Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Stress management

Exercise and stress: Get moving to manage stress
Exercise in almost any form can act as a stress reliever. Being active can boost your feel-good endorphins and distract you from daily worries.
You know that exercise does your body good, but you're too busy and stressed to fit it into your routine. Hold on a second — there's good news when it comes to exercise and stress.
Virtually any form of exercise, from aerobics to yoga, can act as a stress reliever. If you're not an athlete or even if you're out of shape, you can still make a little exercise go a long way toward stress management. Discover the connection between exercise and stress relief — and why exercise should be part of your stress management plan.
Exercise and stress relief
Exercise increases your overall health and your sense of well-being, which puts more pep in your step every day. But exercise also has some direct stress-busting benefits.
- It pumps up your endorphins. Physical activity may help bump up the production of your brain's feel-good neurotransmitters, called endorphins. Although this function is often referred to as a runner's high, any aerobic activity, such as a rousing game of tennis or a nature hike, can contribute to this same feeling.
- It reduces negative effects of stress. Exercise can provide stress relief for your body while imitating effects of stress, such as the flight or fight response, and helping your body and its systems practice working together through those effects. This can also lead to positive effects in your body — including your cardiovascular, digestive and immune systems — by helping protect your body from harmful effects of stress.
It's meditation in motion. After a fast-paced game of racquetball, a long walk or run, or several laps in the pool, you may often find that you've forgotten the day's irritations and concentrated only on your body's movements.
As you begin to regularly shed your daily tensions through movement and physical activity, you may find that this focus on a single task, and the resulting energy and optimism, can help you stay calm, clear and focused in everything you do.
- It improves your mood. Regular exercise can increase self-confidence, improve your mood, help you relax, and lower symptoms of mild depression and anxiety. Exercise can also improve your sleep, which is often disrupted by stress, depression and anxiety. All of these exercise benefits can ease your stress levels and give you a sense of command over your body and your life.
Put exercise and stress relief to work for you
A successful exercise program begins with a few simple steps.
- Consult with your doctor. If you haven't exercised for some time or you have health concerns, you may want to talk to your doctor before starting a new exercise routine.
Walk before you run. Build up your fitness level gradually. Excitement about a new program can lead to overdoing it and possibly even injury.
For most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends getting at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity a week, or a combination of moderate and vigorous activity. Examples of moderate aerobic activity include brisk walking or swimming, and vigorous aerobic activity can include running or biking. Greater amounts of exercise will provide even greater health benefits.
Also, aim to do strength training exercises for all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
Do what you love. Almost any form of exercise or movement can increase your fitness level while decreasing your stress. The most important thing is to pick an activity that you enjoy. Examples include walking, stair climbing, jogging, dancing, bicycling, yoga, tai chi, gardening, weightlifting and swimming.
And remember, you don't need to join a gym to get moving. Take a walk with the dog, try body-weight exercises or do a yoga video at home.
- Pencil it in. In your schedule, you may need to do a morning workout one day and an evening activity the next. But carving out some time to move every day helps you make your exercise program an ongoing priority. Aim to include exercise in your schedule throughout your week.
Stick with it
Starting an exercise program is just the first step. Here are some tips for sticking with a new routine or refreshing a tired workout:
Set SMART goals. Write down SMART goals — specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-limited goals.
If your primary goal is to reduce stress in your life, your specific goals might include committing to walking during your lunch hour three times a week. Or try online fitness videos at home. Or, if needed, find a babysitter to watch your children so that you can slip away to attend a cycling class.
- Find a friend. Knowing that someone is waiting for you to show up at the gym or the park can be a powerful incentive. Try making plans to meet friends for walks or workouts. Working out with a friend, co-worker or family member often brings a new level of motivation and commitment to your workouts. And friends can make exercising more fun!
- Change up your routine. If you've always been a competitive runner, take a look at other, less competitive options that may help with stress reduction, such as Pilates or yoga classes. As an added bonus, these kinder, gentler workouts may enhance your running while also decreasing your stress.
Exercise in short bursts. Even brief bouts of physical activity offer benefits. For instance, if you can't fit in one 30-minute walk, try a few 10-minute walks instead. Being active throughout the day can add up to provide health benefits. Take a mid-morning or afternoon break to move and stretch, go for a walk, or do some squats or pushups.
Interval training, which entails brief (60 to 90 seconds) bursts of intense activity at almost full effort, can be a safe, effective and efficient way of gaining many of the benefits of longer duration exercise. What's most important is making regular physical activity part of your lifestyle.
Whatever you do, don't think of exercise as just one more thing on your to-do list. Find an activity you enjoy — whether it's an active tennis match or a meditative meander down to a local park and back — and make it part of your regular routine. Any form of physical activity can help you unwind and become an important part of your approach to easing stress.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://health.gov/our-work/physical-activity/current-guidelines. Accessed Aug. 10, 2020.
- AskMayoExpert. Physical activity (adult). Mayo Clinic; 2020.
- Working out boosts brain health. American Psychological Association. https://www.apa.org/topics/exercise-stress. Accessed Aug. 10, 2020.
- Seaward BL. Physical exercise: Flushing out the stress hormones. In: Essentials of Managing Stress. 4th ed. Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2017.
- Bodenheimer T, et al. Goal-setting for behavior change in primary care: An exploration and status report. Patient Education and Counseling. 2009; doi:10.1016/j.pec.2009.06.001.
- Locke E, et al. Building a practically useful theory of goal setting and task motivation: A 35-year odyssey. American Psychologist. 2002; doi:10.1037//0003-066x.57.9.705.
- Olpin M, et al. Healthy lifestyles. In: Stress Management for Life. 4th ed. Cengage Learning; 2016.
- Laskwoski ER (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. Aug. 12, 2020.
Products and Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to Pain Relief
- Alternative cancer treatments: 11 options to consider
- Mindfulness exercises
- Relaxation techniques
- Guided meditation video
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Exercise and stress Get moving to manage stress
We’re transforming healthcare
Make a gift now and help create new and better solutions for more than 1.3 million patients who turn to Mayo Clinic each year.
Jump to navigation
Find What You Need Get targeted resources quickly!

Stress Management: How to Reduce, Prevent, and Cope with Stress

While it may seem like there’s nothing you can do about stress at work and home, there are steps you can take to relieve the pressure and regain control.
The importance of managing stress
If you’re living with high levels of stress, you’re putting your entire well-being at risk. Stress wreaks havoc on your emotional equilibrium, as well as your physical health. It narrows your ability to think clearly, function effectively, and enjoy life. It may seem like there’s nothing you can do about stress. The bills won’t stop coming, there will never be more hours in the day, and your work and family responsibilities will always be demanding. But you have a lot more control than you might think.
Effective stress management helps you break the hold stress has on your life, so you can be happier, healthier, and more productive. The ultimate goal is a balanced life, with time for work, relationships, relaxation, and fun—and the resilience to hold up under pressure and meet challenges head on. But stress management is not one-size-fits-all. That’s why it’s important to experiment and find out what works best for you. The following stress management tips can help you do that.
Tip 1: Identify the sources of stress in your life
Stress management starts with identifying the sources of stress in your life. This isn’t as straightforward as it sounds. While it’s easy to identify major stressors such as changing jobs, moving, or going through a divorce, pinpointing the sources of chronic stress can be more complicated. It’s all too easy to overlook how your own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors contribute to your everyday stress levels.
Sure, you may know that you’re constantly worried about work deadlines, but maybe it’s your procrastination, rather than the actual job demands, that is causing the stress.
To identify your true sources of stress, look closely at your habits, attitude, and excuses:
- Do you explain away stress as temporary (“I just have a million things going on right now”) even though you can’t remember the last time you took a breather?
- Do you define stress as an integral part of your work or home life (“Things are always crazy around here”) or as a part of your personality (“I have a lot of nervous energy, that’s all”)?
- Do you blame your stress on other people or outside events, or view it as entirely normal and unexceptional?
Until you accept responsibility for the role you play in creating or maintaining it, your stress level will remain outside your control.
Start a stress journal
A stress journal can help you identify the regular stressors in your life and the way you deal with them. Each time you feel stressed, keep track of it in your journal or use a stress tracker on your phone. Keeping a daily log will enable you to see patterns and common themes. Write down:
- What caused your stress (make a guess if you’re unsure).
- How you felt, both physically and emotionally.
- How you acted in response.
- What you did to make yourself feel better.
Tip 2: Practice the 4 A’s of stress management
While stress is an automatic response from your nervous system, some stressors arise at predictable times: your commute to work, a meeting with your boss, or family gatherings, for example. When handling such predictable stressors, you can either change the situation or change your reaction. When deciding which option to choose in any given scenario, it’s helpful to think of the four A’s: avoid, alter, adapt, or accept.
Tip 3: Get moving
When you’re stressed, the last thing you probably feel like doing is getting up and exercising. But physical activity is a huge stress reliever—and you don’t have to be an athlete or spend hours in a gym to experience the benefits. Exercise releases endorphins that make you feel good, and it can also serve as a valuable distraction from your daily worries.
While you’ll get the most benefit from regularly exercising for 30 minutes or more, it’s okay to build up your fitness level gradually. Even very small activities can add up over the course of a day. The first step is to get yourself up and moving. Here are some easy ways to incorporate exercise into your daily schedule:
- Put on some music and dance around.
- Take your dog for a walk .
- Walk or cycle to the grocery store.
- Use the stairs at home or work rather than an elevator.
- Park your car in the farthest spot in the lot and walk the rest of the way.
- Pair up with an exercise partner and encourage each other as you work out.
- Play ping-pong or an activity-based video game with your kids.
The stress-busting magic of mindful rhythmic exercise
While just about any form of physical activity can help burn away tension and stress, rhythmic activities are especially effective. Good choices include walking, running, swimming, dancing, cycling, tai chi, and aerobics. But whatever you choose, make sure it’s something you enjoy so you’re more likely to stick with it.
While you’re exercising, make a conscious effort to pay attention to your body and the physical (and sometimes emotional) sensations you experience as you’re moving. Focus on coordinating your breathing with your movements, for example, or notice how the air or sunlight feels on your skin. Adding this mindfulness element will help you break out of the cycle of negative thoughts that often accompanies overwhelming stress.
Tip 4: Connect to others
There is nothing more calming than spending quality time with another human being who makes you feel safe and understood. In fact, face-to-face interaction triggers a cascade of hormones that counteracts the body’s defensive “fight-or-flight” response. It’s nature’s natural stress reliever (as an added bonus, it also helps stave off depression and anxiety). So make it a point to connect regularly—and in person—with family and friends.
Keep in mind that the people you talk to don’t have to be able to fix your stress. They simply need to be good listeners. And try not to let worries about looking weak or being a burden keep you from opening up. The people who care about you will be flattered by your trust. It will only strengthen your bond.
Of course, it’s not always realistic to have a pal close by to lean on when you feel overwhelmed by stress, but by building and maintaining a network of close friends you can improve your resiliency to life’s stressors.
Tips for building relationships
- Reach out to a colleague at work.
- Help someone else by volunteering .
- Have lunch or coffee with a friend.
- Ask a loved one to check in with you regularly.
- Accompany someone to the movies or a concert.
- Call or email an old friend.
- Go for a walk with a workout buddy.
- Schedule a weekly dinner date.
- Meet new people by taking a class or joining a club.
- Confide in a clergy member, teacher, or sports coach.
Tip 5: Make time for fun and relaxation
Beyond a take-charge approach and a positive attitude, you can reduce stress in your life by carving out “me” time. Don’t get so caught up in the hustle and bustle of life that you forget to take care of your own needs. Nurturing yourself is a necessity, not a luxury. If you regularly make time for fun and relaxation, you’ll be in a better place to handle life’s stressors.
Set aside leisure time. Include rest and relaxation in your daily schedule. Don’t allow other obligations to encroach. This is your time to take a break from all responsibilities and recharge your batteries.
Do something you enjoy every day. Make time for leisure activities that bring you joy, whether it be stargazing, playing the piano, or working on your bike.
Keep your sense of humor. This includes the ability to laugh at yourself. The act of laughing helps your body fight stress in a number of ways.
Take up a relaxation practice. Relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing activate the body’s relaxation response , a state of restfulness that is the opposite of the fight or flight or mobilization stress response. As you learn and practice these techniques, your stress levels will decrease and your mind and body will become calm and centered.
Tip 6: Manage your time better
Poor time management can cause a lot of stress. When you’re stretched too thin and running behind, it’s hard to stay calm and focused. Plus, you’ll be tempted to avoid or cut back on all the healthy things you should be doing to keep stress in check, like socializing and getting enough sleep. The good news: there are things you can do to achieve a healthier work-life balance.
Don’t over-commit yourself. Avoid scheduling things back-to-back or trying to fit too much into one day. All too often, we underestimate how long things will take.
Prioritize tasks. Make a list of tasks you have to do, and tackle them in order of importance. Do the high-priority items first. If you have something particularly unpleasant or stressful to do, get it over with early. The rest of your day will be more pleasant as a result.
Break projects into small steps. If a large project seems overwhelming, make a step-by-step plan. Focus on one manageable step at a time, rather than taking on everything at once.
Delegate responsibility. You don’t have to do it all yourself, whether at home, school, or on the job. If other people can take care of the task, why not let them? Let go of the desire to control or oversee every little step. You’ll be letting go of unnecessary stress in the process.
Tip 7: Maintain balance with a healthy lifestyle
In addition to regular exercise, there are other healthy lifestyle choices that can increase your resistance to stress.
Eat a healthy diet. Well-nourished bodies are better prepared to cope with stress, so be mindful of what you eat. Start your day right with breakfast, and keep your energy up and your mind clear with balanced, nutritious meals throughout the day.
Reduce caffeine and sugar. The temporary “highs” caffeine and sugar provide often end with a crash in mood and energy. By reducing the amount of coffee, soft drinks, chocolate, and sugar snacks in your diet , you’ll feel more relaxed and you’ll sleep better.
Avoid alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs. Self-medicating with alcohol or drugs may provide an easy escape from stress, but the relief is only temporary. Don’t avoid or mask the issue at hand; deal with problems head on and with a clear mind.
Get enough sleep. Adequate sleep fuels your mind, as well as your body. Feeling tired will increase your stress because it may cause you to think irrationally.
Tip 8: Learn to relieve stress in the moment
When you’re frazzled by your morning commute, stuck in a stressful meeting at work, or fried from another argument with your spouse, you need a way to manage your stress levels right now . That’s where quick stress relief comes in.
