- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Law School Toolbox®
All the tools you need for law school success

Five Tips for a Great Legal Writing Assignment
September 25, 2012 By Lee Burgess 2 Comments

- Follow the format outlined by your professor. It is likely your legal writing professor has given you instructions for the overall format of your legal writing assignment. In addition, your professor may have given you formatting instructions for the body of your assignment, such as that you need to follow IRAC. Whatever the instructions, follow them . Sure, you may think it is an overly formal or a frustrating way to write—but to be honest, no one cares. You need to write for your professor . It is more important to write in the way your professor has outlined, than as you personally prefer. And it is not going to be the last time your writing will need to conform to someone else’s rules. As a working attorney you often need to write in the format requested by your boss or even by the court. So get used to it!
- Remember, your writing doesn’t need to be full of legalese—the best legal writing is often simple! So many law students make the mistake of thinking that to “sound like a lawyer” they must use every possible legal term out there. This is just not the case. Often the most effective legal writing is very clear and concise and only uses legal terms or “legalese” when appropriate (say, when you are using a term of art). It is also important to work on writing in a clear, concise way because your assignments may have maximum word count. So using extra words to sound “more professional” won’t really help your grade in the end.
- Answer the question asked by your assignment. Often students get so caught up in writing their assignment that they forget to focus on the question that was asked of them. It is important to read and re-read (and even read again) the assignment sheet. You don’t want to make a mistake and write something off topic. Remember, answering the question is key to getting a good grade!
- Plan before you write. A great legal writing assignment is organized. And for most of us this means that you need to plan your paper just as you would plan an essay or any other project. Organization is key and it takes time to sit with the research and develop your answer. Make sure you build this time into your plan of how you are going to get your assignment done.
- Proofread and double-check citations. As an attorney-in-training, it is very important to present yourself in a professional way. That means that you need to proofread your assignments to present yourself in a professional way to your professor as well. If your assignment is riddled with typos, it is distracting for the professor and likely will cause your grade to drop. Also, students often are lax when handling citations. You are typically graded on the accuracy of your citations. Citations are not hard, but you must be detail oriented and look things up! I have seen many a legal writing grade go down because students didn’t spend adequate time or energy on citations. Don’t let this happen to you.
Legal writing, like most things, gets easier the more that you do it. So do every practice assignment assigned and get as much feedback as you can. This will help you become an excellent legal writer, which is a critical skill in our profession.
Check out these other helpful posts:
- Surviving the first weeks of law school .
- Law school exam prep 101 .
- Getting feedback on past exams is critical .
- Pay attention in class, it can save you time !
Are you on our mailing list? Sign up now and we’ll send you lots of great stuff, totally free!
Image by nh313066 via stock.xchng .

Looking for some help to do your best in law school? Find out about our law school tutoring options.
About Lee Burgess
Lee Burgess, Esq. is the co-founder of the Law School Toolbox , a resource for law students that demystifies the law school experience and the Bar Exam Toolbox , a resource for students getting ready for the bar exam. Lee has been adjunct faculty at two bay area law schools teaching classes on law school and bar exam preparation. You can find Lee on Twitter at @leefburgess , @lawschooltools , & @barexamtools .
Reader Interactions
Thank very much for the tips i have just read they been beneficial to me because am a distance law school student.
I need more guide to legal writing because am lecturing this course for Magistrates
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Want Better Law School Grades?
Sign Up for Our Exam Tips!
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Copyright 2024 Law School Toolbox®™
How to write a case brief for law school: Excerpt reproduced from Introduction to the Study of Law: Cases and Materials,
Third Edition (LexisNexis 2009) by Michael Makdisi & John Makdisi
C. HOW TO BRIEF
The previous section described the parts of a case in order to make it easier to read and identify the pertinent information that you will use to create your briefs. This section will describe the parts of a brief in order to give you an idea about what a brief is, what is helpful to include in a brief, and what purpose it serves. Case briefs are a necessary study aid in law school that helps to encapsulate and analyze the mountainous mass of material that law students must digest. The case brief represents a final product after reading a case, rereading it, taking it apart, and putting it back together again. In addition to its function as a tool for self-instruction and referencing, the case brief also provides a valuable “cheat sheet” for class participation.
Who will read your brief? Most professors will espouse the value of briefing but will never ask to see that you have, in fact, briefed. As a practicing lawyer, your client doesn’t care if you brief, so long as you win the case. The judges certainly don’t care if you brief, so long as you competently practice the law. You are the person that the brief will serve! Keep this in mind when deciding what elements to include as part of your brief and when deciding what information to include under those elements.
What are the elements of a brief? Different people will tell you to include different things in your brief. Most likely, upon entering law school, this will happen with one or more of your instructors. While opinions may vary, four elements that are essential to any useful brief are the following:
(a) Facts (name of the case and its parties, what happened factually and procedurally, and the judgment)
(b) Issues (what is in dispute)
(c) Holding (the applied rule of law)
(d) Rationale (reasons for the holding)
If you include nothing but these four elements, you should have everything you need in order to recall effectively the information from the case during class or several months later when studying for exams.
Because briefs are made for yourself, you may want to include other elements that expand the four elements listed above. Depending on the case, the inclusion of additional elements may be useful. For example, a case that has a long and important section expounding dicta might call for a separate section in your brief labeled: Dicta. Whatever elements you decide to include, however, remember that the brief is a tool intended for personal use. To the extent that more elements will help with organization and use of the brief, include them. On the other hand, if you find that having more elements makes your brief cumbersome and hard to use, cut back on the number of elements. At a minimum, however, make sure you include the four elements listed above.
Elements that you may want to consider including in addition to the four basic elements are:
(e) Dicta (commentary about the decision that was not the basis for the decision)
(f) Dissent (if a valuable dissenting opinion exits, the dissent’s opinion)
(g) Party’s Arguments (each party’s opposing argument concerning the ultimate issue)
(h) Comments (personal commentary)
Personal comments can be useful if you have a thought that does not fit elsewhere. In the personal experience of one of the authors, this element was used to label cases as specific kinds (e.g., as a case of vicarious liability) or make mental notes about what he found peculiar or puzzling about cases. This element allowed him to release his thoughts (without losing them) so that he could move on to other cases.
In addition to these elements, it may help you to organize your thoughts, as some people do, by dividing Facts into separate elements:
(1) Facts of the case (what actually happened, the controversy)
(2) Procedural History (what events within the court system led to the present case)
(3) Judgment (what the court actually decided)
Procedural History is usually minimal and most of the time irrelevant to the ultimate importance of a case; however, this is not always true. One subject in which Procedure History is virtually always relevant is Civil Procedure.
When describing the Judgment of the case, distinguish it from the Holding. The Judgment is the factual determination by the court, in favor of one party, such as “affirmed,” “reversed,” or “remanded.” In contrast, the Holding is the applied rule of law that serves as the basis for the ultimate judgment.
Remember that the purpose of a brief is to remind you of the important details that make the case significant in terms of the law. It will be a reference tool when you are drilled by a professor and will be a study aid when you prepare for exams. A brief is also like a puzzle piece.
The elements of the brief create the unique shape and colors of the piece, and, when combined with other pieces, the picture of the common law takes form. A well-constructed brief will save you lots of time by removing the need to return to the case to remember the important details and also by making it easier to put together the pieces of the common law puzzle.
D. EXTRACTING THE RELEVANT INFORMATION: ANNOTATING AND HIGHLIGHTING
So now that you know the basic elements of a brief, what information is important to include under each element? The simple answer is: whatever is relevant. But what parts of a case are relevant? When you read your first few cases, you may think that everything that the judge said was relevant to his ultimate conclusion. Even if this were true, what is relevant for the judge to make his decision is not always relevant for you to include in your brief. Remember, the reason to make a brief is not to persuade the world that the ultimate decision in the case is a sound one, but rather to aid in refreshing your memory concerning the most important parts of the case.
What facts are relevant to include in a brief? You should include the facts that are necessary to remind you of the story. If you forget the story, you will not remember how the law in the case was applied. You should also include the facts that are dispositive to the decision in the case. For instance, if the fact that a car is white is a determining factor in the case, the brief should note that the case involves a white car and not simply a car. To the extent that the procedural history either helps you to remember the case or plays an important role in the ultimate outcome, you should include these facts as well.
What issues and conclusions are relevant to include in a brief? There is usually one main issue on which the court rests its decision. This may seem simple, but the court may talk about multiple issues, and may discuss multiple arguments from both sides of the case. Be sure to distinguish the issues from the arguments made by the parties. The relevant issue or issues, and corresponding conclusions, are the ones for which the court made a final decision and which are binding. The court may discuss intermediate conclusions or issues, but stay focused on the main issue and conclusion which binds future courts.
What rationale is important to include in a brief? This is probably the most difficult aspect of the case to determine. Remember that everything that is discussed may have been relevant to the judge, but it is not necessarily relevant to the rationale of the decision. The goal is to remind yourself of the basic reasoning that the court used to come to its decision and the key factors that made the decision favor one side or the other.
A brief should be brief! Overly long or cumbersome briefs are not very helpful because you will not be able to skim them easily when you review your notes or when the professor drills you. On the other hand, a brief that is too short will be equally unhelpful because it lacks sufficient information to refresh your memory. Try to keep your briefs to one page in length. This will make it easy for you to organize and reference them.
Do not get discouraged. Learning to brief and figuring out exactly what to include will take time and practice. The more you brief, the easier it will become to extract the relevant information.
While a brief is an extremely helpful and important study aid, annotating and highlighting are other tools for breaking down the mass of material in your casebook. The remainder of this section will discuss these different techniques and show how they complement and enhance the briefing process.
Annotating Cases
Many of you probably already read with a pencil or pen, but if you do not, now is the time to get in the habit. Cases are so dense and full of information that you will find yourself spending considerable amounts of time rereading cases to find what you need. An effective way to reduce this time is to annotate the margins of the casebook. Your pencil (or pen) will be one of your best friends while reading a case. It will allow you to mark off the different sections (such as facts, procedural history, or conclusions), thus allowing you to clear your mind of thoughts and providing an invaluable resource when briefing and reviewing.
You might be wondering why annotating is important if you make an adequate, well-constructed brief. By their very nature briefs cannot cover everything in a case. Even with a thorough, well-constructed brief you may want to reference the original case in order to reread dicta that might not have seemed important at the time, to review the complete procedural history or set of facts, or to scour the rationale for a better understanding of the case; annotating makes these tasks easier. Whether you return to a case after a few hours or a few months, annotations will swiftly guide you to the pertinent parts of the case by providing a roadmap of the important sections. Your textual markings and margin notes will refresh your memory and restore specific thoughts you might have had about either the case in general or an individual passage.
Annotations will also remind you of forgotten thoughts and random ideas by providing a medium for personal comments.
In addition to making it easier to review an original case, annotating cases during the first review of a case makes the briefing process easier. With adequate annotations, the important details needed for your brief will be much easier to retrieve. Without annotations, you will likely have difficulty locating the information you seek even in the short cases. It might seem strange that it would be hard to reference a short case, but even a short case will likely take you at least fifteen to twenty-five minutes to read, while longer cases may take as much as thirty minutes to an hour to complete. No matter how long it takes, the dense material of all cases makes it difficult to remember all your thoughts, and trying to locate specific sections of the analysis may feel like you are trying to locate a needle in a haystack. An annotation in the margin, however, will not only swiftly guide you to a pertinent section, but will also refresh the thoughts that you had while reading that section.
When you read a case for the first time, read for the story and for a basic understanding of the dispute, the issues, the rationale, and the decision. As you hit these elements (or what you think are these elements) make a mark in the margins. Your markings can be as simple as “facts” (with a bracket that indicates the relevant part of the paragraph). When you spot an issue, you may simply mark “issue” or instead provide a synopsis in your own words. When a case sparks an idea — write that idea in the margin as well — you never know when a seemingly irrelevant idea might turn into something more.
Finally, when you spot a particularly important part of the text, underline it (or highlight it as described below).
With a basic understanding of the case, and with annotations in the margin, the second read-through of the case should be much easier. You can direct your reading to the most important sections and will have an easier time identifying what is and is not important. Continue rereading the case until you have identified all the relevant information that you need to make your brief, including the issue(s), the facts, the holding, and the relevant parts of the analysis.
Pencil or pen — which is better to use when annotating? Our recommendation is a mechanical pencil. Mechanical pencils make finer markings than regular pencils, and also than ballpoint pens. Although you might think a pencil might smear more than a pen, with its sharp point a mechanical pencil uses very little excess lead and will not smear as much as you might imagine. A mechanical pencil will also give you the freedom to make mistakes without consequences. When you first start annotating, you may think that some passages are more important than they really are, and therefore you may resist the urge to make a mark in order to preserve your book and prevent false guideposts. With a pencil, however, the ability to erase and rewrite removes this problem.
Highlighting
Why highlight? Like annotating, highlighting may seem unimportant if you create thorough, well-constructed briefs, but highlighting directly helps you to brief. It makes cases, especially the more complicated ones, easy to digest, review and use to extract information.
Highlighting takes advantage of colors to provide a uniquely effective method for reviewing and referencing a case. If you prefer a visual approach to learning, you may find highlighting to be a very effective tool.
If annotating and highlighting are so effective, why brief? Because the process of summarizing a case and putting it into your own words within a brief provides an understanding of the law and of the case that you cannot gain through the process of highlighting or annotating.
The process of putting the case into your own words forces you to digest the material, while annotating and highlighting can be accomplished in a much more passive manner.
What should you highlight? Similar to annotating, the best parts of the case to highlight are those that represent the needed information for your brief such as the facts, the issue, the holding and the rationale.
Unlike annotating, highlighting provides an effective way to color code, which makes referring to the case even easier. In addition, Highlighters are particularly useful in marking off entire sections by using brackets. These brackets will allow you to color-code the case without highlighting all the text, leaving the most important phrases untouched for a more detailed highlight marking or underlining.
Highlighting is a personal tool, and therefore should be used to the extent that highlighting helps, but should be modified in a way that makes it personally time efficient and beneficial. For instance, you might combine the use of annotations in the margins with the visual benefit of highlighting the relevant text. You may prefer to underline the relevant text with a pencil, but to use a highlighter to bracket off the different sections of a case. Whatever you choose to do, make sure that it works for you, regardless of what others recommend. The techniques in the remainder of this section will describe ways to make full use of your highlighters.
First, buy yourself a set of multi-colored highlighters, with at least four, or perhaps five or six different colors. Yellow, pink, and orange are usually the brightest. Depending on the brand, purple and green can be dark, but still work well. Although blue is a beautiful color, it tends to darken and hide the text.
Therefore we recommend that you save blue for the elements that you rarely highlight.
For each different section of the case, choose a color, and use that color only when highlighting the section of the case designated for that color. Consider using yellow for the text that you tend to highlight most frequently. Because yellow is the brightest, you may be inclined to use yellow for the Conclusions in order to make them stand out the most. If you do this, however, you will exhaust your other colors much faster than yellow and this will require that you purchase an entire set of new highlighters when a single color runs out because colors such as green are not sold separately. If instead you choose to use yellow on a more frequently highlighted section such as the Analysis, when it comes time to replace your yellow marker, you will need only to replace your yellow highlighter individually. In the personal experience on one of the authors, the sections of cases that seemed to demand the most highlighter attention were the
Facts and the Analysis, while the Issues and Holdings demanded the least. Other Considerations and
Procedural History required lots of highlighting in particular cases although not in every case.
Experiment if you must, but try to choose a color scheme early on in the semester and stick with it. That way, when you come back to the first cases of the semester, you will not be confused with multiple color schemes. The basic sections of a case for which you should consider giving a different color are:
(b) Procedural History
(c) Issue (and questions presented)
(d) Holding (and conclusions)
(e) Analysis (rationale)
(f) Other Considerations (such as dicta)
Not all of these sections demand a separate color. You may find that combining Facts and Procedural History or Issues and Holdings works best. Furthermore, as mentioned above, some sections may not warrant highlighting in every case (e.g., dicta probably do not need to be highlighted unless they are particularly important). If you decide that a single color is all that you need, then stick to one, but if you find yourself highlighting lots of text from many different sections, reconsider the use of at least a few different colors. Highlighters make text stand out, but only when used appropriately. The use of many colors enables you to highlight more text without reducing the highlighter’s effectiveness. Three to four colors provides decent color variation without the cumbersomeness of handling too many markers.
Once you are comfortable with your color scheme, determining exactly what to highlight still may be difficult. Similar to knowing what to annotate, experience will perfect your highlighting skills. Be careful not to highlight everything, thus ruining your highlighters’ effectiveness; at the same time, do not be afraid to make mistakes.
Now that we have covered the basics of reading, annotating, highlighting, and briefing a case, you are ready to start practicing. Keep the tips and techniques mentioned in this chapter in mind when you tackle the four topics in the remainder of this book. If you have difficultly, refer back to this chapter to help guide you as you master the case method of study and the art of using the common law.
More Helpful Links
The american legal system, how to brief a case, how to read a casebook 101, top 20 things you need to know about law school, learn to spot issues like a lawyer, why an internet search is not legal research, why go to law school, what’s the most challenging part of law school, what advice would you give yourself about law school.
Video Series
Prepare for class with Westlaw
Tips to help you get ahead in your first year.
Translate Legal Terms with Black's Law Dictionary
Access Restatements, Federal Rules and More
Brief Cases with West Headnotes
Law School Resource Center on Practical Law
Come and join in the conversation on our social channels..

