
- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths PDF
The passage-based questions are commonly known as case study questions. Students looking for Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths can use this page to download the PDF file.
The case study questions on Vector Algebra are based on the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus, and therefore, referring to the Vector Algebra case study questions enable students to gain the appropriate knowledge and prepare better for the Class 12 Maths board examination. Continue reading to know how should students answer it and why it is essential to solve it, etc.
Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths with Solutions in PDF
Our experts have also kept in mind the challenges students may face while solving the case study on Vector Algebra, therefore, they prepared a set of solutions along with the case study questions on Vector Algebra.
The case study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Vector Algebra case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
Why Solve Vector Algebra Case Study Questions on Class 12 Maths?
There are three major reasons why one should solve Vector Algebra case study questions on Class 12 Maths - all those major reasons are discussed below:
- To Prepare for the Board Examination: For many years CBSE board is asking case-based questions to the Class 12 Maths students, therefore, it is important to solve Vector Algebra Case study questions as it will help better prepare for the Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Class 12 Maths Vector Algebra case study questions require students to analyze a given situation, identify the key issues, and apply relevant concepts to find out a solution. This can help CBSE Class 12 students develop their problem-solving skills, which are essential for success in any profession rather than Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Understand Real-Life Applications: Several Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths Case Study questions are linked with real-life applications, therefore, solving them enables students to gain the theoretical knowledge of Vector Algebra as well as real-life implications of those learnings too.
How to Answer Case Study Questions on Vector Algebra?
Students can choose their own way to answer Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths, however, we believe following these three steps would help a lot in answering Class 12 Maths Vector Algebra Case Study questions.
- Read Question Properly: Many make mistakes in the first step which is not reading the questions properly, therefore, it is important to read the question properly and answer questions accordingly.
- Highlight Important Points Discussed in the Clause: While reading the paragraph, highlight the important points discussed as it will help you save your time and answer Vector Algebra questions quickly.
- Go Through Each Question One-By-One: Ideally, going through each question gradually is advised so, that a sync between each question and the answer can be maintained. When you are solving Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths case study questions make sure you are approaching each question in a step-wise manner.
What to Know to Solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Vector Algebra?
A few essential things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Vector Algebra are -
- Basic Formulas of Vector Algebra: One of the most important things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Vector Algebra is to learn about the basic formulas or revise them before solving the case-based questions on Vector Algebra.
- To Think Analytically: Analytical thinkers have the ability to detect patterns and that is why it is an essential skill to learn to solve the CBSE Class 12 Maths Vector Algebra case study questions.
- Strong Command of Calculations: Another important thing to do is to build a strong command of calculations especially, mental Maths calculations.
Where to Find Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths?
Use Selfstudys.com to find Case Study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths. For ease, here is a step-wise procedure to download the Vector Algebra Case Study for Class 12 Maths in PDF for free of cost.
Since you are already on this page, you can scroll to the top section of this page to get access to the Case Study on Vector Algebra. To help others reach this page let them know these steps:
- Open Selfstudys.com on your computer/laptop or Smartphone
- Once the website gets loaded, click on the navigation button
- Find CBSE from the given menu
- Click on Case Study
- Choose Class 12
- Search Maths and then navigate to the Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths Case Study
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu


Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

12th Standard CBSE
CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Vector Algebra Case Study Questions With Solution 2021

CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Vector Algebra Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Shalini Sharma - Udaipur May-21 , 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 12th standard maths vector algebra case study questions with solution 2021.
Final Semester - June 2015
Case Study Questions
(ii) What is the magnitude of the teams combined force ?
(iii) In what direction is the ring getting pulled?
(iv) What is the magnitude of the force of Team B?
| KN | KN |
(v) How many KN force is applied by Team A?
| \(3 \hat{i}+5 \hat{j}\) | \(5 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}\) | \(-5 \hat{i}-3 \hat{j}\) | \(-5 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}\) |
(ii) Position vector of D is
| \(5 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}\) | \(3 \hat{i}+5 \hat{j}\) | \(8 \hat{i}+9 \hat{j}\) | \(9 \hat{i}+8 \hat{j}\) |
(iii) Find the vector \(\overrightarrow{B C}\) in terms of \(\hat{i}, \hat{j}\) .
| \( \hat{i}-2 \hat{j}\) | \( \hat{i}+2 \hat{j}\) | \(2\hat{i}+ \hat{j}\) | \(2\hat{i}- \hat{j}\) |
(iv) Length of vector \(\overrightarrow{A D}\) is
| \(\sqrt 67\) | \(\sqrt 85\) |
(v) If \(\vec{M}=4 \hat{\jmath}+3 \hat{k}\) , then its unit vector
| \(\frac{4}{5} \hat{j}+\frac{3}{5} \hat{k}\) | \(\frac{4}{5} \hat{j}-\frac{3}{5} \hat{k}\) | \(-\frac{4}{5} \hat{j}+\frac{3}{5}\hat{k}\) | (d) \(-\frac{4}{5} \hat{j}-\frac{3}{5} \hat{k}\) |
If two vectors are represented by the two sides of a triangle taken in order, then their sum is represented by the third side of the triangle taken in opposite order and this is known as triangle law of vector addition. lased on the above information, answer the following questions. (i) If \(\vec{p}, \vec{q}, \vec{r}\) are the vectors represented by the sides of a triangle taken in order, then \( \vec{q} +\vec{r}\) =
(ii) If ABCD is a parallelogram and AC and BD are its diagonals, then \( \vec{AC} +\vec{BD}\) =
(iii) If ABCD is a parallelogram, where \(\overrightarrow{A B}\) \(=2\overrightarrow{a}\) and \(\overrightarrow{BC}\) \(=2\overrightarrow{b}\) , then \( \vec{AC} -\vec{BD}\) =
| \(4\vec{b}\) |
| \(\overrightarrow{A C}+\overrightarrow{D B}\) | \(\overrightarrow{A C}+\overrightarrow{B D}\) | \(\overrightarrow{B C}+\overrightarrow{A D}\) |
| \(2 \hat{i}-3 \hat{j}-6 \hat{k}\) |
(ii) Which of the following is not true?
