How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Entrepreneurial Process
Task Summary:
Lesson 3.1.1: The Entrepreneurial Process: Part 1
Lesson 3.1.2: The Entrepreneurial Process: Part 2
Lesson 3.1.3: Entrepreneurial Planning: Part 1
Lesson 3.1.4: Entrepreneurial Planning: Part 2
Lesson 3.1.5: Entrepreneurial Planning: Part 3
Activity 3.1.1: SDG Simulation
Unit 3 Assignment: Your Plan of Action
Learning Outcomes:
- Identify exciting entrepreneurial opportunities
- Evaluate exciting entrepreneurial opportunities
- Model the entrepreneurial process for the exciting entrepreneurial opportunities
- Create entrepreneurial planning documents
Successful entrepreneurship occurs when creative individuals bring together a new way of meeting needs and or wants. This is accomplished through a patterned process, one that mobilizes and directs resources to deliver a specific product or service to those in a way that is financially viable. While these could be 100% business ideas, they could also be concepts that are based in the spirit of altruism or non-profit. For innovative ideas that are strictly business concepts. sustainability can (and should) be embedded in the design of a product and operations by applying the criteria of reaching toward benign (or at least considerably safer) energy and material use, a reduced resource footprint, and elimination of inequitable social impacts due to the venture’s operations, including its supply-chain impacts.
Entrepreneurial innovation combined with sustainability principles can be broken down into the following four key elements, each of which requires analysis. Each one needs to be analyzed separately, and then the constellation of factors must fit together into a coherent whole. These four elements are as follows:
- Opportunity
- Entrepreneur/team
Successful ventures are characterized by coherence or “fit” across and throughout these steps. The interests and skills of the entrepreneur must fit with the product design and offering; the team’s qualifications should match the required knowledge needed to launch the venture. There needs to be a financially viable demand (enough people at a financially viable price) for the product or service, and of course, early adopters (those willing to purchase) have to be identified. Finally, sufficient resources, including financial resources (e.g., operating capital), office space, equipment, production facilities, components, materials, and expertise, must be identified and brought to bear. Each piece is discussed in more detail in the sections that follow.
Identify, Analyze, and Plan the Opportunity
As discussed in the last section, Opportunity Recognition is the active, cognitive process (or processes) through which individuals conclude that they have identified the potential to create something new that has the potential to generate economic value and that is not currently being exploited or developed and is viewed as desirable in the society in which it occurs (i.e. its development is consistent with existing legal and moral conditions). (Baron, 2004b, p. 52) Because opportunity recognition is a cognitive process, according to Baron (2004b), people can learn to be more effective at recognizing opportunities by changing the way they think about opportunities and how to recognize them.
The opportunity is a chance to satisfy the needs and desires of a certain group of people while generating returns that enable you to continue to operate and to build your organization over time. Many different conditions in society can create opportunities for new goods and services. As a prospective entrepreneur, the key questions are as follows:
- What is a need that is not being met?
- What are the conditions that have created an opportunity for my idea?
- Why do people want and need something new at this point in time?
- What are the factors that have opened up the opportunity?
- Will the opportunity be enduring, or is it a window that is open today but likely to close tomorrow?
- If you perceive an unmet need, can you deliver what the customer wants while generating durable margins and profits?
- How can I take on this venture while supporting the Sustainable Development Goals?
Opportunity conditions arise from a variety of sources. At a broad societal level, they are present as the result of forces such as shifting demographics, changes in knowledge and understanding due to scientific advances, a rebalancing or imbalance of political winds, or changing attitudes and norms that give rise to new needs. Certain demographic shifts and pollution challenges create SDG opportunities. When you combine enhanced public focus on health and wellness, advanced water treatment methods, clean combustion technologies, renewable “clean” energy sources, conversion of used packaging into new asset streams, benign chemical compounds for industrial processes, and local and sustainability has grown organic food, you begin to see the wide range of opportunities that exist due to macrotrends.
Identify, Analyze, and Plan the Market
What are you offering/doing/selling/contributing? New ventures offer solutions to people’s problems. This concept requires you to not only examine the item or service description but also further understand the group of people whose unmet needs you are meeting (often called market analysis). In any entrepreneurial innovation circumstance you must ask the following questions:
- What is the solution for which you want someone to pay?
- Is it a service or product, or some combination?
- To whom are you selling it? Is the buyer the actual user? Who makes the purchase decision?
- What is the customer’s problem and how does your service or product address it?
Understanding what you are selling is not as obvious as it might sound. When you sell an electric vehicle you are not just selling transportation. The buyer is buying a package of attributes that might include cutting-edge technology, lower operating costs, and perhaps the satisfaction of being part of a solution to health, environmental, and energy security problems.
Identify, Analyze, and Plan the Entrepreneur & Entrepreneurial Team
The opportunity and the entrepreneur must be intertwined in a way that optimizes the probability for success. People often become entrepreneurs when they see an opportunity. They are compelled to start something to find out whether they can convert that opportunity into an ongoing source of fulfillment and potential financial gain. That means that, ideally, the entrepreneur’s life experience, education, skills, work exposure, and network of contacts align well with the opportunity. We have covered this in previous sections, so if you need to refer back to consider the role of the entrepreneur’s skills, abilities, and cognition.
Entrepreneurs sometimes act alone, but this can only take us so far. A good entrepreneurial plan, an interesting product idea, and a promising opportunity are all positive, but in the end it is the ability of the entrepreneur to attract a team, get a product out, and provide it to customers is the thing that counts.
Typically there is an individual who initially drives the process through his or her ability to mobilize resources and sometimes through sheer force of will, hard work, and determination to succeed. In challenging times it is the entrepreneur’s vision and leadership abilities that can carry the day.
Ultimately, led by the entrepreneur, a team forms. As the organization grows, the team becomes the key factor. The entrepreneur’s skills, education, capabilities, and weaknesses must be augmented and complemented by the competencies of the team members they bring to the project. The following are important questions to ask:
- Does the team as a unit have the background, skills, and understanding of the opportunity to overcome obstacles?
- Can the team act as a collaborative unit with strong decision-making ability under fluid conditions?
- Can the team deal with conflict and disagreement as a normal and healthy aspect of working through complex decisions under ambiguity?
If an organization has been established and the team has not yet been formed, these questions will be useful to help you understand what configuration of people might compose an effective team to carry the business through its early evolutionary stages.
Identify, Analyze, and Plan the Resources
Successful entrepreneurial processes require entrepreneurs and teams to mobilize a wide array of resources quickly and efficiently. All innovative and entrepreneurial ventures combine specific resources such as capital, talent and know-how (e.g., accountants, lawyers), equipment, and production facilities. Breaking down an opportunity’s required resources into components can clarify what is needed and when it is needed. Although resource needs change during the early growth stages of an opportunity, at each stage the entrepreneur should be clear about the priority resources that enable or inhibit moving to the next stage of growth. What kinds of resources are needed? The following list provides guidance:
- Capital. What financial resources, in what form (e.g., equity, debt, family loans, angel capital, venture capital), are needed at the first stage? This requires an understanding of cash flow needs, break-even time frames, and other details. Even non-profits need to make money to stay afloat. Back-of-the-envelope estimates must be converted to pro forma income statements to understand financial needs.
- Know-how. Record keeping and accounting and legal process and advice are essential resources that must be considered at the start of every venture. Access to experts is important, especially in the early stages of making an opportunity happen. New opportunities require legal incorporation, financial record keeping, and rudimentary systems and resources to provide for these expenses need to be considered.
- Facilities, equipment, and transport. Does the venture need office space, production facilities, special equipment, or transportation? At the early stage of analysis, ownership of these resources does not need to be determined. The resource requirement, however, must be identified.
The Overall Process
The process of entrepreneurship melds these pieces together in processes that unfold over weeks and months, and eventually years if the business is successful. Breaking down the process into categories and components helps you understand the pieces and how they fit together. What we find in retrospect with successful launches is a cohesive fit among the parts. The entrepreneur’s skills and education match what the start-up needs. The opportunity can be optimally explored with the team and resources that are identified and mobilized. The resources must be brought to bear to launch the opportunity with an entry strategy that delivers the value-driven concept in a way that solves customers’ problems.
With all of these things in mind, documenting answers to the questions above, and the analysis undertaken to answer them is contained in an entrepreneurial plan. This is a document that you would use to plan out the details for the elements outlined above. Making sure you identify, analyze, and plan these elements is a great starting point, and to make sure this is all done really well, have a look at the principles below.
Entrepreneurial Plan Communication Principles
As Hindle and Mainprize (2006) note, business plan writers must strive to communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future. However, the liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new opportunities difficult (more so than for existing organizations). They outline five communications principles:
- Translation of your vision of the venture and how it will perform into a format compatible with the expectations of the readers
- you have identified and understood the key success factors and risks
- the projected market is large and you expect good market penetration
- you have a strategy for commercialization, profitability, and market domination
- you can establish and protect a proprietary and competitive position
- Anchoring key events in the plan with specific financial and quantitative values
- your major plan objectives are in the form of financial targets
- you have addressed the dual need for planning and flexibility
- you understand the hazards of neglecting linkages between certain events
- you understand the importance of quantitative values (rather than just chronological dates)
- Nothing lasts forever—things can change to impact the opportunity: tastes, preferences, technological innovation, competitive landscape
- the new combination upon which venture is built
- the magnitude of the opportunity or market size
- market growth trends
- venture’s value from the market (% of market share proposed or market share value in dollars)
- Four key aspects describing context within which new opportunity is intended to function (internal and external environment)
- how the context will help or hinder the proposal
- how the context may change and affect the organization and the range of flexibility or response that is built into the venture
- what management can or will do in the event the context turns unfavorable
- what management can do to affect the context in a positive way
- A brief and clear statement of how an idea actually becomes a business that creates value
- Who pays, how much, and how often?
- The activities the company must perform to produce its product, deliver it to its customers, and earn revenue
- And be able to defend assertions that the venture is attractive and sustainable and has a competitive edge
Entrepreneurial Plan Credibility Principles
Entrepreneurial plan writers must strive to project credibility (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006), so there must be a match between what the entrepreneurship team (resource seekers) needs and what the resource providers expect based on their criteria. A take it or leave it approach (i.e. financial forecasts set in concrete) by the entrepreneurship team has a high likelihood of failure in terms of securing resources. Hindle and Mainprize (2006) outline five principles to help entrepreneurs project credibility:
- Without the right team, nothing else matters.
- What do they know?
- Who do they know?
- How well are they known?
- sub-strategies
- ad-hoc programs
- specific tactical action plans
- Claiming an insuperable lead or a proprietary market position is naïve.
- Anticipate several moves in advance
- View the future as a movie vs. snapshot
- Key assumptions related to market size, penetration rates, and timing issues of market context outlined in the entrepreneurial plan should link directly to the financial statements.
- Income and cash flow statements must be preceded by operational statements setting forth the primary planning assumptions about market sizes, sales, productivity, and basis for the revenue estimate.
- If the main purpose is to enact a harvest, then the entrepreneurial plan must create a value-adding deal structure to attract investors.
- Common things: viability, profit potential, downside risk, likely life-cycle time, potential areas for dispute or improvement
General Entrepreneurial Plan Guidelines
Many entrepreneurs must have a plan to achieve their goals. The following are some basic guidelines for entrepreneurial plan development.
- A standard format helps the reader understand that the entrepreneur has thought everything through and that the returns justify the risk.
- Binding the document ensures that readers can easily go through it without it falling apart.
- everything is completely integrated: the written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part
- all financial statements are completely linked and valid (make sure all balance sheets validly balance)
- the document is well-formatted (layout makes the document easy to read and comprehend—including all diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions)
- everything is correct (there are NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors)
- It is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once. To avoid unnecessarily duplicating information, you should combine sections and reduce or eliminate duplication as much as possible.
- all the necessary information is included to enable readers to understand everything in your document
- For example, if your plan says something like “there is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units,” a reader is left completely confused. Does this mean there is a total shortage of 100,000 units, but competitors are filling this gap by producing 25,000 per year (in which case there will only be a shortage for four years)? Or, is there an annual shortage of 100,000 units with only 25,000 being produced each year, in which case the total shortage is very high and is growing each year? You must always provide the complete perspective by indicating the appropriate time frame, currency, size, or another measurement.
- if you use a percentage figure, you indicate to what it refers, otherwise, the figure is completely useless to a reader.
- This can be solved by indicating up-front in the document the currency in which all values will be quoted. Another option is to indicate each time which currency is being used, and sometimes you might want to indicate the value in more than one currency. Of course, you will need to assess the exchange rate risk to which you will be exposed and describe this in your document.
- If a statement is included that presents something as a fact when this fact is not generally known, always indicate the source. Unsupported statements damage credibility
- Be specific. An entrepreneurial plan is simply not of value if it uses vague references to high demand, carefully set prices, and another weak phrasing. It must show hard numbers (properly referenced, of course), actual prices, and real data acquired through proper research. This is the only way to ensure your plan is considered credible.
The purpose of this assignment is to connect all of the dots that you have been learning about and engaging with over the past unit when it comes to the entrepreneurial planning process. Watch this video on developing a process map . You are going to develop your own process map outlining the steps you need to take to develop a robust and well-thought-out entrepreneurial plan. Have a look at the Unit 4 Assignment: Entrepreneurial Plan for more information on what you’re going to be building.
The submission should be methodical and outline the process you will go through (i.e. what steps you will complete), and the information sources you will need to fill in the gaps and fill out your plan. Your submission should include a process map diagram, and be about 250 words, which is one page double spaced, or it could be done as an infographic, or a two-three minute presentation. If you are doing this as part of a formal course and have a different approach that you would like to take for developing this assignment, please check with your instructor.
Text Attributions
The content related to how it all starts and the process steps was taken from “ Sustainability, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship” by LibreTexts (2020) CC BY-NC-SA
The content related to the opportunity identification cognition and the entrepreneurial plan was taken from “ Entrepreneurship and Innovation Toolkit, 3rd Edition ” by L. Swanson (2017) CC BY-SA
Baron, R. A. (2004b). Opportunity recognition: Insights from a cognitive perspective. In J. E. Butler (Ed.), Opportunity identification and entrepreneurial behavior (pp. 47-73). Greenwich, Conn.: Information Age Pub
Hindle, K., & Mainprize, B. (2006). A systematic approach to writing and rating entrepreneurial business plans. The Journal of Private Equity, 9 (3), 7-23.
Introduction to Entrepreneurship Copyright © 2021 by Katherine Carpenter is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
A business journal from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania
Knowledge at Wharton Podcast
How entrepreneurs can create effective business plans, march 2, 2010 • 16 min listen.
When an entrepreneur has identified a potential business opportunity, the next step is developing a business plan for the new venture. What exactly should the new plan contain? How can the entrepreneur ensure it has the substance to find interest among would-be investors? In this installment of a series of podcasts for the Wharton-CERT Business Plan Competition, Wharton management professor Ian MacMillan explains that business plans must contain several crucial elements: They must articulate a market need; identify products or services to fill that need; assess the resources required to produce those products or services; address the risks involved in the venture; and estimate the potential revenues and profits.