Cozy up with Westlaw to win an Amazon Fall Haul!
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Westlaw for Law Students (@trlawschool.us)
Fuel Your Research with Key Numbers - Bonus Entries
Need some inspiration check out these key numbers by using the digest searches below., find your rhythm with black's law dictionary - bonus entries, need some inspiration check out these legal terms by using the the links below., westlaw's "no skips" tips playlist, real property, civil procedure, criminal law, constitutional law, show westlaw some love, statutes on westlaw - bonus entries, need some inspiration check out the statutes below., key numbers on westlaw - bonus entries, searching on westlaw - bonus entries, need some search inspiration for your entries check out the sample searches below.
Because neurodivergent people often need visual prompts or sensory tools, it is helpful to figure out what works best for you. Maybe you need a quiet fidget to use under your desk in class to help you focus. Maybe you need to incorporate the use of timers throughout your day. If you struggle with time blindness, you can use hourglasses to help you visualize time. Perhaps you struggle with extraneous sounds and need to use noise-cancelling headphones. More and more tools and gadgets are being made for neurodiverse individuals that can help you throughout law school.

Society can dictate when you are supposed to be most productive. See the traditional 9-5 work schedule. However, that model does not always work best for neurodiverse individuals. Some people are not morning people, and that is fine. Figure out when you have the most energy during your day to be your most productive self.
Find one system to use for organization and don’t change it. Trying too many organizational systems can become overwhelming. If your phone calendar works best, use that. If you are a list person, write all the lists. If you are a planner person, find the coolest one to use throughout the school year.

It would be nice to think that you can remember every task or deadline, but let’s be honest, that’s probably not true. Write down every deadline, every task, meeting, assignment, important date, etc. in the organizational system that you use.

Just like you can only put so much gasoline in a car, most neurodiverse individuals only have so much room in their focus tank. Figure out how long you can truly focus and apply yourself to a task before you need a break. That amount of time is typically shorter for neurodiverse individuals. If you can only truly focus for 20 minutes, study for 20 minutes, take a break, and then come back for another 20 minutes.
You may have started law school with your mind full of horror stories. Throw them out the window. Most of the people you attend law school with are genuinely kind and helpful people. Try to find a group or a couple of people that you can trust and lean on when necessary. Your law school friends can help you stay on task, body double, and even provide notes on the days you may be struggling. These friends can be one of your greatest assets throughout your law school journey.

Only discuss your neurodivergence with your professors to the extent that you are comfortable. If there are things you are concerned about related to your neurodivergence, it can be beneficial to make your professors aware at the beginning of the semester. Whether you are worried about cold calling or need a topic broken down, most professors love opportunities to discuss their area of law! They can’t know that you may need help if you don’t let them know. This is especially important if you aren’t successful in getting accommodations from your school’s Disability Services.

As a neurodivergent student, you may not fit the traditional mold of all the things a law student is “supposed to do” in order to be successful. You have been in school for years, and now is the time to trust yourself and not be afraid to be an “outside of the box” law student. There is no harm in trying new study methods, but never fear going back to your personal basics. If you need help figuring those out, see if your law school has a learning center or faculty member that can assist you.
Outlining with jury instructions.
- On your Westlaw Precision home screen, click on Secondary Sources and then Jury Instructions .
- On the Jury Instructions page, use the Jurisdiction filter to select your desired jurisdiction.
- Search for your cause of action. (Ex. elements of libel in Federal Jury Practice & Instructions )
- Open your relevant jury instruction and don't forget to check the related notes.
- To see more instructions, check out the table of contents to your left or click on View Full TOC.

