The effect of credit risk management and bank-specific factors on the financial performance of the South Asian commercial banks
Asian Journal of Accounting Research
ISSN : 2459-9700
Article publication date: 14 October 2021
Issue publication date: 27 May 2022
Among all of the world's continents, Asia is the most important continent and contributes 60% of world growth but facing the serving issue of high nonperforming loans (NPLs). Therefore, the current study aims to capture the effect of credit risk management and bank-specific factors on South Asian commercial banks' financial performance (FP). The credit risk measures used in this study were NPLs and capital adequacy ratio (CAR), while cost-efficiency ratio (CER), average lending rate (ALR) and liquidity ratio (LR) were used as bank-specific factors. On the other hand, return on equity (ROE) and return on the asset (ROA) were taken as a measure of FP.

Design/methodology/approach
Secondary data were collected from 19 commercial banks (10 commercial banks from Pakistan and 9 commercial banks from India) in the country for a period of 10 years from 2009 to 2018. The generalized method of moment (GMM) is used for the coefficient estimation to overcome the effects of some endogenous variables.
The results indicated that NPLs, CER and LR have significantly negatively related to FP (ROA and ROE), while CAR and ALR have significantly positively related to the FP of the Asian commercial banks.
Practical implications
The current study result recommends that policymakers of Asian countries should create a strong financial environment by implementing that monetary policy that stimulates interest rates in this way that automatically helps to lower down the high ratio of NPLs (tied monitoring system). Liquidity position should be well maintained so that even in a high competition environment, the commercial is able to survive in that environment.
Originality/value
The present paper contributes to the prevailing literature that this is a comparison study between developed and developing countries of Asia that is a unique comparison because the study targets only one region and then on the basis of income, the results of this study are compared. Moreover, the contribution of the study is to include some accounting-based measures and market-based measures of the FP of commercial banks at a time.
- South Asian countries
Credit risk
Bank-specific factors.
- Generalized method of moment
Siddique, A. , Khan, M.A. and Khan, Z. (2022), "The effect of credit risk management and bank-specific factors on the financial performance of the South Asian commercial banks", Asian Journal of Accounting Research , Vol. 7 No. 2, pp. 182-194. https://doi.org/10.1108/AJAR-08-2020-0071
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Asima Siddique, Muhammad Asif Khan and Zeeshan Khan
Published in Asian Journal of Accounting Research . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
Around the globe, depository institutions perform a crucial job in bringing financial stability and economic growth by mobilizing monetary resources across multiple regions ( Accornero et al. , 2018 ). The commercial plays an intermediary role by collecting the excessive amount from savers and issuing loans to the borrowers. In return, banks can earn a high interest rate ( Khan et al. , 2020 ; Ghosh, 2015 ). Banks tried to increase their financial performance (FP) by issuing loans while playing their intermediary role; banks have a high chance of facing credit risk. Accornero et al. (2018) found that the country's banking industry mostly collapses due to high credit risk. Sometimes, it leads to the failures of the whole financial system. Credit risk is expected to be arises when a borrower cannot meet their obligation about future cash flows. Commercial banks' FP is affected by two factors: one is external and the other is internal. Bank-specific factors are internal and able to control factors of the commercial banks. Ofori-Abebrese et al. (2016) pointed out that adverse selection and moral hazards were created due to mismanagement of internal factors. The abovementioned financial problems are turmoil period in the banking/financial sector.
Among the entire continent of the world, Asia is the most crucial continent and contributing 60% of world growth but facing the serving issue of high nonperforming loans (NPLs). It is well known that a high ratio of NPLs weakens the economy or country's financial position. The growth level in South Asia was the highest in 2015, and the ratio is 9.3%, which is the highest among all continents. According to the Asian Development Bank (2019), the NPLs in the south are approximately $518bn, which is relatively high compared to previous years. The soaring of NPLs in South Asian countries enforces a massive burden on commercial banks' financial position (mainly banks' lending process effected). The massive increase in NPL is observed after the global financial crisis (2007–2008). According to Masood and Ashraf (2012) , the credit risk high ratio of NPLs is the main reason for most of the financial crisis because NPLs alarmingly high during the Asian currency crisis in 1997 and subprime crises in 2007, and some loans are declared bad debts. The alarmingly high ratio of NPL resulted in an increasing depression in the financial market, unemployment and a slowdown of the intermediary process of banks (see Figure 1 ).
The World Bank statistics of different regions show that NPLs exist in almost all regions. Still, the ratio of NPLs is relatively high in the South Asian area compared to other regions. Therefore, the study is conducted in South Asia. Two proxies of credit risk are used in this study: NPLs and capital adequacy ratio (CAR). Moreover, the study also incorporates bank-specific factors to increase FP.
Various studies ( Louzis et al. , 2012 ; Ofori-Abebrese et al. , 2016 ; Hassan et al. , 2019 ) are conducted to address the issue, but literature shows that the results of these studies are inconclusive and also ignore the most important region of South Asia. Therefore, the study objective is to investigate that credit risk and banks specific factors affect FP of commercial banks in Asia or not? We have selected two from South Asia, Pakistan and India, as sample countries. In 2019, the NPLs were 13% and 10% in Pakistan and India, respectively. This ratio is relatively high as compared to the other countries of the world. Due to these reasons, we have mainly selected India and Pakistan from South Asian countries ( Siddique et al. , 2020 ). The present study uses secondary panel data set of 19 commercial banks from 2009 to 2018.
Two serious threats may exist: The first is autocorrelation and the second is endogeneity. If the data do not meet these CLRM assumptions, then the regression results are not best linear unbiased prediction (BLUE) ( Sekaran, 2006 ; Kusietal, 2017 ). And in this situation, apply pooled regression is applied, and then the results were biased because the coefficient results cannot give accurate meaning. After all, pool regression ignores year and cross section-wise variation. Therefore, in this study, an instrumental regression can be used that handle all these issues. Generalized method of moments (GMM) is used to analyze the data to overcome endogeneity. Our study is unique by addressing the autocorrelation and endogeneity issue at a time. Our study results show that credit risk measure NPLs decrease the FP due to having negative relation, while CAR has a positive relation with South Asian banks’ FP. The remainder of the research study is organized as follows: Section 2 consists of a detailed literature review; Section 3 consists of data and methodology. Sections 4 contains information about finding and suggestions. Finally, Section 5 discusses the conclusion.
Literature review
The Literature Review has mainly divided into two crucial sections; First part consists of the literature review related to credit risk and FP. The other part is related to the literature review of bank-specific variables and FP. In the hypothesis development, we have used commercial banks' profitability that represents the FP of commercial banks.
Credit risk and financial performance
While operating in the banking industry, three categories of risks that the bank has to face include environmental, financial and operational risks. Banks generate their incomes by issuing a massive amount of credit to borrowers. Still, this activity involves a significant amount of credit risk. When borrowers of the banking sector default cannot meet their debt obligation on time, it is called credit risk ( Accornero et al. , 2018 ). When there is a large amount of loan defaulter, then it adversely affects the profitability of the banking sector. Berger and DeYoung (1997) pointed out that the absence of effective credit risk management would lead to the incidence of banking turmoil and even the financial crisis. Siddique et al. (2020) explain that NPLs are related to information asymmetric theory, principal agency theory and credit default theory. When asymmetric information unequal distribution of information of high NPLs is spread, there is a chance that banks or financial declared bankrupt. According to Pickson and Opare (2016), the principal agency must separate corporate ownership from managerial interest. Because each management has its interest, they want more prestige, pay increment and want the stock options for management. Effective management of credit risk or nonperformance exposure in the banking sectors increases profitability. It enhances the development of banking sectors by adequate allotment of working capital in the economy ( Ghosh, 2015 ).
There is a growing literature ( Louzis et al. , 2012 ) on credit risk and its empirical relationship with the monetary benefits of the banking sector. Ekinci and Poyra (2019) investigate the relationship between credit risk and profitability of deposit banks in Turkey. The data sample used 26 commercial banks from 2005 to 2017. All data of this study are secondary and collected from annual reports of commercial Turkey banks. The proxies of profitability were taken as return on equity (ROE) and return on the asset (ROA), while NPLs of commercial banks were used as a proxy to measure credit risk. The research paper reveals that credit risk and ROA are negatively correlated as well as the relation between credit risk and ROE is also significantly negative relation. Therefore, the study suggests that the Turkey government tightly monitors and controls the alarmingly soaring ratio of NPLs. Upper management introduced some new measures to trim the credit risk.
There is a negative and significant relationship between NPLs and commercial banks' FP.
There is a positive and significant relationship between capital adequacy ratio and commercial banks' FP.
Bank-specific variables and financial performance
Bank-specific variables or internal factors are the product of business activity. Diversifiable risk is associated with these factors ( Louzis et al. , 2012 ) and can be reduced by efficient management. This risk is controllable compared to an external factor, which cannot be diversified because this risk is market risk ( Ghosh, 2015 ; Rachman et al. , 2018 ). If a firm can manage its internal factor effectively, then the firm can be high profitability, while, on the other hand, these factors are mismanaged. It would adversely affect the firm's balance sheet and income statement ( Ofori-Abebrese et al. , 2016 ). Different authors ( Akhtar et al. , 2011 ; Louzis et al. , 2012 ; Chimkono et al. , 2016 ; Hamza, 2017 ) discuss different bank-specific variables and firm performance in their studies. The bank-specific variables used in this study are cost-efficiency ratio (CER), average lending rate (ALR) and liquidity ratio (LR). Aspal et al. (2019) used two types of factors (macro and bank-specific factors) and inspected their connection with the FP of the commercial bank in India. Gross domestic product (GDP) and inflation are used as proxies of macroeconomic factors.
