenting and discussing existing data on your topic, identifying gaps or issues in the current understanding, and explaining why addressing them is important.
Objectives and Significance:
Your rationale should clearly outline your research objectives – what you hope to discover or achieve through the study. It should also emphasize the subject’s significance in your field and explain why more or better research is needed.
Methodological Approach:
The rationale should briefly describe your proposed research method , whether qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (experimental), and justify this choice.
Justifying the Need for Research:
The rationale isn’t just about what you’re doing and why it’s necessary. It can involve highlighting methodological, contextual, or conceptual limitations in previous studies and explaining how your research aims to overcome these limitations. Essentially, you’re making a case for why your research fills a crucial gap in existing knowledge.
Presenting Before and After Research:
Interestingly, the rationale can be presented before and after the research. Before the research, it forms a central part of the research proposal, setting out the plan for the work. After the research, it’s presented in a research article or dissertation to explain the focus on a specific research question and link it to the study’s aims and outcomes.
Elements to Include:
A good rationale should include a summary of conclusions from your literature review, identify what is currently unknown, discuss inconclusive or contested results from previous studies, and emphasize the necessity to improve or build on previous research.
Creating a rationale is a vital part of the research process, as it not only sets the stage for your study but also convinces readers of the value and necessity of your work.

How to Write a Rationale:
Writing a rationale for your research is crucial in conducting and presenting your study. It involves explaining why your research is necessary and important. Here’s a guide to help you craft a compelling rationale:
Identify the Problem or Knowledge Gap:
Begin by clearly stating the issue or gap in knowledge that your research aims to address. Explain why this problem is important and merits investigation. It is the foundation of your rationale and sets the stage for the need for your research.
Review the Literature:
Conduct a thorough review of existing literature on your topic. It helps you understand what research has already been done and what gaps or open questions exist. Your rationale should build on this background by highlighting these gaps and emphasizing the importance of addressing them.
Define Your Research Questions/Hypotheses:
Based on your understanding of the problem and literature review, clearly state the research questions or hypotheses that your study aims to explore. These should logically stem from the identified gaps or issues.
Explain Your Research Approach:
Describe the methods you will use for your research, including data collection and analysis techniques. Justify why these methods are appropriate for addressing your research questions or hypotheses.
Discuss the Potential Impact of Your Research: Explain the significance of your study. Consider both theoretical contributions and practical implications. For instance, how does your research advance existing knowledge? Does it have real-world applications? Is it relevant to a specific field or community?
Consider Ethical Considerations:
If your research involves human or animal subjects, discuss the ethical aspects and how you plan to conduct your study responsibly.
Contextualise Your Study:
Justify the relevance of your research by explaining how it fits into the broader context. Connect your study to current trends, societal needs, or academic discussions.
Support with Evidence:
Provide evidence or examples that underscore the need for your research. It could include citing relevant studies, statistics, or scenarios that illustrate the problem or gap your research addresses.
Methodological, Contextual, and Conceptual Limitations:
Address any limitations of previous research and how your study aims to overcome them. It can include methodological flaws in previous studies, changes in external factors that make past research less relevant, or the need to study a phenomenon within a new conceptual framework.
Placement in Your Paper:
Typically, the rationale is written toward the end of the introduction section of your paper, providing a logical lead-in to your research questions and methodology.
By following these steps and considering your audience’s perspective, you can write a strong and compelling rationale that clearly communicates the significance and necessity of your research project.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What makes a good research rationale.
A good rationale clearly identifies a gap in existing knowledge, builds on previous research, and outlines why your study is necessary and significant.
How detailed should my literature review be in the rationale?
Your literature review should be comprehensive enough to highlight the gaps your research aims to fill, but it should not overshadow the rationale itself.
Conclusion:
A well-crafted rationale is your ticket to making your research stand out. It’s about bridging gaps, challenging norms, and paving the way for new discoveries. So go ahead, make your rationale the cornerstone of your research narrative!
Award-Winning Results
Team of 11+ experts, 10,000+ page #1 rankings on google, dedicated to smbs, $175,000,000 in reported client revenue.
Up until working with Casey, we had only had poor to mediocre experiences outsourcing work to agencies. Casey & the team at CJ&CO are the exception to the rule.
Communication was beyond great, his understanding of our vision was phenomenal, and instead of needing babysitting like the other agencies we worked with, he was not only completely dependable but also gave us sound suggestions on how to get better results, at the risk of us not needing him for the initial job we requested (absolute gem).
This has truly been the first time we worked with someone outside of our business that quickly grasped our vision, and that I could completely forget about and would still deliver above expectations.
I honestly can't wait to work in many more projects together!

Related Articles
View All Post

Conversion Rate Optimization , Copywriting , Customer Experience
How to Tap Into What Your Customers Love & Hate
Casey Jones

Advertising , Copywriting
What does a Copywriter do at an Ad Agency: Things You Should Know if You’re a Copywriter

Copywriting
How to Write a Marketing Script: Take Your Marketing to the Next Level in 2023
*The information this blog provides is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as financial or professional advice. The information may not reflect current developments and may be changed or updated without notice. Any opinions expressed on this blog are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer or any other organization. You should not act or rely on any information contained in this blog without first seeking the advice of a professional. No representation or warranty, express or implied, is made as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this blog. The author and affiliated parties assume no liability for any errors or omissions.