An edited transcript of the interview appears below:
Knowledge at Wharton: Professor MacMillan, thank you for speaking with us about the necessity of entrepreneurs writing business plans. To start with a basic question, what exactly is a business plan?
Ian MacMillan: A business plan to me is a 25-page, maximum 30-page, document, which is a description, analysis and evaluation of a venture that you want to get funded by somebody. It provides critical information to the reader — usually an investor — about you, the entrepreneur, about the market that you are going to enter, about the product that you want to enter with, your strategy for entry, what the prospects are financially, and what the risks are to anybody who invests in the project.
Knowledge at Wharton: Could you explain some of these elements in a little more detail and describe how entrepreneurs can develop an effective business plan?
MacMillan: Let me start by saying that you probably want to avoid developing a detailed business plan unless you have done some initial work. Basically what happens is that by doing a little bit of work, you earn the right to do more work. The first thing I would do before you start a business plan is think about a concept statement. A concept statement is about three to five pages that you put together and share with potential customers or investors just to see if they think it’s worth the energy and effort of doing more detailed work.
The concept statement has a few pieces to it. You are going to have a description of the market need that has to be fulfilled; a description of the products or services that you think are going to fulfill that need; a description of the key resources that you think are going to be needed to provide that product or service; a specification of what resources are currently available; an articulation of what you think the risks are; and then a sort of rough and ready estimate of what you think the profits and profitability will be.
The idea is to put together this concept document and begin to share it around with people who are going to have to support your venture if you take it forward. This allows you to rethink as a result of feedback that you get. You might get word back from the various stakeholders — like potential customers or distributors — that this really wasn’t such a good idea after all. That saves you the energy and effort of putting together a big business plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Assuming the concept statement works out and you want to move towards the business plan, what else would you need? And where can you find the information? Some information can be hard to locate, especially about your competitors.
MacMillan: It’s really important to go out and speak to your potential customers. You need to find the people who you think will buy your product and talk to them about what dissatisfies them with their current offerings. You should get a sense from them about who is providing the alternative at the moment. Remember, the world has gone for maybe 100,000 years without your idea — and people are getting by; they’re not dying. Something out there is servicing their need. So what is the closest competitive alternative to what you want to offer?
That is what you need to find out — and that involves talking and listening. And for all the enthusiasm you have for your venture or your idea, you really need to listen to people who are eventually going to write a check for it.
Before you go on to write a business plan, you have to do some more work. If the concept statement looks good, then the next step is to do a 15- to 20-page feasibility analysis. This means we are now going to take this idea to the next level. We’ve learned from potential customers and distributors. We’ve learned who the major competitors are. We’ve shaped the idea more clearly, and now we’re digging deeper.
The next challenge you face is to say, well, if you start this business, what evidence do you have that the market actually wants it? Who do you think would write a check for your product? You need to articulate what makes your product or your service feasible. What has to be done in order to make this thing real? You need a description of how you intend to enter the market, a description of who the major competitors are, a preliminary plan — a very rough plan — which specifies what you think your revenues and profits are going to be, and an estimate of what you think the required investment will be. And only then, once you have articulated that, and once again shared it with your stakeholder community, will you perhaps be able to go and write a business plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Once you have done your feasibility analysis and assuming you get the go ahead from your stakeholders, what is the next step?
MacMillan: The idea of the business plan is to convince the stakeholders. First, what we need to do in a business plan is show that we understand the needs — the unmet needs — of potential customers. Second, we need to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the current most competitive offering out there. Third, we need to understand the skills and capabilities that you and your team have as entrepreneurs. Next we need to understand what the investors need to get out of their investment, because they have to put their money in and they need to have some kind of sense of what they are going to get in terms of returns. In addition, the investment needs to be competitive with alternative investments that the investors might make.
The most important idea in the business plan is to articulate and satisfy the different perspectives of various stakeholders. This process sets in motion some basic requirements in the business plan — to tee up right from the start — evidence that the customer will accept it. Probably a third of the ventures out there that fail are because some person came up with the right product that they thought the world would love and then found out that the customers couldn’t care less. What you want to try to do in a business plan is convince the reader that there are customers out there who will in fact buy the product — not because it’s a great product, but because they want it and they are willing to pay for it.
Moreover, you need to convince the reader that you have some kind of proprietary position that you can defend. You also need to convince your readers that you have an experienced and motivated management team and that you have the experience and the management capabilities to pull it off. You need to convince potential investors that they are going to get a better return than they could get elsewhere, so you need to estimate the net present value of this venture. You need to show that the risk they are taking will be accompanied by appropriate returns for that risk. If we look at the contents of a typical business plan, you need to be able to articulate all these issues in some 25 to 30 pages. People get tired if they have to read too much.
Now let’s look at the various components of the business plan document:
First, you need an executive summary that grabs the attention of the potential investor. This should be done in no more than two pages. The executive summary is meant to convince the potential investor to read further and say, “Wow! This is why I should read more about this business plan.”
Next, you need a market analysis. What is the market? How fast is it growing? How big is it? Who are the major players? In addition, you need a strategy section. It should address questions such as, “How are you going to get into this market? And how are you going to win in that marketplace against current competition?”
After that, you need a marketing plan. How are we going to segment the market? Which parts of the market are we going to attack? How are we going to get the attention of that market and attract it to our product or service?
You also need an operations plan that answers the question, “How are we going to make it happen?” And you need an organization plan, which shows who the people are who will take part in the venture.
You need to list the key events that will take place as the plan unfolds. What are the major things that are going to happen? If your plan happens to be about a physical product, are you going to have a prototype or a model? If it happens to be a software product, are you going to have a piece of software developed — a prototypical piece of software? What are the key milestones by which investors can judge what progress you are making in the investment? Remember that you will not get all your money up front. You will get your funds allocated contingent on your ability to achieve key milestones. So you may as well indicate what those milestones are.
You should also include a hard-nosed assessment of the key risks. For example, what are the market risks? What are the product risks? What are the financial risks? What are the competitive risks? To the extent that you are upfront and honest about it, you will convince your potential investors that you have done your homework. You need to also be able to indicate how you will mitigate these risks — because if you can’t mitigate them, investors are not going to put money into your venture.
After that, what you get down to is a financial plan where you basically do a five-year forecast of what you think the finances are going to be — maybe with quarterly data or projections for the first two years and annual for the next three years.
You need a pro forma profit and loss statement. You need a pro forma balance sheet if you have assets in the balance sheet. You need to have a pro forma cash flow. Your cash flow is important, because it is the cash flow that kills. You may have great profits on your books but you may run out of money — so you need a pro forma cash flow statement. And you need a financing plan that explains, as the project unfolds, what tranches of financing you will need and how will you go about raising that money.
Finally you need a financial evaluation that tells investors, if you make this investment, what is its value going to be to you as an investor. That is basically the structure of the plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Let’s say you have written a business plan and presented it to your investors. How closely do you have to be tied to the plan? Does it mean that once you are executing against the plan, you should reject new opportunities you find because they are not part of your plan? Or should you build in some flexibility that allows you to explore emerging opportunities?
MacMillan: Is this an opportunity for me to speak about discovery-driven planning?
Knowledge at Wharton: Of course.
MacMillan: Okay. The thing about most entrepreneurial ventures is that your outcome is uncertain — because what you are doing is very new. It is very, very hard to predict what the actual outcome is going to be. One of the most fundamental flaws is that in the face of unfolding uncertainty, you single-mindedly and bloody-mindedly pursue the original objective.
The reality is that the true opportunity will emerge over time. What venture capitalists do is they will put a small amount of money into the project, allow the entrepreneur to enter that market space and then — contingent on performance and contingent on what apparent traction you can get in that market space — completely re-plan to find out what the true opportunity really is. It is insanity to insist that people actually meet their plan as it was originally written.
This doesn’t mean you compromise your objectives. The idea is that I want to keep on trying to meet my objectives, but how I meet them must change as the plan unfolds. That’s basically what led to all the work that Wharton has done in the last few years on discovery driven planning. It’s a way of thinking about planning that says, “I’m going to make small investments. If I’m wrong early, I can fail fast, fail cheap and move on. But as I find out what the true opportunity is, I can aggressively invest in what this opportunity is.”
Knowledge at Wharton: Could you give an example of a company that has used this discovery-driven planning process to take its business to the next level?
MacMillan: One company that has done the most in this area is Air Products. What they have been able to do is use discovery-driven planning to unfold completely different businesses from the ones that they were in. Air Products makes things like carbon dioxide and oxygen and nitrogen. It is a very old-line company. Using discovery-driven planning, they have been able to move aggressively into, for instance, the service sector. Once they recognized that they were able to deliver reliably and predictably in the face of uncertain demand, they developed a set of skills that allowed them to enter the service business where the return on investment and return on assets are far higher than putting a huge plant in place.
Knowledge at Wharton: Professor MacMillan, thanks so much.
More From Knowledge at Wharton

How Financial Frictions Hinder Innovation

How Early Adopters of Gen AI Are Gaining Efficiencies

How Is AI Affecting Innovation Management?
Looking for more insights.
Sign up to stay informed about our latest article releases.

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
Writing a Solid Business Plan: Fundamentals and Principles
I’ve worked as a business plan writer since 2006, and it’s been a remarkably fun and fulfilling career for me. I get to see entrepreneurs of all sorts, from all over the world, live out their dreams.
When I’m out and about meeting people in the real world, I don’t dread the question, “What do you do for a living,” like some people do, because I love talking about what I do for a living.
But what I am quite used to is the blank stare that I tend to get, and the follow-up question, “What does that mean?” Other people nod their heads knowingly, especially if they have some experience with business or finance, but once they ask subsequent questions I realize they’re thinking of something completely different. So, I thought it might be helpful to talk about the top questions the Masterplans team gets about business plan writing and what happens when you hire a business plan writer.
What even is a business plan?
The most basic possible question, and what people really mean when they ask me what my job title really means. I love to answer this question, except when I’m trying to explain it to relatives in Greece, or my Spanish-speaking friends! My second- and third-language skills are not strong enough to begin to explain what a business plan is. But, when I try to explain it to them, I break it down into the simplest terms, so maybe that’s the best place to start here. I do this with a series of questions and statements that go like this:
- Have you ever thought about starting your own business? (Inevitably, the answer is yes)
- Well, when you want to start your own business, you will probably need to apply for a loan, or ask an investor for funding. (People nod at this one… I’ve still got their comprehension).
- When you do that, you need to present a document that tells all about the business you’re starting. I write that document.
And bingo, we have a basic level of understanding of what I do. But of course, it’s so much more complicated than that . A traditional business plan is made up of a complete outline of topics and sub-topics that any entrepreneur needs to be able to answer. It’s not always about funding either, even though that’s how I present it to friends. The truth is that every entrepreneur needs a business plan, even if they’re bootstrapping the project out of their own pocket.
In actuality, a business plan is a comprehensive document that explains the details about your business, sets goals and objectives, and guides you going forward. That said, if you are pursuing funding like most entrepreneurs, your document needs to cover a range of required topics.
Let’s take a look at the SBA requirements for the sections that need to be in a business plan:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Organization and Management
- Service or Product line
- Marketing and Sales
- Funding request
- Financial projections
- Appendix (optional)
However, this is an overly broad listing, which doesn’t include many of the sub-sections that are involved. For example, at Masterplans, our Market Analysis covers a variety of sub-sections like Market Segmentation, Market Need, Industry Analysis, Competitive Comparison, and Competitive Edge.
Part of being a good business plan writer means understanding what goes within each section and keeping the content organized into the appropriate area. Some customers have a hard time keeping straight the difference between the "Competitive Comparison" and the "Competitive Edge" sections, but they are quite distinct. Or, it can be tempting to talk about who your customers are in the "Market Analysis" instead of the "Market Segmentation." I’ve even had people mix up marketing tactics with products or services. It takes an experienced hand to keep the content organized.
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan’s highest purpose is to guide entrepreneurs in operating their business on the day-to-day level. It is a foundational document that I think of as the constitution of your business. It tells you everything you need to know about your idea, your goals, your strategy, and the financial picture of a business.
Here at Masterplans, we strongly believe that entrepreneurs need to understand that a business plan is not a one-time use product, like applying for a business loan. Instead, we want our clients to use their business plan all the time, for years into the future, as long as the business exists. It should guide board meetings and management decisions. Your employees should read it so that they understand what your mission is, what steps you need to take to achieve success, and what their role is within your company.
But we admit that there are those one-time, single-serving uses for a business plan that will likely come up for you. You need it to apply for a bank loan. You need it to ask for investment. You need it when applying for a lease on a location. You often need it when applying for certain permits, especially those dealing with compliance issues. And for those of you who are foreign investors seeking a visa , you need it to include in your application packet to USCIS.
Thus, a comprehensive business plan needs to be able to not just guide you in your daily decision-making, but it also needs to answer all the questions that an outside party might ask you when deciding whether to fund your idea or let you lease their space.
Who should write a business plan?
Why, the entrepreneurial team should take the helm in writing a business plan, of course. Did you expect a different answer from a professional business plan writer? At Masterplans, we don’t shy away from delivering honest truth to our clients, because we thrive when they thrive.
The truth is that an entrepreneur who isn’t intimately involved in the writing of their business plan from the start will never fully understand it, and that can hamper them on their path to achieving their goals. It’s imperative that an entrepreneur have a deep understanding of their business plan, or else they won’t be able to follow it!
But, writing a business plan is an intense endeavor that requires a better-than-average command of English writing and style, as well as business theory and financial modeling. Very few people represent the total package, which is why at Masterplans, we work in teams of specialists who together have those skills.
I can write a beautiful market analysis summary, analyze your competitive landscape in-depth, and wrap it all up with an attention-grabbing executive summary, but don’t ask me to explain a complex financial concept like Internal Rate of Return. (I’m being modest; I can tell you all about it, but I’ll leave that to our brilliant financial modelers who understand it in more depth than I do.)
While some entrepreneurs may somehow possess the bare minimum of skills that are required to create a decent business plan, they most certainly don’t have the time. Starting a business involves numerous steps, and entrepreneurs are often pursuing each of those steps while juggling a full-time career and sometimes a family. It’s a lot.
But a key quality shared by the best leaders is knowing when and what to delegate. If you have a dual major in English and Business, and you’ve done this a few times before, then sure, you could probably write a stellar business plan from scratch.
But if you have virtually any other combination of experience, you could benefit greatly from delegating it to a company like ours that can counsel you every step of the way, scheduling out the project into meetings and discrete tasks so that you can be as involved as you should be in the process while still freeing up your time to handle the many other to-dos on your plate. (This benefit still holds true for the dual major, as well!)
Remember, the most important thing is that the business plan actually gets done so that you can use it to start your business, but like any long writing project, it can fall to the wayside when life’s pressures get in the way. Working with a deadline-driven consultancy like ours can help you reach the finish line.
Now that you have a basic introduction to the traditional business plan document, you probably have plenty of questions that go deeper. We’ve done our best to address those with our frequently asked questions about writing business plans .