In contrast, a bank-specific variables’ proxy includes capital adequacy ratio, asset quality, management efficiency, liquidity and earnings quality. Data of 20 private banks have been used from 2008 to 2014. The panel data pointed out that one macroeconomic factor is significant (GDP), and another factor (Inflation) is insignificant. All bank's specific factors (earning quality, asset quality, management efficiency and liquidity) significantly affect the FP except the CAR (insignificant). Hasanov et al. (2018) conducted their study to explore the nature of the interrelation between bank-specific (BS) and macroeconomic determinants with the banking performance of Azerbaijan (oil-dependent economy). The study used the GMM to analyze the panel data set. The results show that bank loans, size, capital and some macro factors (inflation, oil prices) were positive and significantly interconnection with the FP of banks; on the other hand, liquidity risk, deposits and exchange rates are significantly affected negatively bonded with the FP.
There is a negative and significant relationship between the CER and commercial banks' FP.
There is a positive and significant relationship between the ALR and commercial banks' FP.
Francis et al. (2015) define liquidity in their study and, according to the liquidity of an asset, determined by how quickly this asset can be converted or transferred into cash. Liquidity is used to fulfill the short-term liabilities rather than the long term ( Siddique et al. , 2020 ; Raphael, 2013 ). Adebayo et al. (2011) mentioned in their study that when banks are unable to pay the required amount to their customers, it is considered bank failure. Sometimes liquidity risk affects the whole financial system of a country. Different studies are conducted on the issue of liquidity and performance, but different studies show different results. FP and liquidity, on the other hand, a chunk of studies ( Francis et al. , 2015 ; Hamza, 2017 ) revealed significant negative tie-up between liquidity and FP, while some other studies pointed out that there is no significant relationship between liquidity and FP. Therefore, the studies show a contradictory result, so the current study takes the bank-specific measures (LR, ALR study and CER) and checks its interconnection with commercial banks' FP.
There is a positive and significant relationship between the LR and commercial banks' FP.
Data and methodology
Our current study has one problem variable, financial performance (FP), while regressors variables are credit risk and bank-specific variables. Our model is consistent with Chimkono et al. (2016) , where ROA and ROE will be used as a measure of FP, while credit risk will be measured by NPL ratio, CAR and three specific variables: CER, LR and ALR.
Various studies ( Hamza, 2017 ; Belas, 2018 ) emphasize some macro and micro variables that need to be controlled when measuring FP because these factors are the influential factors. Three control variables: size of the bank, age of the banks and Inflation are used in this study and shown as yes in the tables. We have chosen these three control and most relevant variables because these variables represent both micro and economic situations. Data have been collected from two South Asian countries Pakistan and India. The nature of data is panel data and the number of banks from Pakistan (10 commercial banks) and India (9 commercial banks) is 19. The data have been collected from bank financial statements throughout 2009 to 2018, so the data of this study are a panel in nature. The final number of observations is 190 (19*10 = 190) for the analysis of this study (see Table 1 ).
Operational definition
The probability of lenders being the default, high credit risk higher FP of banks ( Louzis et al. , 2012 ).
Bank-specific factors are those which are under the control of the management of commercial banks ( Chimkono et al. , 2016 ).
Nonperforming loans
A loan becomes nonperforming when the duration of the loan has been passed, and after that duration, banks 90 days are passed unable to receive the principal amount of loan and interest payment ( Hamza, 2017 ).
Methodology
The current study investigates the interrelationship between credit risk, bank-specific factors and FP. Panel data set is used in our study, and two serious threats usually faced when using panel data set: (1) autocorrelation and (2) endogeneity. For this purpose, a GMM can be used. GMM model has many advantages on simple ordinary least square regression. And when in any study GMM model applies, it allows by adding the fixed effect model; this model can be able to tackle the problem of heterogeneity, and it also removes the problem of endogeneity by introducing some instrumental variables.
Model specification
The regression model is as follows:.
γ 0 = intercept; γ 1 - γ 8 = estimated coefficient of independent variables and control variables.
ε it represents error terms for those variables that are omitted or added intentionally/unintentionally.
According to Lassoued (2018) , panel data regression has two significant problems: autocorrelation and endogeneity, and this problem is existed due to the fixed effect. Therefore, our study checked the basic two assumptions of ordinary least squares.
Testing for autocorrelation
The fifth assumption of CLRM is that data should be free from autocorrelation. Sekaran (2006) pointed out the relationship between two different error terms should be zero; it means that there is no autocorrelation between error terms. There are different tests for testing autocorrelation, but the Wooldridge test is used in the present paper to test the autocorrelation.
Table 2 shows that the p -value of the Wooldridge test result is zero, so it means that all p -values are less than 0.05. It means that reject the null hypothesis. And the null hypothesis is that our data have no autocorrelation, but the results show that our data have autocorrelation problems.
Testing for endogeneity
The seventh assumption of CLRM is that data have no issue of endogeneity. Sekaran (2006) found that the relationship between the error term and explanatory or independent variable should be zero. If this relationship is not zero, then the problem of endogeneity exists. Brooks (2014) pointed out that Hausman test results probabilities can be used to test the endogeneity, and the null hypothesis of this test is that errors are uncorrelated. He also pointed out that if the probabilities are more than 0.10, then accept the null hypothesis. It means that there is no problem of endogeneity, and if the values are less than 0.1, then our data have the problem of endogeneity. Appendix 1 shows that some values of the Hausman test are less than 0.10, so it means that data have the problem of endogeneity. Our panel data results prove that our data have the problem of autocorrelation and endogeneity. Some CLRM model assumptions are not met, so ordinary least square regression results are not BLUE. And GMM model can be applied to any study because this model can be able to tackle the problem of autocorrelation, and it also removes the problem of endogeneity by introducing some instrumental variables.
Findings and discussion
The present research paper provides empirical evidence on the interconnection between credit risk and bank-specific/internal factors on FP commercial banks. To analyze the data set, first, the study applies the descriptive analysis to identify the big picture of the data, then the correlation section and at the end, regression results are discussed. Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics of the all variables used in the study: credit risk indicator which are the ratio of NPL, CAR; indicators of bank-specific factors (CER, ALR, LR); some control variables SIZE, AGE, INF and the measure of FP: ROA, ROE. The mean value of ROA and ROE is 0.986 and 7.964 with a standard deviation of 1.905 and 39.175, respectively, which shows that ROE has much higher variation than ROA. The standard deviation of NPL is 9.659, which is double that of CAR, whose standard deviation is 4.183 among all bank-specific factors (see Table 4 ).
Factor (CER, ALR, LR) LR has high dispersion (14.177) because there is a remarkable difference between minimum 25.027 and maximum value (107.179) of LR. ROA has 0.986 with a range between 10.408 and −6.234 with a standard deviation of 1.905, and it shows that there is a low level of dispersion in developed countries. The dispersion of ROE 39.175 is highest among all other variables, which means that some outliers exist in the ROE variable.
Correlation analysis is used to check the linear relationship between the two explanatory variables ( Brooks, 2014 ). If the sample size of any approaches to 100, greater than 100 and the correlation coefficient is 0.20, then the correlation is significant at 5% ( Lassoued, 2018 ). Most of the variables in the current study are significant at 5%.NPLs, and CER loans are negatively correlated with almost all independent variables, which supports the literature point that NPLs and CER are negatively associated with FP and bank-specific factors. The negative correlation of NPLs with ROE is loan −0.378, and this correlation is high as compared to other countries. At the same time, all bank-specific factors, CER, ALR and LR are mostly positively correlated with most of the other, almost all dependent and independent variables, while AGE and INF are mostly negatively correlated with the other variables of the study.
Regression results and discussion
Tables 5 and 6 have shown the regression results of pooled regression and GMM models. Tables include all independent, control variable coefficients, t -statistics, standard error and probability values. Additionally, tables have the values of R 2 , adjusted R 2 and Durbin Watson statistics. The adjusted R 2 under pooled regression are 0.250 and 0.231 in both models (ROA and ROE). While adjusted R 2 under the GMM are 0.358 and 0.249 in both models ROA and ROE.
It means the GMM more and better explains our model than pooled regression. Moreover, we also apply a Hausman test on both models. The p -value of both models is less than 0.05, so our data have the problem of endogeneity null hypothesis. To eliminate the endogeneity issue, the GMM coefficient was measured.
NPL has a significant and negative measure of FP: ROA and ROE. In contrast, CAR has significant and positive with all proxies of FP: ROE and ROA, which supports H1 and H2 of the paper. Our finding is consistent with Masood and Ashraf (2012) who conducted their study on credit risk and FP and found a significant negative relationship between NPL and FP, so NPLs hinder banks' profitability. Therefore, NPLs affect the whole financial system of a country especially in developing countries. The findings of CAR matched with Accornero et al. ’s (2018) study and pointed out that CAR has a significantly positive link with FP. CER has a significant negative relationship with ROA and ROE, which is consistent with the study of Francis et al. (2015) who pointed out a significant negative relationship between CER and ROE. Therefore, banks need to adapt strategies to control these costs and tried to increase their profitability. ALR had a significant and positive relationship with both measures of FP. ALR is significant at 1% with ROA and 10% significant with ROE. The result is supported by the study of Chimkono et al. (2016) who found a positive relationship between the ALR and FP of commercial banks.
LR has a significantly negative relationship with ROA and ROE. This finding is consistent with Siddique et al. (2020) who pointed out a significant negative relationship between LR and ROE; the more liquidity is maintained, the lesser the profitability level. In short, most of the independent variables are significant at 5% and 1%, and control variables are also significant in both models size of the bank and inflation except AGE. This result is matched with Ghenimi et al. ’s (2017) findings that prove that total assets or investment increment are directly proportional to the FP. Both variables of credit risk NPL and CAR are significant with the FP of commercial banks in both models. Banks try to reduce bank-specific factors risk, and by doing so, ultimately the amount of bad debt decreased, and another benefit is that it also reduces the amount of loan loss provision.
