

Lean Business Plan Template & How-To Guide
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Historically, business owners have devoted months to constructing a detailed plan to establish strategy, executive, and financial numbers for their business. Although a strategic plan is often created, these entrepreneurs often miss a big piece: gathering feedback from potential customers.
Without collecting data and insight from target customers, the detailed business plan becomes a document of assumptions and guesses rather than a proven success blueprint.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Lean business planning allows you to more quickly and accurately develop your business plan based on actual customer feedback and interactions.
On this page:
Key benefits of lean startup business planning, can you use a lean plan to raise funding, key elements of a lean business plan.
- Lean Planning Process
- Putting The Lean Plan Into Action
Review Your Results & Revise Your Plan
Lean business plan faqs, other helpful business plan articles & templates.

The lean startup business model is supported by a one-page business plan that does not require extensive financial forecasting or long-term market research and development plans. While the traditional business plan details every aspect of your company’s operations, the lean business plan focuses on key factors that present immediate opportunities for new companies to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors. This approach allows you to maintain company focus on your core mission and avoid adding unnecessary information that can weigh down your final document.
The lean startup movement has encouraged entrepreneurs to shorten their plans down from hundreds of pages to a one-page business plan or less – essentially eliminating the need for small businesses to create traditional plans at all. Rather than spending time creating lengthy reports, owners can simply list their core values, mission statement, market analysis, marketing strategies, and projected financial statements – all on one page.
Some companies even document their entire value proposition on a single sheet of paper which serves as both the foundation for further market research and development to improve its product or service offering. By having this type of information readily available to share with investors or clients, your company will appear more professional and prepared without taking up too much time creating unnecessary documentation.
Developing a lean business plan is a critical step in launching or growing your business. However, it’s important to note that if you’re seeking VC funding , bank funding, or angel investors , a traditional business plan is required. Such a plan includes additional research, strategy, and financial forecasts to give investors and lenders the information they need to determine whether they will receive an adequate ROI (return on investment) if they provide funding to you.
Below are nine key elements of a lean business plan example:
Business overview
Describe what the business does.
Value propositions
Detail the value your business brings to the market and the industry.
Key partnerships
List the key partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, vendors, or software firms, with whom your business will work.
Key activities
List the key activities your business will perform to gain a competitive advantage, grow market share, and fuel profits.
Key resources
List the resources that your business has at its disposal to create maximum value. This could include human capital (your own experience or that of your core team), intellectual property, patents, funding, etc.
Customer relationships
Describe how your customers will interact with your business. Will you have personal or automated channels of communication available? Chart out the end-to-end customer experience journey and how you intend on building customer relationships.
Customer segments and channels
Specify your target audience, what requirements of theirs you cater to, how you reach out to them, and, most importantly, the steps you are taking to generate a customer experience that will result in long-term loyalty.
Cost structure
Define your key costs and variable costs, and how they represent a competitive advantage if applicable. A lean startup business plan (versus a lean business plan for an existing company), needs to also include key startup costs you anticipate in launching your company.
Revenue streams
Describe how your business generates money. What are your revenue streams or sources, for example, selling advertising space on your app or publication, membership fees, direct sales, etc? List all your revenue sources in this section, starting with the source that delivers the largest revenue.
Download Your Free Lean Business Plan Template
Lean Business Planning Process
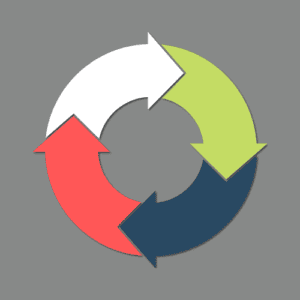
To create your lean business plan, follow these 4 steps:
Create the Plan
Your lean business plan will start with you, your business idea, and one sheet of paper. Yes, one sheet is all you will need.
Business Strategy
You will first begin by explaining your business strategy. This is simply a summary of what you are planning to do, who your customers are, and who your competitors are.
Identify the problem you are trying to solve along with your solution and potential alternative solutions. Then, describe your target customers. Focus on defining and describing the audience you expect to serve, who they are, where they live, etc. Lastly, explain who your competitors are. Describe what they’re doing and how they’re doing it.
Easy enough, that is all you need for your plan. With lean business planning, you simply create a business strategy that focuses on the essence and function of your business: what you’re doing and who it’s for.
Course of Action
The next piece of your lean business plan is laying out an outline of your course of action. This section will illustrate how you’re going to make your strategy happen. Here, you will focus on sales, marketing, your team members, and any potential key partners or future relationships in the business world.
Sales Strategy
It is important to first begin creating your course of action by establishing just what your sales strategy is. Will you be selling in a physical store or online? Or both? Consider whether or not your product will be sold in stores owned by other companies, and who these companies would be.
Marketing Strategy
Next up is creating your marketing strategy. Think about how you will effectively and attractively reach your potential customers. Here, consider the following:
- Target market
- Online presence
- Advertising
- Public relations
- Special promotions
Team Members
The success of your course of action will be dependent on the team members who execute it. If you need to build a team, think about who the key people are that you will need to hire. What are their qualifications and characteristics? If you already have an existing business, highlight the key members that help run your company and accomplish strategy and success.
Partners and Business Resources
Begin to think of the other businesses that you might want to work with. Most likely there are other companies that you will have to work with to make your strategy work. Brainstorm all key resources, business partners, distributors, and key suppliers that you will need to have relationships with.
After constructing your Course of Action, it’s time to create your schedule. Since lean business planning is centered around efficiency, designing an organized schedule is key.
For startups:
If you’re starting a new business, you should begin with getting to know your customers. For you to grow a viable business, you must understand your customers’ views, wants, and needs. Your goal here will be to ensure that you’ve developed a strategic, organized strategy. A startup’s schedule will often include sending out surveys, interviewing customers, and researching locations.
For established businesses:
For most businesses that have been around, your schedule should be focused on achieving the business goals you have identified. Your schedule should have specific actions with names, dates, and even times. The schedule you create should hold your business and its employees accountable for their work and progress.
The final part of scheduling is to make time to regularly review your Lean Business Plan. As your business progresses, so will your Lean Business Plan. Setting a regular review time is critical to get your business moving in the right direction and your team members on board.
Forecast and Budget
Even if you have the best business idea in the world, if the numbers aren’t there, it won’t work out. The final section of your Lean Business Plan should depict a business model that forecasts and budgets for the future.
Here, all you have to do is create basic bottom-up sales forecasts and a basic budget for expenses. Do not try to sugarcoat here, these numbers should be as practical as possible. With this, you will be able to identify just what will and won’t work for your business.
By taking on this pragmatic sense, you may begin to feel like your business will not be able to succeed unless you are flooding with customers or getting daily news coverage. You may need to alter your business model here and adjust your pricing and expenses to ensure that you can turn a profit. Also, keep in mind any funding options for large-scale marketing and PR campaigns. Keep a realistic view, but also be sure to acknowledge offers that may be available to help you out.
Putting The Lean Business Plan Into Action
After you have completed your lean business plan, it’s time to put it into action. Your main goal here should be to get a deeper understanding of your customers. Is your product solving their problem? Are they willing to pay for it? Do they want something else?
Reaching out to your customers early on will help you get a grasp on their wants and needs to make the necessary alterations to your Lean Business Plan for ultimate success. It will also provide you with some insight as to what products you may want to produce in the future.

As earlier mentioned, your lean plan should be reviewed regularly to discern just what is working and what isn’t. Compare your results with your lean plan. Are sales growing according to plan? Does the plan need to be changed?
For startups who have little to no metrics to track, review your customer interviews, surveys, or any other information that you have gathered about the industry. Here, you can begin to continually refine your plan and strategy if necessary.
If you are an established business, review your recent results with those from the past. Take note of your key metrics as well as foot traffic in stores, website visits, and any other critical units of measure for your business success.
After analyzing your results, it’s time to revise your plan. Remember that your Lean Business Plan is a process rather than a finalized document, and it is made for continuous improvements. Don’t be afraid to make any necessary changes to aid in your business’s success.
Lean business planning might just be the key to your company’s ultimate success. This simple method of business planning has helped many startups and existing businesses advance and flourish such as Google, Facebook, YouTube, and Amazon. By focusing on reviewing, revising, and business management, lean planning allows you to test out different strategies to find the best one to create a successful business.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
What is a lean business plan?
A lean business plan is a compact, single-page document typically for internal use. Lean planning is a short-term business plan strategy for making small changes and measuring the results to improve the efficiency of the business. This compares to the formal business plan which is typically very detailed, includes 10 key components , and can be up to 15-25 pages in length.
What is the purpose of a lean business plan?
The lean business plan is primarily for internal use, so it doesn’t have to be a fancy document. The purpose of this plan is for you to document the changes you’ve made to your business so that you can analyze their effectiveness in improving business operations, marketing, and/or sales over a short period.
How long is a lean business plan?
The lean business plan is typically a one-page document to describe your business strategy including your goals, targeted audience, your business model, and how your sales and marketing strategies work to support your business goals.
How do you create a lean business plan?
Refer to our article on ‘ Lean Business Plan: How-To Guide & Template ’ for the 4 steps in creating a lean business plan or a lean startup business plan template . You can also download our free lean plan template to help you get started.

Lean business plan
Discover the lean business plan template, perfect for entrepreneurs and small businesses. Simplify planning with key sections on strategy, market analysis, and financials.
Share this Template
Streamline your business strategy: The essential lean business plan template
Dive into strategic planning with our lean business plan template, designed specifically for entrepreneurs, startups, and small business owners looking for a streamlined approach to business planning. This template strips away the complexities, helping you focus on the core elements necessary to articulate your business vision, strategy, and action plan efficiently.
What's inside this lean business plan template?
- Company name & mission : Begin with the basics, establishing your business identity and mission to guide all your strategic decisions.
- Our offer : Clearly articulate what your business offers, highlighting your unique value proposition to stand out in the market.
- Problem statement : Define the problem you're solving, ensuring your business targets real needs for a solid market fit.
- Solution : Summarize your solution in one sentence, showcasing how you uniquely address the problem.
- Target market : Identify and describe your primary audience segments, tailoring your approach to meet their specific needs.
- Key competitors : Offer insights into your competition, helping you position your business effectively in the marketplace.
- Sales and marketing strategy : Outline how you'll reach and convert your target audience, detailing sales channels and marketing tactics.
- Financial projections : Present a snapshot of your financial outlook, including key expenses, revenue streams, and growth trends.
- Management team and partners : Highlight the people behind the business and their roles, underscoring your team's expertise and capabilities.
- Action plan : Set clear milestones and deadlines, assigning responsibilities to ensure progress towards your business goals.
Key benefits of using this lean business plan template
- Focused strategy : Concentrate on what truly matters to get your business off the ground or to the next level with a clear, concise plan.
- Efficient planning : Save time and resources with this streamlined business plan tempalate that covers the essentials without the fluff.
- Clear direction : Eliminate ambiguity in your business strategy, making it easier for your team and partners to align with your vision.
- Competitive insight : Understand your market and competition better, enabling you to position your business more strategically.
- Financial clarity : Gain insights into your financial health and projections, aiding in better decision-making and investor communications.
- Action-oriented : Move from planning to doing with a structured action plan that keeps your team focused and accountable.
Get started
Elevate your business strategy without the complexity. Our lean business plan template is your first step towards a more focused, effective, and successful business journey. Start shaping your strategy today, driving your business forward with clarity and purpose.
And, for a more comprehensive approach to business planning try our business plan template.
FAQ About the Lean business plan Template
Trusted by millions, including teams at

Discover More Templates
Take impactful to a whole new level
Always with you
Easy to use
Works your way
Powerful Features
Get in or get out
Offline first
Beautiful sharing
You’re not alone
We’re here to help

Deconstruct Your Big Idea on 1-Page
Business plans take too long to write, are seldom updated, and almost never read by others. You need dynamic models, not static plans, when going fast and under extreme uncertainty. The Lean Canvas replaces long and boring business plans with a 1-page business model that takes 20 minutes to create and gets read.

Lean Canvas is used by over a million people that span startups, universities, and large enterprises.

What is a Lean Canvas?
Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan template created by Ash Maurya that helps you deconstruct your idea using twelve business modeling building blocks.
A Lean Canvas can describe a business model, a product release, or even a single feature, making it a highly popular business model innovation and product management tool used by millions worldwide.
If you have ever written a business plan or created a slide deck for investors, you’ll immediately recognize most of the building blocks on the canvas.

