Tips for Allocating Work Assignments

It’s probably a no-brainer that improper delegation of tasks has obvious consequences, such as increased frustration, stress and workload. The quality of work and team morale may suffer while trust, productivity, efficiency and profitability dwindles. In such a situation, the organizational structure fails, clients’ trust dies, reports of unaccountability emerge, staff may underperform and project failure becomes imminent. This is why it’s vital to ensure that work assignments are delegated efficiently and to the appropriate team member.
Approximately 94% of companies lack exceptionally good management. The 6% of firms with excellent management culture and style tend to be dedicated to their workforce and team building rather than external stakeholders.
Achieving excellence in organizational operations is an enormous challenge for most organizations and begins with the manner and style of delegation of assignments.
Management has to choose the right team , build trust and accountability , develop its team through delegation, manage performances, have tough conversations and acknowledge and reward excellence to enhance employee engagement and lower turnover.

What exactly are work assignments?
Work assignments are remarkable tools for enhancing employee growth and must be managed deliberately; otherwise, they could limit efforts towards building a diverse workforce.
Evidence shows that experimental learning accounts for 70% of leadership development , particularly, effective delegation of work assignments.
Work assignments are tasks that are deliberately designed for organizational purposes. They are allocated to staff to achieve results. In the simplest terms, these assignments are activities or projects for a specific end. Work assignments should come with a task description, deadline and expected results.

Work assignments tips
Why delegate work assignments?
Employee empowerment.
Managers with great team building skills understand the importance of instilling trust in team members for enhanced morale and performance because they believe they are wired to drive organizational objectives.
Strengthens trust
Assigning work means trusting the employee’s ability to achieve a particular result through task performance. Frequent delegation builds the trust needed to create collaborative skills within organizations.
Helps lower workload
Successful delegation of work assignments lessens the burden of tasks that pile up. It saves the time needed to focus on other important organizational tasks and goals.
Planning for fair distribution of work assignments
Most industries, such as hospitality, telecommunications and healthcare need to ensure uninterrupted service delivery. At the same time, they must consider the health of their employees, who need regular breaks and leave to stay productive and rested.
With the rise of flexi-workers , ensuring everyone gets a fair share of leave could become a logistics nightmare for business owners. This also applies to contractual staff who may feel overburdened.
When planning and distributing work assignments, managers must take into account employees’ vacation days, sick leave, emergency absences and so on. Things to consider include, but are not limited to:
- Employees should have their preferences fulfilled to avoid bias.
- Organizations should try to accommodate employees’ requests for rest days as much as possible.
- The duty roster should be planned in such a way as to allow enough time for deadlines and urgent tasks.
- There is also an allowance for fair leave/day swapping among employees.
The manager planning the duty roster should keep track of requests and demands in real time. This enables the planner to synchronize replacement leave and overtime pay calculations at the end of the roster period.
Delegating work assignments to employees
Create an effective work plan.
An effective work plan is the key to the success of every project. Approximately 58% of organisations don’t understand the value of project management, which explains why most projects fail as soon as they begin.
The planning phase determines either the failure or success of such project. Organizations must have a solid work plan, including a weekly action plan for greater efficiency and productivity. You can create a good work plan by following the steps below.
- Set specific goals that include actual numbers and quantifiable terms and scope.
- Lay out the objectives and deliverables, including the project schedule. Consider rewarding your team based on achievement. The incentives will boost productivity.
- Brainstorm and detail the key resources that your team needs. Brainstorming and planning will help colleagues become creative, forecast unforeseen obstacles and promote teamwork. Converse with your them about the resources that can help them achieve set objectives and give them available resources.
- Identify task sequencing . The schedule of a project outlines activity sequencing, tracks performance and calculates the duration of tasks sequences.
Delegate assignments based on aptitude
By assigning work to employees based on their areas of strength and skills, you set them up to excel. This means you need to understand your employees’ strengths, preferences and weaknesses. You may also allow your staff to choose their preferred tasks. This is important for building trust.
Give your team prior notice
No need to stress everyone out and kill their morale with endless impromptu and urgent work assignments. As far as is feasible, try to give your employees a couple of days’ notice at least.
Foster project ownership
Encourage your team to ask questions for clarity. Determine your availability and take the time to give them clear instructions, feedback and assistance. Giving them a sense of ownership allows your team members to see the big picture.
Real delegation is when you encourage your team to own the project. This gives them the authority to take initiative for the execution process.
Most companies spend hours and weeks planning and generating roasters manually when they can use TimeTrack Duty Roster to save time. TimeTrack Duty Roster creates a perfect overview of both employers and employees and allow managers to personalize shifts according to preferences.
TimeTrack Duty Roster
Monitoring work assignments
Monitoring work assignments helps your team complete their duties successfully and meet the desired outcomes. There’s no need to micromanage, but you can certainly help keep employees focused while tracking processes.
Ensure an effective project plan
- Compile a clear project outline, including a schedule. Collaborate with your team to create the plan and include the project scope, tasks, deadlines and resources. Creating a timeline is vital; use a flow chart to make things clearer. A clear work plan helps you understand the key performance indicators you can monitor.
Set SMART goals
- One of the key ways to monitor assigned work is to create specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound goals. This SMART criteria helps you identify detailed and quantifiable goals with effective deadlines. You then have quantifiable items to monitor the performance of the assignments.
Steady check-ins
- Creating a schedule for progress check-ins is a key step in monitoring assignments. The regularity of the check-in depends on the project. For example, check-ins for long-term and short-term projects differ in intervals. Check-ins should be balanced to support effective monitoring of performance indicators.
Records and analysis of data
- For each of the scheduled check-ins, keep records and analyze data to understand the progress of projects. You can gather data through team meetings and input into spreadsheets or project management tools. The data will then be analyzed to determine the status of the assigned work.
Every organization wants to empower its workforce for enhanced morale, focus, accountability, efficiency and productivity. These achievements are only possible with effective delegation of work assignments and tasks.

I am a researcher, writer, and self-published author. Over the last 9 years, I have dedicated my time to delivering unique content to startups and non-governmental organizations and have covered several topics, including wellness, technology, and entrepreneurship. I am now passionate about how time efficiency affects productivity, business performance, and profitability.
Time Tracking
- Absence Management Software
- Clock In System
- Time Attendance System
- Auto Scheduling
- Duty Roster
- Shift Planning
- Appointment Planning
- Task Planning
- Info Center
- Timesheet Templates
- Rota Templates
- Promotional Program
- Affiliate Program
- Success Stories

What Every Job Seeker Should Know About Work Assignments During the Interview Process