The current study empirically investigates the causal interrelation between credit risk, bank-specific factors and FP of commercial banks in two South Asian countries (Pakistan and India). The study's finding suggests that managers in South Asian countries should be focused on increasing capital adequacy to enhance the monetary gain (FP) while for the contraction of NPLs by implementing modern techniques and strategies for credit risk (NPLs) management. One indicator of the bank-specific variable (ALR) has a significant and positive interrelation with the FP of commercial banks. In contrast, CER and LR have a significant and positive relationship with the FP of commercial banks of South Asia. Control variables of the study (size of the bank and inflation) are also significant in both models except AGE. There are several policy implications that commercial banks of South Asian countries should be followed. NPLs are soaring due to the following reasons: less supervision and monitoring of customers, the problem of the market and lack of customer knowledge related to loans. Bank management should be efficient in judging that their customers have viable means of repayment or not. Moreover, banks can offer expert opinion to the professional loan take on feasible techniques of efficiently endow the borrowing to secure the required return on total firms investment is acquired. Liquidity position should be well maintained so that even in a high competition environment, the commercial can survive in that environment.
The scope of the study is only limited to commercial banks, but this model can also be applied to Islamic banks. And future researchers can also apply this model to a comparison-based study of commercial and Islamic banks. Data of this study have been collected only from 19 banks; future research can also increase the number of banks and increase the number of years to conduct their study. And if the number of banks and the number of the year increased, the results are a more reliable and accurate representation of the population. The data of this study have been taken only from two countries of South Asia, but this study can be extended by adding more countries in Asia. When we add the number of countries, the results are a better and accurate representation of developing and developed countries of Asia. This model can also be applied to some other continents because the macro environment and bank-specific factors are pretty different from continent to continent Appendix A1 .
NPLs-continent wise
Summary of explanatory variables and dependent variables
Results for autocorrelation for South Asia countries
Descriptive statistics
Correlation figures
ROA model (pooled regression and fixed effect GMM result)
Extra tables and figures in the Google drop box and available at: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/dro0gkowf3t542r/AAC3QQ5lKQTpLdke7UNxRUEea?dl=0
Accornero , M. , Cascarino , G. , Felici , R. , Parlapiano , F. and Sorrentino , A.M. ( 2018 ), “ Credit risk in banks' exposures to non-financial firms ”, European Financial Management , Vol. 24 No. 5 , pp. 775 - 791 .
Adebayo , M. , Adeyanju , D. and Olabode , S. ( 2011 ), “ Liquidity management and commercial banks' profitability in Nigeria ”, Research Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 2 No. 8 .
Akhtar , M.F. , Ali , K. and Sadaqat , S. ( 2011 ), “ Factors influencing the profitability of Islamic banks of Pakistan ”, International Research Journal of Finance and Economics , Vol. 66 , pp. 125 - 132 .
Aspal , P.K. , Dhawan , S. and Nazneen , A. ( 2019 ), “ Significance of bank specific and macroeconomic determinants on performance of Indian private sector banks ”, International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues , Vol. 9 No. 2 , p. 168 .
Belas , J. , Smrcka , L. , Gavurova , B. and Dvorsky , J. ( 2018 ), “ The impact of social and economic factors in the credit risk management of SME ”, Technological and Economic Development of Economy , Vol. 24 No. 3 , pp. 1215 - 1230 .
Berger , A.N. and DeYoung , R. ( 1997 ), “ Problem loans and cost efficiency in commercial banks ”, Journal of Banking and Finance , Vol. 21 , pp. 849 - 870 .
Blum , J. and Hellwig , M. ( 1995 ), “ The macroeconomic implications of capital adequacy requirements for banks ”, European Economic Review , pp. 739 - 749 .
Brooks , C. ( 2014 ), Introductory Econometrics for Finance , Cambridge University Press .
Chimkono , E.E. , Muturi , W. and Njeru , A. ( 2016 ), “ Effect of non-performing loans and other factors on performance of commercial banks in Malawi ”, International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management , Vol. IV , pp. 1 - 15 .
Ekinci , R. and Poyraz , G. ( 2019 ), “ The effect of credit risk on financial performance of deposit banks in Turkey ”, Procedia Computer Science , Vol. 158 , pp. 979 - 987 .
Francis , B.B. , Hasan , I. , Song , L. and Yeung , B. ( 2015 ), “ What determines bank-specific variations in bank stock returns? Global evidence ”, Journal of Financial Intermediation , Vol. 24 No. 3 , pp. 312 - 324 .
Ghenimi , A. , Chaibi , H. and Omri , M.A.B. ( 2017 ), “ The effects of liquidity risk and credit risk on bank stability: evidence from the MENA region ”, Borsa Istanbul Review , Vol. 17 No. 4 , pp. 238 - 248 .
Ghosh , A. ( 2015 ), “ Banking-industry specific and regional economic determinants of non-performing loans: evidence from US states ”, Journal of Financial Stability , Vol. 20 , pp. 93 - 104 .
Hamza , S.M. ( 2017 ), “ Impact of credit risk management on banks performance: a case study in Pakistan banks ”, European Journal of Business and Management , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 57 - 64 .
Hasanov , F. , Bayramli , N. and Al-Musehel , N. ( 2018 ), “ Bank-specific and macroeconomic determinants of bank profitability: evidence from an oil-dependent economy ”, International Journal of Financial Studies , Vol. 6 No. 3 , p. 78 .
Hassan , M.K. , Khan , A. and Paltrinieri , A. ( 2019 ), “ Liquidity risk, credit risk and stability in Islamic and conventional banks ”, Research in International Business and Finance , Vol. 48 , pp. 17 - 31 .
Khan , M.A. , Siddique , A. and Sarwar , Z. ( 2020 ), “ Determinants of non-performing loans in the banking sector in developing state ”, Asian Journal of Accounting Research .
Kusi , B.A. , Agbloyor , E.K. , Ansah-Adu , K. and Gyeke-Dako , A. ( 2017 ), “ Bank credit risk and credit information sharing in Africa: does credit information sharing institutions and context matter? ”, Research in International Business and Finance , Vol. 42 , pp. 1123 - 1136 .
Lassoued , M. ( 2018 ), “ Comparative study on credit risk in Islamic banking institutions: the case of Malaysia ”, The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance , Vol. 70 , pp. 267 - 278 .
Louzis , D.P. , Vouldis , A.T. and Metaxas , V.L. ( 2012 ), “ Macroeconomic and bank-specific determinants of non-performing loans in Greece: a comparative study of mortgage, business and consumer loan portfolios ”, Journal of Banking and Finance , Vol. 36 No. 4 , pp. 1012 - 1027 .
Masood , O. and Ashraf , M. ( 2012 ), “ Bank-specific and macroeconomic profitability determinants of Islamic banks: the case of different countries ”, Qualitative Research in Financial Markets , Vol. 4 Nos 2/3 , pp. 255 - 268 .
Ofori-Abebrese , G. , Pickson , R.B. and Opare , E. ( 2016 ), “ The effect of bank specific factors on loan performance of HFC bank in Ghana ”, International Journal of Economics and Finance , Vol. 8 No. 7 , p. 185 .
Oluwafemi , A.S. , Adebisi , A.N.S. , Simeon , O. and Olawale , O. ( 2013 ), “ Risk management and financial performance of banks in Nigeria ”, Journal of Business and Management , Vol. 14 No. 6 , pp. 52 - 56 .
Rachman , R.A. , Kadarusman , Y.B. , Anggriono , K. and Setiadi , R. ( 2018 ), “ bank-specific factors affecting non-performing loans in developing countries: case study of Indonesia ”, The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business (JAFEB) , Vol. 5 No. 2 , pp. 35 - 42 .
Raphael , G. ( 2013 ), “ Bank-specific, industry-specific and macroeconomic determinants of bank efficiency in Tanzania: a two stage analysis ”, European Journal of Business and Management , Vol. 5 No. 2 , pp. 142 - 154 .
Sekaran , U. ( 2006 ), Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach , John Wiley & Sons .
Siddique , A. , Masood , O. , Javaria , K. and Huy , D.T.N. ( 2020 ), “ A comparative study of performance of commercial banks in ASIAN developing and developed countries ”, Insights Into Regional Development .
