Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 27 September 2021

Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap
- Sébastien Goudeau ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7293-0977 1 ,
- Camille Sanrey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3158-1306 1 ,
- Arnaud Stanczak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2596-1516 2 ,
- Antony Manstead ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7540-2096 3 &
- Céline Darnon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2613-689X 2
Nature Human Behaviour volume 5 , pages 1273–1281 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
148 Citations
129 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced teachers and parents to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers developed online academic material while parents taught the exercises and lessons provided by teachers to their children at home. Considering that the use of digital tools in education has dramatically increased during this crisis, and it is set to continue, there is a pressing need to understand the impact of distance learning. Taking a multidisciplinary view, we argue that by making the learning process rely more than ever on families, rather than on teachers, and by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities. To address this burning issue, we propose an agenda for future research and outline recommendations to help parents, teachers and policymakers to limit the impact of the lockdown on social-class-based academic inequality.
Similar content being viewed by others

Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures
Elementary school teachers’ perspectives about learning during the COVID-19 pandemic
Uncovering Covid-19, distance learning, and educational inequality in rural areas of Pakistan and China: a situational analysis method
The widespread effects of the COVID-19 pandemic that emerged in 2019–2020 have drastically increased health, social and economic inequalities 1 , 2 . For more than 900 million learners around the world, the pandemic led to the closure of schools and universities 3 . This exceptional situation forced teachers, parents and students to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers had to develop online academic materials that could be used at home to ensure educational continuity while ensuring the necessary physical distancing. Primary and secondary school students suddenly had to work with various kinds of support, which were usually provided online by their teachers. For college students, lockdown often entailed returning to their hometowns while staying connected with their teachers and classmates via video conferences, email and other digital tools. Despite the best efforts of educational institutions, parents and teachers to keep all children and students engaged in learning activities, ensuring educational continuity during school closure—something that is difficult for everyone—may pose unique material and psychological challenges for working-class families and students.
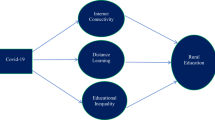
Not only did the pandemic lead to the closure of schools in many countries, often for several weeks, it also accelerated the digitalization of education and amplified the role of parental involvement in supporting the schoolwork of their children. Thus, beyond the specific circumstances of the COVID-19 lockdown, we believe that studying the effects of the pandemic on academic inequalities provides a way to more broadly examine the consequences of school closure and related effects (for example, digitalization of education) on social class inequalities. Indeed, bearing in mind that (1) the risk of further pandemics is higher than ever (that is, we are in a ‘pandemic era’ 4 , 5 ) and (2) beyond pandemics, the use of digital tools in education (and therefore the influence of parental involvement) has dramatically increased during this crisis, and is set to continue, there is a pressing need for an integrative and comprehensive model that examines the consequences of distance learning. Here, we propose such an integrative model that helps us to understand the extent to which the school closures associated with the pandemic amplify economic, digital and cultural divides that in turn affect the psychological functioning of parents, students and teachers in a way that amplifies academic inequalities. Bringing together research in social sciences, ranging from economics and sociology to social, cultural, cognitive and educational psychology, we argue that by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources rather than direct interactions with their teachers, and by making the learning process rely more than ever on families rather than teachers, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities.
First, we review research showing that social class is associated with unequal access to digital tools, unequal familiarity with digital skills and unequal uses of such tools for learning purposes 6 , 7 . We then review research documenting how unequal familiarity with school culture, knowledge and skills can also contribute to the accentuation of academic inequalities 8 , 9 . Next, we present the results of surveys conducted during the 2020 lockdown showing that the quality and quantity of pedagogical support received from schools varied according to the social class of families (for examples, see refs. 10 , 11 , 12 ). We then argue that these digital, cultural and structural divides represent barriers to the ability of parents to provide appropriate support for children during distance learning (Fig. 1 ). These divides also alter the levels of self-efficacy of parents and children, thereby affecting their engagement in learning activities 13 , 14 . In the final section, we review preliminary evidence for the hypothesis that distance learning widens the social class achievement gap and we propose an agenda for future research. In addition, we outline recommendations that should help parents, teachers and policymakers to use social science research to limit the impact of school closure and distance learning on the social class achievement gap.
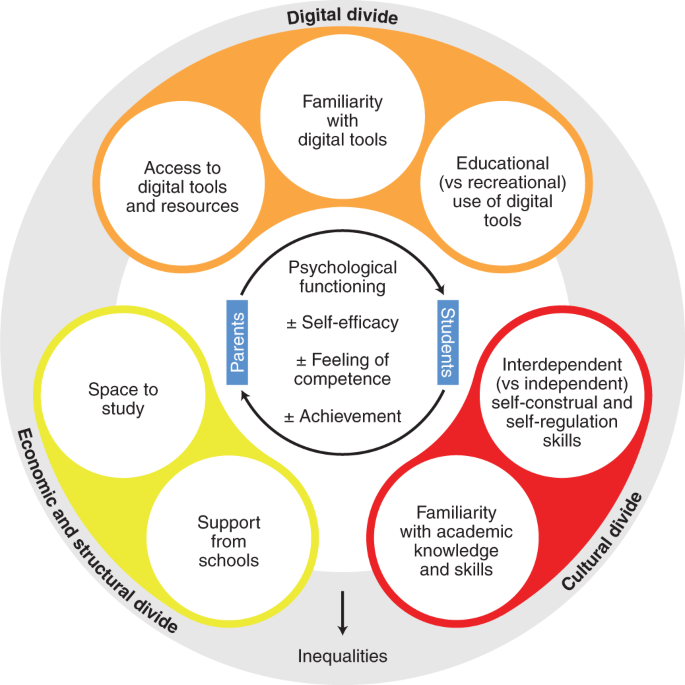
Economic, structural, digital and cultural divides influence the psychological functioning of parents and students in a way that amplify inequalities.
The digital divide
Unequal access to digital resources.
Although the use of digital technologies is almost ubiquitous in developed nations, there is a digital divide such that some people are more likely than others to be numerically excluded 15 (Fig. 1 ). Social class is a strong predictor of digital disparities, including the quality of hardware, software and Internet access 16 , 17 , 18 . For example, in 2019, in France, around 1 in 5 working-class families did not have personal access to the Internet compared with less than 1 in 20 of the most privileged families 19 . Similarly, in 2020, in the United Kingdom, 20% of children who were eligible for free school meals did not have access to a computer at home compared with 7% of other children 20 . In 2021, in the United States, 41% of working-class families do not own a laptop or desktop computer and 43% do not have broadband compared with 8% and 7%, respectively, of upper/middle-class Americans 21 . A similar digital gap is also evident between lower-income and higher-income countries 22 .
Second, simply having access to a computer and an Internet connection does not ensure effective distance learning. For example, many of the educational resources sent by teachers need to be printed, thereby requiring access to printers. Moreover, distance learning is more difficult in households with only one shared computer compared with those where each family member has their own 23 . Furthermore, upper/middle-class families are more likely to be able to guarantee a suitable workspace for each child than their working-class counterparts 24 .
In the context of school closures, such disparities are likely to have important consequences for educational continuity. In line with this idea, a survey of approximately 4,000 parents in the United Kingdom confirmed that during lockdown, more than half of primary school children from the poorest families did not have access to their own study space and were less well equipped for distance learning than higher-income families 10 . Similarly, a survey of around 1,300 parents in the Netherlands found that during lockdown, children from working-class families had fewer computers at home and less room to study than upper/middle-class children 11 .
Data from non-Western countries highlight a more general digital divide, showing that developing countries have poorer access to digital equipment. For example, in India in 2018, only 10.7% of households possessed a digital device 25 , while in Pakistan in 2020, 31% of higher-education teachers did not have Internet access and 68.4% did not have a laptop 26 . In general, developing countries lack access to digital technologies 27 , 28 , and these difficulties of access are even greater in rural areas (for example, see ref. 29 ). Consequently, school closures have huge repercussions for the continuity of learning in these countries. For example, in India in 2018, only 11% of the rural and 40% of the urban population above 14 years old could use a computer and access the Internet 25 . Time spent on education during school closure decreased by 80% in Bangladesh 30 . A similar trend was observed in other countries 31 , with only 22% of children engaging in remote learning in Kenya 32 and 50% in Burkina Faso 33 . In Ghana, 26–32% of children spent no time at all on learning during the pandemic 34 . Beyond the overall digital divide, social class disparities are also evident in developing countries, with lower access to digital resources among households in which parental educational levels were low (versus households in which parental educational levels were high; for example, see ref. 35 for Nigeria and ref. 31 for Ecuador).
Unequal digital skills
In addition to unequal access to digital tools, there are also systematic variations in digital skills 36 , 37 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with digital tools and resources and are therefore more likely to have the digital skills needed for distance learning 38 , 39 , 40 . These digital skills are particularly useful during school closures, both for students and for parents, for organizing, retrieving and correctly using the resources provided by the teachers (for example, sending or receiving documents by email, printing documents or using word processors).
Social class disparities in digital skills can be explained in part by the fact that children from upper/middle-class families have the opportunity to develop digital skills earlier than working-class families 41 . In member countries of the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), only 23% of working-class children had started using a computer at the age of 6 years or earlier compared with 43% of upper/middle-class children 42 . Moreover, because working-class people tend to persist less than upper/middle-class people when confronted with digital difficulties 23 , the use of digital tools and resources for distance learning may interfere with the ability of parents to help children with their schoolwork.
Unequal use of digital tools
A third level of digital divide concerns variations in digital tool use 18 , 43 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more likely to use digital resources for work and education 6 , 41 , 44 , whereas working-class families are more likely to use these resources for entertainment, such as electronic games or social media 6 , 45 . This divide is also observed among students, whereby working-class students tend to use digital technologies for leisure activities, whereas their upper/middle-class peers are more likely to use them for academic activities 46 and to consider that computers and the Internet provide an opportunity for education and training 23 . Furthermore, working-class families appear to regulate the digital practices of their children less 47 and are more likely to allow screens in the bedrooms of children and teenagers without setting limits on times or practices 48 .
In sum, inequalities in terms of digital resources, skills and use have strong implications for distance learning. This is because they make working-class students and parents particularly vulnerable when learning relies on extensive use of digital devices rather than on face-to-face interaction with teachers.
The cultural divide
Even if all three levels of digital divide were closed, upper/middle-class families would still be better prepared than working-class families to ensure educational continuity for their children. Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with the academic knowledge and skills that are expected and valued in educational settings, as well as with the independent, autonomous way of learning that is valued in the school culture and becomes even more important during school closure (Fig. 1 ).
Unequal familiarity with academic knowledge and skills
According to classical social reproduction theory 8 , 49 , school is not a neutral place in which all forms of language and knowledge are equally valued. Academic contexts expect and value culture-specific and taken-for-granted forms of knowledge, skills and ways of being, thinking and speaking that are more in tune with those developed through upper/middle-class socialization (that is, ‘cultural capital’ 8 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ). For instance, academic contexts value interest in the arts, museums and literature 54 , 55 , a type of interest that is more likely to develop through socialization in upper/middle-class families than in working-class socialization 54 , 56 . Indeed, upper/middle-class parents are more likely than working-class parents to engage in activities that develop this cultural capital. For example, they possess more books and cultural objects at home, read more stories to their children and visit museums and libraries more often (for examples, see refs. 51 , 54 , 55 ). Upper/middle-class children are also more involved in extra-curricular activities (for example, playing a musical instrument) than working-class children 55 , 56 , 57 .
Beyond this implicit familiarization with the school curriculum, upper/middle-class parents more often organize educational activities that are explicitly designed to develop academic skills of their children 57 , 58 , 59 . For example, they are more likely to monitor and re-explain lessons or use games and textbooks to develop and reinforce academic skills (for example, labelling numbers, letters or colours 57 , 60 ). Upper/middle-class parents also provide higher levels of support and spend more time helping children with homework than working-class parents (for examples, see refs. 61 , 62 ). Thus, even if all parents are committed to the academic success of their children, working-class parents have fewer chances to provide the help that children need to complete homework 63 , and homework is more beneficial for children from upper-middle class families than for children from working-class families 64 , 65 .
School closures amplify the impact of cultural inequalities
The trends described above have been observed in ‘normal’ times when schools are open. School closures, by making learning rely more strongly on practices implemented at home (rather than at school), are likely to amplify the impact of these disparities. Consistent with this idea, research has shown that the social class achievement gap usually greatly widens during school breaks—a phenomenon described as ‘summer learning loss’ or ‘summer setback’ 66 , 67 , 68 . During holidays, the learning by children tends to decline, and this is particularly pronounced in children from working-class families. Consequently, the social class achievement gap grows more rapidly during the summer months than it does in the rest of the year. This phenomenon is partly explained by the fact that during the break from school, social class disparities in investment in activities that are beneficial for academic achievement (for example, reading, travelling to a foreign country or museum visits) are more pronounced.
Therefore, when they are out of school, children from upper/middle-class backgrounds may continue to develop academic skills unlike their working-class counterparts, who may stagnate or even regress. Research also indicates that learning loss during school breaks tends to be cumulative 66 . Thus, repeated episodes of school closure are likely to have profound consequences for the social class achievement gap. Consistent with the idea that school closures could lead to similar processes as those identified during summer breaks, a recent survey indicated that during the COVID-19 lockdown in the United Kingdom, children from upper/middle-class families spent more time on educational activities (5.8 h per day) than those from working-class families (4.5 h per day) 7 , 69 .
Unequal dispositions for autonomy and self-regulation
School closures have encouraged autonomous work among students. This ‘independent’ way of studying is compatible with the family socialization of upper/middle-class students, but does not match the interdependent norms more commonly associated with working-class contexts 9 . Upper/middle-class contexts tend to promote cultural norms of independence whereby individuals perceive themselves as autonomous actors, independent of other individuals and of the social context, able to pursue their own goals 70 . For example, upper/middle-class parents tend to invite children to express their interests, preferences and opinions during the various activities of everyday life 54 , 55 . Conversely, in working-class contexts characterized by low economic resources and where life is more uncertain, individuals tend to perceive themselves as interdependent, connected to others and members of social groups 53 , 70 , 71 . This interdependent self-construal fits less well with the independent culture of academic contexts. This cultural mismatch between interdependent self-construal common in working-class students and the independent norms of the educational institution has negative consequences for academic performance 9 .
Once again, the impact of these differences is likely to be amplified during school closures, when being able to work alone and autonomously is especially useful. The requirement to work alone is more likely to match the independent self-construal of upper/middle-class students than the interdependent self-construal of working-class students. In the case of working-class students, this mismatch is likely to increase their difficulties in working alone at home. Supporting our argument, recent research has shown that working-class students tend to underachieve in contexts where students work individually compared with contexts where students work with others 72 . Similarly, during school closures, high self-regulation skills (for example, setting goals, selecting appropriate learning strategies and maintaining motivation 73 ) are required to maintain study activities and are likely to be especially useful for using digital resources efficiently. Research has shown that students from working-class backgrounds typically develop their self-regulation skills to a lesser extent than those from upper/middle-class backgrounds 74 , 75 , 76 .
Interestingly, some authors have suggested that independent (versus interdependent) self-construal may also affect communication with teachers 77 . Indeed, in the context of distance learning, working-class families are less likely to respond to the communication of teachers because their ‘interdependent’ self leads them to respect hierarchies, and thus perceive teachers as an expert who ‘can be trusted to make the right decisions for learning’. Upper/middle class families, relying on ‘independent’ self-construal, are more inclined to seek individualized feedback, and therefore tend to participate to a greater extent in exchanges with teachers. Such cultural differences are important because they can also contribute to the difficulties encountered by working-class families.
The structural divide: unequal support from schools
The issues reviewed thus far all increase the vulnerability of children and students from underprivileged backgrounds when schools are closed. To offset these disadvantages, it might be expected that the school should increase its support by providing additional resources for working-class students. However, recent data suggest that differences in the material and human resources invested in providing educational support for children during periods of school closure were—paradoxically—in favour of upper/middle-class students (Fig. 1 ). In England, for example, upper/middle-class parents reported benefiting from online classes and video-conferencing with teachers more often than working-class parents 10 . Furthermore, active help from school (for example, online teaching, private tutoring or chats with teachers) occurred more frequently in the richest households (64% of the richest households declared having received help from school) than in the poorest households (47%). Another survey found that in the United Kingdom, upper/middle-class children were more likely to take online lessons every day (30%) than working-class students (16%) 12 . This substantial difference might be due, at least in part, to the fact that private schools are better equipped in terms of online platforms (60% of schools have at least one online platform) than state schools (37%, and 23% in the most deprived schools) and were more likely to organize daily online lessons. Similarly, in the United Kingdom, in schools with a high proportion of students eligible for free school meals, teachers were less inclined to broadcast an online lesson for their pupils 78 . Interestingly, 58% of teachers in the wealthiest areas reported having messaged their students or their students’ parents during lockdown compared with 47% in the most deprived schools. In addition, the probability of children receiving technical support from the school (for example, by providing pupils with laptops or other devices) is, surprisingly, higher in the most advantaged schools than in the most deprived 78 .
In addition to social class disparities, there has been less support from schools for African-American and Latinx students. During school closures in the United States, 40% of African-American students and 30% of Latinx students received no online teaching compared with 10% of white students 79 . Another source of inequality is that the probability of school closure was correlated with social class and race. In the United States, for example, school closures from September to December 2020 were more common in schools with a high proportion of racial/ethnic minority students, who experience homelessness and are eligible for free/discounted school meals 80 .
Similarly, access to educational resources and support was lower in poorer (compared with richer) countries 81 . In sub-Saharan Africa, during lockdown, 45% of children had no exposure at all to any type of remote learning. Of those who did, the medium was mostly radio, television or paper rather than digital. In African countries, at most 10% of children received some material through the Internet. In Latin America, 90% of children received some remote learning, but less than half of that was through the internet—the remainder being via radio and television 81 . In Ecuador, high-school students from the lowest wealth quartile had fewer remote-learning opportunities, such as Google class/Zoom, than students from the highest wealth quartile 31 .
Thus, the achievement gap and its accentuation during lockdown are due not only to the cultural and digital disadvantages of working-class families but also to unequal support from schools. This inequality in school support is not due to teachers being indifferent to or even supportive of social stratification. Rather, we believe that these effects are fundamentally structural. In many countries, schools located in upper/middle-class neighbourhoods have more money than those in the poorest neighbourhoods. Moreover, upper/middle-class parents invest more in the schools of their children than working-class parents (for example, see ref. 82 ), and schools have an interest in catering more for upper/middle-class families than for working-class families 83 . Additionally, the expectation of teachers may be lower for working-class children 84 . For example, they tend to estimate that working-class students invest less effort in learning than their upper/middle-class counterparts 85 . These differences in perception may have influenced the behaviour of teachers during school closure, such that teachers in privileged neighbourhoods provided more information to students because they expected more from them in term of effort and achievement. The fact that upper/middle-class parents are better able than working-class parents to comply with the expectations of teachers (for examples, see refs. 55 , 86 ) may have reinforced this phenomenon. These discrepancies echo data showing that working-class students tend to request less help in their schoolwork than upper/middle-class ones 87 , and they may even avoid asking for help because they believe that such requests could lead to reprimands 88 . During school closures, these students (and their families) may in consequence have been less likely to ask for help and resources. Jointly, these phenomena have resulted in upper/middle-class families receiving more support from schools during lockdown than their working-class counterparts.
Psychological effects of digital, cultural and structural divides
Despite being strongly influenced by social class, differences in academic achievement are often interpreted by parents, teachers and students as reflecting differences in ability 89 . As a result, upper/middle-class students are usually perceived—and perceive themselves—as smarter than working-class students, who are perceived—and perceive themselves—as less intelligent 90 , 91 , 92 or less able to succeed 93 . Working-class students also worry more about the fact that they might perform more poorly than upper/middle-class students 94 , 95 . These fears influence academic learning in important ways. In particular, they can consume cognitive resources when children and students work on academic tasks 96 , 97 . Self-efficacy also plays a key role in engaging in learning and perseverance in the face of difficulties 13 , 98 . In addition, working-class students are those for whom the fear of being outperformed by others is the most negatively related to academic performance 99 .
The fact that working-class children and students are less familiar with the tasks set by teachers, and less well equipped and supported, makes them more likely to experience feelings of incompetence (Fig. 1 ). Working-class parents are also more likely than their upper/middle-class counterparts to feel unable to help their children with schoolwork. Consistent with this, research has shown that both working-class students and parents have lower feelings of academic self-efficacy than their upper/middle-class counterparts 100 , 101 . These differences have been documented under ‘normal’ conditions but are likely to be exacerbated during distance learning. Recent surveys conducted during the school closures have confirmed that upper/middle-class families felt better able to support their children in distance learning than did working-class families 10 and that upper/middle-class parents helped their children more and felt more capable to do so 11 , 12 .
Pandemic disparity, future directions and recommendations
The research reviewed thus far suggests that children and their families are highly unequal with respect to digital access, skills and use. It also shows that upper/middle-class students are more likely to be supported in their homework (by their parents and teachers) than working-class students, and that upper/middle-class students and parents will probably feel better able than working-class ones to adapt to the context of distance learning. For all these reasons, we anticipate that as a result of school closures, the COVID-19 pandemic will substantially increase the social class achievement gap. Because school closures are a recent occurrence, it is too early to measure with precision their effects on the widening of the achievement gap. However, some recent data are consistent with this idea.
Evidence for a widening gap during the pandemic
Comparing academic achievement in 2020 with previous years provides an early indication of the effects of school closures during the pandemic. In France, for example, first and second graders take national evaluations at the beginning of the school year. Initial comparisons of the results for 2020 with those from previous years revealed that the gap between schools classified as ‘priority schools’ (those in low-income urban areas) and schools in higher-income neighbourhoods—a gap observed every year—was particularly pronounced in 2020 in both French and mathematics 102 .
Similarly, in the Netherlands, national assessments take place twice a year. In 2020, they took place both before and after school closures. A recent analysis compared progress during this period in 2020 in mathematics/arithmetic, spelling and reading comprehension for 7–11-year-old students within the same period in the three previous years 103 . Results indicated a general learning loss in 2020. More importantly, for the 8% of working-class children, the losses were 40% greater than they were for upper/middle-class children.
Similar results were observed in Belgium among students attending the final year of primary school. Compared with students from previous cohorts, students affected by school closures experienced a substantial decrease in their mathematics and language scores, with children from more disadvantaged backgrounds experiencing greater learning losses 104 . Likewise, oral reading assessments in more than 100 school districts in the United States showed that the development of this skill among children in second and third grade significantly slowed between Spring and Autumn 2020, but this slowdown was more pronounced in schools from lower-achieving districts 105 .
It is likely that school closures have also amplified racial disparities in learning and achievement. For example, in the United States, after the first lockdown, students of colour lost the equivalent of 3–5 months of learning, whereas white students were about 1–3 months behind. Moreover, in the Autumn, when some students started to return to classrooms, African-American and Latinx students were more likely to continue distance learning, despite being less likely to have access to the digital tools, Internet access and live contact with teachers 106 .
In some African countries (for example, Ethiopia, Kenya, Liberia, Tanzania and Uganda), the COVID-19 crisis has resulted in learning loss ranging from 6 months to more 1 year 107 , and this learning loss appears to be greater for working-class children (that is, those attending no-fee schools) than for upper/middle-class children 108 .
These findings show that school closures have exacerbated achievement gaps linked to social class and ethnicity. However, more research is needed to address the question of whether school closures differentially affect the learning of students from working- and upper/middle-class families.
Future directions
First, to assess the specific and unique impact of school closures on student learning, longitudinal research should compare student achievement at different times of the year, before, during and after school closures, as has been done to document the summer learning loss 66 , 109 . In the coming months, alternating periods of school closure and opening may occur, thereby presenting opportunities to do such research. This would also make it possible to examine whether the gap diminishes a few weeks after children return to in-school learning or whether, conversely, it increases with time because the foundations have not been sufficiently acquired to facilitate further learning 110 .
Second, the mechanisms underlying the increase in social class disparities during school closures should be examined. As discussed above, school closures result in situations for which students are unevenly prepared and supported. It would be appropriate to seek to quantify the contribution of each of the factors that might be responsible for accentuating the social class achievement gap. In particular, distinguishing between factors that are relatively ‘controllable’ (for example, resources made available to pupils) and those that are more difficult to control (for example, the self-efficacy of parents in supporting the schoolwork of their children) is essential to inform public policy and teaching practices.
Third, existing studies are based on general comparisons and very few provide insights into the actual practices that took place in families during school closure and how these practices affected the achievement gap. For example, research has documented that parents from working-class backgrounds are likely to find it more difficult to help their children to complete homework and to provide constructive feedback 63 , 111 , something that could in turn have a negative impact on the continuity of learning of their children. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that during lockdown, parents from upper/middle-class backgrounds encouraged their children to engage in practices that, even if not explicitly requested by teachers, would be beneficial to learning (for example, creative activities or reading). Identifying the practices that best predict the maintenance or decline of educational achievement during school closures would help identify levers for intervention.
Finally, it would be interesting to investigate teaching practices during school closures. The lockdown in the spring of 2020 was sudden and unexpected. Within a few days, teachers had to find a way to compensate for the school closure, which led to highly variable practices. Some teachers posted schoolwork on platforms, others sent it by email, some set work on a weekly basis while others set it day by day. Some teachers also set up live sessions in large or small groups, providing remote meetings for questions and support. There have also been variations in the type of feedback given to students, notably through the monitoring and correcting of work. Future studies should examine in more detail what practices schools and teachers used to compensate for the school closures and their effects on widening, maintaining or even reducing the gap, as has been done for certain specific literacy programmes 112 as well as specific instruction topics (for example, ecology and evolution 113 ).
Practical recommendations
We are aware of the debate about whether social science research on COVID-19 is suitable for making policy decisions 114 , and we draw attention to the fact that some of our recommendations (Table 1 ) are based on evidence from experiments or interventions carried out pre-COVID while others are more speculative. In any case, we emphasize that these suggestions should be viewed with caution and be tested in future research. Some of our recommendations could be implemented in the event of new school closures, others only when schools re-open. We also acknowledge that while these recommendations are intended for parents and teachers, their implementation largely depends on the adoption of structural policies. Importantly, given all the issues discussed above, we emphasize the importance of prioritizing, wherever possible, in-person learning over remote learning 115 and where this is not possible, of implementing strong policies to support distance learning, especially for disadvantaged families.
Where face-to face teaching is not possible and teachers are responsible for implementing distance learning, it will be important to make them aware of the factors that can exacerbate inequalities during lockdown and to provide them with guidance about practices that would reduce these inequalities. Thus, there is an urgent need for interventions aimed at making teachers aware of the impact of the social class of children and families on the following factors: (1) access to, familiarity with and use of digital devices; (2) familiarity with academic knowledge and skills; and (3) preparedness to work autonomously. Increasing awareness of the material, cultural and psychological barriers that working-class children and families face during lockdown should increase the quality and quantity of the support provided by teachers and thereby positively affect the achievements of working-class students.
In addition to increasing the awareness of teachers of these barriers, teachers should be encouraged to adjust the way they communicate with working-class families due to differences in self-construal compared with upper/middle-class families 77 . For example, questions about family (rather than personal) well-being would be congruent with interdependent self-construals. This should contribute to better communication and help keep a better track of the progress of students during distance learning.
It is also necessary to help teachers to engage in practices that have a chance of reducing inequalities 53 , 116 . Particularly important is that teachers and schools ensure that homework can be done by all children, for example, by setting up organizations that would help children whose parents are not in a position to monitor or assist with the homework of their children. Options include homework help groups and tutoring by teachers after class. When schools are open, the growing tendency to set homework through digital media should be resisted as far as possible given the evidence we have reviewed above. Moreover, previous research has underscored the importance of homework feedback provided by teachers, which is positively related to the amount of homework completed and predictive of academic performance 117 . Where homework is web-based, it has also been shown that feedback on web-based homework enhances the learning of students 118 . It therefore seems reasonable to predict that the social class achievement gap will increase more slowly (or even remain constant or be reversed) in schools that establish individualized monitoring of students, by means of regular calls and feedback on homework, compared with schools where the support provided to pupils is more generic.
Given that learning during lockdown has increasingly taken place in family settings, we believe that interventions involving the family are also likely to be effective 119 , 120 , 121 . Simply providing families with suitable material equipment may be insufficient. Families should be given training in the efficient use of digital technology and pedagogical support. This would increase the self-efficacy of parents and students, with positive consequences for achievement. Ideally, such training would be delivered in person to avoid problems arising from the digital divide. Where this is not possible, individualized online tutoring should be provided. For example, studies conducted during the lockdown in Botswana and Italy have shown that individual online tutoring directly targeting either parents or students in middle school has a positive impact on the achievement of students, particularly for working-class students 122 , 123 .
Interventions targeting families should also address the psychological barriers faced by working-class families and children. Some interventions have already been designed and been shown to be effective in reducing the social class achievement gap, particularly in mathematics and language 124 , 125 , 126 . For example, research showed that an intervention designed to train low-income parents in how to support the mathematical development of their pre-kindergarten children (including classes and access to a library of kits to use at home) increased the quality of support provided by the parents, with a corresponding impact on the development of mathematical knowledge of their children. Such interventions should be particularly beneficial in the context of school closure.
Beyond its impact on academic performance and inequalities, the COVID-19 crisis has shaken the economies of countries around the world, casting millions of families around the world into poverty 127 , 128 , 129 . As noted earlier, there has been a marked increase in economic inequalities, bringing with it all the psychological and social problems that such inequalities create 130 , 131 , especially for people who live in scarcity 132 . The increase in educational inequalities is just one facet of the many difficulties that working-class families will encounter in the coming years, but it is one that could seriously limit the chances of their children escaping from poverty by reducing their opportunities for upward mobility. In this context, it should be a priority to concentrate resources on the most deprived students. A large proportion of the poorest households do not own a computer and do not have personal access to the Internet, which has important consequences for distance learning. During school closures, it is therefore imperative to provide such families with adequate equipment and Internet service, as was done in some countries in spring 2020. Even if the provision of such equipment is not in itself sufficient, it is a necessary condition for ensuring pedagogical continuity during lockdown.
Finally, after prolonged periods of school closure, many students may not have acquired the skills needed to pursue their education. A possible consequence would be an increase in the number of students for whom teachers recommend class repetitions. Class repetitions are contentious. On the one hand, class repetition more frequently affects working-class children and is not efficient in terms of learning improvement 133 . On the other hand, accepting lower standards of academic achievement or even suspending the practice of repeating a class could lead to pupils pursuing their education without mastering the key abilities needed at higher grades. This could create difficulties in subsequent years and, in this sense, be counterproductive. We therefore believe that the most appropriate way to limit the damage of the pandemic would be to help children catch up rather than allowing them to continue without mastering the necessary skills. As is being done in some countries, systematic remedial courses (for example, summer learning programmes) should be organized and financially supported following periods of school closure, with priority given to pupils from working-class families. Such interventions have genuine potential in that research has shown that participation in remedial summer programmes is effective in reducing learning loss during the summer break 134 , 135 , 136 . For example, in one study 137 , 438 students from high-poverty schools were offered a multiyear summer school programme that included various pedagogical and enrichment activities (for example, science investigation and music) and were compared with a ‘no-treatment’ control group. Students who participated in the summer programme progressed more than students in the control group. A meta-analysis 138 of 41 summer learning programmes (that is, classroom- and home-based summer interventions) involving children from kindergarten to grade 8 showed that these programmes had significantly larger benefits for children from working-class families. Although such measures are costly, the cost is small compared to the price of failing to fulfil the academic potential of many students simply because they were not born into upper/middle-class families.
The unprecedented nature of the current pandemic means that we lack strong data on what the school closure period is likely to produce in terms of learning deficits and the reproduction of social inequalities. However, the research discussed in this article suggests that there are good reasons to predict that this period of school closures will accelerate the reproduction of social inequalities in educational achievement.
By making school learning less dependent on teachers and more dependent on families and digital tools and resources, school closures are likely to greatly amplify social class inequalities. At a time when many countries are experiencing second, third or fourth waves of the pandemic, resulting in fresh periods of local or general lockdowns, systematic efforts to test these predictions are urgently needed along with steps to reduce the impact of school closures on the social class achievement gap.
Bambra, C., Riordan, R., Ford, J. & Matthews, F. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 74 , 964–968 (2020).
Google Scholar
Johnson, P, Joyce, R & Platt, L. The IFS Deaton Review of Inequalities: A New Year’s Message (Institute for Fiscal Studies, 2021).
Education: from disruption to recovery. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse (UNESCO, 2020).
Daszak, P. We are entering an era of pandemics—it will end only when we protect the rainforest. The Guardian (28 July 2020); https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2020/jul/28/pandemic-era-rainforest-deforestation-exploitation-wildlife-disease
Dobson, A. P. et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 369 , 379–381 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Harris, C., Straker, L. & Pollock, C. A socioeconomic related ‘digital divide’ exists in how, not if, young people use computers. PLoS ONE 12 , e0175011 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhang, M. Internet use that reproduces educational inequalities: evidence from big data. Comput. Educ. 86 , 212–223 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Bourdieu, P. & Passeron, J. C. Reproduction in Education, Society and Culture (Sage, 1990).
Stephens, N. M., Fryberg, S. A., Markus, H. R., Johnson, C. S. & Covarrubias, R. Unseen disadvantage: how American universities’ focus on independence undermines the academic performance of first-generation college students. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 102 , 1178–1197 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Andrew, A. et al. Inequalities in children’s experiences of home learning during the COVID-19 lockdown in England. Fisc. Stud. 41 , 653–683 (2020).
Bol, T. Inequality in homeschooling during the Corona crisis in the Netherlands. First results from the LISS Panel. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/hf32q (2020).
Cullinane, C. & Montacute, R. COVID-19 and Social Mobility. Impact Brief #1: School Shutdown (The Sutton Trust, 2020).
Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 84 , 191–215 (1977).
Prior, D. D., Mazanov, J., Meacheam, D., Heaslip, G. & Hanson, J. Attitude, digital literacy and self efficacy: low-on effects for online learning behavior. Internet High. Educ. 29 , 91–97 (2016).
Robinson, L. et al. Digital inequalities 2.0: legacy inequalities in the information age. First Monday https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v25i7.10842 (2020).
Cruz-Jesus, F., Vicente, M. R., Bacao, F. & Oliveira, T. The education-related digital divide: an analysis for the EU-28. Comput. Hum. Behav. 56 , 72–82 (2016).
Rice, R. E. & Haythornthwaite, C. In The Handbook of New Media (eds Lievrouw, L. A. & Livingstone S. M.), 92–113 (Sage, 2006).
Yates, S., Kirby, J. & Lockley, E. Digital media use: differences and inequalities in relation to class and age. Sociol. Res. Online 20 , 71–91 (2015).
Legleye, S. & Rolland, A. Une personne sur six n’utilise pas Internet, plus d’un usager sur trois manques de compétences numériques de base [One in six people do not use the Internet, more than one in three users lack basic digital skills] (INSEE Première, 2019).
Green, F. Schoolwork in lockdown: new evidence on the epidemic of educational poverty (LLAKES Centre, 2020); https://www.llakes.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/RP-67-Francis-Green-Research-Paper-combined-file.pdf
Vogels, E. Digital divide persists even as americans with lower incomes make gains in tech adoption (Pew Research Center, 2021); https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/06/22/digital-divide-persists-even-as-americans-with-lower-incomes-make-gains-in-tech-adoption/
McBurnie, C., Adam, T. & Kaye, T. Is there learning continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic? A synthesis of the emerging evidence. J. Learn. Develop. http://dspace.col.org/handle/11599/3720 (2020).
Baillet, J., Croutte, P. & Prieur, V. Baromètre du numérique 2019 [Digital barometer 2019] (Sourcing Crédoc, 2019).
Giraud, F., Bertrand, J., Court, M. & Nicaise, S. In Enfances de Classes. De l’inégalité Parmi les Enfants (ed. Lahire, B.) 933–952 (Seuil, 2019).
Ahamed, S. & Siddiqui, Z. Disparity in access to quality education and the digital divide (Ideas for India, 2020); https://www.ideasforindia.in/topics/macroeconomics/disparity-in-access-to-quality-education-and-the-digital-divide.html
Soomro, K. A., Kale, U., Curtis, R., Akcaoglu, M. & Bernstein, M. Digital divide among higher education faculty. Int. J. Educ. Tech. High. Ed. 17 , 21 (2020).
Meng, Q. & Li, M. New economy and ICT development in China. Inf. Econ. Policy 14 , 275–295 (2002).
Chinn, M. D. & Fairlie, R. W. The determinants of the global digital divide: a cross-country analysis of computer and internet penetration. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 59 , 16–44 (2006).
Lembani, R., Gunter, A., Breines, M. & Dalu, M. T. B. The same course, different access: the digital divide between urban and rural distance education students in South Africa. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 44 , 70–84 (2020).
Asadullah, N., Bhattacharjee, A., Tasnim, M. & Mumtahena, F. COVID-19, schooling, and learning (BRAC Institute of Governance & Development, 2020); https://bigd.bracu.ac.bd/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/COVID-19-Schooling-and-Learning_June-25-2020.pdf
Asanov, I., Flores, F., McKenzie, D., Mensmann, M. & Schulte, M. Remote-learning, time-use, and mental health of Ecuadorian high-school students during the COVID-19 quarantine. World Dev. 138 , 105225 (2021).
Kihui, N. Kenya: 80% of students missing virtual learning amid school closures—study. AllAfrica (18 May 2020); https://allafrica.com/stories/202005180774.html
Debenedetti, L., Hirji, S., Chabi, M. O. & Swigart, T. Prioritizing evidence-based responses in Burkina Faso to mitigate the economic effects of COVID-19: lessons from RECOVR (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/prioritizing-evidence-based-responses-burkina-faso-mitigate-economic-effects-covid-19-lessons
Bosumtwi-Sam, C. & Kabay, S. Using data and evidence to inform school reopening in Ghana (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/using-data-and-evidence-inform-school-reopening-ghana
Azubuike, O. B., Adegboye, O. & Quadri, H. Who gets to learn in a pandemic? Exploring the digital divide in remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 2 , 100022 (2021).
Attewell, P. Comment: the first and second digital divides. Sociol. Educ. 74 , 252–259 (2001).
DiMaggio, P., Hargittai, E., Neuman, W. R. & Robinson, J. P. Social implications of the Internet. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 27 , 307–336 (2001).
Hargittai, E. Digital na(t)ives? Variation in Internet skills and uses among members of the ‘Net Generation’. Sociol. Inq. 80 , 92–113 (2010).
Iivari, N., Sharma, S. & Ventä-Olkkonen, L. Digital transformation of everyday life—how COVID-19 pandemic transformed the basic education of the young generation and why information management research should care? Int. J. Inform. Manag. 55 , 102183 (2020).
Wei, L. & Hindman, D. B. Does the digital divide matter more? Comparing the effects of new media and old media use on the education-based knowledge gap. Mass Commun. Soc. 14 , 216–235 (2011).
Octobre, S. & Berthomier, N. L’enfance des loisirs [The childhood of leisure]. Cult. Études 6 , 1–12 (2011).
Education at a glance 2015: OECD indicators (OECD, 2015); https://doi.org/10.1787/eag-2015-en
North, S., Snyder, I. & Bulfin, S. Digital tastes: social class and young people’s technology use. Inform. Commun. Soc. 11 , 895–911 (2008).
Robinson, L. & Schulz, J. Net time negotiations within the family. Inform. Commun. Soc. 16 , 542–560 (2013).
Bonfadelli, H. The Internet and knowledge gaps: a theoretical and empirical investigation. Eur. J. Commun. 17 , 65–84 (2002).
Drabowicz, T. Social theory of Internet use: corroboration or rejection among the digital natives? Correspondence analysis of adolescents in two societies. Comput. Educ. 105 , 57–67 (2017).
Nikken, P. & Jansz, J. Developing scales to measure parental mediation of young children’s Internet use. Learn. Media Technol. 39 , 250–266 (2014).
Danic, I., Fontar, B., Grimault-Leprince, A., Le Mentec, M. & David, O. Les espaces de construction des inégalités éducatives [The areas of construction of educational inequalities] (Presses Univ. de Rennes, 2019).
Goudeau, S. Comment l'école reproduit-elle les inégalités? [How does school reproduce inequalities?] (Univ. Grenoble Alpes Editions/Presses Univ. de Grenoble, 2020).
Bernstein, B. Class, Codes, and Control (Routledge, 1975).
Gaddis, S. M. The influence of habitus in the relationship between cultural capital and academic achievement. Soc. Sci. Res. 42 , 1–13 (2013).
Lamont, M. & Lareau, A. Cultural capital: allusions, gaps and glissandos in recent theoretical developments. Sociol. Theory 6 , 153–168 (1988).
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Phillips, L. T. Social class culture cycles: how three gateway contexts shape selves and fuel inequality. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 65 , 611–634 (2014).
Lahire, B. Enfances de classe. De l’inégalité parmi les enfants [Social class childhood. Inequality among children] (Le Seuil, 2019).
Lareau, A. Unequal Childhoods: Class, Race, and Family Life (Univ. of California Press, 2003).
Bourdieu, P. La distinction. Critique sociale du jugement [Distinction: a social critique of the judgement of taste] (Éditions de Minuit, 1979).
Bradley, R. H., Corwyn, R. F., McAdoo, H. P. & Garcia Coll, C. The home environments of children in the United States part I: variations by age, ethnicity, and poverty status. Child Dev. 72 , 1844–1867 (2001).
Blevins‐Knabe, B. & Musun‐Miller, L. Number use at home by children and their parents and its relationship to early mathematical performance. Early Dev. Parent. 5 , 35–45 (1996).
LeFevre, J. A. et al. Pathays to mathematics: longitudinal predictors of performance. Child Dev. 81 , 1753–1767 (2010).
Lareau, A. Home Advantage. Social Class and Parental Intervention in Elementary Education (Falmer Press, 1989).
Guryan, J., Hurst, E. & Kearney, M. Parental education and parental time with children. J. Econ. Perspect. 22 , 23–46 (2008).
Hill, C. R. & Stafford, F. P. Allocation of time to preschool children and educational opportunity. J. Hum. Resour. 9 , 323–341 (1974).
Calarco, J. M. A Field Guide to Grad School: Uncovering the Hidden Curriculum (Princeton Univ. Press, 2020).
Daw, J. Parental income and the fruits of labor: variability in homework efficacy in secondary school. Res. Soc. Strat. Mobil. 30 , 246–264 (2012).
Rønning, M. Who benefits from homework assignments? Econ. Educ. Rev. 30 , 55–64 (2011).
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R. & Olson, L. S. Lasting consequences of the summer learning gap. Am. Sociol. Rev. 72 , 167–180 (2007).
Cooper, H., Nye, B., Charlton, K., Lindsay, J. & Greathouse, S. The effects of summer vacation on achievement test scores: a narrative and meta-analytic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 66 , 227–268 (1996).
Stewart, H., Watson, N. & Campbell, M. The cost of school holidays for children from low income families. Childhood 25 , 516–529 (2018).
Pensiero, N., Kelly, A. & Bokhove, C. Learning inequalities during the Covid-19 pandemic: how families cope with home-schooling (University of Southampton, 2020); https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0025
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Townsend, S. S. Choice as an act of meaning: the case of social class. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 93 , 814–830 (2007).
Kraus, M. W., Piff, P. K. & Keltner, D. Social class, sense of control, and social explanation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 97 , 992–1004 (2009).
Dittmann, A. G., Stephens, N. M. & Townsend, S. S. Achievement is not class-neutral: working together benefits pople from working-class contexts. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 119 , 517–539 (2020).
Zimmerman, B. J. Investigating self-regulation and motivation: historical background, methodological developments, and future prospects. Am. Educ. Res. J. 45 , 166–183 (2008).
Backer-Grøndahl, A., Nærde, A., Ulleberg, P. & Janson, H. Measuring effortful control using the children’s behavior questionnaire–very short form: modeling matters. J. Pers. Assess. 98 , 100–109 (2016).
Johnson, S. E., Richeson, J. A. & Finkel, E. J. Middle class and marginal? Socioeconomic status, stigma, and self-regulation at an elite university. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 100 , 838–852 (2011).
Størksen, I., Ellingsen, I. T., Wanless, S. B. & McClelland, M. M. The influence of parental socioeconomic background and gender on self-regulation among 5-year-old children in Norway. Early Educ. Dev. 26 , 663–684 (2015).
Brady, L. et al. 7 ways for teachers to truly connect with parents. Education Week (31 December 2020); https://www.edweek.org/leadership/opinion-7-ways-for-teachers-to-truly-connect-with-parents/2020/12
Montacute, R. Social mobility and Covid-19: implications of the Covid-19 crisis for educational inequality (Sutton Trust, 2020); https://dera.ioe.ac.uk/35323/2/COVID-19-and-Social-Mobility-1.pdf
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and student learning in the United States: the hurt could last a lifetime (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-student-learning-in-the-united-states-the-hurt-could-last-a-lifetime
Parolin, Z. & Lee, E. K. Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 522–528 (2021).
Saavedra, J. A silent and unequal education crisis. And the seeds for its solution (World Bank, 2021); https://blogs.worldbank.org/education/silent-and-unequal-education-crisis-and-seeds-its-solution
Murray, B., Domina, T., Renzulli, L. & Boylan, R. Civil society goes to school: parent–teacher associations and the equality of educational opportunity. Russell Sage Found. J. Soc. Sci. 5 , 41–63 (2019).
Calarco, J. M. Avoiding us versus them: how schools’ dependence on privileged ‘helicopter’ parents influences enforcement of rules. Am. Sociol. Rev. 85 , 223–246 (2020).
Rist, R. Student social class and teacher expectations: the self-fulfilling prophecy in ghetto education. Harv. Educ. Rev. 40 , 411–451 (1970).
Tobisch, A. & Dresel, M. Negatively or positively biased? Dependencies of teachers’ judgments and expectations based on students’ ethnic and social backgrounds. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 20 , 731–752 (2017).
Brantlinger, E. Dividing Classes: How the Middle-class Negotiates and Rationalizes School Advantage (Routledge, 2003).
Calarco, J. M. ‘I need help!’ Social class and children’s help-seeking in elementary school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 76 , 862–882 (2011).
Calarco, J. M. The inconsistent curriculum: cultural tool kits and student interpretations of ambiguous expectations. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 77 , 185–209 (2014).
Goudeau, S. & Cimpian, A. How do young children explain differences in the classroom? Implications for achievement, motivation, and educational equity. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 16 , 533–552 (2021).
Croizet, J. C., Goudeau, S., Marot, M. & Millet, M. How do educational contexts contribute to the social class achievement gap: documenting symbolic violence from a social psychological point of view. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 18 , 105–110 (2017).
Goudeau, S. & Croizet, J.-C. Hidden advantages and disadvantages of social class: how classroom settings reproduce social inequality by staging unfair comparison. Psychol. Sci. 28 , 162–170 (2017).
Kudrna, L., Furnham, A. & Swami, V. The influence of social class salience on self-assessed intelligence. Soc. Behav. Personal. 38 , 859–864 (2010).
Wiederkehr, V., Darnon, C., Chazal, S., Guimond, S. & Martinot, D. From social class to self-efficacy: internalization of low social status pupils’ school performance. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 18 , 769–784 (2015).
Jury, M., Smeding, A., Court, M. & Darnon, C. When first-generation students succeed at university: on the link between social class, academic performance, and performance-avoidance goals. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 41 , 25–36 (2015).
Jury, M., Quiamzade, A., Darnon, C. & Mugny, G. Higher and lower status individuals’ performance goals: the role of hierarchy stability. Motiv. Sci. 5 , 52–65 (2019).
Autin, F. & Croizet, J.-C. Improving working memory efficiency by reframing metacognitive interpretation of task difficulty. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 141 , 610–618 (2012).
Schmader, T., Johns, M. & Forbes, C. An integrated process model of stereotype threat effects on performance. Psychol. Rev. 115 , 336–356 (2008).
Usher, E. L. & Pajares, F. Self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: a validation study. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68 , 443–463 (2008).
Bruno, A., Jury, M., Toczek-Capelle, M.-C. & Darnon, C. Are performance-avoidance goals always deleterious for academic achievement in college? The moderating role of social class. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 22 , 539–555 (2019).
Holloway, S. D. et al. Parenting self-efficacy and parental involvement: mediators or moderators between socioeconomic status and children’s academic competence in Japan and Korea? Res. Hum. Dev. 13 , 258–272 (2016).
Tazouti, Y. & Jarlégan, A. The mediating effects of parental self-efficacy and parental involvement on the link between family socioeconomic status and children’s academic achievement. J. Fam. Stud. 25 , 250–266 (2019).
Andreu, S. et al. Évaluations 2020, repères CP, CE1: premiers résultats [2020 assessments, first and second grades benchmarks: first results] (Ministère de l’Éducation nationale, de la Jeunesse et des Sports, 2020); https://www.education.gouv.fr/evaluations-2020-reperes-cp-ce1-premiers-resultats-307122
Engzell, P., Frey, A. & Verhagen, M. D. Learning loss due to school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , e2022376118 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Maldonado, J. E. & De Witte, K. The effect of school closures on standardized student test outcomes (KU Leuven—Faculty of Economics and Business, 2020); https://limo.libis.be/primo-explore/fulldisplay?docid=LIRIAS3189074&context=L&vid=Lirias&search_scope=Lirias&tab=default_tab&lang=en_US
Domingue, B., Hough, H. J., Lang, D. & Yeatman, J. Changing patterns of growth in oral reading fluency during the COVID-19 pandemic (PACE, 2021); https://edpolicyinca.org/publications/changing-patterns-growth-oral-reading-fluency-during-covid-19-pandemic
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and learning loss—disparities grow and students need help (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-learning-loss-disparities-grow-and-students-need-help
Angrist, N. et al. Building back better to avert a learning catastrophe: estimating learning loss from COVID-19 school shutdowns in Africa and facilitating short-term and long-term learning recovery. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 84 , 102397 (2021).
Reddy, V., Soudien, C. & Winnaar, L. Disrupted learning during COVID-19: the impact of school closures on education outcomes in South Africa (The Conversation, 2020); https://theconversation.com/impact-of-school-closures-on-education-outcomes-in-south-africa-136889
Entwisle, D. R. & Alexander, K. L. Summer setback: race, poverty, school composition, and mathematics achievement in the first two years of school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 57 , 72–84 (1992).
Kieffer, M. J. Catching up or falling behind? Initial English proficiency, concentrated poverty, and the reading growth of language minority learners in the United States. J. Educ. Psychol. 100 , 851–868 (2008).
Calarco, J. M., Horn, I. & Chen, G. A. ‘You need to be more responsible’: how math homework operates as a status-reinforcing process in school. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/xf96q (2020).
Kaiper-Marquez, A. et al. On the fly: adapting quickly to emergency remote instruction in a family literacy program. Int. Rev. Educ. 66 , 1–23 (2020).
Barton, D. C. Impacts of the COVID‐19 pandemic on field instruction and remote teaching alternatives: results from a survey of instructors. Ecol. Evol. 10 , 12499–12507 (2020).
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
IJzerman, H. et al. Use caution when applying behavioural science to policy. Nat. Hum. Behav. 4 , 1092–1094 (2020).
Taylor, J. & Mallery, J. In person and online learning go together (Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research, 2020); https://siepr.stanford.edu/research/publications/person-and-online-learning-go-together
Dietrichson, J., Bøg, M., Filges, T. & Klint Jørgensen, A. M. Academic interventions for elementary and middle school students with low socioeconomic status: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 87 , 243–282 (2017).
Núñez, J. C. et al. Teachers’ feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors, and academic achievement. J. Educ. Res. 108 , 204–216 (2015).
Singh, R. et al. In Artificial Intelligence in Education (eds Biswas, G.et al.) 328–336 (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011).
Harackiewicz, J. M., Rozek, C. S., Hulleman, C. S. & Hyde, J. S. Helping parents to motivate adolescents in mathematics and science: an experimental test of a utility-value intervention. Psychol. Sci. 23 , 899–906 (2012).
Jeynes, W. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of different types of parental involvement programs for urban students. Urban Educ. 47 , 706–742 (2012).
Mol, S. E., Bus, A. G., De Jong, M. T. & Smeets, D. J. Added value of dialogic parent–child book readings: a meta-analysis. Early Educ. Dev. 19 , 7–26 (2008).
Angrist, N., Bergman, P. & Matsheng, M. School’s out: experimental evidence on limiting learning loss using “low-tech” in a pandemic (National Bureau of Economic Research, 2021); https://www.nber.org/papers/w28205
Carlana, M. & La Ferrara, E. Apart but connected: online tutoring and student outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic (Institute of Labor Economics, 2021); http://hdl.handle.net/10419/232846
Pagan, S. & Sénéchal, M. Involving parents in a summer book reading program to promote reading comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary in grade 3 and grade 5 children. Can. J. Educ. 37 , 1–31 (2014).
Sénéchal, M. & LeFevre, J. A. Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: a five‐year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 73 , 445–460 (2002).
Starkey, P. & Klein, A. Fostering parental support for children’s mathematical development: an intervention with Head Start families. Early Educ. Dev. 11 , 659–680 (2000).
Buheji, M. et al. The extent of Covid-19 pandemic socio-economic impact on global poverty: a global integrative multidisciplinary review. Am. J. Econ. 10 , 213–224 (2020).
The world economy on a tightrope (OECD, 2020); http://www.oecd.org/economic-outlook/june-2020/
Martin, A., Markhvida, M., Hallegatte, S. & Walsh, B. Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Econ. Disasters Clim. Change 4 , 453–479 (2020).
Jetten, J., Mols, F. & Selvanathan, H. P. How economic inequality fuels the rise and persistence of the Yellow Vest movement. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 33 , 2 (2020).
Wilkinson, R. G. & Pickett, K. E. Income inequality and social dysfunction. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 35 , 493–511 (2009).
Sommet, N., Morselli, D. & Spini, D. Income inequality affects the psychological health of only the people facing scarcity. Psychol. Sci. 29 , 1911–1921 (2018).
Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-analyses Relating to Achievement (Routledge, 2008).
Cooper, H., Charlton, K., Valentine, J. C., Muhlenbruck, L. & Borman, G. D. Making the most of summer school: a meta-analytic and narrative review. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child 65 , 1–127 (2000).
Heyns, B. Schooling and cognitive development: is there a season for learning? Child Dev. 58 , 1151–1160 (1987).
McCombs, J. S., Augustine, C. H. & Schwartz, H. L. Making Summer Count: How Summer Programs can Boost Children’s Learning (Rand Education, 2011).
Borman, G. D. & Dowling, N. M. Longitudinal achievement effects of multiyear summer school: evidence from the teach Baltimore randomized field trial. Educ. Eval. Policy 28 , 25–48 (2006).
Kim, J. S. & Quinn, D. M. The effects of summer reading on low-income children’s literacy achievement from kindergarten to grade 8: a meta-analysis of classroom and home interventions. Rev. Educ. Res. 83 , 386–431 (2013).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Reis for editing the figure. The writing of this manuscript was supported by grant ANR-19-CE28-0007–PRESCHOOL from the French National Research Agency (S.G.).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Université de Poitiers, CNRS, CeRCA, Centre de Recherches sur la Cognition et l’Apprentissage, Poitiers, France
Sébastien Goudeau & Camille Sanrey
Université Clermont Auvergne, CNRS, LAPSCO, Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale et Cognitive, Clermont-Ferrand, France
Arnaud Stanczak & Céline Darnon
School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK
Antony Manstead
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sébastien Goudeau .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Human Behaviour thanks Daniele Checchi and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Goudeau, S., Sanrey, C., Stanczak, A. et al. Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap. Nat Hum Behav 5 , 1273–1281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Download citation
Received : 15 March 2021
Accepted : 06 September 2021
Published : 27 September 2021
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Socioeconomic inequalities in psychosocial well-being among adolescents under the covid-19 pandemic: a cross-regional comparative analysis in hong kong, mainland china, and the netherlands.
- Gary Ka-Ki Chung
- Xiaoting Liu
- Roger Yat-Nork Chung
Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology (2024)
Digital gender gaps in Students’ knowledge, attitudes and skills: an integrative data analysis across 32 Countries
- Diego G. Campos
- Ronny Scherer
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Microlearning as a Concept to Optimize Integrated Services for Racially/Ethnically Diverse Families of Autistic Children
- Zhiwen Xiao
- Sandra Vanegas
Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities (2024)
The ethicality of the COVID-19 response in children and adolescents
- Fiona McNicholas
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -) (2024)
Health-related quality of life of young refugees in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic: comparisons to non-refugees and pre-pandemic times
- Johanna Braig
- Pia Schmees
- Heike Eschenbeck
Current Psychology (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how

With schools shut across the world, millions of children have had to adapt to new types of learning. Image: REUTERS/Gonzalo Fuentes
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Cathy Li
Farah lalani.
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Education, Gender and Work is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, education, gender and work.
- The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom.
- As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms.
- Research suggests that online learning has been shown to increase retention of information, and take less time, meaning the changes coronavirus have caused might be here to stay.
While countries are at different points in their COVID-19 infection rates, worldwide there are currently more than 1.2 billion children in 186 countries affected by school closures due to the pandemic. In Denmark, children up to the age of 11 are returning to nurseries and schools after initially closing on 12 March , but in South Korea students are responding to roll calls from their teachers online .
With this sudden shift away from the classroom in many parts of the globe, some are wondering whether the adoption of online learning will continue to persist post-pandemic, and how such a shift would impact the worldwide education market.

