- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1 million entrepreneurs and business owners write business plans. These plans have been used to raise funding and grow countless businesses.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
From working with all these businesses, we know what the 10 elements in any great business plan. Providing a comprehensive assessment of each of these components is critical in attracting lenders, angel investors, venture capitalists or other equity investors.
Get started with a title page that includes your company name, logo and contact information, since interested readers must have a simple way to find and reach out to you. After that be sure to include the 10 parts of a business plan documented below.
What are the 10 Key Components of a Business Plan?
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company’s mission statement and description of the products and services. It’s recommended by me and many experts including the Small Business Administration to write the executive summary last.
The executive summary must communicate to the prospective investor the size and scope of the market opportunity, the venture’s business and profitability model, and how the resources/skills/strategic positioning of the company’s management team make it uniquely qualified to execute the business plan. The executive summary must be compelling, easy-to-read, and no longer than 2-4 pages.
2. Company Analysis
This business plan section provides a strategic overview of the business and describes how the company is organized, what products and services it offers/will offer, and goes into further detail on the business’ unique qualifications in serving its target markets. As any good business plan template will point out, your company analysis should also give a snapshot of the company’s achievements to date, since the best indicator of future success are past accomplishments.
3. Industry or Market Analysis
This section evaluates the playing field in which the company will be competing, and includes well-structured answers to key market research questions such as the following:
- What are the sizes of the target market segments?
- What are the trends for the industry as a whole?
- With what other industries do your services compete?
To conduct this market research, do research online and leverage trade associations that often have the information you need.
4. Analysis of Customers
The customer analysis business plan section assesses the customer segment(s) that the company serves. In this section, the company must convey the needs of its target customers. It must then show how its products and services satisfy these needs to an extent that the customer will pay for them.
The following are examples of customer segments: moms, engaged couples, schools, online retailers, teens, baby boomers, business owners, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of business you operate as different segments often have different needs. Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. With regards to psychographic variables, discuss whether your customers have any unique lifestyles, interests, opinions, attitudes and/or values that will help you market to them more effectively.
5. Analysis of Competition
All capable business plan writers discuss the competitive landscape of your business. This element of your plan must identify your direct and indirect competitors, assesses their strengths and weaknesses and delineate your company’s competitive advantages. It’s a crucial business plan section.
Direct competitors are those that provide the same product or service to the same customer. Indirect competitors are those who provide similar products or services. For example, the direct competitors to a pizza shop are other local pizza shops. Indirect competitors are other food options like supermarkets, delis, other restaurants, etc.
The first five components of your business plan provide an overview of the business opportunity and market research to support it. The remaining five business plan sections focus mainly on strategy, primarily the marketing, operational, financial and management strategies that your firm will employ.
6. Marketing, Sales & Product Plan
The marketing and sales plan component of your business plan details your strategy for penetrating the target markets. Key elements include the following:
- A description of the company’s desired strategic positioning
- Detailed descriptions of the company’s product and service offerings and potential product extensions
- Descriptions of the company’s desired image and branding strategy
- Descriptions of the company’s promotional strategies
- An overview of the company’s pricing strategies
- A description of current and potential strategic marketing partnerships/ alliances
7. Operations Strategy, Design and Development Plans
These sections detail the internal strategies for building the venture from concept to reality, and include answers to the following questions:
- What functions will be required to run the business?
- What milestones must be reached before the venture can be launched?
- How will quality be controlled?
8. Management Team
The management team section demonstrates that the company has the required human resources to be successful. The business plan must answer questions including:
- Who are the key management personnel and what are their backgrounds?
- What management additions will be required to make the business a success?
- Who are the other investors and/or shareholders, if any?
- Who comprises the Board of Directors and/or Board of Advisors?
- Who are the professional advisors (e.g., lawyer, accounting firm)?
9. Financial Plan
The financial plan involves the development of the company’s revenue and profitability model. These financial statements detail how you generate income and get paid from customers,. The financial plan includes detailed explanations of the key assumptions used in building the business plan model, sensitivity analysis on key revenue and cost variables, and description of comparable valuations for existing companies with similar business models.
One of the key purposes of your business plan is to determine the amount of capital the firm needs. The financial plan does this along with assessing the proposed use of these funds (e.g., equipment, working capital, labor expenses, insurance costs, etc.) and the expected future earnings. It includes Projected Income Statements, Balance Sheets (showing assets, liabilities and equity) and Cash Flow Statements, broken out quarterly for the first two years, and annually for years 1-5.
Importantly, all of the assumptions and projections in the financial plan must flow from and be supported by the descriptions and explanations offered in the other sections of the plan. The financial plan is where the entrepreneur communicates how he/she plans to “monetize” the overall vision for the new venture. Note that in addition to traditional debt and equity sources of startup and growth funding that require a business plan (bank loans, angel investors, venture capitalists, friends and family), you will probably also use other capital sources, such as credit cards and business credit, in growing your company.
10. Appendix
The appendix is used to support the rest of the business plan. Every business plan should have a full set of financial projections in the appendix, with the summary of these financials in the executive summary and the financial plan. Other documentation that could appear in the appendix includes technical drawings, partnership and/or customer letters, expanded competitor reviews and/or customer lists.
Find additional business plan help articles here.
Expertly and comprehensively discussing these components in their business plan helps entrepreneurs to better understand their business opportunity and assists them in convincing investors that the opportunity may be right for them too.
In addition to ensuring you included the proper elements of a business plan when developing your plan always think about why you are uniquely qualified to succeed in your business. For example, is your team’s expertise something that’s unique and can ensure your success? Or is it marketing partnerships you have executed? Importantly, if you don’t have any unique success factors, think about what you can add to make your company unique. Doing so can dramatically improve your success. Also, whether you write it on a word processor or use business plan software , remember to update your plan at least annually. After several years, you should have several business plans you can review to see what worked and what didn’t. This should prove helpful as you create future plans for your company’s growth.
Download The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan Here
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Stephen Armstrong