Citation in a Click
- Highlight the text you want to copy. Try it out with Miranda v. Arizona
- Select "Copy with Reference" from the pop-up box.
- Paste into your word document...and you're done!
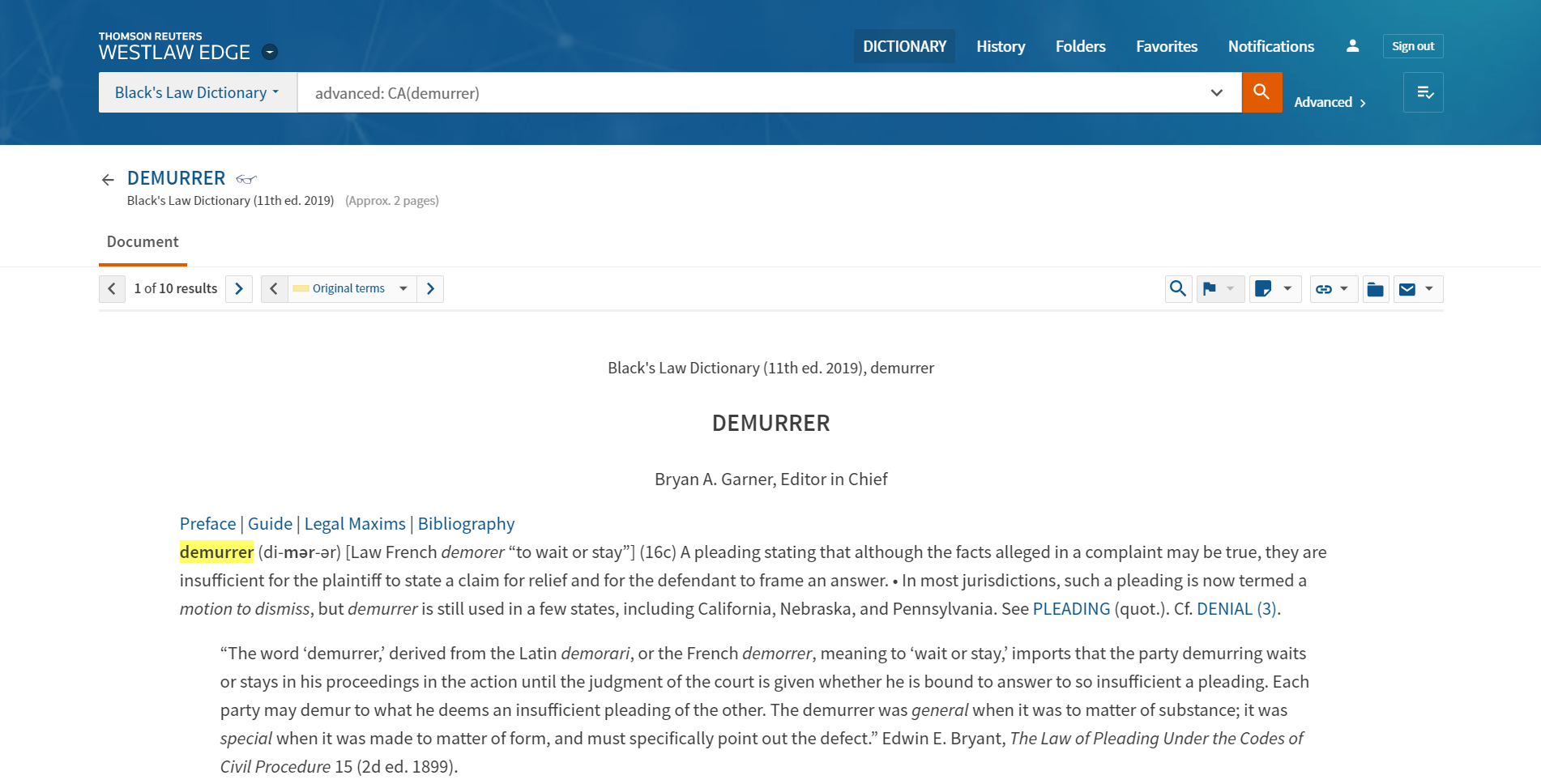
Black's Law Dictionary
Don't guess the meaning of a legal term. know it., by using black’s law dictionary, exclusively on westlaw , you’ll know the meanings of key terms that will help you understand your cases faster, be prepared for cold-calls and beef up your class notes. 1. access black's law dictionary on westlaw., 2. type your term into the dictionary term box. (ex. demurrer ) if your term contains multiple words, place the terms in quotes. (ex. "rule against perpetuities" ), 3. open up your desired term, copy it and paste it into your notes., looking for some inspiration here are a few legal terms to get you started contracts - collateral estoppel - consequential damages civil procedure - minimum contacts - in personam jurisdiction torts - negligence - invasion of privacy criminal law - mayhem - wobbler, where can i learn more about a firm so i can ask good questions in an interview, news is an excellent source for learning about a firm. you’ll see the clients and matters they represent along with the accolades they earned from their communities. 1. click on news under “specialty areas” on your westlaw edge home screen., 2. start by trying a plain language search for your firm. (ex. gibson dunn crutcher ), 3. to up your search game, consider running a terms & connectors search with an index field. (ex. gibson /2 dunn /s crutcher & in(law lawsuit legal) ), start writing your brief without starting from scratch, what is a brief, a brief is a summary of a case in your own words that includes the key facts, procedural history, issues addressed, along with the court's holdings. how can i find a case on westlaw, cases on westlaw contain a synopsis, a summary of the main facts, issues and holdings of a case, and headnotes, summaries of points of law organizes by topic. you can locate cases on westlaw in a variety of ways. find by citation: if you know your case's citation, just type one of the citations in the search box. (ex. 113 sct 2217 ), find by party name: if you know the names of your parties, just start typing them in the search box and select corresponding case from the drop-down menu. (ex. international shoe).
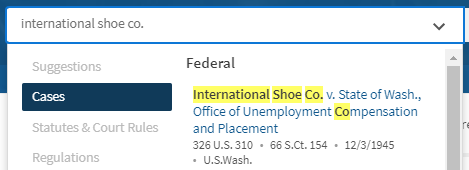
Note: If your case has common party names, you may need to enter more than one party.
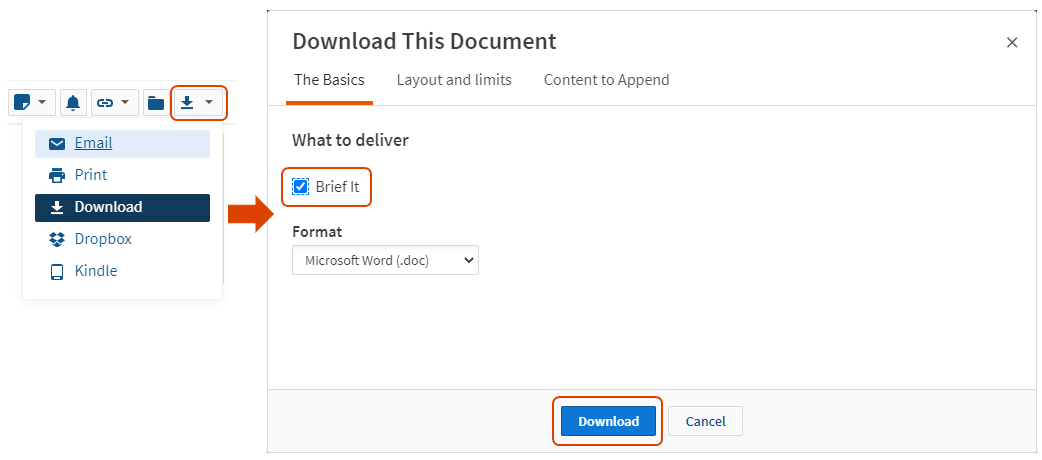
Download your synopsis and headnotes: once you've pulled up your case, click on download under delivery options, select brief it under what to deliver and click on download..
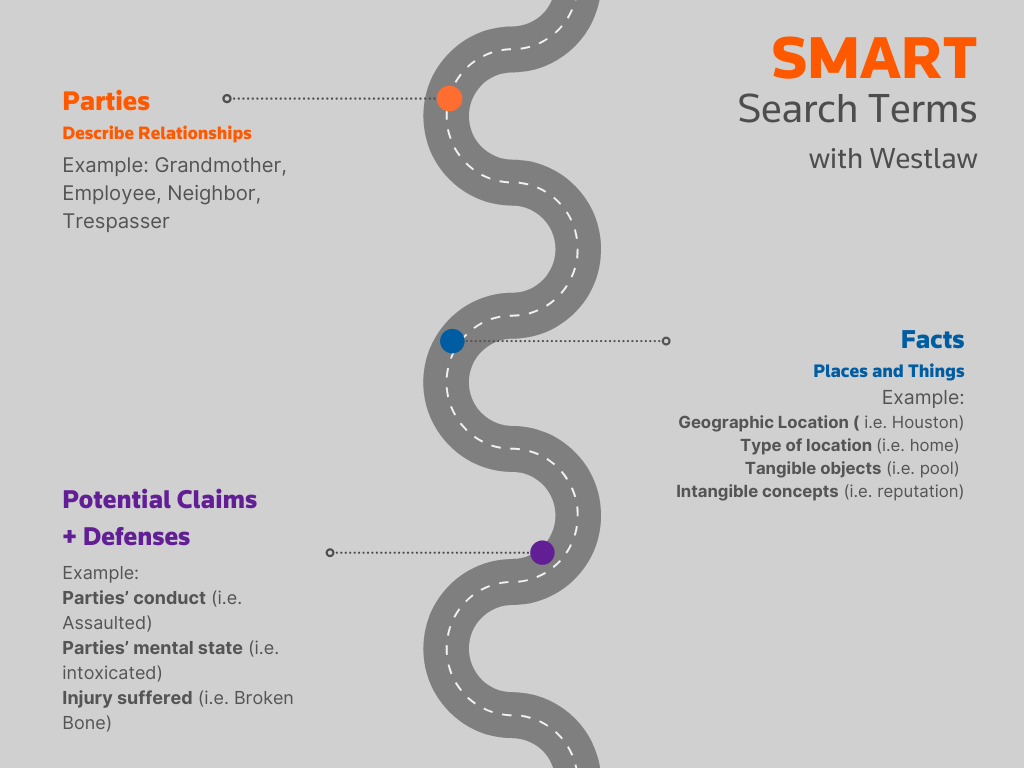
The right search terms can make a difference. Here is an easy way to come up with smart search terms.
Rules, Codes & Restatements
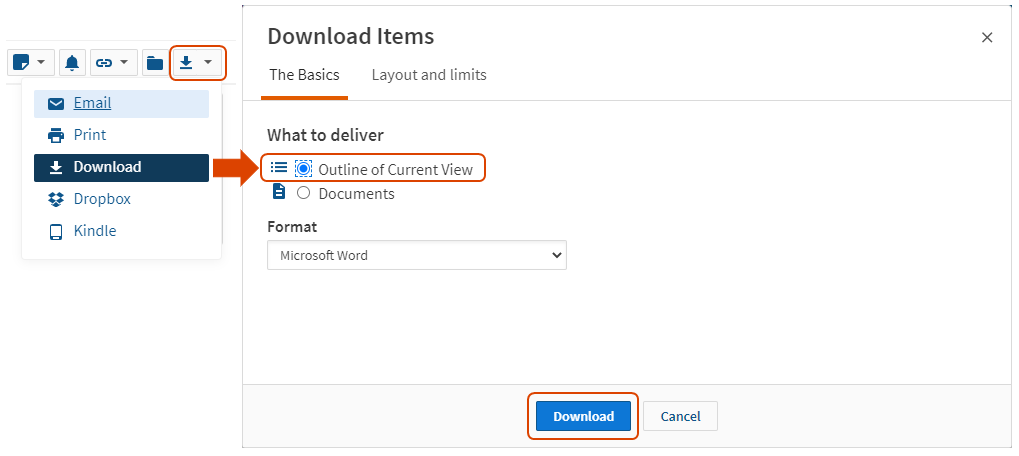
Exporting tables of contents, exporting a table of contents is an easy way to get access to a list of rules, codes or restatements that you can reference on the fly and add to your outlines, as needed. locate your rules, codes or restatement: to export a toc (table of contents), you'll first want to locate your resource. restatement of torts restatement of contracts restatement of property federal rules of civil procedure ucc article 2 federal rules of evidence united states constitution, export your toc: click on download, select outline of current view under what to deliver and then click on download..
Strengthen Your Interview Discussions with News
- Search for a particular firm, attorney, or agency. (Ex. Kirkland and Ellis or Fourth Circuit )
- Or select a specific practice area (Ex. Mergers & Acquisitions )
American Law Reports
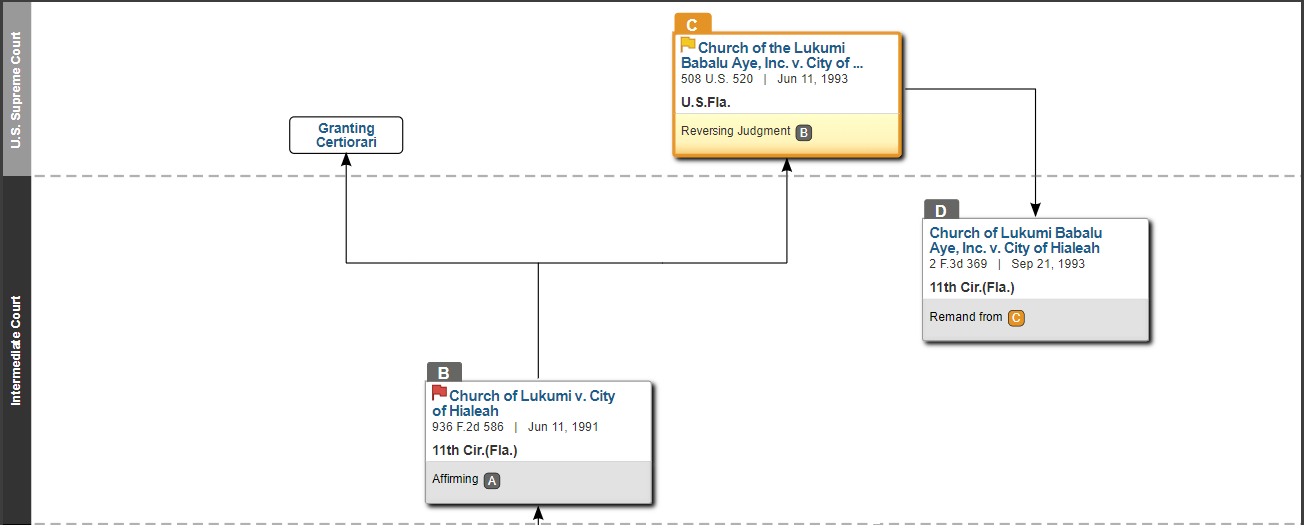
Your go-to secondary source, finding an a.l.r. (american law reports) article covering your topic is a great starting point for research. you'll get a quick summary of the legal issue you're researching and a table of cases, laws, and rules to see the law across all jurisdictions. you can also use annotations to find additional secondary sources, such as legal encyclopedias, treatises, and periodicals. no wonder they're nicknamed already done legal research see it in action: the legal discussion to compensate student athletes is heating up. check out this alr article to see how the legal picture for tomorrow’s student athletes comes together in one place., keycite graphical history, procedural history made easy, are you reading a case and not sure how you got there procedurally reversed, remanded or otherwise, we got you. just sign into westlaw and follow the steps below... 1. grab one of the citations you see in your case book and type it into the search box on westlaw . (ex. 480 u.s. 102), 2. click on your case in the drop-down menu., 3. click on the history tab to see your procedural history., keycite graphical history works best when you have a federal case and a complex issue. check out some additional examples from your classes below. contracts - koken v. black & veatch const., inc. - lamps plus, inc. v. varela civil procedure - national equipment rental v. szukhent - helicopteros nacionales de colombia, s.a. v. hall torts - palsgraf v. long island r. co. - kentucky fried chicken of cal., inc. v. superior court, law school resource center, flowcharts, overviews & more..