Lean Canvas helps you communicate your idea clearly and concisely to key stakeholders.
You can outline multiple business models on a Lean Canvas in one afternoon instead of writing a business plan, which can take several weeks or months. More importantly, a single-page business model is much easier to share with others, so it will be read by more people and updated more frequently.
Lean Canvas helps you systematically build and launch successful products.
When taking on a complex project, like, say, building a house, you wouldn’t start by putting up walls. You’d probably start with an architectural plan or blueprint — even if it’s just a sketch.
Building and launching an idea is no different.
Most entrepreneurs start with a strong initial vision and a Plan A to realize that vision. Unfortunately, most Plan As don’t work.
It has statistically been shown that two-thirds of successful startups report drastically changing (or pivoting) their plans along the way.
So, what separates successful startups then isn’t necessarily starting with a better initial plan (or Plan A) but finding a plan that works before running out of resources .
Until now, finding this better Plan B or C or Z has been based largely on gut, intuition, and luck. There has been no systematic process for rigorously stress testing a Plan A.
The first step to iterating your Plan A is gaining clarity on your Plan A.
This is what the Lean Canvas helps you do.
What is the difference between Lean Canvas and Business Model Canvas?
Lean Canvas was adapted from Alex Osterwalder's Business Model Canvas and optimized for the Lean Startup methodology.
The motivation behind Lean Canvas was creating a more founder-focused business modeling tool better suited for early-stage products.
It replaces these boxes on the Business Model Canvas: key partners, key resources, key activities, and customer relationships with these boxes: problem, solution, key metrics (KPIs), and unfair advantage (a defensible competitive advantage).

See what's different

Lean Business Plan Template

What is a Lean Business Plan?
A Lean Business Plan is a streamlined, highly measurable approach to achieving your business goals. It helps teams of any size and industry to create a comprehensive strategy with clear focus areas, objectives, and measurable targets (KPIs). By taking small steps, measuring results, and making frequent course corrections, teams can optimize their business performance and ensure they are taking the best steps to reach their goals.
What's included in this Lean Business Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Lean Business Plan template for?
The Lean Business Plan Template is designed for teams of any size and industry looking to take small steps, consistent tracking, and frequent course corrections for optimize the business. It is an effective and efficient way to organize, track, and optimize the performance of any business.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a broad category that is related to your business. Examples of focus areas could include optimizing cash flow, increasing customer satisfaction, or improving productivity.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the specific tasks you need to complete in order to reach your overall focus area goal. When defining objectives, be sure to be as specific as possible and think about measurable targets (KPIs) that will help you track your progress. Examples of some objectives for the focus area of Optimize Cash Flow could be: Increase Cash Flow, and Increase Revenue.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs (key performance indicators) are measurable targets that you set to help track your progress. KPIs can be financial, operational, or customer-related goals that give you insight into the performance of your business. An example of a KPI for the focus area of Optimize Cash Flow could be: Decrease avg payment time from 30 days to 15 days.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects (or actions) are specific initiatives that need to be completed in order to reach your objectives. Think about the resources, time, and budget required to complete each action and how it will help you reach your goals. An example of a project related to Optimize Cash Flow could be: Launch Payment Process.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
The Cascade Strategy Execution Platform is a comprehensive tool that helps teams to track progress, and make frequent course corrections to reach their goals faster. With user-friendly dashboards, and easy-to-track metrics, Cascade helps teams to easily track, measure, and optimize their business performance.
Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

Noah Parsons
11 min. read
Updated April 15, 2024
Let’s face facts: Writing a traditional business plan is a hassle.
- A traditional business plan takes too long to write.
- Most people won’t even read it from cover-to-cover.
- It’s often outdated by the time you finish writing it.
- It doesn’t lend itself to frequent and easy updating—and that’s the core of the problem.
Historically, entrepreneurs have taken months to craft detailed plans without even gathering feedback from potential customers. They’ve viewed business planning as a single hurdle to get their business up and running or a thick wad of paper to shove across a banker’s desk in order to get the funding they need.
These business plans end up as just a collection of guesses and assumptions, instead of a proven roadmap for growth.
But planning is still critical, even if the business plan might be broken. Studies have shown that businesses that set goals and track their progress grow 30 percent faster than those who “just wing it.” Furthermore, even established businesses grow faster when they have a plan .
So what if I told you there was a better way to do business planning? One that lets you adjust and refine your plan as you gather more information about your business and customers.
A method known as Lean Planning.
- Welcome to the Lean Planning method
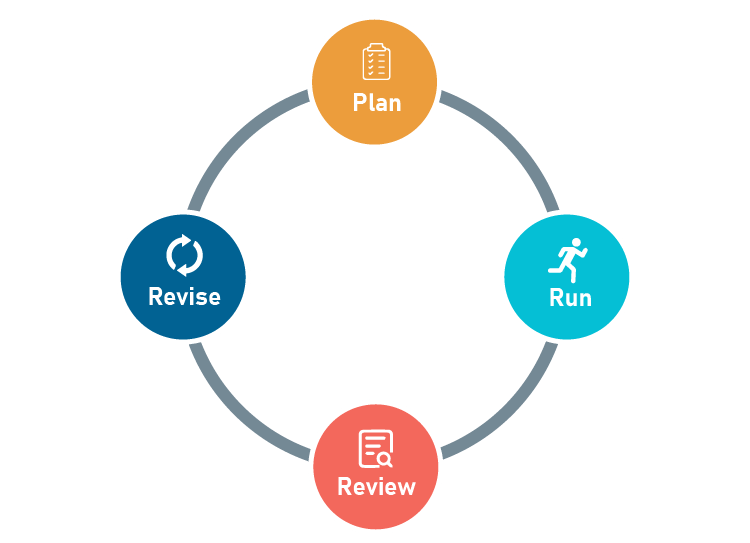
Lean Planning is a 4-step process that helps you discover a business model that works and manage your company successfully.
Here’s the Lean Planning process:
- Create a one-page plan
- Test the plan
- Review your results
- Revise your plan
These 4-steps replace the traditionally lengthy business plan with a 20-minute planning process. This ensures that you are taking small steps, reviewing your results, and creating incremental improvements—all while reducing your risk of failure.
It’s also simpler and faster than writing a traditional business plan. And, possibly, the greatest benefit is that this method can benefit both startups and established businesses.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
If you’re a startup
Lean Planning helps you quickly figure out if your idea is any good and what you need to change to build a viable business.
If you’re an established business
Lean Planning works even if you’re already up and running. It helps you continually refine and tweak your strategy while measuring your progress toward your goals. After all, planning is about making better management decisions, not about producing a thick document that sits in a drawer.
Read on to learn how to make the lean model work by creating your own one-page business plan .
- Step 1: Create a one-page plan
The Lean Planning methodology starts with a one-page plan you can create in 20 minutes .
That’s right—one page. Lean Planning is a simple methodology and your one-page plan should be simple, too. You can download a lean planning template and fill it in as you follow the steps below.
What to include in your one-page plan
- Strategy: What you’re going to do
- Tactics: How you’re going to do it
- Business model: How you’re going to make money
- Schedule: Who is doing what and when
Let’s dive into each section.
Your business strategy
Your business strategy is simply an overview of what you want to do and who your customers and competitors are. Start by identifying the problem you are solving for people and follow up by explaining your solution to this problem.
The problem you’re solving
Businesses exist to solve problems for customers. Their products and services fill a need or satiate a desire. If all you have is a solution that is in search of a problem, you’re going to have a hard time building a successful business. So, start with the other side of the equation and focus on how you can help your customers solve a problem.
Start small with just one or two sentences or a few bullet points to identify the problem you are solving. Do the same thing to describe your solution.
Your ideal customer
Now, quickly describe your target market. Who is your ideal customer? If you know how many potential customers are out there, great. If you’re in the early stages of fleshing out your business idea, don’t worry too much about detailed market research . Instead, focus on defining your ideal customer —who are they, and what are their key attributes?
Your competition
Finally, create a shortlist of your competition . How do your potential customers solve their problems today?
That’s it. A business strategy doesn’t have to be complicated with Lean Planning. It’s just a few bullets points that describe the essence of your business: what you’re doing and who you’re doing it for.
The next section of your one-page plan is a short outline of your business tactics. This is just an outline of how you will make your strategy happen. You’ll be thinking about sales, marketing, the team you might need , and any partners or outside resources you’ll need to leverage.
Your sales strategy
Start by thinking through your sales strategy. Are you selling online or building a physical store? Maybe both? Or, perhaps your product will be sold in stores owned by other companies.
Your marketing strategy
Next comes your marketing strategy. How are you going to reach your customers? How do they find out that you exist and that you solve their problem?
If you need to build a team to grow your business, who are the key people that you’ll need to hire? If you’re an existing business, who are the critical employees that run the company and execute your strategy?
Key partners and resources
Finally, think about other businesses that you might need to work with to make your strategy happen. Are their key suppliers or distributors that you’ll need to have relationships with?
Remember, this is on a single page, so each of these sections should just be three to five bullet points each.
Now it’s time to build a schedule. Lean Planning is all about getting things done, so you need a timeline to follow.
Your next step is to get out from behind your desk and go talk to your potential customers (I’ll go into more detail on this in a moment). Your goal will be to verify that you’ve defined a solid strategy . To that end, a startup’s schedule should include things like conducting customer interviews, sending out surveys, researching physical locations, interviewing potential suppliers, and so on.
Your schedule will probably be focused on specific business milestones that are related to executing your strategy and implementing your tactics.
It’s critical to have accountability here. Your schedule should have dates and people responsible for completing each task.
Finally, make sure to include a time to regularly review your plan. You’ll want to review and revise this plan frequently, so having a regular review point is critical. I recommend a monthly review cycle, but reviewing more frequently is fine, too.
Business model
Even if you have a problem that’s worth solving, a solid solution to the problem, and a target market that needs your solution, you don’t have a business unless the numbers work out. You need a business model that works. The last component of your one-page plan is a basic forecast and budget to ensure that a great idea can actually lead to a great business.
Yes, forecasting and budgeting do mean looking into the future, and no one knows the future (at least I don’t!). But, it doesn’t have to be as difficult as it sounds.
Putting together some basic, bottom-up sales forecasts and a basic budget for expenses will quickly tell you if you have a business model that works—one that can create a viable business that will pay the bills.
At this stage, it’s important not to paint an incredibly rosy picture of your financial prospects. Instead, the sales forecasts should be as realistic as possible. Assume that not nearly as many people as you think will show up in your store. Assume that your website won’t get mainstream press coverage.
With this “realistic” forecast, do you still have a viable business? Can you turn a profit ? If you can only be successful with incredibly high volumes of customers, you may need to take a second look at your pricing, expenses, and other aspects of your business model. Or, make sure that you get the kind of funding that’s needed for large marketing and PR campaigns.
You can get started on your one-page plan right away by downloading our free template . You should be able to complete an initial draft in under an hour—that’s much faster than writing a traditional business plan.
- Step 2: Test the plan
Now that you have your one-page plan in hand, you’re ready to start putting the plan into action to see if your ideas will work.
Depending on your business stage, you’ll do this in different ways. If you’re a startup with an unproven idea or an existing business that’s considering a new strategic direction—your next step is to validate them.
Your one-page plan is just a set of assumptions about a business. Ask yourself:
- Do the target customers actually have the problem that you think they have?
- Does the solution you’re proposing actually solve their problem?
- Do your target customers want to pay for your solution? How much?
Reducing risk is your goal in the early stages of starting a business
Starting a business is full of risks . There are just so many unknowns, and it’s incredibly risky to just build your business based on a set of assumptions about your target market, their problems, and how they’ll react to your solution.
Your plan is a really just a set of educated guesses that need to be answered and then revised on a continuous basis until most unknowns are removed. That’s how you reduce risk.
So, you need to take the very simple, but very challenging step of actually talking to your potential customers .
Look at your first version of your plan as a set of assumptions that need to be proven true or false and then go back and revise your assumptions as you go. Refining your plan so that it’s a collection of facts instead of guesses can be the difference between a successful business and a failure.
If your business is up and running, focus on implementation
For more mature businesses that already know a lot about their target customers, the goal of the plan is to help guide implementation. In this situation, use a one-page plan to get everyone on the same page, set goals, and manage the business.
- Step 3: Review your results
Both Silicon Valley startups and Main Street small businesses need to know how they are doing. Which means Are they growing according to plan? Why or why not? If not, what changes need to be made? Should the plan change?
For new startups
If you’re just getting started and don’t have many (or any) metrics to track yet, you should be reviewing the results of your customer interviews and any other information that you’ve gathered that would change your strategy. Perhaps you’ll be refining your solution or even tweaking the definition of the problem you are solving. Perhaps you’ll refine your marketing and sales strategy.
For established businesses
Beyond tracking key financial metrics such as cash , sales, expenses, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, businesses must track the other key metrics that are critical to their success. These other key metrics might be website visits, foot traffic in the store, tables turned in a restaurant or any other core number that drives business success.
Reviewing your results regularly is key to better management and success. These metrics should be reviewed at least monthly in a regular plan review meeting with key business partners and employees. This is when you refine your plan and your pitch if necessary and track your ongoing action plan.
- Step 4: Revise your plan
Lean Planning is a process, not just a document. It’s is all about continuous improvement. You’re quickly defining a strategy, experimenting to see if that strategy works, reviewing the results, and revising the plan before you start again.
Lean Planning is never finished. It’s simply a process for running your business better, more efficiently, and setting you and your team up for success.
What if you need a more detailed business plan?
There may be a time when you need a more detailed business plan. There’s nothing wrong with that. Some people might want to read it, you may need to submit a full plan for funding and you might even want to document your strategy in more detail.
Your detailed business plan will be born from your one-page plan. The ideas will transfer from bulleted lists to sentences and paragraphs. You’ll add more detail to your sales and marketing strategy, your pricing strategy, and perhaps your manufacturing plans and distribution strategy.
For a step-by-step guide to creating a detailed business plan, check out our guide .
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
8 Steps to Write a Useful Internal Business Plan

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Start diagramming Start diagramming
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
FigJam Simplify your plan with our lean canvas template
Streamline the path to success with a lean canvas diagram that inspires your team to break down every big business idea, discover opportunities, and contend with internal and external influences—on one concise document.