(iii) Area of \(\Delta\) ABC is
| \(\sqrt 1937 sq. unit\) |
(iv) Suppose, if the given slogans are to be placed on a straight line, then the value of \(|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}+\vec{b} \times \vec{c}+\vec{c} \times \vec{a}|\) will be equal to
(v) If \(\vec{a}=2 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}+6 \hat{k}\) then unit vector in the direction of vector \(\vec{a}\) is
| \(\frac{2}{7} \hat{i}+\frac{3}{7} \hat{j}+\frac{6}{7} \hat{k}\) |
(ii) Position vector of B is
(iii) Find the vector \(\vec{AC}\) in terms of \(\hat{i}, \hat{j}\)
(iv) If \(\vec{A}=\hat{i}+2 \hat{j}+3 \hat{k}\) , then its unit vector is
(v) If \(\vec{A}=4 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}\) and \(\vec{B}=3 \hat{i}+4 \hat{j}\) , then IAI+ IBI = ___________.
*****************************************
- Previous 12th Maths Vector Algebra Chapter Case Study Question with Answers CBSE
- Next 12th Maths Three Dimensional Geometry Chapter Case Study Question with Answers C...
Reviews & Comments about CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Vector Algebra Case Study Questions With Solution 2021

Write your Comment

12th Standard CBSE Maths Videos
CBSE 12th Maths Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
12th Standard CBSE Maths Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 12th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 12th Standard CBSE Maths Study material
12th maths vector algebra chapter case study question with answers cbse click to view, 12th maths three dimensional geometry chapter case ... click to view, 12th maths probability chapter case study question with answers cbse click to view, 12th maths linear programming chapter case study question with answers cbse click to view, 12th maths differential equations chapter case study question with answers cbse click to view, 12th maths continuity and differentiability chapter case ... click to view, 12th maths application of integrals chapter case ... click to view, cbse 12th standard maths subject differential equations ... click to view, cbse 12th standard maths subject determinants value ... click to view, cbse 12th standard maths subject value based ... click to view, register & get the solution for cbse 12th standard maths subject vector algebra case study questions with solution 2021.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 10 Class 12 Vector Algebra
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Learn Chapter 10 Class 12 Vector Algebra free with solutions of all NCERT Questions, Examples as well as Supplementary Questions from NCERT.
Suppose we have to go 10km from Point A to Point B.
This 10km is the distance travelled.
It is only value - 10, nothing else.
This is a scalar quantity.
Now, suppose we say,
We go 10 km East from Point A to Point B.
So, we have travelled 10 km East
It has value - 10, and direction - East.
So, this is a vector quantity .
In this chapter, we will talk about vectors. The topics include
- Basics - Difference between scalars and vectors , with example
- Graphical Displacement - Where we represent Displacement like 40 km, 30° East of North, in the Graph.
- We also discuss what is a position vector, and different types of vectors
- Then we learn what happens when a scalar is multiplied to a vector
- We learn what are Equal Vectors and Unit Vectors , and do some questions on them
- Finding Direction Ratios and Direction Cosines
- Then, adding two vectors
- Finding vector joining two points
- Section formula in vectors
- Checking if 3 points make a right angled triangle
- Checking if 2 vectors are collinear
- Checking if 3 points (or vectors) are collinear
- Then, Scalar Product of Vectors and its properties
- Finding projection using scalar product
- Vector product of vectors, and its properties
- Finding area using vector product (Area of parallelogram = Vector Product)
All the questions are solved, with step by step explanation. Click on an exercise or a topic to start learning
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Vector Class 12 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 10 [Free PDF Download]
- Revision Notes
- Chapter 10 Vector

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 (Vector algebra) - Free PDF Download
The topics included in the syllabus of Class 12 Mathematics focus on the development of basic and advanced mathematical concepts. Chapter 10 focuses on the topic of vector algebra. In this chapter, students will learn what is a vector quantity and how it can be represented or calculated. To comprehend this chapter easily, students can refer to the Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths revision notes prepared by the highly experienced teachers at Vedantu. The simplest explanation of the concepts in these revision notes Class 12 Chapter 10 will help them understand the topics and prepare the chapter more efficiently.
Students will also learn how to calculate its magnitude and the direction of the vector quantities. It is an algebraic subject that a student should learn to calculate velocity, acceleration, displacement, force, momentum, weight, and other vector quantities in Physics. Hence, it is one of the most important chapters of Class 12 maths syllabus.
CBSE Class 12 Maths Revision Notes 2024-25 - Chapter Wise PDF Notes for Free
In the table below we have provided the PDF links of all the chapters of CBSE Class 12 Maths whereby the students are required to revise the chapters by downloading the PDF.
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter-wise Notes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chapter 10: Vector Notes |
|
|
| |
Vector algebra Related Important Links
It is a curated compilation of relevant online resources that complement and expand upon the content covered in a specific chapter. Explore these links to access additional readings, explanatory videos, practice exercises, and other valuable materials that enhance your understanding of the chapter's subject matter.
Vector algebra Related Study Materials |
|
|
|
Class 12 Study Materials Important Links
Find a curated selection of study resources for Class 12 subjects, helping students prepare effectively and excel in their academic pursuits.