- Researching
How to write a research rationale

When you are doing a research assessment piece in History, you’ll often be asked to write a rationale. This is particularly true for the source investigation assessment piece.
What is a ‘rationale’?
A rationale is a written explanation about your research task that helps your teacher understand the decisions you made before beginning your source research .
A research rationale is a statement that explains the reasons behind conducting a particular research study.
It outlines the background, context, and significance of the research and why it is important to answer the main inquiry question.
A rationale seeks to answer three questions:
- Why have you chosen this particular topic to research?
- What questions do you specifically want answered as a result of your research?
- How do you plan on finding the best sources during your research?
How to write a rationale
Based upon the three questions mentioned above, your rationale should have three distinct sections that answer each one.
Please note that you can answer all three in a single paragraph, but the examples below will show them as three separate paragraphs.
Part 1: Explain your topic choice
You should explain as clearly as possible why this particular subject interested you.
Don’t just say “it is interesting”: give specific reasons why.
The more precise you are, the better your mark will be.
Useful sentence starters for explaining topic choice:
- I was curious to discover…
- I wanted to know…
- I was confused by…
- I always wanted to know…
- I have always been fascinated by…
- I am particularly interested in…
- I was surprised to learn that … and I wanted to know more
Example explanation of topic choice:
Imperial Japan’s decision to surrender at the end of World War II seemed like a historical anomaly based upon what we learned in class about the Japanese ideologies behind bushido and the samurai. I wanted to know to what degree the atomic bombs had an influence upon the ultimate decision to surrender. I specifically want to know what the Japanese primary sources said at the time of the events to see their perspective. In particular, want to know if Emperor Hirohito left any documents that explained his decisions.
Part 2: Explain your research questions
You need to explain the steps that helped you to create your Key Inquiry Question and Sub-Questions .
Remember that these questions should constantly be refined to include specific historical terms and information that you found during your background research .
Explain to your teacher why you have included specific information in your research questions.
Useful sentence starters for explaining research questions:
- The three specific aspects that I wanted to focus upon are…
- I knew that I had to develop my understanding of…
- My background research focused upon…
Example explanation of research questions:
Since I wanted to focus my research on the Japanese primary sources, my Key Inquiry Question is primarily about the role that the atomic bombs had upon the emperor’s decision to surrender at the end of World War II. I guess that there may not be a lot of primary sources written by the emperor himself, so I have formed three separate questions to look at his decisions from different angles. My first question focuses on what Japanese primary sources said at the time, including the emperor. My second question looks at how contemporary Japanese historians interpret this event. Finally, my third question seeks to understand how western historians understand Hirohito’s motivations.
Part 3: Explain how you will find your sources
You need to explain what strategies you have to help you find great sources to answer your research questions.
In this section, you want to specifically name the databases, museums or other research resources you know you will utilise to find the best sources on your topic.
It may also be useful to specifically name important historians or primary sources that you know in advance that you’ll need to read closely to help answer your questions.
Useful sentence starters for explaining source research:
- I have chosen to use…
- One of the best sources I found was…
- The most important sources I have use are…
- To ensure I had a range of perspectives I…
- It was important to include as one of my sources…
Example explanation of source research:
I knew that finding Japanese primary sources was going to be hard, as I fear that many of them have not been translated into English. As a result, I am going to start my research by looking at what western historians say by gathering some academic articles from the JSTOR database. I hope that these historians will reference some translated Japanese primary sources and that will lead me to some great resources. After that, I know that the Tokyo Museum website has some primary source documents that may be of use to me, so look through their resources. Finally, during my background research, I stumbled across the prominent Japanese historian, Suzuki, who focuses a lot on this period, so I want to find out what his opinion is of these events. I believe that these resources should give me ample information to help answer my research questions.
Word limit advice
Answering all of these sections in a limited word count can be a challenge.
Therefore, don’t waste space on things that don’t matter, such as simply describing a historical event or person, or talking about simplistic decision-making choices (such as “I just really like wars”).
The rationale’s purpose is to explain your decision-making process. Therefore, if what you’re saying is not relevant, don’t waste space talking about it.
Example rationale
After learning about Ned Kelly in class, I was fascinated to discover that historians disagree about his motivations. What I wanted to learn about is the role that racist attitudes towards the Irish in colonial Australia had upon his life. I don’t know much about the social division between the English and Irish in Australian history, so I want to see how people who lived during these events described Ned Kelly, in order to see if racism was an important factor.
As a result, I have written my Key Inquiry Question to focus on the representation of Ned Kelly in the popular media. To help answer this, I have written my sub-questions to focus on different media types: my first question asks about how the newspapers reported on Kelly; my second is about how he is mentioned in religious sermons of the day; and my third question focuses on his representation in public posters, such as the ‘wanted’ signs for his arrest.
Since my questions are focused heavily on the primary sources, I know that I will have to start my source research on the Trove newspaper database website. This will allow me to quickly find newspaper reports about the main events in Kelly’s life. Secondly, I know that I will have trouble finding church sermons and public posters, so I will have to look for museum websites that may have these resources already, such as the Museum of Victoria and the State Library of New South Wales. I know that they often have educational resources for teachers that include primary sources. Finally, I know from my background research that Manning Clark has done a lot of research on Kelly’s life, so I hope he will mention important primary sources that can help me out, including the Jerilderie Letter.
Watch a video explanation on the History Skills YouTube channel:
Watch on YouTube
Need a digital Source Investigation template?

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
How To Make Rationale in Research: A Thorough Overview
Struggling to make the right rationale for your research? Learn how to make rationale in research to create the perfect plan for success.
Any academic or scientific discipline relies heavily on research. However, in order to do research properly, it is necessary to comprehend the rationale behind it. A research rationale is a succinct explanation of why a certain research project is required, describing the justifications for the study as well as the advantages it is expected to provide.
Writing a persuasive rationale is critical for obtaining approval for your research project and communicating the importance of your research. However, developing a convincing one can be difficult, especially for people new to research or unfamiliar with academic expectations.
After reading this thorough overview on “how to make rationale in research”, you will be better equipped to justify your research and communicate its significance to your academic community. Whether you are a student or a seasoned researcher, this article will provide valuable insights and strategies for creating a powerful research rationale.
What is a Rationale in Research?
A research rationale provides an organized strategy for the whole research and acts as the cornerstone of the research project. It contributes to the research’s rationale by stating why the study is significant, what its aims are, and what the expected findings are. In essence, it is a compelling argument for why the study should be carried out.
A well-written research rationale should be concise, precise, and persuasive. It should clarify the problem or issue that the study attempts to solve, the knowledge or understanding gap that the study seeks to fill, and the possible advantages that it may provide. Furthermore, the reasoning should demonstrate that the research is possible, ethical, and pertinent to the subject of study.
A research project that lacks a strong rationale may lack direction and may fail to address the stated problem or issue. It can also make obtaining financing or permission from institutional review boards (IRBs) or other governing bodies difficult. As a result, devoting effort to developing a compelling research rationale is critical to the success of any research.
Why is a Research Rationale Important?
For many reasons, a research rationale is crucial. For starters, it helps to explain the necessity for the research project by demonstrating why the study is required and what gaps in knowledge or understanding it attempts to fill.
Second, it includes a clear and succinct problem statement that outlines the precise research questions or objectives that the study intends to answer.
Finally, it aids in demonstrating the research’s potential influence by demonstrating how it may lead to the creation of new knowledge, practices, or policies.
To achieve this, you should focus on communicating the potential benefits of your project, while also acknowledging its limitations. This requires a thorough understanding of the research problem and a critical evaluation of the proposed methods and approaches.
It is also important to include sufficient detail about the methods you plan to use, any ethical considerations to consider, and how you will evaluate your results. This helps to demonstrate that you have a well-developed and thoughtful research plan, which is essential for securing funding or gaining approval from academic institutions.
Consider an example of a research project to demonstrate this. Assume you want to investigate the effectiveness of a new teaching style in enhancing student learning results. A compelling rationale for this study might include:
- Demonstrating the need for the study: You may explain that there is a rising concern in the educational environment about low student performance and that standard teaching approaches may not be helpful for all students.
- Providing a clear problem statement: For example, you might say that the study will look into whether the new teaching approach is effective at enhancing student learning outcomes and what factors may impact its effectiveness.
- Highlighting the research’s potential impact: You might argue that if the study shows that if the new teaching approach is effective, it will be adopted in other schools, increasing student learning results.
The research rationale in this example gives a clear and compelling explanation for the necessity to perform the study, emphasizing its relevance, problem statement, and possible impact.
A Model: Problem-Solution-Rationale
The Problem-Solution-Rationale model is a helpful framework for developing a strong research rationale, it can assist you in organizing your rationale and ensuring that it clearly conveys all information required for an effective research rationale. This model consists of three major components: identifying the problem, proposing a solution, and explaining the rationale for why the proposed solution is necessary.
Identifying the Problem
The first stage in this model is to identify the problem that the study will attempt to solve. This could entail assessing existing research on the topic, finding gaps in knowledge or understanding, or emphasizing new difficulties or issues that have occurred. A clear problem statement serves as the research’s foundation, outlining the specific research questions or objectives that the study seeks to address.
Proposing a Solution
The model’s second stage is to suggest a solution to the identified problem. This might include creating a new theoretical framework, putting a new hypothesis to the test, or suggesting a new intervention or practice. The proposed solution should be based on a thorough review of the literature and a clear understanding of the research problem.
Providing a Rationale
The model’s final stage is to present a rationale for why the suggested solution is required. This might include emphasizing the possible advantages of the suggested solution, explaining how it builds on past research, or demonstrating how it fills a knowledge or understanding gap.
Language to Signal Rationale
Effective communication is crucial when it comes to justifying the significance of your research. One of the ways you can achieve this is by using specific language that signals the rationale to your intended audience. By doing so, you can clearly convey the reasons for your study and its potential benefits to your audience. Here are a couple of such examples:
- “The goal of this research is to fill a knowledge gap on…”
- “We selected this methodology because it allows us to address the research question more effectively.”
- “Our approach is informed by the need to address the practical challenges of…”
- “This research is significant because it contributes to our understanding of…”
Using statements like these can assist to convey the rationale to your audience and stress the significance of your research.
Language for Further Justification – Showing Importance
Once you’ve indicated the rationale for your research, it’s critical to give further justification that emphasizes the relevance of your study. Here are some sentences that might be used to emphasize the significance of your research:
- “By addressing this gap in knowledge, we can gain a better understanding of…”
- “This study is significant because it contributes to the development of…”
- “The implications of this research are far-reaching, and it can inform…”
- “By examining this issue, we can shed light on the broader implications of…”
How to Make Rationale In Research
Writing a compelling rationale for a research proposal is critical to obtaining funds and support for the research you are conducting. In this section, you will learn how to make rationale in research by implementing the four crucial aspects of a rationale: background on all previous research on the issue, the study’s open questions, identification of gaps in the literature, and the importance of filling these gaps.
Background on All Previous Research:
You must clarify the existing level of knowledge of the topic to offer a clear grasp of your research proposal. This entails analyzing all past research on the subject and determining what has been done previously. It is critical to present a thorough summary of existing research, including major results, hypotheses, and methodology. This can assist in demonstrating that you have a deep awareness of the field’s present state of knowledge and how your planned study might contribute to it.
The Study’s Open Questions
The next stage is to identify the study’s open questions. This entails investigating areas where existing knowledge falls short and comprehension gaps exist. You may highlight the need for more research and explain how your research will address these gaps by identifying unanswered questions.
Literature Gaps
Once you’ve discovered the open questions, describe how your research will solve them. This requires recognizing gaps in the current literature and describing how your research will address these gaps. Make it a point to explain how the proposed research differs from prior studies and how it will add to existing knowledge in the subject.
The Importance of Filling These Gaps:
Finally, it is critical to demonstrate the importance of filling these gaps in the current literature. This includes showing the possible advantages of the research and outlining how it will help the field if it can result in new ideas or new approaches, or the impact it will have on real society implications.
Unleash the Power of Infographics with Mind the Graph
Whether you’re a seasoned scientist or just starting out in your research career, Mind the Graph is a valuable, user-friendly, and intuitive tool that can help to elevate the impact of your research by making it more engaging, accessible, and understandable to a wider audience.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Study Rationale
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 57,514 times.
A study rationale explains the reason for a study and the importance of its findings for a particular field. Commonly, you'll need to write a study rationale as part of a university course of study, although you may also need to write one as a professional researcher to apply for funding or other support. As a student, your study rationale also justifies how it fulfills the requirements for your degree program or course of study. Do research before you write your study rationale so that you can discuss the previous work your study builds on and explain its significance to your field. Thorough research is also important in the professional context because your rationale will likely become part of the contract if funding or support is approved. [1] X Research source
Describing What You Hope to Accomplish