Lean canvas template
Outline goals and unlock new insights with your team with editable lean canvas examples.
Think inside the boxes
Distill your mission, metrics, and milestones on a portable, easy-to-read one-pager that everyone in your orbit can understand—and enjoy.
Spread the word: Share plans and milestones to instill an understanding of the collective purpose.
Learn from past successes: Reflect on your progress—and refine plans—by easily revisiting your lean canvas model template.
No decisions in a vacuum: Make informed decisions when you focus on detailed metrics and the broader landscape.

FigJam Your next steps, in a nutshell
Want to get your project in shape? Strengthen your core. With collaborative chat and commenting features, community-built widgets, and easy-to-use workspaces, FigJam’s lean canvas model templates unite teams around metrics, goals, and insights.
Snapshots that aren’t stuck in time
Get a clear picture of your key metrics and goals on a shared lean canvas. Then, zoom in on any aspect of your business plan with more templates from our Community.

Process map
Outline collaborative processes for a more efficient workflow.

Strategic plan template
Define your strategy, refine your approach, and align across teams.
Other templates from the community
Scale in style with more templates from our Community.
What is a lean canvas?
A lean canvas is a one-page diagram, divided into boxes, that shows your venture’s key characteristics at a glance. While you can customize your diagram, many lean canvases include boxes for the following categories: key metrics, cost structure, customer segments, channels, unique value propositions, and any problem that you’re facing.
When making your lean canvas, it’s important to know your project, business, and landscape well. Bring your whole team on board for a brainstorming session and distill ideas and priorities from there.
What are key metrics in a lean canvas?
Key metrics are your definition of success and are an essential part of a lean canvas diagram. They function as a set of shared goals for your team as well as a measuring stick that helps track performance.
Key metrics depend on specific goals, so they vary from company to company, project to project, and lean canvas to lean canvas. Are you scaling up? Are you testing out a new product? Perhaps your key metrics would include the number of subscribers, daily visitors to your website, or your lead conversion rate.
What is a high-level concept in lean canvas?
When considering how to use lean canvas templates effectively, you’ll want to understand the key points of the one-pager—including the high-level concept box.
The high-level concept, a sub-category under the unique value proposition (UVP) box on the lean canvas model example, is a succinct one-sentence description of what your company stands for and how it differentiates itself from the market. You can think of it as your elevator pitch.
Distilling the whole of your company into a sharp one-liner is no easy task so tackle this category last. On FigJam, you can work it out together. Invite the whole team and share any business idea freely on our editable, customizable template.
How do I create a lean canvas template?
Deconstruct your business plan with a lean canvas template. Follow these steps to use this template effectively:
- Explain your business model scenario.
- Fill out the relevant sections of the template using the prompts as a guide. Evaluate key elements of your business, including the problems your business solves, and the solutions it offers. List your unique value proposition and unfair advantage, and identify key customer segments.
- Identify the costs of your business and the estimated revenue it will bring in.
What are the benefits of using a lean canvas template?
A lean canvas template is a one-page business plan that helps teams easily visualize their business model. By following a simplified framework, teams can focus on the most important elements of their model to inform their business strategy and overall decision-making process. Plus, a lean canvas template is easily shareable with others making it easy for key partners to review and provide feedback.

Other templates you might like
Explore 1,000+ templates on the Figma community
Explore even more templates, widgets, and plugins—all built by the Figma community.
A Guide to Creating a Lean Business Plan (2022)
Don’t have the time to develop a formal business plan for your startup? Here’s how to create a lean business plan to put things into motion.

Vivienne Chen
Vivienne is a Product Marketer at Bubble. She is a storyteller and is passionate about meaningful ways technology can help foster social solidarity.
More posts by Vivienne Chen.
The dramatic increase of small businesses in the United States during the last five years prompted the business community to rekindle the concept of Lean Business Plans. While having all these start-ups is laudable, 45% of them fail after five years.
The key to having a successful business, small or large, is having the right idea at the right time and crafting a viable business plan to fill that market niche . However, many entrepreneurs don't write business plans because they recoil at writing a voluminous traditional or formal business plan that spans 30 pages and has multi-year income statements and layers of operational complexity.
A lean business plan is the perfect solution for that problem.
Traditional Business Plan vs. Lean Business Plan
Traditional business plans tend to be written for start-ups that have multi-million-dollar revenue objectives and require large amounts of seed funding for a large staff and large office spaces that keep the enterprise running until it turns a profit. Investors want to know how their money will get spent, the potential market share, and the founders' experience. Hence, the 30-page masterwork loaded with numbers, graphs, and charts takes three months to create.
A lean business plan, however, is more effective for a small- to medium-sized business (SMB) because it concentrates on the key elements of the company. You’ll give a traditional plan a big haircut by writing a lean plan that outlines your business idea, what market problem you’re solving, how you’ll solve it, how much money you need, and when you’ll break even.
Why Lean Business Plan Methodology Is Gaining in Popularity
The Small Business Association (SBA) encourages entrepreneurs to develop a lean business plan first , even when contemplating writing a traditional plan later. This approach helps lean startups organize their concepts without getting bogged down with unwieldy traditional plans that often discourage writing a plan in the first place.
Start-ups commonly fail for six reasons . However, entrepreneurs today have access to a greater variety of resources than ever. Web-based apps, digital libraries, government agencies like the SBA, and mobile solutions provide a robust ecosystem for new companies.
These invaluable support systems often mitigate the need to write traditional plans for SMB start-ups because vast data stores are but a click away that can help entrepreneurs and potential investors validate any business model.
Benefits of a Lean Business Plan
Lean Business Plans continue to grow in popularity for these important reasons:
- Accessibility: Lean plans are relatively easy to conceive, formulate, and understand. Anyone with basic business sense can discern the unique value proposition (UVP) and unique selling proposition (USP) without being a former CEO.
- Speed: A lean business plan only takes two to four days to write and requires only three to five pages to complete. Compared to a traditional plan, this lean approach moves at light speed.
- Flexibility: A lean plan allows you to organize the business concept and summarize the UVP and USP in short, easy-to-digest thoughts, which can be modified when new information or investor inputs are presented. And it can be upgraded to a traditional plan later if needed.
The Major Components of a Lean Business Plan
Since you’re writing a lean business plan, you’ll be pleased to learn that such plans still have all the key elements of a traditional plan (again, making it a great foundation to build on later as you grow your business).
- Business Model : There’s no way around this essential requirement. Everyone, especially you, must understand the business model you’re starting to make a profit (e.g., retail, manufacturing, fee-for-service, etc.).
- Strategy: This describes how your company will solve a problem or addresses a market need and how it differs from competitors (aka the differentiator).
- Tactics: Outlines the operational steps needed to manage marketing, sales, and business objectives.
- Schedule: Explains when your business starts operations, where it’s located, when it expects to break even, and when it’s profitable.
- Income/Expense Statement: Summarizes revenues, sales, and expense projections for one year.
What to Include in a Lean Business Plan
The value of “lean” means describing these elements in a few short and clear sentences; write only one paragraph per subject.
- Overview: Describes your company’s mission
- Problem: Shows what problem you’ll solve or market need
- Solution: Outlines how you solve the problem
- Target Market: Defines your customers and the market
- Competition: Identifies competitors and what differentiates your company
- Marketing: Explains how you’ll reach customers
- Sales Channels/POS : Outlines where you’ll meet customer needs
- Revenue: Shows how you’ll make money
- Expenses: Summarizes start-up costs and ongoing expenses
- Milestones/Growth: Projects timelines for attaining business goals
- Partners/Resources: Indicates your business connections and other professional assets
- Talent/Roles: Identifies the team, relevant experience, and type of expertise you still need
How to Write a Lean Business Plan
Since you now understand the requisite elements of a good lean business plan, these links provide excellent resources and apps to help you write a lean business plan document.
- Hoshin Planning Process : Outlines a step-by-step thought process needed to develop a lean business plan.
- SBA Guide to Lean Business Plans : Shows how to write a lean business plan.
- What It Costs to Start a Business in 2022 : The Bubble community offers excellent tips on what it costs to start a business.
- Emerald Insight : Provides insights on what kind of business plan to use.
- Startly : A one-stop service that provides enhanced time and expense solutions.
Important Next Steps
- Add an MVP Summary. A start-up that plans to sell a new version of an existing product should consider adding a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) summary. The MVP protocol is an important testing and engineering process that ensures a prototype gets the proper development and testing prior to release.
The MVP methodology plays well with the lean business philosophy because it enhances the development of existing products rather than starting from square one.
- Get Funding. Once you have a solid lean business plan, you'll be in an excellent position to look for funding. The Bubble community can show you how to get seed funding .
- Getting Started. There is no time like the present to start building your dream. This is your Call to Action (CTA): wake up, get up, and start-up. Today.
How a No-Code Solution Like Bubble Can Help
Bubble’s numerous no-code platform solutions are invaluable tools that help entrepreneurs start new businesses. In addition to saving considerable time and money during the development phase, the Bubble community offers a wealth of know-how and support tools that guide entrepreneurs during the daunting start-up process.
These support structures complement the lean business plan approach because Bubble eliminates many infrastructure costs and operational hurdles a new company must overcome.
About Bubble
Bubble is a leader in the no-code movement. Bubble offers a powerful point-and-click web editor and cloud hosting platform that allows users to build fully customizable web applications and workflows, ranging from simple prototypes to complex marketplaces, SaaS products, and more.
Millions of users are building and launching businesses on Bubble — many have gone on to participate in top accelerator programs, such as Y Combinator, and even raised $365M in venture funding. Bubble is more than just a product. We are a strong community of builders and entrepreneurs who are united by the belief that everyone should be able to create technology.
Start building with a free account

Build the next big thing with Bubble
- How to build
- Responsive design
- Version control
- Feature index
- Integrations
- Marketplace
- Partnerships
- Brand guidelines
How to make a lean business model canvas
Imagine that you have an idea for a new product or business. Yet, as enthusiastic as you are about the potential for this nugget of inspiration, you’re also plagued by this question: Will it work? Is it actually a viable idea?
A lean business model canvas is a one-page business plan that helps you break down your product or business model, question and test your assumptions, and determine if your idea actually has legs.
Lean business model canvas explained: What is a lean canvas?
You might also hear a lean business model canvas referred to as a variety of other, similar terms like a lean business canvas, lean business plan, or even simply a lean canvas.
This tool was created by Ash Maurya and is an adaptation of the original business model canvas by Alex Osterwalder .
You can think of a lean business model canvas as a straightforward business plan that skips the fluff and gets to the most important elements you need to identify or evaluate (primarily, the problem you’re solving).
When you have an idea for a product or business, you’ll use a lean business model canvas template to fill in the various sections (more on those in a minute) and validate your idea.
The lean canvas is most frequently used by lean startups, which use a lean startup methodology to deliver products to customers faster and determine whether or not the business model itself is viable. In short, lean startups and lean canvases are all about moving fast, testing, and iterating.
Lean canvas example
One of the best ways to understand a lean business model canvas is to see one. So, let’s set up a lean canvas as an example.
Perhaps you have an idea for a business: You want to create an app or a website that’s essentially a database of parks and playgrounds, which parents can search and filter using location, features (splash pad, baby swings, etc.), and more.
You want to dig into your idea even further using a lean business model canvas. Here’s a simple peek at what that could look like after jotting your initial notes down:

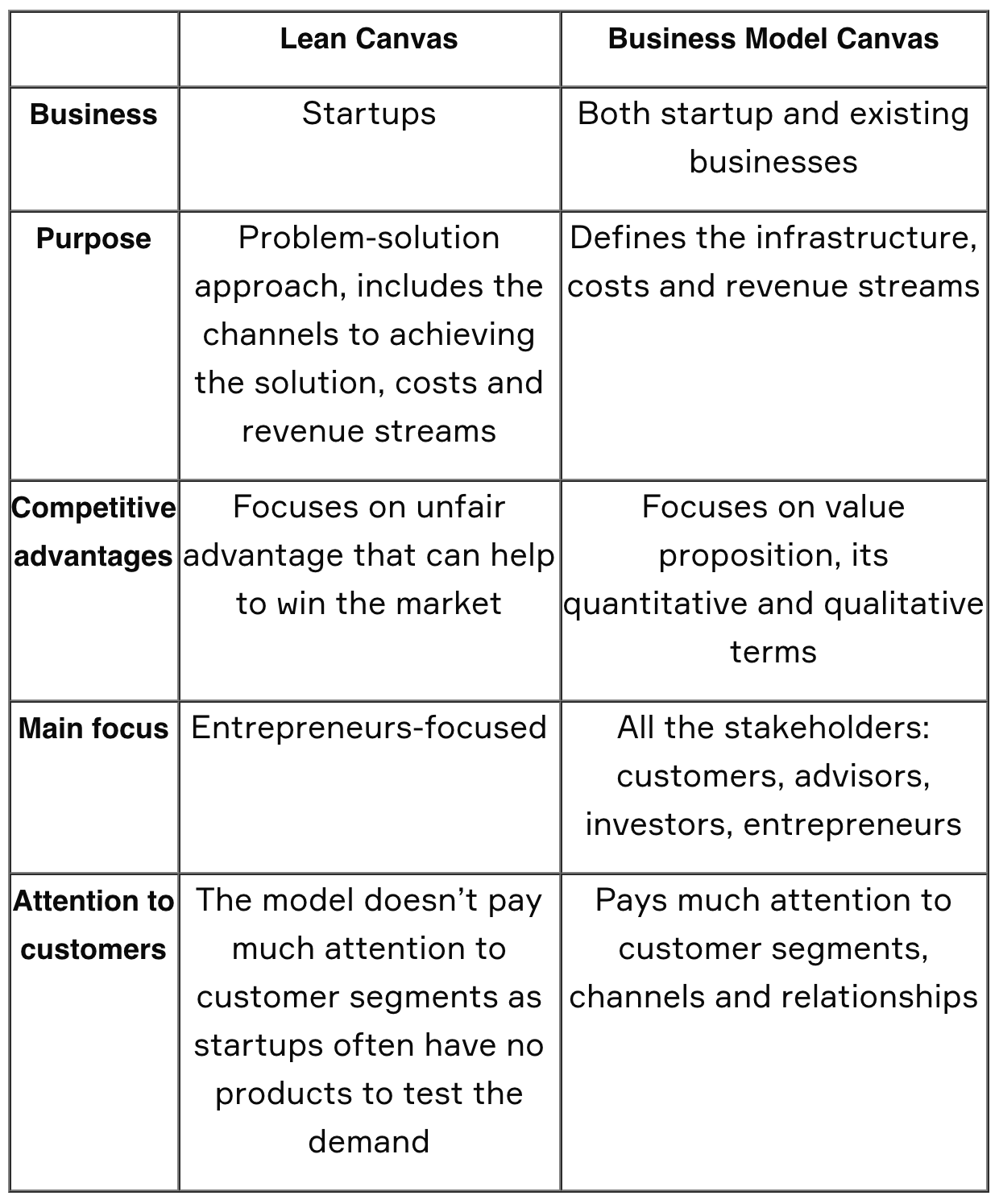
Lean canvas vs. business model canvas
There’s a lean business model canvas and then simply a business model canvas . The two terms are often confused, as they have a lot in common — and the lean canvas is an adaptation of the business model canvas.
However, the biggest difference is that a business model canvas is focused on a specific product while a lean canvas focuses on a specific problem.
This means that the business model canvas has a few blocks that you won’t see on a lean canvas. These are:
- Key partners (lean canvas replaced with problem)
- Key activities (lean canvas replaced with solution)
- Key resources (lean canvas replaced with key metrics)
- Customer relationships (lean canvas replaced with unfair advantage)
That’s the gist, but here’s a chart that digs even more into the difference between a business model canvas and a lean canvas:
What is included in a lean canvas?
Now that you have a better grip on what exactly a lean canvas is let’s break it down even further. The typical lean business model canvas has nine elements or quadrants. These are:
- Problem: A brief description of the top three problems you’re addressing.
- Solution: The proposed fix for the problem you’ve identified.
- Unique value proposition: Why your solution is different and what will make people buy.
- Unfair advantage: Something you have that can’t be easily copied or bought.
- Customer segments: Who your target customers or users are and if they can be further segmented.
- Key metrics: The important numbers that will indicate how your business is doing.
- Channels: The free and paid channels you’ll use to reach your customers.
- Cost structure: All of your fixed and variable costs.
- Revenue streams: How your business model will earn income.
However, our lean canvas template here at Miro dives even deeper with the addition of a few more elements, including:
- Existing alternatives: How these problems are currently solved today.
- High-level concept: A simple X for Y analogy (e.g., “Zillow for playgrounds”).
- Early adopters: Characteristics of your ideal customers who will jump right on the bandwagon.
How to make a lean canvas in Miro
A lean canvas can provide a lot of clarity about a business model or a product idea. Ready to create one with your own team? Getting started is easy.
- Grab our lean business model canvas template and create a new Miro board . You can put as many canvases on one board as you need.
- Define the product or business idea you’re working on, and then fill in the blocks with different types of content. You don’t just have to use text — you can also use pictures, videos, and more.
- Invite your team and/or advisors to the board so you can brainstorm , collect feedback, and collaborate in real-time.
- Come back to the board regularly to make necessary changes, add new information, and discuss progress.
And that’s it! Once you’ve created your own lean business model canvas, you can move forward with a product or business idea with more strategy — and a lot more confidence too.
Get started on your own lean business model canvas with Miro
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together..
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
Keep reading
How to make a concept map – with examples.
Learn Miro basics with new template pack
5 insights from leaders transitioning teams back to the office


Lean Business Plan Template
Create a plan that adds value without getting lost in the tiny details. monday.com's lean business plan template will help you create a streamlined visual that focuses on your business model, schedule, strategy, and tactics..
Integrate with your favorite tools

Tips for creating a lean business plan with our template
Include key aspects, organize assets, collaborate with ease, lean business plan template key features.
- monday Workdocs Create your business plan on a collaborative document where stakeholders can add input without disrupting your work.
- Views Get the full picture of your strategy. Choose from views such as Gantt charts, Calendar, Kanban, Table, and others.
Create a flexible, customizable plan with monday.com
Related templates.

Client management template

Content management template

Go to market strategy
Frequently asked questions.
- What is a lean business model? A lean business emphasises value and minimizes waste. This model focuses on optimizing processes to deliver value to the customer.
- What is a lean start up plan? A lean startup business plan is a short roadmap that specifies the startup's goals and what's needed to reach them. This plan often begins by identifying a problem and solution.

- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
- AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
- TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
- BY USE CASE
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan seamlessly with your team members and clients
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Lean Business Planning: The Modern approach to Business Plan Writing

Free Lean Canvas Template
Ayush Jalan
- December 12, 2023
10 Min Read

Planning is essential for any business to attain success and sustain itself in the market. Traditionally, the goal was to formulate a lean business plan that lasts and works in the long run. However, this conventional way of creating a business plan isn’t flexible and doesn’t provide much room for improvement over time.
In an ever-changing business environment, you need a plan that can adapt to your changing needs and not hold you back with its rigidity. This is true especially when immediate actions are needed.
To facilitate the convenience to make modifications, a new method of planning has surfaced. This is called a lean business plan. This simple yet effective method of planning a business reduces the hassle of dealing with complicated documents—all while increasing efficiency and productivity.
What is Lean Business Planning?
A lean business plan is essentially a one-page business plan for companies to kickstart their businesses. Contrary to traditional business plans which are often bulky and complex documents, a lean business plan is a simple, reader-friendly, and easy-to-make document.
It is a streamlined core plan that acts as a basis for a more elaborate one.
If you want to skip the trouble of creating a plan from scratch, a lean business plan template can help you save a couple of hours. If done right, a lean business plan can guide you to reach your goals, keep track of your progress, and manage cash flow .
Why Choose Lean Business Planning?
A lean business plan is similar to creating a map with steps laid out to run your business. It is favorable compared to a traditional plan because:
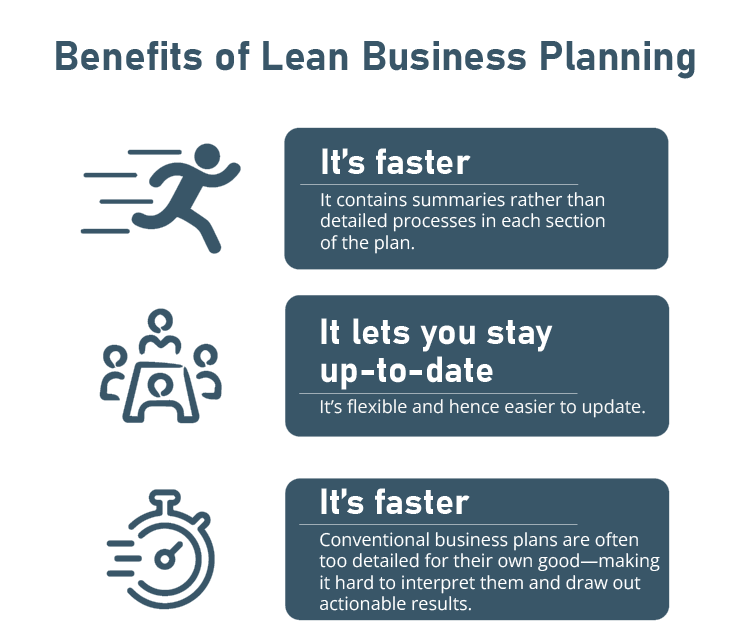
- It’s faster: It contains summaries rather than detailed processes in each section of the plan. Consequently, making it a simple process that you can complete within minutes—saves you time.
- It lets you stay up-to-date: It’s flexible and hence easier to update. As your business starts to expand, your goals and strategies need to be modified accordingly.
- It’s concise: Conventional business plans are often too detailed for their own good—making it hard to interpret them and draw out actionable results. A lean business plan is simpler, shorter, and smarter.