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
When Should Entrepreneurs Write Their Business Plans?
- Francis J. Greene
- Christian Hopp

Don’t write a plan before you understand your customer.
It pays to plan. Entrepreneurs who write business plans are more likely to succeed, according to research. But while this might tempt some entrepreneurs to make writing a plan their very first task, a subsequent study shows that writing a plan first is a really bad idea. It is much better to wait, not to devote too much time to writing the plan, and, crucially, to synchronize the plan with other key startup activities.
It pays to plan. Entrepreneurs who write business plans are more likely to succeed, according to our research, described in an earlier piece for Harvard Business Review . But while this might tempt some entrepreneurs to make writing a plan their very first task, our subsequent study shows that writing a plan first is a really bad idea. It is much better to wait, not to devote too much time to writing the plan, and, crucially, to synchronize the plan with other key startup activities.
- FG Francis J. Greene is Chair in Entrepreneurship in the University of Edinburgh Business School.
- CH Christian Hopp is Chair in Technology Entrepreneurship in the TIME Research Area, the Faculty of Business and Economics, RWTH Aachen University.
Partner Center

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2 Developing a Business Plan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles [1]
Hindle and Mainprize suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model.
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture. [2]
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
- If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
- Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
- Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
- The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.” This statement might mean there is a total shortage of 100,000 units, but competitors are filling this gap by producing 25,000 per year; in which case there will only be a shortage for four years. However, it could mean that the annual shortage is 100,000 units and only 25,000 are produced each year, in which case the total shortage is very high and is growing each year.
- You must always provide the complete perspective by indicating the appropriate time frame, currency, size, or other measurement.
- If you use a percentage figure, you must indicate to what it refers—otherwise the number is meaningless to a reader.
- If your plan includes an international element, you must indicate in which currency or currencies the costs, revenues, prices, or other values are quoted. This can be solved by indicating up-front in the document in which currency all values will be quoted. Another option is to indicate each time which currency is being used, and sometimes you might want to indicate the value in more than one currency. Of course, you will need to assess the exchange rate risk to which you will be exposed and describe this in your document.
6. Ensure credibility is both established and maintained. [3]
- If a statement presents something as a fact when this fact is not generally known, always indicate the source. Unsupported statements damage credibility.
- Be specific. A business plan is simply not of value if it uses vague references to high demand, carefully set prices, and other weak phrasing. It must show hard numbers (properly referenced, of course), actual prices, and real data acquired through proper research. This is the only way to ensure your plan is considered credible.
- Your strategies must be integrated. For example, your pricing strategy must complement and mesh perfectly with your product/service strategy, distribution strategy, and promotions strategy. For example, you probably shouldn’t promote your product as a premium product if you plan to charge lower-than-market prices for it.
7. Before finalizing your business plan, re-read each section to evaluate whether it will appeal to your targeted readers.
Useful Resources for Business Planning
- Financial Performance Data : Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
- BizPal for accessing licensing and other needs
- Canada Revenue Agency for CRA asset classifications
- Canadian Company Capabilities database to use to find suppliers and buyers
- Merx for finding possible Canadian Government contracts
- The Conference Board of Canada
- Bank of Canada
- Scotia Bank
- Bank of Montreal
- Business Loan Calculator
Library Resources
NSCC Library – Business Databases [journals and other resources]
Employee compensation calculators
- Salary Data & Career Research Center – Canada
Existing business plans
The Word and Excel templates in this book
- Business Plan Template (Word)
- Business Plan Template (Excel)
Business Plan Development Tools
Credibility and communication.
According to Hindle and Mainprize, strong business plans effectively communicate the necessary information to the targeted readers while also establishing the credibility of the plan and the entrepreneur. [4] The Credibility and Communication Meter icon is used throughout this book to highlight where and how business plan writers can improve the quality of the information and enhance their and their plan’s credibility.
Use the following tools to improve the information in and credibility of your plans:
The Ratchet Effect
A ratchet is a tool that most of us are familiar with. It is useful because it helps its user accomplish something with each effort expended while guarding against losing past advancements.
With each word, sentence, paragraph, heading, chart, figure, and table you include in your final business plan, the ratchet should move ahead a notch because you achieve two important things.
First, only needed and relevant information is included.
Second, your additions build credibility in a relevant way.
Apply the ratchet effect by making sure that each and every sentence and paragraph conveys needed and relevant information that adds to your and your plan’s credibility. Use the following principles: Rarely—and only if it truly needs to be said again—repeat something that you have already said in your plan.
Avoid using killer phrases, like “there is no competition for our product” or “our product will sell itself, so we will not need to advertise it.” Any savvy reader will understand that these kinds of statements are naive and demonstrate a lack of understanding about how the market and other real-life factors actually work.
Avoid contradicting yourself. Make sure that what is said in the written part of your plan completely syncs with what is said in the other parts of your plan. Likewise, ensure that what you include in the financial parts of your plan is completely in sync with what is said the written part.
The Magic Formula
Apply the following magic formula throughout your write your plan.
- …consideration X affects my business because…
- …consideration X is subject to this trend into the future…
- …which means that we have decided to do this…(or) will implement this strategy…in response to how the expected trends for consideration X will affect my business
Here is an example of how you can use the magic formula to develop part of the pricing strategy in the marketing plan part of your business plan: We expect that our expenses to run our business will rise with the rate of inflation, which means that we must plan to increase the prices on our products to establish and maintain our profitability. The Bank of Canada (201x) has projected that the general inflation rate in <the city in which my business will operate> will be 3.0% in 201x, 3.5% in 201y, and 4.0% in 201z. In our projected financial statements, therefore, we have inflated both our expenses and our prices by those rates in those years.
Context and Framing
You must provide the right context when you describe situations, strategies, and other components of your plan. Business plan readers should never be left to guess why you indicate in a business plan that you will do something. Proper context is needed to help you frame the information you present.
When you frame the stories you tell correctly, the ratchet effect will happen and your plan will be stronger. One example of effective framing is when you, as the writer of the plan and the entrepreneur, clearly indicate how your education, expertise, relevant experiences, and network of contacts will make up for any lack of direct experience you have in running this particular kind of business. An example of ineffective framing is when you indicate that you lack experience with this type of business, or when you fail to specify how and why your levels of experience will affect the business’s development.
Prioritizing Problems
Don’t get hung up on something that doesn’t need an immediate solution. Instead, flag it for future consideration and move on. When you return to re-address the issue, it might no longer be a problem or you might have by then figured out a solution.
Process for Developing Business Plans
The business plan development process described next has been extensively tested with entrepreneurship students and has proven to provide the guidance entrepreneurs need to develop a business plan appropriate for their needs: a high power business plan .
Developing a high power business plan has six stages, which can be compared to a process for hosting a dinner for a few friends. A host hoping to make a good impression with their anticipated guests might analyze the situation at multiple levels to collect data on new alternatives for healthy ingredients, what ingredients have the best prices and are most readily available at certain times of year, the new trends in party appetizers, what food allergies the expected guests might have, possible party themes, and so on. This analysis is the Essential Initial Research stage.
In the Business Model stage, the host might construct a menu of items to include with the meal along with a list of decorations to order, music to play, and costume themes to suggest to the guests. The mix of these kinds of elements chosen by the host will aid in the success of the party.
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage is where the host rolls up their sleeves and begins to make some of the food items, puts up some of the decorations, and generally gets everything started for the party.
During this stage, the host will begin to realize that some plans are not feasible and that changes are needed. The required changes might be substantial, like the need to postpone the entire party and ultimately start over in a few months, and others might be less drastic, like the need to change the menu when an invited guest indicates that they can’t eat food containing gluten. These changes are incorporated into the plan during the Making the Business Plan Realistic stage to make it realistic and feasible.
The Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur stage involves further changes to the party plan to make it more appealing to both the invited guests and to make it a fun experience for the host. For example, the host might learn that some of the single guests would like to bring dates and others might need to be able to bring their children to be able to attend. The host might be able to accommodate those desires or needs in ways that will also make the party more fun for them—maybe by accepting some guests’ offers to bring food or games, or maybe hiring a babysitter to entertain and look after the children.
The final stage— Finishing the Business Plan— involves the host putting all of the final touches in place for the party in preparation for the arrival of the guests.
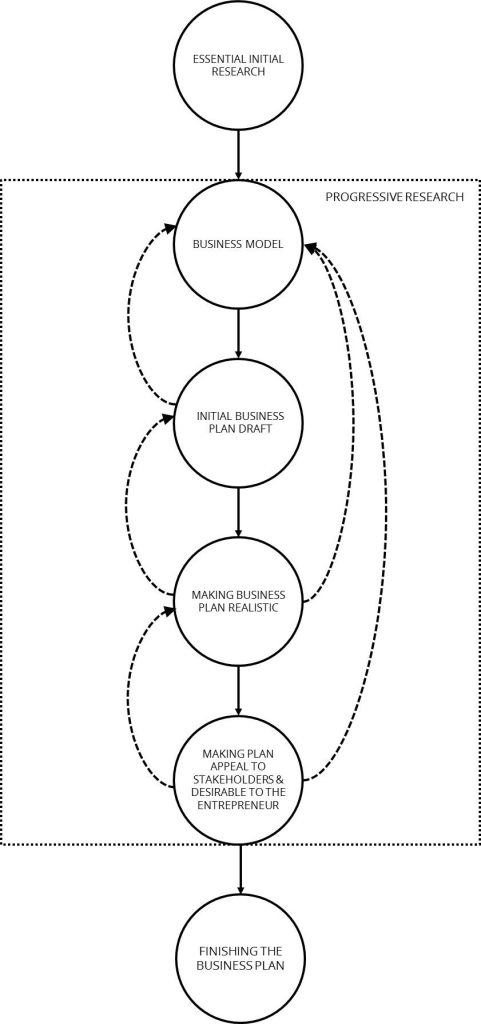
Essential Initial Research
A business plan writer should analyze the environment in which they anticipate operating at each of the levels of analysis: Societal , Industry , Market , and Firm . This stage of planning is called the Essential Initial Research stage, and it is a necessary first step to better understand the trends that will affect their business and the decisions they must make to lay the groundwork for, which will improve their potential for success.
In some cases, much of this research should be included in the developing business plan as its own separate section to help show readers that there is a market need for the business being considered and that it stands a good chance of being successful.
In other cases, a business plan will be stronger when the components of the research are distributed throughout the business plan to provide support for the outlined plans and strategies outlined. For example, the industry- or market-level research might outline the pricing strategies used by identified competitors, which might be best placed in the Pricing Strategy part of the business plan to support the decision made to employ a particular pricing strategy.
Business Model
Inherent in any business plan is a description of the Business Model chosen by the entrepreneur as the one that they feel will best ensure success. Based upon their analysis from the Essential Initial Research stage, an entrepreneur should determine how each element of their business model—including their revenue streams, cost structure, customer segments, value propositions, key activities, key partners, and so on—might fit together to improve the potential success of their business venture (see Chapter 3 – Business Models ).
For some types of ventures, at this stage an entrepreneur might launch a lean start-up (see the “Lean Start-up” section in Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research ) and grow their business by continually pivoting, or constantly adjusting their business model in response to the real-time signals they get from the markets’ reactions to their business operations. In many cases, however, an entrepreneur will require a business plan. In those cases, their initial business model will provide the basis for that plan.
Of course, throughout this and all of the stages in this process, the entrepreneur should seek to continually gather information and adjust the plans in response to the new knowledge they gather. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the business model and moving on to the initial business plan draft.
Initial Business Plan Draft
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage involves taking the knowledge and ideas developed during the first two stages and organizing them into a business plan format. Many entrepreneurs prefer to create a full draft of the business plan with all of the sections, including the front part with the business description, vision, mission, values, value proposition statement, preliminary set of goals, and possibly even a table of contents and lists of tables and figures all set up using the software features enabling their automatic generation. Writing all of the operations, human resources, marketing, and financial plans as part of the first draft ensures that all of these parts can be appropriately and necessarily integrated. The business plan will tell the story of a planned business startup in two ways: 1) by using primarily words along with some charts and graphs in the operations, human resources, and marketing plans and 2) through the financial plan. Both must tell the same story.
The feedback loop shown in Figure 1 demonstrates that the business developer may need to review the business model. Additionally, as shown by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Initial Business Plan Draft stage and moving on to the Making Business Plan Realistic stage.
Making Business Plan Realistic
The first draft of a business plan will almost never be realistic. As the entrepreneur writes the plan, it will necessarily change as new information is gathered. Another factor that usually renders the first draft unrealistic is the difficulty in making certain that the written part—in the front part of the plan along with the operations, human resources, and marketing plans—tells the exact same story as the financial part does. This stage of work involves making the necessary adjustments to the plan to make it as realistic as possible.
The Making Business Plan Realistic stage has two possible feedback loops. The first means going back to the Initial Business Plan Draft stage if the initial business plan needs to be significantly changed before it is possible to adjust it so that it is realistic. The second feedback loop circles back to the Business Model stage if the business developer needs to rethink the business model. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Making Business Plan Realistic stage and moving on to the Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders stage.
Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
A business plan can be realistic without appealing to potential investors and other external stakeholders, like employees, suppliers, and needed business partners. It might also be realistic (and possibly appealing to stakeholders) without being desirable to the entrepreneur. During this stage, the entrepreneur will keep the business plan realistic as they adjust plans to appeal to potential investors, stakeholders, and themselves.
If, for example, investors will be required to finance the business’s start, some adjustments might need to be relatively extensive to appeal to potential investors’ needs for an exit strategy from the business, to accommodate the rate of return they expect from their investments, and to convince them that the entrepreneur can accomplish all that is promised in the plan. In this case, and in others, the entrepreneur will also need to get what they want out of the business to make it worthwhile for them to start and run it. So, this stage of adjustments to the developing business plan might be fairly extensive, and they must be informed by a superior knowledge of what targeted investors need from a business proposal before they will invest. They also need to be informed by a clear set of goals that will make the venture worthwhile for the entrepreneur to pursue.
The caution with this stage is to balance the need to make realistic plans with the desire to meet the entrepreneur’s goals while avoiding becoming discouraged enough to drop the idea of pursuing the business idea . If an entrepreneur is convinced that the proposed venture will satisfy a valid market need, there is often a way to assemble the financing required to start and operate the business while also meeting the entrepreneur’s most important goals. To do so, however, might require significant changes to the business model.
One of the feedback loops shown in Figure 1 indicates that the business plan writer might need to adjust the draft business plan while ensuring that it is still realistic before it can be made appealing to the targeted stakeholders and desirable to the entrepreneur. The second feedback loop indicates that it might be necessary to go all the way back to the Business Model stage to re-establish the framework and plans needed to develop a realistic, appealing, and desirable business plan. Additionally, this stage’s enclosure in the Progressive Research box suggests that the business plan developer might need to conduct further research.
Finishing the Business Plan
The final stage involves putting the important finishing touches on the business plan so that it will present well to potential investors and others. This involves making sure that the math and links between the written and financial parts are accurate. It involves ensuring that all the needed corrections are made to the spelling, grammar, and formatting. The final set of goals should be written to appeal to the target readers and to reflect what the business plan says. An executive summary should be written and included as a final step.
Chapter Summary
This chapter described the internal and external purposes for business planning. It also explained how business plans must effectively communicate while establishing and building credibility for both the entrepreneur and the venture. The general guidelines for business planning were covered as were some important business planning tools. The chapter concluded with descriptions of the stages of the business development process for effective business planning.
- Hindle, K., & Mainprize, B. (2006). A systematic approach to writing and rating entrepreneurial business plans. The Journal of Private Equity, 9(3), 7-23. ↵
- Ibid. ↵
Business Plan Development Guide Copyright © 2023 by Lee A. Swanson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
How to Prepare and Write the Perfect Business Plan for Your Company Here's how to write a business plan that will formalize your company's goals and optimize your organization.
By Matthew McCreary May 5, 2021
Are you preparing to start your own business but uncertain about how to get started? A business plan ought to be one of the first steps in your entrepreneurial journey because it will organize the ideas that have been spinning around in your brain and prepare you to seek funding, partners and more.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines a company's goals and how the business, well, plans to achieve those goals over the next three or more years. It helps define expected profits and challenges, providing a road map that will help you avoid bumps in the road.
Stever Robbins writes in an Entrepreneur article titled, "Why You Must Have a Business Plan," that a business plan "is a tool for understanding how your business is put together…. Writing out your business plan forces you to review everything at once: your value proposition, marketing assumptions, operations plan, financial plan and staffing plan." But, a business plan is about more than just reviewing the past state of your business or even what your business looks like today.
Robbins writes that a well-written business plan will help you drive the future by "laying out targets in all major areas: sales, expense items, hiring positions and financing goals. Once laid out, the targets become performance goals."
The business plan can help your company attract talent and funding, because when prospects ask about your business, you already have an articulated overview to offer them. How they react can allow you to quickly understand how others see your business and pivot if necessary.
What should you do before you write your business plan?
It might sound redundant, but you actually need to plan your business plan. Business plans can be complicated, and you'll be held accountable for the goals you set. For example, if you plan to open five locations of your business within the first two years, your investors might get angry if you only manage to open two.
That's why it's essential that, before writing your business plan, you spend some time determining exactly which objectives are essential to your business. If you're struggling to come up with a list of goals on your own, Entrepreneur article "Plan Your Business Plan" offers some questions you can ask yourself to spark some inspiration.
How determined am I to see this venture succeed?
Am I willing to invest my own money and work long hours for no pay, sacrificing personal time and lifestyle, maybe for years?
What's going to happen to me if this venture doesn't work out?
If it does succeed, how many employees will this company eventually have?
What will be the business's annual revenue in a year? What about in five years?