You’re progressing well through an interview process, and you think you’re close to landing that coveted offer, when the employer says, “One more thing—we have a little homework for you.”
This tactic is used by a lot of companies (especially startups), and with good reason: The hiring manager gets a firsthand look at your approach, creativity, quality, turn-around speed, and communication and presentation style and can gauge how serious you are about the position.
If you really want that job, your instinct will likely be to put your best foot forward and provide the most fabulous project the employer has ever seen. But there’s something else to consider: You may end up putting in many hours of work, creating an awesome deliverable—and at the end of it all, still not getting the job. There’s even a chance that the company will take the ideas you labored over for its own benefit, and you’re left not only without an offer, but without compensation for all that hard work.
It’s happened to me: Once, at the end of a second round interview, a hiring manager asked me for a list of quick-hit ideas on increasing user engagement for his consumer website. I spent almost half a day coming up with a list of 10 great ideas, including many examples from other sites. After I proudly sent over my recommendations, I didn’t hear from the company for over two weeks. When I finally got a response, he thanked me for all my hard work and said that the company decided not to pursue the position at this time due to “internal matters.”
Who knows if this really was the case; but to my surprise, I noticed a handful of my ideas were actually implemented within the next few months on their site. Maybe these were ideas already in motion and my assignment only confirmed what was planned, but I couldn’t help but feel that I had been somewhat “used” and regretted putting so much time and effort into this homework.
While there are times you may want to go to the moon and back for a job , it’s also important to be careful how you approach these homework assignments—especially if you’re investing your time into applying to multiple jobs. Here are some tips on how to handle this tricky situation.
1. Understand General Goals and Expectations
First, it’s important to get a sense of how this assignment will factor into the overall evaluation of your candidacy. Is this the final hurdle before the job offer? (It should be.) How will this be weighed with other elements of your interview? (You should get some positive reinforcement that the company’s very interested and just wants to get a sense of how you work.) How long will the assignment take? (Being asked to spend more than 2-3 hours on an assignment before getting hired is bordering on disrespect.)
Don’t be afraid to ask questions like, “Can you help me understand how this assignment will be evaluated?” “Are you looking more for big-picture ideas, or a detailed look at my recommendations?” “Roughly how much time do you recommend I put into this assignment?” It’ll help you understand what the company is looking for and how much time you’re willing to put forth.
2. Ask for Data
Next, remember that you have every right to ask for information that’ll help you better tackle the assignment and not start from scratch (if you were hired, that’s what you’d obviously do , right?). So, put some onus on the company to provide relevant data. For example, if the company is asking for your ideas on potential partners, ask questions that’ll point you in the right direction, like, “Who are your current partners?” “What types of partners are you currently pursuing?” “What are the key metrics that define a successful partnership?”
And if the company doesn’t provide any more information? Do your best, but also make sure you express where you’ve made assumptions based on lack of information—e.g., “Without knowing what your current metrics for successful partnerships are, I’ve made suggestions for partners that will boost both brand awareness and website traffic. Obviously, if the company has different goals, I would be able to adjust these recommendations.”
And then don’t worry—if the hiring manager doesn’t offer it, he or she will understand that you’re operating under lack of information and history.
3. Outline Main Points, Only Tease the Details
More often than not, the primary reason companies dole out homework is to get a better sense of your thought process, as well as how you structure and convey your thoughts and ideas. There’s not necessarily a “right” answer, nor is there a need to get way down in the weeds.
So, don’t stress about providing a ton of information—just outline the main points (bullets and numbered lists usually work well). You can tease out more details as you’re talking through your assignment in the interview without having to write down your specific plans and fully fleshed out ideas. Remember: You don’t want the hiring manager to have the blueprints for your fabulous ideas—you want him or her to hire you so that you can be the one implement them!
4. If You’re Worried, Get an NDA in Place
Depending on the type of job function and level you’re interviewing for, it may not be a bad idea to request a non-disclosure agreement. If there is any confidential information you do not want shared widely, your assignment involves using data from your current employer, or you just have a nagging concern that the company may steal your best ideas, take a precaution and get a simple mutual NDA executed (many template NDA forms are available online for download). Don’t make it too legally formal—the company may get turned off by this move—just let the hiring manager know you just want to make sure things stay confidential and you’d be more comfortable providing details with a simple NDA in place. If he or she refuses to sign, this may be another warning flag.
Knocking a homework assignment out of the park can be an amazing chance to show you’re the best candidate of the bunch, but you never want to get in a situation where you’re wasting your time or being used for free labor. Follow these guidelines, and you’ll be able to present a great deliverable while making sure you’re spending your time and effort the right way.
Photo of man working courtesy of Shutterstock .
Assignment vs. Delegation
What's the difference.
Assignment and delegation are two different ways of distributing tasks and responsibilities within a group or organization. Assignment refers to the act of allocating specific tasks or projects to individuals or teams based on their skills, expertise, or availability. It involves providing clear instructions and expectations to the assigned person, who then becomes solely responsible for completing the task. On the other hand, delegation involves entrusting someone with the authority to make decisions and take actions on behalf of the delegator. It involves not only assigning tasks but also granting the necessary power and autonomy to the delegatee to accomplish the assigned tasks. While assignment focuses on task distribution, delegation emphasizes the transfer of authority and decision-making power.
| Attribute | Assignment | Delegation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assigning a task or responsibility to someone | Transferring authority and responsibility to another person |
| Control | The assignor retains control over the task | The delegator transfers control to the delegate |
| Authority | The assignor has the authority to assign the task | The delegator has the authority to delegate the task |
| Responsibility | The assignor remains responsible for the task | The delegator transfers responsibility to the delegate |
| Decision-making | The assignor makes decisions related to the task | The delegate makes decisions related to the task |
| Accountability | The assignor is accountable for the task | The delegate is accountable for the task |
| Level of involvement | The assignor may be less involved in the task | The delegator may be less involved in the task |
Further Detail
Introduction.
When it comes to managing tasks and responsibilities, two common approaches are assignment and delegation. Both methods involve distributing work among individuals or teams, but they differ in terms of authority, control, and accountability. In this article, we will explore the attributes of assignment and delegation, highlighting their key differences and benefits.
Assignment refers to the act of allocating specific tasks or projects to individuals or teams. It involves providing clear instructions, setting deadlines, and defining the expected outcomes. Assignments are typically made by a person in a position of authority, such as a manager or supervisor, who has the power to distribute work among subordinates.
One of the key attributes of assignment is the level of control it offers to the assignor. By assigning tasks, the assignor retains a significant degree of authority over the process and outcome. They have the power to dictate how the work should be done, provide guidance, and make decisions along the way. This level of control can be beneficial in situations where strict adherence to guidelines or standards is crucial.
Another attribute of assignment is the clear accountability it establishes. When tasks are assigned, the assignee becomes responsible for completing them within the given timeframe and meeting the specified requirements. This accountability ensures that individuals are held responsible for their work and can be evaluated based on their performance.
Furthermore, assignment allows for a structured approach to task distribution. The assignor can carefully assess the skills, capabilities, and workload of each individual or team before making assignments. This enables a more efficient allocation of resources and ensures that tasks are assigned to the most suitable individuals or teams.
However, assignment also has its limitations. The assignor may become overwhelmed with the responsibility of distributing tasks and overseeing their progress. This can lead to micromanagement and a lack of autonomy for the assignees. Additionally, if the assignor is unavailable or lacks the necessary expertise, it may result in suboptimal task allocation.
Delegation, on the other hand, involves entrusting a task or responsibility to another person or team while retaining overall accountability. It is a process that empowers individuals or teams to make decisions, take ownership, and exercise their judgment in completing the delegated tasks.
One of the key attributes of delegation is the level of autonomy it provides to the delegatee. Unlike assignment, delegation allows individuals or teams to have more control over the process and decision-making. They are given the authority to determine how the task should be accomplished, which can foster creativity, innovation, and a sense of ownership.
Another attribute of delegation is the opportunity for skill development and growth. By delegating tasks, the delegator can empower individuals or teams to take on new challenges, learn new skills, and expand their capabilities. This not only benefits the delegatee but also helps in building a more versatile and resilient workforce.
Furthermore, delegation can enhance collaboration and teamwork. When tasks are delegated, it encourages individuals or teams to work together, share knowledge, and support each other in achieving the common goal. This collaborative approach can lead to improved communication, increased efficiency, and a stronger sense of camaraderie.
However, delegation also comes with its own set of challenges. The delegator needs to carefully select the right individuals or teams to delegate tasks to, considering their skills, experience, and availability. Inadequate delegation can result in tasks being mishandled or not completed to the desired standard. Additionally, the delegator needs to strike a balance between providing guidance and support while allowing the delegatee to exercise their autonomy.
Now that we have explored the attributes of assignment and delegation, let's compare them to understand their differences more clearly.
Authority and Control
Assignment provides a higher level of authority and control to the assignor. They have the power to dictate how the work should be done and make decisions along the way. In contrast, delegation empowers the delegatee with more autonomy and decision-making authority, allowing them to determine the best approach to completing the task.
Accountability
Both assignment and delegation establish accountability, but in different ways. In assignment, the assignee is directly responsible for completing the task within the given timeframe and meeting the specified requirements. In delegation, while the delegatee is responsible for the task's execution, the delegator retains overall accountability for the outcome.
Task Allocation
Assignment follows a structured approach to task distribution, where the assignor assesses the skills and workload of individuals or teams before making assignments. Delegation, on the other hand, requires the delegator to carefully select the right individuals or teams based on their skills, experience, and availability.
Level of Autonomy
Assignment limits the autonomy of the assignee, as they are expected to follow the instructions and guidelines provided by the assignor. In contrast, delegation grants a higher level of autonomy to the delegatee, allowing them to exercise their judgment, make decisions, and determine the best course of action.
Development and Growth
While assignment focuses on task completion, delegation provides an opportunity for skill development and growth. By delegating tasks, the delegator empowers individuals or teams to take on new challenges, learn new skills, and expand their capabilities.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Assignment primarily focuses on individual tasks, whereas delegation encourages collaboration and teamwork. Delegated tasks often require individuals or teams to work together, share knowledge, and support each other in achieving the common goal.
Assignment and delegation are two distinct approaches to task distribution, each with its own attributes and benefits. Assignment provides control, clear accountability, and a structured approach to task allocation. On the other hand, delegation empowers individuals or teams with autonomy, fosters skill development, and enhances collaboration. The choice between assignment and delegation depends on the nature of the task, the level of control desired, and the development opportunities sought. By understanding the attributes of assignment and delegation, managers and leaders can make informed decisions to optimize task distribution and achieve organizational goals.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
How to Give Assignments to Team Members
Table of Contents
The project has been divided into milestones, goals and objectives broken into tasks, and now it’s time to assign them. But as you open the project management platform, you’re faced with the unflattering process of wording the tasks, and choosing whom to assign them to.
Well, in this article, we offer advice on how to make that jumbled first moment a little clearer. There are actionable tips, learning the difference between allocating and delegating tasks, and suggested criteria on how to choose the best person for the job.
For a more precise overview, here’s a table of contents:
How do you assign employees tasks?
We normally think that assigning tasks is a time-consuming process that focuses on clearing out task lists to keep the project going. However, task assignment should actually be a more employee-oriented process that requires additional dedication and effort, which yields incredible results. But what do we mean by that?
Properly assigned tasks push your employees, projects, and the overall company forward. Here’s how.
- They strengthen accountability and trust between managers and employees;
- They help teach new skills and perfect old ones;
- They allow employees to get familiar with other teams and avenues of work;
- It becomes easier to make project estimates;
- Makes for great bases for performance reviews, etc.
The list could go on, but we’ll stop there for now.
Of course, such long-term benefits don’t come without some proverbial blood and sweat in the planning stage. Let’s take a look at the general ideas on assigning employee tasks, and specific steps you can take.
Motivation comes from knowing the bigger picture
When we talk about the bigger picture in project management, we talk about each team member’s task affecting their peer’s down the line. Since all tasks are usually small pieces of the puzzle, it helps to remind employees how their work contributes. For example:
- A high-quality draft can make a great foundation for the final version, and it can be completed more quickly.
- A well-prepared presentation can shave time off unnecessary questions and additional email inquiries.
It comes as no surprise that people work better and are more productive, when they know that their work has an impact on the company level.
And so, when you assign tasks, try to emphasize how they fit in the bigger picture. Simply saying: “ You doing X will help with Y and Z ” and how it reflects on the project as a whole will let an employee know that the task they were assigned is important.
Get your employees excited to commit
Telling people about the bigger picture and showing them what’s possible can only get them so far. It’s enough to ignite the initial spark, but for them to fully commit to the task, you need to define what that task entails.
They should be able to picture how to go about the work, what skills to use, and how to reach the desired result. The clearer the instructions, the more motivated they will be to work.
Simply put, give directions on how the task should be done, and make sure they understand. You can’t read each other’s minds, so it’s important everyone is on the same page.
Ask for task transparency
One of the best practices a company can employ is transparency among coworkers.
This is achieved by having everyone input their tasks for the day in a timesheet. The purpose of timesheets is to get an accurate idea of what everyone is working on at any given time.
When people know who works on what tasks, it’s easier for them to know if a person is available or busy, how far along they are with a task, etc.
So, when you give assignments to employees, label them with deadlines. Alternatively, you can ask for employees’ assessments on how long the work would take them, and use those timeframes.
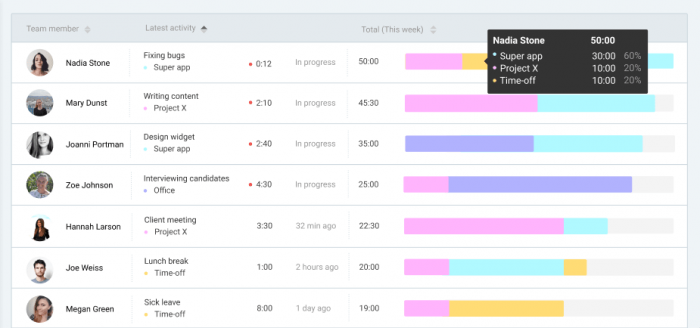
Source: Clockify team timesheet
Timesheets are a great way to keep an eye on tasks and the people doing them. You get to:
- see who struggles with what (helps assess people’s skill sets);
- who burns through their workload and is available for additional tasks;
- whether your time estimates need correction;
- identify any wasted time.
💡 If your employees are insecure about keeping public records of their tasks, here are a few resources that can help:
- How to create order in your daily work tasks
- How to be more efficient with your tasks
Keep a crystal clear timeframe
While we’re discussing timesheets and deadline transparency, it’s important to mention that the times you set for task completions need to be clear-cut.
As we’ve mentioned, the safest way to assign deadlines is to consult the employees. They are better at assessing how long it will take them due to the tasks’ difficulty, overall deadlines, the standards that need to be met, and the skill required to complete it.