- For example, suppose you want to study how working the night shift affects the academic performance of college students who are taking classes during the day. A narrow question would measure a specific impact based on a specific amount of hours worked.

- Justify the methodology you're using. If there's another methodology that might accomplish the same result, describe it and explain why your methodology is superior — perhaps because it's more efficient, takes less time, or uses fewer resources. For example, you might get more information out of personal interviews, but creating an online questionnaire is more cost-effective.
- Particularly if you're seeking funding or support, this section of your rationale will also include details about the cost of your study and the facilities or resources you'll need. [3] X Research source
Tip: A methodology that is more complex, difficult, or expensive requires more justification than one that is straightforward and simple.

- For example, if you're studying the effect of working the night shift on academic performance, you might hypothesize that working 4 or more nights a week lowers students' grade point averages by more than 1 point.

- Use action words, such as "quantify" or "establish," when writing your goals. For example, you might write that one goal of your study is to "quantify the degree to which working at night inhibits the academic performance of college students."
- If you are a professional researcher, your objectives may need to be more specific and concrete. The organization you submit your rationale to will have details about the requirements to apply for funding and other support. [5] X Research source
Explaining Your Study's Significance

- Going into extensive detail usually isn't necessary. Instead, highlight the findings of the most significant work in the field that addressed a similar question.
- Provide references so that your readers can examine the previous studies for themselves and compare them to your proposed study.

- Methodological limitations: Previous studies failed to measure the variables appropriately or used a research design that had problems or biases
- Contextual limitations: Previous studies aren't relevant because circumstances have changed regarding the variables measured
- Conceptual limitations: Previous studies are too tied up in a specific ideology or framework

- For example, if a previous study had been conducted to support a university's policy that full-time students were not permitted to work, you might argue that it was too tied up in that specific ideology and that this biased the results. You could then point out that your study is not intended to advance any particular policy.
Tip: If you have to defend or present your rationale to an advisor or team, try to anticipate the questions they might ask you and include the answers to as many of those questions as possible.
Including Academic Proposal Information

- As a student, you might emphasize your major and specific classes you've taken that give you particular knowledge about the subject of your study. If you've served as a research assistant on a study with a similar methodology or covering a similar research question, you might mention that as well.
- If you're a professional researcher, focus on the experience you have in a particular field as well as the studies you've done in the past. If you have done studies with a similar methodology that were important in your field, you might mention those as well.
Tip: If you don't have any particular credentials or experience that are relevant to your study, tell the readers of your rationale what drew you to this particular topic and how you became interested in it.

- For example, if you are planning to conduct the study as fulfillment of the research requirement for your degree program, you might discuss any specific guidelines for that research requirement and list how your study meets those criteria.

- In most programs, there will be specific wording for you to include in your rationale if you're submitting it for a certain number of credits. Your instructor or advisor can help make sure you've worded this appropriately.
Study Rationale Outline and Example

Expert Q&A
- This article presents an overview of how to write a study rationale. Check with your instructor or advisor for any specific requirements that apply to your particular project. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://research.com/research/how-to-write-research-methodology
- ↑ https://ris.leeds.ac.uk/applying-for-funding/developing-your-proposal/resources-and-tips/key-questions-for-researchers/
- ↑ https://www.cwauthors.com/article/how-to-write-the-rationale-for-your-research
- ↑ http://www.writingcentre.uct.ac.za/sites/default/files/image_tool/images/167/Rationale.pdf
- ↑ https://www.niaid.nih.gov/grants-contracts/write-research-plan
- ↑ https://www.esc.edu/degree-planning-academic-review/degree-program/student-degree-planning-guide/rationale-essay-writing/writing-tips/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Privacy Policy

