- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring

Medical Tourism, Essay Example
Pages: 5
Words: 1457
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Over the years, there has been an unceasing rise in the demand for health services globally. People’s movement from one area to another is being exhibited by the quest for health services, primarily by the aged. This, together with epidemiological alterations, the increase in cases of chronic illnesses, has contributed to the rise in the demand for better and advanced medical services. A persistent variation in the medical field has been evident due to the speedy advancement of medical tourism and the private healthcare field, which is currently one of the most profitable industries in the globe (Simons, Pike, Hulseberg, Prouty, & Swierczewski, 2016). The continuous rise in healthcare costs in several nations and cheaper options of attaining competent care in third-world nations have contributed to the constant growth in medical tourism. Nonetheless, many of the medical practices in this tourism happen with no regulatory structure that contributes to the observation that the medical practice highly focuses on profit. Furthermore, medical tourism receives many criticisms since it threatens the equitable delivery of healthcare globally. Therefore, medical tourism has numerous adverse effects on the overall health and well-being of people.
Many risks might arise with medical tourism practices. Some of the hazards include the likelihood of the tourist evolving embolisms because of the long flights. Such risk can be in the pulmonary embolisms’ form arising from prolonged immobility since the patient has to travel for several hours (Mogaka et al., 2017). This kind of tourism might also interfere with the tourist’s care plan as they might require moving back to the nations they came from before they are fully integrated into the new care plan. Individuals seeking new treatment options may also suffer from medical malpractices because of a lack of sufficient laws that govern these medical practices in many tourist destinations. The lack of adequate laws to oversee these practices has resulted in healthcare being a dangerous option for medical travellers. Nonetheless, these hazards are still present as a result of the steady growth of this industry.
Another adverse effect evident in medical tourism is the lack of equitability in distributing public funds in the host nations. The activity often threatens equity in the usage of public resources. The development of these tourism businesses in the host nations vastly relies on the government’s help through subsidies and government funds (Takuli, Bhatt & Pokhriyal, 2014). These aids might be in the form of cheaper duties and importation of health equipment that are of great aptitude to offer services in private healthcare facilities aiding the medical tourists. Despite these private healthcare institutions providing services to the entire population, including domestic patients, some of these facilities do not meet these necessities, with hospitals offering medical services only to tourists because of the extraordinary profits. Furthermore, this kind of tourism may also have adverse effects on the health services that are financed by the public sector. This may contribute to a form of public subsidization since well-trained doctors are employed by the private hospitals as a result of good salaries and better medical equipment. As a result, inequality has spiked with the use of public resources.
Imbalances in offering healthcare services in host nations are also highly associated with medical tourism. The tourism is accountable for the worsening medical practices through actions like brain drain as the better salaries and equipment adopted by the healthcare facilities entice doctors from other public hospitals. The tourism activity is also accountable for the rural deficiency in eligible health care employees (Abd Mutalib et al., 22016). Many of these services offered by medical tourist institutions are primarily located in urban areas. An increase in medical tourist practices may lead to a scenario where the rural dwellers cannot afford the healthcare system due to the rise in the number of tourists seeking health services, which leads to an increase in the care expense for the inhabitants of the host countries. Medical tourism has given rise to healthcare reserves, which highly depend on technology, and in turn, scaling up costs of essential health services. The outcome is that a large number of the population is unable to access these high-cost healthcare services.
This kind of tourism might also have adverse effects on the departure nation of these tourists. This can occur in a situation where difficulties arise after a medical process is done on a patient within the medical tourist facility. The care expenses for such an individual might, in turn, be double equated to whether the patient could have received health services in their host nation initially. In a situation where the medical tourists’ medical procedures are partially or fully funded by public financing, the medical complications might contribute to a rise in the public expenses of post supportive care. Besides, medical tourism might adversely affect the tourists’ host nation as it diminishes fair access to healthcare (Snowdon, Bassi, Scarffe, & Smith, 2015). Wealthy individuals might decide to opt-out of the medical systems offered in their host nation and, in turn, negatively affects the necessity to alter medical ideals in those nations since the high-class population can solve their health problems abroad. This leaves the low-class population with poor services in their host nation.
This form of tourism offers a platform and opportunity for a patient to attain affordable and rapid healthcare services linked to the amenities received in the host country (Snowdon, Bassi, Scarffe, & Smith, 2015). Nonetheless, travelling overseas is connected to many risks, especially for the patient, and additional long-term expenses that the patient’s home health system may spend. Seeking medical health services in other countries also deteriorates the patient’s health when experimental services contribute to other side effects. Even if healthcare institutions in a majority of the states are of superior and excellent quality, failing to investigate some of these institutions may contribute to insufficient care and problems that may need follow-up services for the sick. A number of services attained by these tourists need follow-up protocols even when the procedures are effective. As a result, complications may be experienced when follow-up management is untimely and efficient in the health tourism native countries. Additionally, challenges may be seen during the handover of medical records from the tourist country to the native country, further aggravating the challenges during follow-up care. The patients may also be host to some infections and carry them back to their native countries like the NDMI superbug; an infection noticed to be significantly related to medical tourists.
Proponents of medical tourism feel that it permits individuals to attain quicker and more effective healthcare services compared to those offered in their host countries. They argue that treatment abroad is more advanced and results in better outcomes as compared to their host nations (Lunt, Smith & Exworthy, 2011). Others feel that medical tourism assists in lowering the treatment costs if an individual chooses a nation offering more affordable healthcare services compared to the native countries. Besides, several healthcare institutions have collaborated with medical tourism organizations to permit the sick to have contact with post-management reviews and examinations. Furthermore, with the practice’s nature, the sick have the capacity to examine different nations while seeking the healthcare intervention that they need.
In conclusion, medical tourism has adverse effects on both the medical systems and the general welfare of the medical tourists. The lack of sufficient laws to govern this practice has led to the deterioration of the practice, leading to increased healthcare costs and reduced contact to healthcare services by resident individuals. In scenarios when a nation rations care, the capacity to portion and dispense medical resources evenly can be affected. This may undermine the needs of local healthcare facilities while attracting profit-motivated facilities. Without regulation, it is impossible to realize the positive benefits of medical tourism.
Abd Mutalib, N. S., Ming, L. C., Yee, S. M., Wong, P. L., & Soh, Y. C. (2016). Medical tourism: ethics, risks and benefits. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research , 50 (2), 261-270.
Lunt, N., Smith, R., & Exworthy, M. (2011). Medical Tourism: Treatments, Markets and Health System Implications: A Scoping Review, Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Mogaka, J. J., Mashamba-Thompson, T. P., Tsoka-Gwegweni, J. M., & Mupara, L. M. (2017). Effects of medical tourism on health systems in Africa. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 6 (1), 1-25.
Simons, M. P., Pike, B. L., Hulseberg, C. E., Prouty, M. G., & Swierczewski, B. E. (2016). Norovirus: new developments and implications for travelers’ diarrhea. Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines , 2 (1), 1. Retrieved from http://tdtmvjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40794-016-0017-x
Snowdon, A. W., Bassi, H., Scarffe, A. D., & Smith, A. D. (2015). Reverse innovation: an opportunity for strengthening health systems. Globalization and health , 11 (1), 1. Retrieved from http://globalizationandhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12992-015-0088-x
Takuli, S. S., Bhatt, S., & Pokhriyal, D. (2014). Medical Tourism: Emerging Challenges and Future Prospects. Avahan: A Journal on Hospitalty and Tourism , 2 (1), 175-188.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Goal Statement, Application Essay Example
Walt Disne, Case Study Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Why Patients Are Turning to Medical Tourism
Statistics, Benefits, and Risks
Planning Ahead
Frequently asked questions.
Medical tourism is a term that refers to traveling to another country to get a medical or dental procedure. In some instances, medical tourists travel abroad seeking alternative treatments that are not approved in the United States.
Medical tourism is successful for millions of people each year, and it is on the rise for a variety of reasons, including increasing healthcare costs in the United States, lack of health insurance, specialist-driven procedures, high-quality facilities, and the opportunity to travel before or after a medical procedure.
According to a New York Times article from January 2021, pent-up demand for nonessential surgeries, as well as the fact that many Americans lost their health insurance during the coronavirus pandemic led to a surge in medical tourism once other countries re-opened.
However, there are specific risks that come with traveling overseas for surgery. If you're thinking of pursuing a medical procedure in another country, here's what to know about the benefits and the risks.
Medical Tourism Benefits
The most common procedures Americans go abroad for include dental care, cosmetic procedures , fertility treatments, organ transplants , and cancer treatment.
This is not to be confused with having an unplanned procedure in a foreign country due to an unexpected illness or injury.
Among the reasons a person might choose to go abroad for a medical procedure are:
Lower Costs
Medical tourists can save anywhere from 25% to 90% in medical bills, depending on the procedure they get and the country they travel to. There are several factors that play into this:
- The cost of diagnostic testing and medications is particularly expensive in the United States.
- The cost of pre- and post-procedure labor is often dramatically lower overseas. This includes labor costs for nurses , aides, surgeons , pharmacists, physical therapists , and more.
- High cost of malpractice insurance—the insurance that protects medical professionals against lawsuits—in the United States.
- Hospital stays cost far less in many overseas countries compared to the United States. In other words, quality care, hospital meals, and rehabilitation are far more affordable abroad for many people.
For someone who doesn't have insurance , or someone having a procedure that is not covered by insurance , the difference can be enormous.
Popular Countries for Medical Tourism
Dominican Republic
South Korea
Culture and Language
Many immigrants prefer to have treatments and procedures done in their country of origin—a sensible decision, considering just how much language barriers alone can affect the quality of their care.
Furthermore, at least 25% of immigrants and noncitizen residents in the United States are uninsured, compared to 9% of American citizens. Children with at least one noncitizen parent are also more likely to be uninsured.
Practicalities aside, many people choose to have their procedure done in their country of origin simply because it allows them to be close to family, friends, and caretakers who can assist them through their recovery .
Insurance Incentives
Some insurance companies have started promoting medical tourism. The reason behind this is simple: savings for the insured means savings for the insurance provider and vice versa.
Several insurance providers, including Aetna have programs specifically geared at promoting safe medical tourism. Some insurance providers even offer financial incentives for medical tourism, like discounts on medical bills .
That said, many insurance companies will not pay for surgery performed outside of the country unless it is an emergency.
Luxury and Privacy
Medical tourism is a lucrative business for many countries, and much of the money brought in by medical tourists is reinvested into the local economy and health infrastructure.
The effect of this is apparent in the spa-like luxury that some foreign hospitals offer, providing medical tourists the opportunity to be pampered during their stay for a fraction of the cost they would pay at home.
Some facilities offer hospital rooms that are more like a hotel suite than a traditional hospital room. Other hospitals offer one-on-one private nursing care, which is far more generous and attentive than the staffing ratios that most hospitals allow.
Medical tourists who seek that added layer of privacy can find it abroad. Many can return home from their "vacation" without anyone knowing they had a procedure at all.
Vacation in a Foreign Country
Medical tourists often take advantage of their stay in a foreign country to travel for pleasure by scheduling a vacation before or after their procedure.
This is an especially inexpensive way to travel to a foreign country, especially if their insurance provider is paying for the flight and the cost of staying is low.
While it seems logical to recover on a beach or in a chalet by the mountains, keep in mind that it's important not to jeopardize your recovery.
Swimming isn't recommended until your incisions are completely closed. You may not feel up to doing much more than napping in the days following your procedure, either.
Don't let your vacation disrupt your recovery. Any time you have a procedure done, especially a surgery, it's important to listen to your body, take your medications as directed, and follow your doctor's recommendations closely.
Bypassing Rules and Regulations
Some travelers seek surgery abroad to bypass rules that are set in place by their own government, insurance company , or hospital. These rules are typically in place to protect the patient from harm, so getting around them isn't always the best idea.
For example, a patient may be told that their weight is too low to qualify for weight loss surgery . A surgeon in a foreign country may have a different standard for who qualifies for weight loss surgery, so the patient may qualify overseas for the procedure they want.
Talented Surgeons
Surgeons in certain countries are known for their talent in a specific area of surgery. For example, Brazilian surgeons are often touted for their strong plastic surgery skills .
Whereas in the United States, insurance companies might only cover cosmetic procedures if it is medically necessary, cosmetic surgery is often free or low-cost in Brazil's public hospitals—giving cosmetic surgeons there ample practice.
Thailand is reported to be the primary medical tourism destination for individuals seeking gender reassignment . It is often easier to qualify for surgery and the cost is significantly reduced. Surgeons are performing the procedures frequently, and as a result, many have become quite specialized in them.
It is often surprising to many medical tourists that their physician was trained in the United States. Not all physicians are, of course, but a surprisingly high percentage of them working in surgery abroad are trained in English-speaking medical schools and residency programs and then return to their home country. These physicians often speak multiple languages and may be board certified in their home country and a foreign country, such as the United States.
Medical tourism isn’t limited to countries outside of the United States, either. Many people travel to the United States for medical care due to the country's cutting-edge technology, prescription medication supply, and the general safety of healthcare.
Medical Tourism Risks
The financial and practical benefits of medical tourism are well known, and you may even know someone who had a great experience. Nonetheless, the downsides of medical tourism can be just as great if not greater. Sometimes, they can even be deadly.
If you are considering a trip abroad for your procedure, you should know that medical tourism isn't entirely without obstacle and risks. These include:
Poorly Trained Surgeons
In any country—the United States included—there will be good surgeons and bad. And just as there are great surgeons abroad, there are also some surgeons who are less talented, less trained, and less experienced.
Regardless of what procedure you are getting or where, you should always do some preliminary research into the surgeon or physician who will be treating you as well as the hospital you will be treated at.
In the United States, it is fairly easy to obtain information about malpractice lawsuits , sanctions by medical boards, and other disciplinary actions against a physician.
Performing this research from afar can be challenging, especially if you don't speak the local language. Yet countless people take the risk anyway, without knowing whether the physicians who will treat them are reputable.
A physician should be trained in the specific area of medicine that is appropriate for your procedure. For example, you should not be having plastic surgery from a surgeon who was trained to be a heart doctor. It isn’t good enough to be a physician, the physician must be trained in the specialty .
Prior to agreeing to surgery, you should also know your surgeon’s credentials : where they studied, where they trained, and in what specialty(s) they are board-certified. Do not rely on testimonials from previous patients; these are easily made up for a website and even if they are correct, one good surgery doesn’t mean they will all be successful.
Quality of Staff
Nurses are a very important part of healthcare, and the care they provide can mean the difference between a great outcome and a terrible one.
A well-trained nurse can identify a potential problem and fix it before it truly becomes an issue. A poorly trained nurse may not identify a problem until it is too late. The quality of the nursing staff will have a direct impact on your care.
Once again, it's important to research the hospital staff where you will be having your procedure done. Read the reviews but don't trust them blindly. If you can, seek out a recommendation from someone who can vouch for the medical staff where you will be going.
Quality of the Facility
While researching healthcare facilities for your procedure, you want to learn not just about the quality of the facilities themselves, but about the country's healthcare system as a whole.
In some countries, there is a marked distinction between public hospitals and private hospitals. In Turkey, for example, private hospitals are considered on-par with hospitals in the states, while many locals will advise you to steer clear of public hospitals if you can.
You will also want to seek out facilities that are internationally accredited. In the United States, the Joint Commission evaluates hospitals and certifies those that provide safe, quality care. The international division does the same for hospitals outside the United States.
Once you have a few options for potential facilities, you can start to investigate specifics. For one, you should find as many pictures and reviews of the facility as you can. Ask yourself whether the facility is state of the art or whether it seems dirty and outdated.
You will also need to find out if the facility has ICU level care available, in case something goes wrong. If not, there should be a major hospital nearby so that you can be transferred quickly.
To learn more about a healthcare facility, consider joining expat groups on social media for the city or country you will be traveling to. Ask the group for recommendations, or inquire about any positive or negative experiences they may have had at a particular facility.
Flying Home After Surgery
Any surgery comes with risks, including infection and blood clots . Flying home increases the risk of blood clots, especially on long-haul flights that are longer than four hours.
Try to avoid flying home in the days immediately after surgery; waiting a week will decrease the chances of developing a blood clot or another serious complication during the flight.
For longer flights, plan on getting up and walking up and down the aisles each hour to improve blood flow in your legs. You might also benefit from wearing compression socks with your doctor's approval.
If you are taking blood thinners or are at-risk of blood clots , be sure to talk to your doctor about how you can reduce your risk of blood clots after your procedure and while traveling.
Furthermore, you should know the symptoms of blood clots and stay alert.
Unplanned Illness
Any time you travel abroad, you run the risk of catching an illness that you have never been exposed to or that your body is not prepared to fight off. This is especially a concern when spending time in a foreign hospital.
If you have a sensitive stomach, you may also want to think long and hard about having surgery abroad. The food is often very different in foreign hospitals, and in some areas, there is a risk that even the water will be upsetting to your body.
Having diarrhea or postoperative nausea and vomiting makes for a miserable recovery experience, especially if you do not have a friend or family member nearby who can help you through it.
Before you travel abroad, check with your doctor to see if you need any vaccines to travel to your destination or if there are any foreign illnesses you should be aware of. Picking up an illness abroad, particularly after your surgery, can potentially be life-threatening.
Language Barriers
If you are having surgery in a country where English is not the primary language, you will need to make preparations in order to be able to communicate with the staff.
You may be pleasantly surprised to learn that the staff speaks your primary language well. If not, then you will need to consider how you will make your wishes and needs known to the surgeon, the staff, and others you will meet.
Whether you are at home or abroad, remember to speak up and advocate for yourself to make sure your needs are met. If you don't speak the local language, download a language translation app on your smartphone and don't hesitate to use it to communicate your needs. Hiring a translator is another option.
A Word About Transplant Tourism
Transplant tourism is one area of medical tourism that is strongly discouraged by organ and tissue transplant professionals in multiple countries. Most international transplants are considered “black market” surgeries that are not only poor in quality, but ethically and morally wrong.
China, for example, the country that is believed to perform more international kidney transplants than any other country, is widely believed to take organs from political prisoners after their execution.
In India, living donors are often promised large sums of money for their kidney donation, only to find out they have been scammed and never receive payment. Selling an organ in India is illegal, as it is in most areas of the world, so there is little recourse for the donor.
Then there is the final outcome: how well the organ works after the surgery is complete. With black market transplants, less care is often taken with matching the donor and recipient, which leads to high levels of rejection and a greater risk of death. Furthermore, the new organ may not have been screened for diseases such as cytomegalovirus , tuberculosis , hepatitis B , and hepatitis C . It is often the new disease that leads to death, rather than the organ rejection itself.
Finally, transplant surgeons are often reluctant to care for a patient who intentionally circumvented the donor process in the United States and received their transplant from an unknown physician.
It is important to arrange your follow-up care prior to leaving your home country.
Many physicians and surgeons are hesitant to take care of a patient who received care outside the country, as they are often unfamiliar with medical tourism and have concerns about the quality of care overseas.
Arranging for follow-up care before you leave will make it easier to transition to care at home without the stress of trying to find a physician after surgery .
Just be sure to inform your follow-up care physician where you are having your procedure done. After you return, they will also want to know what prescription medications you were given, if any.
What are popular countries for medical tourism?
Mexico, India, Costa Rica, Turkey, Singapore, Canada, and Thailand are among the many countries that are popular for medical tourism.
How safe is medical tourism?
Medical tourism is generally considered safe, but it's critical to research the quality of care, physician training, and surgical specialties of each country. There are several medical tourism organizations that specialize in evaluating popular destinations for this purpose.
What countries have free healthcare?
Countries with free healthcare include England, Canada, Thailand, Mexico, India, Sweden, South Korea, Israel, and many others.
A Word From Verywell
If you are considering medical tourism, discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor, and consider working with your insurance provider to arrange a trip that balances financial savings with safety. (Also, before you embark on a trip overseas for your procedure, make sure you are financially prepared for unexpected events and emergencies. Don't go abroad if you don't have enough money to get yourself home in a crisis.)
A medical tourism organization such as Patients Without Borders can help you evaluate the quality and trustworthiness of healthcare in various countries. Making sure a high level of care is readily available will lead to a safer, more relaxing experience.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Medical Tourism: Getting medical care in another country . Updated October 23, 2017.
University of the Incarnate Word. Center for Medical Tourism Research .
Patients Beyond Borders. Facts and figures .
Kaiser Family Foundation. Health coverage of immigrants . Published July 2021.
Paul DP 3rd, Barker T, Watts AL, Messinger A, Coustasse A. Insurance companies adapting to trends by adopting medical tourism . Health Care Manag (Frederick). 2017 Oct/Dec;36(4):326-333. doi: 10.1097/HCM.0000000000000179
Batista BN. State of plastic surgery in Brazil . Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open . 2017 Dec;5(12):1627. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000001627
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health - Global Health Now. Brazilians' risky right to beauty . Published May 2018.
Chokrungvaranont P, Selvaggi G, Jindarak S, et al. The development of sex reassignment surgery in Thailand: a social perspective . Sci World J . 2014 Mar;2014(1):1-5. doi:10.1155/2014/182981
The Joint Commission. For consumers .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Blood clots and travel: what you need to know . Reviewed February 2021.
Hurley R. China harvested organs from political prisoners on substantial scale, says tribunal . BMJ . 2018 Dec;363(1):5250. doi:10.1136/bmj.k5250
Ambagtsheer F, Van Balen L. I'm not Sherlock Holmes: suspicions, secrecy, and silence of transplant professionals in the human organ trade . Euro J Criminol . 2019 Jan;17(6):764-783. doi:10.1177/1477370818825331
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Transplant Surgery. Key facts . Reviewed January 2019.
By Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FN Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FNP-C, is a board-certified family nurse practitioner. She has experience in primary care and hospital medicine.
Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks
Medical tourism is a growing industry, with its demand changing with the advancement of insurance services and emerging global healthcare challenges. Besides cost and quality considerations, most patients have identified privacy and adventure as one of their key determinants in selecting a destination. Patients seeking private attention are always trying to avoid negative reporting surrounding them and their families, which is important for psychological reasons. Before making a medical trip, one needs to consider factors such as cost, legal implications, and language barriers. Overall, foreign medication has proved beneficial because one gets to receive a different opinion in an enabling environment.
Medical tourism is the movement of people from their native country to a foreign country searching for affordable, specialized, and quality medical care. Besides these, other patients who are immigrants prefer to seek medical attention from their native countries due to social-political and economic beliefs. For instance, politicians and influential people in society prefer seeking medical attention in foreign countries because of their security. The most sought-out treatments abroad are procedures such as heart and cosmetic, dentistry, and cancer treatment. Regarding the common destination for medical tourism, the most common region are in Asia and South America, precisely India, Colombia, Cuba, Thailand, Singapore, and South Korea. Despite the growing demand for medical tourism, there are related risks such as failure to get any meaningful change after medication. Other risks include aggravated medical conditions and communication barriers. Therefore, before deciding on abroad medication, consumers should do a comparative analysis on prices and social constraints which contribute to their wellbeing.
Medical tourism benefits include cost-effective and high-quality healthcare as compared to the ones available in the native country. Firstly, cost-effective medical care is a service that is quality at affordable prices. For instance, according to Sag and Zengul (2019), the cost of hip replacement in countries such as Indian and the Philippines is thirty percent less than the cost in the United States and the United Kingdom. In the same aspect, the cheap services are quality and specialized with other advantages such as family ambiance and added tourism aspects. Ideally, with an affordable air ticket and cheap medication, a patient can afford to travel with their loved ones to a foreign country. Besides receiving medical attention, they will also get the opportunity to tour some of the tourist attractions in the country. Besides, medical tourism hubs have much healthcare provides that can provide one on one services to patients. This is attributed to their high training outputs and less workload, such as appointments in some countries.
Secondly, there is strong growth in insurance-funded foreign tourism, with most companies offering such plans for their clients. In their study to promote tourism in Turkey, Sag & Zengul (2019) note that having a flexible and attractive foreign insurance-funded medical system is key in opening medical tourism. Notably, this has been used by countries such as India that make it easy for healthcare providers to finance their clients when on international visits. The growth and diversification of insurance services have facilitated the expansion of medical tourism, making it one of the biggest niches in the tourism industry (Ile & Tigu, 2017). Further, they note that it is a merging of two industries, medicine, and tourism, which has attracted several investors creating a competitive space for price and packaging purposes. In fact, there are insurance providers that provide travel arrangements for their clients.
The major reason people resort to medical tourism is quality, cost, privacy, and adventure. Quality in the healthcare industry is an important aspect because it determines the healing process of a patient. According to Kim et al. (2017), quality services in any industry are vital in attracting clients and investors, explaining why some countries are considered the best for medical tourism. For example, in the countries considered best to visit, you will find an entire healthcare system working efficiently, with few medical mishaps. A patient will not have to queue for long or a payment delay in the hospital system. Moreover, they have integrated Electronic Health Records (EHR), which make everything seamless and communication with family members is efficient. Notably, according to the Centre for Disease Control (CDC), when looking for a foreign country to visit for tourism purposes, it is important to look at the communication systems of the hospital. This allows for a holistic healing process for the patient.
Privacy and adventure are other reasons why people seek medical help from other countries. Regarding privacy, most of the patients seeking medical help from foreign countries do so to protect their privacy and those of their loved ones. The trend is common with influential people in the community, such as politicians who decide to seek medical help away from their purported enemies. Kim et al. (2017), note that providing privacy should be a key aim for all medical service companies. In the modern social space, medical conditions and struggles have been used in advancing political propaganda and hate speech, which most influential persons try to avoid. Besides privacy, some people view medical tourism as an opportunity of traveling with their loved ones to new places. For instance, one will take along their family members to their target country where they can enjoy different weather while one receives medical attention. According to Sag and Zengul (2019), this is a therapeutic approach in providing healthcare. In essence, the patient receives medication while enjoying the “usual” company around them, which makes the healing process fast and psychologically fulfilling.
Planning for a medical visit before and after is important for a patient to avoid financial and psychological stress. First, a patient needs to plan with their local service providers on the traveling arrangements, which include securing a comfortable means of transport. Secondly, it is vital to ask the insurance provider if their services cover the target country and the amount that one will be needed to top up in case their premium is not sufficient enough (Ile & Tigu, 2017). Thirdly, the patient should take into consideration factors such as language barriers in their destination country. Consequently, this will inform their decision to choose a travel partner or going individually. According to CDC, good communication between the patient and the doctor is important for quality service. Therefore, having a clear insurance and communication organization is crucial.
Fourth, one needs to make the necessary agreements before traveling abroad, which include documentation with relevant authorities and local service providers. These agreements include legal documents that will ensure one is provided with their healthcare records when leaving their destination country. It also includes financial agreements with insurance providers. Finally, according to the CDC, a patient intending to travel has to conduct background research on the doctors that will be providing healthcare services to them, which will ensure they are dealing with accredited persons. Consequently, this will ensure that the patient receives quality and professional healthcare from their providers.
Medical tourism varies because of the price and quality of services in the providing country. For example, patients seeking help from countries in Asia have cited cost and quality as their major attraction (Sag & Zengul, 2019). A close analysis of healthcare structures in purported countries such as Singapore and India show a systematic emphasis on quality. This is achieved through sufficient training to provide both quality and quantity supply to the medical industry (Kim et al., 2019). Compared to countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom, the same service is provided, but cost and quality are not justifiable. For example, Kim et al. (2019) point out that spinal fusion in the United States is $62.000, while in Thailand, it is $7000. The difference is significant, which will play an integral role in the consumers’ decision-making process. Besides price, there are factors such as weather and environment for patients. For some medical conditions, the patient needs certain weather conditions for quick recovery. This is a key determinant in deciding which country to visit for medical attention.
Conclusively, medical tourism is a growing industry characterized by different aspects that one needs to consider before making trips to their destination country. Some of the key factors to consider before travelings are comparative costs and quality of services. Countries that have been noted as a good destination for medical tourism are Singapore, Thailand, India, and Cuba. Besides their quality services, most patients have quoted favorable climatic conditions as the attractive features. However, before traveling, it is important to make the necessary legal and financial agreements. Finally, knowing the qualification of the service providers is key to a successful medical visit.
Center for Disease Control. (n.d.). Medical tourism: Getting medical care in another country.
Ile, F. L., & Ţigu, G. (2017). Balneary tourism face to face with medical tourism – A comparative exploratory research. Romanian Economic and Business Review, 12 (4), 72-81.
Kim, M., Koo, D., Shin, D., & Lee, S. (2017). From servicescape to loyalty in the medical tourism industry: A medical clinic’s service perspective. The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing; Thousand Oaks , 54(1), 1-16.
Sag, I., & Zengul, F. D. (2019). Why medical tourists choose Turkey as a medical tourism destination? Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights, 2 (3), 296-306.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, June 29). Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks. https://studycorgi.com/medical-tourism-and-its-benefits-and-risks/
"Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks." StudyCorgi , 29 June 2022, studycorgi.com/medical-tourism-and-its-benefits-and-risks/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks'. 29 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks." June 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/medical-tourism-and-its-benefits-and-risks/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks." June 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/medical-tourism-and-its-benefits-and-risks/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks." June 29, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/medical-tourism-and-its-benefits-and-risks/.
This paper, “Medical Tourism and Its Benefits and Risks”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 30, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
What is Medical Tourism?
- Download PDF Copy