When they get a say in how long they should be doing an assignment, people tend to feel more accountable for the whole process. They will do their best to finish in time, since they actively participated in setting the deadline.
Set very clear expectations
Assigning a task should always include your (the supervisor’s) expectations pointed out. For example:
- Does a logo pitch need as many drafts as possible, or just a few finished pieces?
If you ask a designer to make some drafts for a logo pitch, you must specify the kind of quality you’re looking for. Explain whether you are looking for some sketches and drafts for a brainstorming meeting, or if you want clean, presentable pieces to show.
Additionally:
- How many pieces should the designer do?
- Is there a specific color palette they need to follow?
- How important is the task? Is this the day they finally decide on a logo, or is it still in the brainstorming stage? (decides on the quality of the work itself)
Assigning the task using the above questions, you help the designer understand how much effort precisely they need to invest. They become more motivated with clear instructions, as they know what is expected of them. There’s no fear of having their work criticized for something that wasn’t communicated in the beginning. And on your end, it prevents breached deadlines or subpar results.
Avoid creating dependency by being less involved
It’s not unusual for employees to ask their supervisors for their opinion on a certain task, or their performance.
The problem arises when a supervisor makes themselves too involved with the process. When they feel like the project might fall apart if they don’t have their eyes on every moving part all of the time. And when you have, say, 20 people waiting for that person’s approval, advice, or consultation, the workflow runs into a gridlock.
And wait time is wasted time.
Plus, people lose motivation, patience, and grow frustrated, as they could be doing other things.
So, learn not to jump in every time people call for your aid. Assign reliable people who can address smaller issues, while you handle the big picture. Learn how to expend your own energy where it is needed more.
For example – making a pitch presentation for potential investors keeps getting put off because one person needs you to check a client email they want to send, another wants your signature on a form, and the third wants to ask something about employee feedback that’s coming up.
In order to not be stretched thin, and have your time wasted on menial tasks, here’s where you can start:
How to mitigate the risk of being over-involved when assigning
- Remember that you match tasks to people
Which means that, by matching the right people with the right tasks, your involvement will be minimal. Take time to carefully choose who gets to do what. What is the point of assigning tasks if they can’t be done without you?
- Have a 10-point scale to judge the importance of items
How important are certain aspects of your leadership role? Are you absolutely necessary in every meeting, or during every call? Which tasks need your approval, and which ones can be approved by someone under you?
Rank these items on a scale of 0 to 10, based on their importance to you and the project. Top priority tasks should get your undivided attention. And what can be delegated, should be.
- Analyze your schedule
Your energy and time are needed on a much broader scale. The best way to spot if you’re wasting time being too involved is to look at your schedule. Identify how much time you’ve spent on low-priority items, and assess which issues could’ve been solved without you.
- Take into account priorities and deadlines
Step in only when absolutely necessary. You are in charge of things getting done on time, by people most qualified for assigned tasks. Determine what your priorities are for each project, and concern yourself only with those issues, unless there is a risk of breaching a deadline.
- Formulate a list of dependable people
If you know your employees (or team members) well enough, then you should be able to single out those who are more dependable and ready to take on a little more responsibilities. Write out the reasons how they could help by getting involved on low-priority items instead of you. When the time comes, rally them and present them with the idea, keeping in mind that this solution helps push the project forward. When authority is delegated to several people, there’s fewer chances of a hold-up in the workflow.
This also falls into the realm of task delegation , which we’ll get into later.
How do you decide what tasks to assign to which employees?
1. assign based on priority.
Naturally, some tasks will be more important than others. When you break down a project into tasks , spend some time assessing their priority level.
High-priority tasks should be the first on your list to allocate. Whether it’s because they’re time-sensitive, or require more effort and dedication.
Low priority tasks can be allocated as fillers to the first available person.
2. Assign based on employee availability
Another factor to consider when assigning tasks is who is available at the moment.
As the project moves along, new tasks will be added. You will have to allocate new work, but odds are you won’t always be able to pick who you want. Especially if a deadline is approaching, the person with the smallest workload should be your first choice.
Overloading an already busy individual just because they’re more skilled or you have faith in them the most puts an unnecessary strain on them. It’s cause for frustration, poorer results, and decreased productivity.
And as we’ve mentioned, if you have a timesheet with an overview of all the tasks and employees working on them, it’ll be much easier to spot who is free and who isn’t.
3. Assign based on employee skill level
High-priority tasks should go to employees with more experience in a given field or skill. However, you should occasionally give such tasks to other employees as well, to help them grow and become just as dependable. Giving people challenging tasks that can boost their experience is essential to productivity and morale.
Not to mention you get to have multiple high-skilled employees.
Low-priority tasks can be assigned to anyone, despite their experience level. They’re a good opportunity to practice, pick up new skills, or get smaller tasks out of the way to make room for more important ones.
4. Assign based on preference
Last, but not the least, preference can also play a big part in how you assign tasks.
It’s a given that some employees will prefer certain tasks over others. So it could be good to assign tasks at a meeting with the team. As you discuss priorities, deadlines, and availability, ask them which tasks they would like to work on.
If someone shows interest in a specific type of work, they should (with some consideration), be allowed to take it. After all, people are more productive when they’re assigned to something they find new or exciting.
Note: Apply this rule with caution. Letting people do only the tasks they want can stunt their career growth. Getting out of our comfort zones and occasionally doing tasks that we don’t like is how we develop and learn. So, don’t forget to document assignments as you hand them out, to spot these potential issues early on.
Allocating vs delegating tasks
While semantically similar words, delegation and allocation in terms of tasks are two different things.
When you allocate tasks , you are assigning tasks without giving the employees much authority, challenge, or room to grow. It includes you keeping all of the responsibility – writing out the tasks, making deadlines, providing resources, tools, etc. These are usually recurring tasks that can become repetitive.
When you delegate tasks , you allow for some of that responsibility to fizzle out from your fingers. All you think about are the objectives, while letting the employees figure out the details and means to get there.
However, that doesn’t mean delegation is right and the allocation is wrong.
Task allocation has its own place. It is just as important, as a lot of tasks come down to repeated processes that are still vital to the project progress. Task delegation is just a good opportunity for employees to learn, challenge themselves, and assess their skills and performance.
When should you allocate tasks?
Management and BizDev consultant Artem Albul shared his concept on task assignment, which he dubbed an “algorithm”. He emphasized how these criteria are useful only and only when you wish that employees perform the tasks based on your guidelines and instructions (aka allocation).
Here is how Albul broke down the algorithm:
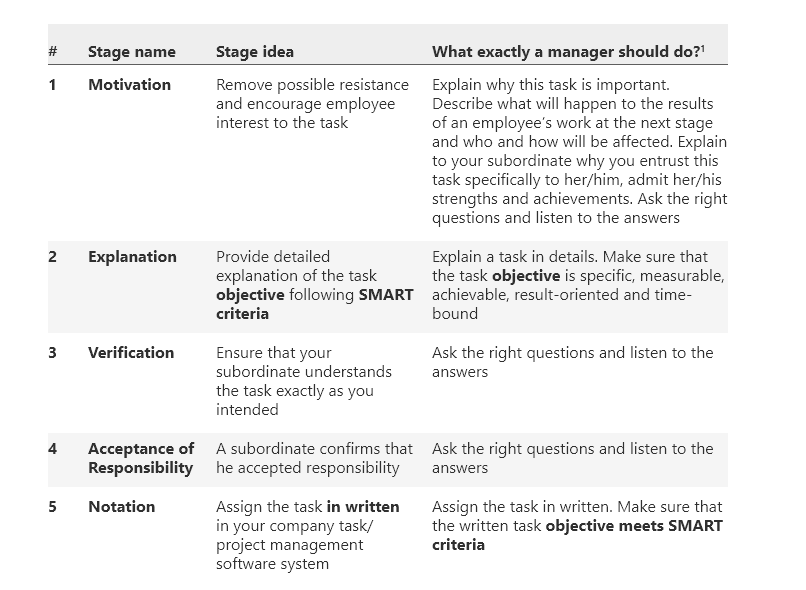
Source: Artem Albul, TWA Consulting
As we can see, task allocation, while the more “controlling” of the two, also gives in-depth instructions and asks for confirmation on task clarity. A lot of it comes down to everyone being on the same page, leaving little to no room for misinterpretation (but also creative freedom).
How should you allocate tasks?
With all that we’ve mentioned in the previous section, here’s how your task allotment could look like, step by step.
- Break down your project
Detail out the goals, objectives, and some individual tasks (not all, be careful not to start micromanaging). Place the most important deadlines.
- Prioritize tasks and sort them
It’s important to know what tasks need to be done faster/better, to properly allocate your resources and manpower from the start.
- Make a list of teams and team members
Assign team leaders (if you don’t have them), and alternatively, ask for their input on individual employees skills, for a more informed decision on who gets what.
- Schedule a meeting
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team’s availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward.
- As team leads – assign tasks further down the pipeline
- Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way
Whether it’s pushing deadlines, reassigning tasks, or shifting around resources. This is perfectly fine and expected, so long as it doesn’t happen on every task you’ve assigned. Then, it is an indicator of poor pre-planning.
- Offer feedback and write performances
Don’t forget to track the progress and make notes of important details that might help the next task allocation/delegation process. It’s also a useful piece of information for the employees on what they need to improve on.
Allocating tasks is somewhat more complicated than we want it to be. But, this kind of thorough research and preparation will make projects run more smoothly. Employees will also be more satisfied with their work, and there will be less hurdles as deadlines approach.
When should you delegate tasks?
Delegation is a great practice in trust for both the employer/supervisor and the employee. The employer learns how to give away some of their control over the process, while the employee learns how to take more accountability for their work.
This lets you focus on big-picture aspects of your job, since you deal less with assignments that are low-priority for you. You save time and energy, while helping others move up in their careers.
How do you effectively delegate tasks as a leader?
As we’ve mentioned, delegating includes more employee independence. There are some additional components which make this type of task assignment more appealing than allocation, with great opportunities for growth.
Focus on delegating objectives instead of actual tasks
When you delegate, you focus on the objective that needs to be done. You shouldn’t give employees a “color by numbers” instruction on how to complete a task.
Communicate clearly what the end result should be and what expectations you (or the higher-ups) have. Leave the means for reaching that end goal to the employees themselves. Because how you solve a task may be completely different to how they will. And that is perfectly fine, so long as the result is the one you are looking for.
Keep the objectives challenging
When the objectives you’re delegating are too easy, chances are the person will either procrastinate, or feel like you don’t trust them enough. And if they’re too difficult, they get frustrated, anxious, and begin to panic.
It’s a good idea to be aware of an employee’s skill level, so you can gauge how much challenge and responsibility they can take on. For them to be the most productive and achieve great results, they need to enter “the state of Flow”.
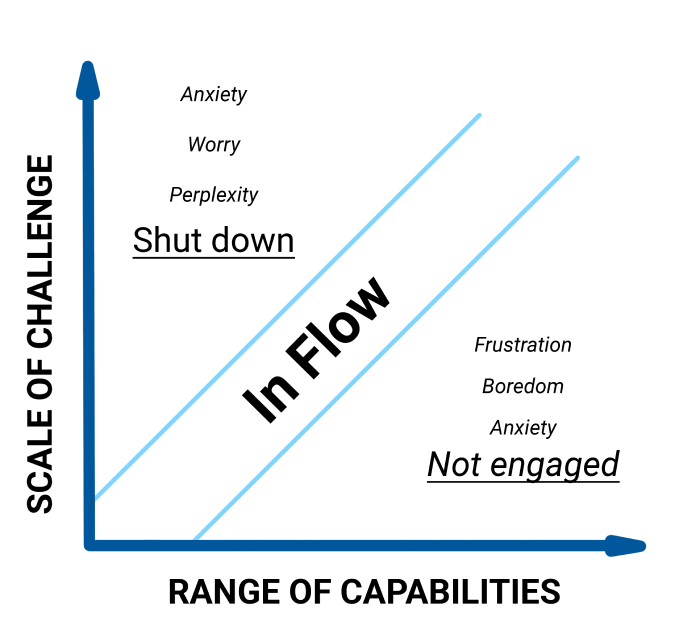
Source: Optimal Experience , M. Csikszentmihalyi
💡 We’ve discussed the state of Flow in more detail in an article on time organization.
Encourage discussion and feedback
Let employees voice their opinions on the topic.
They should ask anything about the task, the goals, or the overall impact their work will have on the later stages or others’ workflow. It means they are interested in the task, and getting involved.
And if they aren’t asking questions themselves, you can always nudge them into proactivity.
- Is there something you’d like me to clarify?
- Do you already have any ideas on how to go about the task?
- Is the time we agreed upon enough for you?
- Will you need other resources, tools, or support?
- Do you see any problems or risks?
Questions like these help them feel valued, their efforts acknowledged, and let them know you care about the task and how well they perform. Just be careful not to overdo it, or you’ll start to look like a micromanager.
Give employees free rein, but offer support
Speaking of micromanaging, delegation means you let people problem-solve their way out on their own. There should be no reason for a manager to step in and control or supervise any step of the process, unless absolutely necessary.
However, what you should do is let them know you’re available for any advice should they feel stuck. Just because employees get authority on a certain task, and are left to their own devices, doesn’t mean the project has to suffer until they pull themselves up.
From time to time, ask them if they need anything from you, and make sure they know you’re there for any kind of support, consultation, or mediation. ANother good practice is to also give them additional learning opportunities – such as training, conferences, courses, etc.
Delegate objectives that move people forward
Choose assignments that boost the skills and employ all of their experiences, instead of something that simply needs to be done. For example:
- Tasks that require they brush up on their team communication skills;
- Learning how to allocate smaller tasks;
- Supervising others’ work and doing quality control;
- Learning to work with a new tool;
- Holding a meeting (or more), etc.
Find out which skills your employees may want or need to develop, and then plan your delegations accordingly. You want them to complete the task while having learned something new at the same time.
How to choose who to delegate to
Paul Beesley, senior director and consultant at Beyond Theory proposed a nifty checklist for when you’re choosing an employee to delegate to. It’s meant to simplify and speed up the process.
To successfully complete the delegated task, your chosen employee needs:
S – the skill to perform and complete a task
T – the time to complete the task, and if needed, learn the required skill
A – the authority to handle everything concerning the task
R – the necessary level of responsibility
R – the recognition for successfully completing the task
This list is a set of important criteria that should be covered when you consider who to assign to a specific task. However, depending on your niche, type of service, company size and the project at hand, the criteria are likely to change. And it should accommodate your needs, not the other way around.
Common task delegation mistakes to avoid
With all being said, there are some common mistakes managers and employers make, sometimes without even realizing it.
- Being too vague concerning deadlines (using: as soon as possible, when you get to it, I need it by yesterday). It creates unnecessary pressure.
- Being unavailable for questions and concerns. While you shouldn’t micromanage, you should still be present for support if an employee feels stuck. Ignoring them or handing them over to someone else could cause distrust. However, if you are usually swamped with work, set consultation hours each day or week.
- Having unclear directions. Specifying the allotted time for task completion and expectations should be the bare minimum when delegating tasks.
- Not providing feedback. No feedback is worse than bad feedback. Employees need to be aware when they’re doing good work, as well. In one company I worked for, the mantra was: “If no one is complaining about your work, that means you’re doing good”. And while it sounds like sound logic, it actually caused a lot of frustration. We were left directionless, and simply “floating” from task to task, never knowing if any of them had a positive impact on our performance.
- Not listening to employees. Take into account how they feel about a task or the objective. Let them give you feedback and if there are potential problems from the get-go.
- Assigning other people to the same task. If you notice a person struggling, the first instinct should be to ask them how they’re faring, and if they need any help. Some managers tend to assign other employees to help them without consultation, which leaves a sore taste. The employee will feel even more incompetent and will be less likely to take on a similar task in the future.
- Assuming people will know what you mean. This is one of the biggest problems. When you’re formulating a task, be as clear as possible about the goals and expectations. Oftentimes managers think that these things are implied, but the truth is – no one is a mind reader. To avoid having information misconstrued or misunderstood, communicate clearly and directly.
There could be more mistakes, especially for every different field and industry. If at all possible, identify the most common ones, made either by you or your peers. Note down all the instances where certain tasks weren’t up to par, and see what you could have changed in your assignment process to fix it. Maybe there wasn’t enough time or resources, you were unclear, or the employee wasn’t ready for such responsibility. Use the same procedure in all future task delegations. It’s the only way to learn and make the process quicker.
Use Clockify to assign tasks with ease
Now you’re a master of task delegation — congrats!
But there’s more to it than meets the eye.
In fact, what if you used a digital tool like Clockify to increase the likelihood that each job would be completed on time and on point?
In Clockify, you can easily create highly descriptive assignments that contain information like:
- Start time,
- Billability status,
- Name of the employee,
- Period for getting the assignment done,
- Hours per day to spend on the assignment, and more.
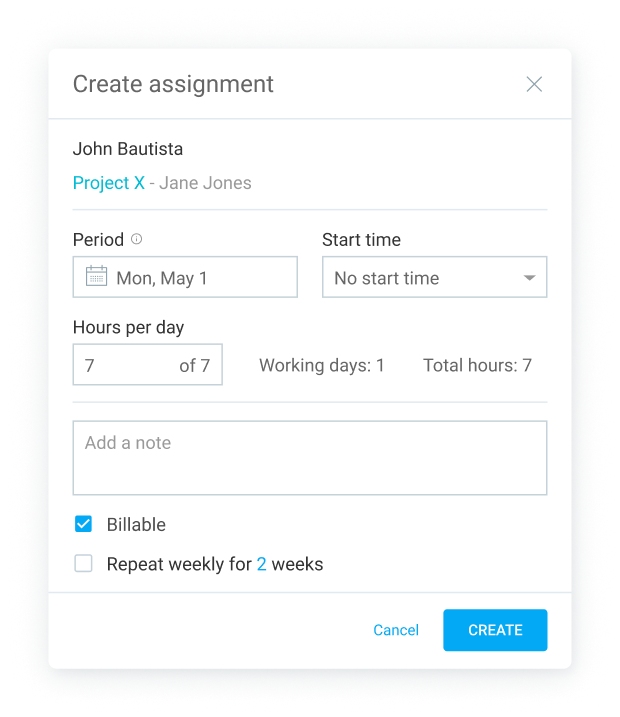
That way, you can plan who works on what, how long, and when.
Similarly, Clockify allows you to create project milestones to achieve results faster.
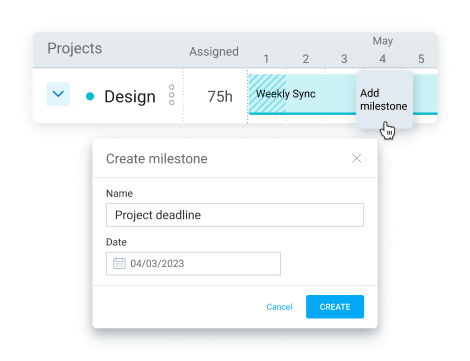
With the Milestones option, you can select dates for deadlines, allowing you to pin down important events in your projects.
For example, if your client expects you to keep them in the loop about developments, you can inform them promptly on whether your team has reached the agreed-upon milestones.
Refocus on your company’s big picture with a project and time tracking tool.

