The Pathway 2 Success
Solutions for Social Emotional Learning & Executive Functioning

Teaching Social Problem-Solving with a Free Activity
February 3, 2018 by pathway2success 5 Comments
- Facebook 77

Kids and young adults need to be able to problem-solve on their own. Every day, kids are faced with a huge number of social situations and challenges. Whether they are just having a conversation with a peer, working with a group on a project, or dealing with an ethical dilemma, kids must use their social skills and knowledge to help them navigate tough situations. Ideally, we want kids to make positive choices entirely on their own. Of course, we know that kids don’t start off that way. They need to learn how to collaborate, communicate, cooperate, negotiate, and self-advocate.
Social problem solving skills are critical skills to learn for kids with autism, ADHD, and other social challenges. Of course, all kids and young adults benefit from these skills. They fit perfectly into a morning meeting discussion or advisory periods for older kids. Not only are these skills that kids will use in your classroom, but throughout their entire lives. They are well worth the time to teach!
Here are 5 steps to help kids learn social problem solving skills:
1. Teach kids to communicate their feelings. Being able to openly and respectfully share emotions is a foundational element to social problem solving. Teaching I statements can be a simple and effective way to kids to share their feelings. With an I statement, kids will state, “I feel ______ when _____.” The whole idea is that this type of statement allows someone to share how their feeling without targeting or blaming anyone else. Helping kids to communicate their emotions can solve many social problems from the start and encourages positive self-expression.
2. Discuss and model empathy. In order for kids to really grasp problem-solving, they need to learn how to think about the feelings of others. Literature is a great way teach and practice empathy! Talk about the feelings of characters within texts you are reading, really highlighting how they might feel in situations and why. Ask questions like, “How might they feel? Why do you think they felt that way? Would you feel the same in that situation? Why or why not?” to help teach emerging empathy skills. You can also make up your own situations and have kids share responses, too.

3. Model problem-solving skills. When a problem arises, discuss it and share some solutions how you might go forward to fix it. For example, you might say, “I was really expecting to give the class this math assignment today but I just found out we have an assembly. This wasn’t in my plans. I could try to give part of it now or I could hold off and give the assignment tomorrow instead. It’s not perfect, but I think I’ll wait that way we can go at the pace we need to.” This type of think-aloud models the type of thinking that kids should be using when a problem comes up.
4. Use social scenarios to practice. Give a scenario and have kids consider how that person might feel in that situation. Discuss options for what that person might do to solve the problem, possible consequences for their choices, and what the best decision might be. Kids can consider themselves social detectives by using the clues and what they know about social rules to help them figure out the solution. These are especially fun in small groups to have kids discuss collaboratively. Use these free social problem solving cards to start your kids off practicing!

5. Allow kids to figure it out. Don’t come to the rescue when a child or young adult has a problem. As long as it’s not a serious issue, give them time to think about it and use their problem-solving skills on their own. Of course, it’s much easier to have an adult solve all the problems but that doesn’t teach the necessary skills. When a child comes to you asking for your help with a social problem, encourage them to think about it for five minutes before coming back to you. By that point, they might have already figured out possible solutions and ideas and might not even need you anymore.
If you are interested in helping your kids learn social problem solving skills right away, consider trying out these Social Problem Solving Task Cards . They highlight real social scenarios and situations that kids can discuss. The scenarios include a variety of locations, such as in classrooms, with family, with friends, at recess, and at lunch. This set is targeted for elementary-age learners.

Of course, older kids need social problem solving skills, too! If you work with older kids, you will love these Social Problem Solving Task Cards for Middle and High School Kids. These situations target age-appropriate issues that come up in classes, with friends, with family, in the hallway, in the cafeteria, and with online and texting.

Remember that teaching social problem skills does take a little bit of planning and effort, but it will be well worth the time! Kids will use these skills to help them make social decisions in their everyday lives now and in the future!

Share this:

February 22, 2018 at 12:03 am
Thank you for sharing>
March 3, 2018 at 8:59 am
Good thought ful
March 20, 2018 at 9:24 pm
They are not free
March 21, 2018 at 8:58 am
They are! Here is the link (it’s listed under number 4): https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Free-Social-Problem-Solving-Task-Cards-2026178 I also have a paid version with a bunch more cards (for both elementary and older kids), but that will give you the freebie. Enjoy!
July 15, 2018 at 3:41 am
Awesome way to teach the skill of social problem solving.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Find It Fast
- Privacy Policy
- Join Pathway 2 Success
- Social Emotional Learning Toolkit
- Self-Control Resources
pathway2success1
⭐ Kristina 💖 SEL & Executive Functioning 💻 Blogger at www.thepathway2success.com 👩🏫 Special Educator turned Curriculum Specialist Links here 👇


71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Scenarios
Do you have kiddos who struggle with their social problem-solving skills? Teach your students the simple process of how to solve a problem along with having them review how well their solution worked or didn’t work.
Why Teach Problem Solving Skills?
Learning to problem solve is an essential skill that is used not only throughout childhood but also into adulthood. Social problem solving is the ability to change or adapt to undesirable situations that arise throughout our day.
On a daily basis, a child will encounter social problems that they will need to solve.
Anything from:
- arguing with another student
- to hurting a friend’s feelings
- to having a difficult conversation
- working with others