How VC firm Index Ventures is hunting for the next Deliveroo
In the 90s, Neil Rimer returned from the US to Geneva to help his father Gerald exit his Swiss-bond-trading firm, Index Securities. He spotted the fledgling European startup scene and, in 1996, founded Index Ventures with his brother David and ex-McKinsey & Company consultant Giuseppe Zocco - long before most Europeans understood what venture capital was. "We started every meeting with a slide that asked, 'What is Venture Capital?'" he says.
A London office followed in 2002 and, ahead of the European VC curve, Index backed companies including Skype, Just Eat, Deliveroo, Supercell, Adyen and TransferWise. US investments include companies such as Dropbox and Slack. "We have 20 years of operating history in Europe, so we have a bigger associated pool of founders and folks who have been part of the Index family," explains Ilya Fushman, a partner at the San Francisco office. "In the US we operate with more hustle and sweat equity."
Read more: How do you spend the first hour of your working day?
Since opening its US office in San Francisco in 2011, however, the company's approach has been more global. Today, 35,000 people work across 24 countries for Index-backed companies, generating close to $10 billion (£7.7bn) in combined annual revenue. In February 2016, Index announced it had raised funds totalling $1.25 billion, split $550 million for seed and first-round funding - roughly seven in ten of the firm's deals - and $700 million for later-stage investments. Most of the funds will be spread equally across Europe and the US, with Australia leading the other territories.
At the company's weekly meetings to decide on investments, every partner in every office has an equal say. "We have all either lived or worked or studied on both sides of the Atlantic," says Jan Hammer, one of the company's London-based partners.
Having focused on tech and life sciences for its first 20 years, the company spun the latter business out into Medicxi Ventures, a standalone life-sciences-investment firm, in 2016. Today, Index partners are particularly interested in security, augmented reality and virtual reality, work and fintech. "Soon, somebody will build the Google for knowledge workers and the Amazon of consumer financial services," Hammer says. "And we have an idea who that might be."
Facebook content
This content can also be viewed on the site it originates from.
Partner, San Francisco
"The core challenge for enterprises today is productivity. I am excited by what could be a foundational technology called extended Berkeley Packet Filter. It allows the real-time, high-fidelity collection of events and metrics from a variety of systems. It's three to five years away and likely to be an enabling tech that not a lot of people talk about, but it's so powerful."
"From Dropbox to Slack, the way people work is fundamentally changing. However, there are still too many industries and processes that are paper-based and offline. In retail, for instance, workers still communicate mainly in the written word. There are huge opportunities for startups fundamentally transforming those sectors by changing their underlying infrastructure."
Principal, London
"I'm a growth-stage investor and I'm tracking Series A companies in healthcare and agricultural tech. There's huge long-term need for the world to produce more food more efficiently, so I think we'll see a tranche of ag-tech companies moving into the growth stage in maybe two to three years' time. There are real and urgent problems to solve."
Principal, San Francisco
"Mobile is connecting an audience we'd traditionally classify as low- or middle-income - the average household. Historically, startups have focused on over-served major urban areas. We'll see entrepreneurs who service the average consumer, making things cheaper through advances in logistics, automation and economies of scale."
Partner, London
"People say mobile is saturated, but there are opportunities in areas such as fintech, food and healthcare. These are tricky to navigate, but the prizes are large. Sweden in particular is ahead of the curve in fintech and healthcare, with experienced founders having strong consumer mobile experience and a government that is forward-thinking."
"Index is multicultural by design; for businesses today to succeed, they have to be born global. It is very important to have diversity of thought, as well as diversity in your team. I'm bullish on Brexit. I believe that entrepreneurs will always find ways to be creative, but what I would hate to see is a reduction in the mobility of talent on either side of the Atlantic."
This article was originally published by WIRED UK

By Carlton Reid

By Will Knight

By Steven Levy

By Celia Ford
Will Knight
Steven Levy

Joel Khalili

Brian Barrett

Brendan I. Koerner

Paresh Dave

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Index Ventures Has Been on a Run. Now It’s Raising Funds to Keep It Up.

By Michael J. de la Merced
- July 9, 2018
Get the DealBook newsletter to make sense of major business and policy headlines — and the power-brokers who shape them. __________
LONDON — When Adyen, a Dutch financial payments processor, began trading publicly last month — and nearly doubled its stock price on its first day — partners at Index Ventures had reason to cheer.
It was the second investment by the venture capital firm to cash out in a short time. Just a month earlier, the European mobile payments company iZettle was sold to PayPal for $2.2 billion, or nearly double what that the start-up had hoped to fetch in its own initial public offering.
Index, founded in Switzerland in 1996 and now based in London and San Francisco, is trying to seize on the moment and amass more financial firepower.
The firm plans to disclose on Monday that it has raised $1.65 billion for its two newest funds: $650 million for its early-stage investment fund, and $1 billion for a so-called growth fund that invests in slightly older companies.
Those figures are up slightly from the $550 million that the firm raised in early 2016 for its last early-stage fund and $700 million for the later-stage round.
The new funds, raised in a matter of weeks, are meant to help Index continue its recent roll, one that has impressed its investors.
“When you find a venture fund that we will back in successive iterations, it tends to be because they’ve figured out that formula or magic where they’re investing early in transformative companies,” said Kathryn Mayne, a managing director at Horsley Bridge Partners, which has invested in every Index fund since 2005.
To be clear, Index does not have the name recognition of Silicon Valley’s biggest boldface names, like Sequoia Capital, Kleiner Perkins or Benchmark Capital. Nor does it have the firepower at the command of those firms: Sequoia, for instance, is reportedly raising $8 billion for its latest fund, and SoftBank’s Vision Fund has nearly $100 billion to spend. (Partners at Index argue that they are not interested in competing with those titans.)
And while Index has had a remarkable run so far this year — in addition to Adyen and iZettle, it was an early backer of the file-sharing company Dropbox, which went public in March, and the speaker company Sonos, which just filed for an initial offering — repeating that performance will be difficult.
But Index has come a long way since 1996, when it was founded as a way to import Bay Area-style venture capital to Europe. It has become one of the top European venture capital firms, investing in start-ups like Skype and the food delivery provider Deliveroo.
And since it opened an office in San Francisco in 2011, it has gained more recognition in the United States by investing early in start-ups like Dropbox. (One of its San Francisco-based partners, Danny Rimer, ranked 17th on a list of the top 100 venture investors from 2009 through March compiled by CB Insights in partnership with The New York Times.)
Still, among the big selling points for Index — both to investors in its funds and to the entrepreneurs it hopes to back — is its international reach and outlook. (Executives speak often of their staff members’ 17 passports and 20 languages.)
“What’s important is how fluent entrepreneurs are about their international opportunities,” Mr. Rimer said in an interview. “They have to win globally from Day 1.”
Drew Houston, chief executive of Dropbox, in which Index invested in 2012, asked for help moving into international markets, with Index helping to introduce the company to European cellphone carriers to create partnerships.
“We were really interested in global expansion,” Mr. Houston said in a telephone interview. “By starting in Europe, they bring that global perspective first.”
And Vladimir Tenev, the chief executive of the online financial brokerage app Robinhood, said he regularly asks the Index partner Jan Hammer, who gave him his first venture financing, for thoughts on political developments that could affect regulation of companies like his.
Meanwhile, Index said that its global perspective helped it recognize early the potential for Bird, one of the big electric scooter sharing companies. Martin Mignot, a London-based partner, said that the success of similar businesses in Europe persuaded the firm to be an early backer and take part in the company’s Series B round in March at a $400 million valuation .
Bird raised money again last month at an enormous $2 billion valuation , with Index again participating.
With the new fund, Index’s partners plan to do more of what they’re already doing: being among the first investors in companies, rather than trying to follow rivals into ever-bigger investments.
“We’re sticking to our knitting,” Mr. Hammer said.
Follow Michael J. de la Merced on Twitter: @m_delamerced .
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Trump’s Financial Future: Donald Trump has treated Trump Media, which runs his social network Truth Social, as a low-cost sideshow. Now a big portion of his wealth hinges on its success .
Who Is Satoshi Nakamoto?: For years, an Australian cryptocurrency enthusiast claimed to be the mysterious creator of Bitcoin. Then the courts got involved .
Renting Forever: Either by choice or because they are priced out of the market, many people plan to never stop renting. Building wealth without home equity requires a different mind-set .
BlackRock Without Larry Fink: Investors in the world’s biggest asset manager are asking how much more room it has to grow and who will drive that growth once its chief executive retires .
MSNBC’s Leftward Tilt: Leaders at NBC have been forced to grapple with how to square its cable news network’s embrace of progressive politics with the company’s straight-news operation.
Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Venture Capital Business Plan: A Guide for Entrepreneurs
Published Aug.01, 2023
Updated Apr.24, 2024
By: Alex Silensky
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 3
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Are you looking for VC funding or funding from other potential investors? You need a good business idea – and an excellent business plan. Business planning and raising capital go hand-in-hand. An investor business plan is required to attract a venture capital firm. And the desire to raise capital (whether from an individual “angel” investor or a venture capitalist) is often the key motivator in business planning.
What is a venture capitalist?
A venture capitalist, often referred to as a VC, strategically allocates financial capital to early-stage, high-potential startup companies to foster exponential growth and catalyze groundbreaking innovation. By leveraging their investments, venture capitalists secure partial ownership and wield a profound influence over critical strategic decisions and operational facets. Furthermore, they impart invaluable guidance and mentorship and harness their extensive network of influential contacts and abundant resources.
Venture capitalists aim to attain considerable returns on their investments through the strategic divestment of their ownership stake in the company at a subsequent stage, commonly facilitated through an IPO or a trade sale, encompassing mergers or acquisitions. Given the inherent risks associated with their investment endeavors, venture capitalists adopt an exceptionally discerning approach, meticulously selecting a mere fraction of the myriad companies that seek their sought-after financial backing.
Their active pursuit centers around identifying enterprises that epitomize disruptive technologies or trailblazing business models, thrive within expansive and rapidly evolving markets, exhibit a significant competitive edge, and are steered by an adept and fervent management team. These are the essential elements of a compelling Business Plan for Investors that can attract the attention and support of venture capitalists.
What is a Venture Capital Firm?
Venture capital firms (VCs) are money companies that put money in and help new and scalable startups. VCs get funds from different investors and then give them to startups they think can change or make new markets. VCs use a team of experts who check the chance of new companies. These experts have different backgrounds and skills in different businesses, and they use their ideas to help VCs pick companies that are likely to do well.
Besides giving money, VCs also give their companies other benefits, such as advice and access to their network of people, which can be very important to early-stage companies.
Types of Venture Capital Investments
Venture capital investments can be classified into different types based on the company’s development stage. The main types are:
1. Seed Capital
Seed capital is the earliest funding given to an innovator or group with a vision for a novel product or service but has yet to transform it into a feasible business. Seed capital is typically used for market exploration, product creation, prototype evaluation, customer verification, etc. Seed capital is very precarious because there is no assurance that the vision will work or that there will be a market appetite for it. However, seed capital can also generate very high rewards if the vision becomes successful and attracts more funding.