What will be the company's market share in that amount of time?
Will the business have a niche market, or will it sell a broad spectrum of goods and services?
What are my plans for geographic expansion? Should it be local or national? Can it be global?
Am I going to be a hands-on manager, or will I delegate a large proportion of tasks to others?
If I delegate, what sorts of tasks will I share? Will it be sales, technical work or something else?
How comfortable am I taking direction from others? Can I work with partners or investors who demand input into the company's management?
Is the business going to remain independent and privately owned, or will it eventually be acquired or go public?
It's also essential to consider your financial goals. Your business might not require a massive financial commitment upfront, but it probably will if you're envisioning rapid growth. Unless you're making your product or service from scratch, you'll have to pay your suppliers before your customers can pay you, and as "Plan Your Business Plan" points out, "this cash flow conundrum is the reason so many fast-growing companies have to seek bank financing or equity sales to finance their growth. They are literally growing faster than they can afford."
How much financing will you need to start your business? What will you be willing to accept? If you're desperate for that first influx of cash, you might be tempted to accept any offer, but doing so might force you to either surrender too much control or ask investors for a number that's not quite right for either side.
These eight questions can help you determine a few financial aspects of your planning stages:
What initial investment will the business require?
How much control of the business are you willing to relinquish to investors?
When will the business turn a profit?
When can investors, including you, expect a return on investment?
What are the business's projected profits over time?
Will you be able to devote yourself full-time to the business?
What kind of salary or profit distribution can you expect to take home?
What are the chances the business will fail, and what will happen if it does?
You should also consider who, primarily, is going to be reading your business plan, and how you plan to use it. Is it a means of raising money or attracting employees? Will suppliers see it?
Lastly, you need to assess the likelihood of whether you actually have the time and resources to see your plan through. It might hurt to realize the assumptions you've made so far don't actually make a successful business, but it's best to know early on, before you make further commitments.
Related: Need a Business Plan Template? Here Is Apple's 1981 Plan for the Mac.
How to Write a Business Plan
Once you've worked out all the questions above and you know exactly what goals you have for your business plan, the next step is to actually write the darn thing. A typical business plan runs 15 to 20 pages but can be longer or shorter, depending on the complexity of the business and the needs of your venture. Regardless of whether you intend to use the business plan for self-evaluation or to seek a seven-figure investment, it should include nine key components, many of which are outlined in Entrepreneur 's introduction to business plans:
1. Title page and contents
Presentation is important, and a business plan should be presented in a binder with a cover that lists the business's name, the principals' names and other relevant information like a working address, phone number, email and web address and date. Write the information in a font that's easy to read and include it on the title page inside, too. Add in the company logo and a table of contents that follows the executive summary.
2. Executive summary
Think of the executive summary as the SparkNotes version of your business plan . It should tell the reader in as few words as possible what your business wants and why. The executive summary should address these nine things:
The business idea and why it is necessary. (What problem does it solve?)
How much will it cost, and how much financing are you seeking?
What will the return be to the investor? Over what length of time?
What is the perceived risk level?
Where does your idea fit into the marketplace?
What is the management team?
What are the product and competitive strategies?
What is your marketing plan?
What is your exit strategy?
When writing the executive summary, remember that it should be somewhere between one-half page to a full page. Anything longer, and you risk losing your reader's attention before they can dig into your business plan. Try to answer each of the questions above in two or three sentences, and you'll wind up with an executive summary that's about the right length.
Related: First Steps: Writing the Executive Summary of Your Business Plan
3. Business description
You can fill anywhere from a few paragraphs to a few pages when writing your business description, but try again to keep it short, with the understanding that more sections will follow. The business description typically starts with a short explanation of your chosen industry, including its present outlook and future possibilities. Use data and sources (with proper footnotes) to explain the markets the industry offers, along with the developments that will affect your business. That way, everyone who reads the business description, particularly investors, will see that they can trust the various information contained within your business plan.
When you pivot to speaking of your business, start with its structure. How does your business work? Is it retail, service-oriented or wholesale? Is the business new or established? Is the company a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation? Who are the principals and who are your customers? What do the distribution channels look like, and how can you support sales?
Next, break down your business's offerings. Are you selling a physical product, SaaS or a service? Explain it in a way that a reader knows what you're planning to sell and how it differentiates itself from the competition (investors call this a Unique Selling Proposition, or USP, and it's important that you find yours). Whether it's a trade secret or a patent, you should be specific about your competitive advantage and why your business is going to be profitable. If you plan to use your business plan for fundraising, you can use the business description section to explain why new investments will help make the business even more profitable.
This, like everything else, can be brief, but you can tell the reader about your business's efficiency or workflow. You can write about other key people within the business or cite industry experts' support of your idea, as well as your base of operations and reasons for starting in the first place.
4. Market strategies
Paint a picture about your market by remembering the four Ps: product, price, place and promotion.
Start this section by defining the market's size, structure and sales potential. What are the market's growth prospects? What do the demographics and trends look like right now?
Next, outline the frequency at which your product or service will be purchased by the target market and the potential annual purchase. What market share can you possibly expect to win? Try to be realistic here, and keep in mind that even a number like 25% might be a dominant share.
Next, break down your business's plan for positioning, which relates to the market niche your product or service can fill. Who is your target market, how will you reach them and what are they buying from you? Who are your competitors, and what is your USP?
The positioning statement within your business plan should be short and to the point, but make sure you answer each of those questions before you move on to, perhaps, the most difficult and important aspect of your market strategy: pricing.
In fact, settling on a price for your product or service is one of the most important decisions you have to make in the entire business plan. Pricing will directly determine essential aspects of your business, like profit margin and sales volume. It will influence all sorts of areas, too, from marketing to target consumer.
There are two primary ways to determine your price: The first is to look inward, adding up the costs of offering your product or service, and then adding in a profit margin to find your number. The second is called competitive pricing, and it involves research into how your competitors will either price their products or services now or in the future. The difficult aspect of this second pricing method is that it often sets a ceiling on pricing, which, in turn, could force you to adjust your costs.
Then, pivot the market strategies section toward your distribution process and how it relates to your competitors' channels. How, exactly, are you going to get your offerings from one place to the next? Walk the reader step by step through your process. Do you want to use the same strategy or something else that might give you an advantage?
Last, explain your promotion strategy. How are you going to communicate with your potential customers? This part should talk about not only marketing or advertising, but also packaging, public relations and sales promotions.
Related: Creating a Winning Startup Business Plan
5. Competitive analysis
The next section in your business plan should be the competitive analysis, which helps explain the differences between you and your competitors … and how you can keep it that way. If you can start with an honest evaluation of your competitors' strengths and weaknesses within the marketplace, you can also provide the reader with clear analysis about your advantage and the barriers that either already exist or can be developed to keep your business ahead of the pack. Are there weaknesses within the marketplace, and if so, how can you exploit them?
Remember to consider both your direct competition and your indirect competition, with both a short-term and long-term view.
6. Design and development plan
If you plan to sell a product, it's smart to add a design and development section to your business plan. This part should help your readers understand the background of that product. How have the production, marketing and company developed over time? What is your developmental budget?
For the sake of organization, consider these three aspects of the design and development plan:
Product development
Market development
Organizational development
Start by establishing your development goals, which should logically follow your evaluation of the market and your competition. Make these goals feasible and quantifiable, and be sure to establish timelines that allow your readers to see your vision. The goals should address both technical and marketing aspects.
Once the reader has a clear idea of your development goals, explain the procedures you'll develop to reach them. How will you allocate your resources, and who is in charge of accomplishing each goal?
The Entrepreneur guide to design and development plans offers this example on the steps of producing a recipe for a premium lager beer:
Gather ingredients.
Determine optimum malting process.
Gauge mashing temperature.
Boil wort and evaluate which hops provide the best flavor.
Determine yeast amounts and fermentation period.
Determine aging period.
Carbonate the beer.
Decide whether or not to pasteurize the beer.
Make sure to also talk about scheduling. What checkpoints will the product need to pass to reach a customer? Establish timeframes for each step of the process. Create a chart with a column for each task, how long that task will take and when the task will start and end.
Next, consider the costs of developing your product, breaking down the costs of these aspects:
General and administrative (G&A) costs
Marketing and sales
Professional services, like lawyers or accountants
Miscellaneous costs
Necessary equipment
The next section should be about the personnel you either have or plan to hire for that development. If you already have the right person in place, this part should be easy. If not, then this part of the business plan can help you create a detailed description of exactly what you need. This process can also help you formalize the hierarchy of your team's positions so that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
Finish the development and design section of your business plan by addressing the risks in developing the product and how you're going to address those risks. Could there be technical difficulties? Are you having trouble finding the right person to lead the development? Does your financial situation limit your ability to develop the product? Being honest about your problems and solutions can help answer some of your readers' questions before they ask them.
Related: The Essential Guide to Writing a Business Plan
7. Operations and management plan
Want to learn everything you'll ever need to know about the operations and management section of your business plan, and read a real, actual web article from 1997? Check out our guide titled, "Writing A Business Plan: Operations And Management."
Here, we'll more briefly summarize the two areas that need to be covered within your operations and management plan: the organizational structure is first, and the capital requirement for the operation are second.
The organizational structure detailed within your business plan will establish the basis for your operating expenses, which will provide essential information for the next part of the business plan: your financial statements. Investors will look closely at the financial statements, so it's important to start with a solid foundation and a realistic framework. You can start by dividing your organizational structure into these four sections:
Marketing and sales (including customer relations and service)
Production (including quality assurance)
Research and development
Administration
After you've broken down the organization's operations within your business plan, you can look at the expenses, or overhead. Divide them into fixed expenses, which typically remain constant, and variable, which will change according to the volume of business. Here are some of the examples of overhead expenses:
Maintenance and repair
Equipment leases
Advertising and promotion
Packaging and shipping
Payroll taxes and benefits
Uncollectible receivables
Professional services
Loan payments
Depreciation
Having difficulty calculating what some of those expenses might be for your business? Try using the simple formulas in "Writing A Business Plan: Operations And Management."
8. Financial factors
The last piece of the business plan that you definitely need to have covers the business's finances. Specifically, three financial statements will form the backbone of your business plan: the income statement, the cash-flow statement and balance sheet . Let's go through them one by one.
The income statement explains how the business can make money in a simple way. It draws on financial models already developed and discussed throughout the business plan (revenue, expenses, capital and cost of goods) and combines those numbers with when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. When the reader finishes going through your income statement, they should understand how much money your company makes or loses by subtracting your costs from your revenue, showing either a loss or a profit. If you like, you or a CPA can add a very short analysis at the end to emphasize some important aspects of the statement.
Second is the cash-flow statement, which explains how much cash your business needs to meet its obligations, as well as when you're going to need it and how you're going to get it. This section shows a profit or loss at the end of each month or year that rolls over to the next time period, which can create a cycle. If your business plan shows that you're consistently operating at a loss that gets bigger as time goes on, this can be a major red flag for both you and potential investors. This part of the business plan should be prepared monthly during your first year in business, quarterly in your second year and annually after that.
Our guide on cash-flow statements includes 17 items you'll need to add to your cash-flow statement.
Cash. Cash on hand in the business.
Cash sales . Income from sales paid for by cash.
Receivables. Income from collecting money owed to the business due to sales.
Other income. The liquidation of assets, interest on extended loans or income from investments are examples.
Total income. The sum of the four items above (total cash, cash sales, receivables, other income).
Material/merchandise . This will depend on the structure of your business. If you're manufacturing, this will include your raw materials. If you're in retail, count your inventory of merchandise. If you offer a service, consider which supplies are necessary.
Direct labor . What sort of labor do you need to make your product or complete your service?
Overhead . This includes both the variable expenses and fixed expenses for business operations.
Marketing/sales . All salaries, commissions and other direct costs associated with the marketing and sales departments.
Research and development . Specifically, the labor expenses required for research and development.
General and administrative expenses. Like the research and development costs, this centers on the labor for G&A functions of the business.
Taxes . This excludes payroll taxes but includes everything else.
Capital. Required capital for necessary equipment.
Loan payments. The total of all payments made to reduce any long-term debts.
Total expenses. The sum of items six through 14 (material/merchandise, direct labor, overhead, marketing/sales, research and development, general and administrative expenses, taxes, capital and loan payments).
Cash flow. Subtract total expenses from total income. This is how much cash will roll over to the next period.
Cumulative cash flow . Subtract the previous period's cash flow from your current cash flow.
Just like with the income statement, it's a good idea to briefly summarize the figures at the end. Again, consulting with a CPA is probably a good idea.
The last financial statement is the balance sheet. A balance sheet is, as our encyclopedia says, "a financial statement that lists the assets, liabilities and equity of a company at a specific point in time and is used to calculate the net worth of a business." If you've already started the business, use the balance sheet from your last reporting period. If the business plan you wrote is for a business you hope to start, do your best to project your assets and liabilities over time. If you want to earn investors, you'll also need to include a personal financial statement. Then, as with the other two sections, add a short analysis that hits the main points.
9. Supporting documents
If you have other documents that your readers need to see, like important contracts, letters of reference, a copy of your lease or legal documents, you should add them in this section.
Related: 7 Steps to a Perfectly Written Business Plan
What do I do with my business plan after I've written it?
The simplest reason to create a business plan is to help people unfamiliar with your business understand it quickly. While the most obvious use for a document like this is for financing purposes, a business plan can also help you attract talented employees — and, if you share the business plan internally, help your existing employees understand their roles.
But it's also important to do for your own edification, too. It's like the old saying goes, "The best way to learn something is to teach it." Writing down your plans, your goals and the state of your finances helps clarify the thoughts in your own mind. From there, you can more easily lead your business because you'll know whether the business is reaching the checkpoints you set out to begin with. You'll be able to foresee difficulties before they pop up and be able to pivot quickly.
That's why you should continue to update your business plan when the conditions change, either within your business (you might be entering a new period or undergoing a change in management) or within your market (like a new competitor popping up). The key is to keep your business plan ready so that you don't have to get it ready when opportunity strikes.
Entrepreneur Staff
Associate Editor, Contributed Content
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock Want to Start a Simple Business That Helps the Planet? After 'One Night's Worth of Research,' He Started an Eco-Friendly Gig and Now Makes $200,000 a Year
- I've Negotiated High-Pressure, Multi-Million-Dollar Deals for Artists Like Bruno Mars and Enrique Iglesias — Here's the Strategy That Always Helps Me Win
- Lock This Toxic Money Habit Is Becoming More Common — If You've Picked It Up, Your Finances Are at Serious Risk , Expert Warns
- 'This Year Almost Broke Me': Tom Schwartz Reveals 'Scandoval' Almost Shut Down His Restaurant After Losing 80% of His Business
- 'Not What Anybody Signed Up For': A Legal Expert Weighs in on the Labor Rule That Could Destroy Franchising
- Lock Anyone Can Try the Simple Strategy That One Billionaire Investor Used to Make His First Million Dollars Tax-Free
Most Popular Red Arrow
These coworkers-turned-friends started a side hustle on amazon — now it's a 'full hustle' earning over $20 million a year: 'jump in with both feet'.
Achal Patel and Russell Gong met at a large consulting firm and "bonded over a shared vision to create a mission-led company."
An Iconic Las Vegas Casino Is Shuttering This Summer After 34 Years
The Mirage will close on July 17.
Samsung's New Ad Pokes Fun at Apple's Controversial 'Crush' Ad
Creative universes overlap in a new ad from Samsung.
Dell Is Labeling Hybrid Employees With 'Red Flags' Based on How Often They're in the Office
Dell will consider the frequency of employee badge swipes when it determines how hybrid employees are reviewed, rewarded, and compensated.
Want to Be More Productive? Here's How Google Executives Structure Their Schedules
These five tactics from inside Google will help you focus and protect your time.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Successfully copied link
The Entrepreneurial Process
Of course, there are many ways to organize the effort of planning, launching and building a venture. But there are a set of fundamentals that must be covered in any approach. We offer the following as a way to break down the basic activities necessary.
It is useful to break the entrepreneurial process into five phases: idea generation, opportunity evaluation, planning, company formation/launch and growth. These phases are summarized in this table, and the Opportunity Evaluation and Planning steps are expanded in greater detail below.
Although it is natural to think of the early steps as occurring sequentially, they are actually proceeding in parallel. Even as you begin your evaluation, you are forming at least a hypothesis of a business strategy. As you test the hypothesis, you are beginning to execute the first steps of your marketing plan (and possibly also your sales plan). We separate these ideas for convenience in description but it is worth keeping in mind that these are ongoing aspects of your management of the business. In the growth phases, you continue to refine you basic idea, re-evaluate the opportunity and revise your plan.
To take this analysis one level deeper, we can break down each of these phases as follows.