Marijana Stojanovic is a writer and researcher who specializes in the topics of productivity and time management.
Where does the time go?
START TRACKING TIME
with Clockify
How Clockify Transformed Team Time Tracking Forever
Learn more about Clockify’s rising to the top and what sets it apart from other time trackers for teams.
How to create a PTO policy
Everything you need to know about creating a PTO policy — from the basics of PTO to choosing a PTO tracking system that suits your workflow.
Working Overtime Without Pay – Know Your Rights and Options
Discover the legal and financial aspects of working overtime without pay. Learn your rights and how to handle common concerns regarding off-clock work.
PTO vs. Vacation: What Is the Difference?
Learn the difference between PTO and vacation and find out the answers to the most frequently asked questions regarding paid leave!
Best methods for tracking team productivity
Find out the most useful methods of tracking team productivity, followed by actual examples of how different teams measure their effectiveness.
Difference between a freelancer, a contractor, and an employee
Learn which work category you fall into, to better protect your rights as a worker and avoid worker exploitation.
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED USERS
Free time tracker
Time tracking software used by millions. Clockify is a time tracker and timesheet app that lets you track work hours across projects.

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .

The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Look up a word, learn it forever.
/əˈsaɪnmənt/.
Other forms: assignments
Whether you’re an international spy with a new mission or a high school student with math homework — when you get an assignment , you’d better do it! An assignment is a task that someone in authority has asked you to do.
The word assignment is just the noun form of the common verb assign , which you use when you want to give someone a duty or a job. When you assign something, that something is called an assignment . The word can also refer to the act of distributing something. If you are distributing new office furniture at work, you might say, “ Assignment of the new chairs will begin tomorrow.”
- noun an undertaking that you have been assigned to do (as by an instructor) see more see less types: show 6 types... hide 6 types... school assignment , schoolwork a school task performed by a student to satisfy the teacher writing assignment , written assignment an assignment to write something classroom project a school task requiring considerable effort classwork the part of a student's work that is done in the classroom homework , prep , preparation preparatory school work done outside school (especially at home) lesson a task assigned for individual study type of: labor , project , task , undertaking any piece of work that is undertaken or attempted
- noun a duty that you are assigned to perform (especially in the armed forces) “a hazardous assignment ” synonyms: duty assignment see more see less types: show 10 types... hide 10 types... guard , guard duty , sentry duty , sentry go the duty of serving as a sentry fatigue , fatigue duty labor of a nonmilitary kind done by soldiers (cleaning or digging or draining or so on) charge , commission , mission a special assignment that is given to a person or group reassignment assignment to a different duty sea-duty , service abroad , shipboard duty naval service aboard a ship at sea shore duty naval service at land bases fool's errand a fruitless mission mission impossible an extremely dangerous or difficult mission martyr operation , sacrifice operation , suicide mission killing or injuring others while annihilating yourself; usually accomplished with a bomb secondment the detachment of a person from their regular organization for temporary assignment elsewhere type of: duty work that you are obliged to perform for moral or legal reasons
- noun the act of putting a person into a non-elective position synonyms: appointment , designation , naming see more see less types: show 6 types... hide 6 types... nomination the act of officially naming a candidate co-optation , co-option the act of appointing summarily (with or without the appointee's consent) delegacy the appointment of a delegate ordinance , ordination the act of ordaining; the act of conferring (or receiving) holy orders recognition designation by the chair granting a person the right to speak in a deliberative body laying on of hands laying hands on a person's head to invoke spiritual blessing in Christian ordination type of: conclusion , decision , determination the act of making up your mind about something
- noun the act of distributing something to designated places or persons “the first task is the assignment of an address to each datum” synonyms: assigning see more see less types: allocation , storage allocation (computer science) the assignment of particular areas of a magnetic disk to particular data or instructions type of: distribution the act of distributing or spreading or apportioning
- noun (law) a transfer of property by deed of conveyance synonyms: grant see more see less types: apanage , appanage a grant (by a sovereign or a legislative body) of resources to maintain a dependent member of a ruling family land grant a grant of public land (as to a railway or college) type of: transferred possession , transferred property a possession whose ownership changes or lapses
- noun the instrument by which a claim or right or interest or property is transferred from one person to another see more see less type of: instrument , legal document , legal instrument , official document (law) a document that states some contractual relationship or grants some right
Vocabulary lists containing assignment