The fastest way to reduce stress is by taking a deep breath and using your senses—what you see, hear, taste, and touch—or through a soothing movement. By viewing a favorite photo, smelling a specific scent, listening to a favorite piece of music, tasting a piece of gum, or hugging a pet, for example, you can quickly relax and focus yourself.
Of course, not everyone responds to each sensory experience in the same way. The key to quick stress relief is to experiment and discover the unique sensory experiences that work best for you.
From Helpguide.org. Used with permission. HelpGuide provides evidence-based mental health education and support to a global audience. Their mission is to empower you with information you can use to help yourself and your loved ones. www.helpguide.org .
- Add new comment
Comments (66)
Please remember, we are not able to give medical or legal advice. If you have medical concerns, please consult your doctor. All posted comments are the views and opinions of the poster only.
Megala replied on Fri, 02/04/2022 - 6:46am Permalink
I tried some nutrition chews, which were delicious and a terrific stress reliever. Adults should take one to two per day so that they can sleep soundly and stay healthy. Thank you for the blog!!
Ashmitha replied on Thu, 11/18/2021 - 5:53am Permalink
Hi, really useful information thanks for sharing this wonderful article.
Anonymous replied on Thu, 10/28/2021 - 2:50am Permalink
This article helps me relax
this article is... replied on Thu, 09/30/2021 - 4:49pm Permalink
this article really helped me a lot thanks
Anonymous replied on Thu, 09/30/2021 - 4:40pm Permalink
the most relaxing thing is yelling at the wall
dipak sarangi replied on Fri, 09/10/2021 - 2:35pm Permalink
Amazing post. Everyone should have a read on this article. All your posts are also really good. Keep it up.
Anonymous replied on Sat, 06/05/2021 - 2:16am Permalink
best article that I have read in a long time
Alex replied on Wed, 04/14/2021 - 3:29pm Permalink
Great tips for managing stress. Sometimes a long term solution is needed though. What worked for me was this simple daily morning ritual. Not only made me more relaxed and stress free but also helped me sleep better. Hope this helps.
The Wellness Way replied on Tue, 03/30/2021 - 7:54am Permalink
Great Blog thanks for sharing this amazing blog this blog help lots of people. Thanks again.
Omkar Mule replied on Sun, 03/07/2021 - 7:35am Permalink
Thank you for sharing this amazing content with us! Literally, I loved this article.
Anonymous replied on Tue, 02/23/2021 - 1:36pm Permalink
When I was younger I used to play with Play Dough, now that I'm older, I still play with Play Dough.
Samina Iftikhar replied on Sat, 12/26/2020 - 4:45am Permalink
it is very helpful.
sadia jarrar replied on Mon, 12/14/2020 - 10:16am Permalink
if we are taking any stress the best way is to calm down our self, listen to light music or go for a walk and think about beautiful things happening around us
Sadaf replied on Sun, 01/03/2021 - 8:16am Permalink
Nazneen Zaidi replied on Sun, 12/20/2020 - 9:15am Permalink
Anonymous replied on Sun, 12/13/2020 - 11:36am Permalink
Worth Reading :)
Saba bajwa replied on Wed, 12/09/2020 - 6:21am Permalink
Very helpful
habiba replied on Tue, 12/08/2020 - 9:36am Permalink
it is beneficial to deal with physical and emotion stress.
annonymous replied on Thu, 12/03/2020 - 2:36am Permalink
Stress management is important to live a healthy life
Emmarisper replied on Thu, 05/20/2021 - 8:25am Permalink
It's helpful
Anonymous replied on Mon, 11/09/2020 - 9:43am Permalink
This is very helpful and i hope it will works
Anonymous replied on Thu, 11/05/2020 - 3:54am Permalink
Stress management gives you a range of tools to reset your alarm system. It can help your mind and body adapt. Without it, your body might always be on high alert.
zahra replied on Wed, 11/04/2020 - 11:43am Permalink
stress is not good for health
Anonymous replied on Sat, 12/26/2020 - 4:46am Permalink
Brira zia replied on Wed, 11/04/2020 - 9:37am Permalink
I give my stress respect, and I let my mind and body process it. It takes time but more often than expected it is a permanent solution
Anonymous replied on Tue, 09/29/2020 - 9:52am Permalink
can we deal with stress by using only one technique.
Anonymous replied on Thu, 11/05/2020 - 12:00am Permalink
i totally agree with your point of view.
Ashfaq replied on Wed, 10/14/2020 - 4:45am Permalink
meditation in prayer
shaziayousaf replied on Mon, 02/01/2021 - 7:40am Permalink
best way is to pray relax mediate and walk in a park
Anonymous replied on Fri, 08/28/2020 - 2:14pm Permalink
The best thing to reduce stress as per me is to have a cup of coffee with your best buddy and discuss your heart openly.
Anonymous replied on Wed, 12/09/2020 - 3:45am Permalink
Saadia Zafar replied on Thu, 09/17/2020 - 1:35pm Permalink
I give my stress respect, and I let my mind and body process it. It takes time but more often than expected it is a permanent solution.
Sadia Iftikhar replied on Tue, 08/25/2020 - 3:55pm Permalink
McClure Law replied on Sat, 07/18/2020 - 6:00am Permalink
Hi, Nice Post and its really good for everyone and very helpful for health. Thanks and Good job.
kwambokaevelyn8... replied on Sat, 09/05/2020 - 7:48am Permalink
Thanks for the good posts.So helpful.
Anonymous replied on Sat, 06/13/2020 - 10:01am Permalink
Anonymous replied on Tue, 09/29/2020 - 2:58pm Permalink
I totally agree with your point of view
Anonymous replied on Tue, 05/19/2020 - 12:12pm Permalink
Thank you that really helped me
Anonymous replied on Tue, 05/12/2020 - 9:40pm Permalink
this really helped me in quarantine, because I moved back to Egypt back to my family and friends.
Anonymous replied on Wed, 04/29/2020 - 7:56am Permalink
My side head is continuously paining due to stress level. Due to lock down, i am continuously working on lap top and having headache and many time it is giving dizziness. I am regularly doing exercise. Please suggest the way forward or particular exercise.
Counsellor replied on Thu, 05/07/2020 - 6:18am Permalink
Take a breather between the work. Working continuously on laptop burn out the energy and procrastinate accuracy in work. Take mini breaks to regain your energy. Have a good laugh it will boost good mood. Do chair exercise to stretch your muscles. All this help you to regain your energy and uplift your mood.
Anonymous replied on Thu, 04/16/2020 - 10:59am Permalink
This helped me with my project
Anonymous replied on Tue, 03/03/2020 - 12:12pm Permalink
hey, i am Alexis and i have been so stressed with my family and school. it is just hard to keep everything going in my life because i have always been someone that does everything for everyone else but never for myself. i just want to be happy with myself and everything in my life. i don't want to be the depressed girl with anger issues and anxiety and well its a long list. but i don't know how to help myself relax and that's the first thing that i want to do, before i change anything else because if i can't relax, i am going to explode and i don't think i am going to get better on my own
Princess replied on Tue, 01/12/2021 - 10:26am Permalink
Alexis, stop expecting so much from yourself and trying to please everyone. Take on things that you can do very well and pass the other things. You are struggling too much and stretching yourself beyond limit. Slow down, take a breather and if you can get a puppy and get your mind off people for a while. Also learn to pray and sing. Its a stress killer! Life is sweet despite Covid virus, so be happy my dear! God bless you!
jaron replied on Thu, 04/02/2020 - 2:44pm Permalink
i think that you should take a deep breath and seperate yourself from the group
and talk to a teacher parent or friend . And talk about this situation and how could you make it better for you and your friends and famliy.
Anonymous replied on Wed, 03/04/2020 - 6:34pm Permalink
Alexis, sounds like you have a lot of people in your life that care about you and that you care about as well. I think that what you need to do is learn to say "No". The people in your life should be understanding, and if not they aren't worth the extra stress in your life. If you want to help them, they might want to help you. Don't be afraid to ask for help if you have too much on your plate. You are worth the extra effort. It is a win-win,, less on your plate and others get to show you that they appreciate you too. Good Luck.
anete replied on Wed, 01/29/2020 - 7:14am Permalink
Stress always occurs especially if there is competition in sport, although the activity itself reduces it. it is about dealing with it during confusion attention to the pleasant things that will work together with the situation we are in.
Nathalie Argueles replied on Fri, 11/22/2019 - 2:03am Permalink
Interesting. This looks super cool. I haven't read it all yet, but I'll be back to read the rest of it.
Anonymous replied on Fri, 10/11/2019 - 11:01am Permalink
Fantastic article, m8
boi replied on Fri, 10/11/2019 - 10:59am Permalink

This program is made possible in part by a grant from the Bob Woodruff Foundation, which is dedicated to ensuring that impacted post-9/11 veterans, service members, and their families are thriving long after they return home.
BrainLine is a national service of WETA-TV, the flagship PBS station in Washington, D.C.
BrainLine, WETA Public Television 3939 Campbell Ave. Arlington, VA 22206 E-mail | Phone: 703.998.2020
© 2023 WETA All Rights Reserved | Contact Us
- No category
pe11 q2 mod1 Physical Education Managing Stress Through Sports
Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
IResearchNet
Stress Management in Sport
Stress management refers to the environmental, physiological, cognitive, and behavioral techniques employed by an individual to manage the factors and components that underlie the stress process or experience of stress. A primary goal of stress management in sport is to allow the athlete to effectively regulate competition related demands to facilitate optimal performance as well as to enhance psychological well-being (PWB). There are numerous stress management techniques that can be classified into various heuristic categories. Many of these are covered in this entry. However, to understand why these techniques are effective under specific conditions, it is important first to understand the stress and emotion process.
Contemporary thinking in sport psychology (SP) conceptualizes stress as a complex dynamic transaction between environmental demands, such as those associated with high-level competition, and the athlete. Stress occurs when the demands tax or exceed the resources, such as skills or support, that the athlete has at his or her disposal. Since competitive sport is by nature demanding, how athletes evaluate and cope with the demands they encounter has a large impact on the stress process. The environmental demands, as well as internally generated demands from personal expectations and goals, are typically called stressors. Stressors can be acute, chronic, or intermittent, and they can also be expected or unexpected.
The stress process is highly influenced by how athletes evaluate the personal and social meaning of stressors. Such evaluation, typically called an appraisal process , can be rapid and automatic or reflective and is shaped by social learning, culture, and memories. In many cases, emotional feelings and patterns of thought and behaviors are activated, with corresponding physiological and neurological activation, action impulses, cognitive plans, and actions. Thus, the stress response can include changes in emotion, feelings, cognitions, behavior, and autonomic physiological systems. Stress responses differ from athlete to athlete, and, for any given athlete, stress responses can take different forms in varying situations. Thus, effective stress management can target the actual demands and/or enhance the athlete’s ability to regulate the factors that are associated with the appraisal, emotion, and cognitive behavioral response.
Stress management techniques in sport typically target somatic, behavioral, and/or cognitive affective symptoms of stress. Somatic responses involve the athlete’s physiological reactions, such as changes in heart rate (HR), respiration (R), sweating, gastrointestinal functioning, muscular tension and control, pupil dilation, urinary system, and salivation. Behavioral responses are the direct actions taken because of the stress, including engagement or disengagement in certain strategies or activities, as well as distraction. Finally, cognitive affective responses include the thoughts associated with the stress, including worries, beliefs, apprehensions, and negative expectations about performance as well as action plans to manage stress. Distinguishing between and being aware of each of these aspects is important for the athlete, coach, and SP consultant, as this knowledge helps to ensure the appropriate stress management skills are applied.
Effective stress management also needs to recognize the temporal aspect of the stress process. Stressful transactions in sport often involve anticipation, confrontation (engagement), and post-engagement stages and can result in an athlete feeling overwhelmed. Stress management techniques can target specific stages or combination of stages.
Types of Stress Management Programs and Techniques
There are a number of stress management approaches in sport to deal with various components of the stress process. Some practitioners advocate a multimodal approach, which involves using different tactics thought to be more effective in combination. Others suggest focusing on the dominant stressor with a unimodal approach, which uses a singular, focused intervention strategy. Multimodal approaches tend to be favored because of their effectiveness on a wide range of factors related to different elements of the stress process (i.e., actual stressor, emotional feeling, cognition, behavior, and physiological responses). However, there is evidence that situations dominated by one particular stressor may be more efficiently treated with a unimodal approach. The effectiveness of any type of stress management ranges depends on variables such as the athlete’s situation, his or her coping resources, and the appropriateness of the approach for the stressor. It is best to create individualized stress management skills programs designed to meet each athlete’s specific needs. Common stress management interventions are briefly outlined next, in alphabetical order. These approaches can been seen as an application of theoretical and clinical knowledge to produce a more practical approach, and each of the approaches has varied levels of empirical support, depending on important factors such as context and person variables.
Anxiety Management Training
Anxiety management training involves an athlete’s learning to employ relaxation strategies under stressful or arousing situations, including those producing emotions such as anger and anxiety. During anxiety management training, the athlete visualizes the stressful situation and allows the accompanying physiological arousal to be generated within himself or herself. Relaxation techniques, such as applied relaxation, progressive muscle relaxation, breath control or deep breathing, or meditation (outlined later), are then used by the athlete to reduce the symptoms of physiological arousal, such as increased HR, R, and blood pressure (BP). This may also promote management of behavioral responses such as loss of coordination, acts of aggression or frustration, “choking,” or withdrawing from sport.
Applied Relaxation
The aim of applied relaxation is to learn the skill of relaxation and develop the ability to apply it rapidly where needed, in any situation. Connected to this approach are six stages. The first stage is progressive muscle relaxation, a technique where muscles are contracted or tensed and subsequently relaxed, which is used to help facilitate relaxation and help the athlete reduce somatic anxiety symptoms. As the athlete becomes proficient in this skill and moves to stage two, muscle relaxation is promoted by relaxing the muscles without tensing them first. In stage three, the term relax is conditioned to bring on a relaxed state when spoken or thought by the athlete. A focus on breathing is also promoted in this stage, as well as a focus on passive concentration, which is an effortless, automatic, yet focused state of mind, similar to mindfulness. Stage four requires the athlete to learn to use the skill in real-life settings, relaxing appropriate muscles while engaging ones needed for activity. Stage five focuses on having an athlete relax while in a naturally occurring, nonstressful situation. Breathing is the trigger of relaxation in this stage and is practiced 15 to 20 times per day. The sixth and final stage is called application training. The relaxation technique is implemented in a practice or training session and then in a low-stakes competition. The more frequently and completely it is implemented, the easier it will be for the athlete to use the strategy in a higher level of competition.