Opportunity Evaluation
I t is helpful to think of the evaluation step as continually asking the question of whether the opportunity is worth investing in. You are actually constructing and then continually revising an “investment prospectus.”
- Is there a sufficiently attractive market opportunity ?
- Is your proposed solution feasible, both from a market perspective and a technology perspective?
- Can we compete (over a sufficiently interesting time horizon): is there sustainable competitive advantage ?
- Do we have a team that can effectively capitalize of this opportunity?
- What is the risk / reward profile of this opportunity, and does it justify the investment of time and money?
If you can answer all of these questions affirmatively, then you have persuaded yourself that this opportunity is worth investing in. This is the first step toward being able to convince others, whether they be prospective customers, employees, partners or providers of capital.
These ideas are developed in the Opportunity Evaluation section
There are four main areas of strategy: determination of the target customer set, business model, position and objectives. These are described briefly below and in more depth in the sections devoted to these topics.
Target customers
The target customer is the set of potential buyers who are your focus as you design your company’s solution. The more you know about them, the better off you are. Your characterization should be both qualitative and quantitative . You should investigate any alternatives the customer has for solving or working around the problem or need that you are targeting. You should understand the buying process in detail, including who are the decision makers and who influences the decision.
Business Model
The business model is your theory about how you will make money. It involves a definition of a solution to the customer’s need, an hypothesis about how and how much the customer will pay for that solution. If there are any assumptions required for your theory to be true (such as the existence of complementary product or services, or the customer’s willingness to change business processes) these should also be articulated.
“Position” refers both to how your company is differentiated from any competitors and also how it relates to other companies in the value chain. This is an opportunity to define, at a fundamental level, what your company will do and what it will not do.
An element of position is your company’s vision : how it wants to be known or thought of. A compelling vision is necessary to inspire investors, recruit and motivate employees, and to excite customers and partners.
Milestones / Objectives
As a first step toward creating your operating plan, you should create a set of high level objectives for your business. This should include:
- Key milestones (prototype, product, customer, partnerships,etc.)
- Share or penetration into your chosen market
A clear articulation of objectives will allow you to set priorities for your venture, which will be critical as you face the many tough decisions that any entrepreneur must face.
These ideas are developed in the Strategy Development section
Operating plan
Your operating plan is where you spell out all of the things that you plan to do and what they will yield for your business. The activities will cover all areas of the business: marketing, selling, engineering, etc. These activities should yield products by a certain date, possibly partners, customers, etc. These activities will drive the financial performance of the company.
Your operating plan will be a combination of plans , i.e., these people working on this topic for this period of time will produce result X, and forecasts or projections , i.e. predictions about what results will occur. The primary and most important forecast concerns revenue, but predictions about costs of materials and other things may be important as well. The operating plan is the core of your business, and you should make it as good as you can – your plans should be as thorough as possible and your forecasts should be based on the best and most complete evidence you can compile.
Begin with your strategy and break down what needs to be accomplished to achieve your objectives – this is the basis of your plan. The more detailed and fine grained analysis you can develop, the more accurate and reliable your plan will be.
Financing plan
This includes the capital needs of the company, the timing of those needs and the desired/expected sources of that capital.
Planning process
Here are a few important principles:
- The actual budget, staffing plans, etc. are then driven by estimates of what it takes to accomplish the tasks in the required timeframe.
- Build a plan that captures everything ( so that you are not hurt by surprises or unexpected expenses)
- Revenue: detailed bottom up plan, based on best information about customer groupings, conversion rates, sales activity, …
- Expenses: usually people driven – build in realistic hiring timetables, training, learning curve, benefits, travel, etc.
- Program expenses: mostly marketing – must support the plan and estimates should be equally comprehensive
- The plan must close – all pieces tie together.
The plan becomes more manageable when you break it down into major functional areas. The traditional breakdown is as follows, but you don’t have to be bound by this except in so far as you should follow Generally Accepted Accounting Practice.
- Research and development
- People management
- Processes & infrastructure
You should monitor your budget carefully and continually, and make adjustments as needed. A more detailed description of the process of building an operating plan may be found at: Operating Plan Development Process
Execution is organized by the core functional areas of the company
2.1 Overview of the Entrepreneurial Journey
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the entrepreneurial journey to explore and discover entrepreneurship as a career choice
- Identify the steps, decisions, and actions involved in the entrepreneurial journey
- Recognize the rewards and risks of the steps in the entrepreneurial journey
Self-Employment as an Entrepreneurial Journey
When the economy and the job market are strong, the entrepreneur has a safety net that decreases the risks in creating a new venture , a startup company or organization that conducts business or is created to satisfy a need, and allows for a quick recovery if the venture is not successful. There are more new startups when there are high levels of confidence in both the venture’s success and the entrepreneur’s confidence in finding employment if the venture fails. People over 40 years of age account for most new startup activity, in part because of the continuing trend in which a business may choose not to hire an employee but instead hire an independent contractor , a person who provides work similar to an employee without being part of the payroll for the contracting business, and who is responsible for paying their own taxes and providing their own benefits. With previous knowledge and expertise, this group of entrepreneurs recognizes opportunities created by this move away from hiring full-time employees to more outsourcing to independent contractors. One contributor is the gig economy , which involves using temporary and often transitional positions hired on a case-by-case basis, rather than keeping a full staff of hired employees. Advantages for the employer include a decrease in cost of benefits and loyalties to specific employees. Advantages for the hired worker or independent contractor (sometimes called a freelancer ) include no long-term commitment and flexibility in accepting contracts. From an entrepreneurial perspective, the creation of websites that support the gig economy offers opportunities for independent ventures. Many people today are becoming small entrepreneurs. This process goes by a variety of names, such as the sharing economy , the gig economy, the peer economy , or the collaborative economy . Maybe it means driving for a company such as Lyft , Uber , or GrubHub , or perhaps offering services through TaskRabbit , UpWork , or LivePerson . The projected numbers of independent contractors and on-demand workers are stated as 42 percent for small businesses by the year 2020, a growth of 8 percent from current figures. 1 And a projection of greater than 50 percent of the workforce will be independent contractors by 2027 if this trend continues at the current pace. 2 In the “Freelancing in America: 2019” report, the sixth annual study by UpWork and Freelancers Union, 57 million United States citizens are estimated to freelance, with income approaching 5 percent of US gross domestic product (GDP) at nearly $1 trillion and earning a median rate of $28.00 an hour, representing an hourly income greater than 70 percent of workers in the overall US economy. 3 One report found that 94 percent of net job growth from 2005 to 2015 was in alternative work categories, with 60 percent due to independent contractors and contract company workers. 4
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the number of self-employed Americans is growing, with 9.6 million self-employed people at the end of 2016. That number is expected to grow to 10.3 million by 2026. 5 A more recent study by FreshBooks’ second annual “Self-Employment” report predicts that 27 million US employees will leave traditional work in favor of self-employment by 2020, tripling the current population of full-time self-employed professionals to 42 million. The main driver for this change in the workforce is a greater desire for control over one’s career with the ability to have greater control over working hours and acceptance of work. 6 , 7 Of course, self-employment is a broad category that includes small-business owners as well as entrepreneurial startups and freelance gig employees. Since 2016, there has been a downward slide in the number of employees working for self-employed businesses, which results from a variety of factors, including difficulties in finding qualified employees, qualified employees having more employment options, such as employment through the gig economy, outsourcing activities, and technology actions that decrease the need for employees, with entrepreneurial activity remaining steady. 8
Entrepreneurship around the World
In a 2017 Business Insider article, “America Needs Immigrant Entrepreneurs,” David Jolley writes that immigrants constitute 15 percent of the US workforce and 25 percent of the country’s workforce of entrepreneurs. 9 Forty percent of startups include at least one immigrant. Jolley’s article cites a study that identified immigrants as twice as likely to start a business as people born in the United States. In 2016, 40.2 percent of Fortune 500 companies were founded by at least one immigrant or a child of immigrant parents. Dinah Brin, writing for Forbes , stated in a 2018 article that immigrants form 25 percent of new US businesses and that new immigrant-owned firms generated 4 to 5 million jobs. 10
These statistics and other findings have prompted countries such as Canada to revise their immigration policies to attract more entrepreneurial-minded immigrants. A World Bank report from May 2018 ranked the United States 53rd out of 190 countries for ease in starting a business, with higher scores representing greater ease. 11 The same report ranks the United States eighth for ease of doing business. The difference in these rankings indicates that once a business is established, factors such as regulations, permits, access to credit, and infrastructure support the business owner’s ability to continue the business, but actually starting the business is more challenging. For any given country, ease in starting a business and the country’s interest in supporting entrepreneurial activity are crucial in both attracting entrepreneurial people and supporting their ability to open a business. Imposing restrictive regulations and processes on new ventures significantly decreases the number of new ventures.
According to a 2018/2019 report, the highest rate of entrepreneurial activity worldwide in 2018 was in Angola at 41 percent. 12 Angola’s low-income economy meant fewer employment opportunities, creating pressures to find other ways to earn an income. Guatemala and Chile reported 28 percent and 25 percent of entrepreneurial activity, respectively, with medium- and high-income economies. These percentages are quite high, considering that these economies offer employment opportunities in existing companies. In terms of innovation, India at 47 percent, and Luxembourg and Chile at 48 percent each, take the lead in offering new products and services not previously available. This entrepreneurial activity reflects the ease of starting a business. The Netherlands, Poland, and Sweden were reported as the easiest countries in which to start a new business, in part because many people in those countries view entrepreneurship as an attractive lifestyle. As you can see, both economic opportunities and a country’s specific support for entrepreneurial behavior contribute to the number of people who enter entrepreneurial activities.
From a gender perspective, there are currently over 11 million woman-owned businesses in the United States. This number includes both small business owners and entrepreneurs. Thirty years ago, there were only 4 million woman-owned businesses. 13 The number of woman-owned businesses has increased 45 percent between 2007 and 2016, five times faster than the national average, with 78 percent of new women-owned businesses started by women of color.
Starting Your Entrepreneurial Journey
How do you fit into this entrepreneurial journey? This chapter will help you to explore and discover your potential for entrepreneurship as a career choice. Think of this exploration and discovery experience as a way to map out a strategy to reach your goals or dreams. Let’s imagine that your dream vacation is a hiking trip to Glacier National Park in the US state of Montana. Just as hikers have different levels of experience, so do entrepreneurs. Just as your plan for a wilderness hike would involve many stages, your entrepreneurial journey involves multiple levels of self-discovery, exploration, experiences, and accomplishments on your way to success. For our purposes, the term entrepreneurial venture means any type of new business, organization, project, or operation of interest that includes a level of risk in acting on an opportunity that has not previously been established. For each story of entrepreneurial success that is shared—such as that of Facebook or Airbnb—there are even more lesser-known entrepreneurial success stories such as Zipline , a company that delivers medical supplies in Rwanda and Ghana by drone. These entrepreneurs faced the same dilemmas in pursuing their passion, or opportunities, which led them to their entrepreneurial destiny. They courageously stepped out of their comfort zones to explore the possibilities that lie ahead. What is the difference between entrepreneurs and you? The main difference is taking that first step. Many people have ideas that fit into the definition of an entrepreneurial idea but never take that first step. Just as the Chinese philosopher Lao Tzu suggests, every journey begins with a single step.
Are You Ready?
Taking the first step.
Go to Fire Nation’s website on taking the first step to learn more. Changing your mindset (your perception of yourself and your life situation) and encountering trigger events (significant external situations) can nudge you into taking the first step toward being an entrepreneur.
- Is there a venture you’ve always thought you should start but never did?
- Think about what factors are stopping you. Consider your mindset and how you might change your mindset so that your venture could become a reality.
- What are some possible trigger events that could make the difference between starting your venture and waiting to start your venture?
Opening your future to the possibility of starting your own venture brings new and exciting experiences ( Figure 2.2 ). Every entrepreneur moves through several steps in considering the entrepreneurial journey. Once you understand this journey, the steps will help you define your path toward creating and starting your new venture. Each step of this process offers another level of understanding that prepares you for long-term success. How will you achieve this success? By taking one step at a time, exploring and learning, considering new ideas and expectations, and applying these experiences to achieve your personal outcome. Think of the entrepreneurial journey as a guide to knowing what is in store for you as you start your new venture.
One benefit of outlining a step-by-step process is the opportunity to explore different paths or behaviors that may lead to an entrepreneurial venture. Think again of your dream visit to Glacier National Park. How would you get there? What equipment would you need? What kinds of experiences would you expect to have? Think of the Glacier National Park journey as your entrepreneurial journey, a metaphor intended to help you as you create your career as an entrepreneur.
What makes someone ready or willing to choose entrepreneurship over becoming an employee of an established business or a small business owner? It takes confidence, courage, determination, resilience, and some know-how to select entrepreneurship as a career as well as the recognition of the opportunity. An entrepreneur is defined as someone who not only recognizes an opportunity but who also is willing to act on that opportunity. Both actions are required. We might identify an opportunity, but many people do not act on the idea. Confidence, courage, and willingness are necessary to take that first step, as well as remembering the following:
- You are unique. Even if two similar people attempted to launch identical ventures, the results would likely not be the same. This is because each one of us has different ideas, approaches, available resources, and comfort levels, all of which influence the venture’s development and eventual success.
- Although there are no hard and fast rules or theories of the best way to launch into entrepreneurship, we can gain wisdom from the lessons learned by experienced entrepreneurs.
- Selecting an entrepreneurial career requires honesty, reflection, and a tendency to be action oriented. You will need to recognize your own strengths, limitations, and commitment as part of that honesty. Reflection is required for self-growth—seeking improvements in your own skills, interactions, and decision making—and commitment is required to maintain consistency in your willingness to make the new venture a top priority in your life. You will also need to understand that you cannot accomplish everything by yourself, and you may need to ask for help. It helps to be curious, open, and able to take calculated risks and to be resourceful and resilient when faced with challenges or obstacles.
Entrepreneurial Potential Self-Assessment
Take this quick Entrepreneurial Potential Self-Assessment to assess your potential to become an entrepreneur. After completing this self-assessment, what new information did you learn about yourself? Do you think your answers will change as you acquire more life experiences and education? Why or why not?
Optimizing Interest Areas
What are three areas that interest you? These could be hobbies, work activities, or entertainment activities. How would someone else describe your skills and interests, or what you are known for? Answering these questions provides insights into your strengths and interests. Next, what is one area that you are passionate about? What strengths could you bring to this passion to build your own business?
Keep an open mind in looking for an opportunity that fits your strengths and interests. If you decide to explore entrepreneurship, what would be your first step? What are your initial thoughts about being an entrepreneur? What would you review or search to find more information on your idea or area of interest? With whom would you first question or discuss this idea? Why?
The Entrepreneurial Journey as a Trip