The Dawes Act, or General Allotment Act of 1887, was a law that allowed the U.S. government to take Native American tribal lands and divide them into 40 acre lots for individual Native Americans. The goal was to break up communal tribal lands and speed the assimilation of Native Americans into American society. The Dawes Act caused great suffering with much of the land winding up in the hands of white settlers.
Learn these words from the autobiography by David Lubar (Inside: Level B, Unit 4). Here are our links to the selections of "Every Body Is a Winner": The Human Machine; My Fabulous Footprint , The Beat Goes On; All Pumped Up , Two Left Feet, Two Left Hands , How Coach Told Me; Bionics Here are our links to the units of Level B: Unit 1 , Unit 2 , Unit 3 , Unit 4 , Unit 5 , Unit 6 , Unit 7 , Unit 8 Here are our links to the Inside books: Level A , Level B , Level C Here is our link to a list of academic vocabulary for Inside: Academic Vocabulary

Prepare for the IELTS exam with this list of words related to education and academics.
Sign up now (it’s free!)
Whether you’re a teacher or a learner, vocabulary.com can put you or your class on the path to systematic vocabulary improvement..
How to Assign Tasks and Responsibilities to Team Members
As a manager or team leader, it’s important to effectively assign tasks and responsibilities to team members in order to ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively.
This can be a challenging task, especially if you have a large team, are working on a complex project, or are leading a team with no experience .
In this blog post, we will provide tips and best practices for assigning tasks and responsibilities to team members in a way that helps your team succeed.
We’ll cover topics such as setting clear expectations, delegating tasks appropriately, and providing support to team members as they complete their work.
By following these guidelines, you can create a productive and collaborative work environment that helps your team achieve its goals.
Setting Clear Expectations
One of the key elements of effective task assignments is setting clear expectations for team members.
This includes outlining the specific tasks that need to be completed, as well as any deadlines or goals that need to be met. It’s also important to communicate the purpose of the tasks and how they fit into the overall goals of the project or organization.
This helps team members understand the context of their work and why it’s important.
To set clear expectations, it’s a good idea to create a written document or task list that outlines the specific responsibilities of each team member.
This can be a simple spreadsheet or project management tool, or a more detailed project plan. Make sure to include details such as the task description, any necessary resources or tools, and any deadlines or milestones.
It’s also a good idea to discuss the task assignments with team members individually, to ensure that they understand their responsibilities and have any questions answered.
By setting clear expectations, you can help team members stay organized and focused as they complete their work.
Delegating Tasks Appropriately
Effective task assignment also involves delegating tasks to the right team members.
This means considering the skills, experience, and workload of each team member, and assigning tasks that are appropriate for their abilities and capacity. Delegating tasks appropriately helps to ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively, and helps to avoid overloading any one team member or causing delays due to a lack of resources.
To delegate tasks appropriately, it’s important to have a good understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each team member. This may involve reviewing their previous work or having candid conversations about their interests and capabilities.
It’s also important to consider the workload of each team member and ensure that they are not taking on more work than they can handle.
Another key aspect of effective task assignments is empowering team members to take ownership of their work . This means giving them the autonomy to complete tasks in their own way, within the parameters set by the project plan or task list.
Empowering team members to take ownership of their work can help to foster a sense of ownership and responsibility, and can lead to higher quality work and greater job satisfaction.
Providing Support to Team Members
Effective task assignment also involves providing support to team members as they complete their work.
This includes making sure that team members have the necessary resources and tools to complete their tasks, as well as offering guidance and assistance when needed. Providing support helps to ensure that team members are able to complete their work efficiently and effectively, and can also help to foster a sense of teamwork and collaboration within the team.
There are several ways that you can provide support to team members as they complete their work. This may include offering training or development opportunities, providing access to necessary resources or tools, and offering feedback and guidance as needed.
It’s also important to be available to team members if they have questions or need assistance with their tasks. By providing support and assistance, you can help team members to feel more confident and capable as they complete their work.
In conclusion, effective task assignment is an important element of managing a team or project. By setting clear expectations, delegating tasks appropriately, and providing support to team members, you can create a productive and collaborative work environment that helps your team succeed.
Communicating Task Assignments and Updates
Effective task assignment also involves effective communication with team members.
This includes not only clearly outlining the tasks and responsibilities that need to be completed, but also keeping team members informed of any updates or changes to the tasks or project plan. This can help to ensure that team members are aware of their responsibilities and are able to stay on track with their work.
There are several ways that you can communicate task assignments and updates to team members. This may include using a project management tool or task list to keep track of assignments and deadlines, as well as regularly holding meetings or check-ins to discuss progress and address any issues that may arise.
It’s also important to be available to team members if they have questions or need clarification on their tasks.
Effective communication is key to ensuring that team members are able to complete their work efficiently and effectively.
By keeping team members informed and providing clear guidance, you can help to ensure that work is completed on time and to the required standards.
Assessing and Adjusting Task Assignments
Effective task assignment also involves ongoing assessment and adjustment of task assignments as needed. This means regularly reviewing the progress of team members and the overall project, and making adjustments to tasks or responsibilities as needed to ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively.
To assess and adjust task assignments, it’s important to regularly check in with team members and review their progress.
This may involve holding meetings or check-ins, as well as reviewing any project management tools or task lists that you are using to track progress. If you notice that a team member is struggling with their tasks or is unable to complete them on time, it may be necessary to adjust their assignments or provide additional support.
Similarly, if you notice that a team member has extra capacity or is particularly skilled in a certain area, you may want to consider reassigning tasks or increasing their responsibilities.
By regularly assessing and adjusting task assignments, you can ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively, and that team members are able to make the most of their skills and abilities.
Encouraging Team Input and Feedback
Effective task assignment also involves encouraging team input and feedback.
This means soliciting ideas and suggestions from team members and actively listening to their concerns or issues related to their tasks or the project as a whole. Encouraging team input and feedback can help to foster a sense of ownership and engagement among team members, and can also lead to better decision-making and problem-solving.
There are several ways that you can encourage team input and feedback. This may include holding regular team meetings or check-ins, as well as setting aside time for open discussion and brainstorming sessions.
It’s also a good idea to create a culture of open and honest communication within your team, where team members feel comfortable speaking up and sharing their ideas or concerns.
By encouraging team input and feedback, you can create a more collaborative and inclusive work environment that helps your team succeed.
Providing Recognition and Rewards
Effective task assignment also involves providing recognition and rewards to team members who excel in their work. This can help to motivate team members and encourage them to continue performing at a high level, as well as foster a positive work culture.
There are many ways that you can provide recognition and rewards to team members. This may include offering verbal praise or written feedback, as well as more tangible rewards such as gift cards, paid time off, or additional responsibilities.
It’s important to consider the preferences and motivations of individual team members when deciding on recognition and rewards, as different people may respond differently to different forms of recognition.
By providing recognition and rewards to team members who excel in their work, you can show appreciation for their efforts and help to motivate and inspire them to continue performing at a high level.
Wrapping Up
Effective task assignment is an important element of managing a team or project.
It involves setting clear expectations for team members, delegating tasks appropriately, and providing support and assistance as needed.
Effective task assignment also involves ongoing communication and assessment, as well as encouraging team input and feedback and providing recognition and rewards for excellent performance.
By following these guidelines, you can create a productive and collaborative work environment that helps your team succeed.
Are you a visionary leader? Find out with our self-assessment!
Disclaimers
All the information on this website - https://melbado.com/ - is published in good faith and for general information purpose only. Melbado does not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. Any action you take upon the information you find on this website (Melbado), is strictly at your own risk. Melbado will not be liable for any losses and/or damages in connection with the use of our website.
From our website, you can visit other websites by following hyperlinks to such external sites. While we strive to provide only quality links to useful and ethical websites, we have no control over the content and nature of these sites. These links to other websites do not imply a recommendation for all the content found on these sites. Site owners and content may change without notice and may occur before we have the opportunity to remove a link which may have gone 'bad'.
Please be also aware that when you leave our website, other sites may have different privacy policies and terms which are beyond our control. Please be sure to check the Privacy Policies of these sites as well as their "Terms of Service" before engaging in any business or uploading any information.
By using our website, you hereby consent to our disclaimer and agree to its terms.

Assignment vs Coursework: Which Should You Use In Writing?