Arousal or Energizing Techniques
Some research suggests that athletes differ on the level of activation needed to produce optimal performance. Various levels of arousal are often conducive to high performance, and it is paramount that the athlete perceives the arousal as beneficial (see Cognitive Control later in this section). While many stress management approaches take an arousal reduction focus, strategies to increase arousal include imagery, self-talk, goal setting, and cognitions or thoughts focused on heightening stimulation.
Autogenic Training
Autogenic training, first introduced in psychiatry by Johannes Heinrich Schultz, involves a series of exercises designed to produce sensations such as warmth or heaviness, to help promote relaxation. The program is based on six stages, each with a separate goal. The stages are learned and practiced in the following order: heaviness in the extremities, warmth in the extremities, regulation of cardiac activity, regulation of breathing, abdominal warmth, and cooling of the forehead. Verbal cues to the athlete can be used to aid in prompting the sensations.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback training (BFBT) can help control autonomic physiological stress responses, such as increased HR and BP. It also has been used to control anxiety disorders as well as anxiety connected to particular environments or contexts. The premise behind biofeedback (BFB) is for the athlete to become aware of how stress is manifested physiologically, such as changes in BP, HR, breathing, or muscle tightness, using different modes of objective feedback and monitoring. With this increased awareness, athletes are better equipped to control their actions. With training, athletes become less reliant on the feedback, learning to control their physiological responses on their own.
Breath Control and Deep Breathing
Breath control is a relaxation technique using the physical strategy of breathing. It is an effective and relatively easy stress management technique to apply. Irregularities in breathing, such as holding one’s breath, hyperventilating, or random shallow breaths, can affect performance, potentially influencing coordination, focus, or rhythm, or can cause the athlete to feel unsettled, causing further stress. Breath control can be practiced by taking a slow, complete breath. Often, the lungs are conceptualized in three parts to aid in proper instruction of a slow, complete breath. The lower lungs are filled by pushing the diaphragm down and forcing the abdomen out. The middle portion of the lungs is then filled by expanding the chest cavity, expanding the rib cage. The upper lungs are then filled by raising the chest and rib cage. The breath is held for several seconds, and then a slow exhalation is made, taking approximately double the time taken for the inhalation process. Breath control is commonly used before a competition or during a natural break during the competition, as it is most practically applied during nonactive times.
Cognitive Affective Stress Management Training
Cognitive affective stress management training is one of the most comprehensive multimodal stress management programs used in sport. Originally designed by Ronald Smith, the program is designed to teach the athlete relaxation and cognitive skills that can aid in controlling physiological reactions and cognitive thought patterns. Intervention consists of both cognitive and physiological strategies, including relaxation skills, cognitive restructuring, and training that is self-instructed and targets the physical and mental reactions to stress. The premise behind the combination of physical and mental coping strategies is the development of an integrated coping response. The program, which has some empirical support, is educational rather than psychotherapeutic in nature and is designed to help athletes increase their self-control.
The cognitive affective stress management program consists of four distinct phases. In the first phase, the pretreatment assessment, the consultant uses an interview approach as well as questionnaires to assess the athlete’s issues with stress—namely, what situations tend to produce stress, how the athlete responds to stress, and how the resultant stress affects performance and other behaviors. The athlete’s cognitive and behavioral skills are assessed to determine existing resources. This stage is integral in understanding the unique aspects and situation of the particular athlete in question, allowing for a personalized program to be tailored for the athlete. The next phase is the treatment rationale phase, the aim of which is to help the athlete better understand his or her stress responses through analysis of personal stress reactions and experiences. Next, in the skill acquisition phase, athletes receive training in muscular relaxation, cognitive restructuring, and self-instruction. Muscular relaxation is taught under the guidelines of progressive relaxation, described earlier in this section. Cognitive restructuring, as described in more detail later in this section, involves the identification of irrational and destructive thoughts and the subsequent refocusing into more positive thoughts. Self-instruction training aims to teach athletes to provide themselves with specific instructions designed to improve concentration and promote problem solving. The final stage is skill rehearsal. In this stage, different levels of stress are induced by the consultant using mediums such as videos or imagery. The athlete is required to apply, and thus practice, the coping skills he or she has learned in the program.
Cognitive Control
Cognitive control involves changes to cognitions that trigger, maintain, exacerbate, or reduce the stress and emotion response process. Many cognitive control strategies were developed for cognitive therapy and help athletes understand how thought processes are involved in the experience of stress. Strategies to control unwanted or maladaptive thoughts include cognitive restructuring, positive thought control, and attentional refocusing. Cognitive restructuring involves helping an athlete to recognize and challenge irrational thoughts and to change these thoughts so that they become more adaptive. There are several steps in cognitive restructuring including identifying automatic thoughts or beliefs that are irrational and negative, challenging or debating the rationality of these thoughts, and then replacing these automatic thoughts with more positive and rational thoughts. Positive thought control involves self-awareness to identify negative thoughts and replace them with more adaptive ones. Positive thought control involves three elements: using negative thoughts in a positive way, controlling negative thoughts, and training positive thoughts. The aim is to have the athlete take a more positive orientation regarding the situation. Attentional refocusing involves shifting attention or focus from a stressful issue to one with fewer negative connotations attached to it. Some athletes may become too focused on their thoughts and stress reactions, causing them to become more anxious. To a large extent, attention refocusing attempts to shift attention from a self-focus to more of a focus on the features of the sporting environment.
Hypnosis involves getting the athlete to an altered state of consciousness in which he or she is relaxed and where perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or actions can be changed through suggestion. Although still somewhat controversial and misunderstood, hypnosis has been employed with athletes to help reduce anxiety and manage stress, as well as enhance other mental skills, focus attention, and increase confidence. Other stress management techniques such as relaxation and imagery or visualization are often used in conjunction with hypnosis, but the athlete is in a hypnotic state before they are applied. Typically, hypnosis is applied in four phases. The induction phase involves putting the athlete in a relaxed state and then inducing hypnosis using imagery and/ or attention-focusing techniques. In the hypnotic phase, athletes are given suggestions designed to target the issue at hand, most of which will be carried out once out of hypnosis. The waking phase consists of the athlete coming back to a conscious state, and the posthypnotic phase involves the athlete carrying out the suggestions given to him or her while in a hypnotized state. Athletes will benefit from hypnosis only to the extent to which they are able to be influenced on a subconscious level.
Meditation is another method of raising self-awareness, allowing an athlete to better manage stress. Through meditation, the athlete becomes more attuned to physical sensations and builds an understanding of the connection between physiological functions (e.g., increased HR, nausea) and psychological state (e.g., anxiety, confidence). There are a variety of approaches to meditation, all directed toward increasing awareness of internal physical and psychological triggers that have potential to prompt certain outcomes. This knowledge can help to promote relaxation or direct other stress management approaches, depending on the situation.
Performance and Competition Planning
Preperformance and competition as well as performance and competition plans can help the athlete manage the stress that is inherent in competition. Such plans allow the athlete to take a proactive stance on stress, identifying ahead of time triggers of stress, and formulating a plan to counteract those issues. Planning allows many athletes to feel more in control of the situation and the self, thereby often decreasing further experiences of stress. It also provides a structure for them to incorporate other stress management and psychological skills into their preperformance and performance routines. Preperformance and performance plans have been suggested to promote proper focus and attention toward task relevant issues and help to attain the proper level of activation for performance, promoting both physical and mental readiness to perform.
Self-Compassion
Self-compassion interventions can help prevent athletes from becoming overly self-critical. Based on the work of psychologist Kristin Neff, self-compassion has three key components. Self-kindness involves being understanding and accepting toward oneself in instances of adversity as opposed to being overly self-critical. Common humanity is the acknowledgment that one’s experiences are not isolating, as others also have these experiences. Finally, mindfulness involves a balanced perspective, keeping thoughts and feelings in a state of equilibrium, as opposed to over identifying with them. Strategies to promote self-compassion include writing, imagery, and psychoeducational components. Interventions are currently being adapted for sport.
Stress Inoculation Training
Stress inoculation training (SIT), developed by Donald Meichenbaum, is based on the idea that if an athlete is exposed to stress and learns to cope or deal with that stress in amounts that increase incrementally, an increased tolerance to stress will be obtained. It is a multimodal approach using coping skills that include creating productive and adaptive thoughts, images, and self-statements designed to benefit the athlete’s psychological state, as well as performance. It has been found to be effective in reducing anxiety and enhancing sport performance. SIT involves three stages. The conceptualization stage aims to raise the athlete’s awareness on the effects of positive and negative thoughts, self-talk, and imagery. The rehearsal stage involves the athlete’s learning to use a number of specific coping skills such as arousal control, imagery, and self-talk, which creates coping resources. The actual skills will depend on the specific needs of the athlete. Finally, the application stage involves the athlete’s practicing the skills in increasingly stressful situations. A key feature of SIT is the gradual exposure to stress such that the athlete becomes “inoculated” and is less affected. The application begins with low-stress situations and gradually builds toward higher stress situations as coping skills become more advanced. Specific application procedures involve imagery, role-playing, and simulations of increasing perceived stressfulness.
Other Associated Psychological Skills
There are a number of other psychological skills, such as imagery, identifying strengths, and goal setting, that can be incorporated into stress management programs. Calming imagery, such as visualizing oneself in a safe, relaxing place, can be used to help reduce cognitive anxiety and arousal and to bring on physical relaxation. Conversely, imagery can be used to energize and motivate by visualizing more stimulating, exciting places or scenarios. Imagery is often incorporated into athletes’ preperformance and performance plans and routines. Identifying strengths can help refocus athletes’ thought processes toward what they can do rather than what they cannot do and assist in developing competition plans that maximize assets. Goal setting can help the athlete stay focused on the task at hand and keep attention on relevant issues. Setting reasonable goals— ones that are measureable and challenging, yet attainable—can also help keep stress from becoming overwhelming. This is most commonly incorporated into preperformance and performance plans and routines.
Stress management techniques can include any intervention that can modify one or more components of the stress process . Stress management techniques need to be directed at individual needs and the issue at hand, as well as take into account the coping resources the athlete has available. As with the acquisition of any skill, application of stress management techniques requires training, time, and practice. Knowledge is not sufficient, as it does not guarantee an athlete can apply the necessary skills or program to his or her specific issue. Application and practice are necessary, and effort is needed on the part of the athlete to make gains in stress management ability.
References:
- Crocker, P. R. E., Kowalski, K. C., & Graham, T. R. (2002). Emotional control intervention for sport. In J. Silva & D. Stevens (Eds.), Psychological foundations of sport (pp. 155–176). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Lehrer, P. M., Woolfolk, R. L., & Sime, W. E. (2007). Principle and practices of stress management (3rd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
- Owen, T., Mellalieau, S. D., & Hanton, S. (2009). Stress management in applied sport psychology. In S. D. Mellalieu & S. Hanton (Eds.), Advances in applied sport psychology (pp. 124–161). New York: Routledge.
- Suinn, R. M. (2005). Behavioral intervention for stress management in sports. International Journal of Stress Management, 12, 343–362.
- Sports Psychology
- Psychological Skills
Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

Introduction
Causes of stress for athletes, effects of demands (stress) to an athlete, importance of stress management.
The demands of an athlete both professional and family life causes stress and anxiety. Therefore, we can not talk of the effects of demands without stress and it is effect. Mental health can also be another issue to be looked at while defining the cause’s demands. we can define stress in many ways. Stress is a harmful physical and emotional response that occur to and individual when the requirements of an activity exceed the capabilities and needs of the individual. ( www.ilo.org).As a matter of fact every individual is affected by anxiety, which is the reaction of an individual when he encounters stress. A great amount of stress can affect the performance of an athlete because he lacks concentration in what he is doing. Pre-competition anxiety has been the great important focus when researching about athletics.
It can also be defined as “the emotional, cognitive, behavioral and physiological reaction to aversive and noxious aspects of work, work environments and work organizations. It is a state characterized by high levels of arousal and distress and often by feelings of not coping.” (www.tcd.ie). from this definition demands can be related with
In relation to sports and specifically athletics it can be defined as a physiological reaction to aversive and noxious aspects of athletics and environments i.e. excessive pressures or the demands placed on them.
It is clear to everyone that you have to be mentally fit for you to be an athletic performer, you must be stress free, you must be a positive thinker, you must be aiming high at all times and even setup goals that you must achieve in life. All this attribute to mental health that one must bear. Therefore, when you see this, alongside other factors then you should be to point out that one could be optimistic athletic performer because this is the major requirements.
A good performing athlete has higher mental resistance and his performance is not affected by his mind. He is resistant to any change, when his mind is disturbed, he continues with his activities well up to the end. He is frank and does not hide anything, even if he realizes any point of weakness; he points it out and tries to improve it.
The athlete must be in good health, he should be free from diseases all the time, he should have a good physical composition and be physically fit because the activities he is involved in are demanding and requires someone to be strong enough to be able to succeed.
There are different types of stress that affect different athletes from different lifestyles. This can be subdivided into two that is personal and situational.
- Cognitive anxiety, which includes worry, and uncertainty,
- Somatic anxiety this includes movement changes in the perceived physiological stimulation
- Behavioral anxiety this involves peoples behaviors.
- Situational is related to the events and uncertainty. An athlete may feel burdened when entering into real action
The physiological reaction athletes to threats or pressure prepare them for intense physical activity of athletic. This can be observed through changes of the heartbeat and inhalation pace. In the body, there will be diversion of more blood to the muscles than to other organs. The result is the release of adrenaline raising levels of glucose and free fatty acids in the blood stream to provide greater energy (www.personal.psu.edu )
Stress can be positive or negative. Under normal circumstances, athletes should be able to find new balances and responses in their reactions to events. Such a stress cannot be said to be negative, as it will act as a motivational factor. “A moderate level of stress can be an important motivational factor and can be instrumental in achieving a dynamic adaptation to new situations. If health is considered as a dynamic equilibrium, stress is part of it. There is no health without interaction with other people and with the environment. Only excesses of stress are pathological.” (International labor organization)
In athletics, therefore stress normal and necessary. What should be avoided is intense, continuous or repeated which a person is unable to cope with, or if support is lacking, stress then becomes a negative phenomenon, which can lead to physical illness and psychological disorders. In a work context, it often results in inadequate adaptation to situations, people, and failure to perform at an optimal level. (International labor organization)
Dik B. (2004); measures of career interest; John Willey.
Doraten B. (1999); cross country runners and track and field athletes.
International labor organization (2007). Web.