2. Startup Capital
Startup capital is the funding given to a company that has created its product or service and has introduced it in the market but has yet to generate substantial revenue or profit. Startup capital is typically used for promotion, sales, distribution, customer acquisition, etc. Startup capital is less precarious than seed capital because there is some indication of product-market fit and traction. However, startup capital can also be challenging to obtain because there is still uncertainty about the scalability and sustainability of the business model.
3. Early Stage Capital
Early-stage capital is the funding granted to a company that has validated its product or service in the market and has begun generating revenue and profit but has yet to attain its full potential. Early-stage capital is typically used to diversify the product or service portfolio, penetrate new segments, recruit more talent, optimize operations, etc. Early-stage capital is less precarious than startup capital because there is more evidence and traction of the business. However, early-stage capital can also be challenging and demanding because there are more expectations and pressure from the investors.
4. Expansion Capital
Expansion capital is the funding given to a company that has attained a significant market presence, revenue, and profit growth and is ready to scale up its business to the next level. Expansion capital is usually used to acquire other entities, develop new products or services, open new outlets, increase production capability, etc. Expansion capital is less perilous than early-stage capital because the business has more stability and predictability. However, expansion capital can also be costly and dilutive because more investors are engaged, and more equity is surrendered.
5. Late Stage Capital
Late-stage capital is the funding bestowed to a company that has reached a mature stage of development and growth and is preparing for an exit event such as an IPO or a trade sale. Late-stage capital is usually used to enhance the company’s valuation, reputation, and visibility, improve financial performance, strengthen governance, etc. Late-stage capital is less perilous than expansion capital because there is more certainty and credibility in the business. However, late-stage capital can also be complex and restrictive because more regulations and obligations are involved. However, a SBA Business Plan can help late-stage companies comply with the requirements and expectations of investors.
6. Bridge Financing
Bridge financing is the interim funding granted to a company that requires short-term capital to fill an urgent need or gap until it obtains a lasting or stable source of financing. Bridge financing is typically utilized for satisfying payroll, settling bills, accomplishing a project, etc. Bridge financing is perilous because there is no assurance that the firm can secure lasting or stable financing. However, bridge financing can also be beneficial and adaptable because it can offer swift and effortless access to cash.
The following table compares the different types of venture capital investments based on their stage, amount, risk, return, and purpose:
Venture Capital and VC Funding Methods
Venture capital is a source of funding for entrepreneurs who need money to grow their businesses. VC funding methods are the terms and conditions venture capitalists agree on when investing in the companies they support. Different methods of making a venture capital deal exist based on the people involved, worth, chance, and choices. The main methods are:
1. Common stock
This is the most straightforward form of VC funding method. It involves issuing shares of common stock to investors in exchange for capital. A common stock gives the investors voting rights and dividends (if any) in proportion to their ownership stake. Common stock is usually preferred by early-stage companies with low valuation and high risk.
2. Preferred stock
This is a more complex and sophisticated form of VC funding method. It involves issuing shares of preferred stock to investors in exchange for capital. Preferred stock gives the investors preference over common stockholders regarding dividends, liquidation, and conversion rights. Preferred stock is usually preferred by later-stage companies that have higher valuations and lower risk.
3. Convertible debt
This is a mixed form of VC funding method. It means giving the investors a debt instrument that can be converted into shares later or when some conditions are satisfied. Convertible debt pays the investors interest and money back until it gets converted. Early companies with unclear worth and a high chance of failure often choose convertible debt.
4. SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity)
This is a newer and simpler form of VC funding method. It means making a deal with the investors that lets them get shares in the future at a fixed worth or lower price. SAFE only involves issuing shares or debt instruments to the investors once a future financing event occurs. SAFE is usually preferred by seed-stage companies that have uncertain valuations and high risk.
Main Sections of a Venture Capital Business Plan
A venture business plan is a document describing your business idea, market opportunity, competitive advantage, financial projections, and funding needs. It is a tool that helps you communicate your vision and strategy to potential investors and partners. A venture business plan sample should include the following sections:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is pivotal in your venture business plan, serving as the primary section that demands attention. It aims to present a concise yet comprehensive overview of your business idea, target market, unique value proposition, traction and milestones, financial summary, and funding request. It is vital to draft the executive summary clearly and compellingly that captivates readers and incites their curiosity to explore your venture further.
2. Company Analysis
The company analysis section delves deeper into your company’s narrative, providing a detailed account of its history, mission, vision, values, goals, objectives, team, culture, and legal structure. This section highlights your company’s noteworthy achievements and inherent strengths while addressing the potential challenges and risks it faces. Moreover, it presents a compelling case for the qualifications and capabilities of your team, demonstrating their aptitude in executing the business plan.
3. Industry Analysis
The industry analysis section demonstrates your understanding of the market you operate in or plan to enter. It should provide relevant information about your industry’s size, growth, trends, drivers, challenges, opportunities, and outlook. It should also identify and analyze your industry’s key segments and sub-segments.
4. Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section is important as it outlines and describes your target market and various customer segments. It should encompass a detailed profile of your ideal customers, covering their demographics, psychographics, behaviors, needs, pains, desires, preferences, and purchasing patterns. Furthermore, this section should include an estimation of your product or service’s total addressable market (TAM), serviceable available market (SAM), and serviceable obtainable market (SOM).
5. Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis section is crucial in identifying and evaluating direct and indirect competitors. It thoroughly assesses their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, products, services, prices, features, benefits, market share, customer satisfaction, and distinctive factors. Additionally, this section explains your market positioning strategy, emphasizing your competitive advantages and unique selling points.
6. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan section outlines your marketing strategy and tactics for reaching and attracting your target customers and generating sales and revenue. It should cover the following elements:
- Product and service
- Distribution
- Marketing process
- Marketing Physical Evidence
7. Operations Plan
The operations plan section describes how you will run and manage your business daily. It should cover the following aspects:
- Human Resources
- Legal issues and requirements
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan section provides a detailed projection of your financial performance and position for three to five years. It should include the following components:
- Income Statement
- Cash Flow Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Break-Even Analysis
- Funding Request
- Funding Sources
- Exit Strategy
OGSCapital for Your Venture Capital Business Plan
Are you looking for an answer to: How to write a venture capital business plan? Our business plan experts at OGSCapital can help. We have a team of professional business plan writers with over 15 years of experience offering business plan writing services. We have helped over 5,000 clients attract more than $2.7 billion in financing. Here are some of the reasons why you should choose OGSCapital for your venture capital business plan:
OGSCapital can provide you with the following benefits:
- A customized and high-quality business plan
- Comprehensive and in-depth market research and analysis
- A realistic and accurate financial model and projections
- A persuasive and compelling executive summary
- A professional and attractive design and layout of your business plan
- Fast and reliable delivery within 10 to 15 days
- A revision after receiving the first draft of your business plan
If you’re also confused about how to write a business plan for venture capital that stands out from the crowd and increases your chances of getting funded, contact our experts at OGSCapital today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What do venture capitalists look for in a business plan?
A business plan to raise venture capital should demonstrate a great business idea, a talented and experienced team, a unique and valuable product or service, a market validation, a huge and expanding market, and a good deal and exit strategy. Plus, it should be clear, concise, well-researched and realistic.
2. What is the golden rule for venture capitalists?
For venture capitalists, people matter more than ideas. They look for entrepreneurs and managers with passion, dedication, flexibility, and willingness to learn from feedback. Venture capitalists believe these are the essential qualities that make or break a venture.
Download Venture Capital Business Plan Sample in PDF
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