Even before COVID-19, there was already high growth and adoption in education technology, with global edtech investments reaching US$18.66 billion in 2019 and the overall market for online education projected to reach $350 Billion by 2025 . Whether it is language apps , virtual tutoring , video conferencing tools, or online learning software , there has been a significant surge in usage since COVID-19.
How is the education sector responding to COVID-19?
In response to significant demand, many online learning platforms are offering free access to their services, including platforms like BYJU’S , a Bangalore-based educational technology and online tutoring firm founded in 2011, which is now the world’s most highly valued edtech company . Since announcing free live classes on its Think and Learn app, BYJU’s has seen a 200% increase in the number of new students using its product, according to Mrinal Mohit, the company's Chief Operating Officer.
Tencent classroom, meanwhile, has been used extensively since mid-February after the Chinese government instructed a quarter of a billion full-time students to resume their studies through online platforms. This resulted in the largest “online movement” in the history of education with approximately 730,000 , or 81% of K-12 students, attending classes via the Tencent K-12 Online School in Wuhan.
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
Other companies are bolstering capabilities to provide a one-stop shop for teachers and students. For example, Lark, a Singapore-based collaboration suite initially developed by ByteDance as an internal tool to meet its own exponential growth, began offering teachers and students unlimited video conferencing time, auto-translation capabilities, real-time co-editing of project work, and smart calendar scheduling, amongst other features. To do so quickly and in a time of crisis, Lark ramped up its global server infrastructure and engineering capabilities to ensure reliable connectivity.
Alibaba’s distance learning solution, DingTalk, had to prepare for a similar influx: “To support large-scale remote work, the platform tapped Alibaba Cloud to deploy more than 100,000 new cloud servers in just two hours last month – setting a new record for rapid capacity expansion,” according to DingTalk CEO, Chen Hang.
Some school districts are forming unique partnerships, like the one between The Los Angeles Unified School District and PBS SoCal/KCET to offer local educational broadcasts, with separate channels focused on different ages, and a range of digital options. Media organizations such as the BBC are also powering virtual learning; Bitesize Daily , launched on 20 April, is offering 14 weeks of curriculum-based learning for kids across the UK with celebrities like Manchester City footballer Sergio Aguero teaching some of the content.
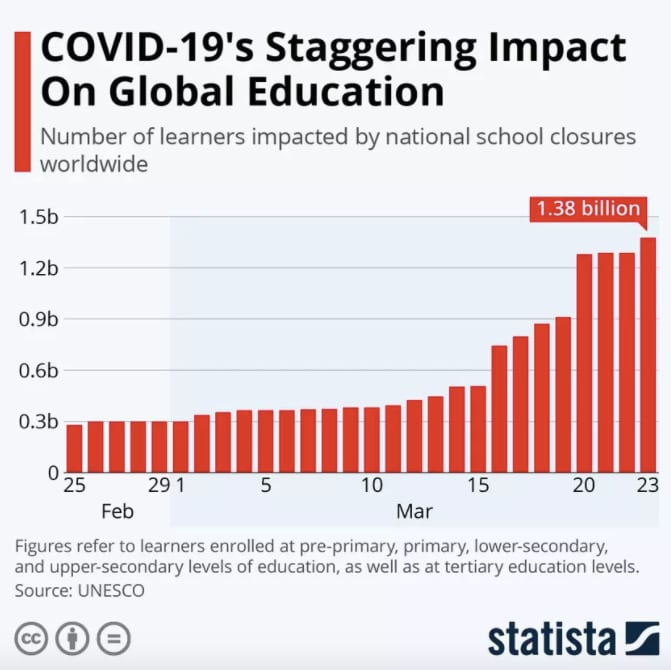
What does this mean for the future of learning?
While some believe that the unplanned and rapid move to online learning – with no training, insufficient bandwidth, and little preparation – will result in a poor user experience that is unconducive to sustained growth, others believe that a new hybrid model of education will emerge, with significant benefits. “I believe that the integration of information technology in education will be further accelerated and that online education will eventually become an integral component of school education,“ says Wang Tao, Vice President of Tencent Cloud and Vice President of Tencent Education.
There have already been successful transitions amongst many universities. For example, Zhejiang University managed to get more than 5,000 courses online just two weeks into the transition using “DingTalk ZJU”. The Imperial College London started offering a course on the science of coronavirus, which is now the most enrolled class launched in 2020 on Coursera .
Many are already touting the benefits: Dr Amjad, a Professor at The University of Jordan who has been using Lark to teach his students says, “It has changed the way of teaching. It enables me to reach out to my students more efficiently and effectively through chat groups, video meetings, voting and also document sharing, especially during this pandemic. My students also find it is easier to communicate on Lark. I will stick to Lark even after coronavirus, I believe traditional offline learning and e-learning can go hand by hand."
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning
The challenges of online learning.
There are, however, challenges to overcome. Some students without reliable internet access and/or technology struggle to participate in digital learning; this gap is seen across countries and between income brackets within countries. For example, whilst 95% of students in Switzerland, Norway, and Austria have a computer to use for their schoolwork, only 34% in Indonesia do, according to OECD data .
In the US, there is a significant gap between those from privileged and disadvantaged backgrounds: whilst virtually all 15-year-olds from a privileged background said they had a computer to work on, nearly 25% of those from disadvantaged backgrounds did not. While some schools and governments have been providing digital equipment to students in need, such as in New South Wales , Australia, many are still concerned that the pandemic will widenthe digital divide .
Is learning online as effective?
For those who do have access to the right technology, there is evidence that learning online can be more effective in a number of ways. Some research shows that on average, students retain 25-60% more material when learning online compared to only 8-10% in a classroom. This is mostly due to the students being able to learn faster online; e-learning requires 40-60% less time to learn than in a traditional classroom setting because students can learn at their own pace, going back and re-reading, skipping, or accelerating through concepts as they choose.
Nevertheless, the effectiveness of online learning varies amongst age groups. The general consensus on children, especially younger ones, is that a structured environment is required , because kids are more easily distracted. To get the full benefit of online learning, there needs to be a concerted effort to provide this structure and go beyond replicating a physical class/lecture through video capabilities, instead, using a range of collaboration tools and engagement methods that promote “inclusion, personalization and intelligence”, according to Dowson Tong, Senior Executive Vice President of Tencent and President of its Cloud and Smart Industries Group.
Since studies have shown that children extensively use their senses to learn, making learning fun and effective through use of technology is crucial, according to BYJU's Mrinal Mohit. “Over a period, we have observed that clever integration of games has demonstrated higher engagement and increased motivation towards learning especially among younger students, making them truly fall in love with learning”, he says.
A changing education imperative
It is clear that this pandemic has utterly disrupted an education system that many assert was already losing its relevance . In his book, 21 Lessons for the 21st Century , scholar Yuval Noah Harari outlines how schools continue to focus on traditional academic skills and rote learning , rather than on skills such as critical thinking and adaptability, which will be more important for success in the future. Could the move to online learning be the catalyst to create a new, more effective method of educating students? While some worry that the hasty nature of the transition online may have hindered this goal, others plan to make e-learning part of their ‘new normal’ after experiencing the benefits first-hand.
The importance of disseminating knowledge is highlighted through COVID-19
Major world events are often an inflection point for rapid innovation – a clear example is the rise of e-commerce post-SARS . While we have yet to see whether this will apply to e-learning post-COVID-19, it is one of the few sectors where investment has not dried up . What has been made clear through this pandemic is the importance of disseminating knowledge across borders, companies, and all parts of society. If online learning technology can play a role here, it is incumbent upon all of us to explore its full potential.
Our education system is losing relevance. Here's how to unleash its potential
3 ways the coronavirus pandemic could reshape education, celebrities are helping the uk's schoolchildren learn during lockdown, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Why health ministers must be at the forefront of global healthcare processes
Shyam Bishen
May 28, 2024

How AI, robotics and automation will reshape the diagnostic lab of the future
Ranga Sampath

How health data collaboration can help unlock inclusive healthcare
Laura Heinrich and Antonio Spina
May 27, 2024

Africa’s cancer burden is taking its toll on women and girls: A new coalition hopes to accelerate progress
Amira Ghouaibi and Emily Fitzgerald

Gender and health equity will only come with universal access to eye health – here's why
Dr. Princess Ifeoma Ike
May 24, 2024
The pandemic has had devastating impacts on learning. What will it take to help students catch up?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, megan kuhfeld , megan kuhfeld senior research scientist - nwea @megankuhfeld jim soland , jim soland assistant professor, school of education and human development - university of virginia, affiliated research fellow - nwea @jsoland karyn lewis , and karyn lewis director, center for school and student progress - nwea @karynlew emily morton emily morton research scientist - nwea @emily_r_morton.
March 3, 2022
As we reach the two-year mark of the initial wave of pandemic-induced school shutdowns, academic normalcy remains out of reach for many students, educators, and parents. In addition to surging COVID-19 cases at the end of 2021, schools have faced severe staff shortages , high rates of absenteeism and quarantines , and rolling school closures . Furthermore, students and educators continue to struggle with mental health challenges , higher rates of violence and misbehavior , and concerns about lost instructional time .
As we outline in our new research study released in January, the cumulative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on students’ academic achievement has been large. We tracked changes in math and reading test scores across the first two years of the pandemic using data from 5.4 million U.S. students in grades 3-8. We focused on test scores from immediately before the pandemic (fall 2019), following the initial onset (fall 2020), and more than one year into pandemic disruptions (fall 2021).
Average fall 2021 math test scores in grades 3-8 were 0.20-0.27 standard deviations (SDs) lower relative to same-grade peers in fall 2019, while reading test scores were 0.09-0.18 SDs lower. This is a sizable drop. For context, the math drops are significantly larger than estimated impacts from other large-scale school disruptions, such as after Hurricane Katrina—math scores dropped 0.17 SDs in one year for New Orleans evacuees .
Even more concerning, test-score gaps between students in low-poverty and high-poverty elementary schools grew by approximately 20% in math (corresponding to 0.20 SDs) and 15% in reading (0.13 SDs), primarily during the 2020-21 school year. Further, achievement tended to drop more between fall 2020 and 2021 than between fall 2019 and 2020 (both overall and differentially by school poverty), indicating that disruptions to learning have continued to negatively impact students well past the initial hits following the spring 2020 school closures.
These numbers are alarming and potentially demoralizing, especially given the heroic efforts of students to learn and educators to teach in incredibly trying times. From our perspective, these test-score drops in no way indicate that these students represent a “ lost generation ” or that we should give up hope. Most of us have never lived through a pandemic, and there is so much we don’t know about students’ capacity for resiliency in these circumstances and what a timeline for recovery will look like. Nor are we suggesting that teachers are somehow at fault given the achievement drops that occurred between 2020 and 2021; rather, educators had difficult jobs before the pandemic, and now are contending with huge new challenges, many outside their control.
Clearly, however, there’s work to do. School districts and states are currently making important decisions about which interventions and strategies to implement to mitigate the learning declines during the last two years. Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) investments from the American Rescue Plan provided nearly $200 billion to public schools to spend on COVID-19-related needs. Of that sum, $22 billion is dedicated specifically to addressing learning loss using “evidence-based interventions” focused on the “ disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on underrepresented student subgroups. ” Reviews of district and state spending plans (see Future Ed , EduRecoveryHub , and RAND’s American School District Panel for more details) indicate that districts are spending their ESSER dollars designated for academic recovery on a wide variety of strategies, with summer learning, tutoring, after-school programs, and extended school-day and school-year initiatives rising to the top.
Comparing the negative impacts from learning disruptions to the positive impacts from interventions
To help contextualize the magnitude of the impacts of COVID-19, we situate test-score drops during the pandemic relative to the test-score gains associated with common interventions being employed by districts as part of pandemic recovery efforts. If we assume that such interventions will continue to be as successful in a COVID-19 school environment, can we expect that these strategies will be effective enough to help students catch up? To answer this question, we draw from recent reviews of research on high-dosage tutoring , summer learning programs , reductions in class size , and extending the school day (specifically for literacy instruction) . We report effect sizes for each intervention specific to a grade span and subject wherever possible (e.g., tutoring has been found to have larger effects in elementary math than in reading).
Figure 1 shows the standardized drops in math test scores between students testing in fall 2019 and fall 2021 (separately by elementary and middle school grades) relative to the average effect size of various educational interventions. The average effect size for math tutoring matches or exceeds the average COVID-19 score drop in math. Research on tutoring indicates that it often works best in younger grades, and when provided by a teacher rather than, say, a parent. Further, some of the tutoring programs that produce the biggest effects can be quite intensive (and likely expensive), including having full-time tutors supporting all students (not just those needing remediation) in one-on-one settings during the school day. Meanwhile, the average effect of reducing class size is negative but not significant, with high variability in the impact across different studies. Summer programs in math have been found to be effective (average effect size of .10 SDs), though these programs in isolation likely would not eliminate the COVID-19 test-score drops.
Figure 1: Math COVID-19 test-score drops compared to the effect sizes of various educational interventions

Source: COVID-19 score drops are pulled from Kuhfeld et al. (2022) Table 5; reduction-in-class-size results are from pg. 10 of Figles et al. (2018) Table 2; summer program results are pulled from Lynch et al (2021) Table 2; and tutoring estimates are pulled from Nictow et al (2020) Table 3B. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals are shown with vertical lines on each bar.
Notes: Kuhfeld et al. and Nictow et al. reported effect sizes separately by grade span; Figles et al. and Lynch et al. report an overall effect size across elementary and middle grades. We were unable to find a rigorous study that reported effect sizes for extending the school day/year on math performance. Nictow et al. and Kraft & Falken (2021) also note large variations in tutoring effects depending on the type of tutor, with larger effects for teacher and paraprofessional tutoring programs than for nonprofessional and parent tutoring. Class-size reductions included in the Figles meta-analysis ranged from a minimum of one to minimum of eight students per class.
Figure 2 displays a similar comparison using effect sizes from reading interventions. The average effect of tutoring programs on reading achievement is larger than the effects found for the other interventions, though summer reading programs and class size reduction both produced average effect sizes in the ballpark of the COVID-19 reading score drops.
Figure 2: Reading COVID-19 test-score drops compared to the effect sizes of various educational interventions

Source: COVID-19 score drops are pulled from Kuhfeld et al. (2022) Table 5; extended-school-day results are from Figlio et al. (2018) Table 2; reduction-in-class-size results are from pg. 10 of Figles et al. (2018) ; summer program results are pulled from Kim & Quinn (2013) Table 3; and tutoring estimates are pulled from Nictow et al (2020) Table 3B. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals are shown with vertical lines on each bar.
Notes: While Kuhfeld et al. and Nictow et al. reported effect sizes separately by grade span, Figlio et al. and Kim & Quinn report an overall effect size across elementary and middle grades. Class-size reductions included in the Figles meta-analysis ranged from a minimum of one to minimum of eight students per class.
There are some limitations of drawing on research conducted prior to the pandemic to understand our ability to address the COVID-19 test-score drops. First, these studies were conducted under conditions that are very different from what schools currently face, and it is an open question whether the effectiveness of these interventions during the pandemic will be as consistent as they were before the pandemic. Second, we have little evidence and guidance about the efficacy of these interventions at the unprecedented scale that they are now being considered. For example, many school districts are expanding summer learning programs, but school districts have struggled to find staff interested in teaching summer school to meet the increased demand. Finally, given the widening test-score gaps between low- and high-poverty schools, it’s uncertain whether these interventions can actually combat the range of new challenges educators are facing in order to narrow these gaps. That is, students could catch up overall, yet the pandemic might still have lasting, negative effects on educational equality in this country.
Given that the current initiatives are unlikely to be implemented consistently across (and sometimes within) districts, timely feedback on the effects of initiatives and any needed adjustments will be crucial to districts’ success. The Road to COVID Recovery project and the National Student Support Accelerator are two such large-scale evaluation studies that aim to produce this type of evidence while providing resources for districts to track and evaluate their own programming. Additionally, a growing number of resources have been produced with recommendations on how to best implement recovery programs, including scaling up tutoring , summer learning programs , and expanded learning time .
Ultimately, there is much work to be done, and the challenges for students, educators, and parents are considerable. But this may be a moment when decades of educational reform, intervention, and research pay off. Relying on what we have learned could show the way forward.
Related Content
Megan Kuhfeld, Jim Soland, Beth Tarasawa, Angela Johnson, Erik Ruzek, Karyn Lewis
December 3, 2020
Lindsay Dworkin, Karyn Lewis
October 13, 2021
Education Policy K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Annelies Goger, Katherine Caves, Hollis Salway
May 16, 2024
Sofoklis Goulas, Isabelle Pula
Melissa Kay Diliberti, Elizabeth D. Steiner, Ashley Woo
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Student’s experiences with online teaching following COVID-19 lockdown: A mixed methods explorative study
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Faculty of Health Sciences, Department of Nursing and Health Promotion, Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Roles Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Primary and Secondary Teacher Education, Faculty of Education and International Studies, Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
Roles Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
- Kari Almendingen,
- Marianne Sandsmark Morseth,
- Eli Gjølstad,
- Asgeir Brevik,
- Christine Tørris