Pendergrass L. (1999); Examination of the concurrent validity of scores from the CISS for student-athlete college major selection; counseling and development.
Penn state, stress management. Web.
Summers J. (2004); sports psychology: theory application and issues; Chichester.
Weinberg R.S (2003/2007); foundations of sports and exercise psychology.
- Implicit Bias in the Workplace
- Risk Management in Athletics
- Genetic Difference in Explaining Athletic Performance
- Professional Trainer Interview
- Sports Performance: Athlete’s Actions
- Barefoot Running: Source Comparison
- Barefoot Running Survey: Evidence From the Field
- "Barefoot Running Strikes Back" by W. Jungers
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, August 28). Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics. https://ivypanda.com/essays/sports-demands-and-stress-management-in-athletics/
"Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics." IvyPanda , 28 Aug. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/sports-demands-and-stress-management-in-athletics/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics'. 28 August.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics." August 28, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/sports-demands-and-stress-management-in-athletics/.
1. IvyPanda . "Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics." August 28, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/sports-demands-and-stress-management-in-athletics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics." August 28, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/sports-demands-and-stress-management-in-athletics/.
- Systematic review update
- Open access
- Published: 21 June 2023
The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model
- Narelle Eather ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6320-4540 1 , 2 ,
- Levi Wade ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4007-5336 1 , 3 ,
- Aurélie Pankowiak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0178-513X 4 &
- Rochelle Eime ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8614-2813 4 , 5
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 102 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
70k Accesses
16 Citations
305 Altmetric
Metrics details
Sport is a subset of physical activity that can be particularly beneficial for short-and-long-term physical and mental health, and social outcomes in adults. This study presents the results of an updated systematic review of the mental health and social outcomes of community and elite-level sport participation for adults. The findings have informed the development of the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model for adults.
Nine electronic databases were searched, with studies published between 2012 and March 2020 screened for inclusion. Eligible qualitative and quantitative studies reported on the relationship between sport participation and mental health and/or social outcomes in adult populations. Risk of bias (ROB) was determined using the Quality Assessment Tool (quantitative studies) or Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (qualitative studies).
The search strategy located 8528 articles, of which, 29 involving adults 18–84 years were included for analysis. Data was extracted for demographics, methodology, and study outcomes, and results presented according to study design. The evidence indicates that participation in sport (community and elite) is related to better mental health, including improved psychological well-being (for example, higher self-esteem and life satisfaction) and lower psychological ill-being (for example, reduced levels of depression, anxiety, and stress), and improved social outcomes (for example, improved self-control, pro-social behavior, interpersonal communication, and fostering a sense of belonging). Overall, adults participating in team sport had more favorable health outcomes than those participating in individual sport, and those participating in sports more often generally report the greatest benefits; however, some evidence suggests that adults in elite sport may experience higher levels of psychological distress. Low ROB was observed for qualitative studies, but quantitative studies demonstrated inconsistencies in methodological quality.
Conclusions
The findings of this review confirm that participation in sport of any form (team or individual) is beneficial for improving mental health and social outcomes amongst adults. Team sports, however, may provide more potent and additional benefits for mental and social outcomes across adulthood. This review also provides preliminary evidence for the Mental Health through Sport model, though further experimental and longitudinal evidence is needed to establish the mechanisms responsible for sports effect on mental health and moderators of intervention effects. Additional qualitative work is also required to gain a better understanding of the relationship between specific elements of the sporting environment and mental health and social outcomes in adult participants.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The organizational structure of sport and the performance demands characteristic of sport training and competition provide a unique opportunity for participants to engage in health-enhancing physical activity of varied intensity, duration, and mode; and the opportunity to do so with other people as part of a team and/or club. Participation in individual and team sports have shown to be beneficial to physical, social, psychological, and cognitive health outcomes [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Often, the social and mental health benefits facilitated through participation in sport exceed those achieved through participation in other leisure-time or recreational activities [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Notably, these benefits are observed across different sports and sub-populations (including youth, adults, older adults, males, and females) [ 11 ]. However, the evidence regarding sports participation at the elite level is limited, with available research indicating that elite athletes may be more susceptible to mental health problems, potentially due to the intense mental and physical demands placed on elite athletes [ 12 ].
Participation in sport varies across the lifespan, with children representing the largest cohort to engage in organized community sport [ 13 ]. Across adolescence and into young adulthood, dropout from organized sport is common, and especially for females [ 14 , 15 , 16 ], and adults are shifting from organized sports towards leisure and fitness activities, where individual activities (including swimming, walking, and cycling) are the most popular [ 13 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Despite the general decline in sport participation with age [ 13 ], the most recent (pre-COVID) global data highlights that a range of organized team sports (such as, basketball, netball volleyball, and tennis) continue to rank highly amongst adult sport participants, with soccer remaining a popular choice across all regions of the world [ 13 ]. It is encouraging many adults continue to participate in sport and physical activities throughout their lives; however, high rates of dropout in youth sport and non-participation amongst adults means that many individuals may be missing the opportunity to reap the potential health benefits associated with participation in sport.
According to the World Health Organization, mental health refers to a state of well-being and effective functioning in which an individual realizes his or her own abilities, is resilient to the stresses of life, and is able to make a positive contribution to his or her community [ 20 ]. Mental health covers three main components, including psychological, emotional and social health [ 21 ]. Further, psychological health has two distinct indicators, psychological well-being (e.g., self-esteem and quality of life) and psychological ill-being (e.g., pre-clinical psychological states such as psychological difficulties and high levels of stress) [ 22 ]. Emotional well-being describes how an individual feels about themselves (including life satisfaction, interest in life, loneliness, and happiness); and social well–being includes an individual’s contribution to, and integration in society [ 23 ].
Mental illnesses are common among adults and incidence rates have remained consistently high over the past 25 years (~ 10% of people affected globally) [ 24 ]. Recent statistics released by the World Health Organization indicate that depression and anxiety are the most common mental disorders, affecting an estimated 264 million people, ranking as one of the main causes of disability worldwide [ 25 , 26 ]. Specific elements of social health, including high levels of isolation and loneliness among adults, are now also considered a serious public health concern due to the strong connections with ill-health [ 27 ]. Participation in sport has shown to positively impact mental and social health status, with a previous systematic review by Eime et al. (2013) indicated that sports participation was associated with lower levels of perceived stress, and improved vitality, social functioning, mental health, and life satisfaction [ 1 ]. Based on their findings, the authors developed a conceptual model (health through sport) depicting the relationship between determinants of adult sports participation and physical, psychological, and social health benefits of participation. In support of Eime’s review findings, Malm and colleagues (2019) recently described how sport aids in preventing or alleviating mental illness, including depressive symptoms and anxiety or stress-related disease [ 7 ]. Andersen (2019) also highlighted that team sports participation is associated with decreased rates of depression and anxiety [ 11 ]. In general, these reviews report stronger effects for sports participation compared to other types of physical activity, and a dose–response relationship between sports participation and mental health outcomes (i.e., higher volume and/or intensity of participation being associated with greater health benefits) when adults participate in sports they enjoy and choose [ 1 , 7 ]. Sport is typically more social than other forms of physical activity, including enhanced social connectedness, social support, peer bonding, and club support, which may provide some explanation as to why sport appears to be especially beneficial to mental and social health [ 28 ].
Thoits (2011) proposed several potential mechanisms through which social relationships and social support improve physical and psychological well-being [ 29 ]; however, these mechanisms have yet to be explored in the context of sports participation at any level in adults. The identification of the mechanisms responsible for such effects may direct future research in this area and help inform future policy and practice in the delivery of sport to enhance mental health and social outcomes amongst adult participants. Therefore, the primary objective of this review was to examine and synthesize all research findings regarding the relationship between sports participation, mental health and social outcomes at the community and elite level in adults. Based on the review findings, the secondary objective was to develop the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model.
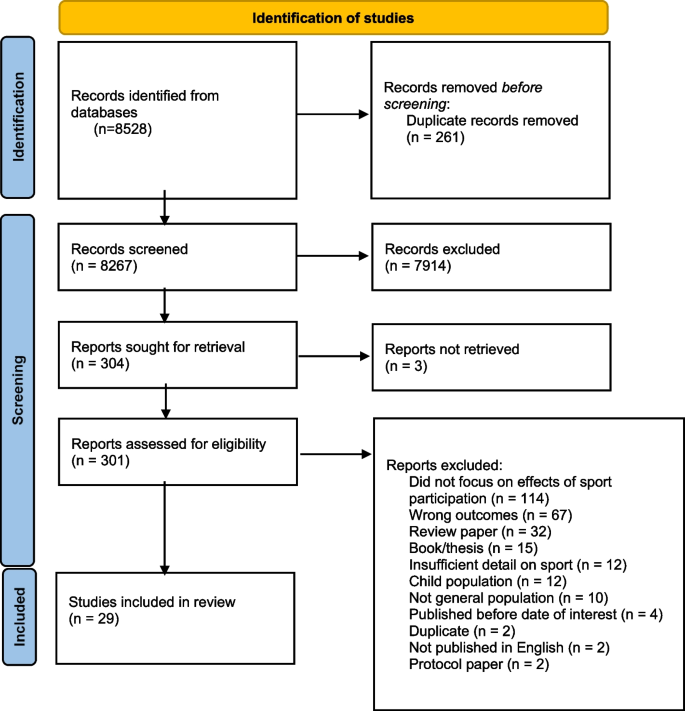
This review has been registered in the PROSPERO systematic review database and assigned the identifier: CRD42020185412. The conduct and reporting of this systematic review also follows the Preferred Reporting for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [ 30 ] (PRISMA flow diagram and PRISMA Checklist available in supplementary files ). This review is an update of a previous review of the same topic [ 31 ], published in 2012.
Identification of studies
Nine electronic databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Informit, Medline, PsychINFO, Psychology and Behavioural Sciences Collection, Scopus, and SPORTDiscus) were systematically searched for relevant records published from 2012 to March 10, 2020. The following key terms were developed by all members of the research team (and guided by previous reviews) and entered into these databases by author LW: sport* AND health AND value OR benefit* OR effect* OR outcome* OR impact* AND psych* OR depress* OR stress OR anxiety OR happiness OR mood OR ‘quality of life’ OR ‘social health’ OR ‘social relation*’ OR well* OR ‘social connect*’ OR ‘social functioning’ OR ‘life satisfac*’ OR ‘mental health’ OR social OR sociolog* OR affect* OR enjoy* OR fun. Where possible, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were also used.
Criteria for inclusion/exclusion
The titles of studies identified using this method were screened by LW. Abstract and full text of the articles were reviewed independently by LW and NE. To be included in the current review, each study needed to meet each of the following criteria: (1) published in English from 2012 to 2020; (2) full-text available online; (3) original research or report published in a peer-reviewed journal; (4) provides data on the psychological or social effects of participation in sport (with sport defined as a subset of exercise that can be undertaken individually or as a part of a team, where participants adhere to a common set of rules or expectations, and a defined goal exists); (5) the population of interest were adults (18 years and older) and were apparently healthy. All papers retrieved in the initial search were assessed for eligibility by title and abstract. In cases where a study could not be included or excluded via their title and abstract, the full text of the article was reviewed independently by two of the authors.
Data extraction
For the included studies, the following data was extracted independently by LW and checked by NE using a customized Google Docs spreadsheet: author name, year of publication, country, study design, aim, type of sport (e.g., tennis, hockey, team, individual), study conditions/comparisons, sample size, where participants were recruited from, mean age of participants, measure of sports participation, measure of physical activity, psychological and/or social outcome/s, measure of psychological and/or social outcome/s, statistical method of analysis, changes in physical activity or sports participation, and the psychological and/or social results.
Risk of bias (ROB) assessment
A risk of bias was performed by LW and AP independently using the ‘Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies’ OR the ‘Quality Assessment of Controlled Intervention Studies’ for the included quantitative studies, and the ‘Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) Checklist for the included qualitative studies [ 32 , 33 ]. Any discrepancies in the ROB assessments were discussed between the two reviewers, and a consensus reached.
The search yielded 8528 studies, with a total of 29 studies included in the systematic review (Fig. 1 ). Tables 1 and 2 provide a summary of the included studies. The research included adults from 18 to 84 years old, with most of the evidence coming from studies targeting young adults (18–25 years). Study samples ranged from 14 to 131, 962, with the most reported psychological outcomes being self-rated mental health ( n = 5) and depression ( n = 5). Most studies did not investigate or report the link between a particular sport and a specific mental health or social outcome; instead, the authors’ focused on comparing the impact of sport to physical activity, and/or individual sports compared to team sports. The results of this review are summarized in the following section, with findings presented by study design (cross-sectional, experimental, and longitudinal).
Flow of studies through the review process
Effects of sports participation on psychological well-being, ill-being, and social outcomes
Cross-sectional evidence.
This review included 14 studies reporting on the cross-sectional relationship between sports participation and psychological and/or social outcomes. Sample sizes range from n = 414 to n = 131,962 with a total of n = 239,394 adults included across the cross-sectional studies.
The cross-sectional evidence generally supports that participation in sport, and especially team sports, is associated with greater mental health and psychological wellbeing in adults compared to non-participants [ 36 , 59 ]; and that higher frequency of sports participation and/or sport played at a higher level of competition, are also linked to lower levels of mental distress in adults . This was not the case for one specific study involving ice hockey players aged 35 and over, with Kitchen and Chowhan (2016) Kitchen and Chowhan (2016) reporting no relationship between participation in ice hockey and either mental health, or perceived life stress [ 54 ]. There is also some evidence to support that previous participation in sports (e.g., during childhood or young adulthood) is linked to better mental health outcomes later in life, including improved mental well-being and lower mental distress [ 59 ], even after controlling for age and current physical activity.
Compared to published community data for adults, elite or high-performance adult athletes demonstrated higher levels of body satisfaction, self-esteem, and overall life satisfaction [ 39 ]; and reported reduced tendency to respond to distress with anger and depression. However, rates of psychological distress were higher in the elite sport cohort (compared to community norms), with nearly 1 in 5 athletes reporting ‘high to very high’ distress, and 1 in 3 reporting poor mental health symptoms at a level warranting treatment by a health professional in one study ( n = 749) [ 39 ].
Four studies focused on the associations between physical activity and sports participation and mental health outcomes in older adults. Physical activity was associated with greater quality of life [ 56 ], with the relationship strongest for those participating in sport in middle age, and for those who cycled in later life (> 65) [ 56 ]. Group physical activities (e.g., walking groups) and sports (e.g., golf) were also significantly related to excellent self-rated health, low depressive symptoms, high health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and a high frequency of laughter in males and females [ 60 , 61 ]. No participation or irregular participation in sport was associated with symptoms of mild to severe depression in older adults [ 62 ].