Start with Small Problems
Many of the “problems” children encounter are often small problems which the child may be over-reacting to, such as wanting a different coloring crayon or wanting to be first in line, however, these small problems are still very real to the child.
Practicing problem-solving with these small problems can be a great learning opportunity. Children can practice problem-solving with a small problem which can help them learn how to handle bigger problems in the future.
Problem Solving Importance
Social problem-solving skills are critical to a child’s social interactions, personal and professional relationships. A child’s ability to handle change, cope with stress, and handle challenges improves with a child’s ability to successfully solve social problems.
The ultimate goal is that the child will be able to solve social problems all on their own, but until they can independently solve a problem they will need to learn how to communicate and self-advocate to positively solve their problems.
Steps to Problem Solving
Children can be taught how to problem solve through a guided process of breaking down the problem and using simple steps to solve the problem.
Learning specific steps to problem-solving can allow children to remember how to solve a problem when they become overwhelmed or stressed.
Although learning to solve a problem independently can take some time and practice it is well worth the investment to have a child who can eventually solve most social situations in a positive manner on their own.
What we learnt about solving problems is don't freak out, if one thing doesn't work , try something else out. And work together as a team. #melthammathsweek #MELTHAMPUPILVOICE @problemsolveit pic.twitter.com/iVm1Im4Aue — yr6melthamce (@yr6melthamce) February 4, 2019
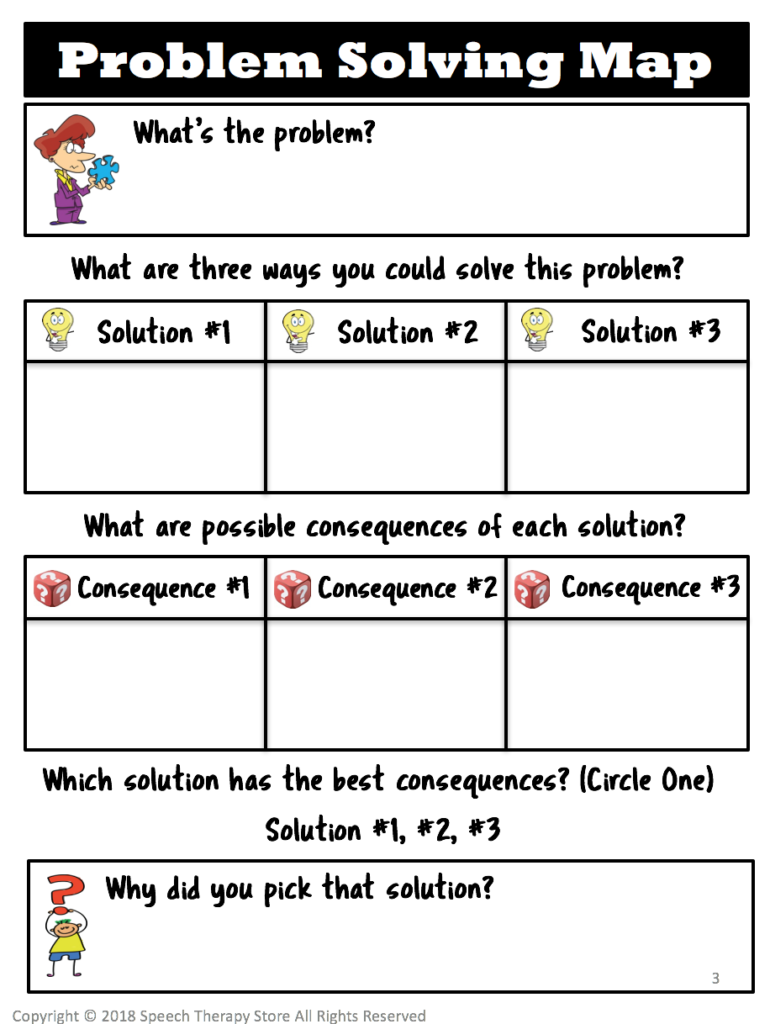
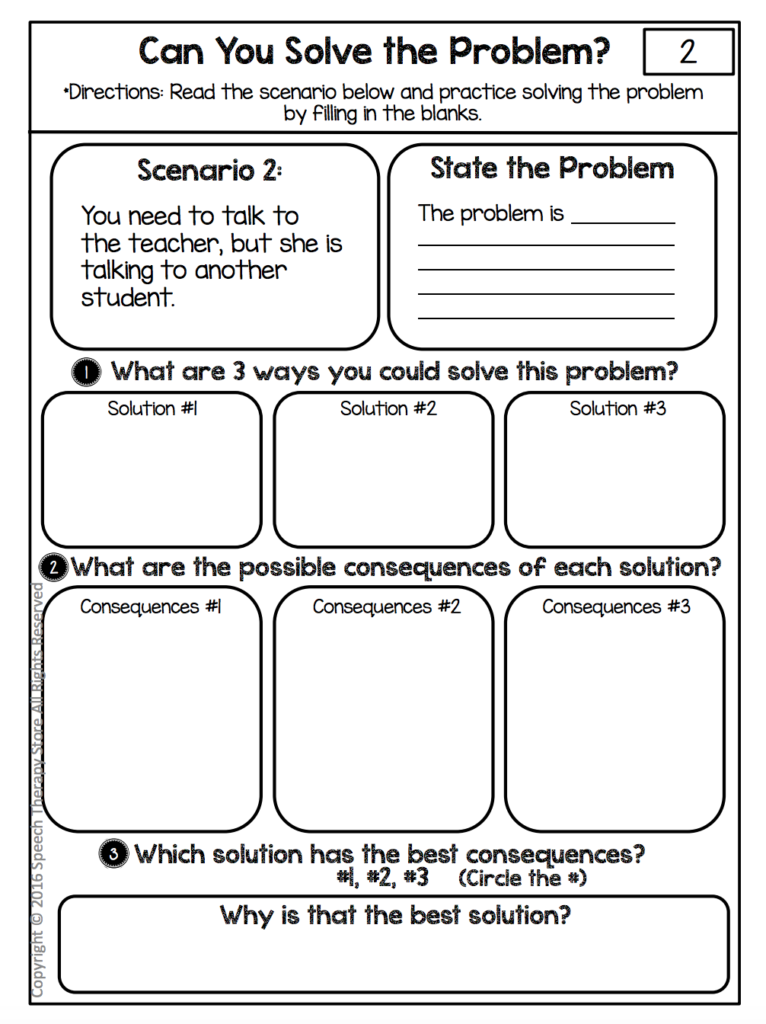
Problem Solving Form
Teach your students the 4 steps to becoming a social problem-solver.
- Identify the problem. For instance, start by having your student identify the social problem.
- Create three solutions. Also, have your student come up with three different solutions that they could use to solve the problem that they identified.
- Identify the consequences. Then, identify the consequence for each individual solution.
- Pick the best solution. Lastly, have your student identify which of their three solutions is the best choice Then have your student put into words why they think that solution is the best solution.
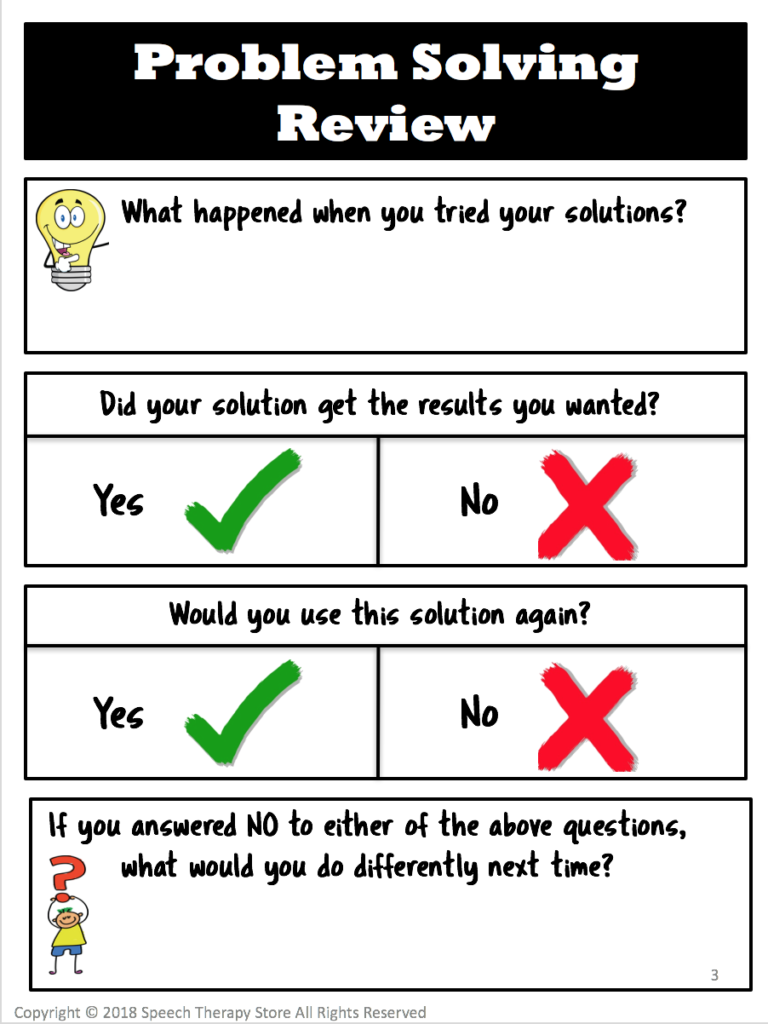
Problem Solving Review Form
After your students go through the social problem-solver have them use the social problem-solving review form.
- What happened. For instance, after your student tried their solution have them explain what happened next.
- Review the results. Also, have your student identify whether or not their solution got them the results they wanted.
- Use this solution again. Furthermore, have your student identify whether or not they would use this solution again in the future to solve the same or similar problem.
- What would you do differently? Finally, have your student explain what they would do differently if they didn’t get the results they wanted or if they wouldn’t use that solution again in the future.
71+ Social Problem Scenarios + 6 Blank Scenarios
Use the 71 social problem-solving scenarios to have your students get great experience practicing how to solve a social problem.
Also, included are 6 blank scenarios. Then laminate them so you can use them over and over again. Therefore, create social problems that the student experiences and needs help solving.
Wordless Video teaching Problem Solving
Watch this super cute wordless animation with your students and have them discuss the problem they see and how to best solve the problem.
Use this as a fun practice example to get your students started towards learning how to problem-solve.
Demonstrate Through Modeling
Model and discuss empathy.
First and foremost, children need to understand how another person might be feeling in a given situation in order to become a good social problem solver. The student needs to learn how to “stand in someone else’s shoes” for a little bit.
One way you can work on this skill is during the reading time you can focus on how a particular character in the story might be feeling.
Ask questions, such as:
- “How do they feel right now?”
- “How would you feel in that same situation?”
- “Why do you think they feel that way?”
Model Problem-Solving Skills as the Teacher
When you are faced with a problem you can solve the problem by thinking aloud for the students to hear how you solve a problem.
You can state the problem, then come up with possible solutions, then identify the possible consequences to each solution, then pick and explain why a solution is the best option.
For example, you could say, “I was hoping to take the class outside for a stress walk around the track before the reading test, but the problem is that it is raining outside. I could still take you outside, but then you will get wet, or we could walk the halls, but then we’d have to be really quiet because there are other classes learning, or we could just skip the walk and take the reading test, but then you might not do as well on the test. I think based on all of those solutions the best solution will be to walk the hallway, but you guys will have to promise to be quiet so that we don’t disrupt other classes.
Modeling the problem-solving process can be very helpful for the students to watch, observe, and later implement themselves.
Teach Communication
Have students communicate how they are feeling.
Teaching your students to share their emotions in a respectful way can improve their ability to problem-solve.
Have students use an “I” sentence frame, such as, “I feel _____ (insert feeling word) when _____ (identify what made you feel that way).”
For example, “I felt sad when Jackson broke my favorite pencil” or “I was mad when I wasn’t picked to be first in line.”
This way students can communicate how they are feeling using honest and open communication. Teaching students to appropriately communicate their emotions can help solve some social problems from the beginning.
Encourage Independency
Encourage your student to problem solve.
If your student is struggling to problem solve independently encourage them to do so using open-ended questions.
- “How could you fix this problem?”
- “What would be a fair solution?”
- “What would happen if you used that solution?”
Let the Student try to Problem Solve Independently
Give your students the space to try and solve their own problems using the guided strategies. Try not to come running to their rescue for every little problem.
Some problems are small and a great opportunity for the student to learn and practice. If an adult does all of the problem solving for a student then what are they really learning?
Give your students the time and space they need to practice solving small problems on their own. Of course, if it is a bigger or more serious problem then have an adult help guide the problem-solving process.
Tell an Adult
Remind your students that there are still some problems that are too big for them to solve on their own and that it is okay to get help from an adult to solve big problems.
For example, if the student doesn’t feel safe, someone is being hurt physically or emotionally, or if they tried to solve a problem independently but it didn’t work and they need help. Let them know that it’s okay to tell an adult.
Teach How to Disagree and How to Make Up
Discuss how to disagree respectfully.
Remind your student that they won’t always agree with their teacher, friends, classmate, or parents and that’s okay. Even the people we like might have different opinions, interests, and likes than we do.
However, even if we disagree with someone we should still treat them with respect. Treating someone with respect means to not call them names, ignore them, yell or hit them. It means that you do try to create solutions that both parties can agree with and to apologize when we hurt others’ feelings.
Role-Play How to Make Up
Practice in everyday life how to make up after a social problem .
Students are really having to stretch their brains today. It's @NSPCC #NumberDay and @problemsolveit are challenging Y9 and 10 to solve the escape room boxes. It's not as easy as it looks! The promise of a few sweet treats for the winners seems to be helping though! pic.twitter.com/AxRRJnJIv2 — CongletonHS (@CongletonHS) February 2, 2018
Be sure to get your free social problem solver today below! I hope you and your students love this freebie.
Have your students use task card scenarios to help them identify how they and others might feel in different social scenarios. Be sure to discuss the problem, identify possible solutions, identify the consequences of those possible solutions, and then based on those consequences pick the best solution.
Make social problem-solving a game by telling the students that they are social detectives and that it is their job to use what they know about social rules to help them identify the possible and best solutions.
Start practicing today with 71+ free social problem social task cards! Do your students need more practice?
Be sure to check out my other freebie for 31 wordless animated videos to teach problem-solving and so much more.
Make Problem Solving Easier with this Freebie!
Download yours today to get started.
Get More Problem Solving Time Saving Materials
Next, be sure to check out the following time-saving materials to continue to teach your students how to solve their social problems in addition to this freebie.
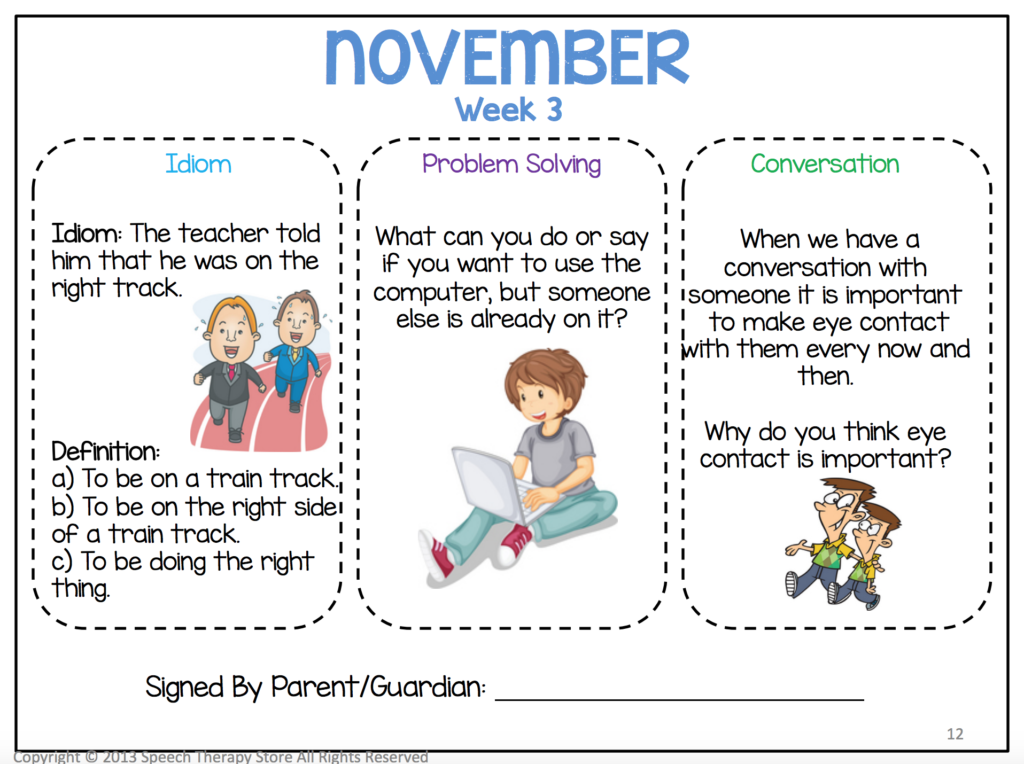
Weekly Social Pragmatics Homework

- Weekly problem-solving. Send home a weekly homework page that includes a problem-solving scenario plus an idiom and a conversational practice scenario.
Restorative Justice Problem Solving Flip Book

- Restorative justice graphic visual. Use this graphic visual to help your student restore a social relationship after a social problem.