Medical tourism can be defined as the process of traveling outside the country of residence for the purpose of receiving medical care. Growth in the popularity of medical tourism has captured the attention of policy-makers, researchers and the media. Originally, the term referred to the travel of patients from less-developed countries to developed nations in pursuit of the treatments not available in their homeland.
Today we are experiencing both qualitative and quantitative shifts in patient mobility, as people travel from richer to less-developed countries in order to access health services. Such shift is mostly driven by the relative low-cost of treatments in less developed nations, the availability of inexpensive flights and increased marketing and online consumer information about the availability of medical services.
What really puts the word "tourism" in medical tourism concept is that people often stay in the foreign country after the medical procedure. Travelers can thus take advantage of their visit by sightseeing, taking day trips or participating in any other traditional tourism activities.
Medical tourism represents a worldwide, multibillion-dollar phenomenon that is expected to grow considerably in the next decade. For the individual interested in health services, cost is the key factor involved in the decision to receive medical care abroad.
As healthcare costs in the US and other parts of the world are excessively soaring, many employers and insurance companies started to view medical tourism as a way to lower them. More and more countries around the globe start to see the financial benefits from this emerging market, so they offer premium medical services at notably lower prices.
The primary reason that clinics and hospitals in the developing countries are able to lower their prices is directly related to the nation's economic status. The direct correlation with per capita gross domestic product of the country is observed, which is a proxy for income levels. As a consequence, surgery prices are from 30% to 70% lower in the countries that are promoting medical tourism when compared to the US.
There are two major components of the service quality in the health care sector - technical or mechanical quality and serviceable or functional quality. Technical equipment is at the core of the patients' diagnostic algorithm, while the functional quality is measured by the service offered in the healthcare centers (such as the services of staffs, nurses and, most importantly, the doctors towards the patient and their assistants). The service quality in medical tourism industry is a vital part in attracting customers.
Related Stories
- Artificial tears linked to drug-resistant bacteria outbreak, CDC finds
One of the fundamental barriers in accepting medical tourism is the perception of inadequate quality. A key to overcome it is using adequate marketing strategies and quality assessment via accreditation from an internationally recognized institution. Such accreditation is pivotal for strengthening confidence in the quality of healthcare.
This confidence can be even stronger if accreditation is followed by an affiliation with reputable hospitals or health care systems in industrialized countries. Once healthcare providers are accredited and become a part of international referral networks, they can be appropriately rated for risks.
Treatment types
Categories of different treatments and their availability also represent an important factor in decision to engage in medical tourism. The most common types of procedures that patients pursue during medical tourism trips are elective cosmetic surgery, dentistry, organ transplantation, cardiac surgery and orthopedic surgery.
However, a wide variety of services can be obtained through medical tourism, ranging from various essential treatments to different kinds of traditional and alternative treatments. Reproductive tourism and reproductive outsourcing are growing in popularity, which is the practice of traveling abroad to engage in surrogate pregnancy, in vitro fertilization and other assisted reproductive technology methods.
In addition to cost, other major factor responsible for the increase of medical tourism is access. The lack of it, either due to the unavailability of the technology or the prohibition in the home country, can subsequently lead to medical tourism. The common examples are cytoplasmic transfer or stem cell therapy.
- wwwnc.cdc.gov/.../medical-tourism
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3469025/
- http://www.oecd.org/els/health-systems/48723982.pdf
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2234298/?report=classic
- http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/10/266
Further Reading
- All Medical Tourism Content
- Medical Tourism History
- Medical Tourism Risks
- Employer-Sponsored Medical Tourism
- Medical Tourism Accreditation
Last Updated: Aug 23, 2018

Dr. Tomislav Meštrović
Dr. Tomislav Meštrović is a medical doctor (MD) with a Ph.D. in biomedical and health sciences, specialist in the field of clinical microbiology, and an Assistant Professor at Croatia's youngest university - University North. In addition to his interest in clinical, research and lecturing activities, his immense passion for medical writing and scientific communication goes back to his student days. He enjoys contributing back to the community. In his spare time, Tomislav is a movie buff and an avid traveler.
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report:
Meštrović, Tomislav. (2018, August 23). What is Medical Tourism?. News-Medical. Retrieved on June 11, 2024 from https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Medical-Tourism.aspx.
Meštrović, Tomislav. "What is Medical Tourism?". News-Medical . 11 June 2024. <https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Medical-Tourism.aspx>.
Meštrović, Tomislav. "What is Medical Tourism?". News-Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Medical-Tourism.aspx. (accessed June 11, 2024).
Meštrović, Tomislav. 2018. What is Medical Tourism? . News-Medical, viewed 11 June 2024, https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Medical-Tourism.aspx.
Cancel reply to comment
- Trending Stories
- Latest Interviews
- Top Health Articles

Breathing New Life into Diagnostics: Plasmion's SICRIT Technology
Revolutionizing Non-Invasive Diagnostics with Plasmion’s SICRIT Breath Analysis.

Discover how SciY empowers scientists
Santi Dominguez
In this interview, NewsMedical talks to Santi Dominguez about the genesis of SCiY, and how the consortium intends to empower scientists and researchers.

Why use light scattering to analyze proteins and viral vectors?
Dr. Michelle Chen
n this interview, Dr. Michelle Chen, Senior Director of Analytical Sciences at Wyatt Technology, talks to NewsMedical about how to use light scattering techniques to analyze proteins for their multi-attribute quantification (MAQ).

Latest News

Newsletters you may be interested in
Your AI Powered Scientific Assistant
Hi, I'm Azthena, you can trust me to find commercial scientific answers from News-Medical.net.
A few things you need to know before we start. Please read and accept to continue.
- Use of “Azthena” is subject to the terms and conditions of use as set out by OpenAI .
- Content provided on any AZoNetwork sites are subject to the site Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
- Large Language Models can make mistakes. Consider checking important information.
Great. Ask your question.
Azthena may occasionally provide inaccurate responses. Read the full terms .
While we only use edited and approved content for Azthena answers, it may on occasions provide incorrect responses. Please confirm any data provided with the related suppliers or authors. We do not provide medical advice, if you search for medical information you must always consult a medical professional before acting on any information provided.
Your questions, but not your email details will be shared with OpenAI and retained for 30 days in accordance with their privacy principles.
Please do not ask questions that use sensitive or confidential information.
Read the full Terms & Conditions .
Provide Feedback
Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism Report
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
An overview of medical tourism
Stakeholders in medical tourism, consumers and motivation for service consumption in the medical tourism industry, impacts of medical tourism, future challenges of medical tourism, recommendations, reference list.
According to Horowitz et al. (2008), the growth in medical travel is accelerating at a very high pace. The average annual revenue generated from the medical travel industry was estimated at $60 billion as at the end of 2008. Furthermore, the industry revenues were estimated to grow at the rate of 20% per year, meaning that the revenue that is generated from the industry as of today has surpassed the $100 billion dollar mark.
Medical tourism is caused and spearheaded by a set of complex interactions among different forces. These forces include medical, political, economic, and social forces. The factors that promote medical tourism include the availability of care in the destination, timeliness of medical care, the cost of care and the ability of people to meet the costs, different preferences for medical service, and the preference of patients for certain type of care.
Reddy, York and Brannon (2010) observed that most medical tourists flow from the United States, the Middle East, Western Europe, and Canada to the South East Asian countries like Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, and India. In addition, trends in the industry point to the flow of medical tourists to South and Central American countries like Argentina, Chile, Mexico, and Costa Rica (Reddy, York & Brannon 2010).
However, it should also be noted that medical tourism is not only pictured from the cross border travel perspective, but also from the broader lenses from the intra-national perspective where people across different regions within national borders move in search for medical services (Behrmann & Smith 2010).
The global medical tourism industry is quite broad. There are a lot of players in the industry, beginning with the consumers of the medical services, hospital doctors and other medical specialists, governments, hotels, tourism operators, the travel industry, and the communities in which medical tourism services are offered (Medical Tourism Association n.d.).
Governments are prominent stakeholders in the industry by virtue of being the main regulators of healthcare provision in any given country. Healthcare is largely regulated by the government. Therefore, all the developments that take place in the medical industry in any country happen under the watchful eye and the regulation of the given national governments.
However, the expanding scope of medical tourism and the pace at which the government allows players to come into the industry results in questioning the ability of the government to regulate the industry effectively (Behrmann & Smith 2010).
The consumers, the medical service providers, and the accommodation and hotel industry are the direct stakeholders in the industry. The accommodation and hotel industry is essential in providing services to both the patients and the people who accompany these patients to the medical destinations.
The medical service providers keep developing services and expanding their capacity to capture as many patients as possible. In addition, aspects of diversification of service provision are embraced by service providers as competition increases (Medical Tourism Association n.d.).
From its very nature, it is apparent that the medical tourism industry attracts a large number of consumers due to the wide range of medical services that are developed and offered by the players in the industry.
The consumers in the industry range from critical patients who seek for specialized medical services that are not available in their countries to patients whose medical costs cannot be covered by the medical schemes due to the cost of health care in their countries, forcing them to seek for such services at affordable rates.
There is also a certain class of consumers in the industry who seek for certain services that are not primary per se, like people who seek for services in cosmetic surgery (Reddy, York & Brannon 2010).
One thing that qualifies this as a form of tourism is that it gives opportunities to the consumers of the services to go for vacation. Therefore, vacation is one of the factors that motivate most people to embrace medical tourism.
According to Behrmann and Smith (2010), consumers in the medical industry highly value anonymity and privacy. This is based on the wide range and nature of services that are sourced by the consumers in the medical tourism industry.
An example of the service that calls for privacy and anonymity is cosmetic surgery. Therefore, the fact that medical services can be sourced from far off regions from the homes of the consumers assures them the two attributes.
Abortion tourism and cosmetic and reconstructive surgery or plastic surgery are forms of services that are offered in the industry. This raises questions about the consideration of ethics in the industry. It is common nowadays to find people seeking for the services that are forbidden in their countries from other countries where such services are legal.
For example, abortion tourism, which is profoundly illegal in most countries, is highly active in a country like Canada whose laws back abortion. Therefore, most women from countries that have banned abortion across the globe fly to Canada where they can freely access the services (Behrmann & Smith 2010). Similar to abortion tourism, a lot of questions are also raised about the validity and worth of cosmetic surgery.
People spend huge sums of money to engage in this practice, yet it poses a large number of risks to the lives of people due to the nature of technology that goes into the service. This, in turn, raises concerns about the responsibility of governments in protecting the lives and promoting the health of the citizens (Sterodimas, Radwanski & Pitanguy 2011).
NaRanong and NaRanong (2011) ascertain that medical tourism has greatly spurred the economic growth of these countries. Taking an example of Thailand, medical tourism boosts the generation of revenue in medical services and the accommodation and tourism revenue. This boosts economic growth. This is expounded in the figure below.
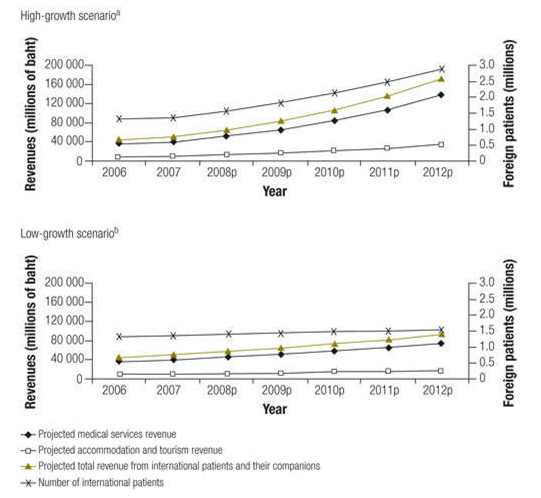
Figure 1.0: High and low growth scenario cases for medical tourism in Thailand.
Source: NaRanong & NaRanong (2011).
The other positive impact of medical tourism is that it encourages professional development and competitiveness in the industry, thereby enhancing quality in the national health care systems (Snyder et al., 2013).
The other important thing that is raised is the increase in the number of medical services. Therefore, questions are raised about the level of quality that goes into the provision of the medical services in given destinations as people seek for affordable services. Problems in this sense involve the difficulty of patients to embrace follow-up care when they have returned from foreign countries where they receive treatment (Snyder & Crooks 2012).
Accompanying the problem of follow-up is the embrace of vices due to the active and competitive environment in the industry. The environment makes it difficult to enforce a number of legal concerns and regulations. An example is the breaking of law by seeking for services that are illegal in some countries, like abortion tourism (Behrmann & Smith 2010).
According to Chakravarthy, Kumar and Deepthi (2008), there is a low level of coordination in the medical industry, with each stakeholder in the industry seeking to promote their services. Moreover, the more players are attracted into the industry, the more it becomes difficult to embrace quality services since more fake players are bound to take advantage of the high demand in the industry.
There is a higher likelihood that the capacity of the providers is likely to get overstretched in the long run as more people continue to seek for certain medical services from certain providers in certain destinations. The quality of medical services provided is watered down when the capacity is stretched.
Areas of medical care provision that attract foreign patients in certain countries are bound to be incapacitated in the event that the level of persistence of the diseases that require those services keeps rising (Reddy, York & Brannon, 2010).
The regulation of the medical industry is one of the key challenges in the industry today. As Behrmann and Smith (2010) point out, the efforts of regulating the developments in the medical tourism industry will be subjected to significant challenges. The industry attracts many players who are allowed by the government to operate to help the government to beef up the capacity of providing medical services to their citizenry.
This happens despite the fact that the healthcare industry is considered to be a primary industry. The industry is quite active and important. This makes it difficult for national governments to fully enforce the regulations and jurisdictions that go beyond national borders.
The modern globalized world continues to embrace liberalization and global connectedness. Based on this fact, national legislations that aim at embracing the regulation of medical tourism are often rendered ineffective when they are deployed across national borders (Behrmann & Smith 2010).
According to Álvarez, Chanda and Smith (2011), medical tourism has been grossly globalized. Medical tourism operates on a multilateral scale. This, in turn, raises questions about the ability of countries to offer quality and affordable health care services to their citizens.
Therefore, the future environment in the medical tourism industry will be dominated by friction between countries as questions of quality, ability, authenticity, and competition among countries gain prominence. This will affect the functioning of the industry. This is another dimension of the issue of future regulation of medical tourism.
The uncertainty in the global economy heaps pressure on the players in the industry, thereby heightening competition in the industry.
The aim of the medical service providers in the industry is to increase their clientele base. The healthiness of the competition in the industry is the determinant of positive practices in the industry; otherwise, the competition is bound to result in malpractices as providers seek to retain their significance and level of competitiveness in the industry.
The medical tourism industry is widely unregulated. This makes the industry attract a lot of players. Therefore, a multi-channel promotional environment has been established in the industry by the players who seek to promote their services and products (Reddy, York & Brannon 2010).
It is important to note that the medical tourism industry is fairly young. The growth in the industry implies heterogeneity in medical services, as well as the service providers in the industry.
The growth in specialization and the increase in the variety of services in the industry are factors that promote the complexity of the industry. While this growth promotes opportunities, it is also bound to result in duplication of services and the conflict of interest in service development, as well service provision by the players in the industry.
One of the most important things that need to be considered in enhancing the industry is the convergence of the stakeholders in the industry to promote a favourable environment that is well regulated. Both the in-country regulation and the regulation of healthcare at the global level are critical for embracing quality and competitiveness.
In addition, it is important to diversify the strategies of dealing with high numbers of medical tourists in certain destinations. One way this can be done is through the embrace of partnerships and joint-venturing in the provision of medical services by the specialized providers.
For instance, special medical service providers can establish ventures in other regions where patients from those regions can access those services quickly, instead of travelling for long distances to get medical attention. This also makes it possible for medical follow-ups to be conducted and emergency situations to be attended promptly.
Álvarez, M., Chanda, R., & Smith, R. 2011, ‘The potential for bi-lateral agreements in medical tourism: A qualitative study of stakeholder perspectives from the UK and India’, Globalization & Health , vol. 7 no. 1, pp. 11-19.
Behrmann, J., & Smith, E. 2010, ‘Top 7 issues in medical tourism: challenges, knowledge gaps, and future directions for research and policy development’, Global Journal of Health Science , vol. 2 no. 2, pp. 80-90.
Chakravarthy, K. K., Kumar, R. C. H., & Deepthi, K. 2008, Swot analysis on: Medical tourism . Web.
Horowitz, M., Marsek, P., Mohanasundaram, S., Pachisa, M., Jones, C., Keith, L., Metaxotos, N., Alexis Heng Boon, C., Yah Yuen, T., & Sze Yiun, T. 2008, ‘Special feature’, Asia Pacific Biotech News , vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 24-53.
Medical Tourism Association n.d., Healthcare Clusters, medical clusters and healthcare associations . Web.
NaRanong, A., & NaRanong, V. 2011, ‘The effects of medical tourism: Thailand’s experience’, Bulletin of the World Health Organization , vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 336-344.
Reddy, S. G., York, V. K., & Brannon, L. A. 2010, ‘Travel for treatment: students’ perspective on medical tourism’, International Journal of Tourism Research , vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 510-522.
Snyder, J., & Crooks, V. A. 2012, ‘Guidelines for reducing the negative public health impacts of medical tourism’, Bioéthique Online , vol. 1, no. 12, pp. 1-4.
Snyder, J., Crooks, V. A., Turner, L., & Johnston, R. 2013, ‘Understanding the impacts of medical tourism on health human resources in Barbados: a prospective, qualitative study of stakeholder perceptions’, Int J Equity Health , vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 2-12.
Sterodimas, A., Radwanski, H. N., & Pitanguy, I. 2011, ‘Ethical issues in plastic and reconstructive surgery’, Aesthetic Plastic Surgery , vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 262-267.
- Tourism Destination Evaluation on Iraq
- Tourism Destination Competitiveness
- Cosmetic Surgery: Dangers and Alternatives
- Workplace Issues in the Tourism Industry
- Niche Tourism Major Characteristics
- Cultural Heritage Tourism: Valletta and Venice
- Volunteer Tourism Development
- Virtual vs. Traditional Tour Operator
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, July 8). Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism. https://ivypanda.com/essays/medical-tourism/
"Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism." IvyPanda , 8 July 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/medical-tourism/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism'. 8 July.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism." July 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/medical-tourism/.
1. IvyPanda . "Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism." July 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/medical-tourism/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Medical Travel Industry: Medical Tourism." July 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/medical-tourism/.
Essays on Medical Tourism
Faq about medical tourism.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Collections
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About Journal of Travel Medicine
- About the International Society of Travel Medicine
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Declaration of interests.
- < Previous
What Do We Know About Medical Tourism? A Review of the Literature With Discussion of Its Implications for the UK National Health Service as an Example of a Public Health Care System
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Johanna Hanefeld, Richard Smith, Daniel Horsfall, Neil Lunt, What Do We Know About Medical Tourism? A Review of the Literature With Discussion of Its Implications for the UK National Health Service as an Example of a Public Health Care System, Journal of Travel Medicine , Volume 21, Issue 6, 1 November 2014, Pages 410–417, https://doi.org/10.1111/jtm.12147
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Medical tourism is a growing phenomenon. This review of the literature maps current knowledge and discusses findings with reference to the UK National Health Service (NHS).
Databases were systematically searched between September 2011 and March 2012 and 100 papers were selected for review.
The literature shows specific types of tourism depending on treatment, eg, dentistry, cosmetic, or fertility. Patient motivation is complex and while further research is needed, factors beyond cost, including availability and distance, are clearly important. The provision of medical tourism varies. Volume of patient travel, economic cost and benefit were established for 13 countries. It highlights contributions not only to recipient countries' economies but also to a possible growth in health systems' inequities. Evidence suggests that UK patients travel abroad to receive treatment, complications arise and are treated by the NHS, indicating costs from medical travel for originating health systems.
It demonstrates the importance of quality standards and holds lessons as the UK and other EU countries implement the EU Directive on cross‐border care. Lifting the private‐patient‐cap for NHS hospitals increases potential for growth in inbound medical tourism; yet no research exists on this. Research is required on volume, cost, patient motivation, industry, and on long‐term health outcomes in medical tourists.
Medical tourism—people traveling abroad with the expressed purpose of accessing medical treatment—is a growing phenomenon associated with globalization. 1 This includes cheaper and more widely available air travel and cross‐border communication through the Internet, which allows medical providers from one country to market themselves to patients in another. 2 At the same time, increased movement of health workers for education means doctors providing care in middle‐ and low‐income countries have in many cases the same qualifications as those in the high‐income countries in Western Europe and the United States. This has been coupled with an increase in foreign direct investment in health care providers in destination countries. 3 The increasing acceptance of health care portability is evident in Europe where greater patient mobility led to an EU Directive on cross‐border health care. 4 Together with a rise in out‐of‐pocket expenditures for health in many high‐income countries at a time of economic crisis, this conspires to form a perfect storm for medical tourism.
Yet, understanding of medical travel is limited. 5 Little is known as to which patients choose to travel and why, when others do not. Details of the volume of patient flows and resources spent remain uncertain. 3 This has hampered efforts to understand the economic costs and benefits to countries experiencing inflows and outflows of patients. Similarly, for the medical tourism industry, the role of private providers and brokers and marketing remain a “black box.” 1 While interest in the issue has grown over the past decade, effects on patients and health systems are not fully understood.
This review of the literature seeks to outline the current level of knowledge on medical tourism. Specifically, it aims to better understand (1) patient motivation, (2) the medical tourism industry, (3) volume of medical travel, and (4) effects of medical travel on originating health systems. Results are reported and discussed, paying specific attention to evidence of impact and lessons for the UK National Health Service (NHS) as an example of how medical tourism affects even universal public health systems. The authors conclude on current levels of knowledge, critical gaps, and future research priorities on medical travel.
The review was conducted between September 2011 and March 2012 as part of wider research, assessing implications of medical tourism on the UK NHS. Authors developed a search strategy based on the aims set out above. They adapted the strategy used by Smith and colleagues, 5 deemed particularly relevant as it presented a recent review of medical tourism albeit focused on bilateral tourism. It was amended to focus more broadly on medical tourism. Initial papers identified were reviewed for inclusion by J. H. and R. S. according to title and where this proved inconclusive according to the abstract. In line with research objectives, papers with general focus on medical tourism, published in English and German (languages read by authors), and focused on the NHS, were included. The following were excluded: papers on well‐being, news items, commentaries, laws or directives, and conference proceedings; papers focusing on stem cell tourism, travel for assisted suicide, and transplant tourism, given the distinct ethical issues. Three hundred and seventy‐four papers remained as initial sample. References of papers identified were further examined to ensure comprehensiveness and four additional papers were included. The initial selection of papers was then reviewed (abstract or full paper) applying these criteria and focusing more specifically on the aims of the review (as above). Two papers were not accessible and therefore excluded. 6,7 A final list of 100 papers was derived for inclusion in this review. This sample was tested based on the criteria by D. H. The literature search is summarized in the PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1 ).