The entrepreneurial journey is your exploration to discover if entrepreneurship is right for you. Every entrepreneurial journey is unique; no two individuals will experience it in the same way. Along the way, you will find opportunities and risks coupled with challenges and rewards. It’s useful to think about the entrepreneurial journey as an exciting trip or other adventure. Most of the preparations and steps involved with planning a trip are like those for starting a venture. Just as you would plan and prepare for a trip—starting with inspiration and leading up to finally traveling on the trip—you might follow similar steps to launch a venture. And just as you would prepare for any challenges that you might encounter on a trip—bad weather, lost luggage, or detours—so you should consider potential obstacles or barriers along your entrepreneurial journey ( Figure 2.3 ). Think of these difficulties as opportunities to learn more about the entrepreneurial process—and about yourself and how you manage challenges.
Developing a venture can be an exciting and active experience. It is also a lot of hard work, which can be equally rewarding and enjoyable. Here we present the entrepreneurial journey as seven specific steps, or experiences, which you will encounter along the road to becoming an entrepreneur. You’ll find more information about the entrepreneurial journey in other chapters in this book.
- Step 1: Inspiration – What is your motivation for becoming an entrepreneur?
- Step 2: Preparation – Do you have what it takes to be an entrepreneur?
- Step 3: Assessment – What is the idea you plan to offer through your venture?
- Step 4: Exploring Resources – What resources and characteristics do you need to make this venture work?
- Step 5: Business Plan – What type of business structure and business model will your venture have?
- Step 6: Navigation – In what direction will you take your venture? Where will you go for guidance?
- Step 7: Launch – When and how will you launch your venture?
As you work through each step of the entrepreneurial journey you should prepare for significant aspects of this experience. You will meet with rewards and challenges, the consequences that result from the decisions made at various points along your journey. To visualize the steps of the entrepreneurial journey, imagine your possible hiking trip to Glacier National Park ( Table 2.1 ). Just as hikers have different levels of experience, so do entrepreneurs. Compare the following aspects of preparing for a hike with aspects of your entrepreneurial journey.
Step 1: Inspiration
When you think of being an entrepreneur, what is the inspiration for your venture? Just as you might have an inspiration for a hiking trip to Glacier National Park, you will have an inspiration behind the decision to become an entrepreneur. When you’re planning a trip to a new and exciting place, one thing you might do is to imagine what you will experience along the journey and on arriving at your destination ( Figure 2.4 ). This portion of the entrepreneurial journey includes imagining yourself as an entrepreneur or as part of an entrepreneurial team. For this stage, you need a creative, open, and innovative state of mind, also known as an entrepreneurial mindset , which is discussed in more detail in The Entrepreneurial Mindset and Creativity, Innovation, and Invention . Dream big about your potential future and opportunities ( Figure 2.5 ).
Step 2: Preparation
Just as when you are preparing for a trip, you need a plan ( Figure 2.6 ) to move forward on your entrepreneurial journey. Before your dream hiking trip, you might gather information about Glacier National Park from a trusted source, such as a good friend with travel experience, or you might conduct online research. Your friend’s feedback could be just the motivation you need to try this experience yourself. Or you might use your research to determine if the trip is possible. You will need to look at maps, either online or on paper. Either way, you might also consider travel and accommodation options, such as booking a flight and finding a place to stay. You might want to create benchmarks to align your journey with your available resources, such as the amount of time and the amount of money you have to spend on the trip. Benchmarking is a method of tracking target expectations with actionable results by comparing one’s own company’s performance with an industry average, a leader within the industry, or a market segment. Benchmarking can help design the trip to meet incremental goals and timelines. From both a travel plan and an entrepreneurial perspective, although benchmarking is used as a control mechanism, we know that situations can arise that require an alteration in the plan, causing the benchmarked items to also need adjustments.
Link to Learning
Which type of benchmarking will help you the most in beginning your entrepreneurial journey? Visit the American Society for Quality’s resource page on benchmarking for help.
To plan for an entrepreneurial journey, you should first conduct some preliminary research regarding your venture idea. Your research must be honest and objective if it is to give you a clear picture of the venture. Next, you might organize and prioritize your research and thoughts. For instance, you might see an idea like yours online or on television, and feel disappointed that someone stole your great idea or beat you to the punch. This is a common occurrence in entrepreneurship, but it should not discourage you. Instead, use that knowledge and energy to find an overlooked or different aspect of your original idea. The difference might even be the focus on a different target market , a specific group of consumers for whom you envision developing a product or service. Further, it is critical to maintain a fluid focus upon expanding the scope of a product or service to uniquely differentiate provisions of benefits apart from existing benefits or those offered by competitors. A focus on a different target market is exactly how the Jitterbug smartphone was created, because it targeted senior citizens. The Jitterbug smartphone offers a larger screen, larger buttons, and simpler features that make it easier for older people to make quick calls or send texts.
Preparation also includes opening space in your life to the time and energy commitment needed to support your new venture. Are the important people in your life willing to support the interest and passion you will need to dedicate the time, energy, and other resources to this new venture? Review the questions shown in ( Figure 2.7 ) to consider your answers to these questions. Preparation through research and other activities is discussed in more detail in Identifying Entrepreneurial Opportunity .
Step 3: Assessment
Now that you have decided where to go for your trip and have gathered information to prepare for it, the next action is to create and set your schedule. This action is simple but critical, because it involves connecting and coordinating information and resources that fit your lifestyle and needs. For example, you might schedule an early-morning Uber or Lyft to the airport and electronic delivery of your plane tickets to your smartphone. For the entrepreneurial journey, this phase might also include recognizing appropriate relationships and gathering needed resources. For many entrepreneurs, the opportunity to receive guidance from trusted advisors or mentors may provide valuable insights on how to manage the process. This step allows for reflection on your idea and intentions. After you’ve done your researching and gathering knowledge about your idea through the preparation step, is the idea still viable? Is the idea still interesting to you? With a better understanding of the industry, your idea, and your own interests that you gained in Step 2, is this idea something that you still want to explore? This step is discussed more fully in Problem Solving and Need Recognition Techniques with deeper coverage on the topic of opportunity recognition ( Figure 2.8 ).
Step 4: Exploring Resources
Regardless of where you might travel, you could not complete your trip without adequate resources such as available financing. There are many ways you might fund a hiking trip: savings, loan, pay-as-you-go, sponsorship (family or friends), or any combination of these options, to name a few. No matter how you finance your trip, it might help to have a balance of available credit and cash on hand to support your day-to-day expenses and any extracurricular activities or even unforeseen emergencies. As discussed in Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting , the US Small Business Administration (SBA) provides funding opportunities.
This scenario is mirrored in the entrepreneurial journey. Just as you wouldn’t begin a trip without adequate resources, including access to cash, you wouldn’t begin your entrepreneurial journey without the necessary resources, including cash. The options between funding a trip and funding a new venture are similar, but they have different names. For example, on a trip, you might use the cash you have on hand, from savings or a personal loan. For an entrepreneurial journey, you might address cash management —management of cash inflows and outflows to support cash needs of the venture—to include bootstrapping , a funding strategy that seeks to optimize use of personal funds and other creative strategies (such as bartering) to minimize cash outflows. (See Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for more information on bootstrapping.) Bootstrapping includes ideas like leasing instead of purchasing, borrowing resources, or trading unneeded resources for needed ones. Another example of cash management includes a business model that offers subscriptions rather than a payment received for an item purchased. Subscriptions provide the entrepreneur with cash up front, with the buyer receiving benefits throughout the year. Consider the example of Amazon. Amazon offers Prime with a yearly subscription service, as well as Subscribe & Save , Amazon Instant Video , Amazon Mom , and Amazon Web Services , all based on a subscription business model.
According to Entrepreneur.com, other potential subscription-based models include services or products geared to older consumers, with 8,000 people turning sixty-five every day. A similar idea offers services to college students. Both ideas would offer family members a subscription that sends monthly gifts or products to either the elderly person or college student. We also see this model offered to pet owners who pay a monthly subscription to receive treats and toys for the family dog. Looking back at Amazon, we see the company offering the ease of repeat purchases for frequently used products such as vitamins and air filters.
Entrepreneur In Action
Prospurly is a subscription-based company that uses Cratejoy ’s subscription platform to sell small-batch artisanal products for bath, body, and home, marketing a natural lifestyle focused on the happiness of living a simple and appreciated life. Conduct your own research on Prospurly and other subscription-based businesses. Read the article, “How I Built a Subscription Business That’s Made over 50k in 6 Months,” on Cratejoy for more information about this company and Prospurly’s move from ideation to profitability.
Other ideas for finding funding include applying for grant funding. The importance of cash and cash management requires in-depth coverage, which is presented in Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting and Business Structure Options: Legal, Tax, and Risk Issues .
The idea of exploring resources includes many other options besides how to fund a new venture. In a trial run , you would offer your product or service for sale within a limited market on a test basis to evaluate what additional resources are needed to support the success of the venture ( Figure 2.9 ). Examples of places where a trial run fits well, depending on your product, include farmers markets, in-home sales, or through friends and family. The idea is to track the feedback you receive about your product or service. How do people react to the price, the quality of the product, the packaging? You can experiment by selecting one variable to adjust—changing the price, the packaging, the sales pitch, the presentation, or the quantity—to track reactions and make improvements based on this feedback. You may then decide to adjust other variables to gather more information, as well as considering what other resources are needed for the success of the new venture. Financing and ideas to preserve your financial stability are discussed more fully in Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting .
Step 5: Business Plan
The ability to travel and visit new locations is a privilege and a great opportunity to gain exposure to new experiences and opportunities. In addition to the work involved in preparing for a trip, the act and process of traveling involves constant decision making to achieve your desired goals and outcomes. For instance, should you travel to one location in Glacier National Park and explore that area in depth? Or should you attempt to visit as many areas of the park as possible with your given resources and abilities?
The challenge at this step of your entrepreneurial journey is to remain focused on managing your resources to meet your goals and outcomes as you write your business plan for your new venture. You will need to focus on the skills, experience, and resources necessary for your venture, and the management and decision making required to ensure success and adjust your plan based on changes and new information. Just as you might find a location in Glacier National Park where you want to stay for a couple of nights, a deviation from your original business plan (discussed in Business Model and Plan ) will also require adjustments and changes based on new information and insights.
Be honest with yourself by running a reality check about your ability to manage a venture, especially from a personal-capacity perspective. For example, if you start a business, will it be a part-time or full-time venture? Will you start while in school? Or will you wait until after graduation? The timing of opening the venture can be the difference between success and failure. Consider the difference between hiking in Glacier National Park in the middle of winter, when the daytime temperature is thirteen degrees below zero, and hiking in the middle of summer, when the daytime temperature is seventy-nine degrees. The timing of your visit to the park is an important part of your enjoyment and success in reaching your destination. In planning for your trip, you would pay attention to your departure time to ensure enjoyment and success in your adventure. Similarly, as part of your business plan, you would also research the best time to open your venture.
Finally, during your travels, getting lost, overwhelmed, or sidetracked is always possible. If you get lost when traveling, you might refer to social navigation apps such as Google Maps , Waze , or HERE WeGo , to find turn-by-turn directions and information. Or you might refer to a weblink, a printed map, or a local expert or guide familiar with the area. The business plan is your map. You should identify decision points and milestones , significant key accomplishments, in your plan. Milestones could include points such as hitting your breakeven point , the point at which income from operations results in exactly enough revenue to cover costs. If the financial projections in your business plan are unattainable, what is your next move within the plan? If you don’t reach the milestones identified in your business plan, what alternative choices can you make to redirect your venture? The business plan, in its first draft, should inform you whether your venture has a chance at success. If there are negative areas, what can you change? Building this plan before starting the business provides you with knowledge and insights about your idea. Make any necessary changes to the plan to strengthen the possibility of success. Then when you open the venture, track whether the reality of the venture aligns with your business plan’s projections and expectations. The business plan functions as both a road map to help you see where you are going next in building your venture and as a checklist to track whether you are on course or need to make adjustments. When entrepreneurs get off track, they can check out self-help websites, speak with a business coach or counselor, or contact local agencies or organizations, including those affiliated with the federal SBA. Organizations that offer free (or low-cost) small business counseling, mentoring, and training, include:
- SCORE (Service Corps of Retired Executives): https://www.score.org/
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): https://www.sba.gov/offices/headquarters/osbdc/resources
- Women’s Business Center (WBC): https://www.sba.gov/local-assistance/find/?type=Women%27s%20Business%20Center&pageNumber=1
- US Export Assistance Center: https://www.export.gov/welcome
- Veterans Business Outreach Center (VBOC): https://veteransoutreachcenter.org/
- Other organizations include locally organized support such as pop-up entrepreneurial schools like PopUp Business School (https://www.popupbusinessschool.co.uk/) and https://www.pbs.org/newshour/show/this-free-program-trains-people-how-to-start-a-business-but-without-debt
These and other resources will be discussed in more depth in Building Networks and Foundations . Look at the review questions and the discussion questions at the end of this section to prepare for creating your business plan. Business plans ( Figure 2.10 ) are discussed more fully in Business Model and Plan .
Step 6: Navigation
Once you’ve completed your trip, reflect on the experiences you had. No matter how well you feel you have planned, there is no way you can prepare for all of the potential challenges, changes, and obstacles that may occur: missed or changed flights, poor weather, an unexpected illness, a trail or road closed for repairs, or sudden good fortune. What parts of the trip went well? If you ran into a problem, how did you handle it? Was the problem something you could have anticipated and planned for? Or was it unexpected? What did you learn from the experience? If you were planning a trip to another national park, what would you do differently in your planning stage? Just as seasoned travelers adjust to their circumstances and learn from their experiences, so should you, as an entrepreneur, learn to adjust by meeting and managing challenges head on.
After completing your business plan, you will probably need to adjust your plan ( Figure 2.11 ). You might decide that you will not have enough resources to survive the time until your venture reaches the breakeven point, or you might determine that the location you selected is no longer available. There are multiple variables that require further exploration and research.
By nurturing an entrepreneurial mindset , you will be better prepared when opportunities, challenges, or obstacles surface. Although you won’t be able to predict or plan for every potential scenario along the entrepreneurial journey, an entrepreneurial mindset helps you to be resourceful when opportunities, challenges, or disappointments occur. By unpacking, or by taking an inventory of your available resources, you can also get a better picture of what you may need to unload, retain, or discard, or even if a new direction is the best course of action. On your entrepreneurial journey, evaluating the experience or situation is a perfect opportunity for you to determine how realistic, overambitious, or shortsighted your dreams and goals for your venture may be. This chapter will explore your vision for your future and your venture. Does your vision include a level of flexibility when you discover new information that supports exploring a new area?
Step 7: Launch
The actual launch is the exciting event when you open your business. By this point, you have made improvements to your product through feedback received in your trial run; you’ve identified the value or benefits provided by your product; you’ve identified your target market; and you’ve identified the location of your launch, whether it is a geographical location or an Internet location.
Inc . magazine provides an analysis of the best locations to launch a new venture, with Austin, Texas, taking the lead (see “Surge Cities: These Are the 50 Best Places in America for Starting a Business,” in Suggested Resources ). Consider your target market and the resources necessary to support your venture when choosing the location for your launch. Advice from within the entrepreneurial world suggests that sometimes the launch should take place “under the radar,” meaning in a location where you can make mistakes, fine-tune your business model and offerings, and even become successful without competitors noticing that you have created a disruption within the industry. (You will learn more about this in Launch for Growth to Success ).