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Credit Risk Management Practices of Indian Banking Industry: An Empirical Study
- Author & abstract
- 5 References
- Most related
- Related works & more
Corrections
(ICFAI Business School, (IBS) IFHE, Hyderabad, India)
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher, references listed on ideas.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
- My Shodhganga
- Receive email updates
- Edit Profile
Shodhganga : a reservoir of Indian theses @ INFLIBNET
- Shodhganga@INFLIBNET
- Symbiosis International University
- Faculty of Management
Items in Shodhganga are licensed under Creative Commons Licence Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CREDIT RISK MANAGEMENT IN BANKS
Related Papers
the tainted patronus
IJMSBR Open Access Journal
A well-organized and efficient banking system is an essential prerequisite for the economic growth of every country. Galloping levels of Non-performing assets (NPAs) is one of the biggest problems faced by the Indian banking industry. The " stressed balance-sheet and bad-loan accounts " that have been hidden till now, would keep the NPA levels rising spread over 3-5 years. As on March 2015, gross NPAs stood at 4.6% and 5.17% of advances, while the stressed assets (NPAs + restructured loans) were 13.2%. It is estimated that the total quantum of stressed assets is about Rs. 10,000 billion. Undoubtedly, mounting NPAs and bad loans in the banking sector have been the focus of media headlines, which is directly affecting their balance sheets (higher provisions), and impacting the economy as well. Concern about asset quality has been one of the biggest challenges for the Indian regulator too. The extent of the challenge for nationalized banks is that " non-action is no longer an option. " In fact, India is seeing a regulatory upheaval in the way the Government and RBI are addressing the present crisis. The efforts are visible, but the results may be achieved only on a medium-to long-term basis. We feel there is an urgent need to solve the rising levels of NPAs and put a roadmap to control the reasons which lead to creation of such high NPAs. Some estimates suggest that around 35-40% of the stressed assets will require being written-off, and hence, banks need to recapitalize to that extent. This research paper explores an empirical approach to the analysis of NPA of public, private, and foreign sector banks in India. As part of this study, we have considered NPAs in Scheduled Commercial Banks, which includes 26 public-sector (nationalized) banks (PSBs), 5 private-sector scheduled banks (PVBs) and 10 scheduled foreign-banks (FBs), which are listed in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. This study is based on data for sampled banks in India for a period of 5 years, from the FY ended 2010-2011 to FY ended 2015-2016. Some statistical tools have been used for analyzing the trend of NPAs of all banks in India. The present study is primarily qualitative, analytical and descriptive, which is based on secondary sources of data. Findings of our study reveals that " extent of NPAs is very high, specifically in PSBs, as compared to PVB and FBs. Some banks have already started adopting predictive and pre-emptive strategies to improve asset quality to minimize NPA levels, but still a lot needs to be done to curb this vicious problem. We suggested all banks to adopt and implement the regulator policy measures of RBI in " true-spirit and substance " ; not just form. " Undoubtedly, the road to recovery is very long and winding, but bankers are optimistic that NPA situation will improve in the near future, albeit at a slow pace.
IAEME Publication
The global rating agency, MOODY’s recently in its report of 2013 as rated that the Indian Public Sector Banks from ‘Stable’ to ‘negative’. The RBI is also observed that in 2012-13 the NPAs of public Sector Banks were significantly increasing due to the poor asset quality and ineffective information systems. The study was taken with an objective of analyzing the impact and effect of NPAs of public sector banks and to suggest the suitable strategies to control and manage NPAs. The sample size taken for the study was 120 and the data was collected by way of questionnaire. The risk matrix for NPAs explains that the cause for NPAs are the internal and external factors among which the willful default by the borrower(external) and inefficient credit appraisal system(internal) are the key determinants. The findings of the study were to suggest the steps to minimize the credit risk and control the NPAs. The various factors determining the NPAs of Public Sector banks at higher degree are identified and various suggestions are given to minimize the NPAs
IJAR Indexing
In the recent scenario loan has become a willingness or ability to pay off which is a nightmare for banks. Basically NPA are default loans in the books of banks or are in arrears on scheduled payments of principal or interest has not been paid off within 90 days. We have analysis the secondary data of public and private sector bank for the year 2016 till the end of December 2017. It highlights those sway for NPA for execution for banks, prudential norms and new methodologies of government, suggestions to dispense with the terrible debts problem; bring, diminish and control NPA.
Nikhil Garg
International Res Jour Managt Socio Human
The Indian banking sector has been facing serious problems of raising Non-Performing Assets (NPAs). The NPAs growth has a direct impact on profitability of banks. Non-performing assets are one of the major concerns for public sector banks in Pune district. There seems to be no unanimity in the proper policies to be followed in resolving this problem. A high level of NPAs suggests high probability of a large number of credit defaults that affect the profitability and net-worth of banks and also erodes the value of the asset. NPAs affect the liquidity and profitability, in addition to posing threat on quality of asset and survival of banks. The problem of NPAs is not only affecting the banks but also the whole economy. In fact high level of NPAs in Indian banks is nothing but a reflection of the state of health of the industry and trade. It is necessary to trim down NPAs to improve the financial health in the banking system. An attempt is made in this paper to understand NPA, the status and trend of NPAs on public sector banks in Pune district. Keywords: NPA's, public sectors banks, Indian economy and recovery of NPA's etc.
Private Sector Banks (PSBs) in India have performed rather poorly over the past 3-4 years. For the most part this has been on account of Non Performing Asset (NPA) related worries which have so far been brushed under the carpet. The current level of NPAs as disclosed by most private sector banks is far from reality and made possible because of the flexibility enjoyed by PSBs in terms of disclosure requirements .A healthy and a sound banking system are very essential for an economy in order to grow and remain in this competitive environment. RBI and other regulatory bodies have taken several policies in the light of developing the functioning of the banking sector. The best indicator for the health of the banking industry in a country is its level of Non-performing assets (NPAs). It reflects the performance of banks. NPAs in the Indian banking sector have become a major concern for the Indian economy. NPA has a direct impact on the profitability, liquidity and solvency position of the bank. Higher NPA indicates inefficiency of the bank and lower NPA indicate better performance and management of funds. To improve the efficiency and profitability of banks the NPA need to be reduced and controlled. This paper basically deals with the trends of NPA in banking industry, the factors that mainly contribute to NPA raising in the banking industry and also provides some suggestions how to overcome this burden of NPA on banking industry. Keywords: Private sector Banks, Non-Performing Asset and Banking system etc. Introduction A non performing asset (NPA) is a loan or advance for which the principal or interest payment remained overdue for a period of 90 days. The most important business implication of the NPAs is that it leads to credit risk management assuming priority over other aspects of bank's functioning. The bank's whole machinery would thus be preoccupied with recovery procedures rather than concentrating on expanding business. A bank with a high level of NPAs would be forced to incur carrying costs on non-income yielding assets. Other consequences would be reduction in interest income, high level of provisioning (as banks are required to keep aside a portion of their operating profit as provisions, as NPAs increases banks have to increase the amount kept aside as provisions which will reduce their net profits) stress on profitability and capital adequacy, gradual decline in ability to meet steady increase in cost, increased pressure on Net Interest Margin (NIM) thereby reducing competitiveness, steady erosion of capital resources and increased difficulty in augmenting capital resources. Developing of sound and healthy
soundarya kodi
Sreejata Banerjee
RELATED PAPERS
Rajveer Rawlin
The IUP Journal of Financial Economics
Ram Pratap Sinha
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Open access
- Published: 03 September 2022

A literature review of risk, regulation, and profitability of banks using a scientometric study
- Shailesh Rastogi 1 ,
- Arpita Sharma 1 ,
- Geetanjali Pinto 2 &
- Venkata Mrudula Bhimavarapu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9757-1904 1 , 3
Future Business Journal volume 8 , Article number: 28 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
1 Citations
Metrics details
This study presents a systematic literature review of regulation, profitability, and risk in the banking industry and explores the relationship between them. It proposes a policy initiative using a model that offers guidelines to establish the right mix among these variables. This is a systematic literature review study. Firstly, the necessary data are extracted using the relevant keywords from the Scopus database. The initial search results are then narrowed down, and the refined results are stored in a file. This file is finally used for data analysis. Data analysis is done using scientometrics tools, such as Table2net and Sciences cape software, and Gephi to conduct network, citation analysis, and page rank analysis. Additionally, content analysis of the relevant literature is done to construct a theoretical framework. The study identifies the prominent authors, keywords, and journals that researchers can use to understand the publication pattern in banking and the link between bank regulation, performance, and risk. It also finds that concentration banking, market power, large banks, and less competition significantly affect banks’ financial stability, profitability, and risk. Ownership structure and its impact on the performance of banks need to be investigated but have been inadequately explored in this study. This is an organized literature review exploring the relationship between regulation and bank performance. The limitations of the regulations and the importance of concentration banking are part of the findings.
Introduction
Globally, banks are under extreme pressure to enhance their performance and risk management. The financial industry still recalls the ignoble 2008 World Financial Crisis (WFC) as the worst economic disaster after the Great Depression of 1929. The regulatory mechanism before 2008 (mainly Basel II) was strongly criticized for its failure to address banks’ risks [ 47 , 87 ]. Thus, it is essential to investigate the regulation of banks [ 75 ]. This study systematically reviews the relevant literature on banks’ performance and risk management and proposes a probable solution.
Issues of performance and risk management of banks
Banks have always been hailed as engines of economic growth and have been the axis of the development of financial systems [ 70 , 85 ]. A vital parameter of a bank’s financial health is the volume of its non-performing assets (NPAs) on its balance sheet. NPAs are advances that delay in payment of interest or principal beyond a few quarters [ 108 , 118 ]. According to Ghosh [ 51 ], NPAs negatively affect the liquidity and profitability of banks, thus affecting credit growth and leading to financial instability in the economy. Hence, healthy banks translate into a healthy economy.
Despite regulations, such as high capital buffers and liquidity ratio requirements, during the second decade of the twenty-first century, the Indian banking sector still witnessed a substantial increase in NPAs. A recent report by the Indian central bank indicates that the gross NPA ratio reached an all-time peak of 11% in March 2018 and 12.2% in March 2019 [ 49 ]. Basel II has been criticized for several reasons [ 98 ]. Schwerter [ 116 ] and Pakravan [ 98 ] highlighted the systemic risk and gaps in Basel II, which could not address the systemic risk of WFC 2008. Basel III was designed to close the gaps in Basel II. However, Schwerter [ 116 ] criticized Basel III and suggested that more focus should have been on active risk management practices to avoid any impending financial crisis. Basel III was proposed to solve these issues, but it could not [ 3 , 116 ]. Samitas and Polyzos [ 113 ] found that Basel III had made banking challenging since it had reduced liquidity and failed to shield the contagion effect. Therefore, exploring some solutions to establish the right balance between regulation, performance, and risk management of banks is vital.