Self-Advocating Role-Play Scenarios

- Self-advocating in high school. Teach your high schoolers the process to self-advocate for what they need.

5th-12th Grade Life Skills Problem Solving

- Life skills problem-solving. In addition, this life skills differentiated bundle includes a problem-solving lesson plan.
I recommend you read Problem Solving Wheel: Help Kids Solve Their Own Problems , 61+ Free Fillable SLP Planner Pages 2020-2021 , 430+ Free Multisyllabic Words List Activity Bundle , or 432+ Free IEP Goal Bank to Save You Time posts because they include freebies as well and who doesn’t want more freebies!
Got questions? Leave a comment. Let’s chat!
Monday 30th of January 2023
Hello! I have entered my name and email twice (yesterday & today) to receive to 71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Senarios, but I have not received anything yet. Not even an email back to mine in order to subcribe. Thanks for your help! Tracy
Melissa Berg
Tuesday 31st of January 2023
Hi Tracy, Thanks so much for reaching out! Sorry about that. We went ahead and sent you an email with the PDF attached. Wishing you all my best, Melissa
Problem Solving Skills
Tuesday 30th of August 2022
I truly love your site. Excellent colors, theme and writing. Thanks for sharing.
Laura Ricca
Monday 11th of April 2022
Tuesday 12th of April 2022
Hi Laura, I'm glad you found this resource helpful. Melissa
Modified Mental Health and Suicide Prevention - Speech Therapy Store
Monday 11th of May 2020
[…] 71+ FREE SOCIAL PROBLEM-SOLVING SCENARIOS […]
Problem Solving Wheel: Help Kids Solve Their Own Problems - Speech Therapy Store
Monday 4th of May 2020
[…] 71+ Free Social Problem Solving Task Cards Scenarios […]
11 Social Skills Worksheets for Seamless Social Interactions

And that’s okay.
All of us, at times, experience similar feelings and find making conversation difficult while we struggle to leave a good impression (MacLeod, 2018).
Social problems can be helped. Shyness and anxiety can be identified and managed, and conversation skills can be practiced and improved.
This article provides a wealth of worksheets for building and developing social skills in children, students, and adults. You can practice them individually, in counseling, and in group sessions to become socially skilled.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Relationships Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients build healthy, life-enriching relationships.
This Article Contains:
2 best social skills worksheets for adults, developing social skills: 3 worksheets for children, 4 best activities for children and teenagers, helpful worksheets for students, 3 cbt worksheets to use with clients, group counseling activities, a look at social skills training in the workplace, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
“After you accept that you’re still going to encounter some social unease from time to time, your aim should be to become socially functional” (MacLeod, 2018, p. 48).
The following are a few worksheets that cover a wide range of social skills and considerations and, when practiced, help increase self-knowledge and social awareness.
How to Support Your Friends
Friends are a crucial part of your social network. While they can provide valuable support mechanisms for you, you must equally be there for them when they need your help (Wendler, 2020).
The How to Support Your Friends worksheet examines a situation when a friend needed your support.
- How did you respond?
- How can you help them in the long term?
- How can you practice self-care?
When providing support, it is essential that you (Wendler, 2020):
- Remain present
- Remember, this is not about you
- Offer support rather than solutions
- Accept their feelings, rather than tell them how to feel
- Try not to panic
Healthy Relationships involve both giving and receiving, and an awareness and consideration of everyone’s needs.
High- and Low-Energy Social Skills
Social skills involve a great deal of nonverbal communication , such as how we stand, how loud we speak, and even the way we tilt our heads. Such cues can provide physical indicators of empathy and help show whether we are currently high or low in energy (Wendler, 2020).
One vital way to improve our social skills is to match our energy with our partner’s or the group we find ourselves in. For example, if we enter a meeting and everyone is excited about a new product launch, low energy may mean we fail to appear part of the team.
The High- and Low-Energy Social Skills worksheet helps us consider the energy exhibited by ourselves and others and whether we match those around us.
Think of a time when a friend, colleague, partner, or group was high in energy. How did you respond? High energy or low energy?
If you matched their energy, it showed empathy and most likely helped you mix and improve your social skills.
Note that there will be times when your circumstances or events prevent you from energy matching, and it is important to practice self-care.

The following worksheets are helpful exercises for children learning to be more socially adept and communicate successfully.
Self-Awareness for Children
Becoming more self-aware involves recognizing feelings, thoughts, and their impact on behavior (Fleming, 2021). Developing self-awareness can help children in social settings interact and be sure their needs are not overlooked.
The Self-Awareness for Children worksheet practices self-awareness and self-knowledge by asking the child (or group of children) a series of questions regarding how they are feeling and what they are thinking.
Becoming more self-aware can increase the child’s empathy and understanding of their own and others’ hopes, wishes, and needs.
Responsible Decision-Making for Children
Making a decision can be stressful, and not making one can be worse. Our choices often have social implications, building or damaging relationships, so they need to be taken carefully (Peters, 2018).
The Responsible Decision-Making for Children worksheet prompts the child to reflect on the likely social implications of their choices and how to show respect to themselves and others.
The important decisions we make can have far-reaching impacts. We should give ourselves time to gather information, consider the options and their impact, and seek the help needed.
Good Choices – Bad Choices for kids
When children have friends making bad choices that are potentially detrimental to themselves and the social groups around them, it can be all too easy to follow suit (Daniels & Rabar, 2019).
The Good Choices – Bad Choices worksheet can help children reflect on their friends’ poor decisions and how to react to the social pressure and the situation.

Download 3 Free Positive Relationships Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients to build healthy, life-enriching relationships.
Download 3 Positive Relationships Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Activities where children visualize, role-play, or work through social interactions and engagements can develop their understanding, awareness, self-confidence, and self-knowledge.
And “like any other skill, practice makes perfect” (Daniels & Rabar, 2019, p. 13).
The following activities can be adjusted according to the child’s age and should include appropriate support and supervision (modified from Daniels & Rabar, 2019):
- Going blindfolded A lack of social skills can feel like walking around blindfolded. Find somewhere safe where the child feels comfortable. Blindfold them and ask them to attempt to make their way toward the door.
Once finished, tell them that, as with walking blindfolded, you may find you bump into things, sometimes feel lost, and need a little help as you develop your social skills.
- People watching Creating narratives can help make sense of a complex social environment. Find a safe location where you can watch people and their lives drift by (perhaps a cafe or transit station). Ask the child to choose a person or couple and make up a story about their lives, including where they are going and why.
Ask the child to say what they saw and heard that helped them make up the story.
- Questions to start conversations Striking up conversations with people they don’t know can be difficult for children (and adults too).
Sit with the child and write down a list of questions that could be helpful when starting conversations in various situations, for example:
Do you have any pets? What are their names? How was your weekend? What did you do?
Then practice the questions and conversation building in pairs.
- Throwing it back It is useful to learn how to keep a conversation going. Explain to the child that one of the easiest ways to continue a conversation is when someone asks you a question, answer it, and then throw another one back. It’s like catching and throwing a ball.
Practice making up situations, questions, and answers in pairs.
For example:
What are you up to over the weekend? I am going swimming. What about you?
It’s a simple trick and can lead to the next point for discussion.

But it takes practice, and mistakes are inevitable.
The following two worksheets consider what friendship means to the individual and help clarify their self-concept.
What Does Friendship Mean to Me?
Use the What Does Friendship Mean to Me? worksheet to reflect on why friendship is so important to the individual. While increasing feelings of relatedness and closeness, understanding friendship can also help clarify social interactions and keep individual needs in mind.
Use this awareness to appreciate your friends and recognize when people are not showing you friendship.
Self-Concept for Conversations
Conversation is easier when you can speak clearly about who you are.
Use the Self-Concept for Conversations worksheet to summarize how you think about yourself. An explicit self-concept will make it easier to introduce yourself in social situations.
Revise the answers before meeting others in a social environment. They can lead to further conversations.
How to comfort a friend who is hurting (exactly what to say) – How Communication Works
Adopting the right mindset is crucial for dealing with anxiety, shyness, and the lack of confidence that causes social discomfort (MacLeod, 2018).
It’s important to recognize that it is not always the situation that causes the problem, but our beliefs regarding that situation.
The following worksheets provide three valuable techniques for considering and replacing unhelpful thinking:
- ABC Functional Analysis By understanding both the causes and the effects of your client’s behavior , you can help them recognize social behavior standing in the way of their goals.
- Coping Styles Formulation When confronted with challenging social situations, we sometimes attempt to escape or put up defenses. Understanding the problem and the existing coping style makes it possible to develop more adaptive coping strategies.
- Graded Exposure Therapy Social situations can lead to fear and avoidance. Safe environments can be created to manage exposure and learn how to become more comfortable in difficult situations.