When it comes to academic writing, two terms that are often used interchangeably are assignments and coursework. While they may seem similar, there are distinct differences between the two that are important to understand. In this article, we will explore the nuances of these terms and help you understand which one to use in different situations.
It’s important to note that both assignment and coursework are proper words that can be used in academic writing. However, they are not always interchangeable. An assignment typically refers to a specific task or project that is given to a student to complete. This could be anything from a short essay to a research paper or a group project. Coursework, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses all of the work that a student is expected to complete for a particular course or subject. This could include assignments, but also exams, quizzes, presentations, and other forms of assessment.
Understanding the difference between these two terms is important because it can help you communicate more clearly with your professors and peers. For example, if you are asked to submit an assignment for a particular course, you should focus on completing the specific task that has been assigned to you. On the other hand, if you are asked to complete coursework for a course, you should be prepared to complete a range of different tasks and assessments over the course of the semester.
Define Assignment
An assignment is a piece of work that is given to a student by a teacher or professor. It is usually a task that requires the student to research, analyze, and present information on a particular topic. Assignments can take many forms, including essays, reports, presentations, and projects. They are designed to test the student’s understanding of the material and their ability to apply it in a practical way.
Define Coursework
Coursework refers to a series of assignments, projects, and other tasks that are completed by a student over the course of a semester or academic year. It is a more comprehensive form of assessment than individual assignments, as it covers a broader range of topics and requires the student to demonstrate a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Coursework can include essays, research papers, lab reports, and other types of assignments. It is designed to evaluate the student’s overall performance in a particular course or subject area.
How To Properly Use The Words In A Sentence
When it comes to academic writing, using the right words is crucial. In this section, we will discuss how to properly use the words “assignment” and “coursework” in a sentence.
How To Use “Assignment” In A Sentence
“Assignment” refers to a task or piece of work that is assigned to a student as part of their coursework. Here are a few examples of how to use “assignment” in a sentence:
- The teacher gave us an assignment to write a research paper on the effects of climate change.
- My math assignment is due tomorrow, so I need to finish it tonight.
- She received a high grade on her history assignment because she put in a lot of effort.
As you can see from these examples, “assignment” is typically used to refer to a specific task or project that is assigned to a student.
How To Use “Coursework” In A Sentence
“Coursework” refers to all of the work that is required for a particular course, including assignments, readings, and exams. Here are a few examples of how to use “coursework” in a sentence:
- I have a lot of coursework to do this semester, including several research papers and exams.
- She spent all weekend working on her coursework for her biology class.
- The professor assigns a lot of coursework, but it’s all relevant to the material covered in class.
As you can see from these examples, “coursework” is used to refer to all of the work that is required for a particular course, rather than a specific task or project.
More Examples Of Assignment & Coursework Used In Sentences
In order to gain a better understanding of the differences between assignments and coursework, it can be helpful to see how these terms are used in context. Below are some examples of how these terms might be used in sentences:
Examples Of Using “Assignment” In A Sentence
- My teacher gave me an assignment to write a research paper on the effects of climate change.
- She completed her math assignment in just under an hour.
- The company’s CEO assigned the new project to the marketing team.
- He forgot to turn in his history assignment and received a zero on the assignment.
- My boss gave me a new assignment that involves working closely with our sales team.
- The assignment was due at midnight, but I managed to submit it just in time.
- She was struggling with her writing assignment, so she decided to seek help from a tutor.
- The assignment required us to read a novel and write a book report on it.
- He received a high grade on his photography assignment because he put in a lot of effort.
- My professor assigned a group project to us that requires us to work together to create a presentation.
Examples Of Using “Coursework” In A Sentence
- She spent all weekend working on her coursework for her online class.
- The coursework for this program is designed to be completed over the course of a year.
- He struggled to keep up with the coursework in his advanced physics class.
- The coursework for this degree program includes a mix of lectures, labs, and independent research.
- She received a B on her coursework for the semester, which was lower than she had hoped for.
- He found the coursework for his business degree to be challenging but rewarding.
- The coursework required us to read several academic articles and write a critical analysis of each one.
- She is currently taking a break from her coursework to focus on an internship she landed.
- He was struggling to keep up with the coursework until he started attending study groups.
- The coursework for this program is designed to be hands-on and practical, with a focus on real-world applications.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
When it comes to academic writing, using the correct terminology is essential. However, many students make the mistake of using “assignment” and “coursework” interchangeably, which can lead to confusion and potentially affect their grades. In this section, we will highlight some common mistakes people make when using assignment and coursework interchangeably, with explanations of why they are incorrect. We will also offer tips on how to avoid making these mistakes in the future.
Mistake #1: Using “Assignment” And “Coursework” Interchangeably
One of the most common mistakes students make is using “assignment” and “coursework” interchangeably. While both terms refer to academic tasks, they have different meanings and implications.
| Assignment | Coursework |
|---|---|
| An individual task given to a student to complete within a specific time frame | A series of tasks, including assignments, projects, and exams, that are completed over the course of a semester or academic year |
| Usually accounts for a smaller portion of the final grade | Usually accounts for a larger portion of the final grade |
Using “assignment” to refer to all academic tasks can lead to confusion, especially when discussing grades or deadlines with professors. It is important to use the correct terminology to ensure clear communication and avoid misunderstandings.
Mistake #2: Assuming All Assignments Are The Same
Another common mistake is assuming that all assignments are the same. While the term “assignment” may refer to a variety of tasks, such as essays, research papers, or presentations, each task has its own requirements and expectations.
For example, an essay assignment may require a different writing style and format than a research paper assignment. Assuming that all assignments are the same can lead to poor grades and missed opportunities to showcase your skills and knowledge.
Tips For Avoiding These Mistakes:
- Read the assignment instructions carefully to understand the requirements and expectations
- Ask your professor or TA for clarification if you are unsure about any aspect of the assignment
- Use the correct terminology when discussing assignments and coursework with professors and classmates
- Plan ahead and manage your time effectively to ensure that you can complete all assignments and coursework on time
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can improve your academic performance and ensure that you are using the correct terminology when discussing assignments and coursework.
Context Matters
When it comes to academic writing, the choice between assignment and coursework can depend on the context in which they are used. In some situations, one may be more appropriate than the other. Understanding the differences between the two can help you make an informed decision that will lead to better results.
Examples Of Different Contexts And How The Choice Between Assignment And Coursework Might Change:
High school vs university.
High school assignments are often shorter and simpler than university coursework. Assignments can be completed in a shorter amount of time and may require less research. On the other hand, university coursework is more complex and in-depth. It requires more research and analysis, and can take weeks or even months to complete.
STEM vs Humanities
The choice between assignment and coursework can also depend on the subject matter. STEM subjects such as math and science may require more assignments that involve problem-solving and calculations. Humanities subjects such as literature and history may require more coursework that involves research and analysis of texts.
Individual vs Group Work
Assignments are often given as individual work, while coursework may involve group work. Group coursework can provide opportunities for collaboration and can lead to a more comprehensive final product. However, individual assignments can help students develop independent research and critical thinking skills.
Formal vs Informal Assessment
Assignments are often used for informal assessment, while coursework is used for formal assessment. Assignments may be used to gauge student understanding of a particular topic, while coursework is used to assess overall learning and understanding of a subject over a longer period of time.
Final Thoughts
As you can see, the choice between assignment and coursework can depend on a variety of factors. By understanding these differences, you can make an informed decision that will lead to better results. Whether you are a high school student or a university student, in a STEM or humanities subject, working individually or in a group, understanding the context in which you are working is key to success.
Exceptions To The Rules
While the terms assignment and coursework are generally used interchangeably, there are some exceptions where the rules for using them might not apply. Here are some explanations and examples for each case:
1. Research Papers
Research papers are typically longer and more in-depth than regular assignments or coursework. They require extensive research, analysis, and critical thinking skills. While research papers are technically a type of assignment, they are often referred to as coursework in academic settings.
2. Capstone Projects
Capstone projects are usually required at the end of a degree program and involve a comprehensive analysis of a particular topic. They are often more extensive and complex than regular assignments or coursework and may involve original research or a practical application of theoretical concepts. Capstone projects are typically considered coursework rather than assignments.
3. Group Projects
Group projects are assignments that are completed by a team of students rather than an individual. While they are still considered assignments, they may be referred to as coursework in certain contexts. This is because group projects often involve collaboration and may require students to apply concepts learned in class to a real-world scenario.
4. Creative Assignments
Some assignments may be more creative in nature, such as writing a short story or creating a piece of art. These types of assignments may be referred to as coursework in certain contexts, as they often require students to apply their creativity and imagination to complete the task.
5. Online Courses
Online courses may use the terms assignment and coursework differently than traditional in-person courses. In some cases, all work completed outside of class may be referred to as coursework, regardless of the specific assignment type. This can include quizzes, exams, and other assessments.
Overall, while the terms assignment and coursework are generally used interchangeably, there are some exceptions where the rules may not apply. It is important to understand the context in which these terms are being used to ensure clear communication and understanding between students and instructors.
Practice Exercises
Now that we have discussed the differences between assignments and coursework, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice. Here are some exercises that will help you improve your understanding and use of these terms in sentences:
Exercise 1: Fill In The Blanks
Choose the correct word (assignment or coursework) to complete each sentence:
- I have a lot of __________ to do this weekend for my English class.
- The final __________ for this course is worth 40% of our grade.
- My professor gave us a written __________ to complete by next week.
- For our history class, we have to write a research paper as part of our __________.
- The __________ for this math class is due at the end of the semester.
Answer Key:
Exercise 2: Writing Prompts
Choose one of the following prompts and write a paragraph using either assignment or coursework in a sentence:
- Describe a time when you struggled with a difficult __________.
- Explain how you manage your time when you have multiple __________ due at once.
- Discuss the importance of __________ in your academic success.
Explanations:
For the first prompt, you could write something like: “Last semester, I had a particularly challenging assignment in my biology class. It required a lot of research and writing, and I found myself struggling to stay focused and motivated.” For the second prompt, you might say: “When I have multiple coursework assignments due at once, I try to prioritize my tasks and break them down into smaller, more manageable pieces.” And for the third prompt, you could write: “Completing coursework on time is essential to achieving academic success. It shows that you are responsible and disciplined, and it helps you stay on track with your learning goals.”
After exploring the differences between assignments and coursework, it is clear that these two terms are not interchangeable. Assignments are usually shorter and more focused on a specific task, while coursework is more comprehensive and covers a wider range of topics.
It is important to understand the differences between these two terms to ensure that you are meeting the requirements of your academic program. By submitting the wrong type of work, you could risk receiving a lower grade or even failing the course.
Furthermore, the use of proper grammar and language is crucial in both assignments and coursework. Clear and concise writing can help convey your ideas effectively and enhance the overall quality of your work.
Key Takeaways:
- Assignments and coursework are not interchangeable terms.
- Assignments are shorter and more focused, while coursework is more comprehensive.
- Understanding the differences between these terms is crucial in meeting academic requirements.
- Proper grammar and language use are important in both assignments and coursework.
Continuing to learn about grammar and language use can help improve your writing skills and enhance your academic performance. By practicing good writing habits and seeking feedback from professors or peers, you can become a more effective communicator and achieve success in your academic pursuits.
Shawn Manaher is the founder and CEO of The Content Authority. He’s one part content manager, one part writing ninja organizer, and two parts leader of top content creators. You don’t even want to know what he calls pancakes.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
You’re Between Assignments at Work. What Do You Do?