Even as you are launching your venture, many variables will require your attention, just as we covered in Step 7. Navigating through these variables as your venture grows requires constant attention as new potential opportunities arise.
Sixto Cancel and Think of Us
Sixto Cancel successfully faced the harsh challenges of aging out of the foster-care system without adult support or guidance. He imagined a better foster-care system for young people then cofounded the firm Think of Us. Think of Us is a platform that helps young people in foster care build their own personalized digital advisory board of supportive adults who act as a virtual life-coaching group. The adults guide the young people through the foster-care system and ensure that they are able to become independent when they leave the system at age eighteen. For more information about this venture, visit www.thinkof-us.org.
- 1 David Pridham. “Entrepreneurs: Here’s Good News for 2018.” Forbes . 2018. https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidpridham/2018/01/10/entrepreneurs-heres-good-news-for-2018/#660f5ebd6659
- 2 UpWork and Freelancers Union. “Freelancers Predicted to Become the U.S. Workforce Majority within a Decade, with Nearly 50% of Millennial Workers Already Freelancing, annual ‘Freelancing in America’ Study Finds.” UpWork . October 17, 2017. https://www.upwork.com/press/2017/10/17/freelancing-in-america-2017/
- 3 UpWork. “Sixth Annual ‘Freelancing in America’ Study Finds That More People Than Ever See Freelancing as a Long-Term Career Path.” UpWork . October 3, 2019. https://www.upwork.com/press/2019/10/03/freelancing-in-america-2019/
- 4 David Pridham. “Entrepreneurs: Here’s Good News for 2018.” Forbes . 2018. https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidpridham/2018/01/10/entrepreneurs-heres-good-news-for-2018/#660f5ebd6659; Lawrence F. Katz and Alan B. Krueger. “The Rise and Nature of Alternative Work Arrangements in the United States, 1995–2015.” 2016. https://scholar.harvard.edu/files/katz_krueger_cws_final_nov2018.pdf.
- 5 Elka Torpey and Brian Roberts. “Small-Business Options: Occupational Outlook for Self-Employed Workers.” US Bureau of Labor Statistics . May 2018. https://www.bls.gov/careeroutlook/2018/article/self-employment.htm
- 6 Carly Moulton and Dave Cosgrave. “Second Annual Self-Employment Report.” FreshBooks . 2017. https://www.freshbooks.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/2018selfemploymentreport.pdf
- 7 OECD Data. “Self-employment Rate.” OECD.org . n.d. https://data.oecd.org/emp/self-employment-rate.htm.
- 8 Arnobio Molrelix. “The Biggest Reason the U.S. Needs Small Businesses to Thrive Has Nothing to Do with Taxes or the Economy.” Inc ., Dec. 20, 2018. https://www.inc.com/arnobio-morelix/inc-entrepreneurship-index-2018-q3.html
- 9 David Jolley. “America Needs Immigrant Entrepreneurs.” Business Insider . September 5, 2017. https://www.businessinsider.com/america-needs-immigrant-entrepreneurs-2017-9
- 10 Dinah Wisenberg Brin. “Immigrants Form 25% of New U.S. Businesses, Driving Entrepreneurship in ‘Gateway’ States.” Forbes . July 31, 2018. https://www.forbes.com/sites/dinahwisenberg/2018/07/31/immigrant-entrepreneurs-form-25-of-new-u-s-business-researchers/#10ee8099713b
- 11 “Ease of Doing Business Rankings.” Doing Business . May 2019. http://www.doingbusiness.org/en/rankings
- 12 Niels Bosma and Donna Kelley. “Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2018/2019 Global Report.” GEM Consortium . January 21, 2019. https://www.gemconsortium.org/report/50213
- 13 Gary Stockton. “Statistics and Obstacles Facing Women Entrepreneurs.” Experian . January 29, 2018. http://www.experian.com/blogs/small-business-matters/2018/01/29/statistics-and-obstacles-facing-women-entrepreneurs/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/2-1-overview-of-the-entrepreneurial-journey
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Entrepreneurial Educational Website
Entrepreneurial Process: Meaning, Overview & Stages – Embarking on the journey of entrepreneurship is like setting sail on uncharted waters. Understanding the entrepreneurial process is akin to having a reliable compass in hand. The intricacies of this venture creation process have become a focal point in the realm of current entrepreneurship. where budding entrepreneurs are on the cusp of turning their ideas into reality. This process is a fascinating terrain to explore, let’s see why it is.
What is the Entrepreneurial Process
The entrepreneurial process is the sequence of steps and activities involved in starting and managing a new venture. It encompasses the identification of opportunities, gathering resources, creating a business plan, launching the venture, and managing its growth and development.
The entrepreneurial process is a thrilling journey filled with opportunities and challenges. It’s about spotting a chance, seizing it with a solid plan, and then creating value that keeps customers coming back for more. It’s where ideas take flight and become thriving ventures that make a difference in the market.
Learn more about Corporate Entrepreneurship – Click here
Stages of the Entrepreneurial Process
We label the first level of the technique opportunity recognition. The invention and assessment of opportunities are part of this technique. Inside the possibility reputation system, initial ideas evolve into fully-fledged enterprise opportunities .
Inside the second stage, ‘opportunity exploitation’, important sources are combined to enable exchange with the market. The acknowledged commercial enterprise opportunity is translated into an actual resource.
When the imparting is taken up with the aid of the market inside the third stage. The possibility of exploitation ended with the advent of value. We use the expression value creation in place of wealth creation to stress the feasible non-economic outcomes of the entrepreneurial process. The advent of cost seems because of the final result of the entrepreneurial system. The process seems to be linear and sequential, whereas, in reality, it is dynamic and iterative.
Let’s discuss the stages of the entrepreneurial process one by one.
01. Opportunity Recognition in Entrepreneurial Process
The process of opportunity recognition begins with an initial idea, which can come from employment, hobbies, social encounters, or observation. Entrepreneurs often seek opportunities for dissatisfaction and are subconsciously motivated by their talents, environmental context, and societal values. A preliminary idea is crucial for the entrepreneurial process, which involves full-scale development, and social, cultural, and personal elements.
The idea is evaluated and refined until it becomes a complete business opportunity. The process is evolutionary and iterative, involving cognitive sports, data accumulation, and idea introduction. The goal is to overcome expected challenges and maximize potential advantages.
- Information Scanning
- Thinking through Talking
- Information Seeking
- Assessing Resources
Through these activities, the preliminary concept is evolved and evaluated into a complete-fledged commercial enterprise opportunity. The evaluation of possibilities, in the course of the filtration or screening system, is a vital step inside the system of growing preliminary ideas into commercial enterprise opportunities.
The new breed of entrepreneurship – Click here
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Opportunity Recognition Process
Entrepreneurship is a crucial factor in recognizing opportunities. Historically, the reason for entrepreneurship was attributed to psychological development. Mental studies can be divided into two groups: identifying entrepreneurial personality traits and examining socio-mental or socio-cultural factors. Socio-cultural attributes, such as ethnicity, gender, and family background, can influence entrepreneurial behavior. Existence-direction changes, such as job loss or cultural influences, can lead to business formation.
However, the effect of personality on entrepreneurial behavior remains inconclusive. Recent research has focused on differences in understanding, statistics, and cognitive behavior, highlighting the importance of prior knowledge and experience in entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurial alertness is also important, as entrepreneurs today interpret statistics differently than executives.
Businessman vs entrepreneur – Click here
The Role of The Environment in the Opportunity Recognition Process
The environment significantly influences the opportunity recognition process, with social contexts playing a crucial role in determining the success of entrepreneurial opportunities. Marketers use their networks to gather information. They gather statistics and access resources and information. To increase their possibilities, entrepreneurs interact with the community. Socioeconomic, cultural, technical, and political issues all have an impact on their success. Technological advancements and favorable political conditions can also stimulate entrepreneurs to start businesses.
02. Opportunity Exploitation in Entrepreneurial Process
Opportunity exploitation is a crucial phase in the entrepreneurial process, involving the transition from idea to concrete business concept, the quest for control, commitment to exploitation, modes of exploitation, factors influencing the decision, resource gathering and integration, and the role of networking. Entrepreneurs must identify specific resource requirements and find potential providers, then engage in strategic maneuvers to obtain these resources. Social networking plays a pivotal role in this process, as entrepreneurs act as organizers and coordinators of resources.
Opportunity exploitation is the bridge between ideation and market success, involving resource gathering, strategic networking, and the transformation of ideas into real-world solutions. The choices made during this phase can determine whether a new business is born or an existing one evolves to seize a fresh opportunity. It’s the heart of entrepreneurship, where ideas become action, and innovation meets the marketplace.
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Opportunity Exploitation Process
Opportunity exploitation in entrepreneurship involves turning potential into tangible products or services. The entrepreneur’s mental attributes, such as risk aversion and prior experience, are crucial in recognizing and exploiting opportunities. Knowledge and experience are key, as they provide insights and expertise needed to make ventures a reality.
Successful entrepreneurs are action-oriented, taking action to turn their ideas into tangible businesses. Information processing styles also play a role in entrepreneurship, with creative individuals better equipped to build a resource base. For example, Alice, a risk-taker with experience in the sustainability industry, sees an opportunity in the growing demand for eco-friendly products. Her creative thinking helps her find unique ways to build her resource base.
The Role of The Environment in the Opportunity Exploitation Process
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship, the environment in which an entrepreneur operates plays a dual role in the opportunity exploitation process. An entrepreneur’s network is a valuable resource, providing access to financial capital, emotional support, valuable information, and advice. The competitive landscape also plays a crucial role in entrepreneurship, with a favorable environment and high demand enabling entrepreneurs to exploit opportunities. Timing matters also play a role, with the age of technology and the competitive landscape influencing opportunity exploitation.
In industries with infancy, innovation is abundant, and lower competition and opportunity costs can be game-changers. For example, Sarah, an entrepreneur with a passion for sustainable fashion, can leverage her network to access investors and gain valuable insights into the eco-friendly textile market. This combination of resources and timing provides a strong foundation for success in the market.
Model of the opportunity exploitation process
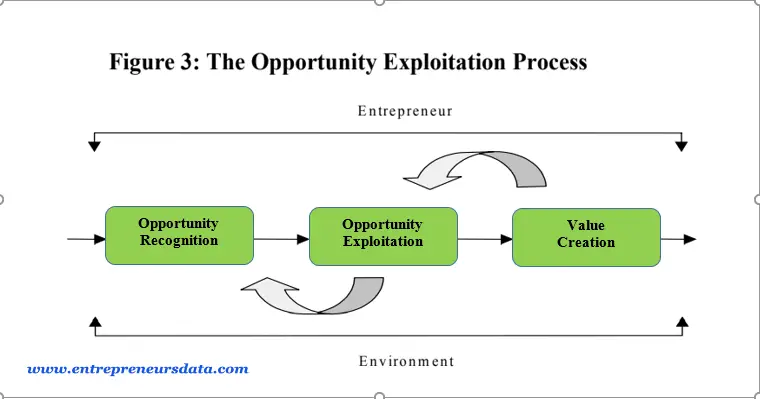
The “opportunity exploitation process” is a crucial phase in the entrepreneurial journey, involving the transformation of a promising business opportunity into a practical business concept. This process includes translating the idea into a complete package, including resources, organizational structure, products or services, and a marketing plan. The entrepreneur plays a pivotal role in driving this transformation. They shape the business concept and set it on the path to success. The environment also plays a significant role, in providing support, resources, and competition. Entrepreneurs must be flexible and pivoting in times of challenges.
03. Value Creation in Entrepreneurial Process
Value creation is a crucial aspect of the entrepreneurial process, as it drives the journey, motivates everyone involved, and serves as a catalyst for future entrepreneurship. The perceived value created through opportunity exploitation motivates entrepreneurs customers, and even potential investors.
The outcomes of the entrepreneurial process can shape the future, as lessons learned and experiences gained to contribute to the development of human and intellectual capital. Even failures can be valuable lessons, leading to new insights, strategies, and innovative ideas. Therefore, value creation is not just about the present but also a driving force in shaping the future of entrepreneurship.
Did you know the “Difference between Businessman and Entrepreneur” – Click here
Levels and Types of Value Creation
Value creation in the realm of entrepreneurship isn’t a one-dimensional concept; it operates on multiple levels and takes various forms. Entrepreneurship impacts both personal and societal levels, with entrepreneurs seeking to accumulate wealth for personal success. This can stimulate economic growth, create new markets, and generate employment, contributing to society’s betterment. However, not all forms of wealth creation lead to societal benefits, such as organized crime or rent-seeking.
Entrepreneurial activities can also trigger changes within specific industries and regional economies. Different forms of value emerge. Including economic, non-economic, positive, negative, immediate, or long-term. Entrepreneurial opportunities can have a spectrum of outcomes, from success to failure.
The Role of The Entrepreneur in the Value Creation Process
The role of the entrepreneur in the value-creation process is a complex interplay of various factors. Let’s dissect this intricate relationship.
1. Ambiguous Impact of Personality
Studies on the direct influence of an entrepreneur’s personality on value creation have shown contradictory findings. Although personality qualities are undoubtedly important, the relationship is not simple. The entrepreneur’s personality can influence value creation, but this influence is often mediated by user behavior and external factors.
2. The Mediating Factors
An entrepreneur’s abilities and personality traits, such as creativity and strategic thinking, indirectly affect value creation. This influence is channeled through their work approach and focus. High-performing entrepreneurs, those driving successful firms, tend to concentrate on strategic tasks that drive sales growth, rather than getting bogged down in operational details.
3. The Critical Evaluation
At a certain juncture, the entrepreneur must evaluate the progress of opportunity exploitation. This involves weighing the expected payoffs against the results achieved. Based on this evaluation, the entrepreneur may decide to continue, pivot, or even abandon the venture. The decision to exit or continue is deeply linked to the company’s financial performance and a predefined performance threshold.
4. Exit Strategies
In the entrepreneurial world, exits are not uncommon. Even when a venture is performing well, entrepreneurs may decide to exit the stage. They might opt to sell the business. Also, aiming to capitalize on its value, as was seen during the dot-com boom. Different exit strategies, such as Initial Public Offerings or mergers and acquisitions, are often considered.
5. Succession and Organizational Mortality
However, the exit of the founding entrepreneur, especially in a relatively young company, can pose a significant challenge. It may lead to a succession problem, potentially threatening the organization’s survival. This challenge can result in organizational mortality, where the company struggles to find suitable leadership to carry it forward.
Corporate entrepreneurship – Click here
This exploration of the entrepreneurial process delves into its fundamental elements, from idea initiation to thriving venture creation. Successful entrepreneurship is a dynamic interplay between an entrepreneur’s unique characteristics and the environment. It’s an art and science, blending individual ingenuity and environmental dynamics. Understanding this journey helps entrepreneurs navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and shape the future of business and society.
FAQs on Entrepreneurial Process
What is the entrepreneurial process.
The entrepreneurial process is the series of steps and activities involved in starting and managing a new business. It includes opportunity identification and resource acquisition. Also, business plan creation, venture launch, and growth and development management.
Why entrepreneurship is a process?
Entrepreneurship is a process because it is not a single event. It is a journey that requires continuous learning. Also, adaptation, and growth. Entrepreneurs must be able to identify opportunities and develop products or services. Then they can meet those opportunities, and then successfully launch and manage their enterprises. The entrepreneurial process is complicated and challenging. It is also one that can be very rewarding.
What are the four (4) aspects of the entrepreneurial process?
The entrepreneurial process has four aspects.
- The capacity to spot market issues or unmet wants that a new good or service may solve is known as opportunity identification.
- The capacity to create and carry out a strategy to take advantage of a chance that has been recognized is known as opportunity exploitation.
- Value creation is the process of creating and delivering goods or services that buyers are prepared to pay for.
- The capacity to get the resources required to launch and run a firm, including cash, personnel, and tools, is known as resource acquisition.
What are the three (3) major parts of the entrepreneurial process?
The three major parts of the entrepreneurial process are:
A. Opportunity Recognition
Entrepreneurial traits and experiences influence identifying untapped market needs, while the entrepreneurial ecosystem provides necessary support, resources, and networks for successful opportunity recognition.
B. Opportunity Exploitation
Opportunity exploitation involves entrepreneurs identifying and utilizing identified opportunities, leveraging resources, and leveraging the environment to access capital, markets, and support. This process involves a step-by-step journey from idea inception to product creation.
C. Value Creation
The value-creation process involves entrepreneurs shaping products and services to cater to customer needs, transforming societal levels from personal wealth to broader economic impact.
What are the six steps in the entrepreneurial process
The six steps in the entrepreneurial process are
- Idea generation – It is the process of coming up with novel business ideas.
- Opportunity evaluation – This is the process of considering the viability of business ideas.
- Business planning – This is the process of developing a roadmap for how the firm will be launched and operated.
- Resource acquisition – This is the process of collecting the resources required to start and operate the business.
- Venture launch – This is the process of getting the business to market.
- Growth management – This is the procedure of growing and extending the business.
Related Posts