How to Start a Plumbing Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Trading Business Plan

How To Write A Textile Manufacturing Business Plan

Start a Vending Machine Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Oil and Gas Business Plan

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
Index Ventures launches web app to help founders calculate employee stock options

The ability to offer stock options is utterly essential to startups. They convince talented people to join when the startup is unlikely to be capable of matching the high salaries that larger, established tech firms can offer.
However, it’s a complex business developing a competitive stock option plan. Luckily, London-based VC Index Ventures today launches both a handy web app to calculate all this, plus new research into how startups are compensating their key hires across Europe and the U.S.
OptionPlan Seed is a web app for seed-stage founders designing ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans). The web app is based on Index’s analysis of seed-stage option grants, drawing on data from more than 1,000 startups.
Index Ventures’ Nina Achadjian and Sarah Cannon: ‘There’s basically an infinite bid’ for growth-stage startups
The web app covers a variety of roles; six different levels of allocation benchmarks; calculates potential financial upside for each team member (including tax); and adjusts according to policy frameworks in the U.S., Canada, Israel, Australia and 20 European countries.
It also builds on the OptionPlan for Series A companies that Index launched a few years ago.
As part of its research for the new tool, Index said it found that almost all seed-stage employees receive stock options. However, while this reaches 97% of technical hires at seed-stage startups and 80% of junior nontechnical hires for startups in the U.S., in Europe only 75% of technical hires receive options, dropping to 60% for junior nontechnical hires.
That said, Index found stock option grant sizes are increasing, particularly among startups “with a lot of technical DNA, and weighted towards the Bay Area”. In less tech-heavy sectors such as e-commerce or content, grant sizes have not shifted much. Meanwhile, grants are still larger overall as seed valuations have grown in the last few years.
Index found the ESOP size is increasing at seed stage, following a faster rate of hiring and larger grants per employee. Index recommends an ESOP size at seed stage is set at 12.5% or 15%, rather than the more traditional 10% in order to retain and attract staff.
The research also found seed fundraise sizes and valuations have doubled, while valuations have risen by 2.5x in Europe and the U.S.
Additionally, salaries at seed have “risen dramatically”, with average salaries rising in excess of 60%. Senior tech roles at seed-stage startups in the U.S. now earn an average $185,000 salary, a 68% increase over three years, and can rise to over $220,000. But in Europe, the biggest salary increases have been for junior roles, both technical and nontechnical.
That said, Index found that “Europe’s technical talent continues to have a compensation gap” with seed-stage technical employees in Europe still being paid 40-50% less on average than their U.S. counterparts. Indeed, Index found this gap had actually widened since 2018, “despite a narrowing of the gap for nontechnical roles”.
Index also found variations in salaries across Europe are “much wider than the U.S.”, reflecting high-cost hubs like London, versus lower-cost cities like Bucharest or Warsaw.
The war for talent is now global, with the compensation gap for technical hires narrowing to 20-25% compared to the U.S.
Index’s conclusion is that “ambitious seed founders in Europe should raise the bar in terms of who they hire, particularly in technical roles”, as well as aim for more experienced and higher-caliber candidates, with larger fundraises to be competitive on salaries.
More TechCrunch
Get the industry’s biggest tech news, techcrunch daily news.
Every weekday and Sunday, you can get the best of TechCrunch’s coverage.
Startups Weekly
Startups are the core of TechCrunch, so get our best coverage delivered weekly.
TechCrunch Fintech
The latest Fintech news and analysis, delivered every Sunday.
TechCrunch Mobility
TechCrunch Mobility is your destination for transportation news and insight.
Featured Article
Spyware found on US hotel check-in computers
Several hotel check-in computers are running a remote access app, which is leaking screenshots of guest information to the interne

Techstars CEO Maëlle Gavet is out
Gavet has had a rocky tenure at Techstars and her leadership was the subject of much controversy.

Connected fitness is adrift post-pandemic
The struggle isn’t universal, however.

A comprehensive list of 2024 tech layoffs
The tech layoff wave is still going strong in 2024. Following significant workforce reductions in 2022 and 2023, this year has already seen 60,000 job cuts across 254 companies, according to independent layoffs tracker Layoffs.fyi. Companies like Tesla, Amazon, Google, TikTok, Snap and Microsoft have conducted sizable layoffs in the first months of 2024. Smaller-sized…

HoundDog.ai helps developers prevent personal information from leaking
HoundDog actually looks at the code a developer is writing, using both traditional pattern matching and large language models to find potential issues.

Google Pay will now display card perks, BNPL options and more
The changes are designed to enhance the consumer experience of using Google Pay and make it a more competitive option against other payment methods.