It’s a great time to get organized and think big picture.
Being in a lull period at work can be a great opportunity to shift gears, recalibrate, get organized, and even stretch yourself. To make the most of a slow period, keep a running list of ways that you could challenge yourself. The list might include taking up new hobbies, enrolling in a short-duration class, or deliberately placing yourself in an uncomfortable situation, such as a public speaking role, for the purpose of growth. What tasks have you been putting off? A slow period at work is an excellent time to cross them off your list. Don’t waste a good slowdown. It can be a great time to step back from work to think big picture, give back to your community, ramp up your fitness routine, or simply recharge your batteries for the next busy period.
A lull between assignments or a dip in your weekly hours can be a chance to recalibrate . Many senior leaders jump at the chance to re-organize their commitments, ponder longer-term initiatives, or relax. But not everyone sees this opportunity; for some, a lull can be debilitating. If you’re a senior manager who draws energy from always being challenged and keeping busy, a lull can make you feel stuck. Here are four steps to help you experience forward motion again.
- AS Anne Sugar is an executive coach and speaker who works with senior leaders in technology, marketing, and pharmaceutical companies. She is an executive coach for the Harvard Business School Executive Program and has guest lectured at MIT. You can reach her at annesugar.com .
Partner Center
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
For the Most Productive Workplace, Assign Employees the Work They Do Best Researchers are finding managers get much more from employees by playing to their strengths than trying to bolster their weaknesses.
By Heather R. Huhman Edited by Dan Bova Apr 13, 2015
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
Don is an extremely busy general manager. He has several departmental managers that report to him directly and is not too involved with the smaller day-to-day operations of his business.
Recently, he decided to take a closer look at how smoothly his business was operating. He sent out a company-wide survey and found his employees were unhappy with some aspects of their jobs.
The main thing he noticed was most of his employees did not feel the company used their strengths effectively.
A 2015 survey from Michelle McQuaid and the Via Institute on Character found that employees perform better and are more engaged in their work when they and their managers focus on building their strengths, rather than improving their weaknesses.
Employers can help identify the strengths of their employees and work on building them to improve their satisfaction and engagement in the workplace.
Here are five ways to make that happen:
1. Evaluate where everyone's strengths lie within the company.
When managers understand where the strengths of their employees lie, they can assign tasks based on those skill sets. In February 2014, Gallup created the Strengths Orientation Index to analyze how engaged employees were when they felt their employers focused on their strengths as opposed to their weaknesses. It was found that of the 1,003 U.S. employees, 37 percent of employees felt their employer focused on their strengths. As a result, this led to 61 percent of employees feeling engaged in their work.
Playing to employees' strengths makes it easier to successfully run a business. For instance, it does not make sense for Don to tell Joann, a sales person, to write the communication pieces when he knows Rylie in marketing is a strong writer.
Related: Today's Most Satisfied Employees Demand These 4 Things
2. Assign tasks related to individual strengths.
In February 2014, the Journal of Positive Psychology found the use of strengths at work was connected with work performance, and this relationship is explained by vitality, concentration and harmonious passion.
With Rylie being a strong writer, she can easily draft introduction letters for the company. While Joann can write, it takes her longer and her writing is often strongly edited. By keeping Joann focused on selling and Rylie focused on writing, Don has two tasks being completed by the best people for the job.
It may not be Don's responsibility to make sure his employees never do a task they hate. However, giving employees jobs that play to their strengths is one way to make sure employees are engaged in their work. The more they enjoy what they do, the better their work will be.
Related: Culture That Counts -- 5 Ways to Dramatically Boost Employee Satisfaction
3. Provide necessary training.
A major frustration for new employees is not knowing how to do their job properly.
This February, Deloitte University Press found 85 percent of respondents cited learning as "important" or "very important," but more companies than ever report they are unprepared to meet this challenge.
By providing hands-on training, employees will be more likely to succeed right off the bat. With leaders interacting with new hires on a regular basis, employers will also get to know sooner what are a new employees' strengths.
Research released in Association of Talent Development's State of the Industry in November 2014 shows employers spend on average $1,208 to train employees. While many managers may not feel they have enough time and money to effectively train their employees, proper training helps avoid costly mistakes down the line for new hires.
Related: 5 Ways You Might Be Failing Your Employees
4. Set up reverse mentorships.
Reverse mentorships are a great way for Don to enlist the help of experienced employees to bring out the strengths of his new employees. While traditional mentorships place the teaching responsibility on the mentor, reverse mentorships place equal responsibility on the mentee as well.
As a person works for a company for a long period of time, they often rely on the skills they learned years ago. Giving new employees the opportunity to show new ways to help a coworker is a great way to promote respect for each other's strengths in the office.
Technology comes easily for Millennials. In October 2014, Elance-oDesk found 82 percent of the hiring managers surveyed felt Millennials were technologically adept. Instead of watching their older coworkers struggle with programs they grew up with, they should offer to help teach their colleagues the basics. In return, older coworkers can teach the ways of the office and proper business etiquette.
Related: 4 Tips on How to Bring Out the Best in Your New Hires
5. Provide feedback frequently.
Don uses software like Feedback Socially to provide feedback to his employees frequently.
Research from Feedback Socially shows employees are more engaged when they receive feedback once a week. Using this software is a quick way to provide the feedback employees need, keeping them engaged and more likely to stay at Don's company.
When Don uses Feedback Socially, he is providing specific feedback on a weekly basis instead of waiting for annual or quarterly employee reviews. While he takes the time to address areas of concern, he focuses mainly on promoting the things his employees do well.
Don doesn't need an office full of jack-of-all-trades, he just wants employees that truly excel at their jobs. Feedback Socially offers a way for Don to acknowledge his employees' strengths on a regular basis.
Related: Seven Steps to Coaching Your Employees to Success
Career and Workplace Expert; Founder and President, Come Recommended
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Steve Jobs' 3 Public Speaking Power Moves Remain Just as Relevant Today, 13 Years After His Final Keynote at the Apple Developers Conference
- Lock I Blocked a Toxic Childhood Friend and It Taught Me an Important Lesson About Managing People
- Lock 10 of the Biggest Business Blunders in 2024 (So Far)
- 'I've Never Regretted Leaving the Corporate World Behind': This Former Lawyer Now Makes Six Figures on YouTube — Here's How
- Lock 5 Ways to Fix Your Lack of Inspiration
- 'Unpredictability in Various Forms' — How Franchisees Can Adapt and Protect Themselves From Election Year Uncertainty
Most Popular Red Arrow
Are your business's local listings accurate and up-to-date here are the consequences you could face if not..
Why accurate local listings are crucial for business success — and how to avoid the pitfalls of outdated information.
Day Traders Often Ignore This One Topic At Their Peril
Boring things — like taxes — can sometimes be highly profitable.
Want to Be More Productive Than Ever? Treat Your Personal Life Like a Work Project.
It pays to emphasize efficiency and efficacy when managing personal time.
'Passing By Wide Margins': Elon Musk Celebrates His 'Guaranteed Win' of the Highest Pay Package in U.S. Corporate History
Musk's Tesla pay package is almost 140 times higher than the annual pay of other high-performing CEOs.
He Immigrated to the U.S. and Got a Job at McDonald's — Then His Aversion to Being 'Too Comfortable' Led to a Fast-Growing Company That's Hard to Miss
Voyo Popovic launched his moving and storage company in 2018 — and he's been innovating in the industry ever since.
I Left the Corporate World to Start a Chicken Coop Business — Here Are 3 Valuable Lessons I Learned Along the Way
Board meetings were traded for barnyards as a thriving new venture hatched.
Successfully copied link

Work Assignments Template
Identify assignees for tasks, define task parameters, submit task parameters to manager for approval, approval: task parameters.
- Define Task Parameters Will be submitted
Initiate Draft Work Assignment Template
Identify required deliverables.
- 3 Prototype
- 4 Completed Task
Input Required Deliverables into Template
Identify timeline for task completion, input timeline into template, identify required resources.
- 2 Equipment
- 3 Access to Systems
Input Required Resources into Template
Review draft work assignment template, approval: draft work assignment template.
- Initiate Draft Work Assignment Template Will be submitted
Address Feedback from Approval Task
Finalize work assignment template, distribute finalized work assignment template to assignees, review assignees’ understanding and acceptance of assignments, approval: assignee understanding and acceptance.
- Review Assignees’ Understanding and Acceptance of Assignments Will be submitted
Initiate Work on Assignments
Monitor progress of assignments.
- 2 Behind Schedule
- 3 Completed
Take control of your workflows today.
More templates like this.
This site uses cookies to store information on your computer. Some are essential to make our site work; others help us improve the user experience. By using the site, you consent to the placement of these cookies. Read our privacy policy to learn more.
- FOREIGN INCOME & TAXPAYERS
Tax Planning Insights for Foreign Work Assignments
- International Tax
- Individual Income Taxation
In today's global economy, U.S. employers are sending workers abroad in increasing numbers. These workers commonly are referred to as expatriates or assignees. It is a trend that helps spread technical expertise throughout an organization, while simultaneously inspiring creativity and innovation. With proper planning, the transition abroad can be beneficial to both the employer and the assignee. Without proper planning, it can be a disaster. Though not a complete road map, the following is a basic overview of what one would want to know when advising clients prior to foreign work assignments.
An understanding of how expatriates, or expats, are taxed is necessary before one can properly plan for an assignment abroad. In short, U.S. citizens are taxed on their worldwide income by the United States, regardless of their residency or the income's source. This means that a U.S. employee's income could potentially be subject to double taxation, in both foreign and U.S. jurisdictions. It seems a bit unfair, right? Well, fortunately, the U.S. government is not completely heartless. Relief is available in many cases. For foreign earned income, an expat can claim either a Sec. 901 foreign tax credit, an itemized deduction for foreign taxes paid, or a Sec. 911 exclusion.
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion
A U.S. taxpayer may exclude up to $100,800 of foreign earned income in 2015 (adjusted for inflation annually) as well as a housing allowance if he or she maintains a tax home in a foreign country and qualifies via either (1) a bona fide residencetest or (2) a foreign physical presencetest (Secs. 911(a) and (b)(2)).
- Bona fide residence test: A taxpayer who is a citizen of the United States satisfies this test if the taxpayer establishes to the IRS's satisfaction that he or she was a bona fide resident of a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that includes an entire tax year. Temporary visits to the United States or elsewhere for vacation or business do not necessarily prevent a taxpayer from establishing a bona fide foreign residence for a continuous period. The expat cannot qualify under this test if he or she submits a statement to the foreign country stating that he or she is not a resident of that country and is held by that country to not be subject to income tax in that country (Secs. 911(d)(5)(A) and (B)).
- Foreign physical presence test: A taxpayer that is a citizen or resident of the United States meets this test if he or she is present in one or more foreign countries (not the United States) during at least 330 "full" days in any given 12-month period (Sec. 911(d)(1)). These days need not be consecutive, which allows for potential partial exclusions when assignments begin in the middle of the calendar year. Also, notice that not all time needs to be spent in the country in which the taxpayer is claiming to have a tax home and not all time needs to be spent doing business. Personal and vacation time count. This test does not require that the taxpayer's income be subject to foreign income tax. Good records substantiating time spent outside the United States are a necessity, however.
If claiming the exclusion, the taxpayer will need to file Form 2555, Foreign Earned Income . U.S. citizens living abroad are allowed an automatic two-month extension until June 15 to file their individual tax returns. This extra time may be needed to properly substantiate certain claims for relief mentioned above. If needed, a U.S. citizen living abroad may apply for an additional extension.
Foreign Tax Credit
U.S. citizens are entitled to a foreign tax credit for income taxes paid or accrued to a foreign country. Though it sounds simple enough, this calculation can be complex in certain situations. Sec. 904 limits the credit by the amount of U.S. tax that is levied on the same amount of income. Sec. 901(j) can cause the credit to be denied entirely if the income earned is from a country whose government the United States (1) does not formally recognize; (2) has severed diplomatic relations with; (3) has not severed diplomatic relations with but with which it does not conduct relations; or (4) has designated as repeatedly supporting acts of international terrorism. Any excess foreign taxes not credited in the current year can be carried back one year and forward 10 years (or just forward 10, if elected) per Sec. 904(c).
Previously, if these tax credit amounts were unused, they could be converted into a deduction in the 10th year. The IRS recently changed its position regarding the 10th-year deduction, so CPAs can no longer rely on the safety net of converting a credit to a deduction in the final year (see Ward, "Foreign Tax Credit: When Is It Too Late to Change Your Mind?" 46 The Tax Adviser 662 (September 2015), where the author writes, "As evidenced by the recent reliance on this position in CCA 201330031 and CCA 201517005, it appears the IRS is holding firm in denying the 10-year period of limitation to taxpayers amending to change elections to claim credits for foreign taxes to elections to claim deductions."). Basically, if a taxpayer can reasonably predict that the expat will be in an excess credit position, the deduction might be the better way to go from the beginning. Foreign tax deductions can still be turned into foreign tax credits, but not the other way around.
It is also worth mentioning that U.S. individuals cannot claim a foreign tax credit for otherwise creditable foreign taxes attributable to income that they elect to exclude from gross income as foreign earned income (Sec. 911(d)(6)). In other words, a taxpayer can get either the exclusion or the credit, but not both. In practice, both are often calculated to see which provides the higher tax benefit for the particular situation.
It sounds simple enough, but it is hardly ever that simple.
A number of things might occur. One aspect that often is not considered is how the taxpayer's home state treats his or her assignment abroad. Practitioners should determine to what extent the relevant state law considers a taxpayer stationed abroad to still be a state resident and subject to state income tax. Most states do not follow federal law in terms of double-taxation relief, i.e., foreign tax credit or exclusion. The state might offer some sort of relief, however, but sometimes it is not much. For example, an Oregon resident is allowed to take a foreign tax deduction up to $3,000, but it phases out at higher income levels. On the other hand, Oregon nonresidents may exclude the foreign earned income.
Depending on the company policy (discussed later), sometimes the employer or the foreign company "gross-up" payments and pay the foreign tax on the expat's behalf. These gross-ups are income to the employee, which can increase the amount of taxes owed in the United States and the home state, making any withholding on the U.S. side insufficient, ultimately causing the employee to fork over some extra cash unexpectedly at the filing deadline. Remember that the entire tax liability is due at the original filing deadline for the return, April 15, not the extended date of June 15. In addition to taxes paid on the assignee's behalf, other items must be considered as well. Compensation packages for foreign assignments often have many additional allowances or income items.
The tax rate in the foreign country compared with the U.S. tax rate also makes a difference. For instance, a higher foreign tax rate means that it costs the employee more to work in the foreign jurisdiction, which is a benefit to the employer. Conversely, if the foreign tax rates are lower, the employee receives a benefit. Basically, the arrangement is not always considered fair.
Structure of the Foreign Assignment
Because of all the possibilities that can occur as a result of an expat's foreign assignment, it is imperative that planning occur well before the assignment begins. A few things should happen.
First, the employer should work with a service provider to develop an expatriate employee policy, often referred to as a global policy. This policy may touch on a variety of items, including, but not limited to, automobile policies, cultural orientation programs, pet policies, emergency and security planning, and, of course, the payment for and preparation of foreign, federal, and state taxes.
As mentioned previously, there is often a disparity between an assignee's U.S. tax liability and foreign tax liability. Employers can choose to handle this disparity in one of three ways:
1. Equalization,
2. Protection, or
3. Laissez-faire.
Equalization: If a company decides to enact an equalization policy, both the employer and the employee are no better or no worse for having participated in the overseas assignment. In other words, the policy is tax-neutral.
If a "hypothetical tax" exceeds the actual tax as filed on the assignee's U.S. tax returns, the assignee would owe the employer the difference. If the actual tax exceeds the hypothetical tax, the employer would reimburse the assignee for the difference.
The mechanics work as follows: After the tax return is filed, the hypothetical tax is figured considering only income and deduction items that the assignee would have incurred had he or she stayed in the United States. The hypothetical tax is then compared with the actual tax liability per the tax return plus any hypothetical withholding. Hypothetical withholding is withholding in addition to regular withholding that the employer holds on to so that in the event that the hypothetical liability exceeds the actual liability, the assignee does not have to settle the entire liability.
Some common questions should be kept in mind when reviewing an equalization policy. How are state taxes handled? If an assignee decides to sell his or her home as a result of the foreign assignment, is this factored in? Is all of the income equalized? Or is it just the employment income?
Protection: If a company enacts a tax-protection policy, the employer makes certain the employee bears no adverse effects from the foreign tax assignment.
When the hypothetical tax exceeds the actual tax, the employee retains the benefit and is not required to reimburse the employer the difference; when the actual tax exceeds the hypothetical tax, the employer will reimburse the assignee.
The actual calculation of tax under a tax-protection policy is a bit simpler in that there generally is no hypothetical withholding. All taxes are paid directly by the assignee. The employer will square up later.
Laissez - faire : This policy is just as it sounds—let the cards lie where they fall. A lot of smaller companies will typically go this route. Implementation of both equalization and protection policies can be time-consuming and expensive.
Structuring a Compensation Package
After the employer settles on a global policy, both the employer and the prospective assignee should sit down with the service provider to structure a compensation package that is both tax-efficient and fair. At this time, the employer and the service provider should explain to the assignee how he or she will be taxed and what to expect as far as services are concerned. These packages are generally much more complex than regular domestic compensation and usually cost employers two to three times more. They usually consist of a base salary and various other allowances, depending on the location of the foreign assignment.
The more common allowances are cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs), housing allowances, and moving allowances.
The COLA allows an expat to live off the same level of income that he or she would have had in the United States. The adjustment is calculated based on the employee's spendable income multiplied by a cost-of-living index. This income is taxable to the assignee.
Housing can be tricky. If the employee receives a cash allowance, it is generally taxable. Generally, the allowance is calculated by subtracting the amount of home country housing costs from the amount it would cost the expat in the foreign country. Sometimes expats are required to live on the employer's property as an unavoidable working condition. When this is the case, the housing is considered a tax-free fringe benefit.
Most of the time, employers will cover an assignee's moving expenses. This either comes in the form of an allowance or reimbursement upon submittal of expenses. This benefit is also taxable.
The benefits received vary by country. Special attention should be paid to the following countries: Iraq, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, United Arab Emirates, and the Republic of Yemen. These countries are specifically listed as boycott countries by Treasury under Sec. 999(a)(3). If an expat takes an assignment in one of these countries, he or she will have to file a Form 5713, International Boycott Report .
Lastly, although this topic probably deserves its own article, prior to the assignment, the company should make sure that it has a solid payroll strategy in place. For less-sophisticated organizations with limited personnel, hiring an outside payroll professional is recommended. Larger companies with a strong internal foreign tax department may be able to handle the payroll function internally. Consultation with a professional is needed in either case.
Planning for foreign work assignments can be time-consuming and requires expert knowledge, but it is necessary to ensure all the relevant tax issues are considered in advance. Only then can both the employer and the expat benefit fully from the experience.
Editor Notes
Michael Koppel is with Gray, Gray & Gray LLP in Canton, Mass.
Unless otherwise noted, contributors are members of or associated with CPAmerica International.
Dual consolidated losses: Recapture considerations
Sec. 338(g) elections for foreign corporations and ‘creeping acquisitions’, the sec. 645 election to treat a trust as part of the estate, wealth transfer strategies amid shifting interest rates, interim guidance for sre expenditures.