- Published: August 31, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378
- Reader Comments
The COVID-19 pandemic lead to a sudden shift to online teaching and restricted campus access.
To assess how university students experienced the sudden shift to online teaching after closure of campus due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Material and methods
Students in Public Health Nutrition answered questionnaires two and 12 weeks (N = 79: response rate 20.3% and 26.6%, respectively) after the lockdown in Norway on 12 March 2020 and participated in digital focus group interviews in May 2020 (mixed methods study).
Findings and discussion
Two weeks into the lockdown, 75% of students reported that their life had become more difficult and 50% felt that learning outcomes would be harder to achieve due to the sudden shift to online education. Twelve weeks into the lockdown, the corresponding numbers were 57% and 71%, respectively. The most pressing concerns among students were a lack of social interaction, housing situations that were unfit for home office purposes, including insufficient data bandwidth, and an overall sense of reduced motivation and effort. The students collaborated well in digital groups but wanted smaller groups with students they knew rather than being randomly assigned to groups. Most students agreed that pre-recorded and streamed lectures, frequent virtual meetings and student response systems could improve learning outcomes in future digital courses. The preference for written home exams over online versions of previous on-campus exams was likely influenced by student’s familiarity with the former. The dropout rate remained unchanged compared to previous years.
The sudden shift to digital teaching was challenging for students, but it appears that they adapted quickly to the new situation. A lthough the concerns described by students in this study may only be representative for the period right after campus lockdown, the study provide the student perspective on a unique period of time in higher education.
Citation: Almendingen K, Morseth MS, Gjølstad E, Brevik A, Tørris C (2021) Student’s experiences with online teaching following COVID-19 lockdown: A mixed methods explorative study. PLoS ONE 16(8): e0250378. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378
Editor: Mohammed Saqr, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, SWEDEN
Received: September 30, 2020; Accepted: April 6, 2021; Published: August 31, 2021
Copyright: © 2021 Almendingen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has caused extraordinary challenges in the global education sector [ 1 , 2 ]. Most countries temporarily closed educational institutions in an attempt to contain the spread of the virus and reduce infections [ 3 ]. In Norway, the move to online teaching and learning methods accelerated as a consequence of the physical closure of universities and university colleges on 12 March 2020 [ 4 ]. Education is better implemented through active, student-centered learning strategies, as opposed to traditional educator-centered pedagogies [ 5 , 6 ]. At the time of the COVID-19 outbreak, the decision to boost the use of active student-centered learning methods and digitalisation had already been made at both the governmental and institutional levels [ 7 , 8 ] because student-active learning (such as use of student response systems and flipping the classroom) increase motivation and improve learning outcomes [ 5 , 7 , 9 ]. However, the implementation of this insight was lagging behind. Traditional educator-centered pedagogies dominated higher education in Norway prior to the lockdown, and only 30% of academic teachers from higher institutions reported having any previous experience with online teaching [ 4 ]. Due to the COVID-19 lockdown, most educators had to change their approaches to most aspects of their work overnight: teaching, assessment, supervision, research, service and engagement [ 4 , 10 ].
Bachelor’s and master’s in Public Health Nutrition (PHN) represents two small-sized programmes at Oslo Metropolitan University (OsloMet). PHN is defined as ‘the application of nutrition and public health principles to design programs, systems, policies, and environments that aims to improve or maintain the optimal health of populations and targeted groups’ [ 11 , 12 ]. Traditional teaching methods dominated on both programs during winter 2020. Following the lockdown, online learning for the continuation of academic activities and the prevention of dropouts from study programmes in higher education were given the highest priority. Due to an extraordinary effort by both the administrative and academic staff, digital alternatives to the scheduled on-campus academic activities were offered to PHN students already in the first week following lockdown. The scheduled on-campus lectures were mainly offered as live-streamed plenary lectures lasting 30–45 minutes, mainly using the video conferencing tool Zoom. Throughout the spring semester educators received training in digital teaching from the institution and increasingly made use of online student response systems (such as Padlet and Mentimeter) as well as tools to facilitate digital group-work (Zoom/Microsoft Teams). Non-theoretical lectures (e.g. cooking classes), were cancelled, and face-to-face exams were re-organized into digital alternatives in order to ensure normal teaching operations. Several small tweaks were employed to minimize dropout. There was no time for coordinating the different courses with regards to the types of online teaching activities, exams and assessments. Social media, i.e Facebook, and SMS were the primary communication channels the first week after lockdown. The use of learning management systems (LMS) Canvas and digital assessment system, Inspera, remained mainly unchanged. Due to the new situation, the deadline for the submission of bachelor theses was postponed by 48 hours. In addition, bachelor students submitting their thesis where given permission to use the submission deadline for the deferred exam in August as their ordinary exam deadline. The deadline for the submission of master theses was extended by one week, but all planned master exams were completed by the end of June, including oral examinations using Zoom instead of the traditional face-to-face examinations on campus. Even though most of the new online activities where put in place with limited regard for subtle nuances of pedagogical theory, and did not allow for much student involvement, the dropout rate from PHN programs remained unchanged compared to previous years. PHN is a small-sized education with close follow up of students. However, although the students experienced a digital revolution overnight, we know little about how they experienced the situation after the university closed for on-campus activities.
Accordingly, the purpose of this study was to assess how Norwegian PHN students experienced the shift to digital teaching following campus lockdown. Students were also asked to provide feedback on what might improve the learning outcomes in future online lectures and courses.
Design and sampling
This study utilised a mixed methods cross-sectional design, where quantitative and qualitative methods complemented each other. An invitation to participate was sent out to 79 eligible students via multiple channels (Facebook, Teams, Zoom, LMS Canvas, SMS), with several reminders. The only eligibility criteria was being a student in PHN during spring 2020. All students received the quantitative survey. Due to few students eligible for each focus group interview, all who wanted to participate were interviewed/included. The invited students were in their second-year (n = 17) and third-year (n = 28) bachelor’s and first-year (n = 13) and second-year (n = 21) master’s programme at PHN in the Faculty of Health Sciences at OsloMet. The response rate was 16/79 (20.3%) and 21/79 (26.6%). Two focus group interviews were scheduled in each class (a total of 8) but only 4 interviews were conducted. The research team was heterogeneously composed of members with both pedagogical and health professional backgrounds.
Online questionnaire
To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first “corona” study at our Faculty. No suitable national or international questionnaire had been developed and /or validated by March 2020. Hence, online questionnaires for the present study were designed virtually ‘over-night’. The questions were however based on experiences from a large-scale interprofessional learning course using the blended learning approach at OsloMet [ 13 , 14 ] and specific experiences that academic staff in Norway reported during the first week of teaching during the lockdown [ 4 ]. The questionnaires were based on an anonymous self-administrated web survey ‘Nettskjema’ [ 15 ]. ‘Nettskjema’ is a Norwegian tool for designing and conducting online surveys with features that are customised for research purposes. It is easy to use, and the respondents can submit answers from a browser on a computer, mobile phone or tablet. During the first week after lockdown, the questionnaire was sent out to university colleagues and head of studies and revised accordingly. The questionnaires were deliberately kept short because the response rate is generally low in student surveys [ 16 ]. Ideally, we should have pretested and validated the questionnaires, but this was not possible within the short-time frame after lockdown. Items were measured on a five-level ordinal scale (Likert scale 0–5). The two forms contained both numerical and open questions, permitting both quantitative and qualitative analyses. The first questionnaire was sent out to the students on 25 March 2020 (two weeks after the closure of university campus; students were asked to submit their answers during the period from 12 March until the link was closed at Easter Holiday), and the second questionnaire was sent on 3 June 2020 (12 weeks after closure; students were asked to submit their answers during the period after Easter and until the end of the spring semester). The questionnaires were distributed as web links embedded in the LMS Canvas application. Because live-streamed lectures were offered primarily through Zoom during the first weeks, students were not asked about interactive digital teaching and tools in the first questionnaire. At the end of both questionnaires, the students were asked what they believed could improve the learning experience in future online education. The qualitative part consisted of text answers to open questions from the two electronic questionnaires.
Digital focus group interview
To capture meaningful insights into the participants experiences, we conducted digital focus group interviews [ 17 ], aiming to conduct one digital focus group interview in each class. PHN is a small sized education, and the teachers know all the students. The focus group interviews were therefore performed by two external independent researchers (EG and CT) who are not directly involved in the PHN education and had no prior knowledge to the students. The two interviewers (moderators) were middle-aged female teachers working in the university, and both have significant experience in digitalizing education. They were presented to the participants as researchers from the university. The report of this study was guided by the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ). The interviews were conducted via the video conferencing system Zoom during May 2020, following internal guidelines [ 18 ]. In the focus group interviews, the participants reflected on their own experiences, and the moderator guided the discussion using a semi-structured interview guide. This guide was prepared based on the research questions. One pilot interview was conducted, which resulted in some minor changes to the interview guide. The results from the pilot interview are not included in the results. The focus group interviews lasted for approximately one hour, and five students were invited to each focus group interview. The interviews were not recorded, but the moderator took notes, ensuring that the participants remained anonymised.
Data analysis
Quantitative data are described descriptively with numbers and percentages. Apart from re-categorization of response categories, no statistical analysis was performed. Quantitative data were extracted directly from the survey system. Answers in categories 0 or 1 were categorised as ‘Disagree/slightly agree’, answers in categories 2 or 3 were categorised as ‘Somewhat agree’ and answers in categories 4 or 5 were categorised as ‘Agree’. Qualitative data were analysed using systematic text condensation (STC), inspired by Giorgi’s phenomenological approach and modified by Malterud [ 17 ]. First, the entire texts (from the interviews) were read to get an overall impression, and preliminary themes were derived from the interviews. Then, meaning units, such as sentences and words, were identified and connected with the preliminary theme to elucidate the study question. The meaning units were then coded and systemized into groups, so that meaning could be abstracted from the different code groups. Finally, the meanings of the various units were summarised. The qualitative data from the questionnaire were then extracted by the moderators, and the words and sentences were identified and abstracted. In order to ensure quality, the notes from the focus group interviews and the text answers from the questionnaires were reviewed by both moderators.
Ethical considerations
All participants gave their informed consent. The questionnaires did not include questions about personal health information or sensitive data. The quantitative data were collected through an anonymous web survey using ‘Nettskjema’ [ 15 ]. Internal routines at OsloMet for using Zoom in research interviews were applied [ 18 ]. In the interviews, the participants provided their written consent in the chat without their names and remained anonymous. The data protection was approved by the Norwegian Centre for Research Data (NSD, reference no. 846363), as PHN is a small-sized study programme and because Zoom was used for the digital focus group interviews.
Quantitative data
There were 16 (20.3%) and 21 (26.6%) students who answered the questionnaires two and 12 weeks after lockdown, respectively ( Table 1 ). Both samples had an even distribution of bachelor and master students.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t001
Among the respondents two and 12 weeks after lockdown, 7/16 students (44%) and 9/21 students (43%) reported having previous experience with online learning, respectively ( Table 1 ). After two weeks of forced online education, 8/16 students (50%) expected that their learning outcomes would be inferior with online education compared to their pre-COVID-19 education at campus. After 12 weeks, 15/ 21 students (71%) expected that their learning outcome would be lower, and, notably, none of the students expected that it would be higher. On both occasions, most students reported that studying had become more difficult compared to the time before the pandemic.
Several of the identified challenges with online education were reported by more than 50% of the students, and there was an uneven spread across categories of answers (Tables 2 and 3 ). Only one of 16 students (6%) agreed that they needed to increase their digital competence, but approximately half reported having technical challenges at home. All of the students agreed that the lack of contact with other students was a challenge. However, after 12 weeks, the lack of contact with academic staff seemed to pose less of a challenge.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t002
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t003
After 12 weeks, 20/21 students (95%) agreed that their motivation and effort had been reduced. At the same time, all students wanted to return to campus. Only 5/21 (24%) reported that their learning outcomes had not deteriorated.
Suggestions for how to increase learning outcome in future digital courses
Two weeks after lockdown, most students answered that the use of different components of online education would improve the learning outcomes in a future online course ( Table 4 ). Regarding participation in digital group work, there was a nearly even spread across the different categories of answers. Finally, participants preferred written home exams and feedback over the digital options suggested ( Table 5 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t004
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t005
After 12 weeks of (forced) online teaching, more ambivalence toward the use of digital learning tools could be detected ( Table 6 ). However, the proportion of students who agreed that digital group work would increase the learning outcomes seemed unchanged (around 1/3 of both samples). In line with the findings obtained only two weeks after lockdown, written submissions and feedback seemed to be preferable to digital exam options ( Table 7 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t006
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t007
After 12 weeks, 16/21 students (76%) agreed that social interaction plays a role in learning outcomes and well-being ( Table 8 ), and an equal proportion agreed that it was important that everyone had their camera on during teaching.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.t008
There were 15/21 students (71%) who agreed that their digital competence and interest in digital teaching methods had increased while 6/21 students (29%) disagreed with this statement.
Qualitative data
In total, there were four master students who participated in digital focus group interviews (on two different occasions, with three students and one student in the groups, respectively).
Digital lectures.
The students were satisfied with the teaching and reported that the lecturers were competent in arranging online teaching. The lecturers were also good at adapting to the students’ wishes regarding teaching. Lectures that were streamed live (synchronous classes) were preferred over recordings (asynchronous). One student said it was a privilege to still be able to study even though the university campus was closed due to corona and all the lectures were digital. The students expressed that it is an advantage if the lecturer has digital competence to ensure that the lecture runs smoothly without digital/technical problems, or if there is a co-host who can assist. Technical competence is also important when invitation links are sent out. It signals that the student group is well taken care of. The informants described a course co-ordinator as a person with a good overview and sense of responsibility—someone who is good at structure and order. These qualities were highlighted as important in a fully digitalised teaching program.
The students did not support compulsory attendance, as it would reduce the feeling of freedom that most students value. If learning activities were compulsory, students felt it might also present challenges in dealing with their children and part-time work. The students expressed that most of their fellow students were present in lectures that went live on Zoom. One student stated that live digital lectures were best because it was easier to ask questions. When using a flipped classroom or recordings, the questions must be written down and asked afterwards, but both options (flipped classroom and live streaming) were perceived as fine.
Interestingly, the qualitative results from the questionnaire indicated that some students found it easy to ask questions, while others thought it had become more difficult. According to one student, ‘As long as we have the opportunity to ask questions online, I think it will go just fine. I commute three hours per school day to get to and from school, so I feel I have more time to work with school now that the lecture is online’.
One of the informants thought that interaction was challenging, and it did not feel as natural to ask questions in online classes. ‘Raising your hand’ was not perceived to be as easy as in the face-to-face setting on campus, which could mean that the students did not always get answers to their questions.
The students’ indicated that recorded lectures should not be longer than one hour, as it is easy to lose focus, and one must rewind the recordings. For live online lectures, two hours was deemed fine, and they were perceived as fun to watch. However, each session of the live online lectures should not be longer than 45 minutes.
The online teaching (mainly in the form of synchronous plenum lectures originally intended as on-campus lectures) was challenging in the beginning because some students fell out of the digital rooms due to technical reasons, but it got better over time. Some students experienced poor bandwidth, which led to them not being able to turn on their camera and reduced sound quality. One student stated that poor internet quality was something he could not do anything about, but it resulted in a non-optimal learning situation. It was suggested that using a flipped classroom/recorded lectures in the first weeks after lockdown could have solved this problem.
The respondents pointed out that the use of several conference systems/channels in addition to LMS Canvas provided a poor overview and ineffective communication, and they would prefer a single learning platform. The students were unsure how to contact their teachers in the first weeks after lockdown due to the use of several platforms. Even with a single contact channel (LMS), the students found that the threshold barrier for sending questions to the teacher through email was high.
When asked what they thought about ‘black screens’ (students turning off the camera), several answered that this reduced the quality of communication between the lecturer and student. The lecturer missed affirmative nods from students, and the students also likely missed parts of the communication when the camera was turned off. In some of the lectures, all of the students were encouraged to keep the camera on, and some of the lecturers asked the students questions to initiate two-way communication. The students expressed that it was nice to see the other attending students on video. Furthermore, the participants felt that the lecturers mainly engaged the students who had their camera on. However, several students said that they turned off their cameras during the lectures because the session was being recorded. Another stated that having the camera on was particularly useful when having discussions in digital groups. The students who participated in the survey wished for more recorded lectures, indicating that their lecturers did not do this often.
One of the informants assumed that she would have turned off the camera when recording the lecture, and she thought she had not contributed much. She would have to consider whether a question was ‘stupid’ before asking it, and probably she had not asked any questions at all. She thought this was due to habit, and she indicated that one might get used to being recorded. That is, if recording had been the norm and she had become accustomed to it, it would have been easier to relate to.
All of the informants agreed that presentations with audio were useful, as the material could be repeated by rewinding to the desired location. They also reported that it sometimes took a while for the teachers to post such files, even though the students found these learning resources very useful.
They noticed an increased attendance rate among their peers in the online lectures, which they perceived as positive. The reason for the increased attendance, they believed, was that many students have to make a long trip to attend class, and the threshold for participating had become lower now that all teaching was online. This was supported by the qualitative results from the questionnaire, where a student said, ‘I commute several hours per school day to get to and from school, so I feel I have more time to work with school now that the lecture is online’.
However, one of the informants pointed out that it is important for students to be able to talk to each other when the lecturer is not present, that group activities should be arranged and that they should be provided with opportunities for voluntary meetings on campus in their spare time. One of the informants believed it to be important that the students themselves have a responsibility to address the learning environment and initiate meetings in both academic and social arenas. One felt that it was not desirable that the university was responsible for social contact between peers. It was suggested that time could be set aside, for example, after teaching, so that only students could talk together. It was expressed that in order to preserve social aspects in digital teaching and learning, the first meeting should be on campus. A mentor scheme was suggested, where former students could give tips and advice on how to function as a ‘digital student’.
Digital group work.
The students expressed that they mainly collaborated well in digital groups (breakout rooms). Communication usually worked well with both the teacher and peers in these digital rooms. Nevertheless, some students reported that group work was not effective when it was carried out in ‘breakout rooms’. The students felt that the allocated time for group work was too short for collaboration, and some of the time was spent on technical challenges. There were also some students who withdrew from the group work, which the respondents believed was because some were shy. One student said that discussions during group work paid off and that communication worked well, but it was a pity that so few students participated. Getting to know the others in the group well was also deemed to be important for the level of collaboration and professional discussions. The students did not like to be randomly assigned into groups. However, they expressed that it would be advantageous to plan for more group work in smaller groups.
Another positive effect of online teaching the students highlighted was the increased amount of written feedback from lecturers on work submitted voluntarily. The students perceived that this was offered as a compensation for shorter teaching sessions.
One of the respondents thought that it was important to socially interact with peers and missed having lunch with fellow students. Others felt that there had not been many social gatherings in the group previously, and so they did not experience the absence of fellow students as a great loss. They also pointed out that students who had met each other physically at an earlier time had a different starting point in online meetings and for online education. One student stated, ‘Getting to know new peers digitally feels weird’. Furthermore, one of the informants pointed out that most people have a general need for physical contact, and that touching and eye-to-eye contact is important.
Motivation.
Some of the students were more motivated to participate in online learning activities, yet it was perceived to require greater effort to stay motivated and ‘in the course’. Some students work alongside their studies and thus do not attend classes, and others have children who must be tended to. Some indicated that student response systems such as Mentimeter, Quizlet, Padlet, Kahoot! and the use of polls was motivating factors, but it depended on the context in which they were used. Some of the students reported that they especially liked Kahoot, but it was important that the use of such response systems was done in a structured way. They expressed that they liked the teaching programme, which consisted of an introductory video and teaching in which the basics were presented, followed by group work and finally teaching, where the teacher went more in depth. This approach made it easier to follow the teaching and to ask questions.
The students said it was good for motivation when an overview of the course content was published, as it contributed to predictability and more people participate when they know what is planned.
Nevertheless, the qualitative results from the questionnaire indicated that it was difficult to get an overview of everything that needed to be done. It could be challenging to concentrate and have self-discipline due to many distractions, which reduced the students’ motivation. Several students expressed that they felt alone in their studies, and it was difficult to feel alone with the responsibility for learning the curriculum. One student wrote that there was considerable uncertainty, which negatively affected concentration, and that the COVID-19 crises was a difficult time for everyone.
Overall, these students were satisfied with the ad hoc online teaching after the lockdown, although they experienced self-perceived reduced learning outcomes compared to the pre-pandemic situation. It appears that they adapted quickly to the new situation, but they also reported difficulties with the transition to new teaching methods. Based on both the surveys and interviews, the most pressing concerns among students were a lack of social interaction, housing situations that were unsuitable for home office purposes, including insufficient data bandwidth, and a sense of reduced motivation and effort. PHN is a small sized education which enables close contact between educators and students. The low student volume might explain why the dropout rate from the bachelor and master programs remained unchanged compared to that in previous years.
Receiving teaching, supervision, exams and assessments solely through online solutions was a new experience for these students. Apart from a 15-credit mandatory bachelor course offered as hybrid learning (7), traditional teaching methods still dominated the bachelor and master study programmes of PHN in winter 2020. Importantly, the students evaluated the ad hoc solutions offered during the chaotic spring of 2020 rather than a well-planned, high-quality online education using student-active methods [ 5 ]. Teachers switched to online teaching without any time to learn the technology, or standard quality online teaching practices [ 4 ]. They had many years of experience teaching in -person, and they had arranged their lessons and interactive elements around this mode of learning. Alternatively, they had very little experience teaching online. The students’ experiences in these online learning environments, which were thrown together at the last minute, are not necessarily indicative of students’ experiences in a quality online course based on principles from Quality Matters online education [ 19 ].
Although the students reported reduced learning outcomes after 12 weeks dominated by synchronous live-streamed lectures lasting for 30–45 minutes on Zoom, they had positive attitudes toward use of digital learning materials and tools in future online courses. For asynchronous lectures, the rule of thumb in online education is less than 10–15 minutes [ 19 ]. Although lectures of 45 minute duration is far beyond what is recommended for digital teaching [ 19 ], the students responded based on their recent experiences where many teachers, for reasons of feasibility, conducted their planned on-campus lectures digitally shortly after lockdown. Some of the students also reported that they especially liked Kahoot, however, since we wanted to keep the research questionnaire short, we did not ask more in detail for concrete digital tools. A pre-corona study from OsloMet reported that physiotherapy students’ attitudes toward a flipped classroom intervention were mainly positive, although the academic outcomes from the final exam were similar to those in previous years [ 20 ]. Further, in a recent large-scale pre-COVID-19 blended learning interprofessional course conducted a few weeks ahead of the lockdown, first-year bachelor’s students at OsloMet reported positive perceptions of the blended learning approach, using only short video clips (less than 10 minutes) [ 21 ]. Approximately 3/4 of the students in that study disagreed that virtual group discussions resulted in better learning outcomes than face-to-face group discussions. The present data do not conflict with the findings from that larger-scale study.
The students expressed in various ways that online teaching with a lack of social interaction leads to worse learning outcomes and lower levels of motivation and well-being. Concerns about lack of face-to-face contact may have been aggravated by the stressful situation, and contentment with teaching methods would likely improve if teachers had been able to integrate the appropriate elements in a fully digitalized course. Face-to-face interactions provide the foundation for social communication, the lack of which can be viewed as a critical disadvantage of online learning [ 5 ]. Face-to-face training may be particular crucial for candidates expected to have communication skills, such as nutritionists [ 11 , 12 , 22 – 24 ]. The ad hoc solutions for teaching offered during the 2020 spring term were thus not in agreement with the suggested conceptual dimensions, which allow students to expand their knowledge beyond the intended learning outcome established by the teacher: motivation and attention [ 5 ].
The students expressed concerns that are common in traditional in‐class teaching as well, and such issues should not be overlooked in online teaching [ 25 , 26 ]: insufficient pre‐class study preparation, limited participation and inadequate depth in class discussions. Quality of education lies in the knowledge, skills and expertise that are conveyed as well as in the manner in which they are communicated and learned [ 7 , 26 ]. In different ways, the students’ responses revolved around central quality aspects, such as learning objectives, content, programme design, adaptation, teaching, work methods, supervision and forms of assessment [ 7 ]. These findings are in agreement with other studies on COVID‐19 and education [ 4 , 25 , 27 ].
The students stated that they received insufficient information about the exams. This is understandable because staff initially did not know how the different exams would be digitally transformed in spring term 2020. Asked about exam preferences students said that they preferred longer written exams at home, over old campus-style exams, with short timelines, adapted to an online format. They also preferred multi-day written home exams over potential alternatives such as video or podcasts, which none of them had tried before. It should be noted that they had limited experience with digital options. Student-produced podcast and video have been used as formative assessment forms at our university [ 14 ], but to lesser extent as formative assessment forms. The preference for written home exams over digital options was thus likely influenced by student’s familiarity with the former since no exams during this time-period were in the form of podcast or video. Feedback and guidance from academic staff have been found to be key aspects of study quality, and good feedback contributes to increased motivation and improved learning outcomes (6). Exam uncertainty causes undue stress, and thus a key recommendation during the transition to online learning is to ensure that all information about exams is communicated to the students clearly and in a timely manner [ 27 ].
‘Black screens’ do not necessarily reflect individuals lack of motivation and attention or embarrassment, but they may reflect a lack of digital training among freshmen or technical issues, such as poor bandwidth. Broadband bandwidth overload issues and a lack of suitable equipment will probably not be significant problems in Norway in the future. The students suggested that both flipped classrooms and live streaming should be used in future online courses. Flipping the classroom [ 9 ] ahead of live streaming, with the possibility for the students to write down questions during the live streaming or afterward in a seminar, increases flexibility. Asynchronous tools may be utilised to support students to work at different times. We cannot overlook the possibility that new students might have needs that differ from those of senior students in terms of getting accustomed to online education. Nevertheless, our date indicates that clarification of expectations constitutes an important success criteria for online teaching, especially when it comes to group work and formative and summative assessment [ 4 , 27 ].
The closure of campus may have unknown implications for society in both the short and long term [ 28 – 30 ], including impacts on educational quality and the mental health of students and academic staff [ 31 ]. If students are unable to study effectively for some unknown reason, it will make online learning ineffective, regardless of educational quality. The situation after the lockdown in Norway was confusing, and many students lost their jobs and moved back in with their parents [ 4 ]. We did not collect person-sensitive data, and thus we know little about these students’ circumstances. The dropout rate remained nearly unchanged among these students as compared to previous years. Being a small-sized education, the staff were able to follow-up each student individually using digital videoconference tools, such as Zoom and Teams. In the future, more sustainable approaches should be developed, for example, by increasing peer-to-peer interactions and through mentoring programs [ 1 ]. Reducing dropout and increasing completion rates was a strategic goal for higher education before the lockdown [ 29 ], and we do not know the impact of the lockdown on future dropout and completion rates. The high dropout rate from Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) has been a major concern of researchers and educators over the years [ 32 ]. Although some universities worldwide had already started offering MOOC-based undergraduate degrees before the COVID-19 pandemic [ 32 ], most MOOCs do not lead to degrees. The online courses offered in spring 2020 after the lockdown were mandatory courses leading to degrees, and thus they were not directly comparable to the voluntary MOOCs. However, such issues are premature for consideration in the present study. OsloMet is currently participating both in the future ‘The COVID-19 Multi-Country Student Well-being Study’[ 33 ] and the ‘Corona and Campus’ study [ 34 ]. The ‘Corona and Campus’ study has secondary outcomes related to teaching satisfaction and learning outcomes, and such data will have the power to inform future decision-making [ 30 ]. However, the present data were collected shortly after the national lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic on aspects of digitalisation relevant to the (post)-pandemic situation.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
This study has several strengths. The most important strength is data collection shortly after a national lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The combined use of both quantitative and qualitative approaches enabled different perspectives to be captured and adds strength to the study. The triangulation allowed us to identify aspects more accurately and helped to offset the weaknesses of each approach alone. Group dynamics in focus group interviews can help bring out nuances in the data material beyond the answers to the predefined quantitative questions in the electronic questionnaires [ 17 ]. Another strength was the research team consisting of both external moderators providing objectivity, lack of vested interest and a fresh perspective, and internal evaluators who were familiar with the education and the students. One limitation is using a questionnaire which was not pre-tested or validated. However, due to time constraints shortly after campus lockdown following the COVID-19 outbreak, it was not possible to perform pre-testing or validation of the instruments used in the present study. Many of the necessary ad hoc changes to the course plans and exams (spring semester 2020) had yet to be made and decided upon when the present study was initiated, even when the first questionnaire was sent out before Easter 2020. The candidates actual achieved learning outcomes and working skills are unknown due to limited opportunities to monitor the quality of their work [ 4 ]. We do not consider it to be relevant to repeat the study, or reuse its instruments, since the acute phase after lockdown is over. PHN is a small-sized education, and the total number of students were only 79 individuals. The stress associated with the unprecedented situation may have contributed to a low response rate. Private circumstances such as poor internet connection, children at home, and lack of an adequate home office may also have contributed to a low response rate. A low response rate is also a limitation in studies performed in a normal situation [ 16 ]. We cannot rule out selection bias in the sample. The students who volunteered for the digital focus group interviews were positive and thorough. In particular, they seemed to reflect on a more general level, not restricted to their own personal situations. However, the range in age among the study participants was representative for the age range of all PHN students, and both bachelor and master students participated in the study. Data are collected from one single university, and the results might not be representative for large sized educations. Since the study is exploratory, we had not planned the data collection in order to test hypotheses. The study seeks to provide a snapshot in time of an evolving situation. Even with some limiting factors we believe the explorative study offers value since it provides a student perspective on an unprecedented black-swan event in higher education.
Conclusions
Although they had little previous experience with online education, these students seemed to adapt quickly to the sudden shift to ad hoc online education due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The most pressing concerns among students were a lack of social interaction, a feeling of being alone in their studies, unfit housing situations for home office purposes, including insufficient data bandwidth, and a sense of reduced motivation and effort. Although our data indicate that face-to-face contact was greatly missed during this time-period, a thoroughly planned online course with numerous contact points between teachers and students would likely have been received more favorably. Finally, the students expressed that they wanted more structure in future digital courses. Due to the very unusual circumstances experienced both by students and teachers in the early stages of national lockdown in Norway, we are hesitant to conclude with regards to students preferences for future online courses.
Supporting information
S1 file. spss file questionnaire 1—please see line 154..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.s001
S2 File. SPSS file Norwegian questionnaire 1—please see line 154.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.s002
S3 File. SPSS file questionnaire 2—please see line 154.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.s003
S4 File. SPSS file Norwegian questionnaire 2—please see line 154.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.s004
S5 File. Structured interview guide–please see line 145.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250378.s005
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the participating students and the academic and administrative staff at Oslo Metropolitan University for their contributions.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. UNESCO. Education: From disruption to recovery 2020 [09/09/2020]. Available from: https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse .
- 3. Tria JZ. The COVID-19 Pandemic through the Lens of Education in the Philippines: The New Normal. International Journal of Pedagogical Development and Lifelong Learning. 2020;1. https://doi.org/10.30935/ijpdll/8311 .
- 4. Langford M, Damşa C. Online Teaching in the Time of COVID-19: Academic Teachers’ Experience in Norway Centre for Experiential Legal Learning (CELL), University of Oslo2020 [cited 2020].
- 5. Lillejord S, Børte K. Learning and Teaching With Technology in Higher Education—a systematic review. 2018.
- 6. Vygotsky LS. Mind in society: the development of higher psychological processes. London: Harvard University Press UK: Gyldendal Akademisk; 1978.
- 7. Ministry of Education and Research. Quality Culture in Higher Education 2017.
- 8. Oslo Metropolitian University. The digital university of the future: Strategy for digital transformation 2018–2024 2018 [17/11/2019]. Available from: https://ansatt.oslomet.no/documents/585743/77463421/Strategy+for+digital+transformation.pdf .
- PubMed/NCBI
- 11. Sisk K CA, Cullinen K Guide for Developing and Enhancing Skills in Public Health and Community Nutrition. Definitions Related to Public Health Nutrition and Community Nutrition 2018 [09/09/2020]. 3rd Ed:[Available from: https://asphn.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Guide-for-Developing-and-Enhancing-Skills-in-Public-Health-and-Community-Nutrition.pdf .
- 12. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Definition of Terms List. Approved by Definition of Terms Task Force Quality Management Committee 2020 May 8, 2020 Report No.
- 13. Almendingen K, Saltyte-Benth J., Molin M. Large Scale Blended Learning Design in an Interprofessional Undergraduate Course in Norway: Context Description and Supervisors’ Perspective. The Journal of Research in Interprofessional Practice and Education (JRIPE) 2021;In press.
- 14. Almendingen K, Molin M, Šaltytė Benth J. Large-scale Blended Learning Design in an Undergraduate Interprofessional Course in Norway: Students’ Perspectives from an exploratory study The Journal of Research in Interprofessional Practice and Education (JRIPE) 2021;In press.