Sharing our insecurities
Discussing real or imagined socially awkward or difficult situations can help us understand our own and others’ fears and reflect on our coping strategies.
Within the group, discuss the following points and their impact (modified from MacLeod, 2018):
- Accept that nervousness comes from valued goals Discomfort can be put in perspective and may even be worthwhile if pursuing something meaningful.
- Accept that it’s okay to show what you are experiencing When we stop worrying whether we appear nervous or scared, anxiety loosens its grip.
- Tell people when you feel shy or insecure Most people have been through similar experiences. Casually share your concerns and move on.
- Recognize that it’s normal to get nervous There is nothing wrong with you. As humans, we are set up to have these feelings. Permit yourself to have them.
Ask the group to share experiences to normalize their insecurities.
Coping with social anxiety
A group setting is a great place to discuss complex social situations that cause anxiety and shyness. Individuals can share helpful strategies they adopt to manage difficult thoughts and feelings.
Discuss within the group how the following might help (modified from MacLeod, 2018):
- Riding out the symptoms We don’t always need to escape or avoid the situation. For example, leading up to a presentation, nervousness may boost your energy and invigorate what you share.
- Challenging your thinking Question whether the thinking that is feeding your anxiety is valid or helpful. Challenging your thoughts can reduce their effect.
- Distracting yourself Find something else to focus on. Thinking through the plot of a favorite film, playing through a cherished piece of music in your head, or thinking about your children can take the focus off what is causing you upset and give you time to become calm.
- Breathing exercises Breathing exercises where you breathe out more slowly than you breathe in can engage the parasympathetic system and settle your mind and body (Nestor, 2020). Take a few slow, deep breaths. Make the out-breath slow through pursed lips if it helps.
Ask the group to share other communication techniques that help them through social situations.
Telling a good story
Sharing personal stories can be a great way to build connections with the people you meet. However, start small. Begin with a semi-personal story and see how they react (Wendler, 2020).
Daniel Wendler (2020) suggests making the story enjoyable by sharing what was going on in your head at the time, rather than simply the facts. It will help the listener experience the narrative and build a connection with you.
Once finished, rather than continue by telling another story, share the spotlight so that everyone gets a turn.
The Telling a Good Story worksheet can help you think about the stories you could share in a social situation and identify the points to cover. Practice them with a partner or in front of the group and ask for their open and honest feedback. Not only is this practice helpful, but it provides valuable insight into what works well and what doesn’t.
Gaining valuable emotional awareness can help us relate to others personally and professionally. While emotional intelligence training benefits social skills in general, it is particularly valuable in the workplace (Goleman, 2018).
Here are some particularly relevant training options:
- Emotional Intelligence Masterclass© Our masterclass is a complete, six-module emotional intelligence training template for helping professionals to understand and use their emotions in life-enriching ways. This masterclass will provide you with all the tools, materials, and knowledge required to make an impactful difference.
- EI Masterclass: Embodied Emotional Intelligence Beyond EI teaches the principles behind emotional intelligence and how to practice them. You will learn to become more aware of what provides meaning in your own life while regaining control.

17 Exercises for Positive, Fulfilling Relationships
Empower others with the skills to cultivate fulfilling, rewarding relationships and enhance their social wellbeing with these 17 Positive Relationships Exercises [PDF].
Created by experts. 100% Science-based.
Improving social skills makes it possible to strengthen communication with friends, family, and colleagues and build stronger, enduring relationships.
Why not download our free emotional intelligence tool pack and try out the powerful tools contained within? Some examples include:
- Building Emotional Awareness Use this valuable script and audio to foster your emotional intelligence by mindfully attending to current emotional states.
- Decoding Emotions by Analyzing Speech, Body, and Face Accurately perceiving and understanding people’s emotions is a core component of emotional intelligence.
Other free resources include:
- Conflict Resolution Checklist This 10-item checklist is a valuable method for ensuring conflict is resolved.
- TRAPS to Avoid and TIPS for Success Adopt these helpful tips to avoid closed thinking and put in place productive, positive, and receptive communication
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but they are described briefly below:
- Small Talk to Build Connection
This tool helps people connect through practicing small talk with people they don’t yet know.
Many of us opt to keep to ourselves rather than strike up a conversation with a stranger, but it doesn’t have to be this way.
- Step one – Identify the reasons for avoiding small talk.
- Step two – Choose a context for engaging in small talk.
- Step three – Find a topic for making the connection.
- Step four – Find a time and a place to practice the approach.
The final stage is to evaluate the success of the approach.
- Team Branding
Perceived, rather than actual, team branding is crucial for effective team performance.
We can foster team interactions by creating team identity.
- Step one – In small groups, identify the team’s strengths.
- Step two – Gather all the responses into cohesive headings.
- Step three – Assign each small group a task such as creating a team name, slogan, mission statement, etc.
- Step four – Have each team present their findings.
Reflect on the new team identity.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others build healthy relationships, this collection contains 17 validated positive relationships tools for practitioners. Use them to help others form healthier, more nurturing, and life-enriching relationships.
Feeling socially uncomfortable – shy, nervous, and awkward – can prevent us from reaching our social and professional potential.
While it is something all of us have faced, we can work through it and build skills for seamless social interactions.
First, we must recognize that we are not likely to remove all of our insecurities. Second, we should remind ourselves that all of us feel a degree of discomfort at times, and it does not have to ruin social engagement.
Importantly, we should remember that social interactions require balance. Taking turns with the spotlight is crucial, and so is focusing on the needs of the parties involved.
We must also consider energy levels, self-awareness, the choices we make, and our self-concept if we are to build lasting, deep relationships with those we meet.
While getting to know new people is not easy, the investment is worthwhile, and practice will make it easier.
This article contains plenty of worksheets and tools to get you started and maintain your journey toward building the social skills to lead the life that is right for you. Good luck.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Relationships Exercises for free .
- Daniels, N., & Rabar, S. (2019). Social skills activities for kids: 50 Fun activities for making friends, talking and listening, and understanding social rules . Rockridge Press.
- Fleming, S. (2021). Know thyself . Basic Books.
- Goleman, D. (2018). The first component of emotional intelligence. In Self-awareness (pp. 1–10). Harvard Business Review Press.
- MacLeod, C. (2018). The social skills guidebook: Manage shyness, improve your conversations, and make friends, without giving up who you are . Author.
- Matson, J. (2018). Handbook of social behavior and skills in children . Springer.
- Nestor, J. (2020). Breath: The new science of a lost art . Penguin Books.
- Peters, S. (2018). The silent guides: Understanding and developing the mind throughout life . Lagom.
- Wendler, D. (2020). Improve your social skills . Author.
Share this article:
Article feedback
Let us know your thoughts cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Enmeshment: Breaking Free From Overbearing Relationships
When boundaries are unclear, particularly in families, relationships can become overbearing, with individuals experiencing a diminished sense of self (Bacon & Conway, 2023). In such [...]

Can a Disorganized Attachment Style Be Overcome?
No individual needs to be defined by the actions or behavior of their parents. However, the attachment strategies we form early in our lives for [...]

Setting Boundaries: Quotes & Books for Healthy Relationships
Rather than being a “hot topic,” setting boundaries is more of a “boomerang topic” in that we keep coming back to it. This is partly [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (21)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (44)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Positive Relationships Exercises Pack
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » General » High School Social Problem Solving Lesson Plan

High School Social Problem Solving Lesson Plan

Why Focus on High School Social Problem Solving?
High school students need to develop resilience, empathy, assertiveness, and decision-making skills for productive social interactions. This High School Social Problem Solving Lesson Plan aims to facilitate that growth. It’s a surefire way to empower your students, boosting their confidence and overall mental well-being. Download this free worksheet mentioned in the lesson plan below.
Breaking Down the High School Social Problem Solving Lesson Plan
Let’s delve into the specifics of this lesson plan designed to develop social problem-solving skills in high school students. The beauty of this plan is that it requires no prep-time – you can dive right in!
Objective: To empower high school students with the essential strategies for solving social problems, making informed decisions, empathizing with others, and communicating assertively.
Materials: None – this is a discussion-based activity.
Duration: Roughly 1 hour
1. Identifying Social Problems (10-15 minutes)
Start with a discussion about the social problems high school students may encounter. This can be conducted in small groups or pairs.
2. Empathizing: Understanding Different Perspectives (10-15 minutes)
Choose a few scenarios from the previous discussion. Invite students to consider the various perspectives involved, promoting empathy and understanding.
3. Generating Solutions: Creative and Critical Thinking (10-15 minutes)
Now, guide students to brainstorm possible solutions for the chosen scenarios. Encourage them to consider the potential outcomes of each approach.
4. Decision Making: Evaluating Solutions (10-15 minutes)
Discuss the potential consequences of each solution. Teach students to weigh the pros and cons of each option, enabling them to make sound decisions.
5. Reflection: Learning Takeaways (5 minutes)
End with a reflection session. Invite students to share what they’ve learned and how they plan to apply these skills in real life.
Quick, No-Prep High School Social Problem Solving Activities
- Role-Play Scenarios: Use role-playing to allow students to practice social problem-solving skills in real-time.
- Daily Dilemmas: Start each session with a social problem or dilemma for students to solve, fostering practical learning.
- Interactive Games: Incorporate games like ‘what would you do if…’ or ‘social problem-solving charades’ to make the learning process more engaging.
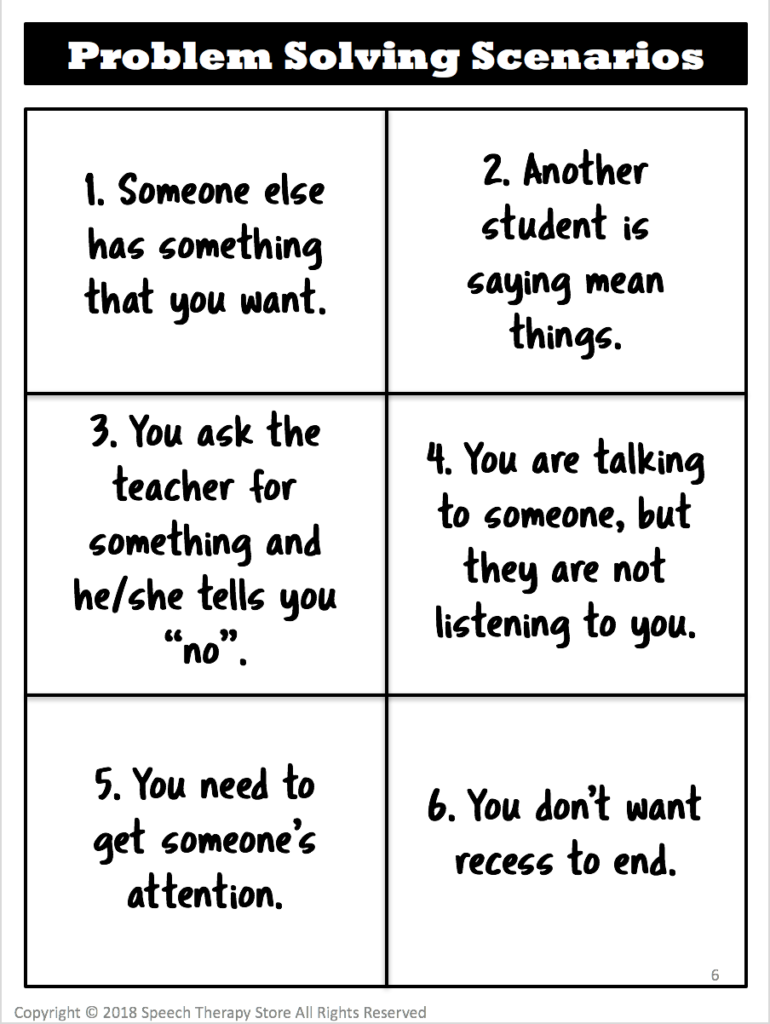
- Everyday Speech Printable Problem-Solving Worksheet: Download the worksheet at the top of this post, discuss the five scenarios given, and have your students focus on coming up with multiple solutions, not just one for each problem.