Fabian Entrepreneurship: Meaning, Characteristics & Examples
- Uncategorized

Imitative Entrepreneurship: Meaning, Characteristics & Examples

20 Common Myths about Entrepreneurs & Entrepreneurship

How OCR Tools Are Transforming Business Operations
Very valuable full detail article
Thank you for your valuable comment. subscribe our website to learn more about entrepreneurship.
[…] per term or a combined term of entrepreneurship or an entrepreneur. Because it is the spark process of entrepreneurship or an entrepreneur, it is a changing process that ends with some world-changing […]
[…] Read Entrepreneurial Process – Click here […]
[…] Read entrepreneurial process – Click here […]
[…] Entrepreneurial Process – Click here […]
[…] core components of the entrepreneurial process—identifying a chance, looking for it, and deciding to take advantage of it—are the focus of […]
[…] the entrepreneurial process, collective dimensions take precedence over individual dimensions, and the percentage of new […]
[…] Read – Entrepreneurial Process […]
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Trending now

- Entrepreneurship
- Organizational Behavior
- Financial Management
- Communication
- Human Resource Management
- Sales Management
- Marketing Management
Stages of Entrepreneurial Process
- by Anuj Kumar
- 18 September 2023 18 September 2023
The entrepreneurial process is a leadership function that centers around the dynamics of entrepreneurial growth and change. It is a process comprising several distinct stages.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 Exploring Entrepreneurial Context
- 1.2 Identifying Opportunities
- 1.3 Starting Venture
- 1.4 Managing Venture
- 1.5 Choosing Competitive Strategy
- 2.1 What are the stages of the entrepreneurial process?
Entrepreneurial Process
From exploring the various aspects of the entrepreneurial context to identifying opportunities, starting and managing the entrepreneurial venture , and choosing the competitive strategy in action. Let’s look at each of these decisions and activities and the following are the stages of the entrepreneurial process:

Exploring Entrepreneurial Context
Why is it important to look at the entrepreneurial context? Because the context determines the “rule” of the game and what decisions are likely to be successful. The context includes the realities of the new economy, society’s laws and regulations that compose the legal environment , and the realities of the changing world of work.
Entrepreneurs should be aware of the context within which entrepreneurial decisions are made. Only through exploring the context can entrepreneurs discover the untapped opportunities and competitive advantage(s) that may lead to the development of a potentially successful entrepreneurial venture.
Identifying Opportunities
A crucial aspect of the entrepreneurial process is identifying opportunities. What are opportunities? These opportunities are positive external trends or changes that provide unique and distinct possibilities for innovating and creating value. There are thousands of opportunities available to an entrepreneur .
Some of them are not real opportunities with high potential. Some opportunities have growth prospects. Entrepreneurs search for profitable ones and then select an attractive business opportunity.
However, just identifying an opportunity isn’t enough. The entrepreneurial process also involves pinpointing a possible competitive advantage. A competitive advantage is what sets an organization apart; it’s an organization’s competitive edge. Having a competitive advantage is crucial for an organization’s long-term success and survival.
Starting Venture
Once entrepreneurs have explored the external context and identified possible opportunities and competitive advantage(s), they must look at the issues involved with actually starting up their entrepreneurial venture.
Included in this phase of the entrepreneurial process are the following activities; researching the feasibility of the venture, planning the venture, organizing the venture, and launching the venture. Financial, physical, and managerial resources must be collected to launch the venture.
Managing Venture
Once the entrepreneurial venture is up and running the next step in the entrepreneurial process is managing the venture. An entrepreneur also must effectively manage the venture by managing processes, managing people, and managing growth. This requires the talents of leading, decision-making, executing, controlling , and various managerial skills.
Choosing Competitive Strategy
Once the entrepreneurial venture is up and running, the last step is to choose the competitive strategy. Peter Drucker mentions the following specific entrepreneurial strategies. These are
- Being fastest with the most.
- Creative imitation.
- Entrepreneurial judo.
- Finding and occupying a specialized ecological niche.
- Changing values and characteristics by creating utility, by delivering what represents true value to the customer, by adopting the customer’s social and economic reality, and by appropriate pricing .
FAQs About the Entrepreneurial Process
What are the stages of the entrepreneurial process.
The stages of the entrepreneurial process are: 1. Exploring Entrepreneurial Context 2. Identifying Opportunities 3. Starting Venture 4. Managing Venture 5. Choosing Competitive Strategy.
Related posts:
- 10 Main Factors Affecting Entrepreneurial Growth
- Essential Traits: 14 Characteristics of Entrepreneur
- 3 Major Theories of Entrepreneurship | Explained
- Entrepreneurial Venture
- How To Get Startup Ideas? 10 Ways Get Startup Ideas
- National Policy on Skill Development NSPD: Policy Framework, Institutions in Aid Development
- District Industry Centre: Objectives, 15 Functions, Schemes, Entrepreneurship Development
- 9 Important Benefits of Entrepreneurship
- 13 Major Limitations of Entrepreneurship
- 15 Personality Traits of an Entrepreneur
- 5 Types of Entrepreneurs Based on Business
- 5 Needs of Maslow Need Hierarchy Theory
- Classification of Projects and Importance
- 8 Stages of Project Report | Explained
- Elements of TQM | Total Quality Management | Explained


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1.5: The Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 73816
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas, which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch, without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections (Figure 5.1.5.1). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.

Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap, that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the co-founder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew. “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse, and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
LINK TO LEARNING
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA). The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan
As the name implies, the executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions, requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. Its suggested sections are shown in Table 5.1.5.1.
ARE YOU READY?
Create a Brief Business Plan
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs, one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 5.1.5.2 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and ensure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 5.1.5.3 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM. This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 5.1.5.4 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 5.1.5.2 and Figure 5.1.5.3. A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.

Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 5.1.5.5 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 5.1.5.6 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture. Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements, a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing. Figure 5.1.5.4 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.

ENTREPRENEUR IN ACTION
Laughing Man Coffee
Hugh Jackman (Figure 5.1.5.5) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.

A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
WHAT CAN YOU DO?
Textbooks for Change
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
WORK IT OUT
Franchisee Set Out
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup. 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan ...
Provide projections for two to four years in the future, including: 1. Forecasted income (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 2. Forecasted cash flows by month (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 3. Forecasted balance sheet for all years (year-end), and. 4.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
7 Entrepreneurial Process. 7. Entrepreneurial Process. Successful entrepreneurship occurs when creative individuals bring together a new way of meeting needs and or wants. This is accomplished through a patterned process, one that mobilizes and directs resources to deliver a specific product or service to those in a way that is financially viable.
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
MacMillan: The idea of the business plan is to convince the stakeholders. First, what we need to do in a business plan is show that we understand the needs — the unmet needs — of potential ...
Entrepreneurial ventures can be start-ups or occur within large companies. Entrepreneurship is an innovation process that mobilizes people and resources. Key to entrepreneurial success is the fit among the entrepreneur/team, the product concept, the opportunity, the resources, and the entry strategy.
A business plan's highest purpose is to guide entrepreneurs in operating their business on the day-to-day level. It is a foundational document that I think of as the constitution of your business. It tells you everything you need to know about your idea, your goals, your strategy, and the financial picture of a business.
a full business plan should be written at the beginning of the entrepreneurial process. false. a business plan is important not just for outside investors and suppliers, but also current and potential employees. true. the process of writing a business plan is NOT as valuable as the plan itself.
Entrepreneurs who write business plans are more likely to succeed, according to our research, described in an earlier piece for Harvard Business Review. But while this might tempt some ...
Developing a Business Plan. This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan. Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business ...
Add in the company logo and a table of contents that follows the executive summary. 2. Executive summary. Think of the executive summary as the SparkNotes version of your business plan. It should ...
A systematic approach to writing and rating entrepreneurial business plans. The Journal of Private Equity, 9 (3), 7-23. This page titled 3.2: Entrepreneurial Process is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Katherine Carpenter via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the ...
In the planning phase you will need to create two things: strategy and operating plan. 4. Company formation/launch: Once there is a sufficiently compelling opportunity and a plan, the entrepreneurial team will go through the process of choosing the right form of corporate entity and actually creating the venture as a legal entity. 5.
Introduction; 10.1 Launching the Imperfect Business: Lean Startup; 10.2 Why Early Failure Can Lead to Success Later; 10.3 The Challenging Truth about Business Ownership; 10.4 Managing, Following, and Adjusting the Initial Plan; 10.5 Growth: Signs, Pains, and Cautions; Key Terms; Summary; Review Questions; Discussion Questions; Case Questions; Suggested Resources
02. Opportunity Exploitation in Entrepreneurial Process. Opportunity exploitation is a crucial phase in the entrepreneurial process, involving the transition from idea to concrete business concept, the quest for control, commitment to exploitation, modes of exploitation, factors influencing the decision, resource gathering and integration, and the role of networking.
After that, the plan should be thoroughly proofread and revised to ensure that all errors are eliminated before the plan is used. After writing a customizedletter of transmittal to introduce the plan, it can be put to use. This page titled 1.7: Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored ...
Entrepreneurial Process. From exploring the various aspects of the entrepreneurial context to identifying opportunities, starting and managing the entrepreneurial venture, and choosing the competitive strategy in action. Let's look at each of these decisions and activities and the following are the stages of the entrepreneurial process:
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is part of the entrepreneurial discovery process? A. Discovering different businesses B. Raising start-up capital C. Finding partners D. Recognizing a need or want not being met, Which of the following is described in the operations section of a business plan? A. Trade area analysis B. Business location C ...
Why should the executive summary, which is the first things that appears in a business plan, be written last? Because it is a summary of the whole business plan, which will evolve as it is written. You don't know everything at the outset and do not want to risk to write the plan fitting the summary rather than a summary that fits the plan.
There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup. His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch, without the detail of a full business plan.
summary, full, operational. Summary business plan. 10-15 pages. Works best for new ventures in the early stages of development. Full business plan. 25-35 pages. Works best for new ventures that are at a point where they need funding; serves as a blueprint. Operational business plan. 40-100 pages.