Scheduled Maintenance
Step 1 - create a new class, step 3 - invite your students, step 2 - assign lessons.
About this event

Love Your Lawyer Day

All the rules you need for class in one place.
Understand the procedural history of your case..
Don't guess the meaning of a term. Know it.
Copy the Code Below
You'll use this code to make a copy of the sample course.
Click on Copy Another Class
Go to the Knowledge Center and click on the Copy Another Class button.
Enter Your Copy Code
Enter your copy code in the Enter Class Copy Code box and click the Validate button.
4. Set Your Options
Change your course title, set your course dates and set your copy option to Assignments Only.
5. Click Copy Course
Click on Copy Course and you're all set to share your course with students.
1. Copy the Code Below
2. click on copy another class, 3. enter your copy code, set your options, click copy course, determining whether a federal court has subject matter jurisdiction over a non-class action case..
If the case arises out of the U.S. Constitution, U.S. laws, rules or regulations, or a treaty signed by the U.S., and the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction, then the case must be litigated in federal court.
If the case does not arise out of the U.S. Constitution, U.S. laws, rules or regulations, or a treaty signed by the U.S., and there is not complete diversity between the plaintiffs and defendants (a.k.a they are both from different states or one is a citizen of a foreign country), then the case must be litigated in state court.
Restatement of Contracts 2d
Counter-offers.
(1) A counter-offer is an offer made by an offeree to his offeror relating to the same matter as the original offer and proposing a substituted bargain differing from that proposed by the original offer.
(2) An offeree’s power of acceptance is terminated by his making of a counter-offer, unless the offeror has manifested a contrary intention or unless the counter-offer manifests a contrary intention of the offeree.
Negligence Defined
Restatement (second) of torts 282.
In the Restatement of this Subject, negligence is conduct which falls below the standard established by law for the protection of others against unreasonable risk of harm. It does not include conduct recklessly disregardful of an interest of others.
Black’s Law Dictionary (10th ed.2014)
Demurrer: A means of objecting to the sufficiency in law of a pleading by admitting the actual allegations made by disputing that they frame an adequate claim. Demurrer is commonly known as a motion to dismiss.
(2) An offeree’s power of acceptance is terminated by his making a counter-off, unless the offeror has manifested a contrary intention or unless the counter-offer manifests a contrary intention of the offeree.
testing footnote
What is common law and is it written by the courts of law?
[ninja_form id=2]

School: West Academic Test Account Only
This email confirms approval of your order of Law School registration keys required on July 02, 2019. View your order in Password Access Central as needed. If requested, your keys are listed below. Keys are registered at lawschool.westlaw.com/register . Users will need to create their individual OnePass credentials (Username and Password) as well as complete a Law School Profile.
Law School Registration Key(s) to be assigned.
Registration Steps are as follows
1. Visit lawschool.westlaw.com/register
2. Create your OnePass credentials The email address you use for OnePass will be the same one used for TWEN communications.
3. Complete a Law School Profile
Please contact Technical Support at 800-850-9378 (WEST) or email [email protected] with questions about registration. For questions about PAC, please contact your Academic Account Manager.
Westlaw Academic Team
Negligence defined
Restatement (second) of torts § 282.
Course Overview
First-Year Legal Research and Writing Program
1 North Griswold Hall 1525 Massachusetts Avenue Cambridge , MA 02138
Before you begin your studies in the First-Year Legal Research and Writing Program (LRW), it will help you to situate the course in the broader context of your legal education and your future law practice. To follow is a brief overview of the program, and an introduction to several themes that will recur throughout the year.
Program Overview
LRW uses a series of writing, research, and advocacy projects to engage you in the process of legal reasoning. The course instructs you in basic methods of legal analysis, effective written and oral communication of your analysis, and essential legal research tools and methodologies.
The first semester of LRW focuses on the writing of two predictive memos, in which you assess the arguments on each side of the issue and predict which side would prevail. In the spring, you will learn how to write an appellate brief, in which you present your client’s best arguments to a court. For all three assignments, you will produce both a draft and a final version, the better to respond to feedback and hone your writing and analysis. In practice, as in LRW, the writing process will help you take your internal understanding of an issue and make it external, so that you may hold it at arm’s length and examine it critically. As novice lawyers become expert lawyers, they develop greater ability to monitor their own level of understanding, and may resort somewhat less frequently (although not infrequently) to a formal written product like a predictive memo. Nevertheless, even when they eschew a formal written memo, they continue to apply the same analytical steps that are required to complete the writing assignments you will undertake in this course.
Lawyers cannot provide effective representation unless they master the necessary research skills. At a minimum, lawyers must be able to find and update the constitutional provisions, statutes, regulations, and cases that determine their clients’ rights and obligations. To that end, the legal research component of LRW will introduce you to core tools and methodologies that will be essential in your internships next summer, as well as in your future law practice. Indeed, without such skills you will have a difficult time satisfying your employers and competing with fellow students in summer practice and the early years of law practice. More advanced research instruction is available in upper-level elective courses.
LRW’s learning model depends on the substantial feedback that we provide on your work. LRW will likely be the first law school course in which you receive any feedback on written work, and it will be the course in which you receive the most individual feedback by far. Keep in mind that our goals for your achievement are quite high, in keeping with your potential. Our feedback will naturally focus on areas for improvement, so you ought not interpret this emphasis negatively. Our feedback is intended not to discourage you, but to facilitate your learning.
LRW meets weekly in the fall and spring semester of your first year. LRW is graded Honors, Pass, Low Pass, and Fail.
In the fall semester, you will complete two major writing assignments. The first is a “Closed Memo,” in which you write a predictive memo based on a set of research materials that are provided for you. The second is an “Open Memo,” in which you must research the applicable law and write a predictive memo based on your own research.
In the spring semester, the major course assignment is the First-Year Ames Moot Court Program. Working in pairs, you will research and draft an appellate brief concerning a simulated case set in a federal or state appeals court. At the end of the semester, you will argue your case before a three-judge panel. Judges are drawn from Harvard Law School faculty, practicing lawyers, and upper-level law students. With this course overview in mind, we turn next to a discussion of several recurring themes in LRW.
The Conventions of Legal Discourse
Any discourse community has its own discourse conventions, and lawyers have done a particularly thorough job of developing theirs. LRW is intended to familiarize you with these discourse conventions.
LRW introduces you to the generally accepted modes of legal reasoning: rule-based reasoning; analogical reasoning; and policy reasoning. As you progress through the course assignments, you will see the interdependence among these three modes of legal reasoning. When LRW turns to advocacy, you will learn how lawyers use narrative devices to complement the conventional modes of legal reasoning and make their arguments more persuasive.
Discourse conventions govern not only the modes of argument, but also the authorities that frame the argument. You will learn what types of materials constitute acceptable sources of authority in legal discourse, as well as the different hierarchies within which those authorities exist.
Most concretely, LRW will introduce you to two basic forms through which lawyers communicate their legal reasoning. You will learn the conventions applicable to a predictive memo and an appellate oral argument.
Of course, you will be learning the conventions of legal discourse in all of your first-year courses, indeed in all of law school. LRW, however, is intended to focus very specifically on the conventions themselves, more so than in your other courses.
Legal Reasoning and Judicial Discretion
Throughout your legal education, you will encounter a debate over the role of judicial discretion in adjudication. At the extremes, some would suggest that adjudication is rationally constrained by the available legal authorities, while others would argue that adjudication is effectively constrained only by the judge’s own beliefs and values. LRW is not intended to resolve that debate. Nevertheless, your work in this course should illustrate several different concepts about the degrees to which legal authorities can constrain judicial discretion.
Over the course of the year’s projects, you should see that a series of authorities applying the same rule can restrict–at least to some degree–the decision in a future situation governed by that rule. For example, if a statute says “No vehicles in the park,” and the state’s highest court interprets the statute to mean no “motor vehicles,” you can be pretty sure that the statute won’t prohibit you from riding your elephant through the park.
One might think that the ever-increasing number of decisions necessarily increases the degree of constraint. That may be so in some situations, but several factors can have a destabilizing influence. One such factor is the contingent nature of language. You may have seen in other contexts, and you will surely see in your legal career, that saying more about a topic often creates more uncertainty, not less. Each new opinion creates the potential for misstatement and misunderstanding, enabling future lawyers to reinterpret the pre-existing rule. A second destabilizing factor is the social context of our legal system. Authorities rest on a foundation of policy, of societal goals and values, even if those values are not always stated explicitly. As societal goals and values shift, a body of law resting on the discarded goals and values may become obsolete, and eventually reoriented in support of a new rule.
Finally, you should recognize that the limits on judicial discretion are often less substantial than they might seem at first. Each of the major projects in LRW should demonstrate that, with regard to a given legal problem, there is usually more than one possible outcome, even if one outcome seems more likely than the others. Skilled lawyers read authorities with a critical eye, constantly on the lookout for the gap of ambiguity within a seemingly solid wall of legal authorities.
Tension Between the Abstract and the Concrete
To complete any substantial task of legal analysis, the lawyer must at some point bridge the boundary between the abstract and the concrete. Rules rarely, if ever, cover every situation imaginable. For example, the “No vehicles in the park” statute could simply list every make and model of car and truck in existence, to clarify that they are all prohibited from the park. But the rule would be unmanageably long, and new makes and models would come into existence after the rule’s enactment. So the drafters would instead choose a term to describe the category of situations to which their rule was addressed. Rules that denote categories rather than specific situations necessarily involve a degree of abstraction, whether a moderate degree (e.g., “motor vehicle”) or a substantial degree (e.g., “best interest of the child”).
Fortunately for us, this inherent uncertainty is one of the things that makes law practice a creative endeavor. For example, if the vehicles in the park statute referred to “motor vehicles,” would that include airplanes? Mopeds? Golf carts? The “Segway” personal scooters? Lawyers and judges would try to use the policies underlying the rule and analogies to prior decisions to decide each example. But the jump from abstract to concrete would involve a measure of uncertainty, and it is this uncertainty that allows lawyers to make plausible arguments on both sides of a case.
Your Audience
In the oral and written communications that you undertake in this course, you must focus not only on the substantive ideas that you try to communicate, but also on the way in which your audience will receive those ideas. Communication is a two-step process, and even brilliant arguments suffer if the audience is distracted by substandard prose. That is why the feedback in this course will consider the form and style of your writing.
Additionally, you must recognize that your audience has a particular task before it, and will be using your communication (i.e., your memo, brief, or oral argument) as an instrument in completing that task. The audience’s task will often be to decide how to advise a client or rule in a case. To be effective, your communication must be suited to your audience’s needs. So in a memo addressed to an attorney who must decide how to advise a client, simply stating your prediction is not enough. You must also help the attorney understand the applicable legal standard and its likely application, as well as any plausible counter-arguments and the reasons why those arguments would not prevail. Only then will your communication allow the attorney to make an informed decision about how to advise the client.
You are at the start of a fascinating journey. We in the First-Year Legal Research and Writing Program wish you great success and enjoyment as you begin your legal education.
Modal Gallery
Gallery block modal gallery.
Student Answers to the Preliminary Sample Exam Question with CD Comments
There is a set of objective questions that deal solely with estates and future at common law. A student in this class (in 2017) answered them according to ‘modern’ law, as we have defined it ( Word Doc ; PDF ). If you want to try your hand at the questions before looking at the answers, click here .
[ Home Page ] [ Syllabus ] [ Announcements ] [ Lectures and Supplements ] [ Assignments and Discussion ] [ Previous Exams ]
Please send comments to Rosemary Spang URL: http://www.law.harvard.edu/faculty/cdonahue/courses/prop/assign/index_assign.html last modified: 12/06/19 © 2000–2019 Charles Donahue, Jr.
- Latest News
- Latest Issue
- Asked and Answered
- Legal Rebels
- Modern Law Library
- Bryan Garner on Words
- Intersection
- On Well-Being
- Mind Your Business
- My Path to Law
- Storytelling
- Supreme Court Report
- Adam Banner
- Erwin Chemerinsky
- Marcel Strigberger
- Nicole Black
- Susan Smith Blakely
- Members Who Inspire
- 5 tips from a law school librarian for assigning…
5 tips from a law school librarian for assigning research projects to interns
By Matthew Flyntz
March 28, 2022, 8:39 am CDT