Important Class 12 Related Links |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Related Chapters
Vector algebra Class 12 Notes Maths - Basic Subjective Questions
Section–a (1 mark questions).
1. Find the values of x and y so that the vectors $2 \hat{i}+3\hat{j}$ and $x \hat{i}+y\hat{j}$ are equal.
Ans. We know that
$$\begin{aligned}& a_1 \hat{i}+b_1 j=a_2 \hat{i}+b_2 j \\& \Leftrightarrow a_1=a_2 \text { and } b_1=b_2 \\& \therefore 2 \hat{i}+3\hat{j}=x \hat{i}+y\hat{j} \\& \Rightarrow x=2 \text { and } y=3 .\end{aligned}$$
2. Find a unit vector parallel to the vector $-3\hat{i}+4\hat{j}$.
Ans . Let, $\vec{a}=-3 \hat{i}+4 j$.
$$|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{(-3)^2+(4)^2}=5$$
$\therefore$ Unit vector parallel to
$$\vec{a}=a=\frac{\vec{a}}{|\vec{a}|}=\frac{1}{5}(-3 \hat{i}+4 j)=-\frac{3}{5}\hat{i}+\frac{4}{5} j .$$
3. The magnitude of the vector $\bar{a}=3 \hat{i}-6 j+2 k$ is.
Ans. Let $\bar{a}=3 \hat{i}-6 j+2 k$. Then,
$$|a|=\sqrt{3^2+(-6)^2+2^2}=7 \text {. }$$
4. Find the projection of the vector $\bar{a}=2 \hat{i}+3\hat{j}+2\hat{k}$ on the vector $\bar{b}=\hat{i}+2\hat{j}+\hat{k}$
Ans. The projection of vector $\vec{a}$ on the vector $\vec{b}$ is given by -
$$\frac{1}{\mid \vec{b}}(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b})=\frac{(2 \times 1+3 \times 2+2 \times1)}{\sqrt{(1)^2+(2)^2+(1)^2}}=\frac{10}{\sqrt{6}}=\frac{5}{3} \sqrt{6}$$
5. If l,m and n are direction cosines of a given vector, then l 2 +m 2 +n 2 = ________.
Ans. We know that,
If $l, m$ and $n$ represents direction cosines of a given vector.
$$l^2+m^2+n^2=1 \text {. }$$
Section–2 (2 Mark Questions)
6. If the position vector $\vec{a}$ of a point (12,n) is such that $\left | \vec{a} \right |=13$, find the value of n.
Ans. The position vector of the point $(12, n)$ is $12 \hat{i}+n j$.
$$\begin{aligned}& \therefore \vec{a}=12 \hat{i}+n j \\& \Rightarrow|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{12^2+n^2}\end{aligned}$$
$|\vec{a}|=13$
$\Rightarrow 13=\sqrt{12^2+n^2}$
$\Rightarrow 169=144+n^2$
$\Rightarrow n^2=25$
$\Rightarrow n= \pm 5$
7. Find the sum of vectors $\hat{a}=\hat{i}-2\hat{i}+\hat{k}, \hat{b}=-2\hat{i}+4\hat{j}+5\hat{k}, \hat{c}=\hat{i}-6\hat{j}-7\hat{k}$.
Ans. We have,
$$\begin{aligned}& \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=(\vec{a}+\vec{b})+\vec{c} \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=\{(\hat{i}-2 j+k)+(-2 \hat{i}+4 j+5 k)\}+(\hat{i}-6 j-7 k) \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=\{(1-2) \vec{i}+(-2+4) j+(1+5) k\}+(\hat{i}-6 j-7 k) \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=(-\hat{i}+2 j+6 k)+(\hat{i}-6 j-7 k) \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=(-1+1) \hat{i}+(2-6) j+(6-7) k \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}+\vec{b}+\vec{c}=0 \hat{i}-4 j-k .\end{aligned}$$
8. Find a vector in the direction of vector \vec{a}=\hat{i}-2 \hat{j} that has magnitude 7 units.
Ans. Given: $\vec{a}=\hat{i}-2 \hat{j}$
$$\therefore|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{1^2+(-2)^2}=\sqrt{5}$$
The unit vector in the direction of the a given vector $\dot{a}$ is
$$\hat{a}=\frac{1}{|\vec{a}|}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}(\hat{i}-2\hat{j})=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\hat{i}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \hat{j}$$
Therefore, the vector having magnitude equal to 7 and in the direction of $\vec{a}$ is
$$7 \hat{a}=7\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \hat{i}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\hat{j}\right)=\frac{7}{\sqrt{5}} \hat{i}-\frac{14}{\sqrt{5}} \hat{j}$$
9. If a vector makes angles $\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma$ with OX, OY, and OZ respectively, prove that $sin^{2}\alpha +sin^{2}\beta +sin^{2}\gamma =2$ .
Ans. Let $l, m, n$ be the direction cosines of the given vector. Then,
$$l=\cos \alpha, m=\cos \beta, n=\cos \gamma .$$
Now, $l^2+m^2+n^2=1$
$$\begin{aligned}& \Rightarrow \cos ^2 \alpha+\cos ^2 \beta+\cos ^2 \gamma=1 \\& \Rightarrow\left(1-\sin ^2 \alpha\right)+\left(1-\sin ^2 \beta\right)+\left(1-\sin ^2\gamma\right)=1 \\& \Rightarrow \sin ^2 \alpha+\sin ^2 \beta+\sin ^2 \gamma=2 .\end{aligned}$$
10. Find $(\vec{a} + 3\vec{b}).(2\vec{a} - \vec{b})$ if $\vec{a}=\hat{i}+\hat{j}+2\hat{k}$ and $\vec{b}=3\hat{i}+2\hat{j}-\hat{k}$.