PRISMA flow diagram for literature review medical tourism.
A rapidly expanding literature over the past 5 years with an “explosion” in 2010 and 2011 is reflected in the dates of publication of papers included in the review—73 were published in 2010 and 2011.
Types of Studies Reviewed
Papers included in the review were classified into the following categories: (1) those based on primary data collection (quantitative and qualitative): interviews, surveys, analysis of datasets collected and obtained by authors, or the calculation of revenue and tourist flows, and case studies of patients; (2) reviews: literature reviews of medical tourism websites or promotional materials; (3) analysis: papers which while drawing on secondary sources, provide substantive new insights or conceptualize it in a new way (a number of papers presented frameworks); and (4) overview articles which gave an introduction to the issue of medical tourism. The results are summarized in Figure 2 .

Type of study reviewed.
Geographic Focus
Papers were grouped according to the region the research investigated (see Figure 3 ), or global where they were general. Europe was the focus of 29 papers, 13 explicitly focus on the UK and a further 11 papers refer to either UK patients or the NHS, thus a total of 24 papers mentioned or focused on the UK.

Countries covered.
Literature reviewed suggests a regional dimension to medical tourism: Japanese companies send their employees to Thailand, 8 or to countries in the Gulf. 9,10 A study of medical tourists in Tunisia found that they were from neighboring countries. 11 Countries are known for specific areas of medicine: Singapore for high‐end procedures, 12 Thailand for cardiac, orthopedic, and gender reassignment surgery, 13 Eastern Europe for dental tourism, 14 and Spain for fertility treatment. 15 While some destinations were recognized as popular with UK patients, eg, Budapest for dental treatment, evidence from literature suggested that proximity alone does explain preference for one destination over another.
Motivation to Travel
Most papers made reference to push and pull factors determining patients' decision to travel. These relate to cost, perceived quality, familiarity, waiting lists or delays in treatment, or the lack of availability of certain treatments in the country of origin. 16 As this list demonstrates, these are often complex and dynamic, 6 and may vary according to the treatment for which a patient travels. Evidence suggests that patients traveling for cosmetic surgery may enjoy the anonymity of a destination far from their country of origin, 17 whereas migrants may prefer to return “home” to feel more comfortable with language or type of care provided. 18 These different factors allow for a division into different subsets of medical tourism.
A number of studies refer to a group of tourists classified as diaspora, documenting the return of recent migrants from India, China, Korea, and Mexico, to access treatment either not available or perceived to be not available in their country of residence, or perceived to be more effective. 9,18–20 While cost plays a part in explaining why, eg, Mexican immigrants to the United States return to Mexico for treatment, trust emerged as the key determining factor. This may partly be linked to language barriers, as a study of Korean immigrants to Australia suggests. 18
Reproductive or fertility travel is comparatively better documented than other forms of medical tourism. 15 Of the 16 papers identified for inclusion in this review, 6 papers focus on equity and ethical issues relating to fertility tourism, highlighting the rights of women in recipient countries and equity concerns where they may be compelled by poverty to donate eggs or act as surrogates. Four papers provide a general overview of the issues relating to fertility tourism. 7,21–23 A review of literature on cross‐border reproductive care 15 finds a consistent gap of empirical research—of 54 papers reviewed only 15 were based on empirical investigation. It noted the absence of evidence about patients' backgrounds and factors motivating their travel, and a gap in research on industry. A specific feature of fertility travel cited across papers reviewed is that availability of treatment (in this case gametes and surrogacy) is a factor in patient decision making. This includes the wish for timely and affordable treatment; in the UK it includes perceptions of the NHS as stressful and less effective. 6 Evidence also highlights health effects of fertility travel on patients, showing an increase in multiple births in a London hospital resulting from fertility treatment received abroad. 24 Combined, these studies show that there is an effect of fertility travel on the health system of the country from which medical tourists originate, in this case the NHS, and that regulation of availability and (perceived) quality of service are factors leading patients to travel.
Dental Tourism, Bariatric and Cosmetic Surgery
Other types of tourism are identifiable, including dental tourism. 25 Three papers 26,27,28 indicated this is likely to be an area of increasing travel by UK citizens, given the high cost of dentistry in the UK private sector, limited availability in the public sector, and lower cost in Eastern Europe. 27 A survey of dental clinics in Western Hungary and Budapest showed the largest group of patients (20.2%) originating from the UK with lower prices cited as main motivating factor. 28 Two papers focused in depth on issues surrounding bariatric surgery, exploring the ethical challenges and a case study of complications experienced by a US patient. 29,30 Papers by Birch and colleagues 31 and Miyagi and colleagues 32 focus on complications from cosmetic tourism in UK patients. Others reported that a poll conducted amongst the members of the UK public found that 92% would consider traveling abroad for cosmetic surgery. 33 The possibility of a large number of UK patients seeking cosmetic surgery abroad appears supported by a survey conducted by the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons which found that 37% of respondents had seen patients in the NHS with complications from overseas surgery. 31
Risks for patients are covered in 29 papers. But surprisingly only 8 of these papers focus exclusively on the issue, and 10 studies mention longer‐term health outcomes of patients. Three describe the recent outbreak of NDM1 bacteria following patients receiving treatment in India, a fourth describes an outbreak of hepatitis B in a London hospital traced to a patient recently returned from surgery in India, pointing to potential risks of diaspora travel. 34–37
While papers tend to mention regulation, only two 38,39 review this more systematically. Both point to a vacuum in regulation, with no one specific regulator or quality assurance standard in place, but rather a number of private companies offering quality assurance through affiliation, creating a market for quality assurance rather than independent standards.
Effect on Countries
As summarized in Table 1 , 37 papers focused on the effects on recipient country's health system. Issues highlighted include the potential for medical tourism to retain or attract doctors in low‐ and middle‐income countries who may otherwise emigrate, thus preventing or reversing a brain drain, and generating foreign currency. 12 Also considered is the danger of creating a two‐tiered health system, resulting in increasing inequities in access and quality of health care for the local population in destination countries, 40,41 mainly as a result of a rise in price where public health services are not provided for free in recipient countries, and the potentially greater concentration of doctors in the private sector. 42
Issues covered
| Fertility | 16 |
| Cosmetic | 5 |
| Dental | 3 |
| Diaspora | 7 |
| Bariatric | 2 |
| Risks in health outcomes | 29 |
| Focus on recipient country's health system | 37 |
| Focus on originating country's health system | 34 |
| Fertility | 16 |
| Cosmetic | 5 |
| Dental | 3 |
| Diaspora | 7 |
| Bariatric | 2 |
| Risks in health outcomes | 29 |
| Focus on recipient country's health system | 37 |
| Focus on originating country's health system | 34 |
A total of 34 papers focused on potential effects on originating countries' health system. These referred to factors leading to patients' travel, including rise in costs. Papers documented patients returning with complications. 43 Seven papers specifically highlighted complications dealt with in the NHS. 31 Research highlighted the need for regulation, the lack of quality control of overseas providers, and the cost (potential or real) arising to the originating country from treating such complications. Two papers calculated the potential cost saving and benefits of sending patients abroad. 20,44 Overall, papers focusing on the effects on originating countries' health system concentrate mainly on perceived negative consequences.
Forty‐one papers reviewed focus at least partly on providers of medical tourism. A subset of 22 papers studied the medical tourism industry in a more focused way. These provide evidence of a highly diversified industry, with no clear typology emerging. For example, in Southeast Asia medical tourism is state‐led, with large hospitals targeting foreign patients. In other cases, such as cosmetic or dental tourism, intermediaries organize travel and treatment for patients. Examining the entire literature, it is clear that there is not a uniform model or chain for medical tourism.
Articles examining communication materials and websites highlight the limited information on follow‐up care and redress in case of complications. 2 They point to an emphasis on testimonies by patients, rather than formal accreditation or qualification of clinicians, a focus on tourism aspects of the destination and on trust—offering services “as good as at home.” 41 These are in addition to low cost used as a selling point. Studies focusing on medical tourism facilitators identify these as a heterogeneous group. 45,46
Papers reviewed mention individual hospitals or a medical tourism provider at the country level to give a flavor of the industry. 8,45 However, only four papers 47–50 report findings of a more systematic assessment of the industry, including focus on the strong state role in the development of medical tourism in Hong Kong, Malaysia, and Singapore, analyzing how these countries have fostered medical tourism, including through tax incentives. Singapore, for example, made a conscious decision to focus on the high‐end complex procedures to have a competitive advantage. 47
Number of People Traveling
The actual volume in flow of medical patients was referred to in many papers but investigated in few 10,11,28,42,51–54 ; all papers provided further estimates or trends. Most papers cited similar figures of patient flows, but often sources were not accessible or based on media reports or other academic papers, which in turn quoted inaccessible sources. Seven papers referred directly to a report by Deloitte Consultancy, and six to McKinsey; the exact ways in which these were calculated remain unclear. Even where these were not referenced, the figures cited suggest these two reports as a source. For example, one paper 33 cites The Economist stating 750,000 US patients traveling abroad for treatment in 2007. This is the figure provided in the report from Deloitte consultancy in 2008.
Eight papers reviewed had either generated or collected own data on patient flows. Only three papers had calculated the total volume of medical tourism for 13 countries, including actual cost and effect on recipient country's health systems. NaRanong and colleagues calculate the contribution of medical tourism to Thai GDP (0.4%), while medical tourists with their higher purchasing power are likely to increase the cost of health services and lessen access in the public sector. 42 This contrasts with Lautier's findings which highlight that export of health services in Tunisia simply makes use of excess capacity in the country's private sector. 11 Siddiqi's 11‐country study in the Middle East showed complex flows within the region. 10 Findings across the different studies suggest that the impact on recipient country's health system depends on the context and capacity, but that there is likely to be a small contribution to overall GDP. How income gained from medical tourism is in turn invested has not been studied.
This review of the literature provides the most comprehensive overview of knowledge on medical tourism to date. The main limitation of the studies is the focus on English (and German) literature, and as set out in the search strategy a narrow definition focused on medical tourism rather than on the inclusion of broader health and well‐being travel literature. This was essential to maintain feasibility of the review, given the large number of papers published.
Main Findings: What We Can Learn From the Literature on Medical Tourism
The literature reviewed clearly indicates that medical tourism is no unified phenomenon. Sub‐types of travel, such as diaspora or fertility travel, travel for bariatric surgery, dental, or cosmetic work, were evident from the review. Decisions by patients to travel are not simply guided by cost considerations or even clinical outcomes. Rather, the literature points to a complex matrix of perceptions of care, waiting times, cost, and others, depending on the type of treatment sought. For example, trust appeared as a motivation for diaspora travelers but not for dental tourists, cost or availability in cosmetic procedures, and regulation in the case of fertility. However, lack of information about patients' characteristics limits deeper understanding of push and pull factors. With very few exceptions, 16,6 the absence of in‐depth interviews with more than one or two patients poses the greatest weakness of the literature reviewed and opens the potential to bias within studies reviewed.
A diverse picture of the medical tourism industry emerges. Some countries have become known for excellence in certain areas of treatment such as Spain for fertility or Hungary or Poland for dental treatment. Yet, this did not appear the case for all medical tourism destinations, eg, while India clearly is a destination for medical tourists, this is for a whole broad spectrum of treatments.
Few studies were able to quantify patient flows and calculate effect on recipient health systems and the economy. Evidence does suggest that the inflow of medical travelers can increase inequities within the recipient country health systems 42 but that depends on the context. 11
Perhaps the most surprising finding was the increase in papers presenting primary research—a shortfall or gap that had been noted by the earlier literature reviews. 5,55,56 The recent publication date of many confirms the increase in research of medical travel.
Implications for the UK NHS
Evidence demonstrates that UK patients travel abroad to receive treatment and return with complications or infections that require follow‐up in the public sector. Based on papers reviewed, cosmetic procedures appear an area of growth for medical travel by UK patients and likely to result in cost to the NHS due to resulting complications, but costs resulting from other types of travel, including fertility and dental tourism, are evident. While complications experienced by UK medical tourists were reported, these were not compared to rates of complications for similar procedures undertaken in the UK, which would have further strengthened such research. However, in individual cases of patients described, these often focused on cases so unusual or extreme that the comparison or lack thereof to the UK was implicit. Case studies also underlined the challenges relating to information and communication, with often limited patient records available for returning medical tourists.
Despite a number of studies focusing on UK patients, overall the evidence presented underlines the need for further research to ascertain the potential impact and costs arising from medical tourism on the NHS. Only one study 42 estimated actual costs arising from complications of returning medical tourists and this was based on a small sample of patients. We found no research calculating the potential savings arising from UK patients traveling abroad for treatment. While research on risks associated with medical travel proved limited, the documented NDM1 outbreak in the UK highlighted the potential of infections that may result from medical travel. 36
Research focused on communication materials and websites highlights the lack of credible information about qualification and an absence of regulation and legal safeguards. This lack of clear information paired with the increasing willingness to travel of the UK public makes a greater numbers of complications a likely scenario.
Considering findings from the literature focused on the UK, these are particularly salient for the NHS at a time of reform. The lifting of the cap on private patients increases the potential for greater earning and marketing of NHS hospitals to foreign private patients. In this context, the lack of evidence on incoming tourists limits the possibility of informed decision making. Moreover, findings about complications of returning medical tourists, which highlight the need of quality control and continuity of care, are likely to mirror some of the policy challenges that will become evident in the implementation of the EU Directive on cross‐border health care implemented from 2013. In this context, it seems opportune for policymakers within the EU to further explore lessons from medical travel.
This review of the literature highlights a growing trend in medical travel that is likely to continue and have an increasing impact on patients, and originating and recipient health systems. It shows a diverse industry and different types of tourism depending on treatment, each with a complex set of patient motivation. Evidence also highlights complications experienced by patients, resulting in health problems and costs to originating health systems. While the review shows an increase in research over the past 2 years, it also clearly identifies limits to current knowledge and areas where the need for further research is evident:
A lack of information about patients' background and numbers of patients traveling abroad for treatment persists. The lack of data also restricts analysis about possible cost and benefits of medical travel.
Limited insights on why some patients travel when others do not.
Little is known about the industry beyond reviews of information materials and websites. Further research is needed to better understand how the sector operates, to ultimately understand impact on health services and outcomes of medical travelers.
Moreover, there is an absence of research examining the long‐term health outcomes of medical tourists when compared to patients treated within their country of residence. As a result, evidence on the comparative effect of treatment received abroad is lacking. Further qualitative and quantitative research beyond immediate clinical outcomes is needed to truly understand the effect of medical travel on patients, and its cost to the health system.
As medical tourism is set to rise, addressing these gaps in the evidence is urgently required to avoid potential harm to patients and health systems by enabling more informed policymaking on aspects of medical tourism.