Steps to Create a Lean Business Plan
Now that we have the ‘what’ and the ‘why’ out of the way, let’s take a look at the ‘how’. Here are the 5 key steps to creating the perfect lean business plan for your company:
- Lay the foundation for your business plan
- Put your ideas to test
- Review your results
- Revise your plan
- Set to launch
For your reference, we’ve created a simple one-page business plan for a barbershop business:
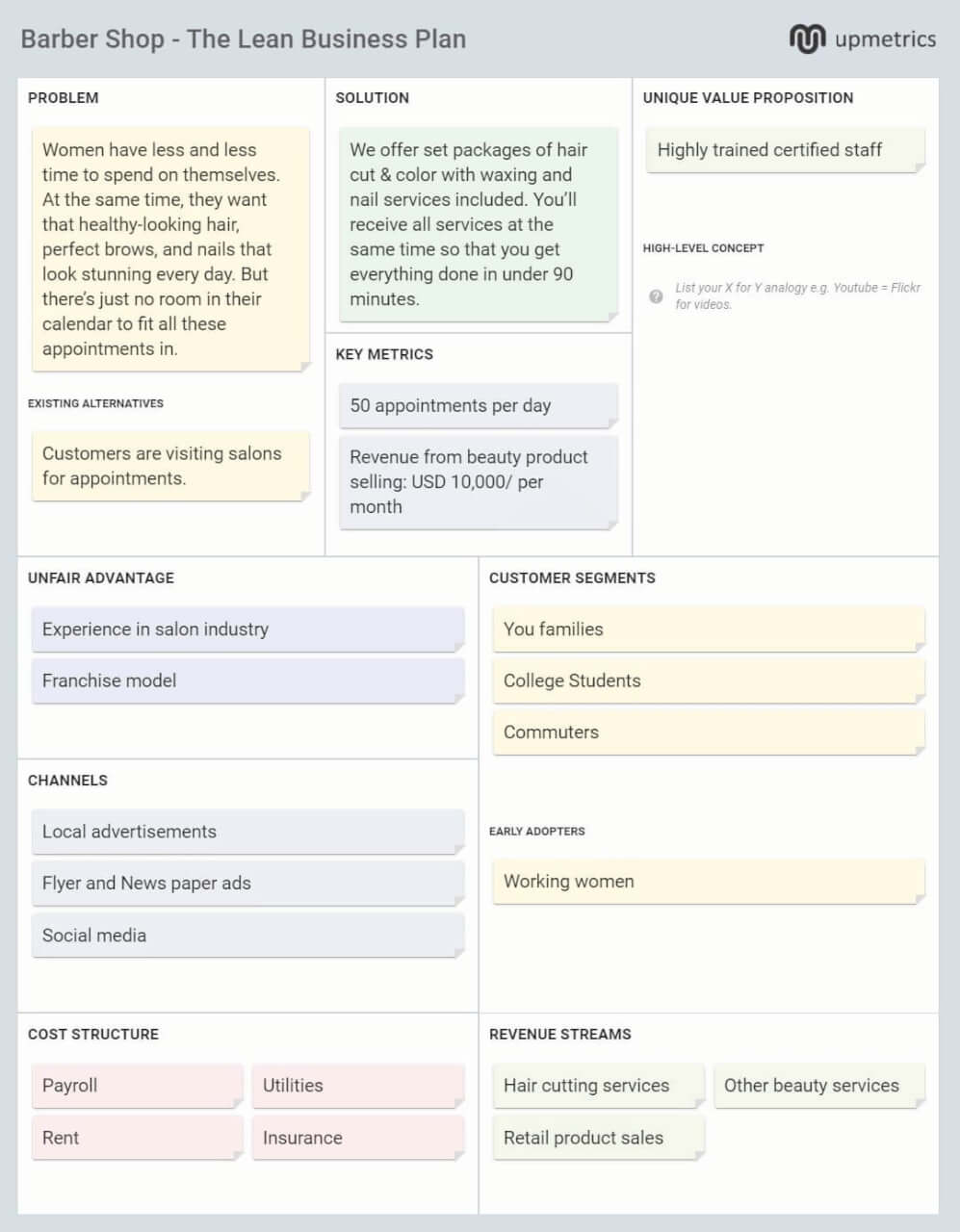
We have used a lean canvas to fit your plan on one page.
Step 1: Lay the foundation for your business plan
The first step is perhaps the most important one. It includes jotting down everything that your business is and does. Here, you summarize who you are, what you do, and how you do it. The plan can also include your target customer base, your goals, your team, and how you schedule tasks.
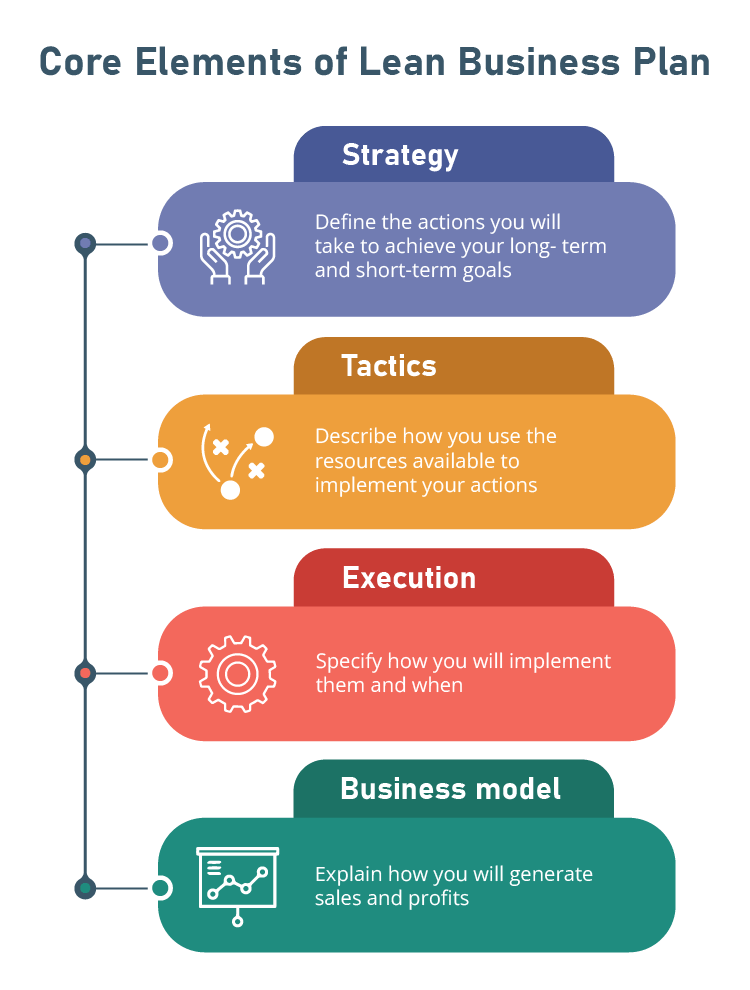
The foundational aspects of your business plan include:
- Strategy: Define the actions you will take to achieve your long-term and short-term goals
- Tactics: Describe how you use the resources available to implement your actions
- Execution: Specify how you will implement them
- Business model: Explain how you will generate sales and profits
1. Strategy
A strategy is the brain of your business. It encompasses the core identity of your business and the steps you take to run it. Here, you write your plans of action in simple and precise statements. This includes:
- Business identity: Here, you need to describe who you are and how you want your customers to identify you. This can include your business philosophy, company history, and mission and vision statement .
- Problem: Specify the problem that your customers are facing. Try to be as specific as possible with the claims you make. It is vital to understand that a business’s success depends on its reliability to solve its customers’ problems.
- Solution: Mention the solution to the problems you are tackling with your product. It’s important to note that your ultimate offering to the customer is not the product itself, but the benefit that it gives.
- Market: Your brand identity determines which market you operate in and who your target audience is. To get a clear idea of who your ideal customer is, you must understand their values and priorities. To do so, it is advisable to create a solid customer profile first before you think about allocating resources to marketing.
- Competition: It is necessary to keep a close eye on your competitors. In this step, you list down your top competitors, their USPs, their market share, and most importantly, how you are different than them.
Tactics are the key to implementing your strategies. They’re primarily all your plans and marketing techniques to steer your business toward growth.
- Sales channels: Simply making a great product isn’t enough. You need to make sure that it’s actually reaching your customers. For this, you need robust sales channels. This can include walk-in stores, online retail outlets, and even both. You may also list down whether you want to work with distributors or go solo.
- Marketing activities: Marketing is non-negotiable for any business. After all, what is seen is sold. This is where you will list down your marketing strategies to draw customers in and inform them about your product and persuade them to buy.
- Partners and resources: If you have business partners that manage or finance the business, mention them in this step. You can also add any key resources that you use for running the business.
- Team: Mention the key team members in this step and their respective roles. If you don’t have a team yet, you can write down the primary roles crucial for your business and later recruit relevant talents.
3. Execution
Strategies and tactics are wasted efforts without well-defined execution. Everything you have learned in the previous sections will not convert into growth unless you have a systematic assigning of tasks and deadlines.
- Schedule: It is essential to keep a timeline of all the events taking place in your business, along with a roadmap of all future activities. Review your schedule regularly to keep track of what’s working and what’s not. Making changes ensures that you don’t deviate from your goals.
- Assumptions: Assumptions are needed so you have some ground to make decisions. Without them, your team will have a hard time figuring out new strategies. Listing the assumptions you’ve made about your business ensures that everyone is on the same page.
- Milestones: Milestones are the achievements you aim to make with your business plan. They act as indicators that a plan is working. On paper, they might look like just to-do lists with deadlines, but they help track your progress and tackle standstills.
- Metric: There are several metrics through which businesses measure their success. Some of the fundamental metrics are sales, costs, expenses, and more. You can tailor this to your company and write how you want to judge your business’s performance.
4. Business model
A business model is a description of how your business will make money. The clearer this description is, the better. A sloppy business model is a recipe for wasted resources, and time, and can lead to liquidation .
- Forecast sales: Forecasting your sales means making educated guesses about your sales performance. It need not be 100% accurate. Here, you write how your business will create sales in the future. As hard as it may sound to play the guessing game, forecasting is important to compare expected sales to actual sales.
- Budget expenses: Estimating your future expenses and costs is essential to good management. Budgeting and regularly reviewing it helps you understand where you need to cut costs or increase investments to reach your milestones.
- Cash flow: Cash flow refers to the net inflow and outflow of cash in your business. Keeping track of it helps you foresee when you might run into a cash deficit or a cash surplus. You want to stay away from extremes. This assists you to manage your sales and expenses accordingly to maintain a good ratio.
Step 2: Put your ideas to test
After having your strategies made, milestones set, schedules in place, and a tactical plan to get your business up and running, it is time to test their utility. This helps reduce risks, gain insight, and avoid inefficient use of resources.
In this step, you verify the integrity of your business methodologies via extensive research. One of the best ways to do so is by surveying your target customers directly. Record their responses and compare them with your assumptions.
- Is the problem you are solving synonymous with the problem your target customers are facing?
- Does the solution you provide align with their expectations?
- Is there a solution you can provide that your customers don’t yet know they want?
- Are the sales channels you decided apt for your potential customers?
- Are your marketing techniques persuasive enough?
Asking all the above questions will give you a detailed view of what should be revised and what needs to stick.
Step 3: Review your results
The next step is to examine your results. After having put your ideas to test, you must have received some significant outcomes of your decisions. This is your data. You will use this data to figure out what went wrong with the last plan and come to conclusions.
You can review your results by using the same measuring metrics that we talked about earlier. It is important to choose reliable metrics that suit well with your business model. Opting for metrics incompatible with your business can give inaccurate results—making it harder to evaluate your performance.
Step 4: Revise your plan
One of the best things about a lean business plan is that it’s not set in stone. In other words, it’s a flexible plan and is open to continuous refinements as you go along with your business activities. Considering everything you have learned so far, this step is where you revise your lean business plan.
It includes making changes to your assumptions, sales channels, marketing techniques, schedules, budgets, and even your target customers as your business continues to evolve over time. The more mistakes you detect and revisions you make, the more reliable your lean business plan becomes.
Step 5: Set your business to launch
Now that you have a complete lean business plan in hand, one that is tested and refined, all you need to do is set your business in motion. Keep in mind to come back, revise, and keep updating your business plan as and when required. Usually, for most businesses, a lean business plan is all you need to get started.
However, sometimes a more detailed business plan is more suitable for large-scale businesses. This could include specific steps and instructions for your team to undertake complex operations and perhaps even comments for your investors. In case that’s your requirement, this business plan checklist might help you stay on track.
Creating a business plan is often a difficult and tedious task, but it doesn’t have to be. With the above-mentioned steps and guidelines, you can create a lean business plan that’s right for your company. This compact, tailored, streamlined, targeted, and easy-to-revise document is sure to get your business up and running in no time.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to use : The Business Model Canvas explained in Few steps