Keeley [ 67 ] introduced the idea of a balance among banks’ profitability, regulation, and NPA (risk-taking). This study presents the balancing act of profitability, regulation, and NPA (risk-taking) of banks as a probable solution to the issues of bank performance and risk management and calls it a triad . Figure 1 illustrates the concept of a triad. Several authors have discussed the triad in parts [ 32 , 96 , 110 , 112 ]. Triad was empirically tested in different countries by Agoraki et al. [ 1 ]. Though the idea of a triad is quite old, it is relevant in the current scenario. The spirit of the triad strongly and collectively admonishes the Basel Accord and exhibits new and exhaustive measures to take up and solve the issue of performance and risk management in banks [ 16 , 98 ]. The 2008 WFC may have caused an imbalance among profitability, regulation, and risk-taking of banks [ 57 ]. Less regulation , more competition (less profitability ), and incentive to take the risk were the cornerstones of the 2008 WFC [ 56 ]. Achieving a balance among the three elements of a triad is a real challenge for banks’ performance and risk management, which this study addresses.
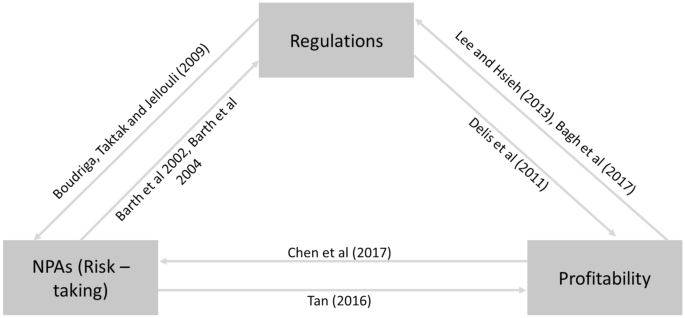
Triad of Profitability, regulation, and NPA (risk-taking). Note The triad [ 131 ] of profitability, regulation, and NPA (risk-taking) is shown in Fig. 1
Triki et al. [ 130 ] revealed that a bank’s performance is a trade-off between the elements of the triad. Reduction in competition increases the profitability of banks. However, in the long run, reduction in competition leads to either the success or failure of banks. Flexible but well-expressed regulation and less competition add value to a bank’s performance. The current review paper is an attempt to explore the literature on this triad of bank performance, regulation, and risk management. This paper has the following objectives:
To systematically explore the existing literature on the triad: performance, regulation, and risk management of banks; and
To propose a model for effective bank performance and risk management of banks.
Literature is replete with discussion across the world on the triad. However, there is a lack of acceptance of the triad as a solution to the woes of bank performance and risk management. Therefore, the findings of the current papers significantly contribute to this regard. This paper collates all the previous studies on the triad systematically and presents a curated view to facilitate the policy makers and stakeholders to make more informed decisions on the issue of bank performance and risk management. This paper also contributes significantly by proposing a DBS (differential banking system) model to solve the problem of banks (Fig. 7 ). This paper examines studies worldwide and therefore ensures the wider applicability of its findings. Applicability of the DBS model is not only limited to one nation but can also be implemented worldwide. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first study to systematically evaluate the publication pattern in banking using a blend of scientometrics analysis tools, network analysis tools, and content analysis to understand the link between bank regulation, performance, and risk.
This paper is divided into five sections. “ Data and research methods ” section discusses the research methodology used for the study. The data analysis for this study is presented in two parts. “ Bibliometric and network analysis ” section presents the results obtained using bibliometric and network analysis tools, followed by “ Content Analysis ” section, which presents the content analysis of the selected literature. “ Discussion of the findings ” section discusses the results and explains the study’s conclusion, followed by limitations and scope for further research.
Data and research methods
A literature review is a systematic, reproducible, and explicit way of identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant research produced and published by researchers [ 50 , 100 ]. Analyzing existing literature helps researchers generate new themes and ideas to justify the contribution made to literature. The knowledge obtained through evidence-based research also improves decision-making leading to better practical implementation in the real corporate world [ 100 , 129 ].
As Kumar et al. [ 77 , 78 ] and Rowley and Slack [ 111 ] recommended conducting an SLR, this study also employs a three-step approach to understand the publication pattern in the banking area and establish a link between bank performance, regulation, and risk.
Determining the appropriate keywords for exploring the data
Many databases such as Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus are available to extract the relevant data. The quality of a publication is associated with listing a journal in a database. Scopus is a quality database as it has a wider coverage of data [ 100 , 137 ]. Hence, this study uses the Scopus database to extract the relevant data.
For conducting an SLR, there is a need to determine the most appropriate keywords to be used in the database search engine [ 26 ]. Since this study seeks to explore a link between regulation, performance, and risk management of banks, the keywords used were “risk,” “regulation,” “profitability,” “bank,” and “banking.”
Initial search results and limiting criteria
Using the keywords identified in step 1, the search for relevant literature was conducted in December 2020 in the Scopus database. This resulted in the search of 4525 documents from inception till December 2020. Further, we limited our search to include “article” publications only and included subject areas: “Economics, Econometrics and Finance,” “Business, Management and Accounting,” and “Social sciences” only. This resulted in a final search result of 3457 articles. These results were stored in a.csv file which is then used as an input to conduct the SLR.
Data analysis tools and techniques
This study uses bibliometric and network analysis tools to understand the publication pattern in the area of research [ 13 , 48 , 100 , 122 , 129 , 134 ]. Some sub-analyses of network analysis are keyword word, author, citation, and page rank analysis. Author analysis explains the author’s contribution to literature or research collaboration, national and international [ 59 , 99 ]. Citation analysis focuses on many researchers’ most cited research articles [ 100 , 102 , 131 ].
The.csv file consists of all bibliometric data for 3457 articles. Gephi and other scientometrics tools, such as Table2net and ScienceScape software, were used for the network analysis. This.csv file is directly used as an input for this software to obtain network diagrams for better data visualization [ 77 ]. To ensure the study’s quality, the articles with 50 or more citations (216 in number) are selected for content analysis [ 53 , 102 ]. The contents of these 216 articles are analyzed to develop a conceptual model of banks’ triad of risk, regulation, and profitability. Figure 2 explains the data retrieval process for SLR.
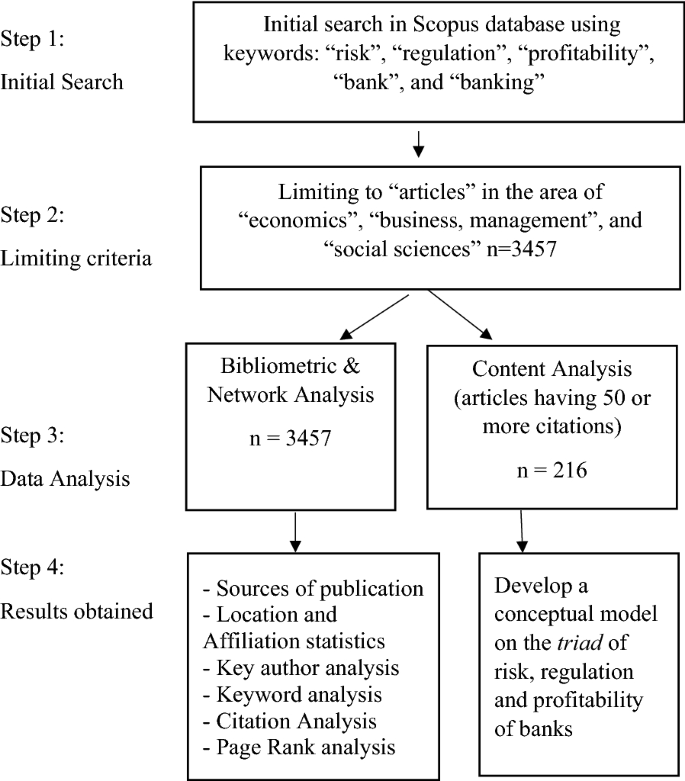
Data retrieval process for SLR. Note Stepwise SLR process and corresponding results obtained
Bibliometric and network analysis
Figure 3 [ 58 ] depicts the total number of studies that have been published on “risk,” “regulation,” “profitability,” “bank,” and “banking.” Figure 3 also depicts the pattern of the quality of the publications from the beginning till 2020. It undoubtedly shows an increasing trend in the number of articles published in the area of the triad: “risk” regulation” and “profitability.” Moreover, out of the 3457 articles published in the said area, 2098 were published recently in the last five years and contribute to 61% of total publications in this area.
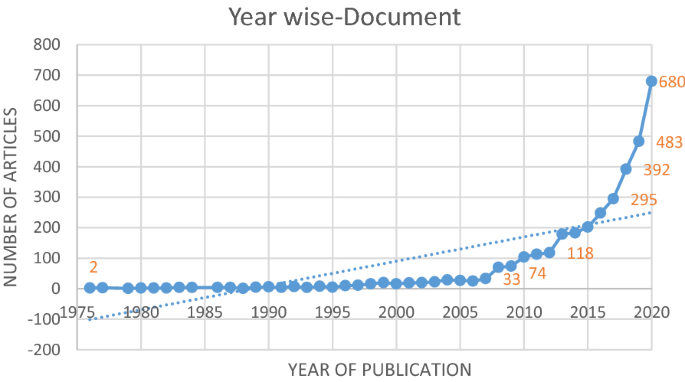
Articles published from 1976 till 2020 . Note The graph shows the number of documents published from 1976 till 2020 obtained from the Scopus database
Source of publications
A total of 160 journals have contributed to the publication of 3457 articles extracted from Scopus on the triad of risk, regulation, and profitability. Table 1 shows the top 10 sources of the publications based on the citation measure. Table 1 considers two sets of data. One data set is the universe of 3457 articles, and another is the set of 216 articles used for content analysis along with their corresponding citations. The global citations are considered for the study from the Scopus dataset, and the local citations are considered for the articles in the nodes [ 53 , 135 ]. The top 10 journals with 50 or more citations resulted in 96 articles. This is almost 45% of the literature used for content analysis ( n = 216). Table 1 also shows that the Journal of Banking and Finance is the most prominent in terms of the number of publications and citations. It has 46 articles published, which is about 21% of the literature used for content analysis. Table 1 also shows these core journals’ SCImago Journal Rank indicator and H index. SCImago Journal Rank indicator reflects the impact and prestige of the Journal. This indicator is calculated as the previous three years’ weighted average of the number of citations in the Journal since the year that the article was published. The h index is the number of articles (h) published in a journal and received at least h. The number explains the scientific impact and the scientific productivity of the Journal. Table 1 also explains the time span of the journals covering articles in the area of the triad of risk, regulation, and profitability [ 7 ].