Several cross-sectional studies examined whether the effects of physical activity varied by type (e.g., total physical activity vs. sports participation). In an analysis of 1446 young adults (mean age = 18), total physical activity, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, and team sport were independently associated with mental health [ 46 ]. Relative to individual physical activity, after adjusting for covariates and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), only team sport was significantly associated with improved mental health. Similarly, in a cross-sectional analysis of Australian women, Eime, Harvey, Payne (2014) reported that women who engaged in club and team-based sports (tennis or netball) reported better mental health and life satisfaction than those who engaged in individual types of physical activity [ 47 ]. Interestingly, there was no relationship between the amount of physical activity and either of these outcomes, suggesting that other qualities of sports participation contribute to its relationship to mental health and life satisfaction. There was also some evidence to support a relationship between exercise type (ball sports, aerobic activity, weightlifting, and dancing), and mental health amongst young adults (mean age 22 years) [ 48 ], with ball sports and dancing related to fewer symptoms of depression in students with high stress; and weightlifting related to fewer depressive symptoms in weightlifters exhibiting low stress.
Longitudinal evidence
Eight studies examined the longitudinal relationship between sports participation and either mental health and/or social outcomes. Sample sizes range from n = 113 to n = 1679 with a total of n = 7022 adults included across the longitudinal studies.
Five of the included longitudinal studies focused on the relationship between sports participation in childhood or adolescence and mental health in young adulthood. There is evidence that participation in sport in high-school is protective of future symptoms of anxiety (including panic disorder, generalised anxiety disorder, social phobia, and agoraphobia) [ 42 ]. Specifically, after controlling for covariates (including current physical activity), the number of years of sports participation in high school was shown to be protective of symptoms of panic and agoraphobia in young adulthood, but not protective of symptoms of social phobia or generalized anxiety disorder [ 42 ]. A comparison of individual or team sports participation also revealed that participation in either context was protective of panic disorder symptoms, while only team sport was protective of agoraphobia symptoms, and only individual sport was protective of social phobia symptoms. Furthermore, current and past sports team participation was shown to negatively relate to adult depressive symptoms [ 43 ]; drop out of sport was linked to higher depressive symptoms in adulthood compared to those with maintained participation [ 9 , 22 , 63 ]; and consistent participation in team sports (but not individual sport) in adolescence was linked to higher self-rated mental health, lower perceived stress and depressive symptoms, and lower depression scores in early adulthood [ 53 , 58 ].
Two longitudinal studies [ 35 , 55 ], also investigated the association between team and individual playing context and mental health. Dore and colleagues [ 35 ] reported that compared to individual activities, being active in informal groups (e.g., yoga, running groups) or team sports was associated with better mental health, fewer depressive symptoms and higher social connectedness – and that involvement in team sports was related to better mental health regardless of physical activity volume. Kim and James [ 55 ] discovered that sports participation led to both short and long-term improvements in positive affect and life satisfaction.
A study on social outcomes related to mixed martial-arts (MMA) and Brazilian jiu-jitsu (BJJ) showed that both sports improved practitioners’ self-control and pro-social behavior, with greater improvements seen in the BJJ group [ 62 ]. Notably, while BJJ reduced participants’ reported aggression, there was a slight increase in MMA practitioners, though it is worth mentioning that individuals who sought out MMA had higher levels of baseline aggression.
Experimental evidence
Six of the included studies were experimental or quasi-experimental. Sample sizes ranged from n = 28 to n = 55 with a total of n = 239 adults included across six longitudinal studies. Three studies involved a form of martial arts (such as judo and karate) [ 45 , 51 , 52 ], one involved a variety of team sports (such as netball, soccer, and cricket) [ 34 ], and the remaining two focused on badminton [ 57 ] and handball [ 49 ].
Brinkley and colleagues [ 34 ] reported significant effects on interpersonal communication (but not vitality, social cohesion, quality of life, stress, or interpersonal relationships) for participants ( n = 40) engaging in a 12-week workplace team sports intervention. Also using a 12-week intervention, Hornstrup et al. [ 49 ] reported a significant improvement in mental energy (but not well-being or anxiety) in young women (mean age = 24; n = 28) playing in a handball program. Patterns et al. [ 57 ] showed that in comparison to no exercise, participation in an 8-week badminton or running program had no significant improvement on self-esteem, despite improvements in perceived and actual fitness levels.
Three studies examined the effect of martial arts on the mental health of older adults (mean ages 79 [ 52 ], 64 [ 51 ], and 70 [ 45 ] years). Participation in Karate-Do had positive effects on overall mental health, emotional wellbeing, depression and anxiety when compared to other activities (physical, cognitive, mindfulness) and a control group [ 51 , 52 ]. Ciaccioni et al. [ 45 ] found that a Judo program did not affect either the participants’ mental health or their body satisfaction, citing a small sample size, and the limited length of the intervention as possible contributors to the findings.
Qualitative evidence
Three studies interviewed current or former sports players regarding their experiences with sport. Chinkov and Holt [ 41 ] reported that jiu-jitsu practitioners (mean age 35 years) were more self-confident in their lives outside of the gym, including improved self-confidence in their interactions with others because of their training. McGraw and colleagues [ 37 ] interviewed former and current National Football League (NFL) players and their families about its impact on the emotional and mental health of the players. Most of the players reported that their NFL career provided them with social and emotional benefits, as well as improvements to their self-esteem even after retiring. Though, despite these benefits, almost all the players experienced at least one mental health challenge during their career, including depression, anxiety, or difficulty controlling their temper. Some of the players and their families reported that they felt socially isolated from people outside of the national football league.
Through a series of semi-structured interviews and focus groups, Thorpe, Anders [ 40 ] investigated the impact of an Aboriginal male community sporting team on the health of its players. The players reported they felt a sense of belonging when playing in the team, further noting that the social and community aspects were as important as the physical health benefits. Participating in the club strengthened the cultural identity of the players, enhancing their well-being. The players further noted that participation provided them with enjoyment, stress relief, a sense of purpose, peer support, and improved self-esteem. Though they also noted challenges, including the presence of racism, community conflict, and peer-pressure.
Quality of studies
Full details of our risk of bias (ROB) results are provided in Supplementary Material A . Of the three qualitative studies assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP), all three were deemed to have utilised and reported appropriate methodological standards on at least 8 of the 10 criteria. Twenty studies were assessed using the Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies, with all studies clearly reporting the research question/s or objective/s and study population. However, only four studies provided a justification for sample size, and less than half of the studies met quality criteria for items 6, 7, 9, or 10 (and items 12 and 13 were largely not applicable). Of concern, only four of the observational or cohort studies were deemed to have used clearly defined, valid, and reliable exposure measures (independent variables) and implemented them consistently across all study participants. Six studies were assessed using the Quality Assessment of Controlled Intervention Studies, with three studies described as a randomized trial (but none of the three reported a suitable method of randomization, concealment of treatment allocation, or blinding to treatment group assignment). Three studies showed evidence that study groups were similar at baseline for important characteristics and an overall drop-out rate from the study < 20%. Four studies reported high adherence to intervention protocols (with two not reporting) and five demonstrated that.study outcomes were assessed using valid and reliable measures and implemented consistently across all study participants. Importantly, researchers did not report or have access to validated instruments for assessing sport participation or physical activity amongst adults, though most studies provided psychometrics for their mental health outcome measure/s. Only one study reported that the sample size was sufficiently powered to detect a difference in the main outcome between groups (with ≥ 80% power) and that all participants were included in the analysis of results (intention-to-treat analysis). In general, the methodological quality of the six randomised studies was deemed low.
Initially, our discussion will focus on the review findings regarding sports participation and well-being, ill-being, and psychological health. However, the heterogeneity and methodological quality of the included research (especially controlled trials) should be considered during the interpretation of our results. Considering our findings, the Mental Health through Sport conceptual model for adults will then be presented and discussed and study limitations outlined.
Sports participation and psychological well-being
In summary, the evidence presented here indicates that for adults, sports participation is associated with better overall mental health [ 36 , 46 , 47 , 59 ], mood [ 56 ], higher life satisfaction [ 39 , 47 ], self-esteem [ 39 ], body satisfaction [ 39 ], HRQoL [ 60 ], self-rated health [ 61 ], and frequency of laughter [ 61 ]. Sports participation has also shown to be predictive of better psychological wellbeing over time [ 35 , 53 ], higher positive affect [ 55 ], and greater life satisfaction [ 55 ]. Furthermore, higher frequency of sports participation and/or sport played at a higher level of competition, have been linked to lower levels of mental distress, higher levels of body satisfaction, self-esteem, and overall life satisfaction in adults [ 39 ].
Despite considerable heterogeneity of sports type, cross-sectional and experimental research indicate that team-based sports participation, compared to individual sports and informal group physical activity, has a more positive effect on mental energy [ 49 ], physical self-perception [ 57 ], and overall psychological health and well-being in adults, regardless of physical activity volume [ 35 , 46 , 47 ]. And, karate-do benefits the subjective well-being of elderly practitioners [ 51 , 52 ]. Qualitative research in this area has queried participants’ experiences of jiu-jitsu, Australian football, and former and current American footballers. Participants in these sports reported that their participation was beneficial for psychological well-being [ 37 , 40 , 41 ], improved self-esteem [ 37 , 40 , 41 ], and enjoyment [ 37 ].
Sports participation and psychological ill-being
Of the included studies, n = 19 examined the relationship between participating in sport and psychological ill-being. In summary, there is consistent evidence that sports participation is related to lower depression scores [ 43 , 48 , 61 , 62 ]. There were mixed findings regarding psychological stress, where participation in childhood (retrospectively assessed) was related to lower stress in young adulthood [ 41 ], but no relationship was identified between recreational hockey in adulthood and stress [ 54 ]. Concerning the potential impact of competing at an elite level, there is evidence of higher stress in elite athletes compared to community norms [ 39 ]. Further, there is qualitative evidence that many current or former national football league players experienced at least one mental health challenge, including depression, anxiety, difficulty controlling their temper, during their career [ 37 ].
Evidence from longitudinal research provided consistent evidence that participating in sport in adolescence is protective of symptoms of depression in young adulthood [ 43 , 53 , 58 , 63 ], and further evidence that participating in young adulthood is related to lower depressive symptoms over time (6 months) [ 35 ]. Participation in adolescence was also protective of manifestations of anxiety (panic disorder and agoraphobia) and stress in young adulthood [ 42 ], though participation in young adulthood was not related to a more general measure of anxiety [ 35 ] nor to changes in negative affect [ 55 ]). The findings from experimental research were mixed. Two studies examined the effect of karate-do on markers of psychological ill-being, demonstrating its capacity to reduce anxiety [ 52 ], with some evidence of its effectiveness on depression [ 51 ]. The other studies examined small-sided team-based games but showed no effect on stress or anxiety [ 34 , 49 ]. Most studies did not differentiate between team and individual sports, though one study found that adolescents who participated in team sports (not individual sports) in secondary school has lower depression scores in young adulthood [ 58 ].
Sports participation and social outcomes
Seven of the included studies examined the relationship between sports participation and social outcomes. However, very few studies examined social outcomes or tested a social outcome as a potential mediator of the relationship between sport and mental health. It should also be noted that this body of evidence comes from a wide range of sport types, including martial arts, professional football, and workplace team-sport, as well as different methodologies. Taken as a whole, the evidence shows that participating in sport is beneficial for several social outcomes, including self-control [ 50 ], pro-social behavior [ 50 ], interpersonal communication [ 34 ], and fostering a sense of belonging [ 40 ]. Further, there is evidence that group activity, for example team sport or informal group activity, is related to higher social connectedness over time, though analyses showed that social connectedness was not a mediator for mental health [ 35 ].
There were conflicting findings regarding social effects at the elite level, with current and former NFL players reporting that they felt socially isolated during their career [ 37 ], whilst another study reported no relationship between participation at the elite level and social dysfunction [ 39 ]. Conversely, interviews with a group of indigenous men revealed that they felt as though participating in an all-indigenous Australian football team provided them with a sense of purpose, and they felt as though the social aspect of the game was as important as the physical benefits it provides [ 40 ].
Mental health through sport conceptual model for adults
The ‘Health through Sport’ model provides a depiction of the determinants and benefits of sports participation [ 31 ]. The model recognises that the physical, mental, and social benefits of sports participation vary by the context of sport (e.g., individual vs. team, organized vs. informal). To identify the elements of sport which contribute to its effect on mental health outcomes, we describe the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ model (Fig. 2 ). The model proposes that the social and physical elements of sport each provide independent, and likely synergistic contributions to its overall influence on mental health.
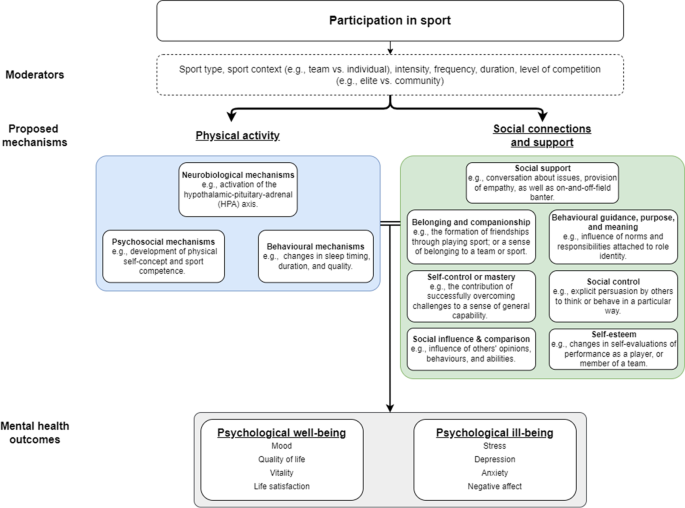
The Mental Health through Sport conceptual model
The model describes two key pathways through which sport may influence mental health: physical activity, and social relationships and support. Several likely moderators of this effect are also provided, including sport type, intensity, frequency, context (team vs. individual), environment (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor), as well as the level of competition (e.g., elite vs. amateur).
The means by which the physical activity component of sport may influence mental health stems from the work of Lubans et al., who propose three key groups of mechanisms: neurobiological, psychosocial, and behavioral [ 64 ]. Processes whereby physical activity may enhance psychological outcomes via changes in the structural and functional composition of the brain are referred to as neurobiological mechanisms [ 65 , 66 ]. Processes whereby physical activity provides opportunities for the development of self-efficacy, opportunity for mastery, changes in self-perceptions, the development of independence, and for interaction with the environment are considered psychosocial mechanisms. Lastly, processes by which physical activity may influence behaviors which ultimately affect psychological health, including changes in sleep duration, self-regulation, and coping skills, are described as behavioral mechanisms.