Matthew Flyntz.
As a law school reference librarian, I field a lot of questions from law students working at internships, externships and summer jobs. Over the years, I’ve seen some recurring issues with the research assignments given to law students, and I thought it might be helpful to discuss some of them here.
Tip 1: Provide as much detail as possible.
Students sometimes come to the reference desk with very vague research questions. Things like, “I’ve been asked to research [insert broad topic],” or “I’ve been asked to find cases on [insert broad topic].” We will then ask clarifying questions to try to make the project more manageable, but students will often respond with “I don’t know.” Unfortunately, when this happens, we have to tell students to go back and ask for clarification. If assigning attorneys can provide a higher level of detail up front, this can save time for everyone.
Ideally, when a student comes to us for research assistance, they should be able to provide: 1) a brief summary of the case they are working on; 2) a concise statement of the specific issue to be researched; and 3) a clear understanding of what they are trying to find (e.g., If they are searching for cases, from which court(s)? If articles, how recent? And so on …).
Tip 2: Suggest a starting point.
Students sometimes say to me, “I’ve been given a research project, and I have no idea where to start.” We librarians are happy to help, of course, but assigning attorneys—as subject-matter experts—may know better than we do about the best starting places. If you know of a relevant treatise, practice guide or article, or you have a citation to a potentially useful statute or case, let the student know. In my experience, students sometimes struggle to find a way into a research project, but once they get a foothold, they have an easier time with it.
Tip 3: Consider setting time limits or check-in points.
Students visit the reference desk frazzled and say, “I’ve been spinning my wheels on this for eight hours, and I am so confused!” This is presumably not how you want your interns spending their time. When I assign research projects to my students, I generally say something like, “If you’ve put in two hours of good faith effort and are still confused, come talk to me.” I’ve also learned that students take significantly longer on research projects than I think they will. For example, if I assign something expecting it to take one or two hours, many students will spend more like three to four hours on it. Setting check-in times can help ensure students are spending a reasonable amount of time on each project.
Tip 4: Cultivate a culture where asking questions is encouraged.
Of course, in order for Tip 3 to work, there needs to be a culture of openness and psychological safety. Students need to feel safe in asking questions. In my experience, students seem very reluctant to go back to the assigning attorney to ask clarifying questions. Even in my classes, I can sense that students are sometimes reluctant to ask me questions. This may have something to do with law student psychology, where students are wary of seeming foolish in front of their peers, professors and employers. Regardless of where this tendency comes from, I think we all need to remind students that asking questions is expected—and even desirable—and that we will not judge them for doing so.
Tip 5: Try to avoid making students ‘prove a negative.’
I field a lot of questions from students like this: “My assigning attorney asked me to research [insert extremely specific topic]. They said they doubt there are any cases out there but have asked me to double-check.” This is essentially asking students to “prove a negative”—that is, they are not finding the law; they are proving that there is no law. I think these make poor research projects for student interns for at least three reasons. First, from a pedagogical standpoint, they don’t reinforce good research habits. Because there are no good secondary sources, and no cases or statutes to start with, students do not get practice using the essential research skills they are taught in law school. And indeed, the research process students are taught to follow essentially breaks down in these situations, and students end up taking a “kitchen sink” approach—frantically searching anywhere and everywhere for any morsel of relevant information.
Second, these assignments put a lot of stress and anxiety on students. In my experience, students are fearful of returning to their assigning attorney empty-handed, even though the assignment is essentially designed for them not to find anything. If this type of assignment must be given, I’d encourage supervising attorneys to make sure interns understand that they may very well find nothing, and that is OK.
Third, this type of research project takes a surprisingly long time to do well. I’ve already mentioned that students take longer than we expect to do most research projects, and this is doubly true with this sort of project. Proving a negative is much more difficult and time-consuming than proving a positive. I’d encourage supervising attorneys to consider if this is really how they want their interns to spend their time.
In conclusion
I love helping students with their research projects; I think most librarians do. It’s a big reason many of us became librarians! These tips are not meant to suggest that we do not want to help student interns or to off-load the burden of helping students with research onto someone else. They are meant to make the research process go more smoothly for everyone involved and to help make sure our students get the most meaningful experiences they can.
Matthew Flyntz is the research law librarian for instructional services at the University of California at Irvine School of Law, where he designs and teaches first-year and upper-level legal research courses. He has published articles on legal information, law librarianship and legal research instruction in Legal Reference Services Quarterly , Legal Information Review, The Second Draft and ABA Student Lawyer, among others.
ABAJournal.com is accepting queries for original, thoughtful, nonpromotional articles and commentary by unpaid contributors to run in the Your Voice section. Details and submission guidelines are posted at “ Your Submissions, Your Voice .”
This column reflects the opinions of the author and not necessarily the views of the ABA Journal—or the American Bar Association.
Related topics:
Law schools | law libraries | practice management | law students | careers | career & practice | legal education | multidisciplinary practice | professional development | columns, you might also like:.
- Narcissistic Lawyers and Artificial Intelligence: A band of dysfunctional brothers?
- Chemerinsky: SCOTUS rulings on election districting likely to affect who's going to Congress in 2025
- What lawyers should know about customer relationship management
- Artificial intelligence tools for brief writing and analysis are a small firm litigator's new best friend
- What's the key to community lawyering? Less lawyering and more community
Give us feedback, share a story tip or update, or report an error.
Your voice submissions.

The ABA Journal wants to host and facilitate conversations among lawyers about their profession. We are now accepting thoughtful, non-promotional articles and commentary by unpaid contributors.
Read the Your Voice submission guidelines.

Law firms either keep up with tech or get left behind
How do catholic church lawyers determine the credibility of sex assault allegations, the case for bar associations: why they matter, judging the judges: with all due respect, of course.
Articles and commentary ...

- Platform Overview All-in-one legal research and workflow software
- Legal Research Unmetered access to primary and secondary sources
- Workflow Tools AI-powered tools for smarter workflows
- News & Analysis Paywall-free premium Bloomberg news and coverage
- Practical Guidance Ready-to-use guidance for any legal task
- Contract Solutions New: Streamlined contract workflow platform
- Introducing Contract Solutions Experience contract simplicity
- Watch product demo
- Law Firms Find everything you need to serve your clients
- In-House Counsel Expand expertise, reduce cost, and save time
- Government Get unlimited access to state and federal coverage
- Law Schools Succeed in school and prepare for practice
- Customer Cost Savings and Benefits See why GCs and CLOs choose Bloomberg Law
- Getting Started Experience one platform, one price, and continuous innovation
- Our Initiatives Empower the next generation of lawyers
- Careers Explore alternative law careers and join our team
- Press Releases See our latest news and product updates
- DEI Framework Raising the bar for law firms
- Request Pricing
- Business of Law
Checklist: Getting the Assignment
February 9, 2023
[This document is part of a series focused on core litigation skills. Bloomberg Law subscribers can access the full Core Litigation Skills Toolkit with practical guidance on key aspects of litigation practice. Not a subscriber? Request a demo .]
Receiving an assignment can be challenging, especially if you aren’t familiar with the client’s case and/or the area of the law. Consider the following before going into a meeting to get a research assignment .
Think ahead, come prepared
Think ahead about questions to ask to make sure you fully understand the assignment. If it is not provided, always ask about background case information, logistical issues such as the deadline, the client/matter number, and billing instructions.
Take a lot of notes
Be ready to take a lot of notes when receiving the assignment and don’t assume you will remember it all later when you start the assignment. Make sure you know whom to contact if you have questions or need your memory refreshed.
Do you understand what is being asked of you?
Confirm your understanding of the question being asked. When the assigning attorney is finished with their initial explanation of the assignment, repeat back to them what they want you to research.
Ask questions
Don’t be afraid to ask questions.
Understand the context
If the assignor doesn’t tell you, ask why they need to know the answer to the research question. Where does it fit into the overall case? What is the best answer for the client? Is there a second-best answer? What if you find the opposite of what they want you to find? These pieces of information can be important in knowing what strands of the research are more relevant, help you know when to stop researching, and make you a more efficient researcher.
What are the key facts of the case?
Knowing the key facts will enable you to keep an eye out for case law that is factually analogous to yours. There may be an existing document or filing that lays out the facts in more detail. If so, that document should be your first stop when you have questions.
What is the jurisdiction?
Be sure to pinpoint the relevant jurisdiction. If it is a pending case, the court where it is pending will tell you that. Also be sure to get the docket number from the assignor. If the research question is for a case that is not yet filed, be sure to ask where the case would be filed. If there is a choice of where to file, determine whether the assignor wants information to compare jurisdictions.
Confirm the final work product
What final product does the assignor want from you? A formal memo for the client? A memo for the file? An email that pinpoints the relevant cases? An oral summary? This is very important, especially for time management.
How will the research be used?
Is the research to be used for a pending motion? If you are helping with a motion for summary judgment, for example, your goal is to find cases that are in the same procedural posture as yours and come out favorably for your side (i.e., if your client is the one filing the motion, try to find cases where a motion for summary judgment was granted, not denied). Keep in mind the burden of proof for different kinds of motions.
How much time?
Ask for an estimate of how much time/money the assignor expects this to take or is willing to initially authorize. Keep track of the estimate, and as soon as it looks like it might be insufficient, check back in with the assignor for more instructions. Do they want you to go past the estimate? Stop with what you know now? Modify to a narrower track?
How does the assignor like to be contacted?
Ask for the best times and method (email, phone call, office visit, etc.) to reach the assignor if you need clarification or have follow-up questions. Knowing how and when your assignor should be contacted is core to building and maintaining a positive and successful working relationship.
Reference Shelf
Article: Artificial Intelligence for Lawyers Explained
Article: How to Conduct Legal Research
Webinar: How to Succeed as a Junior Associate
Analysis: RTO or WFH? Attorneys and Employers Find Common Ground
Article: They’ve Got Next: The 40 Under 40—Meet Our 2022 Honorees
Recommended for you
See bloomberg law in action.
From live events to in-depth reports, discover singular thought leadership from Bloomberg Law. Our network of expert analysts is always on the case – so you can make yours. Request a demo to see it for yourself.
- Help and information
- Comparative
- Constitutional & Administrative
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Environment
- Equity & Trusts
- Competition
- Human Rights & Immigration
- Intellectual Property
- International Criminal
- International Environmental
- Private International
- Public International
- IT & Communications
- Jurisprudence & Philosophy of Law
- Legal Practice Course
- English Legal System (ELS)
- Legal Skills & Practice
- Medical & Healthcare
- Study & Revision
- Business and Government
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter

The Successful Law Student: An Insider's Guide to Studying Law (2nd edn)
- Acknowledgements
- Student Voices in The Successful Law Student
- 1. Introducing The Successful Law Student
- 2. Studying Law at University: Opportunities and Considerations
- 3. Preparing for Success
- 4. Learning and Studying Law
- 5. Making the Most of Your Classes in Law
- 6. Developing Legal (and Other) Skills
- 7. Finding and Using Legal Materials and Resources
- 8. Preparing for Assessments and Assignments
- 9. Assessments and Assignments in Law
- 10. Feedback, Reflection, and Looking Forward from Assessment
- 11. Study Abroad
- 12. Expanding Legal Skills— Mooting, Negotiation, and More
- 13. Volunteering, Paid Work, and Other Opportunities
- 14. Preparing to Move On
- 15. Career Pathways
- 16. A Successful Future
p. 249 9. Assessments and Assignments in Law
- Imogen Moore Imogen Moore Professor of Law and Director of Education in the Law School, University of Exeter
- and Craig Newbery-Jones Craig Newbery-Jones Associate Professor in Legal Education, University of Leeds
- https://doi.org/10.1093/he/9780198865650.003.0009
- Published in print: 28 February 2022
- Published online: September 2022
This chapter looks at some of the many different forms of assessment a law student may come across, depending on where they are studying and the subjects they choose. These include coursework, exams, multiple-choice tests, advocacy or other oral presentations, posters, and reflective reports. The chapter also considers dissertations and other research projects, and group work for assessment. The chapter gives advice on how to approach different types of assessment to enhance their chances of success. Specific guidance is also provided on responding to problem questions and essays, whether in coursework or exams including consideration of the IRAC and CEEO methods.
- assessments
- problem questions
- multiple-choice
- dissertation
You do not currently have access to this chapter
Please sign in to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Law Trove. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 31 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.136]
- 81.177.182.136
Characters remaining 500 /500
- Cleveland State University
- News + Events
- Student Resources
Records, Forms, and Academic Information.
- Current Students
- Admitted Students
- Student Life
CSU|LAW Faculty Blog
Stay up to date on the work and achievements of our faculty..
- Meet our Faculty
- Faculty Profiles
- Faculty Publications
- Adjunct Faculty
- Emeriti Faculty
CSU|LAW Hall of Fame
- Alumni Overview
- Career Services for Alumni
- Alumni News
- Alumni Events
- Engage with CSULAW
Building Access and Research Services
Law library blog.
- Law Library Home
- About the Law Library
- Student Services
- Faculty Services
- Alumni Services
- Study Room Reservation
Dean's Living Justice Living Leadership Podcast
Monday morning message.
- Latest Headlines
- Event Calendar
- Newsletters, blogs, podcasts
- Stay Informed
Support CSU|LAW
- Giving To CSU|LAW
- Designated Areas of Support
- Meet the Advancement Staff
- Ways to Give
Request Information
Get in touch about in-person and virtual events, sharing updates and announcements..
- General Information
- Faculty/Staff Directory

- My CSU LAW Home
Course Information
- Faculty Resources
- Law School Technology
- Law School Room Reservations
We are a community of leaders for justice.
- About our Law School
- Living in Cleveland
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Law School History
- JD Application Process
- Financing Your Legal Education
- Connect with Us
- For Admitted Applicants
- Master of Legal Studies
- Certificates
- Online Part-time JD
- Online MLS Cybersecurity
Academic Calendar
- Academics Overview
- Degrees / Concentrations / Certificates
- Centers & Programs
- Academic Advising and Support
For Employers
Career connect.
- Career Overview
- Employment Statistics
- Your Career Path
- Hire CSU|LAW
- Solo Practice Incubator
- Non-Discrimination Policy
- First Assignments
- Course & Exam Schedules
(404) 738-5471

Ultimate Checklist for Understanding Contract Assignment Rules
- February 28, 2024
- Moton Legal Group

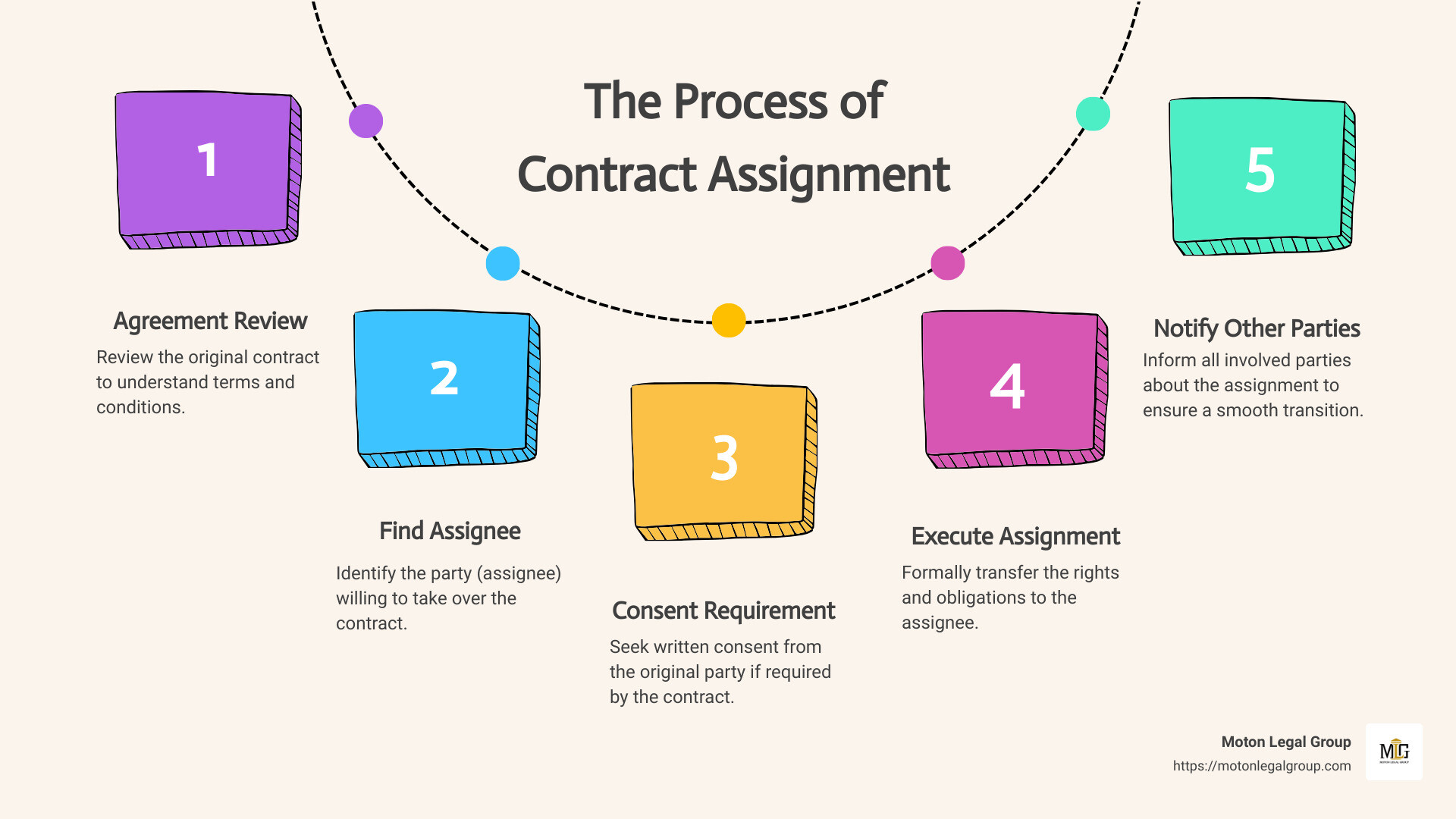
In contracts, understanding assignment is key. Simply put, an assignment in contract law is when one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and responsibilities under a contract to another party (the assignee). This can include anything from leasing agreements to business operations. But why is this important? It’s because it allows for flexibility in business and personal dealings, a critical component in our world.
Here’s a quick rundown: – Contract Basics: The foundational agreements between parties. – Assignment Importance: Allowing the transfer of obligations and benefits to keep up with life’s changes.
Contracts are a staple in both personal and business worlds, acting as the backbone to many transactions and agreements encountered daily. Understanding the nuances, like assignments, can empower you to navigate these waters with confidence and ease. Whether you’re a business owner in the Southeast looking to expand or an individual managing personal agreements, grasp these basics, and you’re on the right path.
Understanding Contract Assignment
Contract Assignment sounds complicated, right? But, let’s break it down into simple terms. In contracts and legal agreements, knowing about assignment can save you a lot of headaches down the road. Whether you’re a business owner, a landlord, or just someone who deals with contracts, this is for you.
Legal Definition
At its core, contract assignment is about transferring rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Think of it as passing a baton in a relay race. The original party (the assignor) hands off their responsibilities or benefits to someone else (the assignee). But, there’s a twist – the race keeps going with the new runner without starting over.
Contract Law
In contract law, assignment comes into play in various ways. For example, if you’re a freelancer and you’ve agreed to complete a project but suddenly find yourself overbooked, you might assign that contract to another freelancer. This way, the job gets done, and your client is happy. However, not all contracts can be freely assigned. Some require the other party’s consent, and others can’t be assigned at all, especially if they involve personal skills or confidential trust.
Property Law
When it comes to property law, assignment often surfaces in landlord-tenant relationships. Say you’re renting a shop for your business, but you decide to move. If your lease allows it, you might assign your lease to another business. This means they take over your lease, stepping into your shoes, with all the rights and obligations that come with it.
The concept might seem straightforward, but there are important legal requirements and potential pitfalls to be aware of. For instance, an assignment could be prohibited by the contract itself, or it may significantly change the original deal’s terms in a way that’s not allowed. Plus, when you’re dealing with something that requires a unique skill set, like an artist or a consultant, those services typically can’t be passed on to someone else without agreement from all parties involved.
To navigate these complexities, understanding the fundamentals of assignment in contract law and property law is crucial. It ensures that when you’re ready to pass that baton, you’re doing it in a way that’s legal, effective, and doesn’t leave you tripping up before you reach the finish line.
The goal here is to make sure everyone involved understands what’s happening and agrees to it. That way, assignments can be a useful tool to manage your contracts and property agreements, keeping things moving smoothly even when changes come up.
For more detailed exploration on this topic, consider checking the comprehensive guide on Assignment (law)). This resource dives deeper into the nuances of contract assignment, offering insights and examples that can help clarify this complex area of law.
By grasping these basics, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of contract assignment. Whether you’re dealing with leases, business deals, or any agreement in between, knowing how to effectively assign a contract can be a game-changer.
Key Differences Between Assignment and Novation
When diving into contracts, two terms that often cause confusion are assignment and novation . While both deal with transferring obligations and rights under a contract, they are fundamentally different in several key aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in contract management or negotiation.
Rights Transfer
Assignment involves the transfer of benefits or rights from one party (the assignor) to another (the assignee). However, it’s important to note that only the benefits of the contract can be assigned, not the burdens. For instance, if someone has the right to receive payments under a contract, they can assign this right to someone else.
Novation , on the other hand, is more comprehensive. It involves transferring both the rights and obligations under a contract from one party to a new party. With novation, the original party is completely released from the contract, and a new contractual relationship is formed between the remaining and the new party. This is a key distinction because, in novation, all parties must agree to this new arrangement.
Obligations Transfer
Assignment doesn’t transfer the original party’s obligations under the contract. The assignor (the original party who had the rights under the contract) might still be liable if the assignee fails to fulfill the contract terms.
In contrast, novation transfers all obligations to the new party. Once a novation is complete, the new party takes over all rights and obligations, leaving the original party with no further legal liabilities or rights under the contract.
Written Agreement
While assignments can sometimes be informal or even verbal, novation almost always requires a written agreement. This is because novation affects more parties’ rights and obligations and has a more significant impact on the contractual relationship. A written agreement ensures that all parties are clear about the terms of the novation and their respective responsibilities.
In practice, the need for a written agreement in novation serves as a protection for all parties involved. It ensures that the transfer of obligations is clearly documented and legally enforceable.
For example, let’s say Alex agrees to paint Bailey’s house for $1,000. Later, Alex decides they can’t complete the job and wants Chris to take over. If Bailey agrees, they can sign a novation agreement where Chris agrees to paint the house under the same conditions. Alex is then relieved from the original contract, and Chris becomes responsible for completing the painting job.
Understanding the difference between assignment and novation is critical for anyone dealing with contracts. While both processes allow for the transfer of rights or obligations, they do so in different ways and with varying implications for all parties involved. Knowing when and how to use each can help ensure that your contractual relationships are managed effectively and legally sound.
For further in-depth information and real-life case examples on assignment in contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Next, we’ll delve into the legal requirements for a valid assignment, touching on express prohibition, material change, future rights, and the rare skill requirement. Understanding these will further equip you to navigate the complexities of contract assignments successfully.
Legal Requirements for a Valid Assignment
When dealing with assignment in contract law , it’s crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let’s break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement.
Express Prohibition
The first stop on our checklist is to look for an express prohibition against assignment in the contract. This is a clause that outright states assignments are not allowed without the other party’s consent. If such language exists and you proceed with an assignment, you could be breaching the contract. Always read the fine print or have a legal expert review the contract for you.
Material Change
Next up is the material change requirement. The law states that an assignment cannot significantly alter the duties, increase the burdens, or impair the chances of the other party receiving due performance under the contract. For instance, if the contract involves personal services tailored to the specific party, assigning it to someone else might change the expected outcome, making such an assignment invalid.
Future Rights
Another important aspect is future rights . The rule here is straightforward: you can’t assign what you don’t have. This means that a promise to assign rights you may acquire in the future is generally not enforceable at present. An effective assignment requires that the rights exist at the time of the assignment.
Rare Skill Requirement
Lastly, let’s talk about the rare skill requirement . Some contracts are so specialized that they cannot be assigned to another party without compromising the contract’s integrity. This is often the case with contracts that rely on an individual’s unique skills or trust. Think of an artist commissioned for a portrait or a lawyer hired for their specialized legal expertise. In these scenarios, assignments are not feasible as they could severely impact the contract’s intended outcome.
Understanding these legal requirements is pivotal for navigating the complexities of assignment in contract law. By ensuring compliance with these principles, you can effectively manage contract assignments, safeguarding your interests and those of the other contracting party.
For anyone looking to delve deeper into the intricacies of contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Moving forward, we’ll explore the common types of contract assignments, from landlord-tenant agreements to business contracts and intellectual property transfers. This will give you a clearer picture of how assignments work across different legal landscapes.
Common Types of Contract Assignments
When we dive into assignment in contract law , we find it touches nearly every aspect of our business and personal lives. Let’s simplify this complex topic by looking at some of the most common types of contract assignments you might encounter.
Landlord-Tenant Agreements
Imagine you’re renting a fantastic apartment but have to move because of a new job. Instead of breaking your lease, you can assign your lease to someone else. This means the new tenant takes over your lease, including rent payments and maintenance responsibilities. However, it’s crucial that the landlord agrees to this switch. If done right, it’s a win-win for everyone involved.