Figure 4 depicts the network analysis, where the connections between the authors and source title (journals) are made. The network has 674 nodes and 911 edges. The network between the author and Journal is classified into 36 modularities. Sections of the graph with dense connections indicate high modularity. A modularity algorithm is a design that measures how strong the divided networks are grouped into modules; this means how well the nodes are connected through a denser route relative to other networks.

Network analysis between authors and journals. Note A node size explains the more linked authors to a journal
The size of the nodes is based on the rank of the degree. The degree explains the number of connections or edges linked to a node. In the current graph, a node represents the name of the Journal and authors; they are connected through the edges. Therefore, the more the authors are associated with the Journal, the higher the degree. The algorithm used for the layout is Yifan Hu’s.
Many authors are associated with the Journal of Banking and Finance, Journal of Accounting and Economics, Journal of Financial Economics, Journal of Financial Services Research, and Journal of Business Ethics. Therefore, they are the most relevant journals on banks’ risk, regulation, and profitability.
Location and affiliation analysis
Affiliation analysis helps to identify the top contributing countries and universities. Figure 5 shows the countries across the globe where articles have been published in the triad. The size of the circle in the map indicates the number of articles published in that country. Table 2 provides the details of the top contributing organizations.
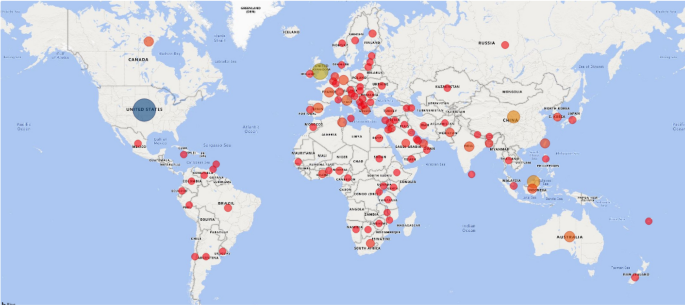
Location of articles published on Triad of profitability, regulation, and risk
Figure 5 shows that the most significant number of articles is published in the USA, followed by the UK. Malaysia and China have also contributed many articles in this area. Table 2 shows that the top contributing universities are also from Malaysia, the UK, and the USA.
Key author analysis
Table 3 shows the number of articles written by the authors out of the 3457 articles. The table also shows the top 10 authors of bank risk, regulation, and profitability.
Fadzlan Sufian, affiliated with the Universiti Islam Malaysia, has the maximum number, with 33 articles. Philip Molyneux and M. Kabir Hassan are from the University of Sharjah and the University of New Orleans, respectively; they contributed significantly, with 20 and 18 articles, respectively.
However, when the quality of the article is selected based on 50 or more citations, Fadzlan Sufian has only 3 articles with more than 50 citations. At the same time, Philip Molyneux and Allen Berger contributed more quality articles, with 8 and 11 articles, respectively.
Keyword analysis
Table 4 shows the keyword analysis (times they appeared in the articles). The top 10 keywords are listed in Table 4 . Banking and banks appeared 324 and 194 times, respectively, which forms the scope of this study, covering articles from the beginning till 2020. The keyword analysis helps to determine the factors affecting banks, such as profitability (244), efficiency (129), performance (107, corporate governance (153), risk (90), and regulation (89).
The keywords also show that efficiency through data envelopment analysis is a determinant of the performance of banks. The other significant determinants that appeared as keywords are credit risk (73), competition (70), financial stability (69), ownership structure (57), capital (56), corporate social responsibility (56), liquidity (46), diversification (45), sustainability (44), credit provision (41), economic growth (41), capital structure (39), microfinance (39), Basel III (37), non-performing assets (37), cost efficiency (30), lending behavior (30), interest rate (29), mergers and acquisition (28), capital adequacy (26), developing countries (23), net interest margin (23), board of directors (21), disclosure (21), leverage (21), productivity (20), innovation (18), firm size (16), and firm value (16).
Keyword analysis also shows the theories of banking and their determinants. Some of the theories are agency theory (23), information asymmetry (21), moral hazard (17), and market efficiency (16), which can be used by researchers when building a theory. The analysis also helps to determine the methodology that was used in the published articles; some of them are data envelopment analysis (89), which measures technical efficiency, panel data analysis (61), DEA (32), Z scores (27), regression analysis (23), stochastic frontier analysis (20), event study (15), and literature review (15). The count for literature review is only 15, which confirms that very few studies have conducted an SLR on bank risk, regulation, and profitability.
Citation analysis
One of the parameters used in judging the quality of the article is its “citation.” Table 5 shows the top 10 published articles with the highest number of citations. Ding and Cronin [ 44 ] indicated that the popularity of an article depends on the number of times it has been cited.
Tahamtan et al. [ 126 ] explained that the journal’s quality also affects its published articles’ citations. A quality journal will have a high impact factor and, therefore, more citations. The citation analysis helps researchers to identify seminal articles. The title of an article with 5900 citations is “A survey of corporate governance.”
Page Rank analysis
Goyal and Kumar [ 53 ] explain that the citation analysis indicates the ‘popularity’ and ‘prestige’ of the published research article. Apart from the citation analysis, one more analysis is essential: Page rank analysis. PageRank is given by Page et al. [ 97 ]. The impact of an article can be measured with one indicator called PageRank [ 135 ]. Page rank analysis indicates how many times an article is cited by other highly cited articles. The method helps analyze the web pages, which get the priority during any search done on google. The analysis helps in understanding the citation networks. Equation 1 explains the page rank (PR) of a published paper, N refers to the number of articles.
T 1,… T n indicates the paper, which refers paper P . C ( Ti ) indicates the number of citations. The damping factor is denoted by a “ d ” which varies in the range of 0 and 1. The page rank of all the papers is equal to 1. Table 6 shows the top papers based on page rank. Tables 5 and 6 together show a contrast in the top ranked articles based on citations and page rank, respectively. Only one article “A survey of corporate governance” falls under the prestigious articles based on the page rank.
Content analysis
Content Analysis is a research technique for conducting qualitative and quantitative analyses [ 124 ]. The content analysis is a helpful technique that provides the required information in classifying the articles depending on their nature (empirical or conceptual) [ 76 ]. By adopting the content analysis method [ 53 , 102 ], the selected articles are examined to determine their content. The classification of available content from the selected set of sample articles that are categorized under different subheads. The themes identified in the relationship between banking regulation, risk, and profitability are as follows.
Regulation and profitability of banks
The performance indicators of the banking industry have always been a topic of interest to researchers and practitioners. This area of research has assumed a special interest after the 2008 WFC [ 25 , 51 , 86 , 114 , 127 , 132 ]. According to research, the causes of poor performance and risk management are lousy banking practices, ineffective monitoring, inadequate supervision, and weak regulatory mechanisms [ 94 ]. Increased competition, deregulation, and complex financial instruments have made banks, including Indian banks, more vulnerable to risks [ 18 , 93 , 119 , 123 ]. Hence, it is essential to investigate the present regulatory machinery for the performance of banks.
There are two schools of thought on regulation and its possible impact on profitability. The first asserts that regulation does not affect profitability. The second asserts that regulation adds significant value to banks’ profitability and other performance indicators. This supports the concept that Delis et al. [ 41 ] advocated that the capital adequacy requirement and supervisory power do not affect productivity or profitability unless there is a financial crisis. Laeven and Majnoni [ 81 ] insisted that provision for loan loss should be part of capital requirements. This will significantly improve active risk management practices and ensure banks’ profitability.
Lee and Hsieh [ 83 ] proposed ambiguous findings that do not support either school of thought. According to Nguyen and Nghiem [ 95 ], while regulation is beneficial, it has a negative impact on bank profitability. As a result, when proposing regulations, it is critical to consider bank performance and risk management. According to Erfani and Vasigh [ 46 ], Islamic banks maintained their efficiency between 2006 and 2013, while most commercial banks lost, furthermore claimed that the financial crisis had no significant impact on Islamic bank profitability.
Regulation and NPA (risk-taking of banks)
The regulatory mechanism of banks in any country must address the following issues: capital adequacy ratio, prudent provisioning, concentration banking, the ownership structure of banks, market discipline, regulatory devices, presence of foreign capital, bank competition, official supervisory power, independence of supervisory bodies, private monitoring, and NPAs [ 25 ].
Kanoujiya et al. [ 64 ] revealed through empirical evidence that Indian bank regulations lack a proper understanding of what banks require and propose reforming and transforming regulation in Indian banks so that responsive governance and regulation can occur to make banks safer, supported by Rastogi et al. [ 105 ]. The positive impact of regulation on NPAs is widely discussed in the literature. [ 94 ] argue that regulation has multiple effects on banks, including reducing NPAs. The influence is more powerful if the country’s banking system is fragile. Regulation, particularly capital regulation, is extremely effective in reducing risk-taking in banks [ 103 ].