Ans. Given:
$\vec{a}=\hat{i}+j+2 k$ and $\vec{b}=3 \hat{i}+2 j-k$.
$$\Rightarrow \vec{a}+3 \vec{b}=(\hat{i}+j+2 k)+3(3 \hat{i}+2 j-k)=10 \hat{i}+7 j-k$$
$\therefore ( 2 \vec{a}-\vec{b}=2(\hat{i}+j+2 k)-(3 \hat{i}+2 j-k)=-\hat{i}+0 j+5 k )$
=(10)(-1)+(7)(0)+(-1)(5)
11. For given vectors, $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}-\hat{}{j}+2\hat{k} a$ and $\vec{b}=-\hat{i}+\hat{j}-\hat{k}$, find the unit vector in the direction of the vector $\vec{a}+\vec{b}$ .
Ans. The given vectors are
$\vec{a}=2 \hat{i}-j+2 k \text { and } \vec{b}=-\hat{i}+j-k$
$\therefore \vec{a}+\vec{b}=(2-1) \hat{i}+(-1+1) j+(2-1) k$
$=\hat{i}+k$
$|\vec{a}+\vec{b}|=\sqrt{1^2+1^2}-\sqrt{2}$
Hence, the unit vector in the direction of $\vec{a}+\vec{b}$ is
$\frac{\vec{a}+\vec{b}}{|\vec{a}+\vec{b}|}=\frac{\hat{i}+k}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\hat{i}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} k \text {. }$
12. Find the magnitude of $\vec{a}$ given by $\vec{a}=(\hat{i}+3\hat{j}-2\hat{k})\times(-1\hat{i}+3\hat{k})$
$$\begin{aligned}& \vec{a}=(\hat{i}+3 j-2 k) \times(-\hat{i}+0 j+3 k) \\& \Rightarrow \vec{a}=\left|\begin{array}{ccc}\hat{i} & j & k \\1 & 3 & -2 \\-1 & 0 & 3\end{array}\right|=(9-0) \hat{i}-(3-2) j+(0+3) k \\& =9 \hat{i}-j+3 k \\& \therefore|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{9^2+(-1)^2+3^2}=\sqrt{91} .\end{aligned}$$
13. Find a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors $\hat{i}-2\hat{j}+3\hat{k}$ and $\hat{i}+2\hat{j}-\hat{k}$.
Ans. Let $\vec{a}=\hat{i}-2 \hat{j}+3 \hat{k}$ and $\vec{b}=\hat{i}+2 \hat{j}-\hat{k}$.
$$\begin{aligned}& \vec{a} \times \vec{b}=\left|\begin{array}{ccc}\hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k} \\1 & -2 & 3 \\1 & 2 & -1\end{array}\right|=(2-6) \hat{i}-(-1-3) \hat{j}+(2+2) \hat{k} \\& =-4 \hat{i}+4 \hat{j}+4 \hat{k} . \\& \Rightarrow|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|=\sqrt{(-4)^2+4^2+4^2}=4 \sqrt{3} .\end{aligned}$$
So, a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors $\vec{a}$ and $\vec{b}$ is given by
$$\hat{n}=\frac{\vec{a} \times \vec{b}}{|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|}=\frac{(-4 \hat{i}+4\hat{j}+4 \hat{k})}{4 \sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}(-\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k})$$
PDF Summary - Class 12 Maths Vector algebra Notes (Chapter 10)
Vector quantities are those quantities that have magnitude and direction. It is generally represented by a directed line segment. We represent a vector as \[\overrightarrow{\text{AB}}\], where initial point of vector is denoted by \[\text{A}\] and the terminal point by \[\text{B}\]. The magnitude of vector is expressed as \[\left| \overrightarrow{\text{AB}} \right|\].
Position Vector
Let us denote the origin as \[\text{O}\] such that this is a fixed point. There is a point, say \[\text{P}\] at a distance from \[\text{O}\]. Now, the position vector of a point \[\text{P}\] is given by the vector \[\overrightarrow{\text{OP}}\].
The next case is when there are two vectors, \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] which represent the position vectors of two points \[\text{A}\] and \[\text{B}\]. Then we can write the vector \[\overrightarrow{\text{AB}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}-\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] or the position vector of \[\text{B}-\] the position vector of \[\text{A}\].
Types of Vectors
1. Zero Vector - It has zero magnitude. This means that vector has the same initial and terminal point. It is denoted by \[\overrightarrow{\text{O}}\]. The direction of zero vector is indeterminate.
2. Unit Vector - It has unit magnitude. Unit vector in direction of a vector \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] is denoted by \[\widehat{\text{a}}\] and symbolically as \[\widehat{\text{a}}\text{=}\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|}\].
3. Co-initial Vectors - Two or more vectors are said to be co-initial if they have the same initial point.
4. Equal Vectors - Two vectors are said to be equal if they have the same magnitude and direction. They represent the same physical quantity.
5. Collinear Vectors - Two or more vectors are said to be collinear if they are parallel to the same line irrespective of their direction. For this reason, they are also called parallel vectors. We have two sub-categories – like vectors (same direction) and unlike vectors (different directions). We can represent it mathematically by taking two non-zero vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\]. They are collinear if and only, if \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=K}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\], where \[\text{K}\in \text{R-}\left\{ \text{0} \right\}\].
6. Coplanar Vectors - Those vectors which lie on the same plane and they are all parallel to the same plane. We must remember that two vectors are always coplanar.
7. Negative Vector - A vector which has same magnitude but opposite direction to another vector is called negative of that vector.
Addition of Vectors
1. Triangle Law - Consider a triangle $ABC$. Let the sum of two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] be represented by $\vec{c}$. The position vectors are represented by \[\overrightarrow{\text{AB}}\text{ , }\overrightarrow{\text{BC}}\text{ }and\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{AC}}\].