Sample Video
Students learn best from watching real students their own age model skills. Try out this sample video-modeling lesson below. We offer our entire Social-Emotional Learning platform free for 30 days here !
Related Blog Posts:
Free High School Problem Solving Material
Free High School Conversation Skills Material
Looking for free social skills samples click here.

Free Elementary Play Skills Lesson
The playground is more than just a place for physical activity; it's a social hub where important life lessons unfold. For special educators, teaching students to include everyone on the playground is vital in fostering an environment of empathy and respect. Keep...
Free Elementary Perspective Taking Goal Poster
Download Activity and Lesson Plan In need of a resource for teaching perspective-taking to your elementary students? Look no further, download our free elementary perspective-taking goal poster! Teaching Perspective Taking to Elementary Students You can successfully...
Free Elementary Handling Change Lesson
Navigating the emotional waves of the classroom is a daily reality for elementary students. As special educators, teaching them how to self-regulate using tools like Everyday Speech's "Self-Controller Scanner" can be game-changing. Keep reading for a free elementary...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Social Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
- Identifying and Structuring Problems
- Investigating Ideas and Solutions
- Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The SkillsYouNeed Guide to Interpersonal Skills

Social problem-solving might also be called ‘ problem-solving in real life ’. In other words, it is a rather academic way of describing the systems and processes that we use to solve the problems that we encounter in our everyday lives.
The word ‘ social ’ does not mean that it only applies to problems that we solve with other people, or, indeed, those that we feel are caused by others. The word is simply used to indicate the ‘ real life ’ nature of the problems, and the way that we approach them.
Social problem-solving is generally considered to apply to four different types of problems:
- Impersonal problems, for example, shortage of money;
- Personal problems, for example, emotional or health problems;
- Interpersonal problems, such as disagreements with other people; and
- Community and wider societal problems, such as litter or crime rate.
A Model of Social Problem-Solving
One of the main models used in academic studies of social problem-solving was put forward by a group led by Thomas D’Zurilla.
This model includes three basic concepts or elements:
Problem-solving
This is defined as the process used by an individual, pair or group to find an effective solution for a particular problem. It is a self-directed process, meaning simply that the individual or group does not have anyone telling them what to do. Parts of this process include generating lots of possible solutions and selecting the best from among them.
A problem is defined as any situation or task that needs some kind of a response if it is to be managed effectively, but to which no obvious response is available. The demands may be external, from the environment, or internal.
A solution is a response or coping mechanism which is specific to the problem or situation. It is the outcome of the problem-solving process.
Once a solution has been identified, it must then be implemented. D’Zurilla’s model distinguishes between problem-solving (the process that identifies a solution) and solution implementation (the process of putting that solution into practice), and notes that the skills required for the two are not necessarily the same. It also distinguishes between two parts of the problem-solving process: problem orientation and actual problem-solving.
Problem Orientation
Problem orientation is the way that people approach problems, and how they set them into the context of their existing knowledge and ways of looking at the world.
Each of us will see problems in a different way, depending on our experience and skills, and this orientation is key to working out which skills we will need to use to solve the problem.
An Example of Orientation
Most people, on seeing a spout of water coming from a loose joint between a tap and a pipe, will probably reach first for a cloth to put round the joint to catch the water, and then a phone, employing their research skills to find a plumber.
A plumber, however, or someone with some experience of plumbing, is more likely to reach for tools to mend the joint and fix the leak. It’s all a question of orientation.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving includes four key skills:
- Defining the problem,
- Coming up with alternative solutions,
- Making a decision about which solution to use, and
- Implementing that solution.
Based on this split between orientation and problem-solving, D’Zurilla and colleagues defined two scales to measure both abilities.
They defined two orientation dimensions, positive and negative, and three problem-solving styles, rational, impulsive/careless and avoidance.
They noted that people who were good at orientation were not necessarily good at problem-solving and vice versa, although the two might also go together.
It will probably be obvious from these descriptions that the researchers viewed positive orientation and rational problem-solving as functional behaviours, and defined all the others as dysfunctional, leading to psychological distress.
The skills required for positive problem orientation are:
Being able to see problems as ‘challenges’, or opportunities to gain something, rather than insurmountable difficulties at which it is only possible to fail.
For more about this, see our page on The Importance of Mindset ;
Believing that problems are solvable. While this, too, may be considered an aspect of mindset, it is also important to use techniques of Positive Thinking ;
Believing that you personally are able to solve problems successfully, which is at least in part an aspect of self-confidence.
See our page on Building Confidence for more;
Understanding that solving problems successfully will take time and effort, which may require a certain amount of resilience ; and
Motivating yourself to solve problems immediately, rather than putting them off.
See our pages on Self-Motivation and Time Management for more.
Those who find it harder to develop positive problem orientation tend to view problems as insurmountable obstacles, or a threat to their well-being, doubt their own abilities to solve problems, and become frustrated or upset when they encounter problems.
The skills required for rational problem-solving include:
The ability to gather information and facts, through research. There is more about this on our page on defining and identifying problems ;
The ability to set suitable problem-solving goals. You may find our page on personal goal-setting helpful;
The application of rational thinking to generate possible solutions. You may find some of the ideas on our Creative Thinking page helpful, as well as those on investigating ideas and solutions ;
Good decision-making skills to decide which solution is best. See our page on Decision-Making for more; and
Implementation skills, which include the ability to plan, organise and do. You may find our pages on Action Planning , Project Management and Solution Implementation helpful.
There is more about the rational problem-solving process on our page on Problem-Solving .

Potential Difficulties
Those who struggle to manage rational problem-solving tend to either:
- Rush things without thinking them through properly (the impulsive/careless approach), or
- Avoid them through procrastination, ignoring the problem, or trying to persuade someone else to solve the problem (the avoidance mode).
This ‘ avoidance ’ is not the same as actively and appropriately delegating to someone with the necessary skills (see our page on Delegation Skills for more).
Instead, it is simple ‘buck-passing’, usually characterised by a lack of selection of anyone with the appropriate skills, and/or an attempt to avoid responsibility for the problem.
An Academic Term for a Human Process?
You may be thinking that social problem-solving, and the model described here, sounds like an academic attempt to define very normal human processes. This is probably not an unreasonable summary.
However, breaking a complex process down in this way not only helps academics to study it, but also helps us to develop our skills in a more targeted way. By considering each element of the process separately, we can focus on those that we find most difficult: maximum ‘bang for your buck’, as it were.
Continue to: Decision Making Creative Problem-Solving
See also: What is Empathy? Social Skills
Second Step® Sample Lessons
Complete sets of materials from select Second Step curricula, the Second Step® Bullying Prevention Unit, and the Second Step® Child Protection Unit are available for Early Learning through Grade 8.
Digital Programs
Classroom kits.
Bullying Prevention Unit (Available for Kindergarten–Grade 5)
Child Protection Unit (Available for Early Learning–Grade 5)
Out-of-School Time (Available for Kindergarten–Grade 5)
Available for Kindergarten through Grade 12 Explore samples from all grades below
Kindergarten
Lesson 18: Apologizing Can Help

In this lesson, students will learn about apologizing as a way of showing kindness and as a tool for problem-solving in a variety of scenarios. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation
Lesson 9: Feeling Frustrated

In this lesson, students will learn which clues tell them when others might be frustrated, and a new way to feel calm when they’re feeling frustrated themselves. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation
Lesson 16: The Way to Say a Problem

In this lesson, students will start learning to be better problem-solvers by managing strong feelings and stating problems without blame. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation Lesson Handout (PDF)
Lesson 14: Asking Questions
In this lesson, students will learn about asking questions to find out how someone else is feeling and to understand what their friends might want or need. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation Lesson Handout (PDF)
Lesson 17: Saying It Respectfully

In this lesson, students will learn how to consider another person’s point of view and to say what they want or need in a respectful way. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation Lesson Handout A (PDF) Lesson Handout B (PDF)
Lesson 17: When? Where? Who?

In this lesson, students will learn how to identify when and where to work on solving a problem, and who should be included. Lesson Plan (PDF) Lesson Presentation
Unit 4, Lesson 23: Respectful Communication

In this lesson, students will learn ways to communicate during a conflict to keep it from escalating through reflecting on their own experiences, defining respectful communication, and practicing using language that will help resolve conflicts. Sample This Lesson Lesson Plan (PDF) Student Handout (PDF)
Unit 3, Lesson 18: Practicing Positive Self-Talk

In this lesson, students will learn how to use positive self-talk to reframe challenging situations, including discussing why it isn’t always easy to see the positives and practicing noticing the positive things in their everyday lives. Sample This Lesson Lesson Plan (PDF) Student Handout (PDF)
Unit 2, Lesson 10: Environmental Factors that Contribute to Bullying

In this lesson, students will learn how the physical layout of and rules within a space can make bullying and harassment more likely to happen, from identifying environmental factors to discussing rules and regulations within their own school community. Sample This Lesson Lesson Plan (PDF) Student Handout (PDF)
High School
Schoolwide Practice
Recognizing Contributions
In this practice, leaders publicly recognize students and staff for their remarkable contributions to the school community.
Pathway 3: Agency & Opportunity
Educator Practice
Choice Boards
In this practice, educators create materials to boost student engagement in an upcoming lesson by giving students choices in their approach to learning.
Student Activity
Guess Who?
In this activity, students guess each other’s strengths, then discuss and reflect on their own positive qualities.
Available for Early Learning through Grade 5 Explore samples from all grades below
Early Learning
Weekly Theme 6: Asking for What You Need or Want

Weekly Theme Card

Take-Home Activity

Brain Builder: Stop and Start
”How to Learn Song”

Listening Rules

Feelings Cards
Lesson 2: Focusing Attention

Weekly Lesson Card

Following Through Card

“The Learner Song”

Brain Builder: Follow, Follow

Skills for Learning Poster

Lesson 11: Showing Care and Concern

Brain Builder: Clap and Wait

Empathy Poster

Lesson 17: Solving Problems, Part 1

Skills for Learning

Brain Builder: Sentence Switcheroo

How to Calm Down Poster

Problem-Solving Steps Poster

“The Empathy Song”

Problem Solving with Anthony
Lesson 8: Accepting Differences

Brain Builder: Common Ground

Student Handout
Lesson 15: Handling Put Downs

Teaching the Lesson Card

Lesson 15 Video (Parts 1 & 2)

“Calm Down” Music Video
Lesson 21: Dealing with Peer Pressure

Lesson 21 Video (Parts 1, 2 & 3)

“Step Up” Music Video
Bullying Prevention Unit
Available for Kindergarten through Grade 5 Explore samples from Grades 2 and 5 below
Lesson 3: Refusing Bullying

Lesson Samples

Classroom Activity

Addy’s Story

Noah and Olivia
Child Protection Unit
Available for Early Learning through Grade 5 Explore samples from Early Learning and Grades 2 and 5 below
Weekly Theme 3: Safe and Unsafe Touches

Weekly Theme Samples

Ways to Stay Safe Poster
“The Safety Rules Song”
“Stop and Think”
Lesson 3: Safe and Unsafe Touches

“Three Ways to Stay Safe”
Lesson 3: Unsafe and Unwanted Touches

“I’m in Charge” Music Video
Out-of-School Time
Available for Kindergarten through Grade 5 Explore samples from Kindergarten and Grade 1 below
Kindergarten–Grade 1
Unit 1, Topic 2: Facing Challenges with Confidence

In this activity from the Growth Mindset & Goal Setting unit for Kindergarten–Grade 1, kids learn three strategies that can help them work through challenges and then use those strategies to build a tower from 10 random items.
Free Resources
Bullying Prevention Resources
Free Activities
Early, Open, Often
Abierto y a menudo
ParenTeen Connect

Problem Solving
Please note, all lessons and resources are supplemental to the Sarasota County Schools curriculum.