Business Contracts
In the business world, contract assignments are a daily occurrence. For example, if a company agrees to provide services but then realizes it’s overbooked, it can assign the contract to another company that can fulfill the obligations. This way, the project is completed on time, and the client remains happy. It’s a common practice that ensures flexibility and efficiency in business operations.

Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (IP) assignments are fascinating and complex. If an inventor creates a new product, they can assign their patent rights to a company in exchange for a lump sum or royalties. This transfer allows the company to produce and sell the invention, while the inventor benefits financially. However, it’s critical to note that with trademarks, the goodwill associated with the mark must also be transferred to maintain its value.
Understanding these types of assignments helps clarify the vast landscape of contract law. Whether it’s a cozy apartment, a crucial business deal, or a groundbreaking invention, assignments play a pivotal role in ensuring these transitions happen smoothly.
As we navigate through the realm of contract assignments, each type has its own set of rules and best practices. The key is to ensure all parties are on the same page and that the assignment is executed properly to avoid any legal pitfalls.
Diving deeper into the subject, next, we will explore how to execute a contract assignment effectively, ensuring all legal requirements are met and the process runs as smoothly as possible.
How to Execute a Contract Assignment Effectively
Executing a contract assignment effectively is crucial to ensure that all legal requirements are met and the process runs smoothly. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate this process without any hiccups.
Written Consent
First and foremost, get written consent . This might seem like a no-brainer, but it’s surprising how often this step is overlooked. If the original contract requires the consent of the other party for an assignment to be valid, make sure you have this in black and white. Not just a handshake or a verbal agreement. This ensures clarity and avoids any ambiguity or disputes down the line.
Notice of Assignment
Next up, provide a notice of assignment to all relevant parties. This is not just common courtesy; it’s often a legal requirement. It informs all parties involved about the change in the assignment of rights or obligations under the contract. Think of it as updating your address with the post office; everyone needs to know where to send the mail now.
Privity of Estate
Understanding privity of estate is key in real estate transactions and leases. It refers to the legal relationship that exists between parties under a contract. When you assign a contract, the assignee steps into your shoes, but the original terms of the contract still apply. This means the assignee needs to be aware of and comply with the original agreement’s requirements.
Secondary Liability
Lastly, let’s talk about secondary liability . Just because you’ve assigned a contract doesn’t always mean you’re off the hook. In some cases, the original party (the assignor) may still hold some liability if the assignee fails to perform under the contract. It’s essential to understand the terms of your assignment agreement and whether it includes a release from liability for the assignor.
Executing a contract assignment effectively is all about dotting the I’s and crossing the T’s . By following these steps—securing written consent, issuing a notice of assignment, understanding privity of estate, and clarifying secondary liability—you’re setting yourself up for a seamless transition.
The goal is to ensure all parties are fully informed and agreeable to the changes being made. This not only helps in maintaining good relationships but also in avoiding potential legal issues down the line.
We’ll dive into some of the frequently asked questions about contract assignment to clear any lingering doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Contract Assignment
When navigating contracts, questions often arise, particularly about the concepts of assignment and novation. Let’s break these down into simpler terms.
What does assignment of a contract mean?
In the realm of assignment in contract law , think of assignment as passing the baton in a relay race. It’s where one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and benefits under a contract to another party (the assignee). However, unlike a relay race, the original party might still be on the hook for obligations unless the contract says otherwise. It’s like handing off the baton but still running alongside the new runner just in case.
Is an assignment legally binding?
Absolutely, an assignment is as binding as a pinky promise in the playground – but with legal muscle behind it. Once an assignment meets the necessary legal criteria (like not significantly changing the obligor’s duties or having express consent if required), it’s set in stone. This means both the assignee and the assignor must honor this transfer of rights or face potential legal actions. It’s a serious commitment, not just a casual exchange.
What is the difference between assignment and novation?
Now, this is where it gets a bit more intricate. If assignment is passing the baton, novation is forming a new team mid-race. It involves replacing an old obligation with a new one or adding a new party to take over an old one’s duties. Crucially, novation extinguishes the old contract and requires all original and new parties to agree. It’s a clean slate – the original party walks away, and the new party steps in, no strings attached.
While both assignment and novation change the playing field of a contract, novation requires a unanimous thumbs up from everyone involved, completely freeing the original party from their obligations. On the other hand, an assignment might leave the original party watching from the sidelines, ready to jump back in if needed.
Understanding these facets of assignment in contract law is crucial, whether you’re diving into a new agreement or navigating an existing one. Knowledge is power – especially when it comes to contracts.
As we wrap up these FAQs, the legal world of contracts is vast and sometimes complex, but breaking it down into bite-sized pieces can help demystify the process and empower you in your legal undertakings.
Here’s a helpful resource for further reading on the difference between assignment and cession.
Now, let’s continue on to the conclusion to tie all these insights together.
Navigating assignment in contract law can seem like a daunting task at first glance. However, with the right information and guidance, it becomes an invaluable tool in ensuring that your rights and obligations are protected and effectively managed in any contractual relationship.
At Moton Legal Group, we understand the intricacies of contract law and are dedicated to providing you with the expertise and support you need to navigate these waters. Whether you’re dealing with a straightforward contract assignment or facing more complex legal challenges, our team is here to help. We pride ourselves on our ability to demystify legal processes and make them accessible to everyone.
The key to successfully managing any contract assignment lies in understanding your rights, the obligations involved, and the potential impacts on all parties. It’s about ensuring that the assignment is executed in a way that is legally sound and aligns with your interests.
If you’re in need of assistance with a contract review, looking to understand more about how contract assignments work, or simply seeking legal advice on your contractual rights and responsibilities, Moton Legal Group is here for you. Our team of experienced attorneys is committed to providing the clarity, insight, and support you need to navigate the complexities of contract law with confidence.
For more information on how we can assist you with your contract review and other legal needs, visit our contract review service page .
In the constantly evolving landscape of contract law, having a trusted legal partner can make all the difference. Let Moton Legal Group be your guide, ensuring that your contractual dealings are handled with the utmost care, professionalism, and expertise. Together, we can navigate the complexities of contract law and secure the best possible outcomes for your legal matters.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the fundamentals of assignment in contract law. We hope you found this information helpful and feel more empowered to handle your contractual affairs with confidence.
For more information Call :
Reach out now.
" * " indicates required fields
Recent Blog Posts:

Expert Tips for Handling Business Purchase and Sale Agreements

How to Craft a Legally Binding Purchase and Sale Agreement

The Complete Guide to Contracts of Sale in Real Estate

Understanding Undue Influence in Contract Law 101

Understanding the Statute of Frauds in Contract Law: A Complete Guide

The Ultimate Guide to Specific Performance in Contract Law

Former President Donald Trump has been found guilty on all 34 felony charges in his historic hush money criminal trial.
Adrian Diaz out as Seattle's top cop, Sue Rahr named interim chief
by Danny Schmidt, KOMO News