- 15. Nettskjema: University of Oslo; 2020. Available from: https://www.uio.no/english/services/it/adm-services/nettskjema/ .
- 16. The Norwegian Agency for Quality Assurance in Education. The students’ judgement 2018 [09/09/2019]. Available from: https://www.nokut.no/en/news/the-students-judgement/ .
- 18. Rutine for bruk av Zoom i forskningsintervjuer (in Norwegian) Oslo Metropolitian University2020 [10/09/2020].
- 19. Quality Matters online education 2021 [09/02/2021]. Available from: https://www.qualitymatters.org/index.php/ .
- 24. Ministry of Health and Care Services. The primary health and care services of tomorrow–localised and integrated. Oslo: Ministry of Health and Care Services; 2015.
- 27. Hjelsvold R, Lorås M, Bahmani A, Nykvist SS, Krokan A. First impressions from educators as NTNU transitions to an online only mode of learning 2020 [20/02/2021]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/project/Research-on-Learning-Activities-During-the-Covid-19-Pandemic .
- 30. McCartney M. BMJ Opinion2020. [cited 2020]. Available from: https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2020/08/28/margaret-mccartney-we-need-better-evidence-on-non-drug-interventions-for-covid-19/?fbclid=IwAR1jFbFk7lKcrOxIkxo7gaNJM3II6nDia_W6hXs4VWF_DI2vllS9jEqJ-vI .
- 33. University of Antwerpen. The COVID-19 Multi-Country Student Well-being Study Netherlands2020 [29/08/2020]. Available from: https://www.uantwerpen.be/en/research-groups/centre-population-family-health/research2/covid-19-internation/ .
- 34. ClinicalTrials.gov. Assocation Between In-person Instruction and COVID-19 Risk (Campus&Corona) ClinicalTrials.gov2020 [30/8/2020].
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Academic and emotional effects of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic on engineering students
Rosó baltà-salvador.
1 Department of Graphic and Design Engineering, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya C, Colom 11, 08222 Terrassa, Spain
Noelia Olmedo-Torre
2 Department of Graphic and Design Engineering, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Av, Eduard Maristany 16, 08019 Barcelona, Spain
Marta Peña
3 Department of Mathematics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Av. Diagonal 647, 08028 Barcelona, Spain
Ana-Inés Renta-Davids
4 Department of Pedagogy, Universitat Rovira i Virgili Ctra. de Valls, 43007 Tarragona, Spain
Associated Data
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
The unprecedented situation of the COVID-19 pandemic has caused the closure of universities worldwide and has forced the transition to online learning. This exceptional context compels us to understand students' experience with online learning. Previous literature identifies relevant factors that intervene in the online education experience and can affect students' academic development. One of the main concerns is the students' mental health, given the lockdown restrictions under which classes have been conducted. Furthermore, the impact of the prolonged lockdown and the pandemic fatigue on university students and their academic experience is still unclear. This study delves into engineering undergraduate students’ online education experience during the COVID-19 pandemic and its emotional impact across time. With this aim, a questionnaire was distributed to second, third, and fourth-year engineering undergraduate students at two time points, approximately six months apart. The results show significant differences in students' connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, and boredom between time points. Besides, the findings indicate significant correlations between academic development and quality of online classes, adaptation of the course, workspace conditions, and connection with other students and teachers, and also between students' emotions and connection with other students and teachers. Finally, the study identifies best practices carried out during online teaching that will be of value for future courses and engineering education beyond the pandemic situation, amongst which those related to effective communication with teachers stand out.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has posed an unprecedented challenge in education, leading to the suspension of face-to-face teaching (UNESCO, 2020 ). This change has been particularly challenging in university undergraduate engineering degrees since much of the learning process is based on practical applications, laboratory classes, and direct contact with teachers and other students. Being an exceptional and novel situation, the potential impact of the health crisis and the prolonged lockdown on students' academic development and emotional state is still unknown.
Recent work has identified some variables that intervene in the online education process, such as the correct adaptation of teaching to the online format, including classes, assessment methods, and teacher support (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ); the quality of the classes received (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ); the conditions of students' workspace (Gelles et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ); and the connection with other students and teachers (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). However, there is a knowledge gap in how these variables are related to students' academic development and whether having been in a prolonged lockdown might have affected them.
Furthermore, educational and psychological research has raised concerns about students' mental health as they have had to suddenly switch to online learning systems and follow classes under lockdown restrictions. Investigations pointed out that students have experienced an increase in stress, anxiety, and depression (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), and have felt some negative feelings intensified, such as fear, worry, or boredom (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Several studies have highlighted the protective effect that the connection with the rest of the academic community can have on anxiety, depression, and stress (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Although mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic has received much attention in the academic field, studies have focused on analyzing adverse mental states such as depression, stress, or anxiety, but a broader perspective on the emotional state of the students, including a wider range of emotions and considering positive emotions such as calm or trust, is still missing.
Within this context, the present study carried out at the Polytechnic University of Catalonia (UPC), Spain, investigates how the COVID-19 pandemic and the lockdown has affected the academic experience of students and their emotional state across time. Two measurements taken six months apart were compared to detect changes potentially caused by a prolonged public health crisis and lockdown, providing new knowledge about pandemic fatigue in university students. Moreover, we assessed the correlations between the variables related to online education and the academic development of students to understand how the change to online teaching may have affected the performance of engineering students. Also, based on Plutchik’s theoretical framework on emotions (Plutchik, 1994 ), a study has been carried out to understand the impact of the pandemic on students' emotional state and how the connection with other students and teachers can help not only to reduce adverse emotions, but also to enhance positive emotions such as calm or confidence. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on engineering university students have considered such a wide spectrum of emotions and have observed the impact of being in contact with the rest of the academic community on these emotions. Furthermore, our research is novel as it encompasses the different variables involved in online education identified in previous studies, and conducts a longitudinal study to understand the impact of time and pandemic fatigue on these variables and students' academic development. Finally, this investigation identifies best practices carried out during distance teaching that can help improve the online learning experience in engineering studies beyond the pandemic situation.
Understanding the academic and emotional effects of the pandemic on engineering students is essential for several reasons. There is a growing trend for universities to offer online courses. However, in engineering, this transition is still a challenge since traditional engineering studies are based fundamentally on the practical application of scientific and technological principles. The unexpected situation generated by COVID-19 has forced engineering universities to offer their studies online, even for students who would not have proactively chosen to learn online. Therefore, it is an opportunity to analyze students' academic experience in distance engineering studies since they are rarely offered online. This information will contribute to the design of remote engineering courses to make them more accessible. On the other hand, the pandemic's scope during the next few years is unclear, so it is essential to understand its impact on learning to develop support actions for students. Also, all these lessons will be relevant if we face a similar situation that requires the confinement of the population in the coming years.
Impact of COVID-19 on students’ learning experience
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus began in late 2019 and spread around the world rapidly within months (Du Toit, 2020 ; Zhou et al., 2020 ). On March 11th, 2020, The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the public health emergency caused by the new coronavirus an international pandemic. Due to the high transmission rate of SARS-CoV-2, most countries took measures to stop the spread, including the blockade of cities, strict implementation of contact isolation, and strict medical system precaution (World Health Organization, 2021 ). This reduction in population mobility caused higher education institutions to cancel in-person classes and move towards remote learning (UNESCO, 2020 ). In the case of traditional engineering studies, this posed a significant challenge since it is a field in which a large part of the curriculum is based on the practical application of knowledge and relies heavily on face-to-face practical and laboratory classes (Jacques et al., 2020 ). This unexpected change in the teaching format has forced engineering students to adapt to new ways of learning under the conditions of the health crisis, potentially affecting their academic development. Furthermore, while previous research has revealed the impact of online education on those students who proactively chose distance learning, the current pandemic situation allows studying the impact on all students and in degrees that are generally not available online, as it is the case for engineering studies. Due to the exceptional nature of the situation, the effect of online classes derived from the emergence of COVID-19 on students is yet unknown, so work providing empirical data is crucial to understand the scope of its impact and to be able to propose support actions for students.
Although literature is still limited in this regard, several studies have tried to explain the impact of the rapid transition to online models during COVID-19 on students’ academic development. However, the results of these investigations are not homogeneous and show remarkable differences in the results. These variations may be due to the start and end dates of the academic years and school holidays, the timing and impact of the pandemic in each country, and the corresponding measures implemented to manage the health crisis. For example, in some countries face-to-face classes were suspended from the beginning of the pandemic while others were less restrictive and just reduced face-to-face teaching or postponed the beginning of the semester (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ). These contrasts can also be related to other factors like the differences between academic fields, the resources available for students, and the methodologies implemented by teachers during online teaching, among others. This lack of consistency opens the door to new studies that provide complementary evidence which might allow for a better understanding of the impact of online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic on university students from different countries and academic fields.
To study the way in which the lockdown and distance teaching have affected engineering students during the COVID-19 pandemic, it is necessary to identify the variables that intervene in the online educational experience. Previous research in psychology and education has identified four relevant constructs in distance education, which have also received attention in studies on remote education in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
First, previous research on online teaching highlighted the courses’ quality as a significant factor in students’ satisfaction and learning (Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ) and pointed out that the effective switch toward online teaching models is influenced by the perceived quality of the classes (Ibrahim et al., 2013 ). When designing online courses, classes cannot simply be transferred from a face-to-face to an online environment. Content, pedagogy, methodology, and technology need to be adapted for successful online teaching (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ). The quality of online teaching has received considerable attention in studies on the effects of COVID-19 on higher education. In some of the studies conducted during the lockdown, university students reported low satisfaction with the quality of online teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ) and higher learning satisfaction in face-to-face learning than in distance learning (Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ). According to the UNESCO ( 2020 ), this disaffection with the online classes stems from the fact that the content offered was never designed within the framework of a distance course but instead tried to make up for the absence of face-to-face classes with virtual classes without sufficient preparation. However, the results of other studies showed that students were satisfied with the overall e-learning provided thus far in their university studies (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Jacques et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ). More specifically, in a study with a sample that included engineering students, 85% of the respondents indicated that online teaching quality during the COVID-19 pandemic was good or very good (Radu et al., 2020 ). Since the quality of teaching is one of the main constructs in the evaluation of distance teaching, it has been included in this research as a study variable. Also, as there is a lack of consistency in the results of previous studies regarding the satisfaction with the online course’s quality during COVID-19, it is necessary to provide more data from samples of engineering students.
Second, there are considerable differences in results among research regarding specific aspects, such as classes, exams, or teachers’ support, in adaptation to distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, the results differ across the investigations. On the one hand, previous research reported students’ low satisfaction with the support received from their teachers (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ) and less satisfaction with the classes and assessment methods in distance education compared to classroom learning (Linh & Trang, 2020 ). This low satisfaction with how teaching was adapted to the online format is associated with an increase in the perceived workload (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Gelles et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, Khalil et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out that the issues related to the implementation and quality of online courses can become barriers to the engagement and acquisition of knowledge. On the other hand, there are studies in university settings in which students were satisfied with the teacher support received and the content of their online classes during the COVID-19 pandemic (Jacques et al., 2020 ; Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al., 2020 ). Also, in Puljak et al.’s ( 2020 ) investigation, students reported that the assessment methods and materials used in their classes during the lockdown were tailored to e-learning. Similar to the courses’ quality, current studies show contradictory results regarding student satisfaction on how their courses were adapted to the remote format. Moreover, adaptation to online teaching was a highly discussed construct during the COVID-19 health crisis due to the short time in which classes, evaluation methods, and teachers' support and guidance had to be readjusted to the online format (UNESCO, 2020 ).
Third, another major challenge on distance education are the feelings of isolation and disconnection in online courses due to lack of face-to-face contact with other students and teachers (Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ). Numerous studies prior to the COVID-19 pandemic indicated that interactions with other students and teachers were essential for student satisfaction and played a decisive role in academic development and students’ achievements (Arbaugh, 2000 ; Hong, 2002 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ). Hence, when designing online courses, the interaction mechanisms must be considered to offer enriching and thriving learning environments. Concerning the perceived connection with other students and teachers during the lockdown, previous research indicated that students felt less connected with fellow students and teachers than in face-to-face education (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Overall, university students indicated that they have missed in-person contact with other students and professors during the lockdown (Puljak et al., 2020 ) and that communication has been more complicated than in face-to-face education (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). In Elmer et al. ( 2020 ) investigation on students enrolled in engineering and natural science programs, students reported fewer study partners and felt significantly more socially isolated. Also, in the study by Tang et al. ( 2020 ) on undergraduate students from engineering majors, almost 70% thought that they had not communicated often with their teachers from the online courses during the pandemic. This lack of contact is worrisome since social contact and socialization routines are part of the daily experience of higher education students and can affect their academic development (UNESCO, 2020 ). In the context of online classes during the pandemic, a greater connection with the community has been related to greater self-efficacy and engagement and lower academic stress (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Connection with fellow students and teachers is one of the variables that has received the most attention in the academic community concerning the experience in online education. Social isolation of students during the pandemic has further increased the importance of this factor and hence, we have included connection with other students and teachers as a variable in this study.
Finally, although it had not received much attention in distance education literature before the pandemic, learning environment conditions, its ergonomics, and access to a quality internet connection are additional and indeed important variables to consider in distance learning. A workspace that does not offer the appropriate conditions represents a risk factor for comfort, well-being, and students’ academic performance (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Parvez et al., 2019 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). The unexpected change to online education due to the COVID-19 pandemic has made researchers and academic staff wonder whether students were prepared to take classes from their home and whether they had an adequate workspace, equipment, and facilities for effective learning. In addition, the lockdown situation has prevented students from going to libraries or study halls and, in many cases, has forced family members to share the spaces of their houses, which might have worsened student workplace conditions by increasing noise and distractions (Driessen et al., 2020 ). In several studies, university students reported that their home has been a distractive environment and mentioned that they were more prone to be interrupted by roommates or family members (Gelles et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Moreover, Realyvásquez-Vargas et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out that environmental factors such as noise, temperature, and lighting had a significant effect on university students’ academic performance during online classes in the pandemic context. These issues were associated with more difficulties in focusing and concentrating while learning (Amir et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ) and can become a barrier to the acquisition of knowledge through online courses (Khalil et al., 2020 ). Another drawback identified in online classes during the pandemic has been inadequate internet access (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ). Several studies have reported that a significant percentage of university students, especially those from disadvantaged families, have had problems accessing internet services (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ). Due to the unexpected lockdown situation and the rapid transition to online learning, students did not have time to adapt their workspace, which may have had an impact on their academic development. Thus, we included workspace conditions as a variable for this study.
All these factors should be considered when designing online courses to avoid detrimental effects on students’ academic development (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). Numerous studies predicted that the change in teaching methods during the pandemic affected students’ academic development and their outcomes, although the results are inconsistent. Some of the studies have shown that confinement had positively affected students’ academic performance and their learning efficiency (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ). The study by Jacques et al. ( 2020 ) carried out with engineering students showed that distance learning did not reduce students’ performance and that the grades obtained were similar to those expected in face-to-face teaching. Contrarily, previous research revealed that students perceived worse performance upon face-to-face classes being canceled (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ) and showed concerns about the negative impact that the pandemic situation will have on their academic outcomes (Nassr et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). The study by Hamann et al. ( 2020 ) suggested that students who followed the course entirely online were significantly less likely to be successful than students who also, or exclusively, attended face-to-face courses during the pandemic. Furthermore, Tang et al. ( 2020 ) indicated in their study during the COVID-19 lockdown that students felt generally dissatisfied with the effects of online engineering courses on their learning.
Based on these assumptions, we expect to find a positive correlation between students' academic development with the variables of quality of teaching, adaptation of the classes to the online format, connection with other students and professors, and workspace conditions (Hypothesis 1). Since many of the studies done so far in the context of the pandemic have identified these variables separately, few correlational studies have analyzed their associations and identified the factors that may have had the greatest impact on students' academic development during COVID-19. Knowing how the variables related to the online experience have affected the performance of the students will allow us to identify relevant points that should be considered in the design of online courses. To complement this information, we also identified the best practices carried out by instructors in online teaching during the pandemic that have helped students transition to this new learning environment. This information can help instructors and institutions improve online teaching beyond the pandemic situation. This approach is aligned with the conclusions of Anderson et al. ( 2011 ), which showed that receiving feedback from students about the online lessons is vital to improve the courses offered.
Emotional effects of COVID-19
Studies before the COVID-19 pandemic already reported the negative psychological effects that lockdown can cause on people (Blendon et al., 2004 ). Quarantine is often described as an unpleasant experience for those who suffer it, and can involve uncertainty about the situation and boredom (Brooks et al., 2020 ; Cava et al., 2005 ). It is also associated with significant psychological distress, depressive symptoms, post-traumatic stress, and aversive emotional states such as anger, confusion, anguish, disgust, fear, or nervousness, among others (Brooks et al., 2020 ; Hawryluck et al., 2004 ). In the studies carried out during the COVID-19 lockdown, university students reported negative effects on their mental health and emotions. Generally, students have experienced an increase in their stress, anxiety, and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Besides, they reported feeling some negative emotions intensified, such as fear, worry, or boredom (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ).
Despite the proven adverse effects that lockdown can have on people, in cases like a public health emergency due to an infectious disease, imposing measures on the population to stop the spread of such disease is needed. Studying which elements can minimize the negative impact and aversive feelings during isolation are of great importance in this context. Some studies have indicated that contact with the academic community can act as a protector and decrease the negative impact of lockdown on students’ mental health (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Others have shown that the lack of relationships and connection with other students and teachers is associated with an increase in academic stress (Zurlo et al., 2020 ).
Most studies during the COVID-19 pandemic on the emotional state of university students have only analyzed negative emotional states such as anxiety, stress, or depression. However, there is a lack of research with a more global perspective on the emotional state of university students that also includes positive emotions to study whether these have decreased during the pandemic. In the study of emotions, psychological theories have proposed some dimensions to measure people’s emotional state, although they have hardly been contemplated in studies on the emotional impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. One of the best known and widely used is Plutchik’s ( 1994 ) theory, which presents eight emotional dimensions in opposite pairs. Compared with other theories such as Ekman ( 1992 ) or Parrot ( 2001 ), Plutchik’s framework is well-founded in psychological studies, presents a good balance between positive and negative emotions, and offers a broader subset of emotional dimensions (Wang et al., 2019 ), the aforementioned reasons being why it has been used as a reference to measure the emotions of the students in this study.
Based on the results of the previous literature, we hypothesize that there is an association between the perceived connection with other students and teachers and the emotional state of the students, so a greater connection with other students and teachers will be associated with a decrease in negative emotions and an increase in positive emotions (Hypothesis 2).
Effects of pandemic fatigue
One of the great unknowns related to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic are the effects of a prolonged lockdown situation. The entire world population has been exposed to a state of exceptionality generated by the COVID-19 pandemic that has required the implementation of invasive measures with unprecedented impact on daily lives. When these measures are prolonged for an extended period of time, it can cause what is known as pandemic fatigue, which is the mental exhaustion caused by a public health crisis and the restrictions derived from it. This state can affect the mental health of those who suffer it, causing boredom, demotivation, alienation, and hopelessness (World Health Organization & Regional Office for Europe, 2020 ). Given the unusual nature of the situation, the literature on the impact of the pandemic and the lockdown implemented is still limited, and there is little evidence to indicate whether the academic and psychological effects of lockdown are greater at the beginning of the pandemic because of the uncertainty of the situation or may become more significant as the pandemic continues due to the feeling of burnout during the prolonged lockdown (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). Additionally, most longitudinal studies in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic in university students assessed only the psychological impact, so more research is required to analyze the academic impact. As Odriozola-González et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out, more longitudinal studies are needed to analyze the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and to draw conclusions about the cause and effect relationships between the variables involved.
In the current literature there is substantial debate about the detrimental effects of pandemic fatigue. In particular, there are two major views: some longitudinal studies supported the theory that adverse effects have intensified as time in lockdown increased and showed significant increments in negative symptoms such as depression, anxiety, or stress (Ausín et al., 2021 ; Cecchini et al., 2021 ; Gopal et al., 2020 ). In contrast, other studies argued that the effects did not increase over time and, in any case, were are greater at the beginning of the pandemic due to uncertainty and fear of the unknown situation (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). Regarding this theory, the study by Ramos-Morcillo et al. ( 2020 ) identified two phases as a pandemic progresses. The first is the so-called shock phase, which occurs during the first weeks, and disorientation and mental performance decreases, along with the ability to concentrate. The second is the normalization phase, in which conditions of confinement start to be assimilated, and the new everyday life is normalized. Thus, based on this second theory, we hypothesize that there is an association between time in lockdown and academic experience, and students will have a worst online learning experience at the beginning of lockdown (Hypothesis 3). We also expect an association between the time in lockdown and students’ emotional state, and we hypothesize that negative feelings will be greater at the beginning of lockdown, and positive feelings will be greater as time progresses (Hypothesis 4). Knowing when the impact of a confinement situation or health crisis is greater and which feelings increase over time will help to develop support plans for students and plan corrective measures in similar situations like climate, political, or security crises that can restrict people’s movement and prevent regular university access.
Context of the current study
In the current study carried out at the UPC, we made two measurements at different time points and compared data collected in spring and fall semesters, 2020, to evaluate the effects of prolonged lockdown and pandemic fatigue on the educational experience and emotional state of engineering students. Regarding the restrictions derived from the pandemic in Spain, the first state of alarm was decreed on March 14th, and the free movement of citizens was limited to essential activities resulting in the confinement of the population in their places of residence and the suspension of face-to-face education. Consequently, educational institutions had to switch the teaching to the online format, and many held the classes and academic activities remotely until the end of the course in June 2020. Due to the increase in cases, on October 16th, all face-to-face activity in universities was suspended again, although many higher education institutions had already started the academic year online after the summer. On October 25th, after exceeding half a million infected countywide, the second state of alarm was established to face the pandemic’s second wave. In this case, a curfew was imposed between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m., and later the population was confined again in their municipalities and social gatherings were restricted.
Participants
The participants of this study were students enrolled in the second, third, and fourth-year of the Bachelor’s Degree in Industrial Design and Product Development Engineering. First-year students were excluded from the sample due to the short time they had been in engineering studies and the inability to compare the impact of the lockdown on their academic activity with previous courses. All students enrolled in the other three courses were invited to participate, that is, a total of 339 students, 168 at Time 1 (T1) and 171 at Time 2 (T2). The required sample size calculated based on a confidence level of 95% and a margin of error of 5% was 181 students for the total sample, 119 for each measurement. Finally, a total of 254 students participated in the study, 122 at T1 and 132 at T2, so the study sample meets the intended size. Participants were self-selected and no incentive was given to students to participate in the study. The protection of personal data was duly taken into account, ensuring that all recipients agreed to receive communications. Both anonymity of the participants and confidentiality of the data to be collected were guaranteed. Data did not include personal characteristics of the students. Table Table1 1 shows the academic year and the conditions in which the participants took the online classes during the pandemic, type of residence and workspace conditions.
Academic course and lockdown conditions of the participants
Due to the exceptional nature of the situation a questionnaire was designed for this study with measures derived from previous literature and adapted to fit the research context. In previous investigations on the impact of online teaching on students' academic experience during the COVID-19 pandemic, these constructs were measured using questionnaires addressed to students. In these questionnaires, students were asked about their perception of the quality of teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ), the adaptation of classes to the online format (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al., 2020 ), the perceived connection with other students and teachers (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ), their workspace conditions (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Driessen et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Realyvásquez-Vargas et al., 2020 ), and the impact on students' academic development (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Realyvásquez-Vargas et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ). These investigations have been used as a foundation to build the measuring instrument for this study.
The quality of the online classes that students received during the lockdown was assessed with a 4-point scale (1 = Very bad to 4 = Very good). To measure students’ perceptions about the adaptation of the course to the online format, a set of 4 items was designed (α = .76) rated on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). Students were asked to indicate if the classes and the assessment methods had been adapted correctly to the online format, if they had been able to follow the course correctly, and if they had received the necessary support from teachers. To assess the level of connection that students felt with other students and teachers a set of 4 items was designed (α = .65) rated on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). Students were asked to indicate if they felt connected with other students and teachers and if they had missed having contact with fellow students and teachers. To measure the workspace conditions, students were asked about the place and the type of room from where they followed the online classes with two multiple-choice questions of three options each (e.g., from a student flat) and an open field. Students also had to indicate if their workspace conditions had been suitable on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). To determine how students perceived the impact of the switch to online classes on their academic development, they were asked to rate on a 3-point scale (1 = It has worsened to 3 = It has improved) if they believed that their academic development had been affected by online teaching.
To measure the emotions students felt during online classes while they were in lockdown, a measure based on Plutchik’s ( 1994 ) wheel of emotions was designed using a multiple-choice question. Students were asked to select their feelings during the lockdown from 8 options adapted from Plutchik’s classification.
Finally, an optional open question was added in which students could share if there was something that teachers did during the online teaching that helped them especially.
For the present study, students completed the exact same questionnaire at two points, approximately six months apart. The first time the questionnaire was distributed was on June 3rd, 2020 (T1), during the spring semester and almost three months after the first lockdown was established and all classes went online. Consequently, students had a reasonable exposure to the online learning experience and the lockdown to answer the questionnaire. The second measurement was made in the fall semester on November 18th, 2020 (T2), approximately one month after the second state of alarm was decreed and the new lockdown was applied to face the second COVID-19 outbreak. Therefore, both measurements were made while students were taking classes online.
The questionnaire, which was anonymous and drawn up using Google Forms, was sent by email together with a motivational letter explaining the purpose of the study. Both times, students had up to 1 week to complete it, and took approximately fifteen minutes to finish. Participants were recruited via email messages sent by the authors of this research and faculty members, and were encouraged to answer all the questions accordingly to their opinions. Before being sent, the questionnaire was submitted to a validation process to identify whether it omitted some question areas, determine whether the questions were clear and well-formulated, and detect possible errors in its preparation.
No outliers were identified, and no missing values were found either since all the questions in the questionnaire were mandatory. Descriptive statistics and frequency analyses were applied to characterize the sample. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used to test the first hypothesis on how the variables related to the online academic experience affected students' academic development. Although the intercorrelations were calculated between all the variables of the online academic experience, the analysis was done using academic development as the independent variable and the variables of connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, quality of online classes, and adaptation of the course as dependent variables. To evaluate our second hypothesis about whether the connection with other students and teachers can affect students' emotional state, a Chi-Square Test for Independence was performed using connection with other students and teachers as the independent variable and emotions as the dependent variables. To fulfill the assumption concerning the minimum expected cell frequency, the measure of connection with other students and teachers was transformed into a dichotomous variable combining the negative and positive values, respectively. To assess our third hypothesis on how the time in lockdown affected the academic experience of the students, we performed a Mann-Whitney U Test using the time in which the measurements were made as the independent variable and the variables of academic development, connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, quality of online classes, and adaptation of the course as dependent variables. Since the emotion variables were dichotomous, for the fourth hypothesis about how time in lockdown affected the emotional state of the students, a Chi-Square Test for Independence was carried out using the time in which the measurements were taken as the independent variable and the different emotions as dependent variables. In the analyzes, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and the effect size was assessed using Cohen’s ( 1988 ) criteria. For the qualitative data, an abductive methodology was used to identify the codes. First, half of the dataset was analyzed, and a preliminary code list was obtained. Next, the entire dataset was processed with the identified codes, and the rest of the codes emerged from the data iteratively, adding new codes if practices not identified in the preliminary list were found.
Descriptive analyses indicated that about half of the students reported that the quality of the online classes received during the pandemic was bad or very bad (T1 = 54.1%, T2 = 46.2%), and more than a half thought that their academic development worsened during online classes compared to face-to-face classes (T1 = 66.4%, T2 = 68.9%). Also, more than half of the students indicated that their workspace conditions had been adequate, especially at T2 (T1 = 58.2%, T2 = 73.5%). Regarding the single items that compose the variable adaptation of the course variable, over half of the students reported that classes were correctly adapted to the online format (T1 = 57.4%, T2 = 68.2%) and that the evaluation methods were also properly adapted (T1 = 56.6%, T2 = 54.5%). Furthermore, the majority indicated that they had been able to follow the course correctly (T1 = 63.9%, T2 = 78.8%) and had the necessary support from teachers (T1 = 57.4%, T2 = 67.4%). Remarkable differences can be observed between the two time points regarding the 4-items that compose the variable connection with other students and teachers. Students felt less connected to other students and teachers in T2 than in T1 (T1 = 67.2%, T2 = 27.3%; and T1 = 51.6%, T2 = 40.1%; respectively) and the vast majority missed having contact with other students and teachers (T1 = 82.0%, T2 = 95.5%; and T1 = 81.1%, T2 = 91.7%; respectively).
As shown in Table Table2, 2 , the workspace conditions in which students took the online classes improved significantly from T1 to T2 with a small effect size. On the other hand, the perceived connection with fellow students and teachers worsened significantly from T1 to T2 with a medium effect size, so that in T2 they felt less connected with other students and teachers. Although the quality of online classes and the adaptation of the course improved at T2 compared with T1, no significant differences were found.
Descriptive Statistics and Mann-Whitney Test at Time 1 and Time 2
At both times, correlations between academic development and quality of online classes and adaptation to the course were relatively high and positive with a medium effect size (see Table Table3). 3 ). Also, the workspace conditions had a positive significant correlation with academic development with a small effect at T1 and T2. Therefore, those students who perceived a better quality and adaptation of the online classes and had better workspace conditions were those who reported a better academic development. On the other hand, academic development had a significant positive correlation with connection with other students and teachers with a small effect size at T2, the time point when they felt more disconnected with fellow students and teachers.
Intercorrelations for Study Variables at Time 1 and Time 2
The results for the Time 1 sample ( n = 122) are shown above the diagonal. The results for the Time 2 sample ( n = 132) are shown below the diagonal
* p < .05; ** p < .01; *** p < .001
As illustrated in Fig. 1 , the emotions that students felt the most during the lockdown were discouragement (22.6% T1, 23.0% T2), boredom (T1 = 17.5%, T2 = 21.8%), confusion (T1 = 18.3%, T2 = 15.7%), worry (T1 = 15.4%, T2 = 14.3%), and annoyance (T1 = 10.8%, T2 = 10.3%). Contrary, the least common were vigilance (T1 = 8.2%, T2 = 7.3%), calm (T1 = 5.7%, T2 = 6.1%), and trust (T1 = 1.5%, T2 = 1.6%). Regarding the differences between T1 and T2, students felt slightly less worried and confused at T2, although no statistically significant difference was found (X2 (1, N = 254) = 0.12, p = .728, phi = -.030; and X2 (1, N = 254) = 1.13, p = .288, phi = -.075; respectively). Besides, they felt more bored at T2 than T1, with a statistically significant difference (X2 (1, N = 254) = 5.30, p = .021, phi = .153) with a small effect.