This is a hospital in Hualien, Taiwan, which has two prominent advertising boards on its front facade promoting the hospital. Taiwan is a hot spot for medical tourism in Asia, attracting thousands of medical tourists mostly from China. Photo Credit: Eric Caumes .
The authors wish to acknowledge the members of the study advisory committee for their input into the review. This project was funded by the National Institute for Health Research Health Services and Delivery Research Programme (project number HSR 09/2001/21). The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the HS&DR Programme, NIHR, NHS, or the Department of Health.
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Lunt N Carrera P . Medical tourism: assessing the evidence on treatment abroad . Maturitas 2010 ; 66 : 27 – 32 .
Google Scholar
Lunt N Hardey M Mannion R . Nip, tuck and click: medical tourism and the emergence of web‐based health information . Open Med Inform J 2010 ; 4 : 1 – 11 .
Smith RD Chanda R Tangcharoensathien V . Trade in health‐related services . Lancet 2009 ; 373 : 593 – 601 .
Legido‐Quigley H Passarani I Knai C , et al. Cross‐border healthcare in the European Union: clarifying patients' rights . BMJ 2011 ; 342 : d296 .
Smith R Martínez Álvarez M Chanda R . Medical tourism: a review of the literature and analysis of a role for bi‐lateral trade . Health Policy 2011 ; 103 : 276 – 282 .
Culley L Hudson N Rapport F , et al. Crossing borders for fertility treatment: motivations, destinations and outcomes of UK fertility travellers . Hum Reprod 2011 ; 26 : 2373 – 2381 .
Ferraretti AP Pennings G Gianaroli L , et al. Cross‐border reproductive care: a phenomenon expressing the controversial aspects of reproductive technologies . Reprod Biomed Online 2010 ; 20 : 261 – 266 .
Connell J . Medical tourism: sea, sun, sand and … surgery . Tour Manage 2006 ; 27 : 1093 – 1100 .
Alsharif MJ Labonte R Lu Z . Patients beyond borders: a study of medical tourists in four countries . Glob Soc Policy 2010 ; 10 : 315 – 335 .
Siddiqi S Shennawy A Mirza Z , et al. Assessing trade in health services in countries of the Eastern Mediterranean from a public health perspective . Int J Health Plann Manage 2010 ; 25 : 231 – 250 .
Lautier M . Export of health services from developing countries: the case of Tunisia . Soc Sci Med 2008 ; 67 : 101 – 110 .
Lee CG Hung W . Tourism, health and income in Singapore . Int J Tour Res 2010 ; 12 : 355 – 359 .
Horowitz MD Rosensweig JA Jones CA . Medical tourism: globalization of the healthcare marketplace . MedGenMed 2007 ; 9 : 33 .
Piazolo M Zanca NA . Medical tourism—a case study for the USA and India, Germany and Hungary . Acta Polytech Hungarica 2011 ; 8 : 137 – 160 .
Hudson N Culley L Blyth E , et al. Cross‐border reproductive care: a review of the literature . Reprod Biomed Online 2011 ; 22 : 673 – 685 .
Glinos IA Baeten R Helble M Maarse H . A typology of cross‐border patient mobility . Health Place 2010 ; 16 : 1145 – 1155 .
Connell J . “Mind and matter: health tourism or cosmetic surgery?” Medical tourism . Wallingford : CABI , 2011 : 23 – 41 .
Lee JY Kearns RA Friesen W . Seeking affective health care: Korean immigrants' use of homeland medical services . Health Place 2010 ; 16 : 108 – 115 .
Horton S Cole S . Medical returns: seeking health care in Mexico . Soc Sci Med 2011 ; 72 : 1846 – 1852 .
Martinez Alvarez M Chanda R Smith RD . The potential for bi‐lateral agreements in medical tourism: a qualitative study of stakeholder perspectives from the UK and India . Global Health 2011 ; 7 : 11 .
Jones CA Keith LG . Medical tourism and reproductive outsourcing: the dawning of a new paradigm for healthcare . Int J Fertil Womens Med 2006 ; 51 : 251 – 255 .
Michelmann HW Himmel W . Considering the possible and choosing the justifiable—The problem of “tourism” in infertility treatment . J Reprod Endokrinol 2007 ; 4 : 118 – 123 (in German).
Bergmann S . Fertility tourism: circumventive routes that enable access to reproductive technologies and substances . Signs 2011 ; 36 : 280 – 289 .
McKelvey A David A Shenfield F Jauniaux ER . The impact of cross‐border reproductive care or “fertility tourism” on NHS maternity services . BJOG 2009 ; 116 : 1520 – 1523 .
Connell J . Tummy tucks and the Taj Mahal? Medical tourism and the globalization of health care . In: Woodside A , Martin D , eds. Tourism management: analysis, behaviour and strategy . Wallingford : CABI , 2008 : 232 – 244 .
Turner L . Cross‐border dental care: “dental tourism” and patient mobility . Br Dent J 2008 ; 204 : 553 – 554 .
Milosevic A . Dental tourism—a global issue? Perspectives . J Esthetic Restorative Dent 2009 ; 21 : 289 – 291 .
Osterle A Balazs P Delgado J . Travelling for teeth: characteristics and perspectives of dental care tourism in Hungary . Br Dent J 2009 ; 206 : 425 – 428 .
Snyder J Crooks VA . Medical tourism and bariatric surgery: more moral challenges . Am J Bioethics 2010 ; 10 : 28 – 30 .
Whiteman RG . Medical tourism and bariatric surgery . Surg Obes Relat Dis 2011 ; 7 : 652 – 655 .
Jeevan R Birch J Armstrong AP . Travelling abroad for aesthetic surgery: informing healthcare practitioners and providers while improving patient safety . J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2011 ; 64 : 143 – 147 .
Miyagi K Auberson D Patel AJ Malata CM . The unwritten price of cosmetic tourism: an observational study and cost analysis . J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2012 ; 65 : 22 – 28 .
Nassab R Hamnett N Nelson K , et al. Cosmetic tourism: public opinion and analysis of information and content available on the Internet . Aesthet Surg J 2010 ; 30 : 465 – 469 .
Harling R Turbitt D Millar M , et al. Passage from India: an outbreak of hepatitis B linked to a patient who acquired infection from health care overseas . Public Health 2007 ; 121 : 734 – 741 .
Chan HL Poon LM Chan SG Teo JW . The perils of medical tourism: NDM‐1‐positive Escherichia coli causing febrile neutropenia in a medical tourist . Singapore Med J 2011 ; 52 : 299 – 302 .
Rogers BA Aminzadeh Z Hayashi Y , et al. Country‐to‐country transfer of patients and the risk of multi‐resistant bacterial infection . Clin Infect Dis 2011 ; 53 : 49 – 56 .
Smith R Lunt N Hanefeld J . The implications of PIP are more than just cosmetic . Lancet 2012 ; 379 : 1180 – 1181 .
Whittaker A . Challenges of medical travel to global regulation: a case study of reproductive travel in Asia . Glob Soc Policy 2010 ; 10 : 396 – 415 .
Turner LG . Quality in health care and globalization of health services: accreditation and regulatory oversight of medical tourism companies . Int J Qual Health Care 2011 ; 23 : 1 – 7 .
Johnston R Crooks VA Snyder J , et al. What is known about the effects of medical tourism in destination and departure countries? A scoping review . Int J Equity Health 2010 ; 9 : 24 .
Vijaya RM . Medical tourism: revenue generation or international transfer of healthcare problems? J Econ Issues 2010 ; 44 : 53 – 69 .
NaRanong A NaRanong V . The effects of medical tourism: Thailand's experience . Bull WHO 2011 ; 89 : 336 – 344 .
Melendez MM Alizadeh K . Complications from international surgery tourism . Aesthet Surg J 2011 ; 31 : 694 – 697 .
Mattoo A Rathindran R . How health insurance inhibits trade in health care . Health Aff 2006 ; 25 : 358 – 368 .
Karuppan CM Karuppan M . Changing trends in health care tourism . Health Care Manag 2010 ; 29 : 349 – 358 .
Snyder J Crooks VA Adams K , et al. The “patient's physician one‐step removed”: the evolving roles of medical tourism facilitators . J Med Ethics 2011 ; 37 : 530 – 534 .
Leng CH . Medical tourism and the state in Malaysia and Singapore . Glob Soc Policy 2010 ; 10 : 336 – 357 .
Whittaker A Speier A . “Cycling overseas”: care, commodification, and stratification in cross‐border reproductive travel . Med Anthropol 2010 ; 29 : 363 – 383 .
Heung VCS Kucukusta D Song H . Medical tourism development in Hong Kong: an assessment of the barriers . Tour Manage 2011 ; 32 : 995 – 1005 .
Sarojini N Vrinda M Anjali S . Globalisation of birth markets: a case study of assisted reproductive technologies in India . Global Health 2011 ; 7 : 27 .
Shenfield F de Mouzon J Pennings G , et al. Cross border reproductive care in six European countries . Hum Reprod 2010 ; 25 : 1361 – 1368 .
Deloitte. Medical tourism: consumers in search of value. Deloitte Center for Health Solutions. 2008. http://www.deloitte.com/assets/Dcom-UnitedStates/Local%20Assets/Documents/us_chs_MedicalTourismStudy%283%29.pdf . (Accessed 2014 Aug 15)
Confederation of Indian Industries and McKinsey & Company. Healthcare in India: the road ahead. New Delhi: CII & McKinsey & Co., 2002.
UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP). Medical travel in Asia and the Pacific. Challenges and opportunities. Thailand UN ESCAP. 2007. http://www.scribd.com/doc/158181361/ESCAP-2009-Medical-Travel-in-Asia-and-the-Pacific-Challenges-and-Opportunities . (Accessed 2014 Aug 15).
Crooks VA Kingsbury P Snyder J , et al. What is known about the patient's experience of medical tourism? A scoping review . BMC Health Serv Res 2010 ; 10 : 266 .
Hopkins L Labonte R Runnels V Packer C . Medical tourism today: what is the state of existing knowledge? J Public Health Policy 2010 ; 31 : 185 – 198 .
- public health medicine
- medical tourism
- national health service (uk)
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| December 2016 | 1 |
| January 2017 | 5 |
| February 2017 | 32 |
| March 2017 | 35 |
| April 2017 | 34 |
| May 2017 | 22 |
| June 2017 | 29 |
| July 2017 | 36 |
| August 2017 | 35 |
| September 2017 | 20 |
| October 2017 | 54 |
| November 2017 | 34 |
| December 2017 | 131 |
| January 2018 | 142 |
| February 2018 | 118 |
| March 2018 | 189 |
| April 2018 | 313 |
| May 2018 | 253 |
| June 2018 | 270 |
| July 2018 | 155 |
| August 2018 | 288 |
| September 2018 | 233 |
| October 2018 | 309 |
| November 2018 | 476 |
| December 2018 | 281 |
| January 2019 | 261 |
| February 2019 | 226 |
| March 2019 | 316 |
| April 2019 | 681 |
| May 2019 | 575 |
| June 2019 | 522 |
| July 2019 | 511 |
| August 2019 | 481 |
| September 2019 | 417 |
| October 2019 | 430 |
| November 2019 | 368 |
| December 2019 | 249 |
| January 2020 | 255 |
| February 2020 | 287 |
| March 2020 | 254 |
| April 2020 | 262 |
| May 2020 | 129 |
| June 2020 | 185 |
| July 2020 | 190 |
| August 2020 | 153 |
| September 2020 | 192 |
| October 2020 | 234 |
| November 2020 | 180 |
| December 2020 | 177 |
| January 2021 | 200 |
| February 2021 | 137 |
| March 2021 | 221 |
| April 2021 | 229 |
| May 2021 | 171 |
| June 2021 | 114 |
| July 2021 | 118 |
| August 2021 | 133 |
| September 2021 | 320 |
| October 2021 | 185 |
| November 2021 | 149 |
| December 2021 | 142 |
| January 2022 | 166 |
| February 2022 | 202 |
| March 2022 | 260 |
| April 2022 | 222 |
| May 2022 | 169 |
| June 2022 | 114 |
| July 2022 | 112 |
| August 2022 | 104 |
| September 2022 | 122 |
| October 2022 | 126 |
| November 2022 | 175 |
| December 2022 | 198 |
| January 2023 | 158 |
| February 2023 | 165 |
| March 2023 | 240 |
| April 2023 | 221 |
| May 2023 | 160 |
| June 2023 | 133 |
| July 2023 | 123 |
| August 2023 | 167 |
| September 2023 | 155 |
| October 2023 | 176 |
| November 2023 | 286 |
| December 2023 | 223 |
| January 2024 | 229 |
| February 2024 | 198 |
| March 2024 | 278 |
| April 2024 | 269 |
| May 2024 | 225 |
| June 2024 | 75 |
Email alerts
More on this topic, related articles in pubmed, citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1708-8305
- Copyright © 2024 International Society of Travel Medicine
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Empirical article
- Open access
- Published: 12 September 2018
Medical tourism: focusing on patients’ prior, current, and post experience
- Soonae Hwang 1 ,
- DonHee Lee ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2799-8547 2 &
- Chang-Yuil Kang 3
International Journal of Quality Innovation volume 4 , Article number: 4 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
16k Accesses
16 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
This study empirically examines the effects of medical tourists’ experience of the decision-making process through a patient’s prior, actual, and post experience after having received the medical services. The research model and associated hypotheses were tested using a structural equation modeling based on data collected from 188 medical tourists who received care in Busan, South Korea. The findings of the study indicate that patients’ experience in medical tourism pre-search (reputation, searching information, and communication) has a partially positive effect on their experience (costs, care quality, and supporting system and/or information) and patients’ current experience during the medical tour process has a positive effect on post-experience (relationship building, recommendation, and feedback). The results of this study provide new insights about how key players (e.g., hospitals, medical travel agencies, hotels, and the medical tourists themselves) in medical tourism can effectively help managers identify medical tourists’ needs based on the decision-making process of prior, current, and post-experience of medical tourists.
Medical tourism has emerged as a result of consumers being exposed to a wider range of choices of medical services and exponential growth in global healthcare market [ 1 ]. A combination of the terms “medical” and “tourism” [ 1 ], its main target is patients who visit other regions or countries for medical treatment. Therefore, the medical tourism industry is geared toward significant efforts to meet people’s desire for a better wellness with quality medical treatment [ 2 , 3 ]. According to the Allied Market Research [ 4 ], the net worth of the medical tourism market worldwide is estimated at $61.172 billion as of 2016 and is expected to increase to $165.3 billion by 2023.
The global growth of the medical tourism industry is most prominent in Asia, with Singapore, Thailand, South Korea, and India being well known as medical tourism countries. In a report “Estimates of the South Korea Medical Tourism Market and Expenditure to 2020,” Orbis Research [ 5 ] presented that highly skilled professionals, advanced medical devices, and well-established infrastructures are the factors that contribute to the rapid growth of medical tourism in South Korea.
Customers opting for medical tourism visit local hospitals in other countries and/or regions, where they use this opportunity to relax and enjoy cultural activities in addition to seeking medical treatment, maintenance, and recovery. Increased promotions of a wide range of one-stop medical services and advancements in medical technology have made traveling for treatment a rather convenient and attractive prospect for medical tourists [ 2 , 5 , 6 ]. Information retrieval for overseas medical care is one of the components in the decision-making process for medical tourism [ 6 ]. The quality of medical services and expertise of institutions in other countries may also be important factors since they influence patients’ access to medical information [ 1 ]. Therefore, the industry should extend greater efforts in this area to attract more patients.
Medical services create value-generating activities through an effective interaction of human resources (service providers and recipients), processes, technologies, and/or material resources. Interaction activities reflect consumer needs, and these activities can lead to improvements in medical services delivery [ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Therefore, the interaction at each service encounter is very important. Also, patient experience upon receiving medical services will influence future decision-making of patients, as has been shown in previous studies on the importance of experience [ 10 , 11 ]. The customer experience consists of multiple independent service encounters throughout the exchange process [ 11 ]. As a matter of fact, customer experience is becoming significantly more important as itself has become the target customer, and ideas proposed by customers can generate a value proposition, which can lead to a newer and improved revenue model [ 12 , 13 ].
Patients’ evaluation of a hospital’s medical services is based on his/her own experience or others’ recommendation influences not just the local population but also potential customers from overseas [ 14 ]. Ofir and Simonson [ 15 ] suggested that customer brand perceptions through purchase evaluations of experience have a significant effect on the customer’s experience. Thus, to obtain favorable customer reviews, healthcare organizations provide patient-oriented medical services mainly by interacting with their patients at each service encounter. This is why it is imperative to build processes that focus on delivering better, customer-oriented medical services for positive customer experience.
A process is a set of activities for creating value for the customer through input–process–output, so the process can vary depending on the requirements of the customer. Medical services are provided only when patients and medical staff meet in a service encounter. Therefore, various processes can be set up depending on the type and severity of the disease and the patient’s health condition. A more comprehensive approach may be needed as patient outcomes are a result of not just one process but a combination of processes before, during, and after the overall process of medical service. While customers search healthcare providers before their visit, their revisit intention is dependent on the institutions’ care processes and outcomes [ 9 , 11 ]. However, due to the nature of medical care, patients may not be able to easily switch medical institutions, their experience will nevertheless have a direct or indirect bearing on other prospective patients’ decisions [ 9 ].
While previous studies already have and continue to examine the importance of experience, they have focused largely on customer experience from arrival to departure rather than comprehensive processes [ 1 , 3 , 6 , 10 , 13 ]. As such, it is necessary to take a more holistic approach to studying customer experience through before, during, and after service provision. This study focuses on the decision-making process in customer experience. More specifically, it aims to examine the patient’s pre-experience of researching medical services abroad, the actual experience during their trip, and the post-experience after having received the medical services.
This study thus attempts to answer the following two basic research questions: (1) Does the experience of those who pre-searched for medical tourism impact their current experience in medical tourism? (2) Does patients’ experience during medical tour impact post-experience? A research model is proposed to answer these questions. The result of the study is expected to contribute to both theory and practice of medical tourism regarding customer experience through the decision-making process of prior, current, and post medical tours.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section “ Review of relevant literature ” reviews relevant literature and proposes conceptual development, section “ Research methodology ” develops the hypotheses; section “ Results ” presents the research methodology is presented, section “ Discussion and conclusions ” reports the results of analysis and concludes the study by articulating the results, implications, and limitations of the study, and future research needs.
Review of relevant literature
- Medical tourism
The definition of medical tourism varies among researchers depending on the choice of place and location (domestic or foreign) of medical tourism, the method and procedure applied, application, and/or processes. Generally, it is referred to as tourism activities related to medical treatments or activities to improve tourists’ well-being. The Medical Tourism Association [ 16 ] defines medical tourism as “where people who live in one country travel to another country to receive medical, dental and surgical care while at the same time receiving equal to or greater care than they would have in their own country, and are traveling for medical care because of affordability, better access to care or a higher level of quality of care.” Wongkit and Mckercher [ 17 ] defined medical tourism as “the travel of people to specific destinations to seek medical help that forms the primary purpose of their trip.”
The Tourism Research and Marketing [ 18 ] presented treatment of illnesses, enhancement/cosmetic surgery, wellness, and fertility-related treatments as types of medical tourism. Lunt et al. [ 19 ] described the range of treatments in the medical tourism sector, focusing mainly on the common factors suggested in many previous studies: “cosmetic surgery (breast, face, liposuction); dentistry (cosmetic and reconstruction); cardiology/cardiac surgery (bypass, valve replacement); orthopedic surgery (hip replacement, resurfacing, knee replacement, joint surgery); bariatric surgery (gastric bypass, gastric banding); fertility/reproductive system (IVF, gender reassignment); organ, cell and tissue transplantation (organ transplantation; stem cell); eye surgery and diagnostics and check-ups.”
The quality of medical services is one of the factors that potential customers consider most important [ 18 ]. This implies that the quality of medical service and its costs are the most important influencers in their decision on the destination for their medical tourism [ 20 ]. Lunt et al. [ 19 ] emphasized that customers should be informed of the potential benefits of medical tourism regarding credible evidence of quality care and safety of their stay. In particular, when compared to other service industries, where word-of-mouth plays a big role, the medical industry is relatively slow in adopting a business model focused on customer satisfaction. With the right focus on quality and outcomes of the medical service processes, including customer interaction with service providers, healthcare organizations should try to improve patient satisfaction. This will have a positive effect on attracting potential future customers, thus promoting medical tourism [ 21 ].
Ehrbeck et al. [ 22 ] suggested five factors that promote medical tourism through a survey of 49,980 patients: most advanced technology (40%), better-quality care for medically necessary procedures (32%), quicker access to medically necessary procedures (15%), lower-cost care for medically necessary procedures (9%), and lower-cost care for discretionary procedures (4%). Crook et al. [ 23 ] presented the following as the most frequently discussed topics on patient experience: (1) decision-making (e.g., push-and-pull factors that shape patients’ decisions); (2) motivations (e.g., procedure, costs, and travel-based factors motivating patients to seek care abroad); (3) risks (e.g., health and travel risks); and (4) first-hand accounts (e.g., patients’ experiential accounts of having gone abroad for medical care). Thus, we consider combining the factors suggested by Ehrbeck et al. [ 22 ] and Crook et al. [ 23 ] to devise new strategic measures for medical tourism.
Few potential medical tourists are aware of what products or services are available through medical tourism. Some may have misconceptions and fear of various situations, including anxiety about traveling possible dangers, culture shock, and language barriers. In addition, it is very difficult for medical tourists to search for healthcare providers with accurate information in different countries individually for the treatment of diseases and for finding relevant wellness/sightseeing information.
In general, unlike making a decision to buy commercial products or services, the decision-making process for medical tourism is very complicated as it also involves emotional aspects that lead to multidimensional behaviors [ 24 ]. A variety of factors can affect decision-making of medical tourism because it influences not only physical (medical services) but also mental (tour) health conditions during and after activities [ 22 , 23 ].
Medical tourism advertisements tend to focus too much on treatment results and outcomes rather than quality improvements and safety [ 25 ]. When customers base their decisions on over- or underestimated advertisements, there tends to be a gap between the expected and actual outcomes. The increasing media interest in medical tourism has made it popular on a global platform, and today, we can obtain information on medical tourism destinations through various channels, including newspapers, magazines, radio, and television programs [ 25 ]. Online marketing efforts via web help publicize medical tourism [ 26 , 27 ]. Ormond and Sothern [ 28 ] analyzed five medical tourism guide books and found that a common factor among the books was to encourage potential customers to tour rather than introduce destinations and international choices for medical services. Thus, a sufficient preliminary investigation in advance is necessary for medical tourism. Customers can make the final decision through proper search of a variety of information and comparing them with services offered by providers in other regions or countries. It is suggested that a synergistic approach is more effective when it is done in a comprehensive way than in a piecemeal information survey [ 29 ].
Medical services comprise those put into the service (patients and medical staff), organization (service providers, service or products), treatment procedures, and outcomes [ 30 ]. As each process generates activities for medical treatment through interaction with patients, Lee [ 12 ] divided the process of value creation into preprocessing, responding process, and resulting processes. The preprocessing refers to a set of preparative activities in advance of care services, the responding process as the one to respond to interactions during treatment, and the resulting processes as related to the prevention and outcome of disease. Thus, sufficient information should be provided to customers about the entire process rather than at the time of experiencing each process. Once customers achieve their goal of getting the desired outcome, they will go back home and may come back for further treatments for better quality of life or wellness (repurchase or any positive activities) or the other way around (negative activities). Customers make their decisions based on what they searched before selecting the destination. It means that they would first experience medical tourism through Googling; feedback from colleagues, friends, or family; or direct communication with the hospital.
Medical tourism is a major decision problem for the patient; it is much more involved than deciding to visit a local healthcare provider. The customer’s experience of medical tourism is the main factor that influences his/her satisfaction which in turn would influence revisit intention. Thus, it should be a major strategic priority for medical tourism hospitals and their administrators to develop a system that can provide positive experience to customers. Many tourism hospitals have a one-stop service system for their customers that may include such services as government documents (visa service), transportation (air flight reservations, airport pickup, shuttle service, etc.), language help, local hotel reservations, insurance processing, financial arrangements, local tour attractions, and the like. For example, Bumrungrad Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand, which is ranked ninth in the top ten hospitals in the world, provides a very efficient one-stop service to foreign customers (VIP airport transfers, interpreters, concierge services, embassy assistance, international insurance arrangements, and medical coordinators, see http://www.bangkok.com/hospitals-private-hospitals.htm ).
Experience of customers
Since customers’ overall satisfaction may be subjective, recent studies have emphasized the importance of customer experience and strategic approaches to improve the quality of medical services [ 12 ].
Merlino and Raman ([ 31 ], p.113) suggested that patient experience is a strategic priority and provided a broad definition: “The patient experience was everyone and everything people encountered from the time they decided to go to the clinic until they were discharged.” Meyer and Schwager ([ 7 ], p.118) defined customer experience as “the internal and subjective response customers have to any direct or indirect contact with a company”, and De Keyser et al. ([ 8 ], p.23) also suggested customer experience as “comprised of the cognitive, emotional, physical, sensorial, spiritual, and social elements.” These definitions imply that patient experience includes cognitive activities (e.g., checking reputation and searching other relevant information) before going to the hospital to the post-discharge behaviors (e.g., recommendation and feedback) with patient’s own emotional and subjective judgments.
In particular, medical tourism needs to be investigated thoroughly prior to the travel, because it focuses not only on information of medical institutions but also on the region or country where they will receive treatment. New advanced technologies can earn positive reviews from consumers and succeed only if they are unique in terms of their functions, convenience, and attractiveness. The positive images created from this could generate favorable responses from customers as they make comparisons based on actual use or indirect experience. In other words, customers’ direct or indirect experiences can affect their future repurchase intention.
The direct and indirect experience gained during the preliminary investigation will affect the process of receiving the actual medical service [ 12 ]. Further, if the gap between expectation and reality increases, there will be a decline in satisfaction. It will also affect revisit intention. In addition, since the medical services provided to patients with various diagnoses and administration services that are multidimensional, it is difficult to directly measure patient experience. As customer satisfaction might be improved based on their experience, customer satisfaction should also be included in the behavior of the customers’ preparation before arriving at the destination [ 12 ].
Verhoef et al. [ 11 ] suggested customer experience as “the total experience, including the search, purchase, consumption, and after-sale phases of the experience.” The prior experience occurs before purchase and consumption, and the purchase and consumption represents current experience, and after-sale/consumption experience represents post-experience. Therefore, in this study, the patient experience in medical tourism can be divided into prior experience for deciding on medical tourism, current experience during the treatment and/or medical tour, and post-experience after treatment and/or tour.
The prior experience includes the direct or indirect experience of customers during various activities before actually experiencing the main service, medical tourism. Patients can search various information, such as reputation, specialized treatment, and interesting tour destinations, directly or indirectly before choosing a hospital for the best possible treatment and service. Since the customer’s decision-making is based on a thorough prior investigation [ 7 ], sufficient communication with the customer is necessary. Patients can of course directly consult with the medical staff or service personnel of a hospital via video chatting (e. g., Skype or FaceTime) or telephone. In this study, the prior experience was categorized into checking reputation, searching information, and communication.
Through prior experience, customers make their final decisions for medical tourism, receive actual medical services, and have various other experiences. They are involved in direct communication with service providers, direct engagement in the service provision processes, and witnessing a gap between what they expected and the service actually received. Therefore, the current experience in this study refers to customer experience while engaging in various activities at the hospital, including interaction with service providers or other customers, use of information and comminutions technology (ICT), and enjoying the service environment. The current experience was categorized into checking costs, care quality, and supporting system and other relevant information.
Customers come to evaluate their own experience based on expectations, current experience, and other activities. Their experiences may generate either positive or negative impact on others. From the customers’ perspective, the post-experience influences the intention to repurchase or has a positive word-of-mouth. Service providers, on the other hand, may search for new ways to retain customers and improve their satisfaction through their post-experience (i.e., surveys or social networking). Sridhar and Srinivasan [ 32 ] suggested that the reviews customers read in advance actually influence purchase intention or encourage them to share their own feedback online after purchase and encouraged organizations to work hard to create positive customer experiences for “leaving good memories.” Thus, the post-experience of customers extends the processes continuously as it affects their prior, current, and post experience [ 10 ]. Consequently, the post-experience in this study refers to experiences that will influence patients’ decision on what to do after service provision. The post-experience includes relationship building, recommendation, and feedback.
As discussed earlier, decision-making for medical tourism can be determined with a variety of patient experiences. Thus, this study examines the effects of experience of medical tourists on the decision-making process. The proposed research model is shown in Fig. 1 .
Proposed research model
Hypotheses development
Prior and current experience.
As it is difficult to set clear standards on hospital selection, which is the most critical factor of medical tourism, and vacation spots, most patients make decisions based on their own experience, information technology, and prior patients’ feedback [ 10 ]. In recent years, with the advent of smart devices and ICT, both patients and providers can access the information they want directly or indirectly and can easily make their own decisions. The decision process is also influenced by the changing business environment as well as purchase patterns of patients [ 33 , 34 ].
Hospital reputation is an important factor in patients’ decision-making [ 18 ]. Ferguson et al. [ 35 ] argued that medical service providers can enforce patient loyalty and maximize word-of-mouth effect efficiently. Based on a study of hospitals in Taiwan, Cheng et al. [ 36 ] suggested that recommendations made by patients form an important factor in attracting patients for medical tourism. Therefore, recommendations from family, friends, or colleagues become a critical factor in hospital selection [ 36 ].
Prior experience begins with customers searching for, reviewing information, or asking someone about key services. Many customers seek information from online reviews, asking medical staff questions, or going through onboarding processes [ 10 ]. For instance, in prior experience, a customer may communicate with physicians by filling out documents before making an appointment, review information about hotels in the destination area, or use a Twitter before the trip. As mentioned above, current experience includes experiences during service delivery through meeting physicians, using hospital facilities, staying at a hotel, or visiting tourist attractions in the selected region [ 10 , 37 , 38 ].
Patients’ positive or negative perceptions are based on the quality of service they received at the hospital. They come to build these positive or negative images after comparing their expectations with what they actually experienced at the selected hospital at the time of getting the medical treatment. Since medical services are delivered through interaction between patients and physicians, patients show mixed responses depending on the kind of services they received at the hospital. Such variations in response result in from the gap between what they expected based on prior experience and their evaluation of the actual services, which will ultimately affect their future decision [ 12 ]. Therefore, prior experience should be considered to have an effect on current experience. The following hypothesis is proposed.
Hypothesis 1: Patients’ experience in medical tourism pre-search has a positive effect on their current experience.
H1-1: Reputation gained through the prior experience of a hospital has a positive effect on costs related with medical tourism.
H1-2: Reputation gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on care quality.
H1-3: Reputation gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on supporting system and/or information.
H1-4: Searching information gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on costs related with medical tourism.
H1-5: Searching information gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on care quality.
H1-6: Searching information gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on supporting system and/or information.
H1-7: Communication gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on costs related with medical tourism.
H1-8: Communication gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on care quality.
H1-9: Communication gained through the prior experience has a positive effect on supporting system and/or information.
Current and post experience
When a customer chooses a service through the evaluation of available information or word-of-mouth and dissatisfied with the service received, he/she may switch to another service provider. Even though patients themselves may not be able to change hospitals easily, owing to the nature of the medical service, their dissatisfaction can have a direct or indirect effect on others. For instance, patient “A” was discharged from hospital “B” after undergoing a surgery. Even if patient A is not satisfied with hospital B, he/she may be compelled to visit hospital B for a follow-up service. However, patient A may discourage potential patients from visiting hospital B through negative word-of-mouth based on his/her own experience. Therefore, to provide medical services with positive effects on other patients, hospital should recognize that the patient has selected a particular hospital after carefully considering and searching hospitals directly or indirectly. Especially, patients choose hospitals for medical tourism abroad because they are not satisfied with their current care providers. Consequently, provision of diverse and accurate information is necessary for medical tourism [ 2 , 3 ].
Previous studies suggest that patients make decision based on their cognitions about something ➔ evaluation and emotions ➔ acting for outcomes [ 10 ]. de al Hoz-Correa et al. ([ 2 ], p.208) pointed out that the key factor to be considered by the medical tourism industry in the future should be the “consequences of commodification in healthcare pressures for privatization of health in departure and host countries.” This means that hospitals should take measures for more effective communication and provide adequate explanations during the medical treatment and try to relieve patient dissatisfaction by offering follow-up options. In addition, hospitals should offer patients guidance regarding medical insurance before treatment so as to prevent any conflict after the treatment. Therefore, medical tourism hospitals should provide all the pertinent information to potential patients so that they can make intelligent decisions in selecting the best hospital for their unique needs with quality care and positive experience. By doing so, they can create positive outcomes. Such activities could encourage patients to have positive experiences, share their satisfaction with others, and make more visits in the future.
Revisit intention is based on patients’ overall experience of the service, which will influence their future decisions. Polluste et al. [ 39 ] stated that revisit intention can be positively influenced by respecting and reflecting patient demands and opinions, and striving to improve patient experience through direct interaction with patients. Therefore, the current experience during treatment or at a tourism spot influences post-experience and encourages multiple visits and positive word-of-mouth effects [ 40 ]. Thus, the following hypothesis is suggested.
Hypothesis 2: Patients’ current experience during the medical tour process has a positive effect on post-experience.
H2-1: Costs related with medical tourism gained through the patients’ current experience has a positive effect on relationship building.
H2-2: Costs related with medical tourism gained through the patients’ current experience has a positive effect on recommendation.
H2-3: Costs related with medical tourism gained through the current experience has a positive effect on feedback.
H2-4: Care quality gained through the current experience has a positive effect on relationship building.
H2-5: Care quality gained through the current experience has a positive effect on recommendation.
H2-6: Care quality gained through the current experience has a positive effect on feedback.
H2-7: Supporting system and/or information gained through the current experience has a positive effect on relationship building.
H2-8: Supporting system and/or information gained through the current experience has a positive effect on recommendation.
H2-9: Supporting system and/or information gained through the current experience has a positive effect on feedback.
Data collection
Data was collected from medical tourists who were in stable enough conditions for this survey and were willing to participate. Hospitals in this survey participated on a voluntary basis. The main reason for using this sampling approach was that South Korea represents a major country with highly skilled professionals, advanced medical devices, and well-established infrastructures for medical tourism [ 5 ]. The target population of this study was the international medical tourists traveling to seeking medical services in selected hospitals in Busan, South Korea during April 2018–May 2018. The researcher was assisted by the hospitals’ administration team, and the hospital staff assisted in finding medical tourists at the time of research and provided the responses to the researcher.
A survey questionnaire was developed using the double translation protocol [ 41 ]. The questionnaire was developed in English first and then translated into Korean by two bilingual operations management faculty in Korea. The Korean version was translated back into English by two American operations management experts who are also bilingual. The two English versions of the questionnaire had no significant difference.
The initial questionnaire was tested in a pilot survey involving 30 participating medical tourists in a Korean hospital. The reasons for this pilot test were to ensure the participating medical tourists clearly and fully understood the questionnaire items. After the pilot study, the number of measurement items of each variable was reduced as some items suggested by managers were difficult to measure precisely. The final questionnaire is shown in Table 1 and provides the measurement items for prior, current, and post experience of medical tourists.
To collect data, we were helped by the medical staff and medical consultants since patients were from various countries (Japan, China, Russia, Mongolia, and others) and the participating hospitals in this study were all medical tourism hospitals. Out of 500 questionnaires that were distributed to medical tourists, subsequently, 188 (37.6%) responses returned useable questionnaires. The respondents’ demographics and their hospitals’ characteristics are summarized in Table 2 .
As shown in Table 2 , majority respondents’ nationality is Japanese (53.7%), Chinese (16.5%), and Russian (10.6%),
Of respondents, 92% traveled to Korea for the first time, and another 18% were here for the second time. Majority of the respondents are going to stay more than 15 days to less than 22 days in Korean (70.4%). A total of 80.9% of respondents’ primary purpose of this visit is to receive medical service, while not medical service was 19.1%. About 30.3% of medical tourist wanted to cosmetic/plastic/reconstructive surgery, and 26.1% wanted to dental treatment during their trip in Korea. Almost (96.3%) of respondents made their decision based on word-of-mouth information and 3.7% on their experiences. More than half (53.7%) of the respondents chose medical tourism because of medical costs, and then quality of care service (24.5%).
Variables of the model
The questionnaire utilized 5-point Likert scales to measure the constructs. The data was analyzed by SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 programs. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was chosen because it provides all the tools necessary to test the hypotheses.
Reliability was tested based on Cronbach’s alpha value (Table 3 ). In the reliability test, Cronbach’s alpha value of relationship building on post-experience was highest (.945), and supporting system and/or information on current experience was lowest (.736). All of the coefficients of reliability measures for the constructs exceeded the threshold value of .70 for exploratory constructs in basic research [ 42 ].
For validity test, the principal component analysis (PCA; minimizes the sum of squared perpendicular distance to the component axis) and the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were used to identify the most meaningful basis and to examine similarities and differences of the data based on Brown’s [ 43 ] recommendation. Eigen values and percent of variance explained for each construct are shown in Table 3 . The cumulative percentages of explained variance were exceeded 70% for the each constructs on statistics of PCA. The loading values of each factor ranged from .566 (CQ5) to .957 (RB4) as shown in Table 3 .
The results of CFA can provide evidence of the convergent and discriminant validity of theoretical constructs [ 44 ]. This measurement model consisted of nine components of reputation, searching information, communication, costs, care quality, supporting system and/or information, relationship building, recommendation, and feedback. The standardized factor loadings and t values for measurement variables, results of CFAs to test the measurement model for all construct using the AMOS 23 program, are presented in Table 3 . The values of standardized regression weight and all variables proposed by the study exceeded .5 and were statistically significant at the .05 level.
The results of goodness of fit test for the measurement model are summarized and shown in Table 4 . Compared to the recommended values for the goodness of fit tests, the values of CFI, RMR, RMSEA, TLI, and χ2/d.f. were satisfactory, while the value of GFI was not. Deepen [ 44 ] suggested that GFI is desired to be over 0.9; however, “this must not automatically require the model to be rejected.” In our model, the majority of fit indices showed good acceptance measures and only GFI and AGFI were below the required thresholds.
To identify whether a single factor does account for the majority of the total variance of all the measurements, common method variance (CMV) was tested. Tehseen et al. [ 45 ] suggested Harman’s single-factor test and controlling for the effects of an unmeasured latent methods factor by Podsakoff et al. [ 46 ] for CMV test. For Harman’s single-factor test, an exploratory factor analysis (estimates factors which influence responses on observed variables in the data) employed the unrotated factor to account for the variance in the variables. Nine factors with an eigenvalue greater than one were identified and that the largest factor accounted for 36.404% of the total variance, less than 50% of the total variance is acceptable as per Harman’s single factor test. For controlling for the effects of an unmeasured latent methods factor, we added a single common latent factor on measurement model to connect it to all observed variables in the measurement model of the study [ 46 ]. As shown in Table 4 , the results indicated that the original measurement was similar to that of the extended model with an inclusion of the common latent factor. It means that common method bias would not be of concern [ 47 ].
Table 5 provides the square roots of average variance extracted (AVE) of latent variables, while the off-diagonal elements are correlations between latent variables. Campbell and Fiske [ 48 ] suggested that the construct validity is tested by discriminant and convergent validity. For discriminant validity, the square root of the AVE of any latent variable should be greater than the correlation between this particular latent variable and other latent variables [ 49 ]. For convergent validity of the measurement model, Fornell and Larcker [ 50 ] recommended that AVE measures the level of variance captured by a construct versus the level due to measurement error, values above .7 are considered very good, and the level of .5 is acceptable. The acceptable value of critical ratio (CR) is .7 and above.
Statistics shown in Table 5 satisfied this requirement, leading to discriminant validity. As the values of AVE and CR of reputation, searching information, communication, costs, care quality, supporting system and/or information, relationship building, recommendation, and feedback were all greater than .6 and .8, respectively, thus convergent validity met the threshold. Statistics shown in Table 5 therefore satisfied this requirement, lending evidence to construct validity as discriminant and convergent validity.
This section presents the results of hypotheses testing, including the standardized coefficient of each path in the model. As a result of the goodness of fit test, compared to the recommended values, in this model the values of GFI (.857), CFI (.929), RMSEA (.058), RMR (.068), TLI (.920), and χ 2 /d.f (1.639) were good for fit. In our model, the majority of fit indices showed good acceptance measures and GFI (.857) and RMR (.068) were below the required threshold.
Table 6 presents the results of the significance test for the proposed research model as well as the summary of the hypotheses test. For H1-1, H1-2, and H1-3 tests, patients’ experience of their decision-making process before care, the standardized path coefficient between reputation and costs related with medical tourism (H1-1), care quality (H1-2), and supporting system and/or information (H1-3) were .030, .112, and .094, respectively. H1-2 was statistically significant at the .05 level, while H1-1 and H1-3 were not significant. Thus, H1-2 ( β = .112) was supported, while H1-1 ( β = .030) and H1-3 ( β = .094) were not supported.
With a well-known hospital for medical tourism, patients seek to ensure a positive experience with quality care by engaging in activities before care to ensure their satisfaction [ 19 ]. Thus, before making a final medical tourism decision, patients research the reputation of a particular hospital in advance, ensure that the hospital’s communication enables them to achieve what they desire, and locate information through various media. Among the pre-care activities for medical tourism examined in the study, the hospital’s reputation was shown to have a positive impact on the quality of care [ 35 , 36 ], but not on the costs related with medical tourism or on the supporting system and/or information within a hospital.
For H1-4, H1-5, and H1-6 test, the standardized path coefficients between searching information on medical tourism and costs related to medical tourism (H1-4), care quality (H1-5), and supporting system and/or information (H1-6) were .519, .796, and .297, respectively, and statistically significant at the .05 level, supporting H1-4, H1-5, and H1-6.
The results of this study supported previous studies [ 6 , 10 , 25 ], which found that searching medical tourism has shown a positive impact on costs related with medical tourism, care quality, and supporting system and/or information. This means that researching for information in advance leads to a positive experience while visiting the hospital abroad. New digital devices provide opportunities for searching for accurate information through easy access to technology systems [ 51 , 52 ].
For H1-7 test, the standardized path coefficient between communication about medical tourism and costs related with medical tourism (H1-7) was .377 and statistically significant at the .001 level, supporting H1-7. For H1-8 and H1-9, the standardized path coefficient between care quality (H1-8) and supporting system and/or information (H1-9) were .108 and .259, respectively, and not statistically significant at the .05 level. The result of H1-7 test was supported, while H1-8 and H1-9 were not supported. From these results, the following can be summarized.
No matter how well-coordinated decisions between a patient and a provider are, what patients expect based on prior experiences does not have a positive impact on care experiences. Some patients did not expect that high-quality care and a good supporting system and information would be provided in advance of the care. When medical tourists have good communication with a potential hospital provider, they positively weigh that communication in making medical tourism decision [ 53 ]. Thus, hospitals should honor the medical costs quoted and provide the quality of care and information that were promised in communications, both before and during care.
For H2-1, H2-2 and H2-3 tests, patients’ current experience during their trip in Korea, the standardized path coefficient between cost related to medical tourism and relationship building with the hospital (H2-1), recommendation for medical tourism (H2-2), and feedback for the hospital (H2-3) were .147, .423, and .372, respectively, and statistically significant at the .05 level. Thus, H2-1, H2-2, and H2-3 were supported.
For H2-4, H2-5, and H2-6, the standardized path coefficients between care quality and relationship building with the hospital (H2-4), recommendation for medical tourism (H2-5), and feedback for the hospital (H2-6) were .800, .732, and .545, respectively, and statistically significant at the .001 level. Thus, H2-4, H2-5, and H2-6 were supported.
For H2-7 and H2-8 tests, the standardized path coefficient between supporting system and/or information to patients and relationship building with the hospital (H2-7) and recommendation for medical tourism (H2-8) were .589 and .165 respectively, and statistically significant at the .05 level. Thus, H2-7 and H2-8 were supported. For H2-9, the standardized path coefficient between supporting system and/or information to patients and feedback for the hospital (H2-9) was .036, and not statistically significant at the .05 level; thus, H2-9 was not supported.
The results of the study are similar to those of previous studies [ 36 , 54 ]. Costs related with medical tourism had a positive impact on the relationship building with the hospital, recommendation for medical tourism, and feedback for the hospital. Thus, costs associated with medical tourism are a key factor that supports a thriving medical tourism industry.
Heung et al. [ 55 ] suggested that key players in medical tourism as hospitals, medical travel agencies, hotels, and the medical tourists themselves. As with previous studies [ 36 , 54 ], the importance of care quality must be acknowledged by service providers because most medical tourists’ expectations exceeded their perceptions of the quality of care provided. Therefore, healthcare facilities with medical tourism should be provided high standards of care quality and be permitted to facilitate cross national travel to improve healthcare services.
Based on the result of this study, medical travel facilitators should consider providing supporting systems and/or information to patients as a one-stop service offering integrated knowledge of medical care services and travel [ 56 ]. Hospital management could actively focus on achieving better care outcomes if supporting systems and/or information were provided by medical travel facilitators in advance.
Discussion and conclusions
Medical tourism industry has drawn attention from international patients, travel agencies, governments, and the international accreditation sector [ 1 , 4 , 5 ]. Medical tourism can be arranged by the patients themselves by researching and booking on the internet, as well as by medical travel agencies [ 24 , 29 ]. Therefore, medical tourists have information on the best and most well-known healthcare providers and travel arrangements before embarking on medical tourism (pre-experience), and then the medical tourism experience (current experience) affects whether the tourist will recommend the medical provider to other potential customers (post-experience). Thus, this paper advances the idea that all three stages of a patient’s experience affect the medical tourism industry.
In this empirical study, we collected data to examine pre-experiences (e.g., reputation, searching information, and communication), current experiences (e.g., cost, care quality, and supporting system and/or information), and post-experiences (e.g., relationship building, recommendation, and feedback) in the medical tourism industry. The results of this study provide new insights about how key players (e.g., hospitals, medical travel agencies, hotels, and the medical tourists themselves) in medical tourism can effectively help managers identify medical tourists’ needs based on medical tourists’ decision-making process of pre, current, and post experience of medical tourism. In addition, the study sheds light on the perception of medical tourists on care quality and costs, as well as their future intention to obtain healthcare in the same hospital or country. Patient experience based on their interaction with medical staff and/or coordinators should be given as much importance as accuracy of diagnosis, treatment, and procedures.
The most important service attributes, which are highly attractive to international patients, will help medical travel agencies improve the information provided and develop innovative ideas among key players in medical tourism. As a variety of information retrieval functions grow and digital devices spread [ 52 ], medical tourism will gain a competitive edge by providing medical tourism information. Consumers will also have more opportunities to access information using comparative searches through different media.
Academically and practically, this paper provides several implications. First, developing and expanding a well-developed medical travel procedure based on patients’ experiences is a prerequisite for successful medical tourism. Such decision-making process could be measured by integrating three types of customer experience to enhance customer satisfaction. Because many hospitals and travel agencies are striving to develop new protocols using advanced technologies, the proposed model should be easy to access and the reservation process should be simple. For example, a one-stop service system can help with travel arrangements, arrange airport pick up and local transportation, hotel recommendations, ancillary services at the hospital, scheduling tours to selected destinations, coordinating with insurance companies, and assisting with other paper work. To build an effective medical travel process for patients, healthcare facilities and travel facilitators must fulfill their promises. In other words, the promised services and costs should be provided without fail. For example, policymakers should ensure that the standard model of medical tourism include internationally accepted standardized care processes and insurance. The qualification criteria for medical tourism agents/brokers should be developed and enforced globally. Since customers from various countries visit a hospital, to overcome barriers to global medical tourism, the use of standardized communication devices should be available for customer convenience.
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting its findings, and future studies should also consider these limitations. First, the study assumed that hospitals visited by medical tourists have the same medical environments. Second, to collect data, we did not consider personal experiences and preferences for researching information. Third, data was collected from medical tourists in Korean hospitals located in Busan, South Korea, without considering the number of beds in the hospitals. Thus, the generalizability of this study’s results may be limited. There are several potential future research opportunities considering these limitations. For example, as there are many different hospital sizes, a comparative study of small and large hospitals in terms of care quality and costs might yield interesting results. In addition, there are many different data characteristics based on the type of patients, disease conditions, and demographic characteristics (e.g., personal experience researching information with different media used, personal income, gender, etc.) that could be studied.
Lajevardi M (2016) A comprehensive perspective on medical tourism context and create a conceptual framework. J Tourism Hospitality 5(5):1–12
Article Google Scholar
de la Hoz-Correa A, Muñoz-Leiva F, Bakucz M (2018) Past themes and future trends in medical tourism research: a co-word analysis. Tour Manag 65:200–211
Ngamvichaikit A, Beise-Zee R (2014) Communication needs of medical tourists: an exploratory study in Thailand. Int J Pharm Healthc Mark 8(1):98–117
Allied Market Research (AMR) (2018) Medical tourism market expected to reach $165,345 million, by 2023. https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/press-release/medical-tourism-market.html .
Google Scholar
Orbis Research (2017) Medical tourism market shaped by innovation, shifting competitive landscape, forecast to 2022. https://www.reuters.com/brandfeatures/venture-capital/article?id=17353
Altin M, Singal M, Kara D (2011) Consumer decision components for medical tourism: a stakeholder approach. The 16th Graduate Student Research Conference in Hospitality and Tourism, University of Massachusetts, pp 1–11
Meyer C, Schwager A (2007) Understanding customer experience. Harv Bus Rev 85(2):116–126
De Keyser A, Lemon K, Keiningham T, Klaus P (2015) A framework for understanding and managing the customer experience. MSI working paper no. 15–121. Marketing Science Institute, Cambridge
Lee S, Lee D, Olson D (2013) Health-care quality management using the MBHCP excellence model. Total Qual Manage Bus Excell 24(1–2):119–137
Voorheesa C, Fombelleb P, Gregoirec Y, Boned S, Gustafssone A, Sousaf R, Walkowiakg T (2017) Service encounters, experiences and the customer journey: defining the field and a call to expand our lens. J Bus Res 79:269–280
Verhoef P, Lemon K, Parasuraman A, Roggeveen A, Schlesinger L, Tsiros M (2009) Customer experience: determinants, dynamics and management strategies. J Retail 85(1):31–41
Lee D (2017) A model for designing healthcare service based on the patient experience. Int J Healthc Manage (on-line) http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/20479700.2017.1359956
Wolf J, Niederhauser V, Marshburn D, LaVela S (2014) Defining patient experience. Patient Exp J 1(1):7–19
Nugraha A, Hamin H, Elliott G (2016) Tourism destination decisions: the impact of risk aversion and prior experience. Asia Pac J Tourism Res 21(12):1274–1284
Ofir C, Simonson I (2007) The effect of stating expectations on customer satisfaction and shopping experience. J Mark Res 44(1):164–174
Medical Tourism Association: http://www.medicaltourismassociation.com/en/medical-tourism-faq-s.html . Accessed 10 May 2018.
Wongkit M, McKercher B (2013) Toward a typology of medical tourists: a case study of Thailand. Tour Manag 38:4–12
Tourism Research and Marketing (TRAM) (2006) Medical tourism: a global analysis/ a report by tourism research and marketing. ATLAS, Arnhem
Lunt N, Smith R, Exworthy M, Green S, Horsfall D, Mannion R (2011) Medical tourism: treatments, market and health system implications: a scoping review. OECD Directorate for Employment, Labour and Social Affairs, p. 7
Tarcan E, Ates M, Sait VE (2015) An evaluation related to the effect of strategic facility management on choice of medical tourism destination. Marketing 46(2):124–131
Youngman I (2011) How medical tourism lost its way…and how it can get back on track. Int Med Trav J Retrieved from http://www.imtj.com/articles/how-industry-lost-its-way-and-how-it-can-get-back-track/
Ehrbeck T, Guevara C, Mango P (2008) Mapping the market for medical travel. McKinsey Quarterly:1-11. Retrieved from https://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/Mapping_the_market_for_travel_2134 .
Crooks V, Kingsbury P, Snyder J, Johnston R (2010) What is known about the patient's experience of medical tourism? A scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res 10(266):1–12
Crouch G, Louviere J (2001) A review of choice modelling research in tourism, hospitality and leisure. Consum Psychol Tourism Hospitality Leis 2:67–86
Horowitz MD, Rosensweig JA, Jones CA (2007) Medical tourism: globalization of the healthcare marketplace. Medscape Gen Med 9(4):33–39
Crooks VA, Turner L, Snyder J, Johnston R, Kingsbury P (2011) Promoting medical tourism to India: messages, images, and the marketing of international patient travel. Soc Sci Med 72(5):726–732
Snyder J, Crooks VA, Adams K, Kingsbury P, Johnston R (2011) The patient’s physician one-step removed: the evolving roles of medical tourism facilitators. J Med Ethics 37(9):530–534
Ormond M, Sothern M (2012) You, too, can be an international medical traveler: reading medical travel guidebooks. Health Place 18(5):935–941
Johnston R, Crooks V, Snyder J, Kingsbury P (2010) What is known about the effects of medical tourism in destination and departure countries? A scoping review. Int J Equity Health 9(24):1–13
Trusko B, Pexton C, Harrington H, Gupta P (2007) Improving healthcare quality and cost with six sigma. FT Press, Upper Saddle River
Merlino J, Raman A (2013) Health care’s service fanatics: how the Cleveland clinic leaped to the top of the patient-satisfaction surveys. Harv Bus Rev 91(5):108–116
Sridhar S, Srinivasan R (2012) Social influence effects in online product ratings. J Mark 76(5):70–88
Gavett G (2015) How self-service kiosks are changing customer behavior. Harv Bus Rev 93(3):1–6
Larivière B, Bowen D, Andreassen T, Kunz W, Sirianni N, Voss C, Wünderlich N, Keyser A (2017) Service encounter 2.0: an investigation into the roles of technology, employees and customers. J Bus Res 79:238–246
Ferguson RJ, Paulin M, Leiriao E (2007) Loyalty and positive word-of-mouth: patients and hospital personnel as advocates of a customer-centric health care organization. Health Mark Q 23(3):59–77
Cheng SH, Yang MC, Chiang TL (2003) Patient satisfaction with and recommendation of a hospital: effects of interpersonal and technical aspects of hospital care. Int J Qual Healthc 15(4):345–355
Lemon K, Verhoef P (2016) Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. J Mark 80(6):69–96
Lee D, Kim K (2017) Assessing healthcare service quality: a comparative study of patient treatment types. Int J Qual Innov 3(1):1–15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-016-0010-5
Polluste K, Kalda R, Lember M (2000) Primary health care system in transition: the patient’s experience. Int J Qual Health Care 12(6):503–509
Jeong J (2014) Healthcare service quality and its effects on perceived service value and consumer satisfaction. Doctoral Dissertation. University of Ga Chon, Korea
Harkness J (2011) Guidelines for best practice in cross-cultural surveys. Survey Research Center, University of Michigan Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor
Nunnally J (1978) Psychometric theory, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, NY
Brown T (2006) Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research. The Guilford Press, NY
Deepen J (2009) Logistics outsourcing relationships. Springer: Physica Verlag, Heidelberg
Tehseen S, Ramayah T, Sajilan S (2017) Testing and controlling for common method variance: a review of available methods. J Manage Sci 4(2):142–168
Podsakoff P, MacKenzie S, Lee J, Podsakoff N (2003) Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol 88(5):879–903
Satorra A, Bentler P (2001) A scaled difference chi-square test statistic for moment structure analysis. Psychometrika 66:507–514
Campbell D, Fiske D (1959) Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychol Bull 56(2):81–105
Barclay D, Thompson R, Higgins C (1995) The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technol Stud 2(2):285–309
Fornell C, Larcker D (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res 18(1):39–50
Al-Maaitah H (2016) An investigation of the acquisition and experience of medical tourism: the case of Jordan. Doctor of Dissertation. Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan
Lee S (2018) Innovation: from small “i” to large “I”. Int J Qual Innov 4(2):1–3 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-018-0022-4
Li R, Suh A (2015) Factors influencing information credibility on social media platforms: evidence from Facebook pages. Procedia Comput Sci 72:314–328
Boulding W, Glickman SW, Manary MP, Schulman KA, Staelin R (2011) Relationship between patient satisfaction with inpatient care and hospital readmission within 30 days. Am J Manage Care 17(1):41–48
Heung V, Kucukusta D, Song H (2010) A conceptual model of medical tourism: implications for future research. J Travel Tour Mark 27(3):236–251
Jagyasi P (2010) Medical tourism impact it’s more than obvious. Retrieved from: http://www.medicaltourismmag.com/medical-tourism-impact-itaes-more-than-obvious/
Saiprasert W (2011) An examination of the medical tourists motivational behavior and perception: a structural model. Doctoral Dissertation. Oklahoma State University, USA
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Busan Women’s College in 2018.
Availability of data and materials
Data will not be shared, and give the reason.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Busan Women’s college, Busan, South Korea
Soonae Hwang
College of Business Administration, Inha University, Incheon, South Korea
Department of Medical Information, Daejeon Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, South Korea
Chang-Yuil Kang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the developing research model, data collection, and writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to DonHee Lee .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hwang, S., Lee, D. & Kang, CY. Medical tourism: focusing on patients’ prior, current, and post experience. Int J Qual Innov 4 , 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-018-0024-2
Download citation
Received : 04 July 2018
Accepted : 28 August 2018
Published : 12 September 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-018-0024-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Prior-current-post experience
- Medical tourists
- Decision-making process
- South Korea
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.186(1); 2014 Jan 7