Home » Background of The Study – Examples and Writing Guide
Background of The Study – Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Background of The Study
Definition:
Background of the study refers to the context, circumstances, and history that led to the research problem or topic being studied. It provides the reader with a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter and the significance of the study.
The background of the study usually includes a discussion of the relevant literature, the gap in knowledge or understanding, and the research questions or hypotheses to be addressed. It also highlights the importance of the research topic and its potential contributions to the field. A well-written background of the study sets the stage for the research and helps the reader to appreciate the need for the study and its potential significance.
How to Write Background of The Study
Here are some steps to help you write the background of the study:
Identify the Research Problem
Start by identifying the research problem you are trying to address. This problem should be significant and relevant to your field of study.
Provide Context
Once you have identified the research problem, provide some context. This could include the historical, social, or political context of the problem.
Review Literature
Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature on the topic. This will help you understand what has been studied and what gaps exist in the current research.
Identify Research Gap
Based on your literature review, identify the gap in knowledge or understanding that your research aims to address. This gap will be the focus of your research question or hypothesis.
State Objectives
Clearly state the objectives of your research . These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Discuss Significance
Explain the significance of your research. This could include its potential impact on theory , practice, policy, or society.
Finally, summarize the key points of the background of the study. This will help the reader understand the research problem, its context, and its significance.
How to Write Background of The Study in Proposal
The background of the study is an essential part of any proposal as it sets the stage for the research project and provides the context and justification for why the research is needed. Here are the steps to write a compelling background of the study in your proposal:
- Identify the problem: Clearly state the research problem or gap in the current knowledge that you intend to address through your research.
- Provide context: Provide a brief overview of the research area and highlight its significance in the field.
- Review literature: Summarize the relevant literature related to the research problem and provide a critical evaluation of the current state of knowledge.
- Identify gaps : Identify the gaps or limitations in the existing literature and explain how your research will contribute to filling these gaps.
- Justify the study : Explain why your research is important and what practical or theoretical contributions it can make to the field.
- Highlight objectives: Clearly state the objectives of the study and how they relate to the research problem.
- Discuss methodology: Provide an overview of the methodology you will use to collect and analyze data, and explain why it is appropriate for the research problem.
- Conclude : Summarize the key points of the background of the study and explain how they support your research proposal.
How to Write Background of The Study In Thesis
The background of the study is a critical component of a thesis as it provides context for the research problem, rationale for conducting the study, and the significance of the research. Here are some steps to help you write a strong background of the study:
- Identify the research problem : Start by identifying the research problem that your thesis is addressing. What is the issue that you are trying to solve or explore? Be specific and concise in your problem statement.
- Review the literature: Conduct a thorough review of the relevant literature on the topic. This should include scholarly articles, books, and other sources that are directly related to your research question.
- I dentify gaps in the literature: After reviewing the literature, identify any gaps in the existing research. What questions remain unanswered? What areas have not been explored? This will help you to establish the need for your research.
- Establish the significance of the research: Clearly state the significance of your research. Why is it important to address this research problem? What are the potential implications of your research? How will it contribute to the field?
- Provide an overview of the research design: Provide an overview of the research design and methodology that you will be using in your study. This should include a brief explanation of the research approach, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- State the research objectives and research questions: Clearly state the research objectives and research questions that your study aims to answer. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Summarize the chapter: Summarize the chapter by highlighting the key points and linking them back to the research problem, significance of the study, and research questions.
How to Write Background of The Study in Research Paper
Here are the steps to write the background of the study in a research paper:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the research problem that your study aims to address. This can be a particular issue, a gap in the literature, or a need for further investigation.
- Conduct a literature review: Conduct a thorough literature review to gather information on the topic, identify existing studies, and understand the current state of research. This will help you identify the gap in the literature that your study aims to fill.
- Explain the significance of the study: Explain why your study is important and why it is necessary. This can include the potential impact on the field, the importance to society, or the need to address a particular issue.
- Provide context: Provide context for the research problem by discussing the broader social, economic, or political context that the study is situated in. This can help the reader understand the relevance of the study and its potential implications.
- State the research questions and objectives: State the research questions and objectives that your study aims to address. This will help the reader understand the scope of the study and its purpose.
- Summarize the methodology : Briefly summarize the methodology you used to conduct the study, including the data collection and analysis methods. This can help the reader understand how the study was conducted and its reliability.
Examples of Background of The Study
Here are some examples of the background of the study:
Problem : The prevalence of obesity among children in the United States has reached alarming levels, with nearly one in five children classified as obese.
Significance : Obesity in childhood is associated with numerous negative health outcomes, including increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers.
Gap in knowledge : Despite efforts to address the obesity epidemic, rates continue to rise. There is a need for effective interventions that target the unique needs of children and their families.
Problem : The use of antibiotics in agriculture has contributed to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which poses a significant threat to human health.
Significance : Antibiotic-resistant infections are responsible for thousands of deaths each year and are a major public health concern.
Gap in knowledge: While there is a growing body of research on the use of antibiotics in agriculture, there is still much to be learned about the mechanisms of resistance and the most effective strategies for reducing antibiotic use.
Edxample 3:
Problem : Many low-income communities lack access to healthy food options, leading to high rates of food insecurity and diet-related diseases.
Significance : Poor nutrition is a major contributor to chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Gap in knowledge : While there have been efforts to address food insecurity, there is a need for more research on the barriers to accessing healthy food in low-income communities and effective strategies for increasing access.
Examples of Background of The Study In Research
Here are some real-life examples of how the background of the study can be written in different fields of study:
Example 1 : “There has been a significant increase in the incidence of diabetes in recent years. This has led to an increased demand for effective diabetes management strategies. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of a new diabetes management program in improving patient outcomes.”
Example 2 : “The use of social media has become increasingly prevalent in modern society. Despite its popularity, little is known about the effects of social media use on mental health. This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health in young adults.”
Example 3: “Despite significant advancements in cancer treatment, the survival rate for patients with pancreatic cancer remains low. The purpose of this study is to identify potential biomarkers that can be used to improve early detection and treatment of pancreatic cancer.”
Examples of Background of The Study in Proposal
Here are some real-time examples of the background of the study in a proposal:
Example 1 : The prevalence of mental health issues among university students has been increasing over the past decade. This study aims to investigate the causes and impacts of mental health issues on academic performance and wellbeing.
Example 2 : Climate change is a global issue that has significant implications for agriculture in developing countries. This study aims to examine the adaptive capacity of smallholder farmers to climate change and identify effective strategies to enhance their resilience.
Example 3 : The use of social media in political campaigns has become increasingly common in recent years. This study aims to analyze the effectiveness of social media campaigns in mobilizing young voters and influencing their voting behavior.
Example 4 : Employee turnover is a major challenge for organizations, especially in the service sector. This study aims to identify the key factors that influence employee turnover in the hospitality industry and explore effective strategies for reducing turnover rates.
Examples of Background of The Study in Thesis
Here are some real-time examples of the background of the study in the thesis:
Example 1 : “Women’s participation in the workforce has increased significantly over the past few decades. However, women continue to be underrepresented in leadership positions, particularly in male-dominated industries such as technology. This study aims to examine the factors that contribute to the underrepresentation of women in leadership roles in the technology industry, with a focus on organizational culture and gender bias.”
Example 2 : “Mental health is a critical component of overall health and well-being. Despite increased awareness of the importance of mental health, there are still significant gaps in access to mental health services, particularly in low-income and rural communities. This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of a community-based mental health intervention in improving mental health outcomes in underserved populations.”
Example 3: “The use of technology in education has become increasingly widespread, with many schools adopting online learning platforms and digital resources. However, there is limited research on the impact of technology on student learning outcomes and engagement. This study aims to explore the relationship between technology use and academic achievement among middle school students, as well as the factors that mediate this relationship.”
Examples of Background of The Study in Research Paper
Here are some examples of how the background of the study can be written in various fields:
Example 1: The prevalence of obesity has been on the rise globally, with the World Health Organization reporting that approximately 650 million adults were obese in 2016. Obesity is a major risk factor for several chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. In recent years, several interventions have been proposed to address this issue, including lifestyle changes, pharmacotherapy, and bariatric surgery. However, there is a lack of consensus on the most effective intervention for obesity management. This study aims to investigate the efficacy of different interventions for obesity management and identify the most effective one.
Example 2: Antibiotic resistance has become a major public health threat worldwide. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are associated with longer hospital stays, higher healthcare costs, and increased mortality. The inappropriate use of antibiotics is one of the main factors contributing to the development of antibiotic resistance. Despite numerous efforts to promote the rational use of antibiotics, studies have shown that many healthcare providers continue to prescribe antibiotics inappropriately. This study aims to explore the factors influencing healthcare providers’ prescribing behavior and identify strategies to improve antibiotic prescribing practices.
Example 3: Social media has become an integral part of modern communication, with millions of people worldwide using platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Social media has several advantages, including facilitating communication, connecting people, and disseminating information. However, social media use has also been associated with several negative outcomes, including cyberbullying, addiction, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on mental health and identify the factors that mediate this relationship.
Purpose of Background of The Study
The primary purpose of the background of the study is to help the reader understand the rationale for the research by presenting the historical, theoretical, and empirical background of the problem.
More specifically, the background of the study aims to:
- Provide a clear understanding of the research problem and its context.
- Identify the gap in knowledge that the study intends to fill.
- Establish the significance of the research problem and its potential contribution to the field.
- Highlight the key concepts, theories, and research findings related to the problem.
- Provide a rationale for the research questions or hypotheses and the research design.
- Identify the limitations and scope of the study.
When to Write Background of The Study
The background of the study should be written early on in the research process, ideally before the research design is finalized and data collection begins. This allows the researcher to clearly articulate the rationale for the study and establish a strong foundation for the research.
The background of the study typically comes after the introduction but before the literature review section. It should provide an overview of the research problem and its context, and also introduce the key concepts, theories, and research findings related to the problem.
Writing the background of the study early on in the research process also helps to identify potential gaps in knowledge and areas for further investigation, which can guide the development of the research questions or hypotheses and the research design. By establishing the significance of the research problem and its potential contribution to the field, the background of the study can also help to justify the research and secure funding or support from stakeholders.
Advantage of Background of The Study
The background of the study has several advantages, including:
- Provides context: The background of the study provides context for the research problem by highlighting the historical, theoretical, and empirical background of the problem. This allows the reader to understand the research problem in its broader context and appreciate its significance.
- Identifies gaps in knowledge: By reviewing the existing literature related to the research problem, the background of the study can identify gaps in knowledge that the study intends to fill. This helps to establish the novelty and originality of the research and its potential contribution to the field.
- Justifies the research : The background of the study helps to justify the research by demonstrating its significance and potential impact. This can be useful in securing funding or support for the research.
- Guides the research design: The background of the study can guide the development of the research questions or hypotheses and the research design by identifying key concepts, theories, and research findings related to the problem. This ensures that the research is grounded in existing knowledge and is designed to address the research problem effectively.
- Establishes credibility: By demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the field and the research problem, the background of the study can establish the researcher’s credibility and expertise, which can enhance the trustworthiness and validity of the research.
Disadvantages of Background of The Study
Some Disadvantages of Background of The Study are as follows:
- Time-consuming : Writing a comprehensive background of the study can be time-consuming, especially if the research problem is complex and multifaceted. This can delay the research process and impact the timeline for completing the study.
- Repetitive: The background of the study can sometimes be repetitive, as it often involves summarizing existing research and theories related to the research problem. This can be tedious for the reader and may make the section less engaging.
- Limitations of existing research: The background of the study can reveal the limitations of existing research related to the problem. This can create challenges for the researcher in developing research questions or hypotheses that address the gaps in knowledge identified in the background of the study.
- Bias : The researcher’s biases and perspectives can influence the content and tone of the background of the study. This can impact the reader’s perception of the research problem and may influence the validity of the research.
- Accessibility: Accessing and reviewing the literature related to the research problem can be challenging, especially if the researcher does not have access to a comprehensive database or if the literature is not available in the researcher’s language. This can limit the depth and scope of the background of the study.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Data Interpretation – Process, Methods and...