Playing sport offers the opportunity to form relationships and to develop a social support network, both of which are likely to influence mental health. Thoits [ 29 ] describes 7 key mechanisms by which social relationships and support may influence mental health: social influence/social comparison; social control; role-based purpose and meaning (mattering); self-esteem; sense of control; belonging and companionship; and perceived support availability [ 29 ]. These mechanisms and their presence within a sporting context are elaborated below.
Subjective to the attitudes and behaviors of individuals in a group, social influence and comparison may facilitate protective or harmful effects on mental health. Participants in individual or team sport will be influenced and perhaps steered by the behaviors, expectations, and norms of other players and teams. When individual’s compare their capabilities, attitudes, and values to those of other participants, their own behaviors and subsequent health outcomes may be affected. When others attempt to encourage or discourage an individual to adopt or reject certain health practices, social control is displayed [ 29 ]. This may evolve as strategies between players (or between players and coach) are discussion and implemented. Likewise, teammates may try to motivate each another during a match to work harder, or to engage in specific events or routines off-field (fitness programs, after game celebrations, attending club events) which may impact current and future physical and mental health.
Sport may also provide behavioral guidance, purpose, and meaning to its participants. Role identities (positions within a social structure that come with reciprocal obligations), often formed as a consequence of social ties formed through sport. Particularly in team sports, participants come to understand they form an integral part of the larger whole, and consequently, they hold certain responsibility in ensuring the team’s success. They have a commitment to the team to, train and play, communicate with the team and a potential responsibility to maintain a high level of health, perform to their capacity, and support other players. As a source of behavioral guidance and of purpose and meaning in life, these identities are likely to influence mental health outcomes amongst sport participants.
An individual’s level of self-esteem may be affected by the social relationships and social support provided through sport; with improved perceptions of capability (or value within a team) in the sporting domain likely to have positive impact on global self-esteem and sense of worth [ 64 ]. The unique opportunities provided through participation in sport, also allow individuals to develop new skills, overcome challenges, and develop their sense of self-control or mastery . Working towards and finding creative solutions to challenges in sport facilitates a sense of mastery in participants. This sense of mastery may translate to other areas of life, with individual’s developing the confidence to cope with varied life challenges. For example, developing a sense of mastery regarding capacity to formulate new / creative solutions when taking on an opponent in sport may result in greater confidence to be creative at work. Social relationships and social support provided through sport may also provide participants with a source of belonging and companionship. The development of connections (on and off the field) to others who share common interests, can build a sense of belonging that may mediate improvements in mental health outcomes. Social support is often provided emotionally during expressions of trust and care; instrumentally via tangible assistance; through information such as advice and suggestions; or as appraisal such feedback. All forms of social support provided on and off the field contribute to a more generalised sense of perceived support that may mediate the effect of social interaction on mental health outcomes.
Participation in sport may influence mental health via some combination of the social mechanisms identified by Thoits, and the neurobiological, psychosocial, and behavioral mechanisms stemming from physical activity identified by Lubans [ 29 , 64 ]. The exact mechanisms through which sport may confer psychological benefit is likely to vary between sports, as each sport varies in its physical and social requirements. One must also consider the social effects of sports participation both on and off the field. For instance, membership of a sporting team and/or club may provide a sense of identity and belonging—an effect that persists beyond the immediacy of playing the sport and may have a persistent effect on their psychological health. Furthermore, the potential for team-based activity to provide additional benefit to psychological outcomes may not just be attributable to the differences in social interactions, there are also physiological differences in the requirements for sport both within (team vs. team) and between (team vs. individual) categories that may elicit additional improvements in psychological outcomes. For example, evidence supports that exercise intensity moderates the relationship between physical activity and several psychological outcomes—supporting that sports performed at higher intensity will be more beneficial for psychological health.
Limitations and recommendations
There are several limitations of this review worthy of consideration. Firstly, amongst the included studies there was considerable heterogeneity in study outcomes and study methodology, and self-selection bias (especially in non-experimental studies) is likely to influence study findings and reduce the likelihood that study participants and results are representative of the overall population. Secondly, the predominately observational evidence included in this and Eime’s prior review enabled us to identify the positive relationship between sports participation and social and psychological health (and examine directionality)—but more experimental and longitudinal research is required to determine causality and explore potential mechanisms responsible for the effect of sports participation on participant outcomes. Additional qualitative work would also help researchers gain a better understanding of the relationship between specific elements of the sporting environment and mental health and social outcomes in adult participants. Thirdly, there were no studies identified in the literature where sports participation involved animals (such as equestrian sports) or guns (such as shooting sports). Such studies may present novel and important variables in the assessment of mental health benefits for participants when compared to non-participants or participants in sports not involving animals/guns—further research is needed in this area. Our proposed conceptual model also identifies several pathways through which sport may lead to improvements in mental health—but excludes some potentially negative influences (such as poor coaching behaviors and injury). And our model is not designed to capture all possible mechanisms, creating the likelihood that other mechanisms exist but are not included in this review. Additionally, an interrelationship exits between physical activity, mental health, and social relationships, whereby changes in one area may facilitate changes in the other/s; but for the purpose of this study, we have focused on how the physical and social elements of sport may mediate improvements in psychological outcomes. Consequently, our conceptual model is not all-encompassing, but designed to inform and guide future research investigating the impact of sport participation on mental health.
The findings of this review endorse that participation in sport is beneficial for psychological well-being, indicators of psychological ill-being, and social outcomes in adults. Furthermore, participation in team sports is associated with better psychological and social outcomes compared to individual sports or other physical activities. Our findings support and add to previous review findings [ 1 ]; and have informed the development of our ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model for adults which presents the potential mechanisms by which participation in sport may affect mental health.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Eime RM, Young JA, Harvey JT, Charity MJ, Payne WR. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for adults: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10:135.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ishihara T, Nakajima T, Yamatsu K, Okita K, Sagawa M, Morita N. Relationship of participation in specific sports to academic performance in adolescents: a 2-year longitudinal study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020.
Cope E, Bailey R, Pearce G. Why do children take part in, and remain involved in sport?: implications for children’s sport coaches. Int J Coach Sci. 2013;7:55–74.
Google Scholar
Harrison PA, Narayan G. Differences in behavior, psychological factors, and environmental factors associated with participation in school sports and other activities in adolescence. J Sch Health. 2003;73(3):113–20.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Allender S, Cowburn G, Foster C. Understanding particpation in sport and physical activity among children and adults: a review of qualitative studies. Health Educ Res. 2006;21(6):826–35.
Adachi P, Willoughby T. It’s not how much you play, but how much you enjoy the game: The longitudinal associations between adolescents’ self-esteem and the frequency versus enjoyment of involvement in sports. J Youth Adolesc. 2014;43(1):137–45.
Malm C, Jakobsson J, Isaksson A. Physical activity and sports-real health benefits: a review with insight into the public health of Sweden. Sports (Basel, Switzerland). 2019;7(5):127.
PubMed Google Scholar
Mills K, Dudley D, Collins NJ. Do the benefits of participation in sport and exercise outweigh the negatives? An academic review. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):172–87.
Howie EK, Guagliano JM, Milton K, Vella SA, Gomersall SR,Kolbe-Alexander TL, et al. Ten research priorities related to youth sport, physical activity, and health. 2020;17(9):920.
Vella SA, Swann C, Allen MS, Schweickle MJ, Magee CA. Bidirectional associations between sport involvement and mental health in adolescence. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(4):687–94.
Andersen MH, Ottesen L, Thing LF. The social and psychological health outcomes of team sport participation in adults: An integrative review of research. Scand J Public Health. 2019;47(8):832–50.
Rice SM, Purcell R, De Silva S, Mawren D, McGorry PD, Parker AG. The mental health of elite athletes: a narrative systematic review. Sports medicine (Auckland, NZ). 2016;46(9):1333–53.
Article Google Scholar
Hulteen RM, Smith JJ, Morgan PJ, Barnett LM, Hallal PC, Colyvas K, et al. Global participation in sport and leisure-time physical activities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev Med. 2017;95:14–25.
Eime RM, Harvey J, Charity M, Westerbeek H. Longitudinal Trends in Sport Participation and Retention of Women and Girls. Front Sports Act Living. 2020;2:39.
Brooke HL, Corder K, Griffin SJ, van Sluijs EMF. Physical activity maintenance in the transition to adolescence: a longitudinal study of the roles of sport and lifestyle activities in british youth. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2): e89028.
Coll CVN, Knuth AG, Bastos JP, Hallal PC, Bertoldi AD. Time trends of physical activity among Brazilian adolescents over a 7-year period. J Adolesc Health. 2014;54:209–13.
Klostermann C, Nagel S. Changes in German sport participation: Historical trends in individual sports. Int Rev Sociol Sport. 2012;49:609–34.
Eime RM, Harvey J, Charity M. Sport participation settings: where and “how” do Australians play sport? BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1344.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lim SY, Warner S, Dixon M, Berg B, Kim C, Newhouse-Bailey M. Sport Participation Across National Contexts: A Multilevel Investigation of Individual and Systemic Influences on Adult Sport Participation. Eur Sport Manag Q. 2011;11(3):197–224.
World Health Organisation. Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2020. Geneva: World Health Orgnaisation; 2013.
Keyes C. Bridging Occupational, Organizational and Public Health. Netherlands: Springer Dordrecht; 2014.
Ryff C, Love G, Urry H, Muller D, Rosenkranz M, Friedman E, et al. Psychological well-being and ill-being: Do they have distinct or mirrored biological correlates? Psychother Psychosom. 2006;75:85–95.
Australian Government. Social and emotional wellbeing: Development of a children’s headline indicator information paper. Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; 2013.
Global Burden of Disease Injury IP. Collaborators, Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789–858.
World Health Organisation. Mental disorders: Fact sheet 2019 [Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders .
Mental Health [Internet]. 2018 [cited 12 March 2021]. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/mental-health ' [Online Resource].
Newman MG, Zainal NH. The value of maintaining social connections for mental health in older people. The Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(1):e12–3.
Eime RM, Harvey JT, Brown WJ, Payne WR. Does sports club participation contribute to health-related quality of life? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(5):1022–8.
Thoits PA. Mechanisms linking social ties and support to physical and mental health. J Health Soc Behav. 2011;52(2):145–61.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021;18(3): e1003583.
Eime RM, Young JA, Harvey JT, Charity MJ, Payne WR. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for adults: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10(1):135.
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. CASP Qualitative Studies Checklist2019 1/12/2021]. Available from: https://casp-uk.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CASP-Qualitative-Checklist-2018.pdf .
National Institutes from Health. Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies 2014 [Available from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools .
Brinkley A, McDermott H, Grenfell-Essam R. It’s time to start changing the game: a 12-week workplace team sport intervention study. Sports Med Open. 2017;3(1):30–41.
Doré I, O’Loughlin JL, Schnitzer ME, Datta GD, Fournier L. The longitudinal association between the context of physical activity and mental health in early adulthood. Ment Health Phys Act. 2018;14:121–30.
Marlier M, Van Dyck D, Cardon G, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Babiak K, Willem A. Interrelation of sport participation, physical activity, social capital and mental health in disadvantaged communities: A sem-analysis. PLoS ONE [Internet]. 2015; 10(10):[e0140196 p.]. Available from: http://ezproxy.newcastle.edu.au/login?url=http://ezproxy.newcastle.edu.au/login?url=http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&CSC=Y&NEWS=N&PAGE=fulltext&D=med12&AN=26451731 .
McGraw SA, Deubert CR, Lynch HF, Nozzolillo A, Taylor L, Cohen I. Life on an emotional roller coaster: NFL players and their family members’ perspectives on player mental health. J Clin Sport Psychol. 2018;12(3):404–31.
Mickelsson T. Modern unexplored martial arts – what can mixed martial arts and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu do for youth development?. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(3):386–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2019.1629180 .
Purcell R, Rice S, Butterworth M, Clements M. Rates and Correlates of Mental Health Symptoms in Currently Competing Elite Athletes from the Australian National High-Performance Sports System. Sports Med. 2020.
Thorpe A, Anders W, Rowley K. The community network: an Aboriginal community football club bringing people together. Aust J Prim Health. 2014;20(4):356–64.
Appelqvist-Schmidlechner K, Vaara J, Hakkinen A, Vasankari T, Makinen J, Mantysaari M, et al. Relationships between youth sports participation and mental health in young adulthood among Finnish males. Am J Health Promot. 2018;32(7):1502–9.
Ashdown-Franks G, Sabiston CM, Solomon-Krakus S, O’Loughlin JL. Sport participation in high school and anxiety symptoms in young adulthood. Ment Health Phys Act. 2017;12:19–24.
Brunet J, Sabiston CM, Chaiton M, Barnett TA, O’Loughlin E, Low NC, et al. The association between past and current physical activity and depressive symptoms in young adults: a 10-year prospective study. Ann Epidemiol. 2013;23(1):25–30.
Chinkov AE, Holt NL. Implicit transfer of life skills through participation in Brazilian Jiu-jitsu. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2016;28(2):139–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10413200.2015.1086447 .
Ciaccioni S, Capranica L, Forte R, Chaabene H, Pesce C, Condello G. Effects of a judo training on functional fitness, anthropometric, and psychological variables in old novice practitioners. J Aging Phys Act. 2019;27(6):831–42.
Doré I, O’Loughlin JL, Beauchamp G, Martineau M, Fournier L. Volume and social context of physical activity in association with mental health, anxiety and depression among youth. Prev Med. 2016;91:344–50.
Eime R, Harvey J, Payne W. Dose-response of women’s health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and life satisfaction to physical activity. J Phys Act Health. 2014;11(2):330–8.
Gerber M, Brand S, Elliot C, Holsboer-Trachsler E, Pühse U. Aerobic exercise, ball sports, dancing, and weight Lifting as moderators of the relationship between Stress and depressive symptoms: an exploratory cross-sectional study with Swiss university students. Percept Mot Skills. 2014;119(3):679–97.
Hornstrup T, Wikman JM, Fristrup B, Póvoas S, Helge EW, Nielsen SH, et al. Fitness and health benefits of team handball training for young untrained women—a cross-disciplinary RCT on physiological adaptations and motivational aspects. J Sport Health Sci. 2018;7(2):139–48.