Travelling Well: Essays in Medical Tourism
Edited by Ronald Labonté, Vivien Runnels, Corinne Packer and Raywat Deonandan (University of Ottawa) . Imagine leaving your own country to buy a surgery or an organ or even a pregnancy. The personal enormity of such actions seems at odds with the frivolous term used to describe them: medical tourism. Whatever one calls them, though, these things are occurring, often to the accompaniment of whispered rumours or blaring journalism.
Travelling Well: Essays in Medical Tourism , a new electronic publication from the Institute of Population Health at the University of Ottawa, attempts to demythologize these stories, to attach muscular facts to a skeleton of gossip and sensationalism. A collection of pieces by scholars from a variety of disciplines, Travelling Well tackles the “who,” “where” and “why” of medical tourism.
Travelling Well’s real purpose is to describe the “how much,” in both quantitative and qualitative senses. Although several authors acknowledge that this description, hampered by the quality of existing data, is incomplete, the picture that emerges is impressively vast. Medical tourism is a multibillion dollar industry that continues to grow. It involves not only the tourists themselves, but the health care professionals who provide services, the companies that employ them, the brokers who make arrangements and the governments that permit (or encourage) it all. And don’t forget those citizens of the destination countries who might provide an organ or a uterus for a price. Travelling Well ambitiously, but successfully, reports the scale of it all, in economic and human terms.
Primarily a descriptive work, Travelling Well gives little attention to what might be medical tourism’s most important question: So what? What are the ultimate effects of medical tourism? Who stands to benefit and who can be harmed? These are complex questions that can be interpreted variously as inquiries about health care, economics, social justice or ethics.