Independent Study – Skills Guide
- Formulating the Research Question
Introduction and Rationale of the Study
- Literature Review
- Research Methodology
- Research Design
- Ethical Considerations
- Data Findings
- Data Analysis
- Conclusions
Introduction and rationale of the study
This should briefly outline your area of interest and what has led you to research your chosen area. The rationale section of the dissertation describes why a particular concept, concern or problem is important within the field you are researching.
A well-constructed rationale demonstrates that you understand your chosen field of research, the competing perspectives that exist, and what you hope to gain by carrying out the research.
At undergraduate level you will be illuminating your understanding and should be aware that whilst the research you undertake can make a positive contribution to the field (on a small scale) you will not be making a new contribution to knowledge which will improve an entire profession.
A message from a former student:
"Your Independent Study research is a tremendous opportunity to pursue and discover new knowledge in the field of education. For me, producing a research project was so intellectually liberating, I was encouraged to be critical, critical , critical - and once you become an employee in any educational institution it all changes - you will never get that level of academic freedom again!"
- Introduction and rationale example 1
- Introduction and rationale example 2
- << Previous: Formulating the Research Question
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 9, 2022 9:55 AM
- URL: https://libguides.derby.ac.uk/independent
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write the Rationale for a Research Proposal
Table of Contents
Writing a research proposal can be intimidating, especially when you are expected to explain the rationale behind your project. This article will help you learn how to write the rationale for a research proposal to provide justification for why it should be pursued. A good rationale should give readers an understanding of why your project is worth undertaking and how it will contribute to existing knowledge. It should outline any practical implications that could come from your work. By thoroughly preparing this section of your proposal , you will increase the chances of having your research approved.
What Is a Rationale in Research?
A research rationale provides a detailed explanation of why a study is necessary and should be carried out. It convinces the reader or examiner of the importance of the research by outlining its relevance, significance, and potential contribution to existing knowledge. Additionally, it helps transition from the research problem to the methods used in the study, connecting both elements into one comprehensive argument. The research rationale justifies why the researcher chose to conduct this particular study over any other possible alternative studies.
Why Is a Research Rationale Important?
A well-written rationale can help demonstrate your commitment to the project. It can convince reviewers that you have put thought into developing a high-quality research plan. When composing this section, focus on the scientific merit of your proposed study by providing clear and concise reasons for conducting the research. Your goal is to communicate the potential benefits of your project and show that you understand its limitations. Include sufficient detail about the methods you plan to use, any ethical considerations to consider, and how you will evaluate your results. Explaining why your research is important and necessary is essential for getting approval from funding bodies or academic institutions. Your rationale should provide a convincing argument for why the project needs to be conducted. The rationale must make it clear that there are potential benefits that justify its costs. Consider the broader impact of your work and describe how it could contribute to furthering knowledge in the field.