Vinod Khosla is coming to Disrupt to discuss how AI might change the future
Few figures in the tech industry have earned the storied reputation of Vinod Khosla, founder and partner at Khosla Ventures. For over 40 years, he has been at the center…

Truecaller partners with Microsoft to let its AI respond to calls in your own voice
AI has already started replacing voice agents’ jobs. Now, companies are exploring ways to replace the existing computer-generated voice models with synthetic versions of human voices. Truecaller, the widely known…

Meta’s Ray-Ban smart glasses now let you share images directly to your Instagram Story
Meta is updating its Ray-Ban smart glasses with new hands-free functionality, the company announced on Wednesday. Most notably, users can now share an image from their smart glasses directly to…

Why Spotify is launching its own font, Spotify Mix
Spotify launched its own font, the company announced on Wednesday. The music streaming service hopes that its new typeface, “Spotify Mix,” will help Spotify distinguish its own unique visual identity. …

Hydrolix seeks to make storing log data faster and cheaper
In 2008, Marty Kagan, who’d previously worked at Cisco and Akamai, co-founded Cedexis, a (now-Cisco-owned) firm developing observability tech for content delivery networks. Fellow Cisco veteran Hasan Alayli joined Kagan…

Bolster, creator of the CheckPhish phishing tracker, raises $14M led by Microsoft’s M12
A dodgy email containing a link that looks “legit” but is actually malicious remains one of the most dangerous, yet successful, tricks in a cybercriminal’s handbook. Now, an AI startup…
Boeing, NASA indefinitely delay crewed Starliner launch
If you’ve been looking forward to seeing Boeing’s Starliner capsule carry two astronauts to the International Space Station for the first time, you’ll have to wait a bit longer. The…

TikTok turns to generative AI to boost its ads business
TikTok is the latest tech company to incorporate generative AI into its ads business, as the company announced on Tuesday that it’s launching a new “TikTok Symphony” AI suite for…

Space VC closes $20M Fund II to back frontier tech founders from day zero
Gone are the days when space and defense were considered fundamentally antithetical to venture investment. Now, the country’s largest venture capital firms are throwing larger portions of their money behind…

Patronus AI is off to a magical start as LLM governance tool gains traction
These days every company is trying to figure out if their large language models are compliant with whichever rules they deem important, and with legal or regulatory requirements. If you’re…

Linktree surpasses 50M users, rolls out its social commerce program to more creators
Link-in-bio startup Linktree has crossed 50 million users and is rolling out the beta of its social commerce program.

Immigrant banking platform Majority secures $20M following 3x revenue growth
For a $5.99 per month, immigrants have a bank account and debit card with fee-free international money transfers and discounted international calling.

Unify helps developers find the best LLM for the job
When developers have a particular job that AI can solve, it’s not typically as simple as just pointing an LLM at the data. There are other considerations such as cost,…

Aerodome is sending drones to the scene of the crime
Response time is Aerodome’s immediate value prop for potential clients.

Granola debuts an AI notepad for meetings
Granola takes a more collaborative approach to working with AI.

AI language translation startup DeepL nabs $300M on a $2B valuation to focus on B2B growth
DeepL, which builds automated text translation and writing tools, has raised a $300 million round led by Index Ventures.

Praktika raises $35.5M to use AI avatars to make learning languages feel more natural
Praktika has secured a $35.5M Series A round to apply AI-powered avatars to language-learning apps.

Humane, the creator of the $700 Ai Pin, is reportedly seeking a buyer
Humane, the company behind the hyped Ai Pin that launched to less-than-glowing reviews last month, is reportedly on the hunt for a buyer.

Oyo, once valued at $10 billion, shelves IPO plans for second time
India’s Oyo, once valued at $10 billion, has withdrawn its IPO application from the market regulator for the second time.

Ore Energy emerges from stealth to build utility-scale batteries that last days, not hours
Ore Energy emerged from stealth today with €10 million in seed funding. The company hopes to make grid-scale batteries that are cheaper and longer lasting.

Paytm warns of job cuts as losses swell after RBI clampdown
Paytm, a leading financial services firm in India, said its net loss widened in the fourth quarter as it grappled with a regulatory clampdown.

In Seoul summit, heads of states and companies commit to AI safety
Government officials and AI industry executives agreed on Tuesday to apply elementary safety measures in the fast-moving field and establish an international safety research network. Nearly six months after the…

Microsoft wants to make Windows an AI operating system, launches Copilot+ PCs
Copilot, Microsoft’s brand of generative AI, will soon be far more deeply integrated into the Windows 11 experience.

VCs wanted FarmboxRx to become a meal kit, the company bootstrapped instead
Some startups choose to bootstrap from the beginning while others find themselves forced into self funding by a lack of investor interest or a business model that doesn’t fit traditional…

What Index Looks for in an Investment
by Index Ventures

Index Ventures, San Francisco
Index Ventures has been lucky to be involved with many exciting and successful entrepreneurs and startups.
Common to all these successful companies were three things: a passionate and committed team; an innovative and disruptive business idea and a large market opportunity. Without these factors, it is unlikely that raising venture capital will be the right thing for a business. Not every business that fulfills these criteria will get funding, but Index Ventures will certainly want to engage with those companies that do.
Passionate and committed founders . The early obstacles that a startup faces are to get funding, recruit talent, build products and gain early customer traction. Without passionate and visionary founders, a business will struggle to engage potential employees, investors and customers. Venture capital is fuel for a fire, but the spark to ignite the startup journey must come from the passion of the founders.
Once the initial hurdles have been overcome, few startups achieve success immediately. There are almost always unseen challenges and building a valuable company requires commitment to overcome or navigate around boulders that block the road.
Finally Index almost always prefers to back a founding team rather than a lone founder. Having commercial, operational and technical talent within the founding DNA of a company will give it a better chance of success and we look for teams that bring together all these elements.
Innovation and Disruption . There are two elements that underpin an innovative business. Firstly the founders must have a unique insight about a market or problem. Secondly they must have a creative and innovative product or service that leverages this insight to disrupt the way a market operates or provides a creative and new solution to a problem. Innovation can involve developing a new technology, but not all innovative businesses are technology businesses. Many of the most successful startups use off-the-shelf technology but devise radical and innovative marketing or distribution techniques which can transform the economics of an industry.
Market Size . Our funds seek to gain “significant minority” stakes in companies where we invest. Our model is always to back founders rather than act as business owners like buyout investors. Since we typically own small stakes, we need to have conviction that a business can ultimately exit for many hundreds of million or ideally billions of dollars/euros. We are unlikely to pursue investment opportunities where the absolute return for investors is capped by market size constraints, even where relative return on investment may be positive.
How best to approach Index Ventures
At Index Ventures, we have visibility on a large number of investment opportunities and have to rapidly focus on a much smaller set of companies where we can devote sufficient time to understand the companies and build a relationship with founders before we invest. Generally our dealflow can be categorized into three types
· Deals sourced through thematic research. We continually undertake research into sectors or industries where we believe disruptive companies can emerge;
· Deals referred through our network of current and former portfolio companies, VC industry colleagues, angel investors and advisors;
· Deals where companies spontaneously and directly contact Index Ventures through email, social media or events.
All three of these routes are important to us and each has yielded successful company relationships in the past. It is true that the companies where we already have strong direct or indirect relationships with founders are more likely to receive investment. However some of our most successful investments have been from backing first time entrepreneurs who had no prior ties to Index Ventures.
If you are considering approaching Index Ventures, you should bear in mind that the approach you take to raising capital provides a prospective investor with a good insight into how you will run a business. An approach that is well researched, well targeted and politely persistent is far better than an undifferentiated shotgun approach. Specifically we would have the following tips:
Be well rehearsed . There are many events and forums where you can see other companies present and road test and iterate your own business plan. These are highly worthwhile and we always give credit to entrepreneurs who over time show an ability to iterate and an openness to change and improve an initial idea.
Be targeted. Think carefully of why your business is likely to be of particular interest to Index Ventures given past and current investments and any comments we have made at events in the press or social media. Think who specifically at the firm is the most relevant person to try to build a relationship with given your sector, stage and geographical focus.
Build a relationship. We are always positively disposed to founders who are able to share with us some information over a period of time about how they are developing their business before we have more explicit dialogue about an investment round. Events and social media as well as email provide a great way to engage with us in a more informal way well in advance of more formal and focused meetings and presentations.
Execute on what is possible with no funding first. How much you are able to achieve without funding is a strong indicator of what you will be able to achieve once funded. We are much more compelled to invest where teams have done extensive market research, built prototypes or alpha products and road-tested marketing campaigns before raising funds.
At Index Ventures we try to get back to all prospective entrepreneurs, however there are inevitably times when we are unable to do so to every company given the volume of inbound leads we receive. Also we make a decision to invest based on something exceptional we see in a particular Company. We therefore will not always be able to elaborate specific reasoning for not pursuing a particular investment opportunity.
Finally we are humble and always learning. Where we have not initially believed in the vision or trusted in the execution of founders, we are always delighted to engage again with entrepreneurs who have proved us wrong.
Published — Oct. 8, 2014