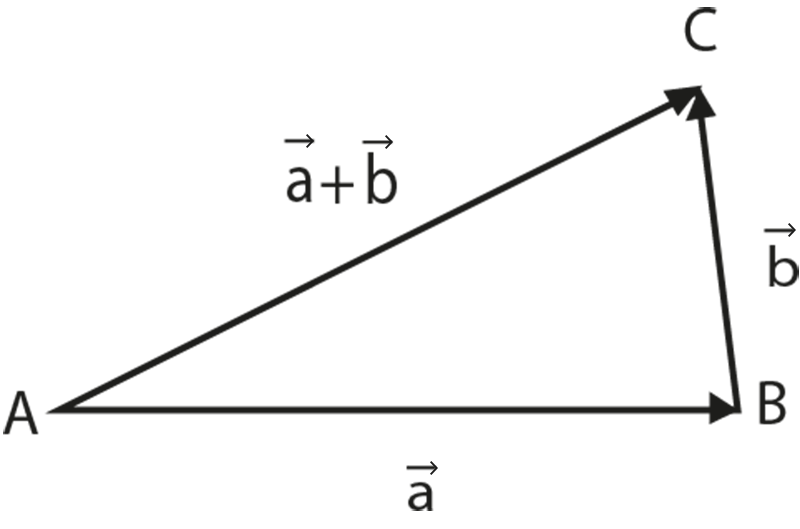
Triangle law of vector addition states that when two vectors are represented as two sides of the triangle with the order of magnitude and direction, then the third side of the triangle represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
So, we can write that $\overrightarrow{AC}=\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}$.
2. Parallelogram Law - Consider a parallelogram $ABCD$. Let the sum of two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] be represented by $\vec{c}$. The position vectors are represented as
\[\vec{a}\text{ =}\overrightarrow{\text{AB}}\text{ = }\overrightarrow{\text{DC}}\]
\[\vec{b}\text{ =}\overrightarrow{\text{AD}}\text{ = }\overrightarrow{\text{BC}}\]
\[\vec{a}+\vec{b}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{AC}}\]
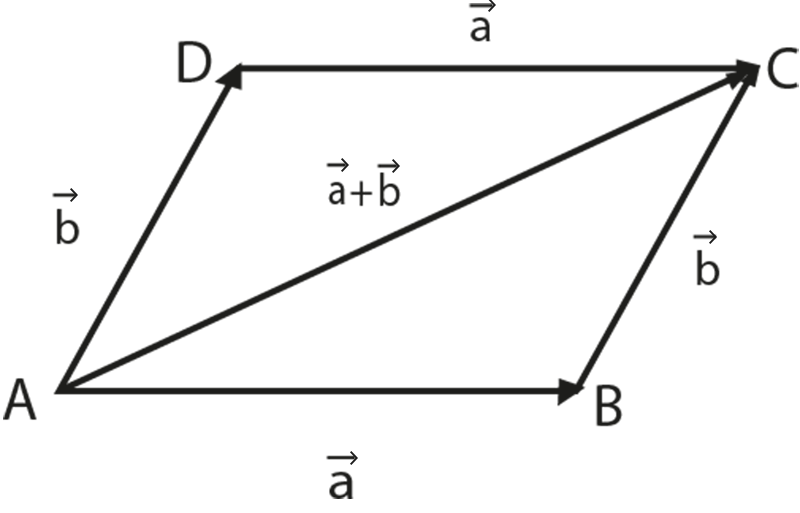
According to the parallelogram law of vector addition if two vectors act along two adjacent sides of a parallelogram (having magnitude equal to the length of the sides) both pointing away from the common vertex, then the resultant is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through the same common vertex and in the same sense as the two vectors.
\[\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}=\overrightarrow{AC}\]
$\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}=\overrightarrow{AC}$
3. Properties of Vector Addition
Commutative property - \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
Associative property - \[\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)\]
Zero is the additive identity - \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{0}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{0}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\left( \text{-}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{0}}\text{=}\left( \text{-}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar
If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] is a vector and \[\text{m}\] is a scalar, then their product is \[\text{m }\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]. The magnitude would be \[\left| \text{m} \right|\] times the magnitude of \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]. This is called scalar multiplication. If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] are vectors and $m$ and $n$ are scalars, then
\[\text{m}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{=}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{m=m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
\[\text{m}\left( \text{n}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{=n}\left( \text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{=}\left( \text{mn} \right)\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
\[\left( \text{m+n} \right)\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+n}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\]
\[\text{m}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\text{=m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+m}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\]
Component Form of Vectors
We have to consider three axis - $x,y,z$ and a point in the coordinate axis. So, the position vector for such a point would be written as $\overrightarrow{OP}=x\hat{i}+y\hat{j}+z\hat{k}$. This is the component form of vector.
The scalar components are $x,y,z$ and the vector components are \[x\hat{i},y\hat{j},z\hat{k}\].
Consider two vectors as \[\vec{A}=a\hat{i}+b\hat{j}+c\hat{k}\] and $\vec{B}=p\hat{i}+q\hat{j}+r\hat{k}$, then
Sum is given by $\vec{A}+\vec{B}=(a+p)\hat{i}+(b+q)\hat{j}+(c+r)\hat{k}$.
Difference is given by $\vec{A}-\vec{B}=(a-p)\hat{i}+(b-q)\hat{j}+(c-r)\hat{k}$.
Multiplication by a scalar $m$ is given by $m\vec{A}=ma\hat{i}+mb\hat{j}+mc\hat{k}$.
The vectors are equal if \[a=p,b=q,c=r\].