The rationale for research is also known as the justification of the study. Make a mention of the following points while writing the rationale for a research proposal:
Background on All Previous Research on the Subject of Your Study
It is important to include background information on what research has already been done on the study topic. This will help to build a foundation for understanding the current knowledge, open questions, and gaps.
The Open Questions of the Study
Highlighting the open questions related to the study topic helps to identify potential areas for further exploration. It gives readers an understanding of where new research could be helpful. It is essential to state these questions to have clear objectives and goals for the research proposal.
Identify the Gaps in Literature
Identifying literature gaps helps highlight areas that have not yet been studied. This provides the opportunity to add new information and understanding to the field. By including these points in the rationale, the writer can showcase how his work will contribute to existing research.
Highlight the Significance of Addressing These Gaps
Emphasizing why it is important to address those gaps is vital in any research proposal. It allows readers to understand why this particular project needs to be undertaken. By clearly outlining why addressing these gaps is crucial, the writer can successfully argue why his proposed project should be given consideration.
A rationale for a research proposal can help convince the reader of the importance and relevance of your study. This article explains the importance of a rationale and discusses the key elements to learn how to write the rationale for a research proposal . Following these tips will let you create a powerful research rationale that will help convince others of the value of your project.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Proposal Generator Articles
Creative terms and conditions agreement in business proposal.
In business, proposals are essential for securing contracts and agreements with clients. However, a proposal is only complete with terms…
- Proposal Generator
Free guide to a statement of proposal sample
A statement of proposal is a document that outlines a proposed project or initiative in detail. It is typically used…
Free Proposal Letter for Training and Development for a Head Start
Training and development are essential to improve employees’ skills, knowledge, and productivity. A well-crafted training proposal can help an organization…
Detailed Guide to Free HR Consulting Proposal
HR consulting is an essential service for businesses of all sizes. HR consultants provide expert guidance to organizations on various…
Key Guide to Better Remote Work Proposal
The rise of remote work has been a significant trend in the business world over the last few years. With…
Guide to Free E-Commerce Proposal Template
E-commerce has become one of the most popular ways of doing business recently. With the increasing number of people using…

AI Generator
A rationale is a detailed explanation or justification for a decision, action, or belief, providing reasons and underlying principles. It helps clarify the logic and thought process behind choices made. In academic contexts, a rationale may be part of a Thesis Summary or a Case Summary , offering sentences that articulate the basis for research or case studies.
What is a Rationale?
50 rationale examples with answers.