Rastogi and Kanoujiya [ 106 ] discovered evidence that disclosure regulations do not affect the profitability of Indian banks, supported by Karyani et al. [ 65 ] for the banks located in Asia. Furthermore, Rastogi and Kanoujiya [ 106 ] explain that disclosure is a difficult task as a regulatory requirement. It is less sustainable due to the nature of the imposed regulations in banks and may thus be perceived as a burden and may be overcome by realizing the benefits associated with disclosure regulation [ 31 , 54 , 101 ]. Zheng et al. [ 138 ] empirically discovered that regulation has no impact on the banks’ profitability in Bangladesh.
Governments enforce banking regulations to achieve a stable and efficient financial system [ 20 , 94 ]. The existing literature is inconclusive on the effects of regulatory compliance on banks’ risks or the reduction of NPAs [ 10 , 11 ]. Boudriga et al. [ 25 ] concluded that the regulatory mechanism plays an insignificant role in reducing NPAs. This is especially true in weak institutions, which are susceptible to corruption. Gonzalez [ 52 ] reported that firm regulations have a positive relationship with banks’ risk-taking, increasing the probability of NPAs. However, Boudriga et al. [ 25 ], Samitas and Polyzos [ 113 ], and Allen et al. [ 3 ] strongly oppose the use of regulation as a tool to reduce banks’ risk-taking.
Kwan and Laderman [ 79 ] proposed three levels in regulating banks, which are lax, liberal, and strict. The liberal regulatory framework leads to more diversification in banks. By contrast, the strict regulatory framework forces the banks to take inappropriate risks to compensate for the loss of business; this is a global problem [ 73 ].
Capital regulation reduces banks’ risk-taking [ 103 , 110 ]. Capital regulation leads to cost escalation, but the benefits outweigh the cost [ 103 ]. The trade-off is worth striking. Altman Z score is used to predict banks’ bankruptcy, and it found that the regulation increased the Altman’s Z-score [ 4 , 46 , 63 , 68 , 72 , 120 ]. Jin et al. [ 62 ] report a negative relationship between regulation and banks’ risk-taking. Capital requirements empowered regulators, and competition significantly reduced banks’ risk-taking [ 1 , 122 ]. Capital regulation has a limited impact on banks’ risk-taking [ 90 , 103 ].
Maji and De [ 90 ] suggested that human capital is more effective in managing banks’ credit risks. Besanko and Kanatas [ 21 ] highlighted that regulation on capital requirements might not mitigate risks in all scenarios, especially when recapitalization has been enforced. Klomp and De Haan [ 72 ] proposed that capital requirements and supervision substantially reduce banks’ risks.
A third-party audit may impart more legitimacy to the banking system [ 23 ]. The absence of third-party intervention is conspicuous, and this may raise a doubt about the reliability and effectiveness of the impact of regulation on bank’s risk-taking.
NPA (risk-taking) in banks and profitability
Profitability affects NPAs, and NPAs, in turn, affect profitability. According to the bad management hypothesis [ 17 ], higher profits would negatively affect NPAs. By contrast, higher profits may lead management to resort to a liberal credit policy (high earnings), which may eventually lead to higher NPAs [ 104 ].
Balasubramaniam [ 8 ] demonstrated that NPA has double negative effects on banks. NPAs increase stressed assets, reducing banks’ productive assets [ 92 , 117 , 136 ]. This phenomenon is relatively underexplored and therefore renders itself for future research.
Triad and the performance of banks
Regulation and triad.
Regulations and their impact on banks have been a matter of debate for a long time. Barth et al. [ 12 ] demonstrated that countries with a central bank as the sole regulatory body are prone to high NPAs. Although countries with multiple regulatory bodies have high liquidity risks, they have low capital requirements [ 40 ]. Barth et al. [ 12 ] supported the following steps to rationalize the existing regulatory mechanism on banks: (1) mandatory information [ 22 ], (2) empowered management of banks, and (3) increased incentive for private agents to exert corporate control. They show that profitability has an inverse relationship with banks’ risk-taking [ 114 ]. Therefore, standard regulatory practices, such as capital requirements, are not beneficial. However, small domestic banks benefit from capital restrictions.
DeYoung and Jang [ 43 ] showed that Basel III-based policies of liquidity convergence ratio (LCR) and net stable funding ratio (NSFR) are not fully executed across the globe, including the US. Dahir et al. [ 39 ] found that a decrease in liquidity and funding increases banks’ risk-taking, making banks vulnerable and reducing stability. Therefore, any regulation on liquidity risk is more likely to create problems for banks.
Concentration banking and triad
Kiran and Jones [ 71 ] asserted that large banks are marginally affected by NPAs, whereas small banks are significantly affected by high NPAs. They added a new dimension to NPAs and their impact on profitability: concentration banking or banks’ market power. Market power leads to less cost and more profitability, which can easily counter the adverse impact of NPAs on profitability [ 6 , 15 ].
The connection between the huge volume of research on the performance of banks and competition is the underlying concept of market power. Competition reduces market power, whereas concentration banking increases market power [ 25 ]. Concentration banking reduces competition, increases market power, rationalizes the banks’ risk-taking, and ensures profitability.
Tabak et al. [ 125 ] advocated that market power incentivizes banks to become risk-averse, leading to lower costs and high profits. They explained that an increase in market power reduces the risk-taking requirement of banks. Reducing banks’ risks due to market power significantly increases when capital regulation is executed objectively. Ariss [ 6 ] suggested that increased market power decreases competition, and thus, NPAs reduce, leading to increased banks’ stability.
Competition, the performance of banks, and triad
Boyd and De Nicolo [ 27 ] supported that competition and concentration banking are inversely related, whereas competition increases risk, and concentration banking decreases risk. A mere shift toward concentration banking can lead to risk rationalization. This finding has significant policy implications. Risk reduction can also be achieved through stringent regulations. Bolt and Tieman [ 24 ] explained that stringent regulation coupled with intense competition does more harm than good, especially concerning banks’ risk-taking.
Market deregulation, as well as intensifying competition, would reduce the market power of large banks. Thus, the entire banking system might take inappropriate and irrational risks [ 112 ]. Maji and Hazarika [ 91 ] added more confusion to the existing policy by proposing that, often, there is no relationship between capital regulation and banks’ risk-taking. However, some cases have reported a positive relationship. This implies that banks’ risk-taking is neutral to regulation or leads to increased risk. Furthermore, Maji and Hazarika [ 91 ] revealed that competition reduces banks’ risk-taking, contrary to popular belief.
Claessens and Laeven [ 36 ] posited that concentration banking influences competition. However, this competition exists only within the restricted circle of banks, which are part of concentration banking. Kasman and Kasman [ 66 ] found that low concentration banking increases banks’ stability. However, they were silent on the impact of low concentration banking on banks’ risk-taking. Baselga-Pascual et al. [ 14 ] endorsed the earlier findings that concentration banking reduces banks’ risk-taking.
Concentration banking and competition are inversely related because of the inherent design of concentration banking. Market power increases when only a few large banks are operating; thus, reduced competition is an obvious outcome. Barra and Zotti [ 9 ] supported the idea that market power, coupled with competition between the given players, injects financial stability into banks. Market power and concentration banking affect each other. Therefore, concentration banking with a moderate level of regulation, instead of indiscriminate regulation, would serve the purpose better. Baselga-Pascual et al. [ 14 ] also showed that concentration banking addresses banks’ risk-taking.
Schaeck et al. [ 115 ], in a landmark study, presented that concentration banking and competition reduce banks’ risk-taking. However, they did not address the relationship between concentration banking and competition, which are usually inversely related. This could be a subject for future research. Research on the relationship between concentration banking and competition is scant, identified as a research gap (“ Research Implications of the study ” section).
Transparency, corporate governance, and triad
One of the big problems with NPAs is the lack of transparency in both the regulatory bodies and banks [ 25 ]. Boudriga et al. [ 25 ] preferred to view NPAs as a governance issue and thus, recommended viewing it from a governance perspective. Ahmad and Ariff [ 2 ] concluded that regulatory capital and top-management quality determine banks’ credit risk. Furthermore, they asserted that credit risk in emerging economies is higher than that of developed economies.
Bad management practices and moral vulnerabilities are the key determinants of insolvency risks of Indian banks [ 95 ]. Banks are an integral part of the economy and engines of social growth. Therefore, banks enjoy liberal insolvency protection in India, especially public sector banks, which is a critical issue. Such a benevolent insolvency cover encourages a bank to be indifferent to its capital requirements. This indifference takes its toll on insolvency risk and profit efficiency. Insolvency protection makes the bank operationally inefficient and complacent.
Foreign equity and corporate governance practices help manage the adverse impact of banks’ risk-taking to ensure the profitability and stability of banks [ 33 , 34 ]. Eastburn and Sharland [ 45 ] advocated that sound management and a risk management system that can anticipate any impending risk are essential. A pragmatic risk mechanism should replace the existing conceptual risk management system.
Lo [ 87 ] found and advocated that the existing legislation and regulations are outdated. He insisted on a new perspective and asserted that giving equal importance to behavioral aspects and the rational expectations of customers of banks is vital. Buston [ 29 ] critiqued the balance sheet risk management practices prevailing globally. He proposed active risk management practices that provided risk protection measures to contain banks’ liquidity and solvency risks.
Klomp and De Haan [ 72 ] championed the cause of giving more autonomy to central banks of countries to provide stability in the banking system. Louzis et al. [ 88 ] showed that macroeconomic variables and the quality of bank management determine banks’ level of NPAs. Regulatory authorities are striving hard to make regulatory frameworks more structured and stringent. However, the recent increase in loan defaults (NPAs), scams, frauds, and cyber-attacks raise concerns about the effectiveness [ 19 ] of the existing banking regulations in India as well as globally.
Discussion of the findings
The findings of this study are based on the bibliometric and content analysis of the sample published articles.