Some of these issues, such as the “internal brain drain” that might result when a developing country devotes scarce resources to visiting medical tourists, are mentioned on occasion, but rarely addressed in depth. A chapter by Raywat Deonandan from the University of Ottawa gets its hands dirty with the ethical bramble of reproductive tourism, and tantalizes the reader with its engaging discussion. However, such discussions might be considered to belong to a different publication.
A discussion of the history of medical tourism would have been appropriate to include. It would seem unwise to think about the future trajectory of this phenomenon without understanding its past. This discussion is largely absent, beyond mention of Middle Eastern oil sheiks who travelled to the United Kingdom for state-of-the-art care that they had not yet financed in their own countries, and the origins of medical tourism remain mythologically obscure.
This important omission aside, Travelling Well is an interesting read that challenges its audience: this is what medical tourism is, now what do we think about it?

- Medical Tourism
Medical Tourism Benefits and Advantages
These days, a growing number of people are discovering the benefits of medical tourism. In the USA and throughout the Western world, it is becoming common knowledge that medical tourism offers a cheaper option for receiving medical treatment without compromising on quality. This article will outline the benefits and advantages of medical tourism, the reasons why people go abroad for treatment and basically, what medical tourism is all about.
Medical Tourism at a Glance
- Certain medical services are not available in their country of residence.
- Their health insurance does not cover the full cost of a procedure.
- Most people are unwilling to compromise their health just because the treatment costs are too high.
Why People Go Abroad for Treatment
- The costs of healthcare in developed nations have increased exceedingly.
- Nowadays, international travel is trouble-free and reasonably priced.
- Global standards of care and technological advancements in healthcare are rapidly improving all over the world.
- Improved communication opportunities make it easier to find and contact medical centers overseas.
The Benefits of Medical Tourism
Affordability and cost-effectiveness, high-quality healthcare, immediate service, improved flight and communication services, travel opportunities, medical tourism guide:, browse by specialty.
- Addiction Treatment
- Aesthetics non surgical
- Anesthesiology
- Bariatric Surgery
- Bone Marrow Transplant
- Cancer Treatment
- Cardiac Surgery
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Dental Care
- Dermatology
- Ear Nose and Throat
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Eye Surgery
- Family Medicine
- Fertility Treatment
- Gastroenterology
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Hair Transplant
- Hyperbaric Therapy
- Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine
- Medical Check Ups
- Neonatology
- Neurosurgery
- Orthopedic Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rehabilitation
- Rheumatology
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Vascular Surgery
Quick Links
- Advertising
- How it Works
- Destinations
- Information
- Terms of use
Featured Cities
- Buenos Aires
- Kuala Lumpur
- Petaling Jaya
Featured Specialties
- View More Specialties

Copyright © 2008 - 2024 Health-Tourism.com, All Rights Reserved
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Travelling Well: Essays in Medical Tourism