Mickelsson T. Modern unexplored martial arts–what can mixed martial arts and Brazilian Jiu-Jiutsu do for youth development? Eur J Sport Sci. 2019.
Jansen P, Dahmen-Zimmer K. Effects of cognitive, motor, and karate training on cognitive functioning and emotional well-being of elderly people. Front Psychol. 2012;3:40.
Jansen P, Dahmen-Zimmer K, Kudielka BM, Schulz A. Effects of karate training versus mindfulness training on emotional well-being and cognitive performance in later life. Res Aging. 2017;39(10):1118–44.
Jewett R, Sabiston CM, Brunet J, O’Loughlin EK, Scarapicchia T, O’Loughlin J. School sport participation during adolescence and mental health in early adulthood. J Adolesc Health. 2014;55(5):640–4.
Kitchen P, Chowhan J. Forecheck, backcheck, health check: the benefits of playing recreational ice hockey for adults in Canada. J Sports Sci. 2016;34(21):2121–9.
Kim J, James JD. Sport and happiness: Understanding the relations among sport consumption activities, long-and short-term subjective well-being, and psychological need fulfillment. J Sport Manage. 2019.
Koolhaas CH, Dhana K, Van Rooij FJA, Schoufour JD, Hofman A, Franco OH. Physical activity types and health-related quality of life among middle-aged and elderly adults: the Rotterdam study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(2):246–53.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Patterson S, Pattison J, Legg H, Gibson AM, Brown N. The impact of badminton on health markers in untrained females. J Sports Sci. 2017;35(11):1098–106.
Sabiston CM, Jewett R, Ashdown-Franks G, Belanger M, Brunet J, O’Loughlin E, et al. Number of years of team and individual sport participation during adolescence and depressive symptoms in early adulthood. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2016;38(1):105–10.
Sorenson SC, Romano R, Scholefield RM, Martin BE, Gordon JE, Azen SP, et al. Holistic life-span health outcomes among elite intercollegiate student-athletes. J Athl Train. 2014;49(5):684–95.
Stenner B, Mosewich AD, Buckley JD, Buckley ES. Associations between markers of health and playing golf in an Australian population. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2019;5(1).
Tsuji T, Kanamori S, Saito M, Watanabe R, Miyaguni Y, Kondo K. Specific types of sports and exercise group participation and socio-psychological health in older people. J Sports Sci. 2020;38(4):422–9.
Yamakita M, Kanamori S, Kondo N, Kondo K. Correlates of regular participation in sports groups among Japanese older adults: JAGES cross–sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(10):e0141638.
Howie EK, McVeigh JA, Smith AJ, Straker LM. Organized sport trajectories from childhood to adolescence and health associations. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(7):1331–9.
Chinkov AE, Holt NL. Implicit transfer of life skills through participation in Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2016;28(2):139–53.
Lubans D, Richards J, Hillman C, Faulkner G, Beauchamp M, Nilsson M, et al. Physical activity for cognitive and mental health in youth: a systematic review of mechanisms. Pediatrics. 2016;138(3):e20161642.
Lin TW, Kuo YM. Exercise benefits brain function: the monoamine connection. Brain Sci. 2013;3(1):39–53.
Dishman RK, O’Connor PJ. Lessons in exercise neurobiology: the case of endorphins. Ment Health Phys Act. 2009;2(1):4–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the work of the original systematic review conducted by Eime, R. M., Young, J. A., Harvey, J. T., Charity, M. J., and Payne, W. R. (2013).
No funding associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Active Living and Learning, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Narelle Eather & Levi Wade
College of Human and Social Futures, School of Education, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Narelle Eather
College of Health, Medicine, and Wellbeing, School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Institute for Health and Sport, Victoria University, Ballarat Road, Footscray, VIC, 3011, Australia
Aurélie Pankowiak & Rochelle Eime
School of Science, Psychology and Sport, Federation University Australia, University Drive, Mount Helen, VIC, 3350, Australia
Rochelle Eime
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conducting of this study and reporting the findings. The titles of studies identified were screened by LW, and abstracts and full text articles reviewed independently by LW and NE. For the included studies, data was extracted independently by LW and checked by NE, and the risk of bias assessment was performed by LW and AP independently. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript and agree with the order of presentation of the authors.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Narelle Eather .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: supplementary table a..
Risk of bias.
Additional file 2: Supplementary Table B.
PRISMA Checklist.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Eather, N., Wade, L., Pankowiak, A. et al. The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model. Syst Rev 12 , 102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02264-8
Download citation
Received : 30 August 2021
Accepted : 31 May 2023
Published : 21 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02264-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Experimental
- Observational
- Psychological health
- Mental health
- Social health
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Essay on Stress Management
500 words essay on stress management.
Stress is a very complex phenomenon that we can define in several ways. However, if you put them together, it is basically the wear and tear of daily life. Stress management refers to a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies for controlling a person’s stress level, especially chronic stress . If there is effective stress management, we can help one another break the hold of stress on our lives. The essay on stress management will throw light on the very same thing.

Identifying the Source of Stress
The first step of stress management is identifying the source of stress in your life. It is not as easy as that but it is essential. The true source of stress may not always be evident as we tend to overlook our own stress-inducing thoughts and feelings.
For instance, you might constantly worry about meeting your deadline. But, in reality, maybe your procrastination is what leads to this stress than the actual deadline. In order to identify the source of stress, we must look closely within ourselves.
If you explain away stress as temporary, then it may be a problem. Like if you yourself don’t take a breather from time to time, what is the point? On the other hand, is stress an integral part of your work and you acknowledging it like that?
If you make it a part of your personality, like you label things as crazy or nervous energy, you need to look further. Most importantly, do you blame the stress on people around you or the events surrounding you?
It is essential to take responsibility for the role one plays in creating or maintaining stress. Your stress will remain outside your control if you do not do it.
Strategies for Stress Management
It is obvious that we cannot avoid all kinds of stress but there are many stressors in your life which you can definitely eliminate. It is important to learn how to say no and stick to them. Try to avoid people who stress you out.
Further, if you cannot avoid a stressful situation, try altering it. Express your feelings don’t bottle them up and manage your time better. Moreover, you can also adapt to the stressor if you can’t change it.
Reframe problems and look at the big picture. Similarly, adjust your standards and focus on the positive side. Never try to control the uncontrollable. Most importantly, make time for having fun and relaxing.
Spend some time with nature, go for a walk or call a friend, whatever pleases you. You can also try working out, listening to music and more. As long as it makes you happy, never give up.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Stress Management
All in all, we can control our stress levels with relaxation techniques that evoke the relaxation response of our body. It is the state of restfulness that is the opposite of the stress response. Thus, when you practice these techniques regularly, you can build your resilience and heal yourself.
FAQ of Essay on Stress Management
Question 1: What is the importance of stress management?
Answer 1: Stress management is very efficient as it helps in breaking the hold which stress has on our lives. Moreover, you can also become happy, healthy and more productive because of it. The ultimate goal should be to live a balanced life and have the resilience to hold up under pressure.
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques.
Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(1); 2023 Jan

Role of Physical Activity on Mental Health and Well-Being: A Review
Aditya mahindru.
1 Department of Psychiatry, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, IND
Pradeep Patil
Varun agrawal.
In addition to the apparent physical health benefits, physical activity also affects mental health positively. Physically inactive individuals have been reported to have higher rates of morbidity and healthcare expenditures. Commonly, exercise therapy is recommended to combat these challenges and preserve mental wellness. According to empirical investigations, physical activity is positively associated with certain mental health traits. In nonclinical investigations, the most significant effects of physical exercise have been on self-concept and body image. An attempt to review the current understanding of the physiological and psychological mechanisms by which exercise improves mental health is presented in this review article. Regular physical activity improves the functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Depression and anxiety appear to be influenced by physical exercise, but to a smaller extent in the population than in clinical patients. Numerous hypotheses attempt to explain the connection between physical fitness and mental wellness. Physical activity was shown to help with sleep and improve various psychiatric disorders. Exercise in general is associated with a better mood and improved quality of life. Physical exercise and yoga may help in the management of cravings for substances, especially in people who may not have access to other forms of therapy. Evidence suggests that increased physical activity can help attenuate some psychotic symptoms and treat medical comorbidities that accompany psychotic disorders. The dearth of literature in the Indian context also indicated that more research was needed to evaluate and implement interventions for physical activity tailored to the Indian context.
Introduction and background
Physical activity has its origins in ancient history. It is thought that the Indus Valley civilization created the foundation of modern yoga in approximately 3000 B.C. during the early Bronze Age [ 1 ]. The beneficial role of physical activity in healthy living and preventing and managing health disorders is well documented in the literature. Physical activity provides various significant health benefits. Mechanical stress and repeated exposure to gravitational forces created by frequent physical exercise increase a variety of characteristics, including physical strength, endurance, bone mineral density, and neuromusculoskeletal fitness, all of which contribute to a functional and independent existence. Exercise, defined as planned, systematic, and repetitive physical activity, enhances athletic performance by improving body composition, fitness, and motor abilities [ 2 ]. The function of physical activity in preventing a wide range of chronic illnesses and premature mortality has been extensively examined and studied. Adequate evidence links medical conditions such as cardiovascular disease and individual lifestyle behaviours, particularly exercise [ 3 ]. Regular exercise lowered the incidence of cardiometabolic illness, breast and colon cancer, and osteoporosis [ 4 ]. In addition to improving the quality of life for those with nonpsychiatric diseases such as peripheral artery occlusive disease and fibromyalgia, regular physical activity may help alleviate the discomforts of these particular diseases [ 5 ]. Exercise also helps with various substance use disorders, such as reducing or quitting smoking. As physical exercise strongly impacts health, worldwide standards prescribe a weekly allowance of "150 minutes" of modest to vigorous physical exercise in clinical and non-clinical populations [ 6 ]. When these recommendations are followed, many chronic diseases can be reduced by 20%-30%. Furthermore, thorough evaluations of global studies have discovered that a small amount of physical exercise is sufficient to provide health benefits [ 7 ].
Methodology
In this review article, a current understanding of the underlying physiological and psychological processes during exercise or physical activity that are implicated in improving mental health is presented. Search terms like "exercise" or "physical activity" and "mental health", "exercise" or "physical activity" and "depression", "exercise" or "physical activity" and "stress", "exercise" or "physical activity" and "anxiety", "exercise" or "physical activity" and "psychosis," "exercise" or "physical activity" and "addiction" were used as search terms in PubMed, Google Scholar, and Medline. An overwhelming majority of references come from works published within the past decade.
The impact of physical health on mental health
There is an increasing amount of evidence documenting the beneficial impacts of physical activity on mental health, with studies examining the effects of both brief bouts of exercise and more extended periods of activity. Systematic evaluations have indicated better outcomes for mental diseases with physical activity. Numerous psychological effects, such as self-esteem, cognitive function, mood, depression, and quality of life, have been studied [ 8 ]. According to general results, exercise enhances mood and self-esteem while decreasing stress tendencies, a factor known to aggravate mental and physical diseases [ 9 ]. Studies show that people who exercise regularly have a better frame of mind. However, it should be highlighted that a consistent link between mood enhancement and exercise in healthy individuals has not been established.
Additionally, human beings produce more of these two neurochemicals when they engage in physical activity. Human bodies manufacture opioids and endocannabinoids that are linked to pleasure, anxiolytic effects, sleepiness, and reduced pain sensitivity [ 10 ]. It has been shown that exercise can improve attention, focus, memory, cognition, language fluency, and decision-making for up to two hours [ 11 ]. Researchers state that regular physical activity improves the functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, lowering cortisol secretion and restoring the balance of leptin and ghrelin (Figure (Figure1) 1 ) [ 12 ].

HPA: hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal
This image has been created by the authors.
Regular exercise has immunomodulatory effects such as optimising catecholamine, lowering cortisol levels, and lowering systemic inflammation. Physical activity has been shown to increase plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is thought to reduce amyloid-beta toxicity linked to Alzheimer's disease progression [ 13 ].
Although no causal correlations have been proven, methodologically sound research has discovered a related improvement in mentally and physically ill populations. These findings are based on research and studies conducted all across the globe, particularly in the Western Hemisphere. In order to address a widespread health problem in India, it is useful to do a literature review that draws on research conducted in a variety of settings. In addition, the prevalence of these mental illnesses and the benefits of exercise as a complementary therapy might be made clear by a meta-analysis of research undertaken in India [ 14 ].
This review also analysed published literature from India to understand the effects of exercise on mental health and the implications for disease management and treatment in the Indian context. Results from Indian studies were consistent with those found in global meta-analyses. The Indian government has made public data on interventions, such as the effects of different amounts of physical exercise. Exercising and yoga have been shown to be effective adjunct therapies for a variety of mental health conditions [ 12 ]. Though yoga may not require a lot of effort to perform, other aspects of the program, such as breathing or relaxation exercises, may have an impact on a practitioner's mental health at the same time. Due to its cultural significance as a common physical practice among Indians and its low to moderate activity level, yoga would be an appropriate activity for this assessment [ 15 ].
Yoga as an adjunctive treatment
Although yoga is a centuries-old Hindu practice, its possible therapeutic effects have recently been studied in the West. Mind-body approaches have been the subject of a lot of studies, and some of the findings suggest they may aid with mental health issues on the neurosis spectrum. As defined by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, "mind-body interventions" aim to increase the mind's potential to alter bodily functions [ 16 ]. Due to its beneficial effects on the mind-body connection, yoga is used as a treatment for a wide range of conditions. Possible therapeutic benefits of yoga include the activation of antagonistic neuromuscular systems, stimulation of the limbic system, and a reduction in sympathetic tone.
Anxiety and depression sufferers might benefit from practising yoga. Yoga is generally safe for most people and seldom causes unintended negative consequences. Adding yoga to traditional treatment for mental health issues may be beneficial. Many of the studies on yoga included meditation as an integral part of their methodology. Meditation and other forms of focused mental practice may set off a physiological reaction known as the relaxation response. Functional imaging has been used to implicate certain regions of the brain that show activity during meditation. According to a wealth of anatomical and neurochemical evidence, meditation has been shown to have far-reaching physiological effects, including changes in attention and autonomic nervous system modulation [ 17 ]. Left anterior brain activity, which is associated with happiness, was shown to rise considerably during meditation. There's also some evidence that meditation might worsen psychosis by elevating dopamine levels [ 18 - 20 ]. We do not yet know enough about the possible downsides of meditation for patients with mental illness, since this research lacks randomised controlled trials.