Self-Management Handouts
- Handout 1: What Can I Do? – Problem Solving Wheel
- Handout 2: SEL Core Competencies
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

How the US is destroying young people’s future - Scott Galloway
Lesson duration 18:38
4,394,366 Views

This piece of paper could revolutionize human waste
Lesson duration 05:35
2,566,283 Views

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
384,078 Views

How to clear icy roads, with science
Lesson duration 06:13
192,682 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
1,200,343 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
488,241 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
760,052 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
933,976 Views

What the fossil fuel industry doesn't want you to know - Al Gore
Lesson duration 25:45
743,624 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
738,529 Views

How the water you flush becomes the water you drink
Lesson duration 05:23
393,415 Views

The growing megafire crisis — and how to contain it - George T. Whitesides
Lesson duration 10:42
56,764 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
651,348 Views

4 epidemics that almost happened (but didn't)
Lesson duration 06:26
394,957 Views

The return of Mongolia's "wild" horses
Lesson duration 04:53
207,259 Views

Whatever happened to the hole in the ozone layer?
Lesson duration 05:13
527,602 Views

The most important century in human history
Lesson duration 05:20
341,020 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
1,064,245 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
108,536 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
43,684 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
80,674 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
782,497 Views

How college loans exploit students for profit - Sajay Samuel
Lesson duration 11:49
229,390 Views

What’s the smartest age?
1,606,790 Views
Learning goal: Problem solving
The ability to quickly and effectively solve problems plays a major role in classroom, college, and career success. Help your students develop these essential skills using the FutureFit resources collected under the “Solve” domain. Skills highlighted in this domain include process acumen, computational thinking, and design thinking.
At the practical level, Solve focuses on skills and abilities that blend well with both core academic concepts and broader social-emotional learning goals articulated by standards organizations, states, and researchers. We’ve meshed the best and most relevant concepts and approaches into an accessible list of skills that is easy to understand and articulate to students, including:
- Computational thinking : The ability to effectively formulate and frame problem-solving strategies that can be applied and carried out by computers, machines, or humans
- Process acumen : The ability to clearly and effectively define and implement replicable processes, as well as to communicate the associated tasks, roles and details to others
- Design thinking : The ability to learn and apply techniques common in solving complex problems (i.e. in engineering and science) to disparate or tangential circumstances and situations
- Solicit assistance : The ability to ask for help, assistance and expertise when one’s own limits become an impediment to progress
Recommended Solve Resources
TEACHING RESOURCE
Pattern Problem Solving: Teach Students to Find a Pattern in Math Problems
LESSON PLANS
Why Do Some Objects Fall Faster Than Others?

Problem-Solving
Math Problem Solving: The Guess and Check Method
Which Metal Corrodes the Fastest?
Do Objects Float Better in Salt Water Than in Fresh Water?
Problem Solving: Draw a Picture
Problem Solving: Choose the Operation
Salt or Sugar: Which Dissolves Faster in Different Liquids?

Analyzing Data
In Which Liquids Do Seeds Grow Best?

Easily Integrate SEL Into Your Existing Curriculum
Practicing Problem Solving Lesson
Does It Matter How Much Air Is in Your Basketball?
Problem Solving: Make a Table Math Strategy

Money Word Problems I (Grade 2)
What Materials Conduct Static Electricity Best?
Problem Solving: Use a Formula
What Foods Attract Ants?
Problem Solving: Eliminating Possibilities
Problem Solving: Simplify the Problem
Can Cloning Make a Better Plant?

Word Problems Involving Time I (Grade 5)

Your cookie preferences
In order to provide you with the best possible experience on the LifeSkills website we use cookies and similar technology to collect data from your device and browser while you are here. Collecting this data helps us to personalise content for you, understand how you use the website, allow access to social media features and deliver personalised service and advert message content. You can find out more in our Cookie Policy . Please select ‘Accept all’ to consent to us collecting your data in this way. To see other data collection options, select ‘Manage data preferences’.
The types of similar technologies used in this website fall into one of four categories - Strictly Necessary, Performance, Functionality & Profile and Targeting. You can find out more information in our Cookie Policy .
Please indicate the categories you wish to consent to by selecting ‘Manage data preferences’ and using the sliders below and then click “Save preferences” to retain your preferences for future visits. You can change these preferences at any time by clicking Cookie Policy on our website.
Strictly necessary
Data collected in this category is essential to provide our services to you. The data is necessary for the website to operate and to maintain your security and privacy while using the website. Data is not used for marketing purposes or for the purposes covered by the other three categories below. This category can’t be disabled.
Performance
These help us improve the experience for all users of the website. Data collected in this category is to inform us how the website is used, improve how our website works and to help us to identify issues you may have when using our website. This data is not used to target you with online advertising.
Data collected in this category is used to help make our messages more relevant to you. The data is shared with other third parties, such as advertisers and platforms we may use to deliver personalised advertisements and messages. If you don’t wish to consent to this category, it’s important to note that you may still receive generic advertising or service messages, but they will be less relevant to you
Functionality & Profile
Data collected in this category enables the website to remember choices you make. This means a more personalised experience for features of the website that can be customised. It may also be used to provide services you've asked for, such as watching a video or commenting on a blog.
For learners from school through to university and beyond
What stage are you at?
For people like teachers, youth group leaders, mentors, local authorities, charities, job centre staff, and parents or carers
Work with a group or a class
Coach an adult
Tools, tips and activities to help your family
Resources for educators
- Login Sign up for free
Save to a group
Would you like to create a subgroup to help organise your saved items?
- I'm here to help others
- Lesson plans
Problem solving
Problem solving lesson plan
Time to complete
Download the full lesson plan pack including all related resources
Choose to download one or more individual resources
Problem Solving: Lesson plan
Problem solving: Presentation slides
Demonstrating your skills quick fire activity
Problem solving in practice: Interactive worksheet
Our problem solving content focuses on one of these skills and develops understanding of the six stages of problem solving, as well as identifying different types of situations in which young people might already be using these skills. Furthermore, it encourages them to use an adaptive approach, explaining that different types of problems can be approached in different ways.
The activities on this page support your teaching of these skills through an independent activity, quick activities or a full length, curriculum-linked lesson plan.
Teaching resources:
- Problem solving: Lesson plan and presentation slides – full lesson plan including icebreaker for use with a group of students in the classroom
- Demonstrating your skills: Quick-fire activity – 10 minute activity for a group of students in the classroom, can be used as an icebreaker for the lesson plan
- Problem solving in practice: Interactive worksheet – activity for independent learning whether remote or in class
Lesson plan
(60 -75 minutes)
This lesson is designed to equip young people with an adaptable approach to solving problems, large or small. It includes a short film and scenarios that encourage development of practical problem solving skills which can be useful for learning, day to day life, and when in employment.
By the end of the lesson, students will be able to:
- Identify problems of different scales and what is needed to solve them
- Illustrate the use of an adaptable approach to solving problems
- Understand that problem solving is a core transferable skill and identify its usefulness in a work setting
- Work on a problem solving activity in a team
The lesson aims to reinforce students’ understanding of the potential future applications of this skill as they move into the world of work, particularly in an activity differentiated for an older or more able group on creating new opportunities.
Quick-fire activity
(5 - 10 minutes)
The demonstrating your skills quick-fire activity focuses on helping young people understand the key skills that are needed in the workplace, including the importance of problem solving.
Students will be asked to name the skills being demonstrated in a variety of scenarios, and identify ways they’re already using those skills in this short activity.
You might find it useful as a starter or icebreaker activity to begin a lesson, or at the end to allow students to put what they have just learnt in the Problem solving lesson into practice.
Interactive worksheet
(20 - 25 minutes)
Please note that students below the age of 14 cannot sign up for their own LifeSkills account. Any independent tasks must be printed or downloaded and provided digitally for them to complete as they are currently hosted on educator pages.
The Problem solving in practice interactive worksheet introduces some of the themes from the full lesson plan and gives students some practical strategies for problem solving, including introducing the six stages of problem solving. The worksheet can be printed or completed digitally, so can be used flexibly to give students practise putting their problem solving skills into action. You might choose to assign it:
- As homework following the Problem solving lesson
- For independent study
- For remote learning
Looking for more ways to boost self confidence with LifeSkills?
Other lessons that may prove useful for students to build on these activities include the Adaptability and Innovation and idea generation lessons. Alternatively, consider encouraging them to apply their skills through Steps to starting a business or the Social action toolkit .
Why not build problem solving in as a focus in your students’ wider curriculum? Refer to our Content guide to find out how this resources can be used as part of your teaching.
Curriculum tags
A free account gives you access to all educator content, tools and resources
Already have an account, get started, thank you for liking.
Help us to continue creating relevant content for you by leaving some additional feedback .
Additional feedback
All feedback will be anonymous and will help us to provide more effective content for you and your student.
Thank you for letting us know what you thought of .
Why not try one of these next?

Staying positive (resilience)
Staying positive and learning through experience are key to succeeding in challenging situations. Try this lesson and help your students succeed at work.

Good leadership styles and effective teamwork can help students excel in their future workplace. Read more about team leader skills in this lesson.