The three fates of work in the age of AI
by Hannah Seal

Startups on the brink: why a boom in innovation is around the corner
by Martin Mignot
This website uses cookies
This website uses cookies and other tracking technologies for functional and analytical purposes. To improve your browsing experience on our site, we would also like to place tracking cookies.
If you prefer to reject the cookies, please use this link to access the video:
Index Ventures’ OptionPlan calculator helps CEOs plan their equity allocation
- User centred design
- User research
Enabling entrepreneurs to retain talent
We worked with Index Ventures to design OptionPlan , a tool that helps startups across the US and Europe calculate and create effective stock option plans, encouraging entrepreneurs to reward and retain their talent.
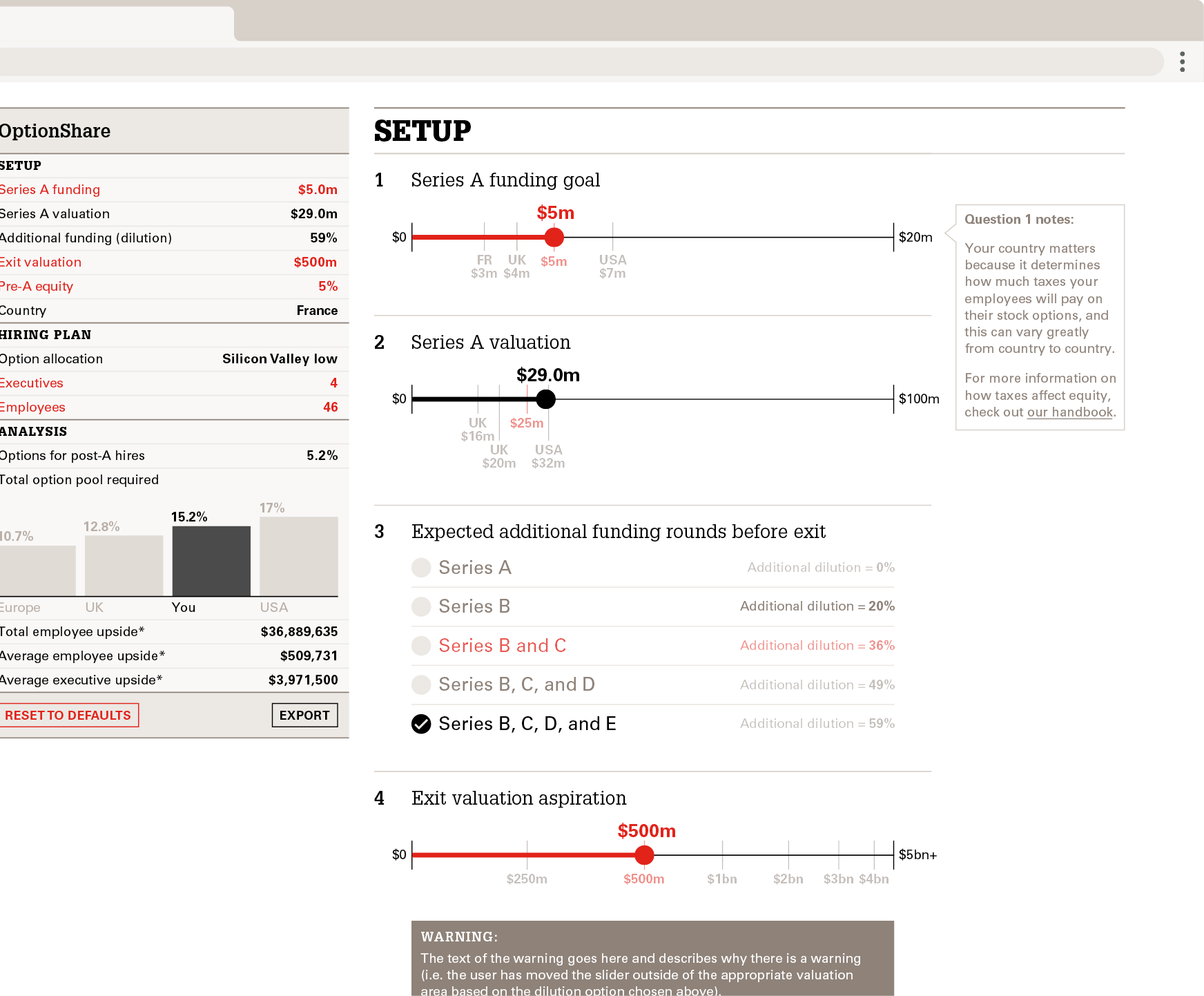
Based on data from 73 companies in Seed and Venture stages we designed OptionPlan to allow entrepreneurs to calculate how much equity to award each team member using easy to understand metrics. Our ability to understand the needs of the business and our creativity, insight and technical prototyping expertise meant we could bring Index Ventures’ unique dataset and model to life.
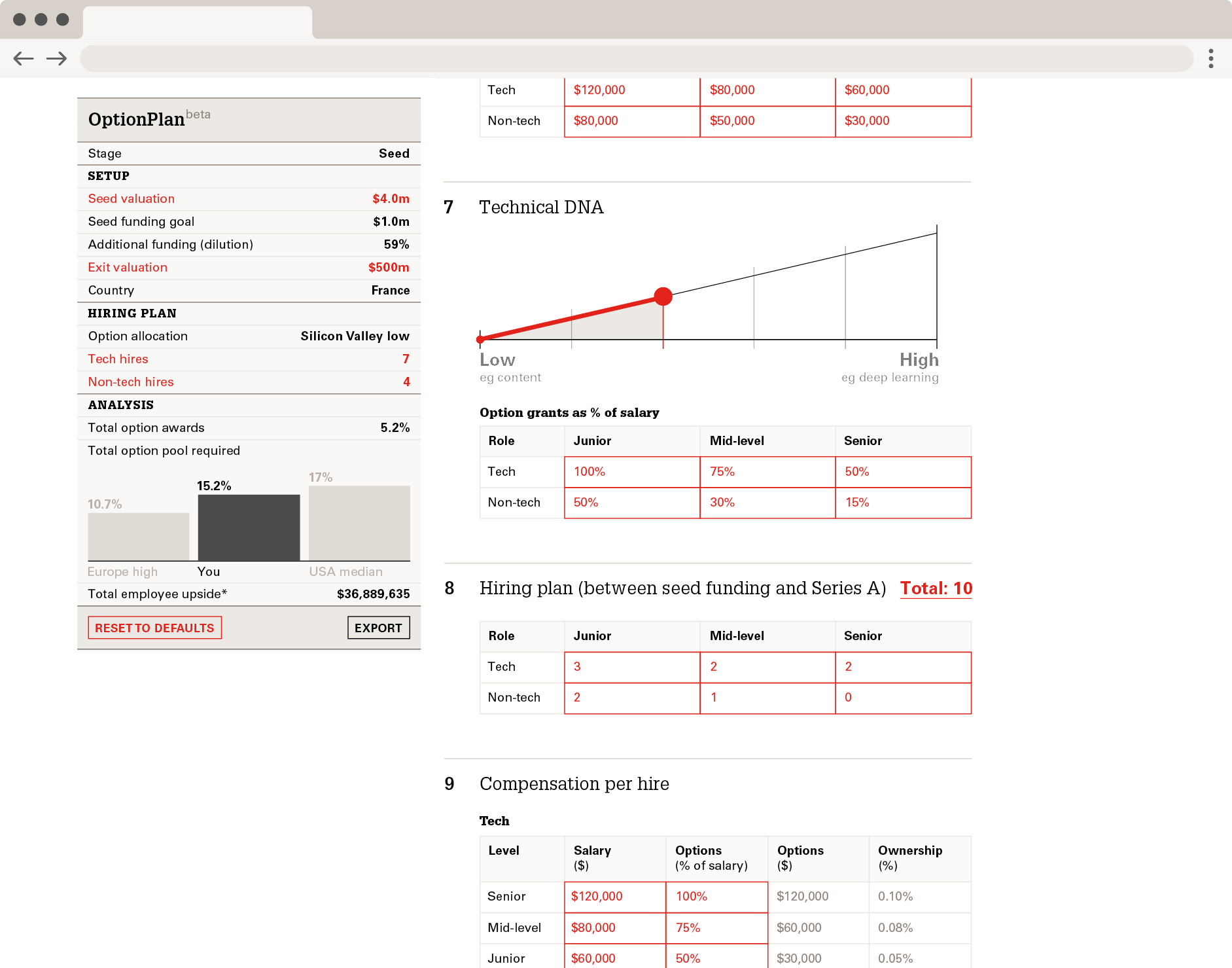
The OptionPlan calculator was released as part of Index Ventures’ Rewarding Talent campaign. The service has received wide recognition. Try OptionPlan out here .
“After the flood not only created an intuitive user experience but got to grips with our business needs really quickly. Their design work on OptionPlan allowed our large audience to seamlessly interact and benefit from our sophisticated data model.” Dominic Jacquesson, VP Talent, Index Ventures
This site is now archived. More here.
- OnlineExamMaker
- Candidate Management System
- Question Bank Software
- Online Proctoring Software
- AI Question Generator
- Quiz Certification Creator
- Online Survey Maker
- Online Exam Tools
- ELearning Resources
- Learning Management
- Questions & Answers
- Create a Quiz
20 Business Plan Quiz Questions and Answers
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections of a business venture. It serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs and stakeholders to understand the direction and viability of the business. Here’s an overview of the key components typically included in a business plan:
Executive Summary: This section provides a concise overview of the entire business plan. It highlights the company’s mission, vision, key objectives, and a summary of the proposed business model.
Company Description: Here, you’ll provide a detailed explanation of your business concept. Include the type of business, its legal structure, location, target market, and any unique selling propositions that set your business apart.
Market Analysis: Conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, target market, and competitors. Identify trends, potential opportunities, and challenges. Explain how your product or service will meet the needs of your target audience better than existing solutions.
Organization and Management: Describe the organizational structure of your business, including key team members, their roles, and relevant experience. Investors want to know that you have a capable team driving the venture.
Article overview
Part 1: 30 business plan quiz questions & answers.