Changes in Students’ Emotions between Time 1 and Time 2
As shown in Table Table4, 4 , a significant association with small effect was found between the connection with other students and teachers and the emotions felt by the students, with the exception of boredom, which did not present significant differences. Those students who felt more connected with other students and teachers were more likely to feel calm and trust. Otherwise, those students who felt more disconnected were the ones who felt more worry, confusion, discouragement, annoyance, and vigilance.
Chi-Square Results for Connection with Other Students and Teachers in Students’ Emotions
The open question regarding best practices carried out during the online teaching received 117 responses, 63 from T1 and 54 from T2. From these responses, 21 best practices were identified, plus the “other practices” code (Table (Table5). 5 ). As some answers referred to more than one code, the total number of best practices identified ( n = 182) is greater than the total number of responses. The codes were classified into four categories: communication, classes, course adaptation to the online format, and teachers.
Best Practices in Online Teaching During COVID-19 Lockdown
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a global change in educational systems, forcing the transition from face-to-face to online learning due to the restrictions and lockdowns imposed in most countries. This study has examined university engineering students’ academic experience and the emotional impact of online education during the COVID-19 pandemic using a longitudinal approach. The results provide novel information and extend prior research on the impact of distance education during the COVID-19 lockdown on engineering students.
Effects of the prolonged lockdown on students’ learning experience
The majority of students in our sample reported that their academic development worsened during online learning, and a high percentage considered that the online teaching they received was of a bad quality. Therefore, students have perceived a negative impact regarding the change to online teaching during COVID-19 in their academic experience, especially in their academic development and the quality of the teaching they have received. These findings are consistent with some studies on university students during the COVID-19 pandemic regarding the quality of teaching received (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ) and the impact on students’ learning outcomes (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Nassr et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ). As UNESCO ( 2020 ) has pointed out, this may be because the change towards online learning has been sudden and consequently the content offered in the classes was not designed to be taught in an online course and online classes were given with limited preparation.
Contrary to our hypothesis (Hypothesis 3), there are no significant differences between T1 and T2 regarding the quality of online classes, the adaptation of teaching to the online format, and the academic development of students. However, we observed a slight increase in the perception of the online classes’ quality and the adaptation of the course, though this difference is not statistically significant. These results suggest that although there may have been an improvement in some aspects of teaching, probably due to enhancements introduced by teachers in the subjects after the first months of the pandemic, these have not been enough to make a significant change in students’ perception. On the other hand, our data show significant differences between T1 and T2 on the workspace conditions and the perceived contact with fellow students and professors. The conditions of the workspace have significantly improved as time progressed in lockdown. This result suggests that students, foreseeing that the new course would also be online, prepared their workspace conditions to suit their needs. As UNESCO ( 2020 ) argues, student's expectations differ if they expect to enroll from the beginning in a distance course or a regular course. So, it is relevant that academic institutions inform students in advance on possible changes in teaching, so that they can adapt their expectations and prepare properly. Contrary to what was expected, the perception of connection with other students and teachers is significantly lower at T2, so the feeling of isolation worsens significantly as the time in lockdown passes and online classes become regular. Students who reported having missed the contact with other students at T2 reach 95.5% and with teachers 91.7%. Similarly, previous studies have highlighted the lack of social contact and the feelings of isolation and disconnection during the COVID-19 lockdown (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Elmer et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). These studies indicate that students have felt less connected to the academic community than in face-to-face teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Our findings reveal that not only do students feel less connected to their peers and teachers in online learning compared to face-to-face classes, but also that this feeling increases as time in lockdown lengthens. This finding reaffirms the importance of social contact and communication mechanisms in online education and suggests that if these mechanisms are not properly implemented in the online education systems, the lack of social contact and its negative effects on students’ educational experience may get worse (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ).
The results of this study indicate that the effects of the prolonged lockdown may impact differently on the variables involved in the online educational experience, and raise new hypotheses regarding the impact of a prolonged lockdown. On the one hand, the impact on variables related to pedagogical aspects of online teaching, such as quality and adaptation of the course, may be more negative at the beginning of the pandemic due to the uncertainty of the situation (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ; Ramos-Morcillo et al., 2020 ). However, these aspects may improve as time passes due to teaching improvements on the online practices and students’ preparation of their workspace environment foreseeing that they will continue the classes remotely (Scull et al., 2020 ). This hypothesis is supported by studies such as Van Nuland et al. ( 2020 ), which indicates that many teachers have been asked, almost overnight, to implement classes remotely in response to the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many of these teachers had no or little prior experience in online teaching and that they lacked the pedagogical content knowledge needed for online teaching. As the pandemic has progressed, teachers and universities have been adapting and have implemented several innovations to improve the online teaching experience of students (Scull et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the variables related to the social aspects of the academic experience, such as the contact with other students and teachers, may be negatively affected by the feeling of burnout as time in lockdown passes (Ausín et al., 2021 ; Cecchini et al., 2021 ; Gopal et al., 2020 ). As other studies have reported, the lockdown situation has triggered the feeling of isolation and disconnection of students (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), feelings already identified in pedagogical research on the challenges of e-learning (Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ). Understandably, this feeling strengthens while students remain locked in their homes, and as the time without seeing their classmates and teachers increases. Therefore, it will be crucial for academic institutions and faculty members to put mechanisms in place that help students feel connected to each other and to their teachers, such as discussion forums or instant messaging channels (Moorhouse, 2020 ; Rosenberg & Asterhan, 2018 ). The study by Scull et al. ( 2020 ) shares some learnings from universities and teachers that might help strengthen the connection and communication with students during the pandemic, such as providing channels through which they can ask for help or by opening the debate to more personal day-to-day issues to relax the atmosphere and enhance engagement.
In line with what was predicted in our first hypothesis (Hypothesis 1), we find significant relationships between academic development and the rest of the variables related to the online academic experience of students. Specifically, students’ academic development is associated with the quality of the classes received, the adaptation of the courses to the distance format, and the workspace conditions. Also, a positive correlation was found in T2 between students’ academic development and contact with other students and teachers. Previous literature already pointed out the relationship between the variables studied and the academic development of students (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). In this line, our results confirm these relationships between the variables under the conditions of a pandemic and lockdown in engineering students. Considering the direction of the correlations, offering students classes of high quality, adapting the class contents, assessing teaching methods properly, and giving support from teachers to the online format relate to a better academic development. Therefore, it is important to offer teachers training and pedagogical tools needed to provide adequate distance teaching (Van Nuland et al., 2020 ). Moreover, having better workspace conditions can enhance students’ academic development. In this regard, academic institutions can ask students about their conditions and offer support, for example, temporarily borrowing computers from the university or granting access to online learning platforms through mobile phones (UNESCO et al., 2020 ).
Furthermore, previous literature has focused on the positive effects that contact with teachers and other students can have on academic development, such as greater self-efficacy and learning engagement, and less academic stress (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Our study suggests that having good connections with other students and teachers is not necessarily associated with academic development (as observed at T1), but if this lack of contact is extended in time (as observed at T2), it may negatively impact students’ academic development. This new finding supports the previous observation that it is necessary to work on the relationships between students themselves and with their teachers in online learning; otherwise, if these connections are lacking, it may have a negative effect on the educational experience and students’ outcomes.
Emotional impact of prolonged lockdown
Students’ most-reported emotions during the lockdown are discouragement, boredom, confusion, and worry, all of them negative emotions. On the contrary, those less prevalent are the positive emotions of calm and trust. Despite previous articles mainly focusing on negative emotions (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), future studies on students’ mental health should also include positive feelings to understand to what extent these decrease due to the pandemic situation. Assessing positive feelings during a public health crisis is essential as it has been shown that positive emotions can help maintain and improve human mental health (Yamaguchi et al., 2020 ). Thus, using a theoretical framework as Plutchik's ( 1994 ), which includes a broad subset of emotional dimensions, can give a more detailed picture of the emotional state of students and can help detect which feelings teachers and academic institutions need to reinforce, such as students' confidence and calm. Based on this information, institutions can work on messages and communications towards their students to counteract the emotional impact and enhance these positive emotions (Heffner et al., 2021 ).
Contrary to what was expected regarding the differences in the emotional state of the students as the lockdown elapses (Hypothesis 2), most emotions do not show significant changes from T1 to T2. However, worry and confusion are less reported in T2. The fact that students feel more concerned and confused at the beginning of confinement is aligned with the phases of the pandemic identified by Ramos-Morcillo et al. ( 2020 ), in which there is a first phase when disorientation prevails due to the novelty of the situation and a second phase as time progresses when the situation is assimilated and normalized. The only emotion that shows a significant increase from T1 to T2 is boredom, a feeling also present in other studies in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Although this result is not consistent with our hypothesis, it is aligned with the effect of mental exhaustion and demotivation the WHO ( 2020 ) claims that pandemic fatigue can cause. These results suggest that burnout does not affect all emotional states in the same way, and while some may not increase as time progresses or even decrease, such as worry or confusion, others such as boredom may increase (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). This information is relevant for teachers and academic institutions to understand how their students feel in each phase of the pandemic and to adapt the type of support provided at each moment.
In line with hypothesis 4 and the results of prior research (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ), the connection with other students and teachers is correlated with students’ emotions. As expected, connection with others acts as a protector and, as the perception of contact with the academic community increases, the negative feelings of worry, confusion, discouragement, annoyance, and vigilance decrease. Besides, it has also been found that contact with fellow students and teachers is positively associated with the feelings of calm and trust, which suggests that social contact is not only a protector against negative emotions, but that it can also enhance positive emotions. Since positive emotions are the least reported by students during the lockdown, it is essential to identify which actions can enhance these emotions to improve students' mood. This finding reinforces the need to create alternative ways to stay in contact, so students can feel more connected with their classmates and teachers. Fostering social contact and communication will improve students’ mental health during online learning in the public health crisis and, as indicated by other studies, even beyond the pandemic situation (Holen et al., 2018 ).
Best practices in online teaching
In addition to validating the hypotheses raised, this study explores best practices carried out by the teaching staff during distance classes that have helped engineering students during online teaching. Although these practices have been identified in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic during the lockdown, they can also be initiatives of interest for regular teaching in university studies or in the design of online courses beyond the pandemic. Concerning the communication between students and teachers, the two most mentioned communication channels are instant messages and emails. Students have highly appreciated those teachers who have opened instant messaging channels such as WhatsApp to communicate with them in a faster and more accessible way. During the classes, the practice that helped students the most was the recording of the online classes allowing students to review them later. Besides, individual or small group video calls with the professor to clarify doubts more closely and in a more comfortable environment were also highly appreciated. Regarding the course adaptation, the two most relevant initiatives have been sharing problems already solved so students have guidelines to self-correct their exercises and sharing support videos with complementary explanations to the subjects’ content. Finally, it was highly appreciated that teachers gave quick answers to students’ questions and that they had a supportive attitude and were attentive to students’ needs. Some students reported on teachers having asked them for feedback to know how they were doing and improve their classes accordingly. Previous research has already highlighted the importance for teachers of receiving feedback from students in order to improve teaching (Anderson et al., 2011 ). The results of our study suggest that the benefits of the feedback are bi-directional, and it is not only helpful for teachers, but also makes students feel heard and valued. Previous research indicates that communication between students and teachers can be more complicated online than in face-to-face teaching (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). Our study supports this claim, showing that most of the outstanding initiatives have been those practices that allowed students to solve their doubts more efficiently, such as faster communication methods, individual or small group tutoring sessions or having problems already solved in order to self-solve possible doubts autonomously. Although other studies already identified some of the initiatives undertaken by teachers to improve the experience during online teaching (Scull et al., 2020 ), our work collects those practices most valued from the students’ perspective and the ones that have been most helpful for them.
Limitations and future directions
The results of this study should be interpreted in the context of some limitations, which can be addressed in future research.
The study was conducted during an exceptional public health crisis, so it is not easily replicable. Also, the results of this study are influenced by the actions to face the COVID-19 pandemic taken by both the state and local governments and the academic institution in which the study was carried out. The measures adopted by the different countries and universities have differed, adapting them to the possibilities and characteristics of each case (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ). These differences may make the results of this study difficult to extrapolate to other countries or university degrees in which different solutions to the COVID-19 crisis have been implemented. For this reason, while it is expected that some of the results may be of value beyond the pandemic situation, it will be necessary to validate their applicability in other contexts.
Participants of this research were recruited from second, third and fourth year from a specific engineering degree, so the lack of random sampling and the representation of a student population limited to one engineering degree seem to be a limitation in generalizing the results to all engineering studies or all academic courses. As the field of engineering is vast and there are many different specializations, it would be interesting to expand the study and validate the results in other engineering degrees and in other courses. For example, the academic experience of first-year students who have started their studies in a pandemic situation may be different from those students from second, third and fourth year. It would also be interesting to extend the sample to other universities and countries since the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has not been the same everywhere. Furthermore, we have only included students in the study sample and not teachers. Perspectives of teachers regarding the switch to online learning would be valuable and should be explored in future studies. The samples of this study have been treated as independent. However, since it is a longitudinal study, it would be interesting to validate the observations with paired samples to compare the changes between time points on an individual basis.
Regarding the instruments used in the research, one limitation is that we created a new questionnaire for this study. Although the questions are based on previous studies, we could not find a similar questionnaire in the literature that incorporated all the measurements. Also, the reliability value of the scale used to measure the contact with other students and teachers is a bit low (α = 0.65) although Cronbach’s alpha is quite sensitive to the number of items in the scale, and short scales often have low Cronbach alpha values. Future research should validate these results and the instrument used and expand the number of items of the proposed scales to improve the scale’s reliability. Moreover, we did not collect participants’ personal data, such as gender or demographic information to preserve participants’ anonymity and favor the predisposition of students to answer the questionnaire.
As the study was conducted using a questionnaire, the results studied are based on students’ perceptions. However, perceptions do not always match reality. For example, while in our study students indicated that their academic development worsened during online teaching, the study of Jacques et al. ( 2020 ) found no differences between the grades of engineering students in online education and those expected in a face-to-face teaching. Thus, it would be interesting for future research to compare students’ perceptions regarding their academic development with their academic qualifications to validate the impact of the lockdown and distance classes on students’ outcomes. Also, we phrased the questions to collect the opinion of students regarding the majority of teachers and courses. We acknowledge that they may be differences between different teachers and courses that may impact individual experiences. However, we were interested in analyzing overall collective students’ opinion towards the online learning experience.
Despite these limitations, the results of this study offer valuable information on the academic and emotional effects that online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic had on engineering students and raises new hypotheses which can be examined in more detail in subsequent work. Moreover, a more specific analysis can be carried out to know how much of the variance in academic development can be explained by the quality of the classes, the adaptation of the teaching to the online format, the conditions of students’ workspace and the connection with other students and teachers.
Conclusions
The findings of this study highlight that the majority of students were not satisfied with the quality of their online education enforced during the lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and that they believe that it has negatively affected their academic performance. Moreover, students' academic development is correlated with the quality of the teaching, the adaptation of the assignments, workspace conditions, and the contact with other students and professors. Regarding their emotional state, students reported feeling discouragement, boredom, confusion, and worry to a greater extent, and calm and trust to a lesser extent. Except for boredom, all emotions are associated with the connection with classmates and teachers perceived by students, hence the students who have perceived a higher level of connection are those who reported more positive emotions and less negative ones. Additionally, we find significant improvements as time in lockdown elapsed regarding the students’ workspace conditions, while perceived contact with other students and teachers and boredom worsened significantly as the pandemic progressed. These results indicate that it is necessary to consider how the courses should be adapted to the online format since their quality and their correct adaptation will have an impact on the students' academic development. Furthermore, it is essential to work on connection and communication mechanisms among students and between students and teachers since these can improve students’ emotional state. These conclusions, along with the good practices that teachers have carried out during online classes in the pandemic and that we have identified in this study, will hopefully help in the design of future online courses and in the implementation of support plans to improve the student learning experience and their emotional state.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all the students from the Bachelor's Degree in Industrial Design and Product Development Engineering of the UPC who took part in answering the questionnaire and the teachers who facilitated the distribution of the questionnaire.
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization, R.B.-S.; Methodology, R.B.-S., N.O.-T. and M.P.; Software, R.B.-S and A.-I.R.-D.; Validation, N.O.-T. and M.P.; Formal analysis, R.B.-S and A.-I.R.-D.; Investigation, R.B.-S.; Resources, N.O.-T. and M.P.; Writing—original draft preparation, R.B.-S., N.O.-T., M.P. and A.-I.R.-D.; Writing—review and editing, R.B.-S, N.O.-T., M.P. and A.-I.R.-D.; Supervision, R.B.-S., N.O.-T. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
The participants have consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Rosó Baltà-Salvador, Email: [email protected] .
Noelia Olmedo-Torre, Email: [email protected] .
Marta Peña, Email: [email protected] .
Ana-Inés Renta-Davids, Email: [email protected] .
- Al-Balas M, Al-Balas HI, Jaber HM, Obeidat K, Al-Balas H, Aborajooh EA, Al-Taher R, Al-Balas B. Distance learning in clinical medical education amid COVID-19 pandemic in Jordan: Current situation, challenges, and perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :341. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02257-4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alnusairat, S., Al Maani, D., & Al-Jokhadar, A. (2020). Architecture students’ satisfaction with and perceptions of online design studios during COVID-19 lockdown: the case of Jordan universities. International Journal of Architectural Research , ahead - of - p . 10.1108/ARCH-09-2020-0195
- Amir LR, Tanti I, Maharani DA, Wimardhani YS, Julia V, Sulijaya B, Puspitawati R. Student perspective of classroom and distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in the undergraduate dental study program Universitas Indonesia. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :392. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02312-0. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson D, Imdieke S, Standerford NS. Feedback Please: Studying Self in the Online Classroom. International Journal. 2011; 4 (1):3–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arbaugh JB. Virtual Classroom Characteristics and Student Satisfaction with Internet-Based MBA Courses. Journal of Management Education. 2000; 24 (1):32–54. doi: 10.1177/105256290002400104. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aristovnik A, Keržič D, Ravšelj D, Tomaževič N, Umek L. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on life of higher education students: A global perspective. Sustainability. 2020; 12 (20):8438. doi: 10.3390/su12208438. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aslan I, Ochnik D, Çınar O. Exploring perceived stress among students in Turkey during the covid-19 pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (23):8961. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17238961. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ausín B, González-Sanguino C, Castellanos MÁ, Muñoz M. Gender-related differences in the psychological impact of confinement as a consequence of COVID-19 in Spain. Journal of Gender Studies. 2021; 30 (1):29–38. doi: 10.1080/09589236.2020.1799768. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blendon RJ, Benson JM, DesRoches CM, Raleigh E, Taylor-Clark K. The public’s response to severe acute respiratory syndrome in Toronto and the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2004; 38 (7):925–931. doi: 10.1086/382355. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braat-Eggen PE, van Heijst A, Hornikx M, Kohlrausch A. Noise disturbance in open-plan study environments: a field study on noise sources, student tasks and room acoustic parameters. Ergonomics. 2017; 60 (9):1297–1314. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2017.1306631. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brooks SK, Webster RK, Smith LE, Woodland L, Wessely S, Greenberg N, Rubin GJ. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. The Lancet. 2020; 395 (10227):912–920. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Canet-Juric L, Andrés ML, del Valle M, López-Morales H, Poó F, Galli JI, Yerro M, Urquijo S. A Longitudinal Study on the Emotional Impact Cause by the COVID-19 Pandemic Quarantine on General Population. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 :565688. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.565688. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cava MA, Fay KE, Beanlands HJ, McCay EA, Wignall R. The experience of quarantine for individuals affected by SARS in Toronto. Public Health Nursing. 2005; 22 (5):398–406. doi: 10.1111/j.0737-1209.2005.220504.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cecchini, J. A., Carriedo, A., Fernández-Río, J., Méndez-Giménez, A., González, C., Sánchez-Martínez, B., & Rodríguez-González, P. (2021). A longitudinal study on depressive symptoms and physical activity during the Spanish lockdown. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology , 21 (1). 10.1016/j.ijchp.2020.09.001 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd edn) . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. 10.4324/9780203771587
- Driessen E, Beatty A, Stokes A, Wood S, Ballen C. Learning principles of evolution during a crisis: An exploratory analysis of student barriers one week and one month into the COVID-19 pandemic. Ecology and Evolution. 2020; 10 (22):12431–12436. doi: 10.1002/ece3.6741. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Du Toit, A. (2020). Outbreak of a novel coronavirus. Nature Reviews Microbiology , 18 (3), 123. 10.1038/s41579-020-0332-0 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Ekman P. An Argument for Basic Emotions. Cognition and Emotion. 1992; 6 (3):169–200. doi: 10.1080/02699939208411068. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elmer T, Mepham K, Stadtfeld C. Students under lockdown: Comparisons of students’ social networks and mental health before and during the COVID-19 crisis in Switzerland. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (7):e0236337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236337. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gelles LA, Lord SM, Hoople GD, Chen DA, Mejia JA. Compassionate flexibility and self-discipline: Student adaptation to emergency remote teaching in an integrated engineering energy course during COVID-19. Education Sciences. 2020; 10 :304. doi: 10.3390/educsci10110304. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gonzalez T, De la Rubia MA, Hincz KP, Comas-Lopez M, Subirats L, Fort S, Sacha GM. Influence of COVID-19 confinement on students’ performance in higher education. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (10):e0239490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239490. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gopal A, Sharma AJ, Subramanyam MA. Dynamics of psychological responses to COVID-19 in India: A longitudinal study. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (10):e0240650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240650. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamann K, Glazier RA, Wilson BM, Pollock PH. Online teaching, student success, and retention in political science courses. European Political Science. 2020 doi: 10.1057/s41304-020-00282-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hawryluck L, Gold WL, Robinson S, Pogorski S, Galea S, Styra R. SARS control and psychological effects of quarantine, Toronto. Canada. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2004; 10 (7):1206–1212. doi: 10.3201/eid1007.030703. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heffner J, Vives M-L, FeldmanHall O. Emotional responses to prosocial messages increase willingness to self-isolate during the COVID-19 pandemic. Personality and Individual Differences. 2021; 170 :110420. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2020.110420. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Holen S, Waaktaar T, Sagatun Å. A Chance Lost in the Prevention of School Dropout? Teacher-Student Relationships Mediate the Effect of Mental Health Problems on Noncompletion of Upper-Secondary School. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research. 2018; 62 (5):737–753. doi: 10.1080/00313831.2017.1306801. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong KS. Relationships between students’ and instructional variables with satisfaction and learning from a Web-based course. Internet and Higher Education. 2002; 5 (3):267–281. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(02)00105-7. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hviid CA, Pedersen C, Dabelsteen KH. A field study of the individual and combined effect of ventilation rate and lighting conditions on pupils’ performance. Building and Environment. 2020; 171 :106608. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106608. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim A, Al Kaabi A, El Zaatari W. Teacher resistance to educational change in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Research Studies in Education. 2013; 2 (3):25–36. doi: 10.5861/ijrse.2013.254. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacques S, Ouahabi A, Lequeu T. Remote Knowledge Acquisition and Assessment During the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Engineering Pedagogy. 2020; 10 (6):120. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v10i6.16205. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khalil R, Mansour AE, Fadda WA, Almisnid K, Aldamegh M, Al-Nafeesah A, Alkhalifah A, Al-Wutayd O. The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :285. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02208-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kyne SH, Thompson CD. The COVID cohort: Student transition to university in the face of a global pandemic. Journal of Chemical Education. 2020; 97 (9):3381–3385. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00769. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Linh PD, Trang TN. Pandemic, social distancing, and social work education: students’ satisfaction with online education in Vietnam. Social Work Education. 2020; 39 (8):1074–1083. doi: 10.1080/02615479.2020.1823365. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luan L, Hong J-C, Cao M, Dong Y, Hou X. Exploring the role of online EFL learners’ perceived social support in their learning engagement: a structural equation model. Interactive Learning Environments. 2020 doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1855211. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Magson NR, Freeman JYA, Rapee RM, Richardson CE, Oar EL, Fardouly J. Risk and Protective Factors for Prospective Changes in Adolescent Mental Health during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 2021; 50 :44–57. doi: 10.1007/s10964-020-01332-9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mcinnerney JM, Roberts TS. Online Learning: Social Interaction and the Creation of a Sense of Community. Journal of Educational Technology & Society. 2004; 7 (3):73–81. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moorhouse BL. Adaptations to a face-to-face initial teacher education course ‘forced’ online due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):1–3. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1755205. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nassr RM, Aborujilah A, Aldossary DA, Aldossary AAA. Understanding Education Difficulty During COVID-19 Lockdown: Reports on Malaysian University Students’ Experience. IEEE Access. 2020; 8 :186939–186950. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3029967. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Odriozola-González P, Planchuelo-Gómez Á, Irurtia MJ, de Luis-García R. Psychological effects of the COVID-19 outbreak and lockdown among students and workers of a Spanish university. Psychiatry Research. 2020; 290 :113108. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parrott WG. Emotions in social psychology. Psychology Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Parvez MS, Rahman A, Tasnim N. Ergonomic mismatch between students anthropometry and university classroom furniture. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science. 2019; 20 (5):603–631. doi: 10.1080/1463922X.2019.1617909. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piccoli G, Ahmad R, Ives B. Web-based virtual learning environments: A research framework and a preliminary assessment of effectiveness in basic it skills training. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems. 2001; 25 (4):401–426. doi: 10.2307/3250989. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plutchik, R. (1994). The Psychology and Biology of Emotion . Harper Collins College Publishers.
- Procentese F, Capone V, Caso D, Donizzetti AR, Gatti F. Academic community in the face of emergency situations: Sense of responsible togetherness and sense of belonging as protective factors against academic stress during covid-19 outbreak. Sustainability. 2020; 12 (22):9718. doi: 10.3390/su12229718. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Puljak L, Čivljak M, Haramina A, Mališa S, Čavić D, Klinec D, Aranza D, Mesarić J, Skitarelić N, Zoranić S, Majstorović D, Neuberg M, Mikšić Š, Ivanišević K. Attitudes and concerns of undergraduate university health sciences students in Croatia regarding complete switch to e-learning during COVID-19 pandemic: a survey. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :416. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02343-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Radu MC, Schnakovszky C, Herghelegiu E, Ciubotariu VA, Cristea I. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of educational process: A student survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (21):7770. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217770. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos-Morcillo AJ, Leal-Costa C, Moral-García JE, Ruzafa-Martínez M. Experiences of nursing students during the abrupt change from face-to-face to e-learning education during the first month of confinement due to COVID-19 in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (15):5519. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155519. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Realyvásquez-Vargas, A., Maldonado-Macías, A. A., Arredondo-Soto, K. C., Baez-Lopez, Y., Carrillo-Gutiérrez, T., & Hernández-Escobedo, G. (2020). The Impact of Environmental Factors on Academic Performance of University Students Taking Online Classes during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Mexico. Sustainability , 12 (21), 9194. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/21/9194
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Sánchez-Paniagua M, Sanz-Landaluze J, Moreno-Guzmán M. Analytical Chemistry Teaching Adaptation in the COVID-19 Period: Experiences and Students’ Opinion. Journal of Chemical Education. 2020; 97 (9):2556–2564. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00923. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenberg, H., & Asterhan, C. S. C. (2018). “WhatsApp, Teacher?” Student Perspectives on Teacher-Student WhatsApp Interactions in Secondary Schools. Journal of Information Technology Education Research , 4081 , 205–226. 10.28945/4081
- Saravanan C, Mahmoud I, Elshami W, Taha MH. Knowledge, Anxiety, Fear, and Psychological Distress About COVID-19 Among University Students in the United Arab Emirates. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2020; 11 :582189. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.582189. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scull J, Phillips M, Sharma U, Garnier K. Innovations in teacher education at the time of COVID19: an Australian perspective. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):497–506. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1802701. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Son C, Hegde S, Smith A, Wang X, Sasangohar F. Effects of COVID-19 on college students’ mental health in the United States: Interview survey study. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2020; 22 (9):e21279. doi: 10.2196/21279. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sun PC, Tsai RJ, Finger G, Chen YY, Yeh D. What drives a successful e-Learning? An empirical investigation of the critical factors influencing learner satisfaction. Computers and Education. 2008; 50 (4):1183–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2006.11.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang T, Abuhmaid AM, Olaimat M, Oudat DM, Aldhaeebi M, Bamanger E. Efficiency of flipped classroom with online-based teaching under COVID-19. Interactive Learning Environments. 2020 doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1817761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO. (2020). COVID-19 and higher education: Today and tomorrow. Impact analysis, policy responses and recommendations . http://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/COVID-19-EN-090420-2.pdf
- UNESCO, UNICEF, & The World Bank. (2020). What Have We Learnt? : Overview of Findings from a Survey of Ministries of Education on National Responses to COVID-19 . https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/34700
- Van Nuland S, Mandzuk D, Tucker Petrick K, Cooper T. COVID-19 and its effects on teacher education in Ontario: a complex adaptive systems perspective. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):442–451. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1803050. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang X, Tang L, (Rebecca), & Kim, E. More than words: Do emotional content and linguistic style matching matter on restaurant review helpfulness? International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2019; 77 :438–447. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.08.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization. (2021). Looking back at a year that changed the world. Who’s Response To COVID-19 . https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/looking-back-at-a-year-that-changed-the-world-who-s-response-to-covid-19
- World Health Organization & Regional Office for Europe. (2020). Pandemic fatigue: reinvigorating the public to prevent COVID-19: policy framework for supporting pandemic prevention and management . https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/337574
- Yamaguchi K, Takebayashi Y, Miyamae M, Komazawa A, Yokoyama C, Ito M. Role of Focusing on the Positive Side During COVID-19 Outbreak: Mental Health Perspective From Positive Psychology. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy. 2020; 12 (S1):S49–S50. doi: 10.1037/tra0000807. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhong, L., Yuan, J., & Fleck, B. (2019). Indoor environmental quality evaluation of lecture classrooms in an institutional building in a cold climate. Sustainability , 11 (23). 10.3390/su11236591
- Zhou P, Yang X. Lou, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang R. Di, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020; 579 (7798):270–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zurlo MC, Volta Cattaneo Della, M. F., & Vallone, F. COVID-19 Student Stress Questionnaire: Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Evaluate Students’ Stressors Related to the Coronavirus Pandemic Lockdown. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 :576758. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.576758. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Takeaways from the ncaa’s settlement.
Laura Mannweiler May 24, 2024