Social action toolkit
Build a comprehensive social action programme and support young people to access enriching experiences that build transferable skills for work.
A Blog About Parenting: Coping Skills, Behavior Management and Special Needs

20 Fun Conflict Resolution Activities for Kids (Printable PDF): Worksheets, Games and Activities

Conflict resolution activities for kids: In this post, we will explore different strategies to help kids deal with conflict. We will also list fun and easy activities that you can add to your conflict resolution lessons or use at home with your kids. And, at the end of the post, you will be able to download some conflict-resolution worksheets.
We all go through conflict and arguments in our everyday life. Learning healthy ways to handle conflict is an invaluable social skill to develop in our kids
Luckily, there are some really creative ways to help teach kids all about conflict resolution.
(Disclosure: We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. There may also be other affiliate links in this post. You can also read our Disclosure & Disclaimer policy here )
What is Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is the process used to manage or settle our differences using different conflict resolution strategies.
Ideally, we will try to achieve positive outcomes that will satisfy or be beneficial for all parties sides.
Conflict-resolution is similar to problem-solving. In conflicts though, we may see ourselves inundated with strong feelings (anger, frustration, sense of injustice).
Managing those feelings will be an important first step before we attempt an effective problem-solving strategy .
Conflict Resolution Techniques
There are different classifications that map conflict resolution styles and techniques.
We will briefly review a couple of them because they are a good foundation for understanding conflict resolution’s intricacies.
We’ll start with one of the most popular ones:
The Five Conflict-Handling Modes
Thomas (1976) classifies interpersonal conflict-handling behavior in a model with two basic dimensions:
- Assertiveness (attempting to satisfy our own concerns)
- Cooperativeness (trying to satisfy other people’s concerns too)
This two-dimensional model results in five conflict-handling modes:
- Collaborating (assertive & cooperative)
- Competing (assertive & non-cooperative)
- Compromising (an intermediate level of both assertiveness and cooperativeness)
- Avoiding (unassertive & uncooperative)
- Accommodating (unassertive & cooperative)
In plain words:
- Collaborating: kids look for ways to solve the conflict that bring the best outcome for both parties (the famous win-win situation)
- Competing: we only care about our own goals and are not trying to accommodate the needs of others
- Compromising: we try to look for a solution that may not be our preferred one but is acceptable for all parties involved
- Avoiding: one of the parties may not be as invested in the problem, or prefers to avoid confrontation, and decides to withdraw from the argument
- Accommodating: a kid may choose to neglect their own preferences to satisfy the preferences of the other person
Related Reading: How to Teach Assertiveness to Kids
Other Conflict Resolution Strategies
If we take into consideration the parties involved in a conflict, we could also list the following strategies:
- Negotiation
- Arbitration
- Litigation (which obviously does not apply to our topic here)
What would these look like for our kids: We will focus on how this translates to conflict resolution for kids:
- Negotiation: kids brainstorm satisfactory solutions to their problems and reach a win-win solution. If they can’t find a good solution, they may need to look for a compromise
- Mediation: when kids can’t resolve the conflict on their own, they may need a neutral third party (teacher, parent, caregiver) that helps them come up with a solution rather than imposing it.
- Arbitration: we would arrive here when kids can’t agree, so the neutral third party will need to put the argument to rest deciding on the best solution after listening to both sides.
Why is Conflict Resolution Important for Kids
Children need essential skills like navigating difficult situations to get a peaceful solution.
Benefits to developing conflict resolution skills:
- develop communication skills
- strengthen friendships
- learn goal setting
- solve conflicts in a peaceful way
Conflict resolution requires the development of a number of social skills like:
- problem-solving
- managing negative feelings and big emotions
- collaboration
- flexible thinking
- compromising
- effective communication
- acceptance of diversity
It is when someone in a conflict situation takes the time to consider the emotions of everyone else involved. If kids are able to develop this skill through effective communication and strong emotional intelligence , it will help them solve problems in a more effective way throughout their life.
There are many ways to help kids grow their ability to resolve conflict that can be fun and informative. Keep reading to learn some of the most popular conflict resolution activities…
Healthy Ways to Deal with Conflict
There are healthy and unhealthy ways to deal with conflict.
These are some examples of unhealthy ways kids can use to deal with conflict:
- Not caring about the other person’s view
- Holding a grudge
- Big emotional reactions like getting very angry, shouting, calling names, threatening
- Not being able to compromise
- Giving up on something that is important to you
Examples of healthy ways to approach conflict may include:
- Caring about the other person’s view
- Using your calm and assertive voice to express your feelings
- Not taking things too personally
- Learning to forgive
- Being able to compromise
- Working to find solutions that can accommodate both sides (negotiation)
20 Conflict Resolution Activities for Kids
Wondering how to teach conflict resolution to kids?
Discuss conflict at home or school. Choose topics from the news, a conflict at work, something that happened at school, or even made-up conflict scenarios.
Beyond having conversations, there are some great activities that kids can do individually or as a group to help foster this vital skill.
Here are 20 of the best conflict resolution activities for kids that can help build the valuable lifelong skill of resolving conflict peacefully.
The activities below fall under the following categories:
Conflict Resolution Worksheets
- Conflict Resolution Activities
- Conflict Resolution Games
Some of these activities will be a great addition to a lesson plan.

Conflict resolution is, in essence, a social problem-solving situation.
In this worksheet, we will follow the steps for problem-solving, with an important addition (calm-down):
- Calm down so that you can deal with the conflict
- What is the problem/conflict
- Listen to the other side
- Think about possible solutions
- Check pros and cons
- Decide what solution works best for all (win-win if possible)
You can download this conflict resolution worksheet at the end of the post.
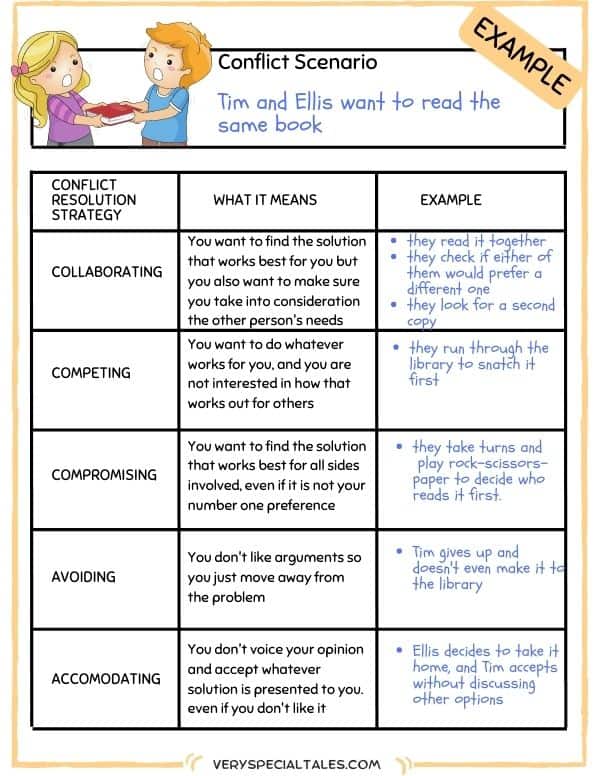
This conflict resolution worksheet will work on the different conflict-handling modes:
- competition
- accommodating.
Identify a conflict scenario, and ask your students to write examples for each conflict resolution strategy.
Your downloadable worksheet includes an example of a conflict scenario (Tim & Ellis want the same book) and a blank worksheet (for your own examples).
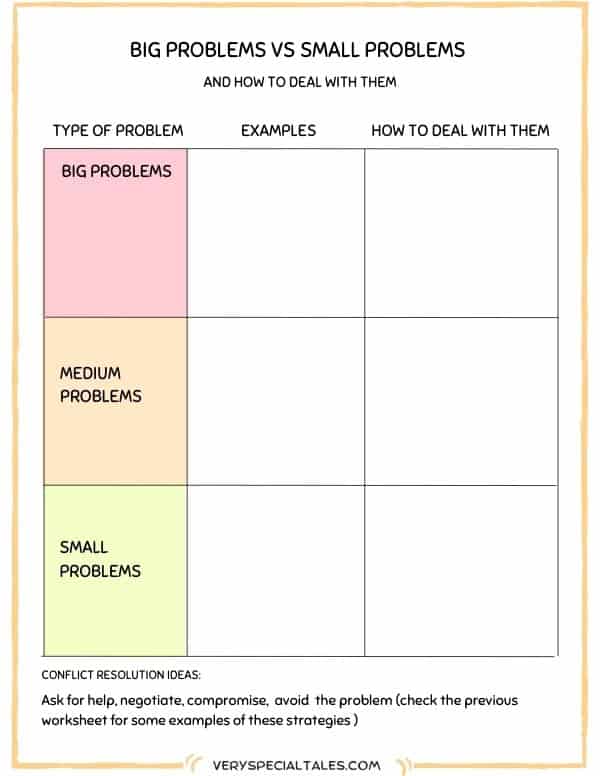
In this activity, we will try to connect the size of our problem, with different ways of dealing with conflict.
Conflict resolution strategies include negotiation, mediation, and arbitration.
Depending on the type of conflict kids are dealing with, they may be able to deal with that conflict on their own (little problem), or they may need to involve an adult in the situation (mediation/arbitration for big problems)
Fun Conflict Resolution Activities for the Classroom / Groups
4. Conflict Resolution Roll-Play
On a popsicle stick, write out common conflicts that children face. Once you have around 20, have two students stand in front of the class and act out the situation that the popsicle stick says.
Once they act it out, have the class discuss different solutions to how the problem could be solved either as a group or in small groups.
Variation: if the different scenarios you are choosing are a bit complicated for the popsicle stick, you can write them down on pieces of paper and put them in a jar or a box.
5. Write it Out
Using the popsicle sticks from the last activity, have the students all draw a different scenario and then write how they think the conflict should be resolved.
In small groups of three or four, have the students share what their popsicle sticks had written on them, and how they would solve the problem.
6. Negotiation Scenario Activity
This is a great conflict resolution activity to help kids understand that there are always different points of view.
Create a conflict scenario where neither of the two parties has all the information about the other party. If both parties negotiate, they can reach a solution that will be good for both of them, but they need to listen to each other to be able to come up with the solution.
An example:
- (Part 1) Two students need the same book for a school essay (for example, “How dinosaurs became extinct”) They only have one day to write their piece, there is only one copy in the school library and neither of them wants to give it up. Let the students discuss how to deal with this conflict
- (Part 2) Provide each student with some additional information: Student A (Annie) would prefer to write about inspiring women role models, but she couldn’t find anything on that topic. Student B (Amanda) loves dinosaurs and is really keen on writing on this topic. On her birthday, she was gifted the Good Night Stories for Rebel Girls book. That could be an excellent choice to inspire Annie’s essay. Ask the students to go back to the negotiations, and suggest they explore why the other party wishes to write about the chosen topic. Are the solutions different this time
7. Create a Short Story
Ask your students to develop a story that recreates a conflict and how it gets solved.
8. Exploring Feelings
Read aloud to your students a scenario that could bring out different emotions.
It could be something as simple as:
- Scenario 1: parent is late for school pick up, and they are going to miss the football match
- Scenario 2: a classmate declines your invitation for a playdate.
Have everyone write down how that would make them feel on a 5×8 notecard, then hold it up.
Ask them to share what they have written and learn how the same scenario can bring different feelings in each person:
- a kid may assume their parents got stuck in traffic, while some other may feel they don’t care if they miss sports
- a student may assume that their friend is very busy, while another may feel their friend doesn’t care and may look for other friendships
Our feelings play an important role in how we deal with a situation.
9. Listening Activity
An important part of conflict resolution is listening to the other side.
Following up on the previous activity, let’s now add new pieces of information
- Scenario 1: there was a big traffic jam, and the parent’s phone was out of battery
- Scenario 2: your friend has swimming lessons on the day you suggested (and since you proposed the same day each time, they kept declining)
After listening to the other side, how would you approach this argument/conflict?
Related Reading: Listening Games and Activities for Kids
10. Conflict Resolution Writing Prompt
Have your students write out the sentence “I would get into a fight with someone if they tried to take away_________.”
Then have them write down why that item is so important to them that they would want to get into a fight.
The idea behind this is that they realize that most conflicts aren’t worth it.
11. Healthy vs. Unhealthy Conflict Resolution
Have your kids write down ways to solve a conflict scenario. They don’t need to be the best solutions. , we are just brainstorming anything that crosses their minds.
Once they have come up with all these solutions, ask them to classify them as healthy vs. unhealthy.
Tip: Go back to our “healthy ways to deal with conflict” section for some inspiration or examples
12. Conflict Resolution Books for Kids
- Speak Up and Get Along is a chapter book for kids age 8 to 12 and is an excellent resource.
This social skills book shares twenty-one strategies children can use to end arguments and fights, make friends and stop bullying. It provides age-appropriate examples and lines they can practice and role-play.
We can’t deal with a conflict if we are feeling overwhelmed with intense feelings. The next suggestions focus on calming down so that we are ready to deal with conflict appropriately
13. Learning to Deal with your Anger
There are many anger management activities that can help kids deal with their emotions.
Check out the Cool Kid Journal (Anger activities for kids) to explore healthy ways of dealing with anger (it includes 70 gorgeous calm down cards).