1. Question: What is the primary purpose of a business plan? a) Secure funding b) Improve employee morale c) Enhance customer service d) Increase market competition Answer: a) Secure funding
2. Question: Which section of a business plan outlines the company’s mission and vision? a) Marketing strategy b) Financial projections c) Executive summary d) Company overview Answer: d) Company overview
3. Question: Which of the following is NOT a common business plan component? a) Competitive analysis b) SWOT analysis c) Cash flow statement d) Social media strategy Answer: d) Social media strategy
4. Question: What is the purpose of conducting a market analysis in a business plan? a) Determine the company’s competitors b) Develop financial projections c) Define the company’s mission d) Set employee goals Answer: a) Determine the company’s competitors
5. Question: Which section of a business plan highlights the company’s unique selling proposition (USP)? a) Marketing strategy b) Company description c) Competitive analysis d) Financial projections Answer: a) Marketing strategy
6. Question: What financial document shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period? a) Balance sheet b) Cash flow statement c) Income statement d) Profit and loss statement Answer: c) Income statement
7. Question: In a business plan, what does ROI stand for? a) Return on Investment b) Revenue on Investment c) Risk of Inflation d) Rate of Interest Answer: a) Return on Investment
8. Question: Which business plan section outlines the marketing tactics to promote a product or service? a) Financial projections b) Market analysis c) Marketing strategy d) Company overview Answer: c) Marketing strategy
9. Question: What is a break-even analysis used for in a business plan? a) Identifying potential customers b) Calculating potential profits c) Determining the point of profitability d) Analyzing competitor strategies Answer: c) Determining the point of profitability
10. Question: In a business plan, what does the term “SWOT” stand for? a) Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats b) Sales, Workforce, Objectives, Technology c) Strategies, Workflow, Operations, Targets d) Success, Wealth, Objectives, Tactics Answer: a) Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
11. Question: What is the purpose of an executive summary in a business plan? a) Provide an overview of the company’s history b) Detail the company’s long-term objectives c) Summarize the key points of the entire plan d) Highlight the company’s competitive advantages Answer: c) Summarize the key points of the entire plan
12. Question: Which financing option involves giving up ownership shares of a company in exchange for capital? a) Debt financing b) Equity financing c) Venture capital d) Angel investing Answer: b) Equity financing
13. Question: What does the term “KPI” mean in a business context? a) Key Performance Indicator b) Key Profit Increment c) Key Planning and Implementation d) Key Personnel Improvement Answer: a) Key Performance Indicator
14. Question: What section of a business plan should discuss the company’s organizational structure and management team? a) Market analysis b) Financial projections c) Company overview d) Marketing strategy Answer: c) Company overview
15. Question: What type of business plan primarily targets internal decision-making and planning? a) Startup business plan b) Strategic business plan c) Operational business plan d) Feasibility business plan Answer: c) Operational business plan
Part 2: Download business plan questions & answers for free
Download questions & answers for free
16. Question: What external factor analysis tool helps identify the political, economic, social, and technological influences on a business? a) PEST analysis b) SWOT analysis c) BCG matrix d) Porter’s Five Forces Answer: a) PEST analysis
17. Question: Which statement best describes a vision statement in a business plan? a) Outlines the short-term goals of the company b) Identifies potential risks and challenges c) Describes the company’s future aspirations d) Analyzes the company’s target market Answer: c) Describes the company’s future aspirations
18. Question: What is the purpose of conducting a competitive analysis in a business plan? a) Identify potential partners b) Analyze customer feedback c) Evaluate strengths and weaknesses of competitors d) Forecast financial performance Answer: c) Evaluate strengths and weaknesses of competitors
19. Question: Which financing option involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest over time? a) Debt financing b) Equity financing c) Venture capital d) Angel investing Answer: a) Debt financing
20. Question: What does the term “ROI” stand for in the context of financial analysis? a) Revenue on Investment b) Return on Innovation c) Risk of Inflation d) Return on Investment Answer: d) Return on Investment
Part 3: Free online quiz creator – OnlineExamMaker
OnlineExamMaker’s secure, powerful web-based quiz maker is an easy-to-use, intelligent online testing software tool for business, training & educational to create exams & quizzes with ease. With its user friendly interface and extensive range of features, OnlineExamMaker simplifies the process of creation and distributing online quizzes to engage learners, improve knowledge retention, and assess performance.
Create Your Next Quiz/Exam with OnlineExamMaker
Related Posts
Flowers are not just beautiful to look at, they are also full of interesting facts…
Pizza is one of the most popular foods in the world, loved by people of…
Athletics is a collection of sporting events that involve running, jumping, and throwing. It is…
Share this post:
Have an account?