Physical activity and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental disorder that often manifests in one's early years of productive life (late second decade). Remission of this disorder occurs in just a small fraction of cases. More than 60% will have relapses, and they might occur with or without noticeable deficits. Apart from delusions, hallucinations, and formal thought disorders, many patients exhibit cognitive deficits that emerge in the early stages of the disease and do not respond adequately to therapy [ 21 ].
Treatment for schizophrenia is challenging to master. Extrapyramidal side effects are a problem with first-generation antipsychotic drugs. Obesity and dyslipidemia have been related to second-generation drugs, which may cause or exacerbate these conditions. The majority of patients do not achieve complete remission, and many do not even experience satisfactory symptom relief. Even though certain antipsychotic medications may alleviate or even exacerbate negative and cognitive symptoms, these responses are far less common. This means that patients may benefit from cognitive rehabilitation. Because of their illness or a negative reaction to their medicine, they may also have depressive symptoms. This would make their condition even more disabling. Many patients also deal with clinical and emotional complications. Tardive extrapyramidal illnesses, metabolic syndromes, defect states, and attempted suicide are all in this category. Patient compliance with treatment plans is often poor. The caregivers take on a lot of stress and often get exhausted as a result.
Evidence suggests that increased physical activity can aid in attenuating some psychotic symptoms and treating medical comorbidities that accompany psychotic disorders, particularly those subject to the metabolic adverse effects of antipsychotics. Physically inactive people with mental disorders have increased morbidity and healthcare costs. Exercise solutions are commonly recommended to counteract these difficulties and maintain mental and physical wellness [ 22 ].
The failure of current medications to effectively treat schizophrenia and the lack of improvement in cognitive or negative symptoms with just medication is an argument in favour of utilising yoga as a complementary therapy for schizophrenia. Even without concomitant medication therapy, co-occurring psychosis and obesity, or metabolic syndrome, are possible. The endocrine and reproductive systems of drug abusers undergo subtle alterations. Numerous studies have shown that yoga may improve endocrine function, leading to improvements in weight management, cognitive performance, and menstrual regularity, among other benefits. In this context, the role of yoga in the treatment of schizophrenia has been conceptualized. However, yoga has only been studied for its potential efficacy as a therapy in a tiny number of studies. There might be several reasons for this. To begin with, many yoga academies frown against the practice being adapted into a medical modality. The second misconception is that people with schizophrenia cannot benefit from the mental and physical aspects of yoga practised in the ways that are recommended. Third, scientists may be hesitant to recommend yoga to these patients because of their lack of knowledge and treatment compliance.
In a randomised controlled experiment with a yoga group (n = 21) and an exercise group (n = 20), the yoga group exhibited a statistically significant reduction in negative symptoms [ 2 ]. In accordance with the most recent recommendations of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), the above research provides substantial evidence for the use of yoga in the treatment of schizophrenia. According to a meta-analysis of 17 distinct studies [ 23 ] on the subject, frequent physical activity reduces the negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia considerably.
Physical activity and alcohol dependence syndrome
Substance abuse, namely alcohol abuse, may have devastating effects on a person's mental and physical health. Tolerance and an inability to control drinking are some hallmarks of alcoholism. Research shows that physical activity is an effective supplement in the fight against alcohol use disorder. In addition to perhaps acting centrally on the neurotransmitter systems, physical exercise may mitigate the deleterious health consequences of drinking. Evidence suggests that persons with alcohol use disorder are not physically active and have low cardiorespiratory fitness. A wide number of medical comorbidities, like diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and other cardiovascular illnesses, occur with alcohol use disorders. Physical exercise may be highly useful in aiding the management of these comorbidities [ 24 ].
Physical exercise and yoga may help in the management of cravings for substances when other forms of therapy, such as counselling or medication for craving management are not feasible or acceptable. Physical exercise has been shown to have beneficial effects on mental health, relieve stress, and provide an enjoyable replacement for the substance. However, the patient must take an active role in physical activity-based therapies rather than passively accept the process as it is, which is in stark contrast to the approach used by conventional medicine. Since most substance use patients lack motivation and commitment to change, it is recommended that physical activity-based therapies be supplemented with therapies focusing on motivation to change to maximise therapeutic outcomes.
One hundred seventeen persons with alcohol use disorder participated in a single-arm, exploratory trial that involved a 12-minute fitness test using a cycle ergometer as an intervention. Statistically, significantly fewer cravings were experienced by 40% [ 24 ]. Exercise programmes were found to significantly reduce alcohol intake and binge drinking in people with alcohol use disorder in a meta-analysis and comprehensive review of the effects of such therapies [ 25 ].
Physical activity and sleep
Despite widespread agreement that they should prioritise their health by making time for exercise and sufficient sleep, many individuals fail to do so. Sleep deprivation has negative impacts on immune system function, mood, glucose metabolism, and cognitive ability. Slumber is a glycogenetic process that replenishes glucose storage in neurons, in contrast to the waking state, which is organised for the recurrent breakdown of glycogen. Considering these findings, it seems that sleep has endocrine effects on the brain that are unrelated to the hormonal control of metabolism and waste clearance at the cellular level. Several factors have been proposed as potential triggers for this chain reaction: changes in core body temperature, cytokine concentrations, energy expenditure and metabolic rate, central nervous system fatigue, mood, and anxiety symptoms, heart rate and heart rate variability, growth hormone and brain-derived neurotrophic factor secretion, fitness level, and body composition [ 26 ].
After 12 weeks of fitness training, one study indicated that both the quantity and quality of sleep in adolescents improved. Studies using polysomnography indicated that regular exercise lowered NREM stage N1 (very light sleep) and raised REM sleep (and REM sleep continuity and performance) [ 22 ]. As people age, both short- and long-term activities have increasingly deleterious effects on sleep. In general, both short- and long-term exercise were found to have a favourable effect on sleep quality; however, the degree of this benefit varied substantially among different sleep components. On measures of sleep quality, including total sleep time, slow-wave sleep, sleep onset latency, and REM sleep reduction, acute exercise had no effect. But both moderate and strenuous exercise has been shown to increase sleep quality [ 27 ]. According to a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, exercise has shown a statistically significant effect on sleep quality in adults with mental illness [ 28 ]. These findings emphasise the importance that exercise plays in improving outcomes for people suffering from mental illnesses.
Physical activity in depressive and anxiety disorders
Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide and is a major contributor to the global burden of disease, as per the World Health Organization. However, only 10%-25% of depressed people actually seek therapy, maybe due to a lack of money, a lack of trained doctors, or the stigma associated with depression [ 29 ]. For those with less severe forms of mental illness, such as depression and anxiety, regular physical exercise may be a crucial part of their treatment and management. Exercise and physical activity might improve depressive symptoms in a way that is comparable to, if not more effective than, traditional antidepressants. However, research connecting exercise to a decreased risk of depression has not been analysed in depth [ 30 ]. Endorphins, like opiates, are opioid polypeptide compounds produced by the hypothalamus-pituitary system in vertebrates in response to extreme physical exertion, emotional arousal, or physical pain. The opioid system may mediate analgesia, social bonding, and depression due to the link between b-endorphins and depressive symptoms (Figure (Figure2 2 ).

The "endorphin hypothesis" states that physical activity causes the brain to produce more endogenous opioid peptides, which reduce pain and boost mood. The latter reduces feelings of worry and hopelessness. A recent study that demonstrated endorphins favourably improved mood during exercise, and provided support for these theories suggested that further research into the endorphin theory is required [ 31 ].
Physical activity and exercise have been shown to improve depressive symptoms and overall mood in people of all ages. Exercise has been implicated in lowering depressive and anxious symptoms in children and adolescents as well [ 32 ]. Pooled research worldwide has revealed that physical exercise is more effective than a control group and is a viable remedy for depression [ 33 ]. Most forms of yoga that start with a focus on breathing exercises, self-awareness, and relaxation techniques have a positive effect on depression and well-being [ 34 ]. Despite claims that exercise boosts mood, the optimal kind or amount of exercise required to have this effect remains unclear and seems to depend on a number of factors [ 35 ].
Exercise as a therapy for unipolar depression was studied in a meta-analysis of 23 randomised controlled trials involving 977 subjects. The effect of exercise on depression was small and not statistically significant at follow-up, although it was moderate in the initial setting. When compared to no intervention, the effect size of exercise was large and significant, and when compared to normal care, it was moderate but still noteworthy [ 36 ]. A systematic evaluation of randomised controlled trials evaluating exercise therapies for anxiety disorders indicated that exercise appeared useful as an adjuvant treatment for anxiety disorders but was less effective than antidepressant treatment [ 37 ].
Conclusions
The effects of exercise on mental health have been shown to be beneficial. Among persons with schizophrenia, yoga was shown to have more positive effects with exercise when compared with no intervention. Consistent physical activity may also improve sleep quality significantly. Patients with alcohol dependence syndrome benefit from a combination of medical therapy and regular exercise since it motivates them to battle addiction by decreasing the craving. There is also adequate evidence to suggest that physical exercise improves depressive and anxiety symptoms. Translating the evidence of the benefits of physical exercise on mental health into clinical practice is of paramount importance. Future implications of this include developing a structured exercise therapy and training professionals to deliver it. The dearth of literature in the Indian context also indicates that more research is required to evaluate and implement interventions involving physical activity that is tailored to the Indian context.
The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Cureus is not responsible for the scientific accuracy or reliability of data or conclusions published herein. All content published within Cureus is intended only for educational, research and reference purposes. Additionally, articles published within Cureus should not be deemed a suitable substitute for the advice of a qualified health care professional. Do not disregard or avoid professional medical advice due to content published within Cureus.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sports help you manage stress. Exercise causes your body to release endorphins, the chemicals in your brain that relieve pain and stress. It also reduces the levels of stress hormones, cortisol ...
It reduces negative effects of stress. Exercise can provide stress relief for your body while imitating effects of stress, such as the flight or fight response, and helping your body and its systems practice working together through those effects. This can also lead to positive effects in your body — including your cardiovascular, digestive ...
Tip 3: Get moving. When you're stressed, the last thing you probably feel like doing is getting up and exercising. But physical activity is a huge stress reliever—and you don't have to be an athlete or spend hours in a gym to experience the benefits. Exercise releases endorphins that make you feel good, and it can also serve as a valuable distraction from your daily worries.
Fitness-related stress management techniques have pronounced effects on the body, particularly through the physiological processes involved in the stress response. Regular exercise is a powerful stress reducer that can help maintain physical and mental health. Increased physical fitness enhances resistance to the adverse effects of stress and ...
Stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress. A healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and taking breaks from work or studying can also help manage stress. By taking steps to reduce stress, individuals can improve their overall health and well-being.
1. For the learner: Welcome to the Physical Education - Grade 11 Alternative Delivery Mode. (ADM) Module on Managing Stress Through Sports. The hand is one of the most symbolized part of the human body. It is often. used to depict skill, action and purpose. Through our hands we may learn, create.
Stress management refers to the environmental, physiological, cognitive, and behavioral techniques employed by an individual to manage the factors and components that underlie the stress process or experience of stress. A primary goal of stress management in sport is to allow the athlete to effectively regulate competition related demands to facilitate optimal performance as well […]
Explain how stress management is effective in doing sports activities. Use the back portion of this - 10241774 ... 10241774. answered Essay. Explain how stress management is effective in doing sports activities. Use the back portion of this paper if necessary. (20 points) See answer Advertisement Advertisement ...
Importance of stress management. Stress can be positive or negative. Under normal circumstances, athletes should be able to find new balances and responses in their reactions to events. Such a stress cannot be said to be negative, as it will act as a motivational factor. "A moderate level of stress can be an important motivational factor and ...
Stress is an inevitable part of life. Seven out of ten adults in the United States say they experience stress or anxiety daily, and most say it interferes at least moderately with their lives, according to the most recent ADAA survey on stress and anxiety disorders. When the American Psychological Association surveyed people in 2008, more people reported physical and emotional symptoms due to ...
Take a deep breath through your nose and hold it for about 5 seconds, then release it slowly through your mouth. Repeat 5 times. You can also try tightening a group of muscles for about 5 seconds, then relaxing them. Do this 5 times, then switch to other muscles, like shoulders, hands, legs, and stomach.
Finally, those who play sports have a higher level of physical activity later in life , and through sport, knowledge of nutrition, exercise, and health can be developed . Negative effects include the risk of failure leading to poor mental health [ 8 , 9 ], risk of injury [ 10 , 11 ], eating disorders [ 12 ], burnout [ 13 ], and exercise-induced ...
Keywords: Psychosocial stressors, Stress responses, Sports, psychosocial interventions, Stressor interactions, Stress management. Practice of yoga Breathe Deeply: Take a 5-minute break and focus ...
Sport is a subset of physical activity that can be particularly beneficial for short-and-long-term physical and mental health, and social outcomes in adults. This study presents the results of an updated systematic review of the mental health and social outcomes of community and elite-level sport participation for adults. The findings have informed the development of the 'Mental Health ...
Sports and games can also be a great teacher of time management, giving them the taste of healthy competition, enabling them to give extra effort. By playing sports, individuals learn to maintain rules and respect authority. Sports and games can bring a change to one's daily routine. It serves as an escape for many by relieving stress from ...
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques. Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Commonly, exercise therapy is recommended to combat these challenges and preserve mental wellness. According to empirical investigations, physical activity is positively associated with certain mental health traits. In nonclinical investigations, the most significant effects of physical exercise have been on self-concept and body image.
Playing a sport can improve strength, agility, and cardiovascular health. It can also help to boost self-esteem and reduce stress. Participating in team sports can help to develop leadership skills, while individual sports can help to build discipline and focus. Leisure activities are also a great way to stay healthy and fit.
Stress management' is a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's level of stress, especially chronic stress, usually for the purpose of and for the motive of improving everyday functioning. In this context, the term 'stress' refers only to a stress with significant negative consequences, or distress in the ...
Stress Management Essay: Stress is a complex phenomenon that can be defined in several ways; however, put together; it is the wear and tear of everyday life. Stress management can be defined as a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies to control a person's stress level, especially chronic stress. Effective methods and techniques of stress management […]
Sports can bring a bunch of benefits for youth, including general health, together with blood circulation and overall physical stamina improvement. Sport develops and improves people's physical, social, and organizational skills, which are beneficial in personal and professional life and must always be obtained. Advertisement.
Stress is defined as the mental and physical pressure a person feels from circumstances perceived as threats called stressors. A stressor is simply a stimulus that causes stress. Stressors can be a multitude of things that worry people most in their life. I will list and explain a few examples that cause stress, things that stress me, and how ...