Test for Collinearity
Three points \[\text{A,B,C}\] with position vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] respectively are collinear, if and only if there exist scalar \[\text{x,y,z}\] not all zero simultaneously such that; \[\text{x}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+y}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+z}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{=0}\], where \[\text{x+y+z=0}\].
Test for Coplanar Points
Four points \[\text{A,B,C,D}\] with position vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{d}}\] respectively are coplanar if and only if there exist scalars \[\text{x,y,z,w}\] not all zero simultaneously such that; \[\text{x}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+y}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+z}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{+w}\overrightarrow{\text{d}}\text{=0}\], where \[\text{x+y+z+w=0}\].
Section Formula
Let \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] be the position vectors of two points \[\text{A}\] and \[\text{B}\]. A point $R$ with position vector as $\vec{r}$ divides $\overrightarrow{AB}$ such that $m\overrightarrow{RB}=n\overrightarrow{AR}$ and this denotes that $\overrightarrow{AB}$ is divided internally in the ratio \[\text{m:n}\] is given by \[\overrightarrow{\text{r}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}+n\overrightarrow{\text{a}}}{\text{m+n}}\].
Let \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] be the position vectors of two points \[\text{A}\] and \[\text{B}\]. A point $R$ with position vector as $\vec{r}$ divides $\overrightarrow{AB}$ such that $m\overrightarrow{RB}=n\overrightarrow{AR}$ and this denotes that $\overrightarrow{AB}$ is divided externally in the ratio \[\text{m:n}\] is given by \[\overrightarrow{\text{r}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}-n\overrightarrow{\text{a}}}{m-n}\].
Now if the ratio is $1:1$, then we can obtain the position vector of the midpoint as \[\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}}{\text{2}}\].
Magnitude of Vector
For a vector \[\vec{A}=a\hat{i}+b\hat{j}+c\hat{k}\], magnitude is $\left| A \right|=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}$.
For vector $\overrightarrow{AB}$ with \[\vec{A}=a\hat{i}+b\hat{j}+c\hat{k}\] and $\vec{B}=p\hat{i}+q\hat{j}+r\hat{k}$, the magnitude is $\left| \overrightarrow{AB} \right|=\sqrt{{{(p-a)}^{2}}+{{(q-b)}^{2}}+{{(r-c)}^{2}}}$.
Product of Vectors
1. Scalar Product
It is also called dot product. For two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\], the dot product can be represented as \[\vec{a}.\vec{b}\] and it is defined as \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|\text{cos }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ ;(0}\le \text{ }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\le \text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ )}\].
From this, we can find the angle between vectors as $\cos \theta =\dfrac{\vec{a}.\vec{b}}{\left| {\vec{a}} \right|\left| {\vec{b}} \right|}$.
We have the below possibilities:
If \[\text{ }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\] is acute, then \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{0}\].
If \[\text{ }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\] is obtuse, then \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{0}\].
If \[\text{ }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\] is zero, then \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}=\left| {\vec{a}} \right|\left| {\vec{b}} \right|\].
If \[\text{ }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\] is $\pi $, then \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}=-\left| {\vec{a}} \right|\left| {\vec{b}} \right|\].
If vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] are non-zero and \[\vec{a}.\vec{b}=0\], then it is the condition for them to be perpendicular vectors.
Considering component form and above point, we get results as
\[\widehat{\text{i}}\cdot \widehat{\text{i}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{j}}\cdot \widehat{\text{j}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{k}}\cdot \widehat{\text{k}}\text{=1}\]
\[\widehat{\text{i}}\cdot \widehat{\text{j}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{j}}\cdot \widehat{\text{k}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{k}}\cdot \widehat{\text{i}}\text{=0}\]
If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=}{{\text{a}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}{{\text{b}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] then \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}{{\text{a}}_{1}}{{\text{b}}_{1}}+{{\text{a}}_{2}}{{\text{b}}_{2}}+{{\text{a}}_{3}}{{\text{b}}_{3}}\].
Properties of Scalar Product
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=}{{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] (Commutative)
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] (Distributive)
\[\left( \text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \left( \text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\text{=m}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\] (Associative), where \[\text{m}\] is scalar.
Projection of vector \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] on \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|}\].
Maximum value of \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|\]
Minimum value of \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=-}\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|\]
A vector in the direction of the bisector of the angle between two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] is \[\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|}+\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{b}}}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|}\].
Hence bisector of the angle between the two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] is \[\text{ }\!\!\lambda\!\!\text{ }\left( \widehat{\text{a}}+\widehat{\text{b}} \right)\], where \[\text{ }\!\!\lambda\!\!\text{ }\in {{\text{R}}^{+}}\].
Bisector of the exterior angle between \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] is \[\text{ }\!\!\lambda\!\!\text{ }\left( \widehat{\text{a}}\text{-}\widehat{\text{b}} \right)\text{ }\!\!\lambda\!\!\text{ }\in \text{R-}\left\{ \text{0} \right\}\].
2. Vector Product
It is also called cross product. For two vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\], the vector product is represented as $\vec{a}\times \vec{b}$ and is defined by \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right|\left| \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|\text{sin }\!\!\theta\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{n}}\], where $\theta $ is the angle between them and \[\widehat{\text{n}}\] is the unit vector perpendicular to both \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] such that \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\], \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] and \[\widehat{\text{n}}\] form a right handed screw system.
From this, we can write the angle between vectors as $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\left| \vec{a}\times \vec{b} \right|}{\left| {\vec{a}} \right|\left| {\vec{b}} \right|}$.
If vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] are non-zero and \[\vec{a}\times \vec{b}=0\], then it is the condition for them to be parallel vectors.
\[\widehat{\text{i}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{i}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{j}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{k}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{k}}\text{=0}\]
\[\widehat{\text{i}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{j}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{k}}\text{,}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{k}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{,}\widehat{\text{k}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\widehat{\text{i}}\text{=}\widehat{\text{j}}\]
If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=}{{\text{a}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}{{\text{b}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] then
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\left| \begin{matrix} \widehat{\text{i}} & \widehat{\text{j}} & \widehat{\text{k}} \\ {{\text{a}}_{\text{1}}} & {{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}} & \text{a} \\ {{\text{b}}_{\text{1}}} & {{\text{b}}_{\text{2}}} & \text{b} \\ \end{matrix} \right|\].
Geometrically, we can define \[\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|\text{=}\] area of the parallelogram whose two adjacent sides are represented by \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\].
Properties of Vector Product
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\ne \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] (Not Commutative)
\[\left( \text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right)\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{m}\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\text{=m}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\] (Associative) where \[\text{m}\] is scalar.
\[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)\text{=}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\text{+}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)\] (Distributive)
Unit vector perpendicular to the plane of \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] is \[\widehat{\text{n}}\text{= }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|}\]
A vector of magnitude \[\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }\] and perpendicular to the plane of \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\] is \[\text{ }\!\!\pm\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{r}\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)}{\left| \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right|}\]
If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] are the position vectors of vertices \[\text{A,B and C}\] of a triangle, then the vector area of triangle is given by \[\text{ABC=}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}+\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}+\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right]\] The points \[\text{A,B and C}\] are collinear if \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{+}\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=0}\].
Area of quadrilateral whose diagonal vectors are \[\overrightarrow{{{\text{d}}_{1}}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{{{\text{d}}_{2}}}\] is given by \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{{{\text{d}}_{1}}}\times \overrightarrow{{{\text{d}}_{2}}} \right|\].
Scalar Triple Product
The scalar triple product of three vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] is defined as \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}.\left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\times \overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)\] and can be represented as \[\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right]\]. It is also referred to as box product.
Geometrically, it represents the volume of the parallelepiped whose three coterminous edges are represented by \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{,}\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] . So \[\text{V=}\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right]\].
Scalar triple product is cyclic, i.e. the order of vectors can be interchanged in a cyclic manner as shown below, \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\times \overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)=\left( \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\times \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\cdot \overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] or \[\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right]=\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \right]=\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right]\] \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \left( \overrightarrow{\text{b}}\times \overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right)=\text{-}\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\cdot \left( \overrightarrow{\text{c}}\times \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right)\] or \[\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right]=\text{-}\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}} \right]\]
If \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{=}{{\text{a}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\]; \[\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{=}{{\text{b}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{b}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] and \[\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\text{=}{{\text{c}}_{\text{1}}}\widehat{\text{i}}\text{+}{{\text{c}}_{\text{2}}}\widehat{\text{j}}\text{+}{{\text{c}}_{\text{3}}}\widehat{\text{k}}\] then $\overrightarrow{\text{a}} \times \overrightarrow{\text{b}} \times \overrightarrow{\text{c}}$ $= \left|\begin{array}{ccc} a_{1} & a_{2} & a \\ b_{1} & b_{2} & b \\ c_{1} & c_{2} & c \end{array}\right|$
Scalar product of three vectors, two of which are equal or parallel is \[\text{0}\].
Vectors \[\overrightarrow{\text{a}},\overrightarrow{\text{b}},\overrightarrow{\text{c}}\] are coplanar if \[\left[ \overrightarrow{\text{a}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{b}}\text{ }\overrightarrow{\text{c}} \right]\text{=0}\].
Vector Algebra Revision notes Class 12 Chapter 10
Download revision notes class 12 maths chapter 10 pdf.
Revision Notes Class 12 Chapter 10 Vector algebra is designed and prepared by the best teachers at Vedantu. All the important concepts are covered with a detailed explanation to help students understand concepts better. These revision notes will play a crucial role in your preparation for all exams conducted by the CBSE, including the JEE.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 9 Vector Algebra notes are prepared by subject expert teachers at Vedantu keeping in mind the latest syllabus and guidelines issued by the CBSE board. You can download Vector Algebra Class 12 Notes Maths Chapter 10 free pdf through the link provided below.
Benefits of Class 12 Notes Maths Vector Algebra
Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Revision Notes provides brief information along with the relevant formulas of all the topics covered in Chapter 10. This enables students to quickly and easily revise the important topics of the chapter before the exams.
Vedantu revision notes Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 can be easily downloaded in a PDF format free of cost.
Class 12 Revision Notes Maths Chapter 10 pdf will be very helpful for the students for the last-minute revision of the chapter.
Revision Notes Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 PDF covers the following topics with important definitions and formulas.
What are Vectors?
A vector quantity is represented by an arrow. This arrow is called the ‘vector’. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude and the head of the arrow represents direction.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
There are ten different types of vectors frequently used in maths. The 10 types of vectors are:
Zero vector
Unit Vector
Co-initial Vector
Like and Unlike Vectors
Coplanar Vector
Collinear Vector
Equal Vector
Displacement Vector
Negative of a vector.
Let us understand each type of Vector Algebra in brief.
Zero Vector or Null Vector
A vector having the magnitude zero and the starting point and the endpoint of the vector is the same as a zero Vector. The zero vector doesn’t have any specific direction.
A vector is a unit vector when the magnitude of the vector is 1 unit in length. Suppose if a is a vector having a magnitude a then the unit vector is denoted by a ^ in the direction of the vector and it has the magnitude equal to 1.
Any point X has taken in the plane simply denotes the position is said to be a position vector. Let us consider O is taken as reference origin and A is an arbitrary point in the plane then the vector is called the position vector of the point.