Lean Business Plan Template

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Try Tactyqal

The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Lean Startup Business Plan
Starting a business can be both thrilling and terrifying. On one hand, you have this brilliant idea and can’t wait to bring it into the world. But there’s also the nagging fear that your amazing concept might fall flat or fail to gain traction.
So how do you make sure your startup succeeds? The answer is charting out a solid business plan.
I know, I know. Just hearing the phrase “business plan” brings back bad memories of dry, long-winded documents from business school. But for startups, there’s a better way to plan out your venture – something called the lean startup business plan.
The lean startup approach focuses on streamlining the business planning process so you can start testing your idea faster, without getting bogged down with lengthy sections and financial projections you can’t possibly predict accurately at such an early stage.
In this beginner’s guide, I’ll walk you through exactly how to create a lean startup business plan template that helps you quickly validate your business idea with real-life customers.
What is a Lean Startup Business Plan?
First things first – let’s define what exactly the lean methodology means when applied to an entrepreneur’s business plan.
Put simply, a lean startup business plan is a streamlined, no-fluff version of a traditional business plan. It’s designed for speed and adaptability rather than comprehensiveness.
The lean startup movement first became popular around 2008. It emphasizes testing a product or service idea quickly, using a minimum viable product (MVP), and getting real user feedback before committing to long development and release cycles.
The key principles of lean startup are:
- Rapid build-test-learn loops
- Scientific testing with real customers from day one
- Iterating based on validated learning
Most new companies that take the lean approach never reach an official launch stage. Instead, they continuously test with and adapt to real customers – refining their MVP and pivoting directions based on evidence of what does or doesn’t get market traction.
So how does that tie in with writing a business plan?
Well, the traditional business plan model doesn’t fit the lean paradigm shift.
Lengthy, complex, intricate business plans take too much time to write. Attempting to project multiple years of expenses, sales, hiring, growth rates etc…..it’s all just guesswork when you haven’t started selling anything yet.
The lean startup business plan tosses unnecessary details out the window and instead focuses only on critical hypotheses and assumptions that must be tested as quickly as possible.
Investors like this approach because it shows you:
- Know what assumptions make or break your business
- Can test them quickly at low cost
- Will adapt based on real data
So if you’re an early stage startup looking for funding or entering an accelerator program like Y Combinator, a lean business plan is likely your best bet to showcase your entrepreneurial abilities.
Now the big question….
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup template pares down the typical business plan format to just the essential elements early-stage investors care about:
- Problem – What pain points will your product address? Why are those needs not being met?
- Solution – How will your product alleviate that pain better than alternatives? Why will customers buy from you over other options?
- Target market — Who has that specific problem and will buy your solution? ( Note: Be specific! “Everyone” is never the right answer.)
- Competition — Who else is tackling that customer problem? How is your solution fundamentally better or different?
- Key features – What’s the minimum feature set to address target customers’ needs on day one and provide value?
- Marketing & sales – What tactics will you use to reach early adopters? ( Note: For most startups, digital sales & marketing channels rule supreme. )
- Operations – Outline your core business processes. Don’t go into granular detail, just highlight how you’ll deliver value to customers.
- Milestones – What big assumptions will you test? Include timelines + costs to conduct experiments so you can demonstrate a logical thought process.
- Financials – Optional Breakdown high-level estimates only if useful. For the lean startup plan, elaborate projections are unnecessary and speculative. Focus everything on testing key assumptions.
You may have noticed one conspicuously absent item – the Executive Summary. We’re skipping it because unlike traditional business plans sent to various stakeholders, your lean startup plan has just one audience – startup investors.
And remember, the lean methodology is all about using real-life data instead of guesses and best-case scenarios. So even if some assumptions in your original lean business plan don’t pan out, that’s actually great news! It gives you hard evidence to adapt intelligently while developing your MVP.
Now that you know what the lean startup template includes at a high-level, let’s go through each of the core sections in more detail.
First and foremost, you need to spell out exactly what customer problem your startup aims to solve. (And yes, it needs to be an actual must-solve problem, not a nice-to-have).
Start by broadly describing the pain points your target customers face. Get tactical by including stats, data or quotes that showcase why this issue is so urgent for them.
Then explain how the problem ties into a larger trend in your target industry. Paint a big picture view of why common solutions up until now have failed to address this pain sufficiently.
Essentially, convincingly convey that there’s a pressing customer need ready for innovation.
You need to display beyond any doubt that you:
- Deeply understand your target customers’ challenges
- Can explain why those problems exist in the first place
- Will provide a compelling solution tailored to fix them
This sets the stage for why launching a startup to address this issue makes so much sense.
2. Solution
Now that you’ve framed the problem, shift gears into explaining your startup’s solution. Start by providing an overview of your product and how it alleviates target customer pains better than alternatives already on the market.
Then embellish with details on:
Product Benefits
How specifically will your product make customers’ lives easier? Don’t just describe product features or functionality. Speak directly to how you’ll empower them to achieve something that’s currently difficult, inconvenient or even impossible for them to accomplish on their own.
Competitive Advantage
What specifically sets your solution apart from potential competitor offerings and substitutes? Is it higher quality, better convenience, lower cost, less hassle, faster performance – or perhaps an innovative model that’s never been seen before in the market?
Highlight your startup’s special sauce that no one else can easily replicate. Explain barriers to entry that will hinder copycats.
Customer Incentive
Why will target users’ purchase from your brand over chasing other options? It usually comes down to believing you can deliver significantly MORE value than alternatives or solve an urgent pain nothing else currently satisfies. Make your case for why you fit one or both scenarios.
Scalability
Particularly if you are pursuing venture capital investors, explain how your business can rapidly scale up to tap a very large global market with your solution. Outline a blueprint for how you realistically grow from thousands to millions of customers in the coming years.
Remember, don’t drown potential investors in intricate details about every single product feature and technical specification. They care most about how your solution nails the value proposition trifecta:
- Targets an urgent customer problem
- Provides 10x+ better value over existing options
- Can scale to a very large market long term
If you can compellingly check all three boxes, you’ll spark investor interest even with limited hard evidence at such an early phase.
Of course, that doesn’t mean you won’t eventually need to back up your claims. However, the lean startup plan is more about framing hypotheses than definitive proof. We’ll cover how to demonstrate enough evidence to warrant launching experiments soon.
For now, stick to crafting an intriguing startup story that sets you up to start testing fundamental assumptions very soon after funding. There will be plenty of time to figure out minor product details once you validate solving a pressing problem for real paying customers.
3. Target Market
Up until now, I’ve used the term “target customer” quite loosely. But it’s time to get very specific on who those real-world people actually are for your startup.
Venture capital investors want to quantify the population size and traits of target buyer personas in precise detail. So you need to describe exact psychographic and demographic qualities of your beachhead market – the subset of overall customers you tackle first to gain a foothold quickly.
Start by explaining your total addressable market (TAM) – the entire population who could plausibly need and want your solution for the core problem it tackles. Depending on the ubiquity of that issue for consumers and/or businesses, the TAM could be very narrow or encompass hundreds of millions globally.
Then segment down from that full market to identify your specific beachhead target customer population. The ideal beachhead often has these characteristics:
- Suffers from the problem much more painfully than casual groups
- Has already tried existing solutions without sufficient success
- Has disposable income to purchase a premium solution for relief
- Is easy to access and serve operationally in early phases
- Isn’t incredibly price sensitive
- Can provide extensive feedback on the product
- Has influencer qualities to attract wider market segments
Nail down quantifiable population size estimates for this core beachhead subset. Combine publicly accessible data from existing market research reports with reasonable inferences or assumptions from adjacent industries.
But resist the founder’s tendency towards magical thinking – “If we nailed even just 1% of the market…!” Generic hypotheticals don’t sway experienced investors focused on tangible traction signals.
Paint a detailed demographic picture of exactly who fits the mold of a hot prospect customer for you in the beginning.
For B2C startups , call out relevant attributes like:
- Marital/family status
- Home ownership
For B2B startups , highlight qualities like:
- Industry vertical
- Company size
- Title seniority
- Annual revenue
- Tech adoption habits
Then outline statistical commonalities across your core beachhead buyers – what key similarities unite this subgroup vs. the entire population facing the problem?
Finally, convey TAM expansion opportunities once you solidify solutions tailored for that first niche. But defer outlining detailed ways to extend your reach right now since nailing product/market fit with just one segment is the critical prerequisite to win over adjacent groups.
Position your solution as optimized for an underserved niche ripe for disruption based on competitors failing to deliver adequate solutions. Then segue into how your distribution plan concentrated on this “low-hanging fruit” beachhead will purposefully evolve later to expand TAM reach long term.
4. Competition
What the competition section lacks by traditional business plan standards in length, it more than makes up for in strategic rigor.
The core question competitive analysis must answer:
Why are current solutions in the market failing to adequately alleviate your target customers’ pain?
Start by inventorying existing competitor products/services currently used by prospects experiencing this problem. List out the main options your target persona has for solving their struggles today, even if those solutions don’t perfectly fix the issue or fully satisfy them.
Then contrast point-by-point specifics on why your solution beats competitors, especially on the metrics most important to your target niche. Show how you will “disrupt the disruptors” because even pioneering products have limitations needing innovation.
Criteria to call out where you claim competitive advantage:
- Convenience
- Scale potential
- Business model innovation
Back up any bold claims of superiority with limited initial evidence beyond conjecture — data from beta user testing prototype versions, customer quotes from initial beachhead outreach, or precedents from analogs in adjacent markets.
Take care to focus specifically on competitors targeting the same early adopter beachhead market segment though. Details contrasting solutions for other peripherical segments are unnecessary right now.
Round out competitor analysis by itemizing macro trends almost certain to diminish prospects for legacy products over the next 5-10 years. These should make the rationale behind your startup now abundantly clear even to skeptics.
5. Key Features
Thus far you’ve made a case for:
- A pressing customer problem inadequately solved
- Your startup’s superior solution
- Quantified target beachhead market
Now it’s time to shift to specifics on the crucial product and feature details enabling your entire value proposition.
Remember – only include what’s absolutely necessary for launch based on addressing revealed target customer needs!
Err on the side of a minimal feature set early on. Describe additional functionality prospects request once you start serving initial customers.
Outline the critical set of features required to deploy a minimum viable product (MVP) with just enough core attributes to satisfy early adopters on day one.
Organize by:
Must-Have Features
What feature absolute “must-haves” must be ready for early adopters to provide enough value converting from current solutions?
Nice-To-Have Features
What would enhance perceived value but aren’t imperative to activate paying users? Defer these to later product milestones.
Future Features
Briefly mention functionality on the long-term roadmap to showcase platform potential.
Think of must-have features as the “walking version” of your product – unscalable manual processes providing baseline value perfect for testing with friendly early adopters.
Then nice-to-haves represent the “jogging version” – automating more of the workflow via technology – while future functionality serves as the “running version” enhanced for steep vertical scaling.
In conjunction with digital tools, brainstorm creative ways to manually deliver MVP experiences centered around must-haves. This showcases your determination to activate solutions for that first tiny niche even sans a fully built production-grade product.
Emphasize with investors that you respect their money enough to not waste it on premature optimizations. Your plan ensures you build and roadmap additional functionality responsibly IF AND ONLY IF initial feature experimentation proves substantial product/market fit warranting doubling down.
6. Marketing & Sales
Thus far you’ve covered the key value proposition and functionality your startup will offer. Now shift to tactical specifics on how you’ll connect your novel solution with that clearly defined target beachhead.
Start by breaking down your blended omni-channel market blueprint to cut through the noise and achieve conversion lift.
Here is an ideal framework pairing both scalable and targeted elements for seed-stage ventures:
Paid Digital Marketing
- Targeted Facebook/Instagram/TikTok Ads
- Search/Display Retargeting
- Streaming Radio Spots
- Industry Forum Sponsorships
- Highly-Targeted Content Marketing
Grassroots Outreach
- Beachhead Email Outreach
- Beachhead Calls/Texts
- Industry Event Networking
- Local University Campus Reps
- Early Adopter Referral Programs
Earned Media
- Contributed Articles
- Podcast Interviews
- Reviews / Testimonials
- Referral Partnerships
- PR Launches & Press Releases
The glaring omission? Sales team headcount.
Early on, founders must handle sales themselves to economize cash burn. Hiring reps too early risks overextending finances before ensuring product viability.
So spotlight your personal founder sales fit first. Play up hands-on selling experience within the specific market context you’re pursuing with this venture.
Then convey a scaling plan centered on refining and automating conversion funnel elements that empirically guide qualified leads to become delighted long-term customers.
The core funnel methodology goes:
- Broad-based brand awareness marketing → Baits wide audience
- Lead capturing mechanisms → Filters for buyers
- Consultative selling touchpoints → Focuses high-potential targets
- Frictionless conversion → Delivers ROI proof
If your business model doesn’t fit this framework, adapt concepts accordingly while sticking to the seed stage constraints of capital efficiency and lean experimentation.
7. Operations
By this point you’ve described WHAT your startup does and WHO it serves. Now it’s time to explain HOW you’ll deliver on ambitious promises to customers.
Start by simply framing core business processes required to get your product or service from raw inputs all the way through to solving target user pain points.
For physical products, that could involve flows like:
- Design concepts → Engineering specifications → Prototyping → Manufacturing → Quality assurance → Packaging → Distributing → Support
For software platforms:
- Product requisites → Cloud infrastructure → Coding → Version control → Usage analytics → Onboarding → Technical support
For services:
- Prospecting → Onboarding → Account Management → Delivery capacity → Quality control → Supplemental services → Support
You get the idea. Just define macro processes without diving into granular details. Those come through experimentation!
Primarily, concentrate operational details on two crucial pillars:
- Proprietary unfair advantages that supercharge efficiency to delight customers while maintaining profit margins despite tight costs. Common examples include algorithms, datasets, novel business model frameworks, or embedded industry experts.
- Partnerships or platforms enabling you to deliver baseline functionality matching incumbent competitors on day one. Don’t attempt to build everything end-to-end or innovate across every dimension from the start! Leverage existing commoditized solutions while you test differentiated value propositions focused on solving target customer problems 10x better.
Essentially, convey you grasp the key 20% inputs that drive 80% of customer value. If the processes seem complex, find ingenious ways to simplify. Position enhanced intricacies as optional add-ons once baseline product/market fit is proven vs. overbuilding the wrong advanced solution.
8. Milestones
The milestones section represents the culmination of everything you’ve documented thus far. Here, outline the step-by-step process for methodically testing the riskiest assumptions underlying your startup.
In conjunction with the experiment design, detail concrete metrics or signals indicating whether hypotheses prove true or false. Then estimate costs, durations, and resource requirements for rapid experiments.
Frame assumptions through statements structured like:
We believe [this capability] will result in [this customer reaction]
Then design tests around the ability to measure:
- behavioral changes
- sentiment improvements
- usage increases
- revenue lift
Common milestone tests to consider:
- Solution Viability – Manual then automated demonstrations quantifying interest
- Demand Validation – Willingness to prepay as a signal
- Market Sizing Accuracy – Applying proxies from analogous use cases
- Business Model Fit – Contrasting pricing sensitivity across customer segments
- Feature Prioritization – Gauging reactions to mockups or limited functionality
- Operational Scalability – Maximizing utilization before adding overhead
Combine testing both internally-facing operations and externally-visible customer experiences. But concentrate on product/solution related hypotheses first.
Beating competitors takes precedence over backend experimentation. Optimize business operations AFTER establishing winning customer value propositions.
The key is conveying to investors an empirical, metrics-driven approach centered on turning critical assumptions into facts or disproving them faster than incumbents hampered by legacies and red tape.
Cement belief you’ll double down on evidence proving repeatable formulas to acquire and monetize target niche segments. And quickly cut losses spending minimal capital if data suggests limited viability.
9. Financials
We’ve made it clear that traditional multi-year financial projections typical of standard business plans are counterproductive guesses for early stage startups.
However, seed investors still want to see back-of-napkin math you’ve done to quantify potential venture scale. So mock up top level metrics more as directional guidelines than definitive targets.
Take utmost care however NOT to pull imaginary hockey stick numbers from thin air. Founders claiming $100 million valuations on basic eCommerce stores face extreme investor skepticism…and deserve to!
Baseline financial model components should include:
- Estimated Customer Acquisition Costs Per Beachhead Channel
- Willingness-To-Pay Price Range For Target Personas
- Logical Volume Estimates Based On Analog Use Cases
- Assumed Conversion Rates Each Funnel Stage
- Operational Unit Economics At Various Scale Points
Use inherently bottom-up thinking grounded in realities of what combination of inputs would need to scale to hit specific 8-figure outcomes. Top-down abstract number picking lacks validity.
And remember, early-stage startup financial models serve more as instruments of learning than definitive targets. Adapt projections based on empirical evidence once live.
Concentrate everything on validating customer demand first. Defer advanced modeling of operational minutiae or elaborating hockey stick projections.
Getting REAL buyers is all that matters initially.
Bringing It All Together
Despite extending 3k+ words at this point, the lean startup methodology boils down to an elementary formula:
- Start by deeply understanding a pressing customer problem
- Design an innovative solution specifically addressing root causes
- Concentrate on dominating an underserved niche beachhead market segment
- Validate demand empirically through rapid testing
- Scale up deliberately only once achieving initial product/market fit
In that sense, think of the lean business plan format as more of an exercise in startup soul searching than a stuffy document.
It pushes founders to pressure test their value proposition, business model, and operational viability through the lens of target customers rather than theoretical academic assumptions.
You can’t survive let alone thrive in the brutally competitive startup game without getting inside the hearts and minds of actual buyers needing your solutions.
So escape the temptation to overly complicate initial planning with intricate spreadsheets and 40-page reports professional managers expect.
Instead, concentrate efforts on distilling explanations of the crucial assumptions requiring testing above all else before launch.
Then close your lean startup business plan with next step calls-to-action so readers clearly understand how you’ll leverage funding to start rapidly experimenting using the scientific method.
Now…go show the world what your brilliance is made of!
Related Posts