New Best Engineering Rankings June 18
Robert Morse and Eric Brooks May 24, 2024

Premedical Programs: What to Know
Sarah Wood May 21, 2024

How Geography Affects College Admissions
Cole Claybourn May 21, 2024

Q&A: College Alumni Engagement
LaMont Jones, Jr. May 20, 2024

10 Destination West Coast College Towns
Cole Claybourn May 16, 2024


Scholarships for Lesser-Known Sports
Sarah Wood May 15, 2024

Should Students Submit Test Scores?
Sarah Wood May 13, 2024

Poll: Antisemitism a Problem on Campus
Lauren Camera May 13, 2024

Federal vs. Private Parent Student Loans
Erika Giovanetti May 9, 2024

Life During Lockdown Essay for Students – 100, 500, 1000+ Words, & 10 Lines
Life During Lockdown Essay for Students: Explore the challenges, experiences, and lessons learned during the pandemic with “Life During Lockdown Essay for Students.” Understand the impact on education, mental health, and daily life, as students navigate through this unprecedented period.
Reflect on resilience, adaptability, and the importance of community support. Discover insights into remote learning, coping mechanisms, and maintaining social connections in the face of isolation. This Life During Lockdown Essay for Students delves into the unique aspects of students’ lives during lockdown, offering a comprehensive perspective on this transformative period.