Co-initial Vectors
A vector is co-initial vectors when two or more vectors share the same starting point. For example, Vectors PQ and PR are called co-initial vectors because they have the same starting point P.
The vectors with the same directions are said to be like vectors whereas vectors with opposite directions are said to be unlike vectors.
Coplanar Vectors
When three vectors lie in the same plane, they are known as coplanar vectors.
Collinear Vectors
Vectors which lie in the same line with respect to their magnitude and direction are known to be collinear vectors.
Equal Vectors
Two vectors having both direction and magnitude equal are said to be equal vectors even if they have different initial points.
If a point is displaced from the position A to B then AB represents a displacement vector.
Two Vectors with the same magnitude but having opposite directions are said to be negative vectors of each other.
Consider two vectors x and y, such that they have the same magnitude but opposite in direction then these vectors can be written as:
Other Chapters Revision Notes
Find here CBSE Class 12 Maths revision notes for other chapters:
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 2 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 9 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 11 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Revision Notes
Other Related Links
CBSE Class 12 Maths Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 NCERT Maths Books PDF
CBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions
CBSE Class 12 Maths Important Formulas
Vector Algebra
Types of Vector
Multiplication of Vector with Scalar
Dot Product of Two Vectors

FAQs on Vector Class 12 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 10 [Free PDF Download]
1. Provide Some Mathematical Tips on How to Practice and Prepare for CBSE Class 12 Vector Algebra.
Any process that aims to attain knowledge needs initiation by students themself, and not by a teacher or textbook. Keeping this view in mind, Vedantu has highlighted some motivational tips to help students go deep in their learning process; these are:
Get a holistic view.
Imagine and wonder.
Understand the concepts.
Practice and practice.
If you find it tough, then someone else would too.
Dig deeper in passion.
2. Mention Some of the Best Study Techniques Listed Out by the Vedantu Experts for Students Appearing in Class 12 Maths.
Some of the best study tips for students appearing in Class 12 exams are:
Eliminate distractions by silencing your mobile, or other background noise like TV, radio, etc.
Get enough sleep before you take hours of study.
Switch your environment as a change in the scenario will improve both your concentration level and memory.
Stick with an environment that works.
Listen to calm music as it can help to pay attention to the task.
Snack on smart food.
3. Should I practice all the Questions in Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th?
Maths is a subject learned better through practice. The number of formulas in chapter 10 of Class 12th Mathematics makes it a little complex for the students. Hence, it is better to practice by solving all the questions given in the book to learn the formulae and their application. It is also a great method to learn the formulas because the regular practice would help you store them in your long-term memory.
4. How will revision notes for Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th help for boards?
Revision Notes for Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th contain brief information as well as essential formulas for all of the subjects discussed in the chapter. This allows students to swiftly and simply review the key fundamentals in the chapter before the examinations. Time is a luxury during the examinations so it is better to focus your energy on revising the precisely created notes than flick through all the chapters intensively.
5. What are vectors according to Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th?
Vector quantity is a physical quantity with magnitude and direction. It denotes the movement of an object from one point to another. It is represented by an arrow. The magnitude is represented by the length of the arrow, and the direction is shown by the head of the arrow. It is an easy and scoring chapter for the students. If well prepared the students can gain full marks in the questions from this particular chapter.
6. What are like and unlike vectors according to Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th?
Like and Unlike vectors are two categories of vectors. In like vectors the direction is the same whereas unlike vectors are where the direction (with respect to each other) is different. There are other types of vectors too as explained in Revision Notes for Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th: Vector Algebra. The students get knowledge about all these types of vectors and solve questions based on that knowledge. The notes and solutions provided by Vedantu are free of cost. They Are also available on Vedantu Mobile app.
7. What is the negative of a vector according to Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th?
Two vectors are recognized as negatives of each other when their magnitude is the same but they have opposite directions. It is important to take note of the magnitude and the direction of a vector to distinguish between various types of vectors. The arrow usually depicts the direction of a vector. The students can gain more insight into the chapter using Revision Notes for Chapter 10 of Maths of Class 12th that are available on Vedantu.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The case study on Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Vector Algebra case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
In this article, we are sharing Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra case study questions. All case study questions of class 12 maths are solved so that students can check their solutions after attempting questions.
CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Vector Algebra Case Study Questions 2021. By QB365 on 21 May, 2021. QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions .
CBSE 12th Standard Maths Vector Algebra Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 12th Standard CBSE. Maths. Time : 01:00:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 25. Case Study Questions. Teams A, B, C went for playing a tug of war game. Teams A, B, C have attached a rope to a metal ring and is trying to pull the ring into their own area (team areas shown below).
Learn Chapter 10 Class 12 Vector Algebra free with solutions of all NCERT Questions, Examples as well as Supplementary Questions from NCERT. Suppose we have to go 10km from Point A to Point B. This 10km is the distance travelled.
Class 12 Mathematics - Case Studies issued by CBSE on the Topic Vector AlgebraThis lecture discusses two case studies on the topic VECTOR ALGEBRA from the b...
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter Vector Algebra explains vector operations, addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, dot and cross products, and their applications. Vectors are quantities with both magnitude (size) and direction. Examples include displacement, force, and velocity.
9.64K subscribers. 31. 1K views 1 year ago Competency Based Questions (MCQs, Source Based Qs, Case Study Qs) : CBSE 2022 - XII Maths. Thanks for Watching this Video.. Pls SUBSCRIBE the...
Get chapter-wise important questions for CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra with answers on Vedantu. Download the PDF for free and revise these important questions for CBSE exam 2024-25.
In this chapter, students will learn what is a vector quantity and how it can be represented or calculated. To comprehend this chapter easily, students can refer to the Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths revision notes prepared by the highly experienced teachers at Vedantu.