SEATTLE — Seattle Mayor Bruce Harrell has removed police Chief Adrian Diaz from his post and replaced him with former King County Sheriff Sue Rahr, noting allegations against Diaz played a role in the move.
A month ago, Harrell said he was evaluating everyone within the SPD, including the chief, amid a string of claims alleging sexual harassment and sexual and racial discrimination from department leaders. Diaz was accused by multiple employees in lawsuits and tort claims. He denied the allegations.
On Wednesday, Harrell said Diaz would step aside and work on “special projects" after the two came to the "mutual decision." Rahr will serve as interim chief beginning Thursday morning, Harrell said.
"His integrity, in my mind, is beyond reproach," Harrell said of Diaz during a press conference Wednesday . "He's a friend, and I want to thank him for his service. He's a human being, and a good human being at that.
ALSO SEE | Elected officials, city leaders and organizations react to Diaz's departure as SPD chief
"I believe in Chief Diaz," Harrell continued. "I believe he's extremely talented as well. He inherited a culture where a lot of the allegations predate him. We believe this is the right thing to do."
Diaz was emotional speaking to the media Wednesday.
I'm proud of the work we've done together, but recognize now is the right time to step away for the best interests of the city and its people,” said Diaz, who added that he's had medical issues he will now address. “I look forward to continuing to serve our communities and neighbors and supporting the department as we move forward.
Rahr told Harrell she does not want the job permanently.
"She is a proven national expert in this space," Harrell said of Rahr, who ran the Washington police academy for most of the 2010s. "We are confident that she will look at the personnel issues and the allegations and make decisions there."
Rahr said she has "big shoes to fill" Wednesday, speaking after Diaz during the press conference.
"I want lots of people," Rahr Wednesday about recruiting, adding that she hopes to improve the SPD's flexible employee schedules. "We need lots of diversity. We need diversity of experience. The Seattle Police Department — if I can do it — is going to be the top recruiter for female recruits. This is going to be the place people want to come to work. I’m confident of that."
Former Seattle police Chief Kathleen O’Toole, who stepped down at the end of 2017, will help conduct a national search alongside Rahr, Harrell said. The search will begin next week, Harrell added.
"There was not one straw that broke the camel’s back," Harrell said of the decision to shake up the police department. "Culture change is very hard. I'm intentionally looking outside of the department. I'm very proud of our Seattle Police Department. They make me proud as a mayor.
"This is how you get better. I'm very confident. I feel pretty excited about the future for us."
Rahr said recruiting and "listening" are her top immediate priorities.
The SPD continues to struggle with staffing, down more than 345 officers at last count, according to Seattle City Council President Sara Nelson, despite the city offering major signing bonuses and a massive back-timed pay increase. Last week, the City Council approved legislation to streamline hiring.
"Recruiting is a critical need, and that’s something I think I can do relatively quickly and can have a quick impact," Rahr said. " The contract has been resolved, so I want to ride that wave of momentum. I need to listen and learn because I don’t have all the information I need to make decisions yet. I need to talk to the people who live and work in the community.
"The Seattle Police Department cannot drive the crime rate down. We need to work with the community."
A "30 By 30 Report" for the SPD in September detailed female employees' allegations of sexual harassment and descriptions of a "masculine police culture" filled with double standards and a lack promotion opportunities for women, especially mothers, in the department.
The SPD said its goal is to increase the number of women in law enforcement to 30% by 2030.
Rahr was asked Wednesday if she has concerns about the culture within the SPD.
I’ll be honest with you, I have concerns about the culture of all police departments," she said. "I think we are all trying to do better. I think it’s a natural thing that happens when you have a profession that is dominated by one gender for half a century, three quarters of a century. And making those transitions are really hard. I don’t think Seattle Police Department is worse or better than others, I think that we have work to do in every department.
One of the reasons I was very anxious to jump in is I think the Seattle Police Department is open to doing something meaningful and implementing a systemic change. Because we can keep playing whack-a-mole every time there’s an allegation here or there, but until we change the system, we’re not going to have meaningful change. And that was one of the things that drew me to this opportunity, to actually do something that’s going to matter.
Turmoil within the SPD
Last month, four female employees stepped forward to accuse Diaz and his top lieutenant, John O’Neill, of a pattern of harassment, discrimination and a hostile work environment. They filed a $5 million claim against the city.
In late April, Harrell said he hired an independent investigator to review the claims made against Diaz and O’Neill, who leads the media relations unit.
Assistant Chief Tyrone Davis was put on administrative leave on May 23, adding to the internal chaos at the SPD. In a message to staff, Diaz said the move was a precautionary step “due to (Office of Police Accountability) allegations.” It’s unclear the nature of the OPA complaint that led to the immediate suspension.
WATCH | Supporters of Seattle police chief back Diaz, argue accusers are 'serial complainers'
Davis — one of five assistant chiefs, according to the SPD’s website — has overseen special operations and joined the SPD in 1999. His department includes SWAT, hostage negotiations, the arson/bomb squad, the harbor unit and the canine unit. He is the highest-ranking African American officer in the department.
Davis was promoted by Diaz and replaced Eric Greening, who recently filed suit against the city of Seattle and Diaz alleging he was retaliated against for reporting on discrimination within the department and the appearance of segregation. Greening also claimed that community outreach was being done solely by female and BIPOC officers.
Last week, supporters of Diaz said accusations of sexual harassment and discrimination were from “disgruntled” employees who are “serial complainers.” Victoria Beach, Rev. Harriet Walden and Carmen Martinez made the claims in a 45-minute news conference in Beacon Hill since, they said, Diaz could not defend himself.
Diaz was hired as interim chief in September 2020 after Carmen Best resigned amid backlash over her handling of that summer's protests and her opposition to the City Council's plan to cut her budget . Two years later, Harrell said he intended to appoint Diaz to the permanent position, and Diaz was sworn in on Jan. 12, 2023.
The Southern California native graduated from Central Washington University before earning his master's in public administration from the University of Washington. Diaz joined the SPD in 1997 and began his career in patrol before joining the investigations bureau. He was promoted to assistant chief in 2017 and deputy chief in 2020, a month before taking over as the SPD's top cop.
Loudermill hearing for officer
With Wednesday's change at the top, Harrell was asked about the Loudermill hearing of Daniel Auderer, the Seattle police union vice president heard on video allegedly mocking the death of Jaahnavi Kandula in January 2023. Kandula was a 23-year-old grad student from India killed when officer Kevin Dave hit her in a South Lake Union crosswalk while speeding nearly three times the legal limit as he responded to an overdose call.
The incident made national — and international — headlines after body-worn camera audio from another officer was released . Auderer responded to the Jan. 23 crash scene and afterward called guild President Mike Solan to report what happened. In the recording released by the SPD, Auderer laughs and suggests that Kandula’s life had “limited value” and the city should “just write a check.”
“Eleven thousand dollars. She was 26 anyway,” Auderer said, inaccurately stating Kandula's age. “She had limited value.”
No criminal charges were filed against Dave.
The hearing, which will determine any disciplinary action for Auderer, began on May 16.
"She will make that decision as the process allows," Harrell said of Rahr. "Likely in a few weeks."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It is important to read and re-read (and even read again) the assignment sheet. You don't want to make a mistake and write something off topic. Remember, answering the question is key to getting a good grade! Plan before you write. A great legal writing assignment is organized. And for most of us this means that you need to plan your paper ...
Try to keep that time of day clear and free from distractions so you can do your work then. Work out how many different tasks you have to complete in any given week (classes to prepare for, assignments to write, etc) and make sure you divide your study time so that you can do each of the tasks.
In contrast, the Holding is the applied rule of law that serves as the basis for the ultimate judgment. Remember that the purpose of a brief is to remind you of the important details that make the case significant in terms of the law. It will be a reference tool when you are drilled by a professor and will be a study aid when you prepare for exams.
Prepare for your law school classes with Westlaw. Check out these tips to help you get ahead in your first year of law school. ... You can copy and paste a list of up to 30 citations into the search box or you can manually enter multiple citations separated by semicolons. ... set your course dates and set your copy option to Assignments Only. 5 ...
Our Services. Find out how LawTeacher can help YOU. LawTeacher.net is a company who aim to be the ultimate supplier of educational law support. From academic law support services to free resources and legal materials, we're here to help you at every stage of your education. View our service portfolio.
Course Overview. 1 North Griswold Hall. 1525 Massachusetts Avenue. , MA 02138. [email protected]. Before you begin your studies in the First-Year Legal Research and Writing Program (LRW), it will help you to situate the course in the broader context of your legal education and your future law practice. To follow is a brief overview of the ...
Restate key supporting arguments. The final stage of creating the plan of your law essay is to pick 2 to 3 key supporting arguments which you discussed in the main body of your paper and outline them again. This time, however, you will not be getting into a detailed discussion of how case law or statute sections justify your supporting arguments.
ASSIGNMENTS. Writing a good paper is an essential skill for any law student. A significant number of the law courses at university will require you to write at least one research paper for assessment. As you would expect, university lecturers will require papers to contain a greater deal of scholarly research than you might have undertaken at ...
These resources address a broad range of legal writing issues, and will be updated periodically. Please contact [email protected] with questions or feedback. For information about the Law School Writing Center, or to make an appointment, please visit the Writing Center main page. Handouts: Structure, Organization, and Clarity.
This is to demonstrate that you understand the relevant principles being assessed. 2. So firstly, you need to divide the start of the essay into parts: Examining rights of common, customary rights, and aboriginal rights. It would be a good idea to split these into three sections. 3.
Record key points, relevant quotations, and references to legal authorities. Create a clear thesis statement or argument based on your initial research and grasp of the subject. It will be your writing's direction. The thesis should present your main point or position on the discussed legal issue.
The most common assignment that represents this type of homework is essay writing. Just like the rest of their peers, law students are being assigned dozens of essays and other academic papers every year. A load of such assignments is so huge that students often look for the write my essay online writing services and platforms. But, it is an ...
ASSIGNMENTS AND DISCUSSIONS. Daily class assignments are found in the syllabus. All of the class outlines for this year may be found by the day on which they were posted under lectures. After we have the class I will substitute the class outline that we used this year. The previous exams tab contains a number of essay questions from previous ...
Tip 5: Try to avoid making students 'prove a negative.'. I field a lot of questions from students like this: "My assigning attorney asked me to research [insert extremely specific topic ...
Be sure to pinpoint the relevant jurisdiction. If it is a pending case, the court where it is pending will tell you that. Also be sure to get the docket number from the assignor. If the research question is for a case that is not yet filed, be sure to ask where the case would be filed. If there is a choice of where to file, determine whether ...
Every legal assignment writing order will provide you with fully referenced and original work, written by one of the UKs finest academic legal writers. We cover all areas of law, including areas such as criminal, tort, jurisprudence and more specialist areas such as international law and shipping law. We check all of the work we produce to ...
This chapter looks at some of the many different forms of assessment a law student may come across, depending on where they are studying and the subjects they choose. These include coursework, exams, multiple-choice tests, advocacy or other oral presentations, posters, and reflective reports. The chapter also considers dissertations and other research projects, and group work for assessment ...
First Assignments. Term/Semester. Select any term/semester to see available assignments. Course & Exam Schedules.
When dealing with assignment in contract law, it's crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let's break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement.
Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court, 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950). An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment ...
Assignment (law) Assignment [a] is a legal term used in the context of the laws of contract and of property. In both instances, assignment is the process whereby a person, the assignor, transfers rights or benefits to another, the assignee. [1] An assignment may not transfer a duty, burden or detriment without the express agreement of the assignee.
New Litigation Partners Discuss Tackling Tricky Assignments and Dealing With Imposter Syndrome. Newly promoted litigation partners in the second half of the Am Law 100 reflect on their career ...
SUBSCRIBE to the Judicial Assignment Notification from the Social Law Library. PLEASE NOTE: Due to COVID 19 the courts are still in a changing environment and not all are sending the judicial assignments out on a monthly basis. Some are sending weekly and others are not yet releasing assignments. Social Law will update this page to the best of ...
FLTS. FAMILY LAW TRIAL AND LONG CAUSE EVIDENTIARY HEARING ASSIGNMENT CALENDAR (also known as Trial Assignment "T.A.") 05-31-24, 8:30 a.m., Dept. 43. The following are the Family Law Trial and Long Cause Evidentiary Hearing dates available as of the date listed above. Parties may agree to a date set forth below for a long cause evidentiary ...
Seattle Mayor Bruce Harrell announced Wednesday that Adrian Diaz will step aside as police chief and "work on special assignment for the mayor with SPD." ... 30 May 2024 05:35:26 GMT ...