Table of Contents
Life During Lockdown Essay in English for Students in 10 Lines
Explore the transformative journey of students during lockdown in “Life During Lockdown Essay for Students.” This Life During Lockdown Essay for Students encapsulates the challenges, adaptations, and resilience displayed by students, providing a comprehensive Life During Lockdown Essay for Students in view of their unique experiences in just 10 lines.
- Shift to Online Learning: With schools and colleges closed, education shifted to virtual platforms like Zoom and Google Meet.
- Work from Home: Many adults adapted to remote work setups, blurring the lines between personal and professional spaces.
- Increased Family Time: Lockdowns brought families together, fostering stronger bonds and shared activities.
- Rediscovery of Hobbies: People explored new hobbies or revisited old ones, finding solace in activities like painting, reading, or gardening.
- Digital Fatigue: Excessive screen time for work, classes, and socializing led to digital fatigue and burnout.
- Heightened Awareness of Health: The pandemic underscored the importance of physical and mental health, leading to increased focus on well-being.
- Challenges of Isolation: Social distancing measures caused feelings of isolation, emphasizing the need for human connection.
- Economic Uncertainty: Many faced financial challenges due to job losses or economic downturns during the pandemic.
- Reflection and Self-Discovery: The quieter pace of life allowed individuals to reflect on their goals and priorities, prompting self-discovery.
- Community Support: Acts of kindness and community support became prominent, with neighbors helping each other during challenging times.
Also See – Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Essay – 100, 500, 1000 Words & 10 Lines
Life During Lockdown Essay for Students in 100 Words
Amidst the lockdown, students experienced a unique blend of challenges and opportunities. From adapting to virtual learning to discovering new hobbies, this Life During Lockdown Essay for Students delves into the multifaceted aspects of their lives during this unprecedented time.
The life of students during the lockdown was a paradigm shift, transforming traditional classrooms into virtual spaces. Adjusting to online learning, students navigated a digital landscape for education and social interaction. The challenges were met with innovation, as virtual classrooms became the new norm. Beyond academics, the lockdown encouraged self-reflection and personal growth.
Students adapted, honing their resilience and creativity. Despite the uncertainties, the experience unveiled new opportunities for learning, collaboration, and adapting to the evolving educational landscape. The lockdown period will be remembered as a time of transformation, where students not only faced challenges but also discovered their capacity to overcome and thrive in an ever-changing world.
Life During Lockdown in English Essay for Students in 500 Words
This Life During Lockdown Essay for Students explores the transformative journey of students during the lockdown, covering aspects such as online education, mental health, and personal growth. Life During Lockdown Essay for Students delves into the challenges faced and the resilience displayed, offering a comprehensive perspective on the student experience during this extraordinary period.
Life During Lockdown: Navigating Challenges and Discovering Resilience
The onset of the global COVID-19 pandemic triggered an unprecedented disruption to normal life, profoundly impacting students and their educational journeys. As classrooms shifted to virtual spaces, students faced a myriad of challenges, yet amidst the chaos emerged stories of resilience and personal growth.
The abrupt transition to online education was a significant hurdle for many students. Technological limitations, internet connectivity issues, and adapting to new learning platforms became recurrent obstacles. However, amidst these challenges, students displayed commendable adaptability. They quickly learned to navigate virtual tools, collaborate effectively in a digital environment, and manage their time efficiently.
The toll on mental health was palpable. Isolation, uncertainty about the future, and the pressure to adapt to new educational norms contributed to heightened stress levels among students. Yet, this period of upheaval also revealed the strength of the human spirit. Many students sought mental health support, and communities rallied together to foster emotional well-being.
The lockdown also provided a unique opportunity for personal reflection and growth. With the constraints of daily routines lifted, students delved into hobbies and passions, rediscovering interests that had been neglected in the hustle of pre-pandemic life. This newfound free time became a catalyst for personal development beyond academic pursuits.
Family dynamics underwent a significant transformation. With extended periods spent at home, students found themselves in the midst of increased family bonding. Shared experiences, conversations, and collaborative activities became integral to this period, fostering stronger familial ties and creating enduring memories.
As students navigated these challenges, they reflected on their priorities. The lockdown became a time of introspection, prompting individuals to reconsider their career goals, academic pursuits, and personal aspirations. Many emerged from this period with a more intentional approach to life, understanding the importance of balance and well-being.
The lessons learned during this period are invaluable, shaping not only the trajectory of education but also the personal development and priorities of students around the globe. As the world moves beyond the pandemic, these experiences will continue to influence how students approach education and life’s challenges in the future.
Life During Lockdown Essay for Students in 1000+ Words
This comprehensive Life During Lockdown Essay for Students delves into the multifaceted experiences of students during the global lockdown, exploring the challenges faced, the lessons learned, and the transformative journey towards personal and academic growth.
Introduction
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019 led to unprecedented global challenges, prompting governments worldwide to implement lockdowns to curb the spread of the virus.
This essay delves into the multifaceted aspects of life during lockdown, exploring the challenges faced by individuals and communities, the shift to remote work and online education, the impact on mental health, and the resilience demonstrated in adapting to the “new normal.”
Challenges Faced During Lockdown
Social Isolation
One of the immediate and palpable challenges of lockdown was social isolation. The restrictions on movement and gatherings meant that people were cut off from their social circles, friends, and extended families. The absence of face-to-face interactions led to feelings of loneliness and a longing for human connection.
Economic Uncertainty
Lockdowns had a severe impact on the global economy, leading to job losses, furloughs, and economic uncertainty for millions. Small businesses faced closures, and various industries experienced significant setbacks. The sudden economic downturn left individuals and families grappling with financial stress and uncertainty about the future.
Education Disruption
Schools and universities worldwide had to adapt swiftly to the new reality of remote learning. The sudden shift to online education posed challenges for both students and educators. Limited access to resources, varying levels of technological proficiency, and the absence of the traditional classroom environment made the learning experience challenging for many.
Work-from-Home Challenges
Remote work became the norm for many professionals, introducing a new set of challenges. Balancing work responsibilities with household chores, the lack of a clear boundary between work and personal life, and the technological adjustments required for effective collaboration presented hurdles for individuals navigating this new work paradigm.
Adapting to Remote Work and Online Education
Remote Work Dynamics
While the sudden transition to remote work posed initial challenges, it also highlighted the adaptability and resilience of individuals and organizations. Video conferencing tools, collaborative platforms, and flexible work hours became integral to maintaining productivity and communication.
Online Education Innovations
Educational institutions embraced technology to ensure continuity in learning. Virtual classrooms, online assessments, and interactive learning platforms became essential components of the educational landscape. The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital tools in education, prompting innovation in pedagogical approaches.
Digital Connectivity
The importance of digital connectivity became more apparent than ever. High-speed internet, online communication tools, and digital platforms became lifelines for individuals working and studying remotely. The digital divide, however, underscored the need for equitable access to technology.
Impact on Mental Health
Isolation and Anxiety
The isolation imposed by lockdowns took a toll on mental health. Anxiety, depression, and feelings of helplessness became prevalent as individuals grappled with uncertainties about the future, health concerns, and the disruption of routine.
Work-Life Balance Challenges
Remote work, while offering flexibility, also blurred the boundaries between professional and personal life. Many individuals found it challenging to establish a work-life balance, leading to burnout and increased stress levels.
Educational Stress
Students faced unique challenges, including the pressure of adapting to online learning, concerns about academic performance, and the absence of the social support traditionally provided by the school environment.
Resilience and Adaptability
Community Support
Communities around the world demonstrated resilience by coming together to support one another. Mutual aid groups, online forums, and community initiatives emerged to provide assistance, share resources, and foster a sense of solidarity.
Innovation and Creativity
The pandemic spurred innovation in various fields. From virtual events and conferences to innovative approaches in education, individuals and organizations showcased creativity in adapting to the constraints imposed by lockdown.
Digital Transformation Acceleration
Businesses and institutions accelerated their digital transformation efforts. E-commerce, telehealth, and virtual services saw increased adoption, reflecting the adaptability of industries in responding to the challenges posed by the pandemic.
Life during lockdown presented a myriad of challenges, from social isolation to economic uncertainties and disruptions in education and work. However, amidst these challenges, individuals and communities showcased remarkable resilience and adaptability. The embrace of remote work and online education, coupled with the acceleration of digital transformation, highlighted the capacity for innovation and creativity in the face of adversity.
As societies gradually emerge from the throes of the pandemic, the lessons learned during lockdown underscore the importance of building resilient systems, prioritizing mental health, and fostering a sense of community. The shared experience of navigating life during lockdown serves as a testament to the collective strength of humanity and the potential for positive transformation in the face of global challenges.
the Life During Lockdown Essay for Students serves as a poignant testament to the resilience and adaptability that define the human spirit. As students navigated the uncharted waters of remote learning, disrupted routines, and the emotional toll of isolation, they discovered hidden strengths within themselves. The challenges posed by the pandemic became catalysts for growth, fostering adaptability and fortitude.
The diverse narratives shared by students underscore the universality of the human experience during these trying times. From moments of frustration to unexpected joys and self-realization, the Life During Lockdown Essay for Students encapsulates the spectrum of emotions and lessons learned.
As the world gradually emerges from the shadows of the pandemic, these insights into life during lockdown become invaluable markers of endurance and perseverance.
This Life During Lockdown Essay for Students not only chronicles the challenges faced by students but also emphasizes the profound lessons embedded in adversity. Life During Lockdown Essay for Students stands as a testament to the resilience cultivated amid uncertainty, providing a hopeful outlook for the future.
Related Essays

Essay on Modern Indian Woman – 100, 500, 1000 Words, 10 Lines

Essay on Future of English in India – 10 Lines, 500 & 1000 Words

Essay on Bhai Dooj – 10 Lines, 100, 500, 1000 Words

Essay About Ooty – 10 Lines, 500 & 1000 Words

Draupadi Murmu Essay – 10 Lines, 100, 500, 1000 Words

Computer Essay – Short Essay, 10 Lines, 500 & 1000 Words
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
by Alissa Wilkinson

The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
- The Vox guide to navigating the coronavirus crisis
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
- A syllabus for the end of the world
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
- What day is it today?
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
- Vox is starting a book club. Come read with us!
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
Most Popular
Take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, red lobster’s mistakes go beyond endless shrimp, cholera is making a comeback — and the world doesn’t have enough vaccines, 20 years of bennifer, explained, the air quality index and how to use it, explained, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in Culture

Furiosa’s hard-won feminism

Hacks shows cancel culture is a joke

What the Biden administration is doing about ludicrously expensive concert tickets

Why AI art will always kind of suck

The real reason it costs so much to go to a concert

Vanderpump Rules shows the limits of making money on reality TV

The enormous stakes of India’s election

One explanation for the 2024 election’s biggest mystery

The obscure federal intelligence bureau that got Vietnam, Iraq, and Ukraine right

The Comstock Act, the long-dead law Trump could use to ban abortion, explained

Red Lobster’s mistakes go beyond endless shrimp Audio


Lockdown diaries: the everyday voices of the coronavirus pandemic
Senior Lecturer in Social Science, Swansea University
Disclosure statement
Michael Ward does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Swansea University provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
A diary is by its very nature an intensely personal thing. It’s a place to record our most intimate thoughts and worries about the world around us. In other words, it is a glimpse at our state of mind.
Now, the coronavirus pandemic, and the impact of the lockdown, have left many people isolated and scared about what the future might bring. As a sociologist, I was keen to hear how people were experiencing this totally new way of life. So in early March I began the CoronaDiaries – a sociological study which aimed to highlight the real voices and the everyday experiences of the pandemic by collecting the accounts of people up and down the UK, before, during and after the crisis.
From the frontline health worker concerned about PPE and exposure to COVID-19, to the furloughed engineer worried about his mental health, these are the voices of the pandemic. Entries take a variety of forms, such as handwritten or word-processed diaries, blogs, social media posts, photos, videos, memes and other submissions like songs, poems, shopping lists, dream logs and artwork. So far, the study has recruited 164 participants, from 12 countries, aged between 11 and 87. These people come from a range of backgrounds.

This article is part of Conversation Insights The Insights team generates long-form journalism derived from interdisciplinary research. The team is working with academics from different backgrounds who have been engaged in projects aimed at tackling societal and scientific challenges.
When I began this project in March, I did not expect the study to prove so popular. I have been studying and working as a sociologist for nearly 20 years and most of my research so far has looked at how young men experience education, gender roles and social inequality.
Like many of us, I was wondering how I could be of use at this time, do my bit in the crisis and make the most of my skills. As the weeks have gone by and more and more people have signed up, I’ve realised this project isn’t just a research study to understand how society is being made and remade – it is also providing hope and acting as a cathartic coping tool for people. While some of the documents have made me cry, especially those from already vulnerable people, others have made me laugh and have been a joy to read. I feel as though I am on a journey with the participants as we move through the crisis.
Reading the entries, what becomes clear as the lockdown is eased is that this pandemic has been – and will continue to be – experienced in very different ways across society. For some, the crisis has been an opportunity, but for others, who are already in a disadvantaged position, it is a very frightening experience.
March – first days
The frontline health worker
Emma is in her late 30s, and a frontline health worker in a rural location in Wales. Like many key workers, Emma is also juggling family life and caring responsibilities. In a diary entry written in mid-march, Emma foresaw issues with PPE in the NHS.
On my shifts over the previous weekend, it became apparent how unprepared we are. I was working on a ‘clean’ ward and four of the patients were found to potentially be infected. There were no clinical indications they were potentially infected on admission and had been nursed without PPE for two days. We may have all been exposed, as these patients are suspected to have COVID-19. We have been given bare bones PPE. It was quite sobering when a rapid response was called and the doctors refused to enter the cubicle without FFP3 masks , blue gown and visor.

Emma said the equipment “magically turned up” after the doctors took this stand but said the sight of them all in surgical gowns, helmets and visors “did verge on the ridiculous”. She added:
I did find it amusing – we’re looking at the doctors wanting their protection and they are looking at the consultant wanting his! It did feel like a farce. Fortunately, the patient was made stable and went to surgery for another issue. But the whole episode was worrying, particularly the crappy surgical mask and aprons we are provided. It’s also galling that they have told staff there is no PPE when clearly there is. Can’t help but think a lack of information is creating fear amongst staff. It’s also weird they aren’t testing staff unless they’re symptomatic. This is crazy when they are so dependent on bank and agency workers who move around.
The worried mum
Beth, 35, is a mother of two young children who lives in a busy city. In the early days of the crisis, she hid her fears from her children. Here is a snapshot from her written diary:
I didn’t sleep well last night, didn’t help I watched the news before going to sleep. Then looked at my phone and full of corona news … Today was the big announcement from Boris (Friday, March 20) ‘to stay in’! Even though he had been saying this all week, the tone and manner of the broadcast was so scary and serious. I felt scared for my family and it just made me fearful of what is to come. I rang my mum straight away … [she] could hear my fear. After a good chat … my mum … remind[ed] me ‘we are all well at this moment’ and to focus on that. My daughter cried later that evening. I said, ‘what are you scared of’ to which she replied, ‘I’m not sure mummy, I don’t know what I am scared of.’ Which made me realise that I need to be brave and make sure that both kids are reassured. Later that evening, I felt tearful and just feeling overwhelmed by the whole situation. How stupid too, because we are all safe.
Read more: How to help with school at home: don't talk like a teacher
The student
Audrey, 21, goes to a university in Birmingham and is in the final months of her degree. The rupture of “normal” student life became clear when the full scale of the lockdown came into force, causing her housemates to leave their shared house.
I’d just lost all three of my housemates, who’d returned to Barbados, Spain and France – literally one day after each other. My landlord really kindly agreed that my sister could stay with me – and she won’t even charge any rent. I almost cried when I got that message. I was having a facetime with my friend, where we paused to watch Boris Johnson’s speech (March 23). It was so scary because we were effectively in lockdown. I had told my sister that I thought it was about to happen earlier in the day, she didn’t believe me – and then unfortunately it came true! I told her to jump on the train from Manchester.
Audrey went on to write how some of her fellow students set up a food bank in one of the student accommodations near her and that she is determined help where she can. But despite her altruistic efforts, the lockdown was still taking its toll.
I feel deflated from everything. I chatted to a friend over Messenger and she suggested I paint something. I painted this rainbow and felt so much better at the end. I added in my favourite quote that gets [me] through any hard times and stuck it on the window.
April – settling in
The cleaner
Eva is a self-employed cleaner, in her mid 50s, who lives in South Wales with her husband, John, who works in a factory making hand sanitiser. As the lockdown entered its second month, she reflected on her relationship with the woman who worked for her and how differently the pandemic was effecting them both.
Today I am cleaning the community centre, which since the lockdown, is running as a food bank three days a week … I bleach everything, door handles, floors, everything. Most staff work from home at the moment so we are going in the morning until all this is over. I’m glad I’m still in business for Beverly, who works with me, as much as anything. I’m her only income, but if I don’t work, I don’t get paid. We have a cigarette break outside and I remind Beverly to stay apart. ‘What, beans for brekkie, was it?’ I laugh. Beverly really doesn’t care about COVID – like many others I meet, who believe if they get it, they get it.

For once I’m glad I’m a worrier, plus I’m not ready to die yet. We are out of there early as no staff equals less mess. I break it to Beverly that I can’t give her a lift home for now. Last week I made her sit in the back [of the car] which felt faintly ridiculous, but John advised even that’s too close. Beverly shrugs and says that’s fine. Her son died unexpectedly two years ago and now she accepts hardship with ease. I feel bad as her life really is crap and now she has to walk two miles home.
The teacher
Sophia is a teacher in her 40s and based in the south of England. She is trying to home school her children during the lockdown and being a parent and a teacher is proving challenging.
We began the day slightly differently with an online PE lesson from someone called Joe Wicks, or The Body Coach. He’s been really popular during the lockdown and a few of my friends recommended the 30-minute workout session he does every day at 9am, so I thought we’d give it a go! Unfortunately, my two have the concentration spans of goldfish so it didn’t go according to plan! My son ended up lying upside down, with his legs on a chair and his head on the floor and my daughter said he moved too fast, before promptly falling on her behind! The only problem with changing the routine was that we were then 30 minutes late for home school and my son does not cope well with change. He needs quite a rigid structure, with clearly defined timings and any changes can be detrimental. The speed of the school lockdown was particularly challenging: school gives his day structure and taking it away so abruptly was very difficult for him.
The civil servant
Sarah is a civil servant in her mid-60s working in a pivotal role for HM Revenue and Customs. She used her diary to document the rapid changes which have taken place in her organisation since the lockdown and how working from home was becoming “normal” from March 23.
My department is changing so quickly – we have introduced a new i-form to promote more ‘web chat’. This is proving popular with the public. We are trialling taking incoming telephone calls at home. We are all now working from home when we can, no more car sharing, unless it’s with someone you live with – we must keep two metres apart. I am beginning to accept that this is a crisis, once in a generation, completely alien to us. Will life in the future be remembered as ‘before and after’ COVID-19? For the first time in many years I feel so proud to work where I do…I understand, possibly for the first time, why we are ‘key workers’. We have a letter as proof to show the police if we are ever stopped whilst travelling into work and NCP carparks are free for us to use if we come into work! No better validation than that!

The furloughed engineer
Lucas, a man in his late 30s from Northern Ireland, is finding the pandemic difficult on multiple levels. It’s a trigger for his mental health, but also it is a reminder of past troubles.
Nightmare. Anxiety, fear, dread, no way to burn off the angst, worry upon worry, like how the inside of my head can be at times. Then there’s the ones that are really in the middle of it, nurses dying because there was no proper PPE at the right time, people losing parents, friends, and IMHO worst of all, kids.
Lucas writes about how he stopped watching the news because in an attempt to “avoid anxiety”. He adds:
I grew up in Northern Ireland during ‘the troubles’ and it was totally normal for me to watch the news every night at tea time [6pm] and hear of various paramilitary groups killing people. That was 100% normal to me. Looking back watching the news in those times did me no good. Sure, I know some facts about it all, but do I feel any better for it … Same as now, I’m going to try to ride this out with my hands over my ears and my head in the sand at times.
Read more: Coronavirus: a growing number of people are avoiding news
The academic
Jack, 72, is a retired academic who used his diary to comment on societal problems. One of which is the narrative of what the “new normal” is and how society is being remade.
April 29 saw the return of Boris, who was to ‘take control of the problem’. An almost religious return for someone who came back from being nearly dead on Easter Sunday! It seems we are being told to be ready for the new normal which again raises the issue of what post-lockdown will be like. On the web I don’t see sociologists rushing in to think about this new normal! A Google search suggests that the new normal is being constructed largely by those in business and is largely focused on the new normal being a more exaggerated (and better?) version of the old normal – more globalisation, more focus on customers and so on. There is little ‘thinking outside the box’.
Read more: What will the world be like after coronavirus? Four possible futures
May – Looking forward
The bell-ringer
Daniel, a man in his mid-20s, had just started a new relationship in February with a woman he met while bell-ringing at a church in the Midlands. However, both he and his girlfriend live apart and have not seen each other since the lockdown began. Over the past few months, Daniel has found this a challenge, but has documented how their relationship has been maintained virtually and through the help of keeping a diary.

Suzy and I have got to know each other a lot quicker and a lot better than what we may have done otherwise, and whilst we do miss each other immensely, it’ll make the good times so much better when we do see each other next. Whenever and however we get out of this, I am determined that I will have made the most of these extraordinary circumstances.
This is just a glimpse of the stories that have been gathered by the CoronaDiaries project, but already patterns are emerging. While this crisis is undoubtedly impacting on people across the globe, what is clear from these accounts is that there are multiple crises across everyday life – for the young, the old, for mothers and for fathers and for those from different class, gender and ethnic backgrounds. These entries are able to highlight the multiple different lives behind the dreaded numbers we hear announced each day.
My diarists have been recording how they feel vulnerable and uncertain about their future – but there is also hope that things will not be like this forever.
The evidence which is being gathered here can play an important part in addressing the social, political and economic changes created by the COVID-19 pandemic. This type of analysis will foster global awareness of crucial issues that can help support specific public health responses to better control future outbreaks and to better prepare people for future problems. The study will run until September and all accounts will then be available to view in a free digital online archive.
All the names used in this piece have been changed at the request of the study participants.