This article discusses the history of the deduction of business meal expenses and the new rules under the TCJA and the regulations and provides a framework for documenting and substantiating the deduction.
PRACTICE MANAGEMENT

CPAs assess how their return preparation products performed.

Work vs Assignment - What's the difference?
As nouns the difference between work and assignment, as a verb work, etymology 1, derived terms, etymology 2.

COMMENTS
Team members usually share work assignments. An advertising firm requires its employees to be at work between the hours of 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m. This work rule allows employees to work additional hours before or after the time period in order to work the full day. ... Her husband elected to work half-time along with a co-worker who also had ...
Work assignments are tasks that are deliberately designed for organizational purposes. They are allocated to staff to achieve results. In the simplest terms, these assignments are activities or projects for a specific end. Work assignments should come with a task description, deadline and expected results. Work assignments tips.
3. Outline Main Points, Only Tease the Details. More often than not, the primary reason companies dole out homework is to get a better sense of your thought process, as well as how you structure and convey your thoughts and ideas. There's not necessarily a "right" answer, nor is there a need to get way down in the weeds.
Work assignments are most common in creative and technical fields of work. For example, writers may need to complete a trial piece before being hired, and marketing professionals may have to create a campaign pitch and outline as part of their interview process. For more technical work, like information technology or computer science, the ...
Accountability. Both assignment and delegation establish accountability, but in different ways. In assignment, the assignee is directly responsible for completing the task within the given timeframe and meeting the specified requirements. In delegation, while the delegatee is responsible for the task's execution, the delegator retains overall ...
Also, job and territorial assignments, which relate to both limiting and classifying, are treated separately. (1) Disparate Treatment - As is indicated in the examples below, disparate treatment occurs where protected group or class members are treated less favorably than other similarly situated employees for reasons prohibited under Title VII.
Clear work directions and parameters are provided and outcomes are reviewed by higher levels. Journey - Fully competent and qualified in all aspects of a body of work and given broad/general guidance. Individuals can complete work assignments to standard under general supervision. Also referred to as the working or fully qualified level.
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team's availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward. As team leads - assign tasks further down the pipeline. Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way.
That's also when you will find their feedback most useful. Assignment formats. Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started. An Overview of Some Kind
assignment: 1 n an undertaking that you have been assigned to do (as by an instructor) Types: show 6 types... hide 6 types... school assignment , schoolwork a school task performed by a student to satisfy the teacher writing assignment , written assignment an assignment to write something classroom project a school task requiring considerable ...
Setting Clear Expectations. One of the key elements of effective task assignments is setting clear expectations for team members. This includes outlining the specific tasks that need to be completed, as well as any deadlines or goals that need to be met. It's also important to communicate the purpose of the tasks and how they fit into the ...
Task assigning involves defining responsibilities and allocating resources for team members to complete a project effectively. While workplace leaders can assign tasks to team members in different departments, managers typically assign tasks to their department's members. Discovering each team member's strengths, potential, and expertise can ...
This could include assignments, but also exams, quizzes, presentations, and other forms of assessment. ... Individual vs Group Work. Assignments are often given as individual work, while coursework may involve group work. ... While research papers are technically a type of assignment, they are often referred to as coursework in academic ...
7 meanings: 1. something that has been assigned, such as a mission or task 2. a position or post to which a person is assigned.... Click for more definitions.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Employees assigned to work in another country are called hosts., Which phase of preparation for an international assignment involves providing information about the employee's community and parent-country workplace?, Geoff has been sent to Paris for an assignment. During his stay there, his compensation package was different from ...
These short-term work assignments allow businesses to mobilize skills and grow their organization while developing employees at the same time. Here, we'll examine some of the benefits and risks. Benefits. The organization fills a skills gap by relocating an employee where their capabilities are needed. Also, the employee can train others and ...
May 31, 2023. An assignment typically refers to a task or project that is given to someone, usually in an educational or professional setting. It is a specific piece of work that is assigned to ...
A lull between assignments or a dip in your weekly hours can be a chance to recalibrate.Many senior leaders jump at the chance to re-organize their commitments, ponder longer-term initiatives, or ...
Employers can help identify the strengths of their employees and work on building them to improve their satisfaction and engagement in the workplace. Here are five ways to make that happen: 1 ...
Identify Assignees for Tasks Identify the individuals or team members who will be responsible for completing each task. Consider their abilities, availability, and workload to ensure proper task assignment. Assignee Name Assignee Role Define Task Parameters Specify the parameters and requirements for each task. This includes the desired outcomes, resources needed, potential challenges, and any
Compensation packages for foreign assignments often have many additional allowances or income items. The tax rate in the foreign country compared with the U.S. tax rate also makes a difference. For instance, a higher foreign tax rate means that it costs the employee more to work in the foreign jurisdiction, which is a benefit to the employer.
Based on this definition, it is clear that skills are not the work or assignments performed by employees, but rather the abilities or expertise that enable them to perform those tasks effectively. Step 2/2 Therefore, the statement "The work and/or assignments performed by employees are referred to as skills" is false.
The assignment of the lease has not been finalised yet. (legal) A document that effects this transfer. Once you receive the assignment in the post, be sure to sign it and send it back as soon as possible. (computing) An operation that assigns a value to a variable. As nouns the difference between work and assignment is that work is employment ...