The opening years of the 21st century have been characterized by a variety of technological, social, political and economic factors that have seen the disintegration of the meaning and importance of international borders. From the power of the Internet to link disparate populations, to the consolidation of blocs of politically intertwined nations such as the European Union (EU), and the rise of affordable international travel, forces have been combining to bring about a globalized world economy that was only theorized in decades past. An obvious facet of this new globalization is the permeability of borders to the movement of consumers seeking a variety of medical services, and providers willing to accommodate, if not also profit, from this demand.
Related Papers
International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 2nd ed.
Meghann Ormond
Each year, millions of people around the world, disenfranchised by the restrictive national laws and unresponsive health systems in their countries of residence, circumvent these barriers by travelling to countries where their desired medical treatment is more accessible to them. These patients’ international medical travels (IMT), sometimes referred to as “medical tourism,” have drawn popular, political, commercial and scholarly attention, first, to the diverse global patchwork of healthcare ideologies and practices; second, to the national containerization of health care; and, third, to the consequences of IMT in traveling patients’ source, transit and receiving countries.
Alexandru Nedelea
Medical tourism is a phenomenon that has been manifested for thousands of years and is now defined by the need of patients from the developed countries to obtain care and medical services combined with certain tourist facilities. Specialty literature emphasizes that this concept is used to designate a journey whose motivation involves a medical procedure or activities that promote the physical and mental well-being of man. The growing presence of patients from the high-income countries in countries with emerging economies and developing economies is explained by the fact that these countries provide high-quality medical services at low costs (a phenomenon known as medical outsourcing). Increasing the flow of patients seeking treatments abroad is a global phenomenon, linked to economic development that generates income growth and education. Tourism is and must become a profitable business, we must struggle with us and with the competition of other international tourism operators to p...
Medical Tourism: A Growth Industry
This essay takes a brief look at services being developed throughout the world to cater to a specific population that has chosen to cross borders in order to receive quality health care: people from wealthier countries who, for a variety of reasons, are unable to receive adequate urgent or elective medical treatment in their places of origin yet who have sufficient personal financial resources that enable them to receive lower cost medical treatments in other generally less-developed countries. How is this type of mobility – oftentimes referred to as ‘health tourism’ or ‘medical tourism’ – accepted and handled by the places that send and receive these ‘tourists’? How does it impact these places and their residents at different scales, bearing in mind their variable levels of development?
SUMMARY 1. The global growth in the flow of patients and health professionals as well as medical technology, capital funding and regulatory regimes across national borders has given rise to new patterns of consumption and production of healthcare services over recent decades. A significant new element of a growing trade in healthcare has involved the movement of patients across borders in the pursuit of medical treatment and health; a phenomenon commonly termed‗ medical tourism '.
Shailesh Tripathi
carissa marie
Explore the growing trend of medical tourism where citizens of highly developed countries travel to less developed areas of the world to receive medical care, bypassing services offered in their own communities. Trends Although physician executives are certainly aware that some patients bypass their hospital, clinic or ambulatory surgery center on the way to the airport to have care in other cities, they may be somewhat surprised to learn that an increasing number of patients are traveling to a wide variety of destinations around the world for medical, surgical and dental care. Driven by a number of forces outside typical medical referral systems, these " medical tourists " seek modern health care at affordable prices in countries at variable levels of development. Medical tourism is different from the traditional form of international medical care where patients typically journey from less developed nations to major medical centers in highly developed countries for advanced medical treatment.
Handbook on Medical Tourism and Patient Mobility
Contemporary medical tourism builds upon long-standing links between travel and the pursuit of physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. It is produced today through the combination of, on the one hand, shifts in concentrations of accessible medical expertise and technologies around the world and, on the other, increased medicalization, care commodification, and perception of bodies as improve-able, malleable property. This chapter considers the impacts of this transnational phenomenon on contexts both generating and receiving medical tourists as well as the lesser-explored virtual and transit spaces between them and the methodological challenges that researchers face in studying medical tourism.
Ass. Prof. Dr. Omer Tontus
Drivers of Healthcare Globalisation and Their Effects on Medical Tourism Globalisation has intensified in many parts of the world, becoming an important challenge for public health institutions and policymakers. Although many studies have been conducted on the role of globalization in healthcare, no consensus has been reached on its effects. In this commentary, we attempt to evaluate the drivers of healthcare globalization and their effect on medical tourism destination selection. The focus of the commentary is the effects of globalization on patients, whose primary purpose is to travel for planned treatment for health reasons. People from developed countries look for alternative healthcare services and travel to developing countries for cost-effective medical care. Factors which foster medical tourism include demographic changes, remodeling of the healthcare industry, modern technological changes and advanced medical practices, including cost and quality considerations. This commentary presents a list of key factors related to globalization and their effects on medical tourism.
Kristen Smith
Medical tourism, or the transnational travel of patients for the consumption of health services, is a rapidly expanding industry across the globe, with a satellite “medicity” being built in Dubai, entire states in India promoted as “medi-hubs” and cruise ships transformed into seaborn hospitals docking in international waters to service patients. Somewhat disturbing advertising slogans such as “First World Treatment at Third World Prices” or “Sun and Surgery” are utilised by corporations and governments alike, driving an industry estimated to be already worth as much as US$60 billion and growing at a rate of 20 percent per annum. However, beyond the luxurious corporate hospitals used by foreign patients in countries such as India, are populations facing critical health issues, unable to access treatment at all. Consequently, this presentation will examine both the practice and industry of medical tourism through the lens of Critical Medical Anthropology in order to examine systemic structures of power manifest in the dominant discourses produced by social actors and institutions across the globe, looking to the impacts of medical tourism upon international health equity.
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Public Health Policy
Vivien Runnels
Global Social Policy
Mohd Alsharif
BMC proceedings
Ronald Labonte
Lucrări Științifice Management Agricol
Sergiu Rusu
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Home — Essay Samples — Geography & Travel — Travelling — Medical Tourism

Essays on Medical Tourism
Medical tourism, impact of the slsfta on private hospital sector and threats and opportunities arising thereon, research of a phenomenon of medical tourism, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Medical Tourism: Cosmetic Surgery Niche
Relevant topics.
- Hospitality
- Tourism Industry
- Travel and Tourism Industry
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Medical Tourism in India
Last updated on January 14, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

Medical tourism is described as any activity that involves a foreign visitor traveling and spending at least one night at the destination to rejuvenate, restore, or maintain health through medical intervention. Since the last decade of the 20th century, India has emerged as a global leader in the medical tourism sector. Read here to learn about the growth of medical tourism in India.
Over the past decade, India has gained a reputation for providing high-quality medical service at low costs to medical tourists traveling from across the globe.
However, with the travel bans during the covid-19 pandemic , the influx of medical tourists had dipped. According to the Tourism Ministry, India registered a negative growth of 79.4% in 2020.
Although, the situation looks positive once more owing to the efforts made to handle the pandemic situation. Market insights suggest the demand forecast to increase at a robust 19 % CAGR in 2022.
Table of Contents
Medical tourism in India
India’s healthcare industry offers a combination of both modern and traditional forms of medicine which sets the country apart from others.
- First, it has a set of world-class doctors and hospitals that provide treatment at fractional rates when compared to other countries.
- Secondly, India’s systems of medicine: AYUSH i.e., Ayurveda, Yoga, Panchakarma, Rejuvenation Therapy, etc, which are the most ancient forms of medicine, are now gaining immense popularity globally.
The government also recently announced plans to launch an AYUSH Mark which is a mark to provide credibility to AYUSH products in India and promote India’s medical tourism sector.

Additionally, the other medical services and facilities are also backed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA).
India’s healthcare industry has advanced significantly over the past 30 years, as seen by the notable accomplishments it has made.
- One of the industries that have contributed the most to revenue and are expanding quickly is healthcare.
- Both public and private providers support the healthcare industry. Over the past few years, national health policies have been crucial in establishing a more inclusive healthcare system to achieve structured Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- In addition, India provides less expensive treatment alternatives than the US and the UK without sacrificing the standard of healthcare. About one-fourth, less is spent on therapy in India than it is in the United States.
In terms of alternate medical treatment, the Indian medical treatment systems of yoga, ayurveda, rejuvenation therapy, and panchakarma are among the most ancient methods of medical treatment in the world.
The southern state of Kerala has developed medical tourism services as one of its core products for promoting tourism in the region.
Based on the Medical Tourism Index 2020-21, India is ranked 10th out of the top 46 countries, 12th out of the world’s top 20 wellness tourism markets, and 5th out of 10 wellness tourism destinations in Asia-Pacific.
- India boasts 39 Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited and 657 National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) accredited hospitals.
India holds an advantage as a medical tourism destination due to the following factors:
- Most of the doctors and surgeons at Indian hospitals are trained or have worked at some of the medical institutions in the US, Europe, or other developed nations.
- Most doctors and nurses are fluent in English.
- Top-of-the-line medical and diagnostic equipment from global international conglomerates is available at many Indian hospitals.
- Indian nurses are among the best in the world. Nearly 1000 recognized nurses-training centers in India, mostly attached to teaching hospitals, graduate nearly 10,000 nurses annually.
- Even the most budget-conscious traveler can afford first-rate service and luxury amenities
Most of the tourists are from Asian or African countries such as Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives, Indonesia, and Kenya, among others.

Chennai, Mumbai, New Delhi, Ahmedabad, and Bengaluru are the top 5 medical tourism destinations in India.
Wellness tourism
Wellness Tourism includes travel for a less stressful lifestyle, promoting a healthier, and finding balance in one’s life.
Ayurveda, Yoga, meditation, Panchakarma, and Rejuvenation Therapy are among the most ancient systems of medical treatment in India and the best way to promote Wellness Tourism.
The Ministry of Tourism has drafted guidelines for wellness tourism. These guidelines address issues regarding making available quality publicity material, training and capacity building for the service providers, participation in international & domestic Wellness related events, etc.
Mushrooming of wellness centers in the country has given rise to the concern for quality service.
- The Guideline for the Accreditation of wellness centers has been developed by National Board for Accreditation of Hospitals & Healthcare Services (NABH) in consultation with AYUSH and released during the workshop on wellness tourism organized by the Ministry of Tourism in 2011.
- The Ministry of Tourism has also extended its Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme to wellness tourism service providers including accredited wellness centers.
Impact of Covid-19 on medical tourism
Planned hospital operations decreased by as much as 80% during the state-wide lockdown in India caused by the new coronavirus outbreak, while unplanned systems decreased by 66%.
With the government of India’s assistance, the healthcare sector launched a comprehensive response strategy to combat the epidemic.
- Specialized COVID-19 hospitals and isolation facilities were established, and resource mapping using technology was started.
- The Indian government created several programs and used technology to combat the pandemic.
- The Aarogya Setu app was utilized across the nation to improve contact tracing, syndromic mapping, and infection self-evaluation.
- India not only met its own needs but also stepped up to help other nations during these difficult times.
Despite having several initiatives in place, the Medical Tourism industry of the country still faces some serious challenges.
- One of the major challenges that India is facing is promoting and creating awareness about state-of-the-art facilities in India.
- India is witnessing strong competition from destinations like Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey, and South Korea with low-cost options.
- In India, there is a lack of cohesiveness amongst the major players in the industry to come together and represent India on a world platform to acquire newer customers.
- Apart from these, inconsistent fee structure and lack of transparency in billing to foreign patients, and absurdly high margins to trade to refer patients are some of the challenges.
- Most Indian hospitals are also facing a lack of trust from foreign patients. The hospitals have observed poor hygiene awareness in medical attendants, unhygienic food handling, and lack of good hospitality services, heterogeneous pricing of services, and industry standards.
The government can play a vital part to upgrade the medical tourism sector. But the industry is facing the following problems which are caused by the governments. They are:
- no regulations
- taxation anomalies
- bureaucratic roadblocks
- no work on land reforms
- lack of long-term investor-friendly policies
- instability concerning terrorism and communal tensions.
On the part of insurance and allied services, the medical tourism industry in India is also facing some key bottlenecks. They are:
- inadequate insurance cover
- the underdeveloped insurance market in India
- insurance frauds
- overseas companies refusing reimbursement.
The following challenges, due to the infrastructural parts of the medical tourism sector in India, are:
- lack of access
- dearth of capital
- Lack of community participation and awareness
- Non-participation in the rural sector
- lack of concern for sustainability
- complex visa procedures
- lack of good language translators
- airport facilities still being inadequate
Government initiatives for medical tourism
The government has implemented various initiatives to overcome the challenges and push India’s rise as a hub of medical tourism through the promotion of ayurveda, yoga, and other Indian systems of medicine in the international market.
Heal India Initiative:
- Heal in India is a new initiative developed under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission in which there will be healthcare professionals, and hospital services to help patients seeking medical help in India.
- With this type of initiative, Government aims at promoting Medical Tourism in India via Heal in India Portal.
- It’s another Programme called Heal by India Government that aims to encourage Indian Health care Workers to go abroad and serve patients globally.
Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme
- MDA scheme offers financial assistance to approved tourism service providers.
Medical Visa provisions
- Special provision has been made for tourists traveling to India for healthcare purposes.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has introduced a new category of visa, Medical Visa, that can be issued to foreigners traveling to India for healthcare reasons.
Setting up a feedback mechanism to obtain testimonials from tourists traveling to the country for medical purposes.
- This ‘one-step’ portal would add convenience and provide credible information for medical tourists coming to India.
Way forward
To become the top-most medical travel destination, there is a need for significant investments into making the healthcare industry and equipment attractive for international patients.
- Patients spend most of their time in guest houses and are prone to further infections from such places.
- Thus, proper infrastructure and standardization need to be brought into the tourism industry and the nexus of guest house service providers urgently.
- Another aspect that needs to be tapped into is the opportunity for selling Indian health insurance to foreigners. This can generate an additional $9 billion in patient inflow to India.
The government is pulling out all its aces to maximize the industry’s potential. The aim is to make India the No.1 Destination for Medical Tourism in the world, tripling its revenue to $13 billion within 4 years.
The government has also proposed an outlay of US$ 28.7 billion for health and well-being, which is 137% higher than the previous year’s budget outlay.
In the post-Covid world, the demand for the healthcare industry is bound to surge and there is a huge potential for India to realize and aggressively advance towards attracting medical tourists from other parts of the world including Europe and the Americas.
With the government making it their priority to make India the hub of medical tourism, the initiatives combined with the surging demand are sure to make India the center for all medical tourists in the future.
-Article written by Swathi Satish

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Take ClearIAS Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
Ias/ips/ifs online coaching: target cse 2025.

Are you struggling to finish the UPSC CSE syllabus without proper guidance?

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
- Daily Updates
Make Your Note
National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism
- 23 Mar 2023
- GS Paper - 2
- Government Policies & Interventions
- GS Paper - 3
For Prelims: National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism, Medical Tourism Index (MTI), Medical Visa, National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH). For Mains: Medical and Wellness Tourism, Steps Taken for the Promotion of Medical and Wellness Tourism.
Why in News?
India has been ranked 10 th in the Medical Tourism Index (MTI) for 2020-2021 out of 46 destinations of the world by the Medical Tourism Association.
- With an aim to improve medical tourism in the country, the Ministry of Tourism has formulated a National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism in 2022.
What are the Key Pillars of the Strategy?
- The National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism has identified the following key pillars for the development of medical-value travel in the country.
- Developing a brand for India as a wellness destination.
- Strengthening the ecosystem for medical and wellness tourism
- Enabling digitalization by setting up Online Medical Value Travel (MVT) Portal
- Enhancing accessibility for Medical Value Travel
- Promoting Wellness Tourism
- Governance and Institutional Framework
- Foreign Tourists Arrival on medical purpose increases from 1.83 lakh in 2020 to 3.04 lakh in 2021.
What is Medical and Wellness Tourism?
- Medical and wellness tourism refer to the practice of travelling to another location to receive medical treatment or to improve one's health and wellbeing.
- These types of tourism are growing in popularity as people become more interested in alternative healthcare options and seek out high-quality medical care at a lower cost.
- This can lead to misunderstandings and miscommunications that could impact the quality of care received.
- Ethical Concerns: There have been concerns about the exploitation of vulnerable populations in medical tourism, particularly in the case of organ transplantation.
- ‘E- Medical Visa’ and ‘E-Medical Attendant Visa’ have also been introduced for 156 countries.
- The Ministry of Tourism provides financial Assistance under Market Development Assistance Scheme to Medical Tourism Service Providers accredited by National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) for participation in Medical/ Tourism activities.
Source: PIB

DESTINATION

1. Overview
Brief introduction to the country and its reputation in medical tourism.
Russia, the world’s largest country by land area, offers a unique blend of history, culture, and cutting-edge technology. While Russia may not be the first destination that comes to mind when considering medical tourism, it has been gaining traction in this field. With substantial investments in healthcare infrastructure and medical research, Russia is slowly but steadily becoming a destination worth considering for various medical procedures. The country has a growing reputation for offering state-of-the-art medical treatments, often at a fraction of the cost you might pay in Western Europe or North America.
Historical and Cultural Significance in Medicine
Russia has a long-standing history of medical research and innovation. From the times of renowned scientists like Ivan Pavlov to contemporary achievements in cardiology and neurology, the country has been instrumental in contributing to global medical science. Russian medical institutions have also been engaged in pioneering work in fields like radiology, organ transplantation, and aerospace medicine, reflecting a cultural emphasis on scientific inquiry and innovation.
The Medical Landscape
The Russian healthcare system is a mix of public and private institutions, providing an array of treatments ranging from general medicine to specialized surgeries. While public healthcare is generally available to citizens, the growing private healthcare sector caters to both local and international patients, often providing services that match global standards.
What Draws Medical Tourists to Russia?
Medical tourists often find Russia appealing due to its advanced technology, specialized treatments, and relatively lower costs. Moreover, the prospect of combining medical treatment with a cultural experience is another attractive feature. Known for its grand architecture, vibrant arts scene, and rich history, Russia offers an all-around travel experience alongside high-quality medical care.
2. Popular Medical Procedures
List and brief descriptions of procedures.
- Cosmetic Surgery : Including procedures like rhinoplasty, liposuction, and breast augmentation, Russia is increasingly becoming a destination for cosmetic surgery.
- Dental Treatments : Dental implants, crowns, and veneers are some of the sought-after treatments.
- Cardiac Surgery : With advanced technology, cardiac procedures like bypass surgeries and angioplasties are performed at specialized centers.
- Orthopedic Surgeries : Hip and knee replacements are commonly done here with a high success rate.
Specializations or Pioneering Treatments
Russia is becoming known for its cancer treatments, including specialized radiation therapies and immunotherapy treatments. Additionally, the country has been involved in research and treatment of neurological conditions, offering specialized services in this domain.
3. Top Hospitals & Clinics
Renowned hospitals and clinics.
- Almazov National Medical Research Centre, St. Petersburg
- European Medical Center, Moscow
- Moscow City Clinical Hospital
Accreditation and Affiliation
Most top hospitals are accredited by Russian healthcare authorities and some even possess international accreditations. These hospitals often collaborate with international medical institutions for research and training purposes.
Special Features, Awards, or Recognitions
Many hospitals have received awards for medical excellence and innovations in treatments. They also offer features like English-speaking staff, modern facilities, and state-of-the-art medical equipment.
4. Cost Comparison
Comparative data.
On average, medical procedures in Russia can cost 30-70% less than in Western Europe or North America. For instance, a dental implant that might cost upwards of $3,000 in the United States could be available for around $1,000 in Russia.
Price Ranges
Costs can vary based on the facility, location, and type of procedure. Always get multiple quotes and consult with healthcare providers to get a more accurate picture.
5. Quality & Safety
Medical standards and practices.
Russia is committed to ensuring high standards of medical care, supported by its educational system that produces skilled doctors and medical professionals. While there might be variations in quality between rural and urban centers, most metropolitan areas have hospitals and clinics equipped with modern technology and well-trained staff.
Accreditation Systems and Regulatory Bodies
In Russia, medical facilities are generally regulated by the Ministry of Health. While not all hospitals may have international accreditations, most top institutions meet or exceed global healthcare standards.
Quality Checks and Patient Safety Protocols
Russian healthcare providers employ a variety of safety measures such as pre-surgical consultations, sterilization protocols, and rigorous post-operative care. They also tend to follow internationally recognized best practices to ensure patient safety.
Patient Rights
Patients have the right to quality healthcare, the right to choose their physician, and the right to confidentiality. These are enshrined in Russian medical law and are generally adhered to by healthcare providers.
6. Medical Visa Information
Guidelines and requirements.
To obtain a medical visa, you generally need a formal invitation from the Russian medical institution where you plan to receive treatment. Proof of financial stability and medical insurance are often required.
Duration, Documentation, and Application Process
The visa can be valid for up to 90 days, with possible extensions in case of medical necessity. Documentation usually includes your passport, invitation letter, visa application form, and photographs. Applications are typically processed within 10 to 20 business days, although expedited services are available for an additional fee.
Travel-related Advisories or Restrictions
It’s advisable to keep an eye on travel advisories and consult your home country's embassy or consulate for the most current information.
7. Cultural Considerations
Local customs and etiquette.
While Russia is generally welcoming to tourists, being aware of local customs and etiquette can enrich your experience. A basic understanding of Russian manners, such as greetings and proper attire, can be beneficial.
Language and Communication
While the primary language is Russian, English is often spoken in large hospitals and medical centers. Nonetheless, it's advisable to confirm the availability of English-speaking staff or interpreters.
Dietary Considerations
Russia offers a variety of cuisine options, though traditional foods might be heavy in meat and dairy. Vegetarian and vegan options are increasingly available, particularly in larger cities.
8. Travel & Accommodation
Popular areas to stay.
Moscow and St. Petersburg are popular destinations with proximity to top medical facilities. Both cities offer a range of lodging options, from luxury hotels to budget-friendly hostels.
Proximity to Medical Facilities
Medical centers are often well-connected by public transportation or are just a short drive away from popular accommodation areas.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Russia has an extensive public transportation network, including subways, buses, and taxis. Apps like Uber are also widely used.
Post-procedure Relaxation and Recuperation Spots
Russia is rich in natural beauty, from the beaches of Sochi to the serene landscapes of Siberia, offering plenty of options for post-procedure relaxation.
9. Legal & Ethical Considerations
Legal rights of patients.
Patients have the right to informed consent, confidentiality, and quality healthcare as per Russian laws.
Medical Malpractice Laws and Patient Recourse
In cases of medical malpractice, patients have the right to legal recourse. However, legal proceedings can be long and complex.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical standards are generally in line with international norms. Issues such as organ transplantation are strictly regulated.
10. Benefits & Risks
Among the benefits are lower costs, high-quality specialized treatments, and the opportunity to explore Russian culture and history.
Potential Risks
Language barriers and variations in quality between rural and urban healthcare centers are some of the risks involved. Always conduct thorough research and consultations before proceeding with any medical treatment.
11. Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care.
Russian medical facilities often offer robust post-operative care programs, including rehabilitation and follow-up appointments.
Availability and Quality of Rehabilitation Centers
Rehabilitation centers, especially in metropolitan areas, are well-equipped and staffed with trained medical professionals.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is English widely spoken in Russian hospitals? In major cities and top healthcare centers, yes. However, it's advisable to confirm this before you travel.
- How do I pay for medical procedures? Payment methods vary, but most top hospitals accept credit cards and wire transfers.
- Is it safe to travel alone? While generally safe, it is always advisable to be cautious and aware of your surroundings, especially in unfamiliar areas.
- Is medical insurance necessary? Yes, proof of medical insurance is usually a requirement for obtaining a medical visa.
- What is the quality of post-procedure care? High-quality post-procedure care is often available, particularly in specialized medical centers.
Global Provider Members

Russian Ruble
144,500,000
With an area the size of Russia, it is difficult to give any sort of general advice about the climate and weather, except that summers are warm to hot, and winters get very cold in some areas. In general, the climate of Russia can be described as highly continental, with warm-to-hot, dry summers and (very) cold winters with temperatures of -30°C or lower. Heavy snowfall is not uncommon.
Facilitators
Featured treatments.