- Education: Project-based learning promotes student engagement, critical thinking, and real-world application.
- Business: Employee training improves skills, productivity, and job satisfaction.
- Healthcare: Regular health screenings detect issues early and improve patient outcomes.
- Technology: Upgrading software enhances security, efficiency, and data management.
- Environmental Conservation: Sustainable manufacturing reduces environmental impact and conserves resources.
- Marketing: Social media campaigns increase brand visibility and engage customers.
- Urban Planning: Public transportation reduces traffic, emissions, and improves mobility.
- Legal System: Stricter penalties deter crime and maintain public safety.
- Psychology: Cognitive-behavioral therapy effectively treats anxiety by changing negative thoughts and behaviors.
- Architecture: Green building designs create energy-efficient, healthy structures.
- Social Work: Community outreach addresses social inequalities and supports marginalized groups.
- Economics: Fiscal policies boost spending, investment, and reduce unemployment during recessions.
- Food Industry: Nutritional labels help consumers make healthier choices.
- Engineering: Safety features in design protect users and comply with regulations.
- Human Resources: Flexible work arrangements improve work-life balance and job satisfaction.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism preserves heritage and supports local economies.
- Education Policy: Inclusive education ensures equal access for all students.
- Finance: Diversifying investments reduces risk and optimizes returns.
- Public Health: Smoking bans reduce secondhand smoke exposure and prevent diseases.
- Transportation: Alternative transportation like bike lanes reduces congestion and promotes active lifestyles.
- International Relations: Diplomacy resolves conflicts peacefully and promotes global stability.
- Art and Design: User-centered design creates products that meet user needs and enhance satisfaction.
- Criminal Justice: Restorative justice repairs harm and promotes offender rehabilitation.
- Education Assessment: Formative assessments provide feedback and guide instruction.
- Environmental Policy: Protected areas conserve biodiversity and offer recreational opportunities.
- Management: Participative leadership empowers employees and fosters innovation.
- Agriculture: Sustainable farming preserves soil and minimizes chemical use.
- Health Promotion: Promoting healthy lifestyles prevents chronic diseases and reduces healthcare costs.
- Technology Integration: Technology in education enhances learning and prepares students for the future.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Fundraising supports the organization’s mission and services.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediation resolves conflicts by facilitating communication and mutual agreements.
- Architecture and Urban Planning: Mixed-use developments create vibrant, walkable communities.
- Public Policy: Social welfare programs address poverty and promote social justice.
- Supply Chain Management: Just-In-Time inventory reduces costs and improves efficiency.
- Environmental Conservation: Marine protected areas safeguard biodiversity and promote sustainable fisheries.
- Occupational Health and Safety: Workplace safety protocols prevent accidents and injuries.
- International Development: Foreign aid alleviates poverty and promotes economic growth.
- Public Administration: Decentralizing services improves efficiency and responsiveness.
- Crisis Management: Emergency plans ensure effective disaster responses.
- Community Development: Community infrastructure enhances quality of life and attracts investment.
- Educational Technology: Blended learning personalizes education and engages students.
- Cultural Preservation: Documenting indigenous traditions preserves cultural heritage.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Sustainable sourcing ensures environmental and social responsibility.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Aid to refugees addresses urgent needs and upholds human dignity.
- Public Safety: Crime prevention strategies build trust and promote safer communities.
- Healthcare Policy: Expanding healthcare access improves health outcomes and reduces disparities.
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Philanthropy and sustainability enhance brand reputation and societal impact.
- Community Engagement: Involving community members promotes transparency and democratic governance.
- International Trade: Free trade agreements stimulate growth and cooperation.
- Urban Regeneration: Redevelopment projects revitalize blighted areas and stimulate investment.
Easy Rationale Examples
- Why do we use group projects in school?: To help students work together, learn from each other, and improve teamwork skills.
- Why do companies offer training programs to employees?: To improve their skills, make them more productive, and keep them happy at work.
- Why do doctors recommend regular check-ups?: To find health problems early and treat them before they get worse.
- Why do we update our computer software?: To keep it secure, make it work faster, and add new features.
- Why do we recycle?: To reduce waste, save resources, and protect the environment.
Types of Rationale
1. educational rationale.
An educational rationale explains the reasoning behind educational policies, curriculum choices, teaching methods, and learning activities. It provides justification for why certain content or instructional strategies are chosen, aiming to enhance student learning and achieve educational goals.
- Justifying the inclusion of a new subject in the curriculum.
- Explaining the use of project-based learning to develop critical thinking skills.
2. Scientific Rationale
A scientific rationale underpins research studies and experiments. It explains the reasoning behind selecting specific research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and interpretations of results. It aims to provide a logical foundation for scientific inquiry and ensure the validity and reliability of findings.
- Justifying the choice of a particular research method for a study.
- Explaining why a specific variable is being measured.
3. Business Rationale
A business rationale supports business decisions, such as launching a new product, entering a new market, or implementing organizational changes. It outlines the logical reasoning and expected benefits behind these decisions, considering factors like market demand, competition, and financial projections.
- Justifying an investment in new technology.
- Explaining the rationale for restructuring a company.
4. Policy Rationale
A policy rationale provides the reasoning behind the creation or modification of policies, laws, or regulations. It explains the intended outcomes, benefits, and potential impacts of the policy, often addressing social, economic, or environmental considerations.
- Justifying a new healthcare policy aimed at increasing accessibility.
- Explaining the rationale for environmental regulations to reduce carbon emissions.
5. Ethical Rationale
An ethical rationale justifies decisions and actions based on ethical principles and values. It considers the moral implications and ensures that the choices align with ethical standards, often involving considerations of fairness, justice, and the greater good.
- Justifying the fair treatment of employees.
- Explaining the rationale behind corporate social responsibility initiatives.
6. Strategic Rationale
A strategic rationale explains the reasoning behind long-term planning and strategic decisions within organizations. It includes the analysis of internal and external factors, goals, and the anticipated benefits of strategic initiatives.
- Justifying the expansion into international markets.
- Explaining the rationale for a merger or acquisition.
7. Design Rationale
A design rationale provides the reasoning behind design choices in various fields, including architecture, software development, and product design. It explains why certain features, materials, or processes were selected to meet specific goals, user needs, and constraints.
- Justifying the user interface design of a software application.
- Explaining the choice of materials in a sustainable building project.
Rationale Synonyms and examples
- Reason: The reason for studying every day is to achieve better grades.
- Justification: The justification for the new policy is to improve workplace safety.
- Explanation: The explanation for his absence was a family emergency.
- Basis: The basis for the decision was thorough research and analysis.
- Grounds: The grounds for the lawsuit were breach of contract.
- Purpose: The purpose of the meeting is to discuss the project timeline.
- Motive: The motive behind his actions was to help the community.
- Cause: The cause of the accident was slippery roads.
- Foundation: The foundation of the theory is extensive scientific research.
- Principle: The principle of fairness guided their decision-making process.
- Rationale: The rationale for the changes is to increase efficiency.
- Premise: The premise of the argument is that everyone deserves equal opportunities.
- Argument: The argument for renewable energy is based on its environmental benefits.
- Assertion: The assertion that exercise improves mental health is supported by research.
- Evidence: The evidence for climate change is overwhelming and clear.
Difference between Rational and Rationale
| Based on or in accordance with reason or logic. | The underlying reason or explanation for a belief, action, or proposal. | |
| Adjective | Noun | |
| Describes behavior or decisions that are logical and reasonable. | Refers to the explanation or justification for a particular decision or action. | |
| “She made a decision based on the available data.” | “The behind the new policy is to improve workplace safety.” | |
| Logical, reasonable, sensible | Explanation, justification, reasoning | |
| Often used to describe actions, thoughts, or behaviors that are influenced by clear and sound reasoning. | Used to provide the reasoning or justification behind a decision, action, or policy. | |
| Derived from the Latin word “rationalis,” meaning “of or pertaining to reason.” | Derived from the Latin word “rationalis” and “ratio,” meaning “reason.” | |
| Confusing it with “rationale,” which refers to the reasoning behind something, not the quality of being logical. | Confusing it with “rational,” which describes a logical state of mind or action, not the explanation for something. |
How do you write a rationale step by step
Writing a rationale involves explaining the reasons and purpose behind a particular decision, action, or project. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an effective rationale:
Step 1: Identify the Purpose : Begin by clearly stating the purpose of the rationale. What is the main goal or objective you aim to achieve?
Step 2: Understand Your Audience: Consider who will be reading the rationale. Tailor your language and depth of explanation to the audience’s level of knowledge and interest in the subject.
Step 3: Provide Context: Give background information to help the reader understand the context. This includes relevant historical, social, or academic context that frames the rationale.
Step 4: State the Problem or Need: Clearly define the problem or need that your project, action, or decision addresses. Use specific examples or data to illustrate the need.
Step 5: Outline Your Solution or Plan: Describe your proposed solution or plan in detail. Explain how it will address the problem or need identified.
Step 6: Justify Your Approach: Provide reasons why your approach is the best course of action. Include evidence such as research findings, expert opinions, or successful case studies to support your rationale.
Step 7: Highlight the Benefits: Explain the benefits and positive outcomes expected from your approach. Highlight how it will impact the audience or stakeholders positively.
Step 8: Address Potential Challenges: Acknowledge any potential challenges or drawbacks of your approach and discuss how you plan to address them.
How do you write a rationale?
To write a rationale, start by clearly stating the purpose or decision. Then, provide detailed reasons and evidence supporting it. Conclude by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the benefits or expected outcomes.
Where is a rationale used?
Rationales are used in various fields, including education, business, healthcare, technology, environmental conservation, and many others.
Can a rationale change over time?
Yes, a rationale can change as new information, circumstances, or insights emerge. It’s important to review and update rationales to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
How long should a rationale be?
The length of a rationale depends on the complexity of the topic and the requirements of the context.
What is the difference between a rationale and a justification?
A rationale provides the underlying reasons and logic behind a decision or action, while a justification focuses on defending or proving that the decision or action is right or necessary.
Can a rationale be used to explain past actions?
Yes, a rationale can be used to explain past actions by outlining the reasons and logic that were considered at the time of the decision.
How can a rationale help in decision-making?
A rationale helps in decision-making by providing a structured approach to evaluating options, considering the reasons and potential outcomes, and ensuring that the decision is well-thought-out and justifiable.
What role does a rationale play in academic writing?
In academic writing, a rationale is often included to justify the choice of research topic, methodology, and theoretical framework. It helps readers understand the significance and relevance of the research.
How does a rationale contribute to effective communication?
A rationale contributes to effective communication by clearly explaining the reasons behind decisions or actions.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Information Impact: Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Journal / Information Impact: Journal of Information and Knowledge Management / Vol. 15 No. 1 (2024) / Articles (function() { function async_load(){ var s = document.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript'; s.async = true; var theUrl = 'https://www.journalquality.info/journalquality/ratings/2406-www-ajol-info-iijikm'; s.src = theUrl + ( theUrl.indexOf("?") >= 0 ? "&" : "?") + 'ref=' + encodeURIComponent(window.location.href); var embedder = document.getElementById('jpps-embedder-ajol-iijikm'); embedder.parentNode.insertBefore(s, embedder); } if (window.attachEvent) window.attachEvent('onload', async_load); else window.addEventListener('load', async_load, false); })();
Article sidebar.

Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
The journal not only allows the authors to hold the copyright without restrictions, the authors also retain the full publishing right without restrictions.| ©; 2017 ISSN: 2141 - 4297 (print) ISSN: 2360 - 994X (e-version)
Main Article Content
Use of open access publications and lecturers research productivity in polytechnics in south-south nigeria, lucky o. akpojotor, okeraghogho ekuerhare.
The rationale behind this study is to find out the availability of materials that are in open access, and to see if the available open access publications enough to enhance lecturers’ productivity in polytechnics in South-South, Nigeria. In accomplishing this, three research questions and one hypothesis guided the study. A sample of 291 lecturers was propositionally drawn from the population of 1,140 lecturers in South-South, Nigeria. Frequency counts was used to analyze the respondents’ bio data and research questions 1-4, while the inferential statistics that was used for the testing of research hypothesis is Pearson Product moment correlation coefficient. From the data collected lecturers make very high use of electronic journals, library print journals, PDFs, and Wiki articles. The result of the analyzed data shows that open access resources improves lecturers’ productivity in lecturing, online publishing, offline publishing, publishing locally, publishing internationally, and publishing scholarly research papers (peer reviewed). Also, it shows that the lecturers have a very high skill in Internet surfing, word processing packages, use of electronic databases, Windows interface, search engines use, browsers use, downloading, uploading, and PDF resources. However, they lacked skill in use of Spreadsheet packages thus posing a challenge to their data analysis skills. Among other, it shows that the benefits accruing from lecturers’ productivity includes: impartation of knowledge on students, impartation of knowledge on researchers, contribution to existing knowledge, updating knowledge, increasing the academic standard of institutions, creation of new knowledge, provision of research materials, provision of research papers in open access databases, improvement of students’ reading culture, and filling gaps in knowledge. Moreover, study reveals that network problems, poor electricity supply constitute technological hindrances to lecturers’ access to open access resources. Furthermore, findings revealed that there is no significant relationship between the use of Open Access (OA) publications and lecturers’ productivity in polytechnics in SouthSouth, Nigeria. The findings further conclude that there is a significant relationship between lecturers’ levels of ICTs skills for use of open access (OA) and their productivity in polytechnics in South-South, Nigeria.
AJOL is a Non Profit Organisation that cannot function without donations. AJOL and the millions of African and international researchers who rely on our free services are deeply grateful for your contribution. AJOL is annually audited and was also independently assessed in 2019 by E&Y.
Your donation is guaranteed to directly contribute to Africans sharing their research output with a global readership.
- For annual AJOL Supporter contributions, please view our Supporters page.
Journal Identifiers


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The rationale of the study is the justification for taking on a given study. It explains the reason the study was conducted or should be conducted. This means the study rationale should explain to the reader or examiner why the study is/was necessary. It is also sometimes called the "purpose" or "justification" of a study.
The rationale for your research is the reason why you decided to conduct the study in the first place. The motivation for asking the question. The knowledge gap. This is often the most significant part of your publication. It justifies the study's purpose, novelty, and significance for science or society.
Rationale for the study, also referred to as justification for the study, is reason why you have conducted your study in the first place. This part in your paper needs to explain uniqueness and importance of your research. Rationale for the study needs to be specific and ideally, it should relate to the following points: 1. The research needs ...
The rationale for research is also sometimes referred to as the justification for the study. When writing your rational, first begin by introducing and explaining what other researchers have published on within your research field. Having explained the work of previous literature and prior research, include discussion about where the gaps in ...
A research rationale is a crucial component of any academic paper, serving as a concise explanation of why your research project is necessary and valuable.. It justifies the importance of your study and outlines its potential contributions to the field, effectively bridging the gap between your research question and the existing body of knowledge.
Overlook the feasibility of the study: "This study will recruit a large sample of adolescents from across the country and conduct extensive assessments over a five-year period. ... After the study is over, the rationale for research goes in the final research paper or dissertation. It explains why the research focused on certain aims and how ...
Research rationale helps to ideate new topics which are less addressed. Additionally, it offers fresh perspectives on existing research and discusses the shortcomings in previous studies. It shows that your study aims to contribute to filling these gaps and advancing the field's understanding. 3. Originality and Novelty.
To write your rationale, you should first write a background on what all research has been done on your study topic. Follow this with 'what is missing' or 'what are the open questions of the study'. Identify the gaps in the literature and emphasize why it is important to address those gaps. This will form the rationale of your study.
19 November, 2021. The rationale for one's research is the justification for undertaking a given study. It states the reason (s) why a researcher chooses to focus on the topic in question, including what the significance is and what gaps the research intends to fill. In short, it is an explanation that rationalises the need for the study.
A rationale in research is essentially the foundation of your study. It serves as the justification for undertaking a particular research project. At its core, the rationale explains why the research was conducted or needs to be conducted, thus addressing a specific knowledge gap or research question.
Answer: The rationale of your research offers the reason for addressing a particular problem with a spscific solution. Your research proposal needs to explain the reasons why you are conducting the study: this forms the rationale for your research, also referred to as the justification of the study. The rationale should explain what you hope to ...
Answer: The rationale for research basically outlines why you wanted to conduct research on the topic of your choice. The rationale is the justification of the study, and specifies the need to conduct research on the topic. In science, in fact, it is easier to come up with a rationale for research. You should first do a thorough literature ...
A research rationale is a statement that explains the reasons behind conducting a particular research study. It outlines the background, context, and significance of the research and why it is important to answer the main inquiry question. A rationale seeks to answer three questions:
A research rationale provides an organized strategy for the whole research and acts as the cornerstone of the research project. It contributes to the research's rationale by stating why the study is significant, what its aims are, and what the expected findings are. In essence, it is a compelling argument for why the study should be carried ...
study's rationale, problem statement, the aims, underlying assumptions, theoretical paradigm and its anticipated value of the study. Chapter Two contains methodological considerations. It details the data collection and sampling process, research tool, approach to data analysis, ethical considerations as well as the study's limitations.
3. Identify the ways your study will correct those shortcomings. Carefully explain the ways in which your study will answer the research question in a way that the previous studies failed to do so. Be persuasive to convince your readers that your study will contribute something both useful and necessary to the field.
convincing rationale for a research study' Coaching: An International Journal of Theory, Research. and Practice 5.1 1-7. Abstract. Explaining the purpos e of a research study and providing a ...
Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate; Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic. Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We've written a step-by-step ...
Directed Research (PSC 395) Independent Study (PSC 391) Senior Honors Thesis (PSC 393W) Based on our current number of majors, we anticipate that the demand will be roughly seventy students per year (i.e., 300 divided by 4). We expect the first four of these options to accommodate ... Sample Rationale ...
Here are the steps to write the background of the study in a research paper: Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the research problem that your study aims to address. This can be a particular issue, a gap in the literature, or a need for further investigation. Conduct a literature review: Conduct a thorough literature review to ...
Introduction and rationale of the study. This should briefly outline your area of interest and what has led you to research your chosen area. The rationale section of the dissertation describes why a particular concept, concern or problem is important within the field you are researching. ... "Your Independent Study research is a tremendous ...
A good rationale should give readers an understanding of why your project is worth undertaking and how it will contribute to existing knowledge. It should outline any practical implications that could come from your work. By thoroughly preparing this section of your proposal, you will increase the chances of having your research approved.
This chapter has situated the context of the research and introduced the research aims, questions and rationale for the inquiry. In Chapter 2, I present the literature review and theoretical framework, which contextualises the research. Chapter 3 outlines the methods used for the research design. In Chapter 4, I present and analyse the data ...
1 Answer to this question. The term used to imply why the study was needed in the first place is "rationale for research" or "rationale of a study." It is also sometimes referred to as the justification of the study. I have edited your question to reflect this. The rationale of a study is a very important part of the manuscript.
Examples: Justifying the choice of a particular research method for a study. Explaining why a specific variable is being measured. 3. Business Rationale. A business rationale supports business decisions, such as launching a new product, entering a new market, or implementing organizational changes.
In the context of research writing, a rationale pertains to the reasons why the study must be conducted. Such justification is provided by the researcher to highlight the significant points of the problem to be addressed in the study. HOW TO WRITE THE RATIONALE OF THE STUDY 4. Research Gap. problems, issues or questions that have not been ...
The rationale behind this study is to find out the availability of materials that are in open access, and to see if the available open access publications enough to enhance lecturers' productivity in polytechnics in South-South, Nigeria. In accomplishing this, three research questions and one hypothesis guided the study. A sample of 291 lecturers was propositionally drawn from the population ...