Partha Chakraborty
Partha Chakraborty is a venture capitalist turned entrepreneur with 17 years of experience. He has worked across India, China & Singapore. He is the founder of Tactyqal.com, a startup that guides other startup founders to find success. He loves to brainstorm new business ideas, and talk about growth hacking, and venture capital. In his spare time, he mentors young entrepreneurs to build successful startups.
You may also like

35 Tips to Raise Funds for Your Startup
- Startup funding

When Does a Company Stop Being a Startup?
- Uncategorized
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Free Google Slides Business Model Canvas Templates
By Courtney Patterson | May 8, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
These customizable Google Slides business model canvas templates are tailored for entrepreneurs, startup enthusiasts, and strategic planners. Download any template to help you develop and refine your business model, establishing a solid base for growth and innovation. This collection includes a Lean business model canvas template , a social enterprise business model canvas template , a tech startup business model canvas template , and more.
Google Slides Simple Business Model Canvas Template
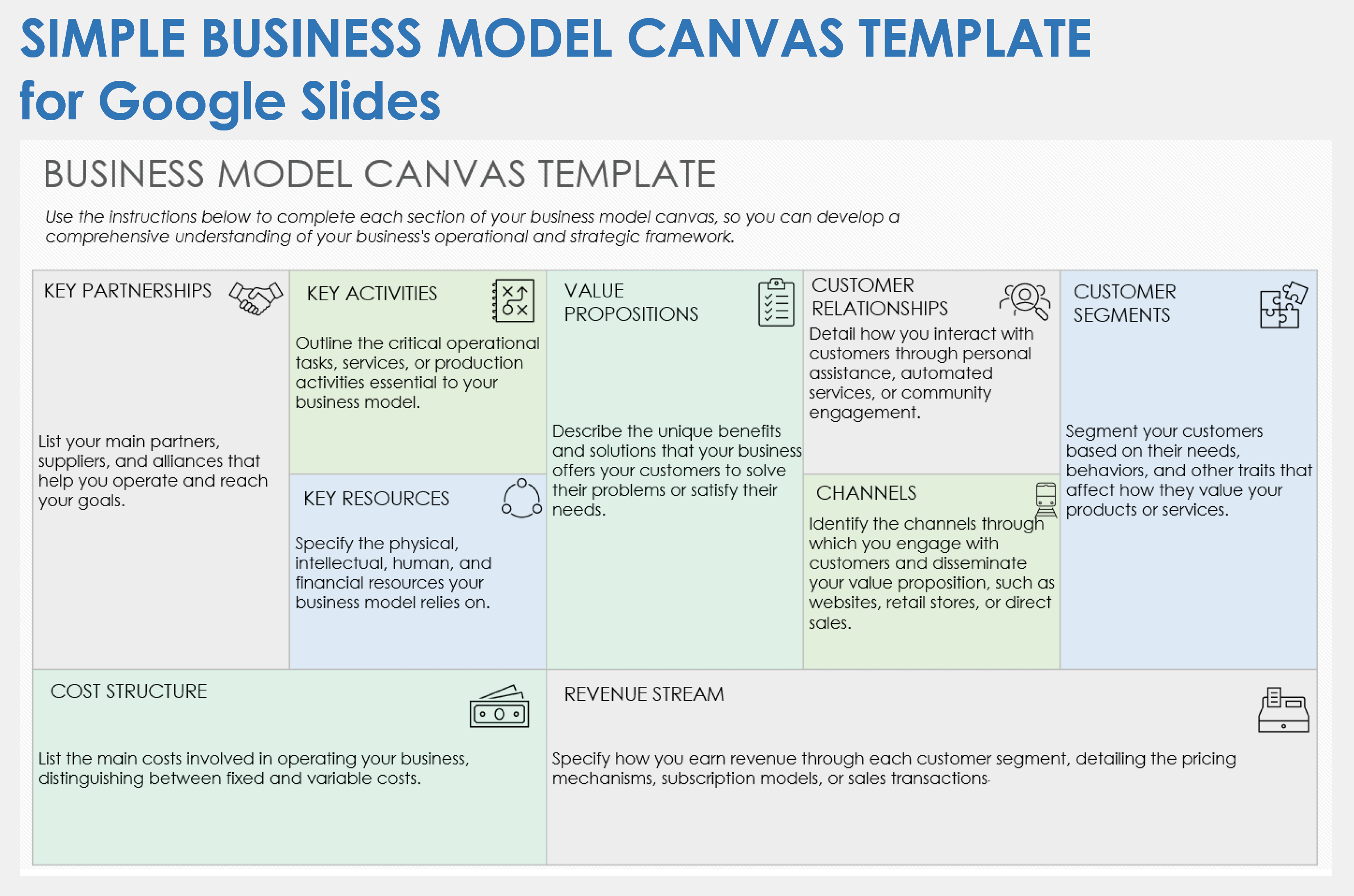
Download the Simple Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this streamlined business model canvas template during dynamic strategy meetings or brainstorming sessions. It's particularly useful for entrepreneurs, startups, and educators looking for a fast way to kick-start planning, facilitate workshops, or clarify ongoing business strategies.
Notable Template Features: This template efficiently outlines key aspects of a business model, such as value propositions, target customer segments, and critical operations. The user-friendly layout ensures swift updates and engaging team discussions, making it an essential resource for visualizing and refining strategic plans.
Access this complimentary collection of free business model canvas templates to effectively visualize your business's fundamental elements.
Google Slides Lean Business Model Canvas Template
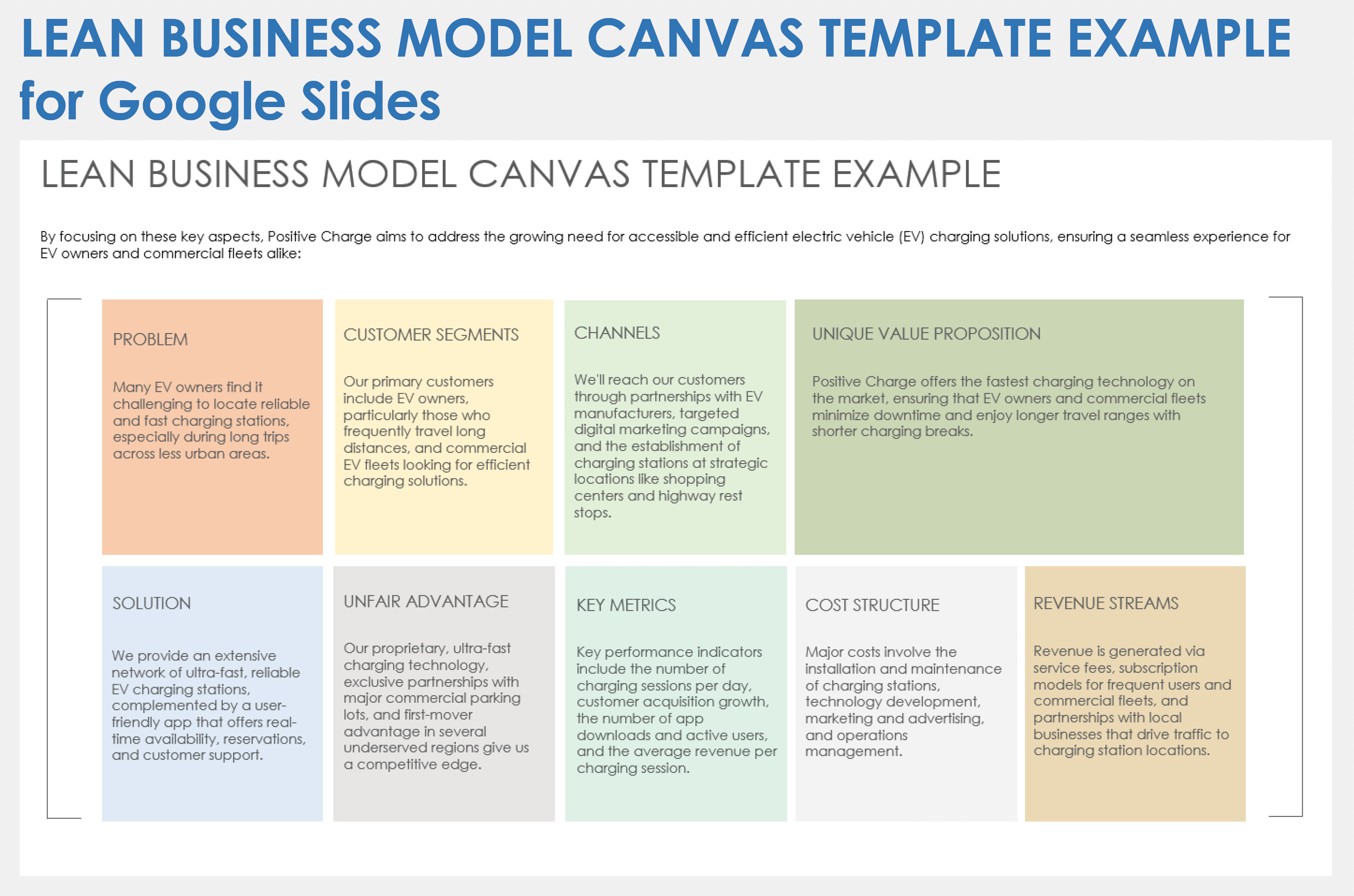
Download the Sample Lean Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
Download the Blank Lean Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Ideal for high-velocity environments, this Lean business model canvas template with or without sample data allows forward-thinking innovators to expedite the testing and validation of their business concepts. It focuses on refining the pivotal aspects of a business strategy to adjust based on real-time market responses.
Notable Template Features: This template highlights critical Lean startup principles, including the alignment of solutions with customer problems, compelling value propositions, and key performance indicators (KPIs). Its interactive and flexible design makes it a vital resource for teams striving for continual progress. Download the sample version for a pre-filled template, or try the blank version to fill in the sections with your own data.
Google Slides Business Capability Model Template
Download the Business Capability Model Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this template to streamline your strategic planning. It is designed to help organizations assess and outline their core business functions and capabilities so that they can synchronize business strategies with operational strengths and identify areas for investment.
Notable Template Features: Across multiple dynamic slides, this template facilitates a thorough analysis of business capabilities, from day-to-day operations to customer interaction tactics. Its organized layout allows for a methodical review of your company's strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities, improving communication and strategic alignment across teams and sectors.
Google Slides Social Enterprise Business Model Canvas Template
Download the Social Enterprise Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: This Google Slides template is ideal for social enterprises and mission-driven organizations that need to strategize how to balance social impact with financial viability. Use this template in brainstorming sessions or strategic planning meetings to navigate the challenges of creating social value and financial stability.
Notable Template Features: This template emphasizes integrating social objectives with core business functions. It includes dedicated sections for outlining social missions, evaluating impact, and building community relationships. Its comprehensive design enables you to map out both the social and economic facets of your business.
Google Slides Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template
Download the Sample Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
Download the Blank Customer-Focused Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this customer-focused template with or without sample data when you're fine-tuning or developing a business strategy with a strong emphasis on customer insights. The template is particularly effective at turning customer needs into unique market positions and customized experiences.
Notable Template Features: Specially crafted to highlight the role of customer perspectives in strategic planning, this template features dedicated areas for detailing customer journeys, preferences, and the feedback process. It offers a comprehensive examination of how your business model caters to customer demands, prioritizing customer satisfaction and active engagement in every strategic move.
Google Slides E-Commerce Business Model Canvas Template