MedicalTourism.com
MedicalTourism.com is a free, confidential, independent resource for patients and industry providers. Our mission is to provide a central portal where patients, medical tourism providers, hospitals, clinics, employers, and insurance companies can all find the information they need. Our site focuses on patients looking for specific knowledge in the fields of medical tourism, dental tourism, and health tourism.
- DOI: 10.31436/iiumlj.v32i1.842
- Corpus ID: 270188532
SHARIAH- COMPLIANT MEDICAL TOURISM: AN EVALUATION OF THE LEGAL IMPEDIMENTS OF ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN MALAYSIA
- Noor Shuhadawati Mohamad Amin , N. Ramli , M. Zawawi
- Published in IIUM Law Journal 31 May 2024
- Law, Business
Tables from this paper

61 References
Scientific and islamic perspectives in relation to the halal status of cultured meat, regenerative medicine therapy in malaysia: an update, twenty years of traditional and complementary medicine regulation and its impact in malaysia: achievements and policy lessons, has the lack of a unified halal standard led to a rise in organised crime in the halal certification sector, healthcare financing and social protection policies for migrant workers in malaysia, islamic tourism: the characteristics, concept and principles, muslim friendly tourism and western creative tourism: the conceptual intersection analysis, the challenges faced by halal certification authorities in managing the halal certification process in malaysia, the need of international islamic standards for medical tourism providers: a malaysian experience, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

Published in IIUM Law Journal 2024
Noor Shuhadawati Mohamad Amin N. Ramli M. Zawawi
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

International travel documents for children
See what documents a child needs to travel to or from the U.S. alone or with a parent or relative.
Children traveling to the U.S.
All children, including infants, must have their own travel documents such as a passport or document from a Trusted Traveler Program to enter the U.S. If you travel or are going to travel with a child, consider taking the following documents:
- If the child is traveling with only one of their custodial parents, they must have a letter of consent, preferably in English and notarized, from the other parent or signed by both parents. The letter should say "I acknowledge that my son/daughter is traveling outside the country with [the name of the adult] with my permission."
- If one parent has sole custody of the child, a copy of the custody document can take the place of the other parent's letter.
- Parents who frequently cross the border by land with a minor must always carry a letter of permission from the other parent.
U.S. citizen children traveling abroad
Ports of entry in many countries have security measures to prevent international child abduction . If you are traveling alone with your child, you may be required to present documentation proving you are the parent or legal guardian. You may also need a letter of permission from the other parent for your child to travel.
If your child travels alone, depending on the country, they may be required to present a notarized letter from both parents or their legal guardian. If a minor is traveling abroad and is not accompanied by both parents or a legal guardian, contact the embassy or consulate of the country you will be visiting and ask about entry and exit requirements for that country.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Dominican Republic
Travel Advisory June 6, 2023
Dominican republic - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with updates to health information.
Exercise increased caution in the Dominican Republic due to crime.
Country Summary: Violent crime, including armed robbery, homicide and sexual assault is a concern throughout the Dominican Republic. The development of a professional tourist police corps, institution of a 911 system in many parts of the country, and a concentration of resources in resort areas means these tend to be better policed than urban areas like Santo Domingo. The wide availability of weapons, the use and trade of illicit drugs, and a weak criminal justice system contribute to the high level of criminality on the broader scale.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to the Dominican Republic.
If you decide to travel to the Dominican Republic:
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry.
- Follow the advice of resort and tour operators regarding local safety and security concerns.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for the Dominican Republic.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Passports must be valid for the period of stay in the Dominican Republic.
1 page required for entry stamp
Not required for visits shorter than 30 days
None required if arriving from the United States
$10,000 and over or its equivalent must be declared
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy santo domingo.
Av. República de Colombia #57 Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic Telephone: +(809) 567-7775 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 7:00 AM to 4:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
Consular Agencies
U.S. Consular Agent - Puerto Plata Plaza el Doral, carretera Luperón KM 3 1/2 Puerto Plata, Dominican Republic Telephone: +(809) 586-4204, +(809) 586-8023 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: (809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
U.S. Consular Agent - Bavaro/Punta Cana Palma Real Shopping Center Business Center 2nd Floor Bavaro, La Altagracia, Dominican Republic Telephone: (809) 552-8990 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visas are not required for visits shorter than 30 days. Visit the Embassy of the Dominican Republic website for current visa information.
All visitors to the Dominican Republic are charged a $10 tourist card fee that is incorporated into airline charges. Cruise passengers must obtain a tourist card if they are disembarking for longer than 24 hours. Once used, the card allows for stays up to 30 days but can be extended at the General Directorate of Migration in Santo Domingo.
Contact the Migration Department in Santo Domingo for visa extension requests. Failure to request an extension will result in a fine at the airport upon departure. The fines range from approximately $55 USD for one month to as high as $1,555 USD for overstays of 10 years or more.
All passengers are required to fill out an E-Ticket or paper form when entering or exiting the Dominican Republic. If using E-Ticket, a new form is required for each entry and exit and the code generated upon form completion can be presented at the airport on a digital device.
Visitors must have a ticket entering and leaving the country, the financial means to pay for their stay, and an address in the Dominican Republic where they will be staying.
Exit Requirements for Children: Minors (children under 18) who are citizens (including dual citizens) or legal residents of the Dominican Republic, if not accompanied by both parents or legal guardian(s), are required to present official proof of parental consent to travel. Please see the Dominican Migration Department's website for detailed instructions on the required documents.
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors to and foreign residents of the Dominican Republic. The Dominican Republic has restrictions on granting residency to people with HIV/AIDS. Please verify information with the Dominican Republic’s Migration Department before you travel.
Yellow Fever Vaccine: Proof of vaccination against yellow fever is required for travelers entering the Dominican Republic from Brazil. Similar requirements may apply to those traveling from other countries with yellow fever risk .
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Crime: Crime is a threat throughout the Dominican Republic. Tourist destinations are generally more policed than metropolitan areas.
- If robbed, hand over your personal belongings without resisting.
- Do not carry or wear valuable items that will attract attention.
- Be wary of strangers.
- Travel with a partner or group if possible.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Dating App Robberies: Several U.S. citizen travelers in the Dominican Republic have reported that they were robbed by people they met through popular online dating applications. If meeting with strangers, you should strongly consider meeting only in public places and avoiding isolated locations where crimes are most likely to occur.
Demonstrations: Avoid areas of demonstrations and exercise caution if you are in the vicinity of large gatherings or protests.
Victims of Crime: Report crimes to the local tourist police (POLITUR) at 809-222-2026 or 911 and contact the U.S. Embassy at 809-567-7775. 911 is operational throughout the country apart from some areas located near the Haitian border. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact POLITUR (809-222-2026), the National Police ( 809-682-2151), and the U.S. Embassy for assistance.
Sexual Assault: Rape and sexual assault has been reported throughout the Dominican Republic, including at major resorts and hotels.
Notes for your safety:
- U.S. citizens have been targeted with date rape drugs.
- Sexual assault victims in the Dominican Republic should not expect the totality of assistance offered in the United States. Rape kits are often not available until the following morning and must be administered by Dominican authorities.
- Victims often have to request medication to avoid transmission of STDs and reduce the chances of pregnancy.
- Prosecution of a rape case moves forward very slowly. Dominican law may require the victim to return to the Dominican Republic at some stages of the judicial process.
- Security outside of the resort area, including beach areas, is unpredictable, especially at night.
Best Practices:
- Contact the police/hotel management if resort staff demonstrate unwanted attention.
- Victims of sexual/other assault should contact the police and the Embassy. Insist that hotel management take immediate action by contacting the police.
- In a resort, avoid secluded places. Always be accompanied by someone you know, even going to the restroom.
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages alone or with new acquaintances. Do not leave drinks unattended. Know your limits and help your friends/travelling companions to remain safe.
- Shout for help immediately if threatened or made uncomfortable.
- Report suspicious activity, including excessive friendliness by hotel employees, to hotel management, the U.S. Embassy, and local police.
- Do not swim alone due to life-threatening undertows.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities may not commonly occur in all parts of the country. Hazardous areas and activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in or near major cities or major tourist zones. First responders may be unable to access areas outside of major cities or major tourist zones. The ability to provide urgent medical treatment may be limited. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in the Dominican Republic are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage and general information on legal assistance for further information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, their possession they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in the Dominican Republic.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in the Dominican Republic prohibits discrimination against persons with physical, sensory, intellectual or mental disabilities, but the law is not enforced consistently. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States. Accessible facilities, information, communication/access to services and ease of movement is limited in most parts of the country. Large resorts and Santo Domingo may have some generally accessible infrastructure, but travelers should not expect the level available in the United States.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Disaster Preparedness: Register with the Embassy on or before your arrival through our travel registration website . In the event of a natural disaster or emergency, this will keep you informed. Additional information on natural disasters and disaster preparedness can be found on our website. Real Estate: Property rights are irregularly enforced, and investors often encounter problems in receiving clear title to land. Consult a reputable attorney before signing documents or closing on any real estate transactions. Real estate investments by U.S. citizens have been subject to legal and physical takeover attempts. Absentee landlords and absentee owners of undeveloped land are particularly vulnerable. Consider purchasing title insurance. Scams: Scammers often target elderly people by pretending to be a law enforcement official, an attorney, or a U.S. Embassy official, claiming that a loved one has been arrested overseas. The caller instructs the victim to wire money. Scammers sometimes impersonate family members, such as a scared grandchild. Contact the U.S. Embassy before wiring money to the Dominican Republic. When in doubt, try to contact your loved one directly.
For emergency services in the Dominican Republic, dial 911 or 809-202-2026 .
Ambulance services:
- The training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards.
- Ambulances are not present or reliable in most areas of the country. They are more reliable and available in Santo Domingo, Santiago, Punta Cana, and Puerto Plata.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Check with the Ministry for Public Health to ensure the medication is legal in the Dominican Republic.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Health facilities in general:
- Public medical clinics lack basic resources and supplies.
- Hospitals and doctors require payment “up front” prior to service or admission.
- Private hospitals usually require advance payment or proof of adequate insurance before admitting a patient.
- Be aware that some hotels, resorts, etc. have exclusive agreements with medical providers, which have costs associated and may limit your choices in seeking emergency medical attention.
- Medical staff may speak little or no English.
- Generally, in public hospitals only minimal staff is available overnight in non-emergency wards. Consider hiring a private nurse or having family spend the night with the patient, especially a minor child.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
U.S. citizens have suffered serious complications or died during or after having cosmetic or other elective surgery.
If you are considering travel to the Dominican Republic for cosmetic surgery, be mindful of the following:
- Have a medical evaluation from a U.S. doctor to determine if you are a good candidate for surgery.
- Before travel, carefully research the doctor (e.g. qualifications, experience performing the surgery, complication rate) and credentials of the recovery facility you plan to use.
- Share all health information (e.g. medical conditions, medications, allergies) with your doctor before your surgery.
- Obtain international travel insurance that covers medical evacuation back to the United States and repatriation of remains. For more information, see: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/insurance .
- See a travel medicine professional in the United States at least 4–6 weeks before your trip to discuss healthy travel and to learn about specific risks related to your surgery and travel. For more information on the risks of medical tourism, see: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/medical-tourism .
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in the Dominican Republic.
Tap Water: Tap water is unsafe to drink. Bottled water and beverages are considered safe. Please note that many restaurants use tap water for ice.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
General Health
The following diseases are prevalent:
- Tuberculosis
- Chikungunya
Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in the Dominican Republic .
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Driving conditions vary across the country. Drive defensively and with extreme caution.
Consider hiring a professional driver instead of driving yourself. You can hire licensed drivers who are familiar with local roads through local car rental agencies. In case of accidents, normally only the driver will be taken into custody. In 2019 six people died per day due to traffic accidents in the Dominican Republic.
Frequent hazards include:
- other drivers not using headlights and/or taillights after dark
- animals in the road
- missing manhole covers and large potholes
- uneven road surfaces
- scooters and motorcycles driving erratically and splitting lanes
- driving on sidewalks or against traffic
- intersections without stop signs
- unregulated and congested traffic patterns
- speeding or the running of stoplights
- heavy urban traffic
Traffic Laws: Traffic laws are not enforced consistently. After an accident causing serious injury or death, authorities will often take the driver into custody, even if the driver is insured and appears to have not been at fault. Detentions frequently last until a judicial decision has been reached or until a waiver has been signed by the injured party.
Seat belts, and helmets for motorcyclists, are required by law. Violators may be fined. There are no child car seat laws. Police stop drivers using cell phones without a hands-free device.
Public Transportation: Public transportation includes a metro and public bus system as well as shared bus or van taxis known as “guaguas” (converted vans or microbuses, often without doors). Guaguas run regular routes within urban areas and between towns in the countryside. Public buses and guaguas operating in the capital do not meet U.S. safety standards. Avoid unregulated taxis, which also often lack basic safety features. Use a reputable taxi service, either one recommended by your hotel or a well-known, vetted company. Rideshare services such as Uber are available in many parts of the country. Private bus lines travel between large cities and to popular tourist destinations.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of the Dominican Republic’s Ministry of Tourism and INTRANT (Instituto Nacional de Transito y Transporte Terrestre) the national authority responsible for road safety.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of the Dominican Republic’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s website. FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: The U.S. Coast Guard has concerns about the security practices in the ports of the Dominican Republic. Until those concerns can be addressed, the Coast Guard advises that Mariners and passengers on commercial vessels traveling through the ports of the Dominican Republic should exercise caution.
Mariners planning travel to the Dominican Republic should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Dominican Republic . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, dominican republic map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Advertisement
Supported by
Their City Has a Plaque From Putin. They Want Zelensky to Tear It Down.
Some residents of Bari, Italy, hope Ukraine’s president will drop by while at a nearby summit to help rid them of a memento of links with Russia.
- Share full article

By Lara Jakes
Reporting from Bari, Italy
A small copper plaque mounted across the piazza from the Basilica of St. Nicholas in Bari, Italy, pledges “friendship and cooperation” between the city and the Russian people. It is signed by someone who, for the past two years in Europe, has pursued anything but: President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia.
The plaque is a replica of a letter Mr. Putin sent in 2003, nearly two decades before his invasion of Ukraine, and for years it drew little notice from Bari’s residents or the tens of thousands of pilgrims who visit the site annually to venerate the saint, whose remains are interred there. But a growing number of people now see it as sign of Mr. Putin’s hypocrisy — particularly among a diaspora of local Ukrainians who want it taken down.
The war will be among the most pressing issues that leaders of the world’s largest advanced economies and President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine will discuss this week at an annual meeting of the Group of 7, which is being hosted by Italy and held just an hour down the road. For the many residents of Bari who have wanted the plaque removed since the war began , the gathering nearby is seen as a chance to enlist Mr. Putin’s fiercest international critics to their cause.
“Since Putin has been declared an international criminal, to have that plaque and to have his signature and his name on it, and display it proudly in front of the church, is offensive,” said Alessandro de Biase, a local businessman.
“If it was down to me, I would bring Zelensky here himself and ask him for help to take down the plaque,” Mr. de Biase said.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

COMMENTS
The tourism is accountable for the worsening medical practices through actions like brain drain as the better salaries and equipment adopted by the healthcare facilities entice doctors from other public hospitals. The tourism activity is also accountable for the rural deficiency in eligible health care employees (Abd Mutalib et al., 22016).
Medical tourism is a lucrative business for many countries, and much of the money brought in by medical tourists is reinvested into the local economy and health infrastructure. The effect of this is apparent in the spa-like luxury that some foreign hospitals offer, providing medical tourists the opportunity to be pampered during their stay for ...
Get a custom Essay on Medical Tourism: Important Aspects. However, the process of regionalization has been associated with the development of a pure form of capitalism in different economies where the private sector has taken charge of the health care system (Connell 1094). For instance, the private health care entities in the United States has ...
Medical tourism benefits include cost-effective and high-quality healthcare as compared to the ones available in the native country. Firstly, cost-effective medical care is a service that is quality at affordable prices. For instance, according to Sag and Zengul (2019), the cost of hip replacement in countries such as Indian and the Philippines ...
Of these, 615 were obtained using the keywords medical tourism or wellness tourism, 157 were located by searching for health tourism, and 30 were discovered using spa tourism as the search term. Using the above keywords and restricting the search to 50 years (1970-2020), the first article was found to be published in 1974.
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. Meštrović, Tomislav. (2018, August 23). What is Medical Tourism?.
role and impact of medical tourism for OECD countries. Whilst there is an increasing amount written on the subject of medical tourism, such material is hardly ever evidence-based. Medical tourism introduces a range of attendant risks and opportunities for patients. This review identifies the key emerging policy
An overview of medical tourism. According to Horowitz et al. (2008), the growth in medical travel is accelerating at a very high pace. The average annual revenue generated from the medical travel industry was estimated at $60 billion as at the end of 2008.
Essays on Medical Tourism. Free essays on Medical Tourism are informative documents that provide valuable insights into the rapidly growing industry of medical tourism. These essays provide an overview of the various aspects of medical tourism, including its history, benefits, risks, and challenges. They discuss the reasons why patients choose ...
Papers reviewed mention individual hospitals or a medical tourism provider at the country level to give a flavor of the industry. 8,45 However, only four papers 47-50 report findings of a more systematic assessment of the industry, including focus on the strong state role in the development of medical tourism in Hong Kong, Malaysia, and ...
History. The first recorded instance of people travelling for medical treatment dates back thousands of years to when Greek pilgrims traveled from the eastern Mediterranean to a small area in the Saronic Gulf called Epidauria. This territory was the sanctuary of the healing god Asklepios.. Spa towns and sanitaria were early forms of medical tourism. In 18th-century Europe patients visited spas ...
Medical tourism has emerged as a result of consumers being exposed to a wider range of choices of medical services and exponential growth in global healthcare market [].A combination of the terms "medical" and "tourism" [], its main target is patients who visit other regions or countries for medical treatment.Therefore, the medical tourism industry is geared toward significant efforts ...
Travelling Well: Essays in Medical Tourism, a new electronic publication from the Institute of Population Health at the University of Ottawa, attempts to demythologize these stories, to attach muscular facts to a skeleton of gossip and sensationalism.
The medical tourism phenomenon is gaining popularity and the number of people going abroad for treatment increases rapidly every year. With many medical tourism benefits, advancements in technology and improvements in healthcare standards within developing countries, it is likely that the advantages of medical tourism will provide a striking ...
This essay takes a brief look at services being developed throughout the world to cater to a specific population that has chosen to cross borders in order to receive quality health care: people from wealthier countries who, for a variety of reasons, are unable to receive adequate urgent or elective medical treatment in their places of origin yet who have sufficient personal financial resources ...
Essay on Benefits of Medical Tourism. Best Essays. 2893 Words. 12 Pages. 8 Works Cited. Open Document. Medical tourism, or the process of leaving a home location for health care treatment in other locations broad is becoming an emerging trend. Outbound medical tourism is most likely going to grow at a fast rate within the next few years.
Medical Tourism: Cosmetic Surgery Niche. 5 pages / 2493 words. As early as 1987, many authors have associated the terminology 'cosmetic surgery tourism' under the umbrella of medical, health and wellbeing tourism. Since then, it has been known as 'aesthetic tourism', 'plastic surgery tourism', 'surgery tourism' and 'surgery ...
The southern state of Kerala has developed medical tourism services as one of its core products for promoting tourism in the region. Based on the Medical Tourism Index 2020-21, India is ranked 10th out of the top 46 countries, 12th out of the world's top 20 wellness tourism markets, and 5th out of 10 wellness tourism destinations in Asia-Pacific.
The National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism has identified the following key pillars for the development of medical-value travel in the country. Developing a brand for India as a wellness destination. Foreign Tourists Arrival on medical purpose increases from 1.83 lakh in 2020 to 3.04 lakh in 2021.
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "DEVELOPMENT OF EXPORT OF MEDICAL SERVICES (MEDICAL TOURISM) IN MOSCOW" by G. D. Petrova et al. ... Semantic Scholar's Logo. Search 218,797,198 papers from all fields of science. Search. Sign In Create Free Account. DOI: 10.51677/2073-0624_2021_60_4_20; Corpus ID: 245490028;
Explore medical tourism in Russia - a blend of advanced treatments, cultural experiences, and cost savings. Discover sought-after procedures, top hospitals, safety standards, visa info, and more. Medical tourism in Russia, Top hospitals in Russia, Cost-effective treatments Russia, Russian medical procedures, Visa for medical tourism Russia.
The article discusses the main problems of providing services in the Moscow agglomeration: the characteristics of internal and external environment for the implementation of medical tourism services, directions for using existing opportunities to prevent threats. The article discusses the main problems of providing services in the Moscow agglomeration. An assessment of the current situation ...
Barcelona: Discover the Top 10 Beach Clubs. 2024 Global City Travel Guide - Your Passport to the World's Top Destination Cities. Exploring Khao Yai 2024 - A Hidden Gem of Thailand. The post ...
Medical tourism. Russia is a destination for medical tourism. A factor in its popularity was the relatively weak ruble post-2014, which saw the industry grow from some 110 thousand clients in 2017 to some 728 thousand clients in the first five months of 2020. Stomatology ...
DOI: 10.31436/iiumlj.v32i1.842 Corpus ID: 270188532; SHARIAH- COMPLIANT MEDICAL TOURISM: AN EVALUATION OF THE LEGAL IMPEDIMENTS OF ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN MALAYSIA @article{MohamadAmin2024SHARIAHCM, title={SHARIAH- COMPLIANT MEDICAL TOURISM: AN EVALUATION OF THE LEGAL IMPEDIMENTS OF ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN MALAYSIA}, author={Noor Shuhadawati Mohamad Amin and N. Ramli and Majdah Zawawi}, journal ...
Children traveling to the U.S. All children, including infants, must have their own travel documents such as a passport or document from a Trusted Traveler Program to enter the U.S. If you travel or are going to travel with a child, consider taking the following documents: If the child is traveling with only one of their custodial parents, they ...
Reissued with updates to health information. Exercise increased caution in the Dominican Republic due to crime.. Country Summary: Violent crime, including armed robbery, homicide and sexual assault is a concern throughout the Dominican Republic.The development of a professional tourist police corps, institution of a 911 system in many parts of the country, and a concentration of resources in ...
Browse Calls for Papers. Browse 5,060 journals and 35,600 books. A; A Review on Diverse Neurological Disorders. Pathophysiology, Molecular Mechanisms, and Therapeutics. Book ... Medical and Social Aspects. Book • 1981. Above Ground Storage Tank Oil Spills. Applications and Case Studies. Book
June 10, 2024. A small copper plaque mounted across the piazza from the Basilica of St. Nicholas in Bari, Italy, pledges "friendship and cooperation" between the city and the Russian people ...