14. Practice Taking Deep Breaths
A simple activity for kids of all ages is to practice taking deep breaths when they are upset.
This will help them calm down so that you can discuss a way to deal with the problem.
Recommended Reading: Fun Breathing Exercises for Kids
15. Model in your own life
Whether you share a story of a time when you needed to resolve conflict or show it in a real-life scenario, adults are the best teachers in explaining conflict resolution.
16. Friendship Activities
If a child in your life seems to be having a hard time staying out of conflict, it might be time to discuss what having a good friend should look like.
While conflict is a part of life, it doesn’t need to be a daily occurrence throughout elementary school and middle school. Instead, encourage your child to work towards healthy friendships.
Recommended reading: Friendship Activities for Kids (includes a worksheet that explores unhealthy bad signs in a friendship /warning signs /healthy/good signs)
17. Conflict Resolution Journal
Have your kids sit down and journal a personal conflict. Then, have them list out different ways that they can resolve that conflict.
Conflict Resolution Games
A great way to learn new skills is playing.
Let’s take a look at some conflict resolution games:
18. 6 Conflict & Resolution Games This game is not just one game, but several great conflict resolution games.
Let’s check a couple of examples
- Spinning the wheel game presents social scenarios, and you need to provide possible solutions. After you spin the wheel, you need to come up with a solution in one of the following categories: me, other, or all (depending on who benefits from the solution). This game explores competition and compromising
- “Are you a bully” is a game inspired by the Snake & Ladders setup that presents bullying/mean situations vs. kind social responses
-> Check out this game
19. Social Skills Group Activity
In this game , players need to discuss socially challenging situations. They include boards on six different topics: morals, manners, empathy, friendship, and two boards on emotions (showing and managing them).
The manners game is actually a conflict resolutions game, and the players have to answer questions like:
- you see a friend stealing something from a shop
- you see a friend cheating during a test
- you are served a meal you don’t like at a friend’s house
These types of questions present a perfect opportunity to brainstorm solutions to a conflict and to discuss the size of the problem and whether it is big enough to engage the help of an adult.
And let’s finish our list with a fun video.
20. How to Explain Conflict to Kids (Video)
In this Sesame Street video, our beloved Robin Williams teaches kids the meaning of conflict.
Other Social Skills Resources
These are some helpful resources to help kids build social skills:
- 25 Problem-Solving Activities for Kids
- I-Statement Worksheets
- Self-Introduction for Kids (Worksheets)
- Social Skills Activities for Kids
- Conversation Starters for Kids
- Listening Games and Activities
- Apology Worksheets and Activities
- Friendship Activities for Kids
- Turn-Taking Activities for Kids
- Fun Emotional Intelligence Activities for Kids
Conflict Resolution Activities (Worksheets / PDF Download)

it s very useful.
Very well made. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are 5 steps to help kids learn social problem solving skills: 1. Teach kids to communicate their feelings. Being able to openly and respectfully share emotions is a foundational element to social problem solving. Teaching I statements can be a simple and effective way to kids to share their feelings. With an I statement, kids will state ...
71+ Social Problem Scenarios + 6 Blank Scenarios. Use the 71 social problem-solving scenarios to have your students get great experience practicing how to solve a social problem. Also, included are 6 blank scenarios. Then laminate them so you can use them over and over again. Therefore, create social problems that the student experiences and ...
Try the no-prep way to teach Problem Solving. Simplify the way you teach social-emotional skills with Everyday Speech! Subscribe to access step-by-step SEL curriculum and over 1,000 videos, games, and more. ... Complete SEL lesson plans to teach Problem Solving . Everyday Speech lesson plans save you time! There's no prep work required ...
Problem solving is another skill people seeking social skills therapy often want to develop further. A lack of opportunity to learn coping strategies and difficulty with emotional regulation have been associated with anxiety and low problem-solving abilities (Anderson & Kazantzis, 2008).. An individual's lack of ability to problem solve in social situations significantly affects their ...
Social skills activities for kids: 50 Fun activities for making friends, talking and listening, and understanding social rules. Rockridge Press. Fleming, S. (2021). Know thyself. Basic Books. Goleman, D. (2018). The first component of emotional intelligence. In Self-awareness (pp. 1-10). Harvard Business Review Press. MacLeod, C. (2018).
1. Identifying Social Problems (10-15 minutes) Start with a discussion about the social problems high school students may encounter. This can be conducted in small groups or pairs. 2. Empathizing: Understanding Different Perspectives (10-15 minutes) Choose a few scenarios from the previous discussion. Invite students to consider the various ...
Create a free account to gain full access to the website. Save & Organize Resources. See State Standards. Manage Classes & Assignments. Sync with Google Classroom. Create Lessons. Customized Dashboard. Find lessons on Social Problem Solving for all grades. Free interactive resources and activities for the classroom and home.
Social problem-solving is generally considered to apply to four different types of problems: Impersonal problems, for example, shortage of money; Personal problems, for example, emotional or health problems; Interpersonal problems, such as disagreements with other people; and. Community and wider societal problems, such as litter or crime rate.
With 50 social problem-solving scenarios, this bundle is perfect for targeting many aspects of social communication such as... Perspective-takingReading nonverbal social cluesMatching behavior to the situationMaking social inferencesAdjusting how we communicate in different social interactionsUnderstanding the tone and mood of social interactions Word choiceTone of voiceYour students will have ...
From problem solving social skills worksheets to solving social problems videos, quickly find teacher-reviewed educational resources. ... The final lesson plan in the "Problem Solving Module" focuses on finding creative solutions to problems that might arise at home. Individuals then create a storyboard that illustrates how they would apply the ...
Problem Solving on the Job. For Teachers 9th - 12th. The truth is there are consequences for actions. The third lesson in the "Problem Solving Module" asks class members to brainstorm a list of problems, select one and invent a system, process, or object that might solve the problem.
Unit 2, Lesson 10: Environmental Factors that Contribute to Bullying. In this lesson, students will learn how the physical layout of and rules within a space can make bullying and harassment more likely to happen, from identifying environmental factors to discussing rules and regulations within their own school community. Sample This Lesson.
Headquarters: (941) 927-0965 1960 Landings Blvd #120 Sarasota, FL 34231
Problem Solving - A Stations Lesson Plan. This lesson is meant to encourage and motivate children to persevere and work through difficult tasks. Although this lesson is specifically tailored for Grade 3, it can easily be adapted to suit any grade level K-6. Complete the lesson by following the instructions found in each section.
TED-Ed lessons on the subject Problem Solving. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. ... Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups? Learn more. Subjects All Subjects. All Subjects; The Arts. ... Social Studies The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani. Lesson ...
Build skills for social problem-solving by getting your students talking! Use these 100 task cards to highlight social scenarios and situations that teach social emotional skills at the very same time. Your students can discuss and identify how they would solve each situation. The cards are organized into five different sets that target different situations: With friends, with family, in the ...
Find social skills problem solving lesson plans and teaching resources. Quickly find that inspire student learning. ... Learning Explorer An all-in-one learning object repository and curriculum management platform that combines Lesson Planet's library of educator-reviews to open educational resources with district materials and district ...
Learning goal: Problem solving. The ability to quickly and effectively solve problems plays a major role in classroom, college, and career success. Help your students develop these essential skills using the FutureFit resources collected under the "Solve" domain. Skills highlighted in this domain include process acumen, computational ...
Lesson plan. (60 -75 minutes) This lesson is designed to equip young people with an adaptable approach to solving problems, large or small. It includes a short film and scenarios that encourage development of practical problem solving skills which can be useful for learning, day to day life, and when in employment.
Some of these activities will be a great addition to a lesson plan. Conflict Resolution Worksheets. 1. Social Problem Solving Worksheet. Conflict resolution is, in essence, a social problem-solving situation. In this worksheet, we will follow the steps for problem-solving, with an important addition (calm-down):
Entire Library lesson-plan Kindergarten Social emotional Problem-Solving Steps. Lesson Plan Problem-Solving Steps. In this lesson, students will learn the steps in solving a problem, discuss solutions from the story "Mr. Rabbit and the Lovely Present," and use these same problem-solving skills when they build shapes with pattern blocks.
Problem Solving and Cooperation Group work can build cooperation and problem-solving skills inside and outside of the classroom! In this lesson, students will discuss cooperation and practice using cooperative techniques in human knot and tower-building activities.
Here's how you can apply problem solving skills to create a comprehensive social media marketing plan. Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Identify Goals. 2. Analyze Data. 3. Creative ...
Find social science problem solving lesson plans and teaching resources. Quickly find that inspire student learning. ... In this problem solving lesson plan, 3rd graders develop mathematical problem solving skills using real-world examples. Get Free Access See Review + Lesson Plan.