Download the E-Commerce Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Try this e-commerce template when you need to elevate your presence in the digital retail space. Ideal for strategizing the launch of a new online store or refining the operations of an existing one, this template facilitates a detailed examination and improvement of an online shopping journey, from the first interaction to follow-up after sales.
Notable Template Features: Tailor-made for the nuances of e-commerce, this template provides a guide for strategizing around online consumer behaviors, digital marketing tactics, and logistical operations. It covers crucial strategic e-commerce activities, such as enhancing the customer experience, streamlining payment systems, and ensuring effective customer support.
Google Slides Tech Startup Business Model Canvas Template
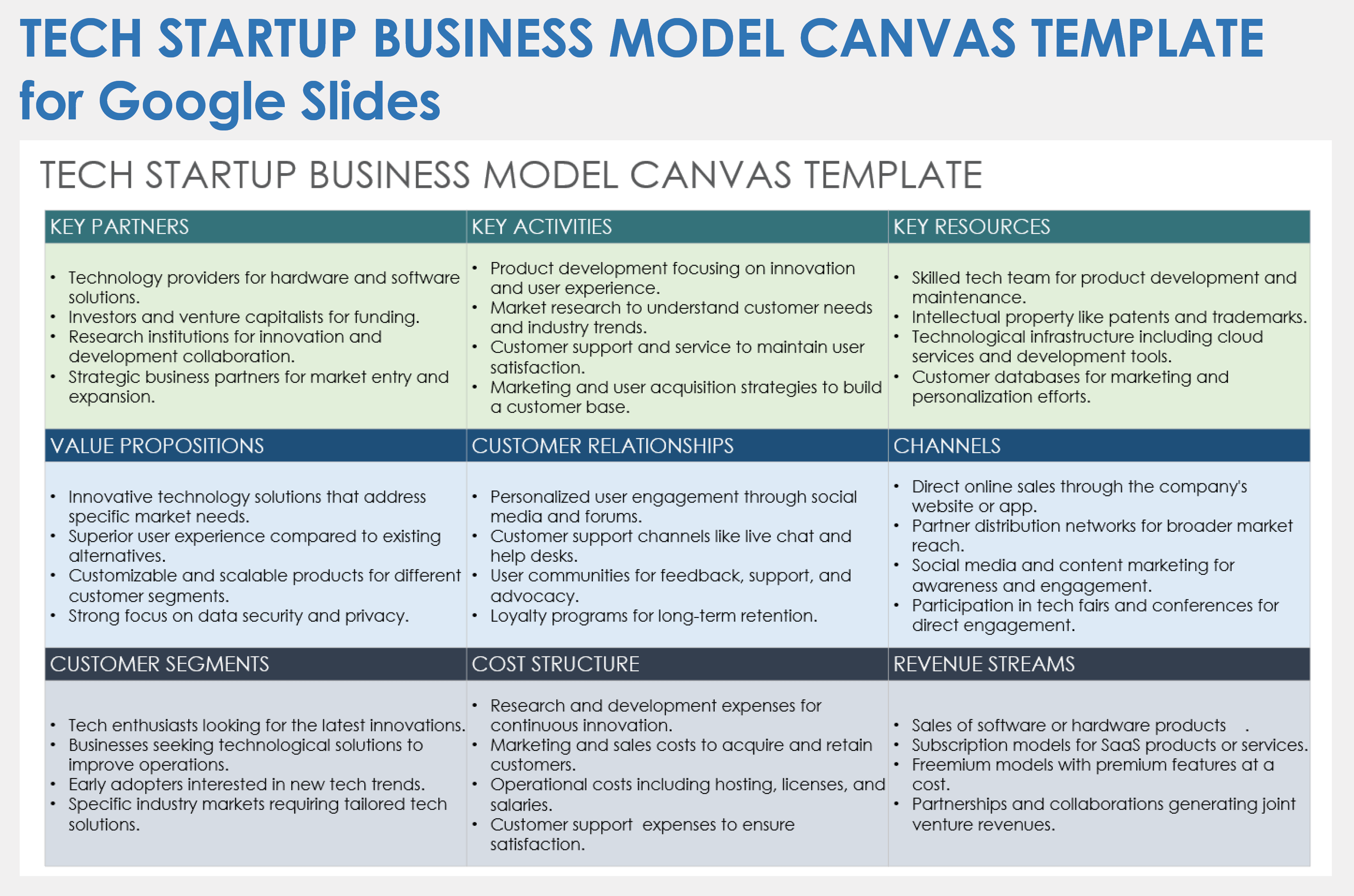
Download the Tech Startup Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this tech startup template during critical phases of brainstorming and entering the market or as you adjust your tech enterprise to meet the changing needs of the industry. It's designed to help you better understand the relationship between your technological innovations and market requirements.
Notable Template Features: Adapted for the unique challenges and opportunities of the tech sector, this template emphasizes research and development, intellectual property management, and strategies for gaining users. It offers a comprehensive layout for mapping out how your tech solutions align with market expectations, with a focus on ensuring scalability, security measures, and innovation.
Related Templates
Explore these complimentary Google Slides templates rooted in business model canvas methodologies. Tailored to boost your strategic business planning, these resources emphasize strategic planning, market analysis, value proposition clarification, and customer journey mapping.
Free SWOT Analysis Templates for Google Slides

Make use of these free SWOT analysis templates for Google Slides to better understand your organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, allowing for new strategic initiatives and insightful decision-making.
Free Google Slides Project Management Templates

These free Google Slides project management templates offer users an intuitive way to organize, track, and present project details, timelines, and milestones, enhancing project visibility and team collaboration.
Free Brand Presentation Templates

See this collection of free brand presentation templates for resources to help you seamlessly integrate and showcase your brand's identity in your business model canvas, enhancing how you communicate your value proposition and market positioning.
Free Marketing Report Templates
Take a look at these free marketing report templates for help analyzing and presenting your marketing efforts and ensuring that they align with the strategies outlined in your business model canvas.
Free Change Management Strategy Templates
Check out these free change management strategy templates to help you effectively plan and execute organizational changes, ensuring they align with your strategic objectives.
Free Go-to-Market Strategy Templates

Explore these free go-to-market strategy templates when you need a targeted strategic approach for launching a product or service.
Free Project Timeline Templates
Dive into these free project timeline templates to help you map out the key milestones and timelines for your strategic initiatives, aligning them with the broader goals outlined in your business model canvas.
Free Annual Plan Templates and Yearly Planning Templates

Discover these free annual plan templates and yearly planning templates to assist you in setting annual goals and strategies that are in harmony with your long-term objectives.
Free Google Timeline Templates
Check out these free Google timeline templates to help you effectively visualize and plan the chronological development and execution of the strategies outlined in your business model canvas.
Refine Your Business Models with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download Your Free Lean Business Plan Template . Lean Business Planning Process. To create your lean business plan, follow these 4 steps: Create the Plan; Your lean business plan will start with you, your business idea, and one sheet of paper. Yes, one sheet is all you will need. Business Strategy . You will first begin by explaining your ...
Lean business plan example Use this lean business plan example as a guide when writing your own: Luke's Instruments Identity We offer high-quality guitars and accessories for experienced musicians and beginners alike. Problem Buying a guitar can be difficult without having a lot of previous experience with instruments. Solution Luke's Instruments is a welcoming environment where anyone can get ...
List your company's key points: name, business model, product/service, USP. Identify the target market and financial highlights. Use bullet points to organize these details in a concise manner. Write a draft of your executive summary, ensuring it's compelling and brief.
Lean Business Plan Template. An alternative to the Business Model Canvas, our Lean Business Plan Template makes it easy to test out new ideas by quickly sketching out a one-page business plan. Download Now. Or plan with expert guidance in LivePlan. Save 50% today.
Streamline your business strategy: The essential lean business plan template. Dive into strategic planning with our lean business plan template, designed specifically for entrepreneurs, startups, and small business owners looking for a streamlined approach to business planning. This template strips away the complexities, helping you focus on the core elements necessary to articulate your ...
Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan template created by Ash Maurya that helps you deconstruct your idea using twelve business modeling building blocks. A Lean Canvas can describe a business model, a product release, or even a single feature, making it a highly popular business model innovation and product management tool used by millions ...
Describe milestone 1. Describe milestone 2. Describe milestone 3. Give specific names and numbers to your milestones. For example, after 2 years in the industry, we plan to reach X, Y, and Z cities too. Or, we plan to increase production and demand by 20% at the end of X year. The more specific, the better.
The Lean Business Plan Template is designed for teams of any size and industry looking to take small steps, consistent tracking, and frequent course corrections for optimize the business. It is an effective and efficient way to organize, track, and optimize the performance of any business. 1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
The lean plan is a faster, easier, and more efficient business plan designed to help startups better manage their strategy, tactics, milestones, and operations. Complete it quickly and update based on performance. ... Download Now: Free 1-Page Business Plan Template. Let's face facts: Writing a traditional business plan is a hassle.
A Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan invented by Ash Maurya to provide a more straightforward business opportunity evaluation. It's a simplified version of the business model canvas template and helps your team break down your idea into key assumptions, replacing cumbersome, time-consuming business plans.
Deconstruct your business plan with a lean canvas template. Follow these steps to use this template effectively: Explain your business model scenario. Fill out the relevant sections of the template using the prompts as a guide. Evaluate key elements of your business, including the problems your business solves, and the solutions it offers.
The lean plan contains four essentials every business needs, and nothing else. It's a streamlined core plan for running the business, not a document or detailed plan, full of descriptions, to be presented to investors or lenders. It's to optimize management. Here's what the lean business plan includes. The principles apply to every ...
one page lean business plan template business/ industry overview product or service product or service offered the problem it solves the solution it provides alternatives unique value proposition marketing and sales plan our customers how they'll hear about us how we'll get our product service to them key objectives and success metrics
Speed: A lean business plan only takes two to four days to write and requires only three to five pages to complete. Compared to a traditional plan, this lean approach moves at light speed. Flexibility: A lean plan allows you to organize the business concept and summarize the UVP and USP in short, easy-to-digest thoughts, which can be modified ...
Grab our lean business model canvas template and create a new Miro board. You can put as many canvases on one board as you need. Define the product or business idea you're working on, and then fill in the blocks with different types of content. You don't just have to use text — you can also use pictures, videos, and more.
There are different ways to develop a lean startup template. You can search the web to find free templates to build your business plan. We discuss nine components of a model business plan here: Key partnerships. Note the other businesses or services you'll work with to run your business.
A fourth and final appendix includes a complete sample lean business plan. Lean Business Planning Step by Step. 7 . Section 1: Fundamentals . Note: Do you like to just dig in? Skip the fundamentals and background. Just skip ... It Starts with a Lean Business Plan . Lean business planning adopts the ideas of small steps, constant tracking, and ...
One way to write a lean business plan is to start with a template that alows you to include all the necessary elements as well as customize it to your exact needs. When writing a lean business plan, you'll want to: 1. Define your business 2. Identify your problem and solution 3. Define your target market and competition 4.Develop a market plan 5.
A lean business plan is essentially a one-page business plan for companies to kickstart their businesses. Contrary to traditional business plans which are often bulky and complex documents, a lean business plan is a simple, reader-friendly, and easy-to-make document. It is a streamlined core plan that acts as a basis for a more elaborate one.
The lean startup movement first became popular around 2008. It emphasizes testing a product or service idea quickly, using a minimum viable product (MVP), and getting real user feedback before committing to long development and release cycles. The key principles of lean startup are: Rapid build-test-learn loops.
LEAN BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE. BUSINESS / INDUSTRY OVERVIEW PRODUCT / SERVICE OFFERING PROBLEM SOLUTION ALTERNATIVES. UNIQUE VALUE PROPOSITION. CUSTOMER SEGMENTS. CHANNELS TO REACH CUSTOMER SEGMENTS. COST STRUCTURE. SOURCES OF REVENUE. KEY METRICS. ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION PERFORMANCE METRIC.
Step One: Strategy is Focus. You can summarize business strategy with a few key points: the problem you solve, your unique solution to that problem, your choice of target market, and your unique business identity. Don't worry about big text, editing, or the document. Just write down your key strategy choices. Make it as simple as a bulleted list.
Download the Blank Lean Business Model Canvas Template for Google Slides. When to Use This Template: Ideal for high-velocity environments, this Lean business model canvas template with or without sample data allows forward-thinking innovators to expedite the testing and validation of their business concepts. It focuses on refining the pivotal ...
The strategic framework template simplifies the process by allowing you to define precise objectives and track the progress of three key results associated with each objective. Using this strategic plan template, you can streamline goal management and enhance productivity. 6. General Strategic Plan Template.
Andrew's Business Plan Template - Lean. Lean business plan example for Wooden Grain Toy Company About this document and download. This example business plan is provided by the Small Business Administration. Download .doc. File size: 247KB. Effective: December 29, 2016 ...