For you: more from our Insights series :
Lockdown lessons from the history of solitude
What will the world be like after coronavirus? Four possible futures
The end of the world: a history of how a silent cosmos led humans to fear the worst
To hear about new Insights articles, join the hundreds of thousands of people who value The Conversation’s evidence-based news. Subscribe to our newsletter .
- Mental health
- Coronavirus
- Social science research
- Insights series
- Coronavirus insights
- COVID-19 lockdowns

Head, School of Psychology

Senior Lecturer (ED) Ballarat

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Speech Writing /
Speech on Things I Learned in Lockdown

- Updated on
- Dec 4, 2023

Speech on Things I Learned in Lockdown: Do you remember the phrase ‘Survival of the fittest’ by Charles Darwin? In his theory of evolution, Darwin explained how humans have evolved over millions of years as part of natural evolution. The lockdowns and curfews imposed due to COVID-19 highlighted the Darwinian theory of evolution, where only the fittest survive. Even in those uncertain times, we humans found new ways of learning and surviving. The concept of social distancing was among other things learned by people. Lockdown was not just about sitting idle at home; it was an opportunity to learn new things and come out like a shining star. Below, there’s a ‘Things I learned in lockdown speech’ for school students.
Also Read: 160+ Easy and Best English Speech Topics for Students
‘Every new beginning comes from some other beginning’s end.’ – Seneca
Also Read: 1-minute Speech on Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
2-Minute Speech on Things I Learned in Lockdown
‘Good morning and welcome to everyone present here. I would like to thank you all for joining me here, as I stand here today to present my speech on ‘Things I learned in lockdown.’ We all went through the difficult times of lockdown during the COVID-19 era. The government’s initial decision to implement a 21-day lockdown was seen as a horror in the nation.’
‘Lockdowns and curfews imposed in 2020 and 2021 completely transformed our way of life. A ‘New Normal’ was introduced, such as work-from-home, social distancing, face masks, parent home-schooling, etc. Lockdown allowed us to take a step back and learn from our mistakes. As students, we have had some responsibilities towards ourselves and understand those critical situations.’
‘The first thing I learned in lockdown was to take good care of my mental health. As a student, I often felt academic-related stress and worried too much about my scores at school. Lockdown allowed me to understand that there are other things where I need to focus.’
‘I created a new timetable that included 8 hours of sleep, 3 healthy meals, 1 hour of a home workout, a new skill every week, helping my mother in the house choir, and reading the newspaper. This new routine provided me with stability and a sense of normalcy.’
‘After 4 weeks, I focused on maintaining social connections with my friends and relatives. Thanks to technology, we can connect with people in far-off places on video calls. Social interactions helped me to fight feelings of isolation. We used to share jokes, talk about movies and starts, and share our grievances on video calls.’
‘Some other things I learned in lockdown were speaking Spanish, graphic designing, creative writing, cooking, and photography. I know I didn’t master any of these, but, I did gain basic skills. Lockdown was a time when we could reflect on ourselves and see what we could do to make ourselves better. We all spend our lockdown time in different ways, and I’m sure we all learned something new, something meaningful.
Thank you.’
Also Read: Speech on Is There Value in Homework
10 Things Learned During Lockdown
Here are 10 things that students focussed on during times like lockdown. Learn these skills to stay ahead.
- Cooking and baking
- Language learning
- Fitness and yoga
- Creative Writing
- Photography and designing
- Networking and IT skills
- Social Media management
- Online Education
- Quality time with family
Also Read: 1 Minute Speech on My Hobbies
Ans: Lockdown was a time to reflect on ourselves and allowed us to gain new skills. We were able to spend quality time with our families, work on our physical and mental health learn new things. Some of the popular things that people learned during lockdown were learning new languages, cooking and baking, socializing on the internet, online education, etc.
Ans: 5 things students learned during lockdown were online learning, physical fitness, music and dancing, networking and IT skills, and cooking.
Ans: Improving vocabulary skills was one of the best things to learn during lockdown for students. This was a simple and worthwhile activity, where students were required to read both academic and non-academic articles. Newspapers and magazines are the best sources to improve reading and vocabulary skills.
Related Articles
For more information on such informative speech topics for your school, visit our speech writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
CBSE Digital Education
#No.1 Educational Portal for Students & Teachers
Essay on Lockdown in English for Students and Children

This long essay on lockdown in English is suitable for students of classes 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10, 11, 12, and also for competitive exam aspirants. All important information related to how to write an amazing essay about Lockdown.
Long Essay on Lockdown in English 800 Words
Lockdown essay in English – Lockdown is a term that exploded collectively around the world in the year 2020. With the widespread attack of an invisible virus, known as the Novel Coronavirus , the entire world was devastated by the Pandemic of this virus. It occurs during a wide variety of emergencies and it disrupts normal life.
Many words became popular after the arrival of Coronavirus, the term “lockdown” being one of them. A lockdown is a period of time when people have to stay home and are only allowed to travel in an emergency. During this period everything is closed except for some essential services like hospitals, grocery stores, medical stores, etc.
Introduction
Coronavirus has been considered the most contagious virus ever in the history of mankind. Its effects have become catastrophic within a short time. To prevent the spread of this Coronavirus in the country, our government has taken some drastic steps.
One of the most important measures implemented is a lockdown, where all businesses have been closed, all people have been confined to their homes and almost all professional, personal, and economic activities have come to a standstill.
The lockdown was announced and enforced on the 25 th of March, 2020. It has been extended, in phases, to continue till mid-June. The government has issued advisories to all citizens to practice social distancing and stay at home. The purpose of the lockdown is to prevent community transmission of this deadly virus so that the chain of transmission can be broken.
Each and every person faced many difficulties during this period but for the daily wagers, it was much more difficult. Work from home, online education , and online business were some of the options during this period, and the Indian government also helped the people a lot.
Online Education During Lockdown
For the first time, schools in India have moved to online classes. It is a struggle for the teacher as well as the students. School students, children, and their parents felt the impact to close schools and educational institutions.
The lockdown situation prompted people to learn and use digital technology and as a result, increased digital literacy.
The teaching material is easily shared among the students and the doubt questions are solved on Telegram, WhatsApp, E-mail, and various social media. Students need to learn digital skills for their own sake and improve the quality of education as well as changes in syllabus, textbooks, teacher training, and examination systems, but at the very least, the quality of online education must also improve needed.
Advantages of Lockdown
Due to the lockdown, on the one hand, while people have been forced to remain imprisoned in the house, on the other hand, many big benefits are also being seen. Some important benefits of essay on lockdown:-
- The rapidly spreading Coronavirus has been controlled by applying Lockdown.
- Due to the lockdown, the movement of vehicles has been reduced very much, factories have been closed, and the air of the cities has started to clear due to the rein in such activities.
- The impact of the lockdown is also being seen on global warming. In early April, scientists showed a hole of 1,000,000 square kilometers in the ozone layer above the North Pole. According to NASA, it has started filling these holes now.
- Earth’s vibration has been reduced by 30 to 50 percent due to less traffic, machines, and noise pollution.
- Due to Coronavirus, there has been a change in the cleanliness habits of the people. People are being more vigilant. Due to the lockdown, more time is also available for cleaning the house.
- People are learning to live with limited resources and insist on being self-sufficient (or Aatmnirbhar ) in the future so that they can produce themselves.
- During this lockdown period, we have got a lot of time for self-development and self-awareness.
- Most people in Lockdown are cooking at home and eating the same. Health will also be good due to good food.
Disadvantage of Lockdown
Some important disadvantages of the essay on Lockdown:-
- Many migrant laborers got trapped in different cities and they could not return to their homes due to which they had to face many difficulties.
- Many industries like agriculture, education, and entertainment are suffering. It has negatively impacted the world economy.
- Unemployment has increased rapidly due to the lockdown. Because of this many people have lost their jobs.
- All schools and colleges were closed due to the lockdown, due to which the students were not able to study well.
Lockdown 2021
The lockdown was imposed due to Coronavirus in March 2020 last year. The same situation is being seen again. Again in April 2021, Coronavirus is spreading rapidly due to which lockdown is being imposed in all the states one by one.
In view of this spreading Coronavirus, the CBSE board canceled the class 10 examination and postponed the class 12 examination.
Lockdown is something that affects people from all backgrounds and especially the daily wagers. Some of the main problems during a lockdown are employment, poverty, and starvation.
Overall, we should keep in mind that lockdowns are only imposed for our welfare, so it is always our duty to follow the rules of lockdown.
Related Article –
- Essay on New Education Policy 2020
- Essay on Article 370
- Essay on Farm Bill 2020
- Essay on Narendra Modi
- Essay on Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- Essay on Independence Day 2021
I hope you like this post “ Essay on Lockdown in English “. If you want to give any suggestions then comment below. Share this essay with your friends.
My Name is Mukesh Kumar. I am a Teacher, Blogger, Educational Content Writer, and Founder of CBSE Digital Education.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay on Lockdown
Students are often asked to write an essay on Lockdown in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Lockdown
What is a lockdown.
A lockdown is when people must stay where they are, usually due to an emergency. This can happen for different reasons, like a dangerous person in the area or a disease outbreak. During a lockdown, you can’t go to places like school or the park. It’s a rule to keep everyone safe.
Lockdown and Staying Home
In a lockdown, you stay home to avoid getting sick or spreading germs. Schools and shops may close, and you might not see your friends for a while. It’s important to listen to adults and stay inside.
Learning in Lockdown
Even in a lockdown, you can keep learning. Schools might do classes online, so you can study from home. You’ll use a computer or tablet to see your teacher and classmates. It’s different but still a way to learn.
Fun at Home
Lockdown doesn’t mean you can’t have fun. You can play games, read, or do crafts. It’s a chance to spend time with family and try new hobbies. Remember, it’s not forever, just for now.
250 Words Essay on Lockdown
A lockdown is when people must stay where they are, usually in their homes, to stay safe. This can happen when there is a big problem, like a dangerous virus spreading. During a lockdown, schools, offices, and shops can close, and people must work, study, and shop from home if they can.
Why Lockdowns Happen
Lockdowns are used to stop people from getting sick or hurt. When too many people get sick at once, hospitals can get too busy. By staying home, fewer people get sick at the same time, and hospitals can help everyone who needs it.
Life During Lockdown
Life changes a lot in a lockdown. You can’t visit friends or go to the park like before. Many turn to books, games, and the internet to learn and have fun. Families spend more time together, and people find new ways to connect, like video calls.
Challenges of Lockdown
Lockdowns can be hard. People might miss their friends or feel sad and worried. It’s not easy to stay inside for a long time. Some people also worry about their jobs and money if they can’t go to work.
After a Lockdown
When a lockdown ends, things slowly start to open again, like schools and stores. It’s important to be careful and listen to rules to keep everyone safe. Lockdown teaches us to be strong, care for each other, and that by working together, we can handle big challenges.
500 Words Essay on Lockdown
A lockdown is when people are told to stay where they are, usually in their homes, because of an emergency. This could be because of a health crisis, like a big outbreak of sickness, or for safety reasons, like when there’s a danger in the community. During a lockdown, schools, offices, and shops may close, and people have to follow special rules.
Reasons for a Lockdown
Lockdowns are used to keep people safe. For example, if a new sickness is spreading very quickly and making lots of people ill, a lockdown can help stop it from reaching more people. It’s like hitting the pause button on normal life so that the problem doesn’t get bigger.
Life During a Lockdown
When there’s a lockdown, daily life changes a lot. People can’t go to school or work like they usually do. Instead, they might have classes or meetings online. Being at home all the time can be hard. Families have to find new ways to stay busy and happy without leaving their houses. This can mean playing games, reading, or learning new hobbies.
The Good and the Bad
Lockdowns can be helpful because they keep people safe from danger. With fewer people moving around, it’s easier for doctors and nurses to take care of those who are sick. But lockdowns can also be tough. People might miss their friends or family members who don’t live with them. Some people might even feel sad or worried because of all the changes.
Following Rules
During a lockdown, it’s important to follow the rules set by leaders. This usually means staying home unless you need to get something important like food or medicine. Washing hands and keeping clean is also very important to stay healthy. People who work in hospitals or stores might still go to work to help others.
Learning from Lockdown
A lockdown can teach us many things. We learn to be patient and to take care of each other. We also learn how to solve problems in new ways, like studying from home or talking to friends and family online. It shows us that by working together and helping each other, we can get through tough times.
After the Lockdown
When a lockdown ends, things slowly start to go back to normal. Schools and shops open again, and people can go outside more. But it’s important to remember what was learned during the lockdown. We should keep washing our hands well and stay home if we feel sick, so we can keep ourselves and others safe.
Lockdowns are not easy, but they are sometimes necessary to protect everyone’s health and safety. By understanding what a lockdown is, why it happens, and how to deal with it, we can all do our part to help during these times. And when it’s over, we can appreciate being able to go out and see our friends and family even more.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Lithuania
- Essay on Do You Believe In Love At First Sight
- Essay on Doctor Career
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Essay on Lockdown
‘Lockdown’ refers to the suspension of the usual privileges of citizens, regarding their movement and socializing. It is imposed by a competent authority to prevent any untoward incident. In India, a lockdown was imposed for many months by the government to contain the spread of novel coronavirus disease. Find here some well-described essays to know in detail about the lockdown.
Short and Long Essay on Lockdown in English
Following short and long essays on Lockdown in different word limits are given here that is useful for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and class 12 in English in 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 500 words. Also find short Lockdown essay 10 lines.
Lockdown Essay 10 Lines (100 – 150 Words)
1) Lockdown refers to the prevention of citizens from moving and socializing as usual.
2) Lockdown is imposed by the government in case of any emergency.
3) India has undergone a lockdown to control the widespread of the Corona virus.
4) The government of India imposed the first lockdown on 25 March 2020, Wednesday.
5) India observed continuous 150 days complete shutdown in the lockdown.
6) Except for the emergency services, everything was closed and restricted.
7) The lockdown was continued for a few months in four parts.
8) The lockdown helped in controlling the widespread coronavirus and massive deaths.
9) Lives and works of many people were affected by the lockdown.
10) Lockdown was not fruitful for the economy as India suffered negative GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
Essay 1 (250 Words)
Introduction
Lockdown is an emergency protocol implemented by the government of India with an objective to contain the spread of a novel coronavirus epidemic. The government implemented a 21 days countrywide lockdown at the beginning which was continued for many months in 4 parts in the entire nation and further the state governments implemented it as per their states need. India was under lockdown for more than 150 days continuously.
Lockdown – The Only Remedy against Novel Coronavirus
Novel coronavirus disease is highly contagious and it spreads fast from person to person. No other disease before has been known to spread such a fast rate as the novel coronavirus. There is no option other than to treat the affected symptomatically; however, the final recovery depends largely on an individual’s stamina and immunity. From the perspective of this scenario, the lockdown seems to be the only practical and effective solution to prevent the spread of the disease.
Although we cannot imagine such scenario for more time our government courage to take such a bold step. It was implemented to keep safe from this deadly virus. Lockdown badly effected our economy and today it is in its fracture mode.
Success of Lockdown
Although we felt safe when the government took such a major but some experts remark lockdown as an unplanned action and it has directly affected the entire nation. Apart from India many other countries also adopted lockdown but they are strong enough to cope up with the economic damage caused due to lockdown.
It would not be wrong to say that the lockdown reduced the flow of this virus, but at the same time cases started to increase rapidly after it was unlocked in India. India became the second-highest infected country. So, in this term, we cannot say that lockdown was truly successful.
Even today schools, colleges, parks, public spaces, cinemas in India are closed. The lockdown can be still seen but the cases are decreasing comparatively. The vaccine has been developed and soon people will get rid of this deadly virus till than keep wearing your mask, wash your hand frequently, use sanitizer and follow social distancing.
Essay 2 (400 Words)
‘Lockdown’ as the name implies is a complete lockdown imposed on the usual movement of the general population of a place. A lockdown can be localized or applied over a wide area, depending on the purpose.
Lockdown in India
- First lockdown : It was 25th March 2020 when it was implemented for the first time, till the 14th of April. When the entire nation was completely shut except for some necessary grocery shops and health facilities.
- Second Lockdown : The second lockdown was announced from 15th April to 4th May with the same set of rules and regulations.
- Third Lockdown : It was implemented from the 4th of May to the 17th of May but in this phase of lockdown some special trains were run to help the daily wages workers. Some people stuck abroad were also bought back. This operation was named ‘Operation Samudrsetu’.
- Fourth Lockdown : It was implemented up to 31st of May and further different states extended as per the condition of their state. Districts were divided into three zones as per the COVID cases in the area. Red zone for most infected areas, Orange for few cases in the area whereas Green for areas with no infection.
Impacts of Lockdown
- On Novel Coronavirus Disease
This is the most significant and most desirable impact of the lockdown. The novel coronavirus is highly contagious, spreading fast from person to person. Lockdown makes social distancing effective; prohibiting human to human contact at the highest level possible. This social distancing helps a lot in containing the spread of the disease.
But at the same time, we cannot imagine continuing lockdown for a long time, because it has directly affected us in many ways.
- On The Economy
A countrywide lockdown isn’t good for the economy and is a setback for the economic growth and development of the nation. With transport suspended, railways and road transport agencies suffer losses to the tunes of crores. Small businesses and daily wage laborers are the most affected. Our GDP is going in negative decimals which is -9.6% this year and it is really a matter of fear because it will directly cause inflation.
- On Pollution Level
This is a significant positive impact of the lockdown. With all types of transport being suspended and also the people being forbidden from roaming unnecessarily, the air quality index improves drastically. The change was felt within a day or two of the lockdown.
- On Emergency Services
Lockdown was good for the emergency services and the personnel in a way that didn’t put additional stress on them. With no traffic and rush like usual days, their job becomes extremely easy and convenient.
Lockdown was very necessary for containing the coronavirus epidemic and preventing it from spreading to the community level. Despite its negative impacts; lockdown was very important. Even today although we have developed the vaccine there are many public places still closed. It is quite good in many ways.

Essay 3 (500 – 600 Words)
Lockdown is an emergency protocol imposed by the government that prohibits people from leaving their homes and venturing into public areas. In the wake of the global coronavirus pandemic spread, several governments across the globe have imposed lockdown in their respective jurisdiction, to prevent the disease from spreading further. The government of India also imposed a countrywide lockdown from midnight of 25th March and followed up to 4 months in every state and further different states followed as per the COVID cases in their states.
Why Is The Lockdown Necessary?
Ever since the coronavirus disease was first reported in China in November 2019 it affected millions of people globally. The disease is highly contagious and spreads at an unprecedented rate as never witnessed before.
The motive of a lockdown is to implement social distancing, preventing people from socializing and unnecessary gathering, so that to prevent the spread of disease from one person to another.
Effects of Lockdown
Lockdown wasn’t easy and was quite harsh experience for daily wage laborers, small businesses, and marginalized sections. These people were devoid of their livelihood and with less saving, find the lockdown financially crippling. That been said; lockdown is still necessary to save lives.
People with permanent employment, usually have the opportunity of working from home and are least affected by the lockdown. Suspension of all modes of transport for the common public caused inconvenience during this period.
Local administration relaxed the lockdown for a couple of hours every day to let people buy the necessary groceries and do other works. However, despite the relaxation people were not allowed to gather in large numbers, roam unnecessarily, and Necessary government offices and emergency services like municipalities, hospitals, police, etc. worked as usual.
Solidarity in Lockdown
Though the lockdown in India is harsh on marginalized sections of the society; people from different walks of life and several organizations have come forward for help. As soon as the lockdown was imposed, many prominent film producers, actors, and business houses have paid thousands of crore of rupees as donation to the Prime Minister Relief Fund. This money was used to be spending on food and providing monetary help to the poor during the lockdown.
Government officers distributed food packages, making sure that no person is left without food in the lockdown phase.
People of India have also displayed a great amount of respect for their emergency services personnel and medical professionals by clapping and celebrating within the premises of their own houses.
Apart from this lockdown today India is second in the list of most affected countries in the world. Lockdown saved us from community spread in India. The vaccine has been developed and soon it will be on the market. Still, some public places, schools, theatres are still closed and it is necessary until and unless all of us get the vaccine.
Lockdown is necessary to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease. It is imperative that we should be strict with the guidelines of lockdown for our own health and safety. The lockdown has been resumed but still, there are some public places under lockdown. Follow the guidelines and cooperate to stay safe and also keep others safe in this epidemic.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions on Lockdown
Ans . Lockdown is the policy that restricts the movement of people and states them to stay in one place.
Ans . The national emergency lockdown in India was implemented for the first time on the 25th of March, 2020.
Ans . The movement of people was restricted in the Covid-19 lockdown to curb the spread of Covid-19 infection.
Ans . Rajasthan was the first state in India to implement lockdown during Covid-19 phase 1.
Ans . Red zones are the areas that are highly infected.
Ans . The first lockdown was implemented by China in Wuhan on 23rd January 2020.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Essay on Impact of lockdown on Students and People
Nobody ever imagined that life could turn like this. Despite being most countries democratic, people are forced to live inside their homes. The basic freedom given to us by our constitutions is taken back from us. Nobody is free to move. If anyone is found breathing in the open air he is beaten by the police and imposed with heavy penalties. What has forced all the governments to take this dictator style decision? Why are people all over the world simultaneously forced to live a completely altered life during lockdown 2020? This Essay on the Impact of lockdown on Students and People will answer all the above questions.
Essay on Impact of lockdown | Coronavirus Impact on Students and other people
With the outbreak of covid 19, the world was locked down. The fast-paced life came to a standstill. Covid 19, a disease caused by Corona Virus, started in China initially and spread all over the globe. All were helpless because the medical fraternity could not invent its antidote. So, the safest and the only option seemed was world lockdown. All the national and international borders were sealed. Some countries announced a 3-6 months stay at home order while others declared complete lockdown in phases.
People, businesses, and governments around the world have changed the way they spend, move, communicate and travel because of COVID-19. Let’s see how life has changed during the lockdown period. Did it alter our life for the better?
Lockdown 2020 in India
Indian Prime Minister Mr Modi announced a country lockdown on 21st march 2020 for 21 days. Later it got extended for more and more days. As Indians are notorious for not following the rules, everyone expected it to last for 3-4 days. But the story was different this time. Police drove away from the people who ventured on roads by giving physical punishments and charging fines. Covid 19 triggered lockdown brought a significant change in the life of all.
Impact of Lockdown on Students in India
This disease has affected all segments of the population. And students are no exception. In India, a lockdown was announced just at the time when CBSE exams were going on. Students of the 10th and 12th classes got stuck in the middle. National level entrance exams had to be postponed. Generally, the months of March and April are very crucial for students preparing for these papers. The pandemic diverted students’ focus from their studies. It has created an atmosphere of anxiety and depression among some students and parents.
Seeing from another angle, Children were the happiest creature in the world after the announcement of lockdown. But due to the setting up of virtual classrooms, their happiness did not last long. Now regular classes were going on with no escape from home assignments. However, they learned a new way of education.
Although, schools and coaching institutes have started online classes. The devices required for attending virtual classrooms are not accessible to all in India. It might create a burden on students’ psychology.
Effect of Lockdown on Senior citizens
The government officials appealed that the elderly people stay inside the home during the period of lockdown. According to doctors adults were more vulnerable to coronavirus. Morning walks and evening strolls were their only way to bring some movement in their stiff bodies. This curtailment left them immobile. But they got the company of all the family members who were otherwise too busy to talk to them. Board games and mythological serial telecasts on national television came to their rescue.
Impact of lockdown on Women
A lockdown increases the burden of household work for all families. While all the domestic helpers were stranded at home, there was no one to share the increased household chores. In Indian families, nobody is empathetic towards the mental and physical health of women due to the increased workload.
Impact of lockdown on Men
Men are the most deeply affected victim of this pandemic. Most of the men leave their homes in the morning to complete the task of bread earning for the family. They spend their whole day outside the house. Lockdown has put them inside the four walls of the house which they are not accustomed to. The absence of professional life is making them sick. Some are lucky to do their work from home with the help of computers.
With the extensions in lockdown, they are adapting to enjoy this altered version of life. Playing online ludo and tambola is a common scene in every house. Some gentlemen are trying their hands on cooking to share a story on Instagram. Watching movies and web series, growing a beard is more a compulsion than a hobby. Sharing basic household work to cheer their better halves makes their bonding even stronger.
Conclusion: Impact of lockdown and coronavirus on people
Today, humans are in cages to save themselves from highly contagious disease covid 19. We were so blindfolded in the race of development that we neglected our spouse, our family, our culture, our environment. We were urgently in a need of some change. But nobody knew that the change would appear like this in the disguise of the Corona Virus.
This period of crisis and global volatility is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity and we should utilise it thoughtfully and productively.
Read More Essays Related to Coronavirus Impact of Covid-19 on Economy Essay Aatmnirbhar Bharat Abhiyan|Self Reliant India Essay in English Social Distancing to Fight Coronavirus How to Boost Immunity during Covid19 Crisis
How to Boost Immunity during Covid19 Crisis Plastic advantage, disadvantage and waste management Tell me about yourself Merits and Demerits of Online Exams Essay Essay on E-Waste in Hindi Online Education versus Traditional Education My First Online Class Experience Essay
Share With Your Friends
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For example, studies conducted during the lockdown in Botswana and Italy have shown that individual online tutoring directly targeting either parents or students in middle school has a positive ...
The transition to an online education during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic may bring about adverse educational changes and adverse health consequences for children and young adult learners in grade school, middle school, high school, college, and professional schools. The effects may differ by age, maturity, and socioeconomic ...
Bhutan first declared closing of schools and institutions and reduction of business hours during the second week of March 2020 (Kuensel, 2020, 6 March).The complete nationwide lockdown was implemented from 1 August 2020 (Palden, 2020).In between, movements were allowed, offices began functioning, schools and college reopened for selected levels and continued with online class for others.
Follow. The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom. As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms. Research suggests that online learning has been shown to ...
The rapid spread of COVID-19 lockdowns forced many females into the traditional roles as caretakers. Common gender disparities that impact a female's education during the pandemic are finances enabling higher dropout rates, domestic violence, child marriage, early pregnancy, and exploitation of child labor. [71]
Even more concerning, test-score gaps between students in low-poverty and high-poverty elementary schools grew by approximately 20% in math (corresponding to 0.20 SDs) and 15% in reading (0.13 SDs ...
The school also serves as an on‐campus site for TCU College of Education teacher candidates as they receive guidance in teaching students with learning disabilities. As COVID‐19 impacted our university community, Starpoint School transitioned to a new online environment, continuing with a focus on literacy learning.
Background The COVID-19 pandemic lead to a sudden shift to online teaching and restricted campus access. Aim To assess how university students experienced the sudden shift to online teaching after closure of campus due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Material and methods Students in Public Health Nutrition answered questionnaires two and 12 weeks (N = 79: response rate 20.3% and 26.6%, respectively ...
The COVID-19 crisis has forced education systems worldwide to find alternatives to face-to-face instruction. As a result, online teaching and learning have been used by teachers and students on an unprecedented scale. Since lockdowns - either massive or localised - may be needed again in the future to respond to new waves of the infection until a vaccine becomes available, it is of utmost ...
This essay is an opportunity to share your pandemic experience and the lessons learned. The college admissions process has experienced significant changes as a result of COVID-19, creating new challenges for high school students. Since the onset of the pandemic, admissions officers have strongly emphasized a more holistic review process.
POLICY BRIEF: EDUCATION DURING COVID-19 AND BEYOND 7 In Africa, particularly in the Sahel region, nationwide school closures due to COVID-19 came at a time when a very large number of
Introduction. The COVID-19 pandemic has posed an unprecedented challenge in education, leading to the suspension of face-to-face teaching (UNESCO, 2020).This change has been particularly challenging in university undergraduate engineering degrees since much of the learning process is based on practical applications, laboratory classes, and direct contact with teachers and other students.
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App ...
The COVID-19 pandemic in the spring dramatically shifted the way children were being educated. From May 28 to June 2, when many school districts across the country are normally in session, 80% of people living with children distance learning reported the children were using online resources. About 20% were using paper materials sent home by the ...
The life of students during the lockdown was a paradigm shift, transforming traditional classrooms into virtual spaces. Adjusting to online learning, students navigated a digital landscape for education and social interaction. The challenges were met with innovation, as virtual classrooms became the new norm.
Conclusion. In conclusion, online classes during lockdown have been a crucial response to an unprecedented global crisis. They have ensured the continuity of education while also revealing both the potential and the challenges of online learning. As we emerge from the pandemic, these insights can guide us in creating a more resilient and ...
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus. Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history. A woman wearing a face mask in Miami. Alissa Wilkinson ...
A diary is by its very nature an intensely personal thing. It's a place to record our most intimate thoughts and worries about the world around us. In other words, it is a glimpse at our state ...
Here are 10 things that students focussed on during times like lockdown. Learn these skills to stay ahead. Cooking and baking. Language learning. Fitness and yoga. Creative Writing. Photography and designing. Networking and IT skills. Social Media management.
Definition. Lockdown essay in English - Lockdown is a term that exploded collectively around the world in the year 2020. With the widespread attack of an invisible virus, known as the Novel Coronavirus, the entire world was devastated by the Pandemic of this virus. It occurs during a wide variety of emergencies and it disrupts normal life.
A lockdown is when people are told to stay where they are, usually in their homes, because of an emergency. This could be because of a health crisis, like a big outbreak of sickness, or for safety reasons, like when there's a danger in the community. During a lockdown, schools, offices, and shops may close, and people have to follow special ...
1) Lockdown refers to the prevention of citizens from moving and socializing as usual. 2) Lockdown is imposed by the government in case of any emergency. 3) India has undergone a lockdown to control the widespread of the Corona virus. 4) The government of India imposed the first lockdown on 25 March 2020, Wednesday.
Essay on Impact of lockdown | Coronavirus Impact on Students and other people. With the outbreak of covid 19, the world was locked down. The fast-paced life came to a standstill. Covid 19, a disease caused by Corona Virus, started in China initially and spread all over the globe. All were helpless because the medical fraternity could not invent ...