Business Plan
8th - 10th grade, specialty, other.
30 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
- 17. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt What are the 7 essential parts to creating a business plan? 1.Executive Summary 2.Company Description 3.Product/Services 4.Market Analysis 5.Strategy 6.Organizational/ management team 7.Finicial Plan none of the above all of the above
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
Lewiston Sun Journal
Account Subscription: ACTIVE
Questions about your account? Our customer service team can be reached at [email protected] during business hours at (207) 791-6000 .
- Livermore Falls Advertiser
Applications open for free online business planning
You are able to gift 5 more articles this month.
Anyone can access the link you share with no account required. Learn more .
With a Lewiston Sun Journal subscription, you can gift 5 articles each month.
It looks like you do not have any active subscriptions. To get one, go to the subscriptions page .
Loading....

“I took the NVME Venturing Forth course in 2019 and I learned more about being an entrepreneur and all of the logistics of starting a business than I did in four years of business school.” Amanda Hatley, Founder & Director, She Summits Co. SUBMITTED PHOTO
AUGUSTA — New Ventures Maine (NVME) has an open call for Venturing Forth , a free, online comprehensive business planning class starting Tuesday, September 3, 2024.
For new entrepreneurs or existing business owners, Venturing Forth helps participants create a written business plan from start to finish with feedback from facilitators and fellow entrepreneurs.
The 60-hour course covers topics including the customer, competition, marketing, recordkeeping, taxes, financing, legal aspects, and more. In-class activities, guest speakers, and homework assignments lead to the completed business plan and road map for success. This comprehensive course includes three follow-up networking sessions.
Individuals complete an online application and attend an orientation and individual interview to participate in the class. The application is accessible online and is due by noon on Tuesday, August 27. Class size is limited to 15.
“This class is designed to support small business owners in all aspects of creating their business plan,” said NVME Microenterprise Specialist Alicia LaFosse. “Participants will not only learn through the class content, but they’ll also learn from their peers and from entrepreneurs in the community as they hone their vision and create their plan.”
The Venturing Forth class will meet via Zoom at the following dates and times: Advertisement
September 3 – October 15: Tuesdays and Thursdays, 9:30 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
October 22 – December 3: Tuesdays only, 9:30 a.m. to 3:00 p.m.
(No class will be held on Tuesday, November 26.)
Anyone with a business idea or current business is welcome to apply.
The class also qualifies for three pass/fail credits from the University of Maine at Augusta upon approval of a completed business plan.
To request or complete an application, register for the orientation, or learn more, contact Alicia LaFosse at 207-621-7457 or [email protected] or visit the New Ventures Maine website.
Comments are not available on this story.
Send questions/comments to the editors.
Livermore Falls Advertiser Headlines
- Enter your email
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Member Log In
Please enter your username and password below. Already a subscriber but don't have one? Click here .
Not a subscriber? Click here to see your options
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Exclusive: Musk pushes plan for China data to power Tesla's AI ambitions
- Medium Text

- Tesla develops plan for data center in China
- But also seeks to transfer EV driving data to US
- Tesla would need local partner for China data center
- China data key to Tesla's pivot to AI
THE CHINA EFFECT
Sign up here.
Reporting by Zhang Yan and Fanny Potkin; Editing by Sonali Paul
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Bristol Myers, Sanofi liability in Hawaii Plavix case grows to $916 million
A judge in Hawaii on Tuesday ordered Bristol Myers Squibb and Sanofi to pay more than $916 million to the state for failing to warn non-white patients of health risks from its blood thinner Plavix, up from an earlier judgment of $834 million.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Index; Learning Objectives. By the end of this section, you will be able to: ... Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. ... Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the ...
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows: 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company's mission statement and description of the products and services.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
Whether it is to raise finance, sell a business or develop a specific project, this is your one-stop guide to producing the most professional and convincing business plan for a new venture. How to Write a Business Plan provides invaluable help with sales, cash and profit forecasts and is supported by the inclusion of full-length plans available ...
Today, 35,000 people work across 24 countries for Index-backed companies, generating close to $10 billion (£7.7bn) in combined annual revenue. In February 2016, Index announced it had raised ...
Reference: Chapter 3, 4, 5, and 16. III. Marketing and Sales. This section of the business plan should clearly communicate an understanding of how to successfully market and sell your product to the identified customer segments. Understanding and communicating your customer development strategy is as important as your product development strategy.
The offices of Index Ventures in San Francisco. The venture capital firm plans to disclose on Monday that it has raised $1.65 billion for its two newest funds.
A business plan to raise venture capital should demonstrate a great business idea, a talented and experienced team, a unique and valuable product or service, a market validation, a huge and expanding market, and a good deal and exit strategy. Plus, it should be clear, concise, well-researched and realistic. 2.
However, it's a complex business developing a competitive stock option plan. Luckily, London-based VC Index Ventures today launches both a handy web app to calculate all this, plus new research ...
Innovation and Disruption. There are two elements that underpin an innovative business. Firstly the founders must have a unique insight about a market or problem. Secondly they must have a creative and innovative product or service that leverages this insight to disrupt the way a market operates or provides a creative and new solution to a ...
The OptionPlan calculator was released as part of Index Ventures' Rewarding Talent campaign. The service has received wide recognition. Try OptionPlan out here. "After the flood not only created an intuitive user experience but got to grips with our business needs really quickly. Their design work on OptionPlan allowed our large audience to ...
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections of a business venture. It serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs and stakeholders to understand the direction and viability of the business. ... Answer: c) Operational business plan. Part 2: Download business plan questions & answers for ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is not part of a business' strategic plan? A) Mission statement B) Values statement C) Goals D) Capital budget E) Objectives, Budgets are used for: A) Planning B) Communication C) Control D) both A & B E) A, B, & C, True or False: The operating plan focuses on how a business plans to meet the goals and ...
Which of the following is not a part of the Business Plan? 1 point. Index. creation process venture. funds. all of the above. Here's the best way to solve it. Powered by Chegg AI. The correct answer is all of the above. The business plan is a crucial document that outlines the g...
Describes yourself and what experiences you bring to the venture. ... Index Venture. Funds. Creation Process. all of the above. 14. Multiple Choice. Edit. 30 seconds. ... This part of a business plan shows the knowledge of the industry and includes statistics on marketing data for the companies products/services, and evaluates competition ...
AUGUSTA — New Ventures Maine (NVME) has an open call for Venturing Forth, a free, online comprehensive business planning class starting Tuesday, September 3, 2024. For new entrepreneurs or ...
Tesla is pushing ahead with plans to power the global development of its self-driving system with data from China that could be processed within the country, part of a strategic shift by Elon Musk ...