The bibliometric study concludes that there is a growing demand for researchers and good quality research
The keyword analysis suggests that risk regulation, competition, profitability, and performance are key elements in understanding the banking system. The main authors, keywords, and journals are grouped in a Sankey diagram in Fig. 6 . Researchers can use the following information to understand the publication pattern on banking and its determinants.
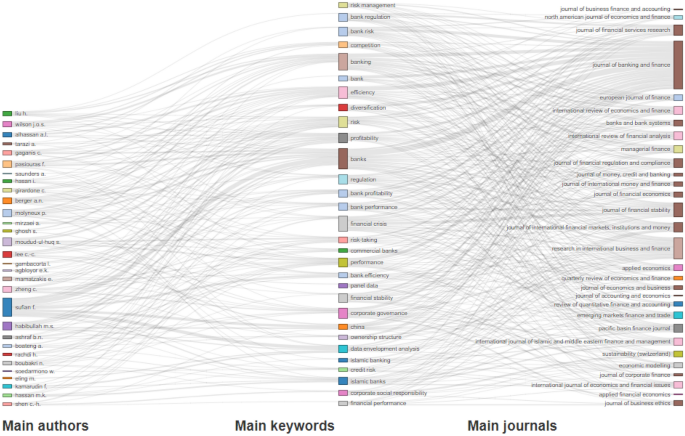
Sankey Diagram of main authors, keywords, and journals. Note Authors contribution using scientometrics tools
Research Implications of the study
The study also concludes that a balance among the three components of triad is the solution to the challenges of banks worldwide, including India. We propose the following recommendations and implications for banks:
This study found that “the lesser the better,” that is, less regulation enhances the performance and risk management of banks. However, less regulation does not imply the absence of regulation. Less regulation means the following:
Flexible but full enforcement of the regulations
Customization, instead of a one-size-fits-all regulatory system rooted in a nation’s indigenous requirements, is needed. Basel or generic regulation can never achieve what a customized compliance system can.
A third-party audit, which is above the country's central bank, should be mandatory, and this would ensure that all three aspects of audit (policy formulation, execution, and audit) are handled by different entities.
Competition
This study asserts that the existing literature is replete with poor performance and risk management due to excessive competition. Banking is an industry of a different genre, and it would be unfair to compare it with the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) or telecommunication industry, where competition injects efficiency into the system, leading to customer empowerment and satisfaction. By contrast, competition is a deterrent to the basic tenets of safe banking. Concentration banking is more effective in handling the multi-pronged balance between the elements of the triad. Concentration banking reduces competition to lower and manageable levels, reduces banks’ risk-taking, and enhances profitability.
No incentive to take risks
It is found that unless banks’ risk-taking is discouraged, the problem of high NPA (risk-taking) cannot be addressed. Concentration banking is a disincentive to risk-taking and can be a game-changer in handling banks’ performance and risk management.
Research on the risk and performance of banks reveals that the existing regulatory and policy arrangement is not a sustainable proposition, especially for a country where half of the people are unbanked [ 37 ]. Further, the triad presented by Keeley [ 67 ] is a formidable real challenge to bankers. The balance among profitability, risk-taking, and regulation is very subtle and becomes harder to strike, just as the banks globally have tried hard to achieve it. A pragmatic intervention is needed; hence, this study proposes a change in the banking structure by having two types of banks functioning simultaneously to solve the problems of risk and performance of banks. The proposed two-tier banking system explained in Fig. 7 can be a great solution. This arrangement will help achieve the much-needed balance among the elements of triad as presented by Keeley [ 67 ].
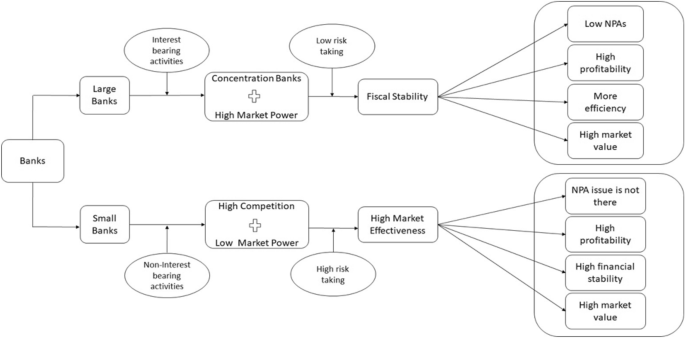
Conceptual Framework. Note Fig. 7 describes the conceptual framework of the study
The first set of banks could be conventional in terms of their structure and should primarily be large-sized. The number of such banks should be moderate. There is a logic in having only a few such banks to restrict competition; thus, reasonable market power could be assigned to them [ 55 ]. However, a reduction in competition cannot be over-assumed, and banks cannot become complacent. As customary, lending would be the main source of revenue and income for these banks (fund based activities) [ 82 ]. The proposed two-tier system can be successful only when regulation especially for risk is objectively executed [ 29 ]. The second set of banks could be smaller in size and more in number. Since they are more in number, they would encounter intense competition for survival and for generating more business. Small is beautiful, and thus, this set of banks would be more agile and adaptable and consequently more efficient and profitable. The main source of revenue for this set of banks would not be loans and advances. However, non-funding and non-interest-bearing activities would be the major revenue source. Unlike their traditional and large-sized counterparts, since these banks are smaller in size, they are less likely to face risk-taking and NPAs [ 74 ].
Sarmiento and Galán [ 114 ] presented the concerns of large and small banks and their relative ability and appetite for risk-taking. High risk could threaten the existence of small-sized banks; thus, they need robust risk shielding. Small size makes them prone to failure, and they cannot convert their risk into profitability. However, large banks benefit from their size and are thus less vulnerable and can convert risk into profitable opportunities.
India has experimented with this Differential Banking System (DBS) (two-tier system) only at the policy planning level. The execution is impending, and it highly depends on the political will, which does not appear to be strong now. The current agenda behind the DBS model is not to ensure the long-term sustainability of banks. However, it is currently being directed to support the agenda of financial inclusion by extending the formal credit system to the unbanked masses [ 107 ]. A shift in goal is needed to employ the DBS as a strategic decision, but not merely a tool for financial inclusion. Thus, the proposed two-tier banking system (DBS) can solve the issue of profitability through proper regulation and less risk-taking.
The findings of Triki et al. [ 130 ] support the proposed DBS model, in this study. Triki et al. [ 130 ] advocated that different component of regulations affect banks based on their size, risk-taking, and concentration banking (or market power). Large size, more concentration banking with high market power, and high risk-taking coupled with stringent regulation make the most efficient banks in African countries. Sharifi et al. [ 119 ] confirmed that size advantage offers better risk management to large banks than small banks. The banks should modify and work according to the economic environment in the country [ 69 ], and therefore, the proposed model could help in solving the current economic problems.
This is a fact that DBS is running across the world, including in India [ 60 ] and other countries [ 133 ]. India experimented with DBS in the form of not only regional rural banks (RRBs) but payments banks [ 109 ] and small finance banks as well [ 61 ]. However, the purpose of all the existing DBS models, whether RRBs [ 60 ], payment banks, or small finance banks, is financial inclusion, not bank performance and risk management. Hence, they are unable to sustain and are failing because their model is only social instead of a much-needed dual business-cum-social model. The two-tier model of DBS proposed in the current paper can help serve the dual purpose. It may not only be able to ensure bank performance and risk management but also serve the purpose of inclusive growth of the economy.
Conclusion of the study
The study’s conclusions have some significant ramifications. This study can assist researchers in determining their study plan on the current topic by using a scientific approach. Citation analysis has aided in the objective identification of essential papers and scholars. More collaboration between authors from various countries/universities may help countries/universities better understand risk regulation, competition, profitability, and performance, which are critical elements in understanding the banking system. The regulatory mechanism in place prior to 2008 failed to address the risk associated with banks [ 47 , 87 ]. There arises a necessity and motivates authors to investigate the current topic. The present study systematically explores the existing literature on banks’ triad: performance, regulation, and risk management and proposes a probable solution.
To conclude the bibliometric results obtained from the current study, from the number of articles published from 1976 to 2020, it is evident that most of the articles were published from the year 2010, and the highest number of articles were published in the last five years, i.e., is from 2015. The authors discovered that researchers evaluate articles based on the scope of critical journals within the subject area based on the detailed review. Most risk, regulation, and profitability articles are published in peer-reviewed journals like; “Journal of Banking and Finance,” “Journal of Accounting and Economics,” and “Journal of Financial Economics.” The rest of the journals are presented in Table 1 . From the affiliation statistics, it is clear that most of the research conducted was affiliated with developed countries such as Malaysia, the USA, and the UK. The researchers perform content analysis and Citation analysis to access the type of content where the research on the current field of knowledge is focused, and citation analysis helps the academicians understand the highest cited articles that have more impact in the current research area.
Practical implications of the study
The current study is unique in that it is the first to systematically evaluate the publication pattern in banking using a combination of scientometrics analysis tools, network analysis tools, and content analysis to understand the relationship between bank regulation, performance, and risk. The study’s practical implications are that analyzing existing literature helps researchers generate new themes and ideas to justify their contribution to literature. Evidence-based research knowledge also improves decision-making, resulting in better practical implementation in the real corporate world [ 100 , 129 ].
Limitations and scope for future research
The current study only considers a single database Scopus to conduct the study, and this is one of the limitations of the study spanning around the multiple databases can provide diverse results. The proposed DBS model is a conceptual framework that requires empirical testing, which is a limitation of this study. As a result, empirical testing of the proposed DBS model could be a future research topic.
Availability of data and materials
SCOPUS database.
Abbreviations
Systematic literature review
World Financial Crisis
Non-performing assets
Differential banking system
SCImago Journal Rank Indicator
Liquidity convergence ratio
Net stable funding ratio
Fast moving consumer goods
Regional rural banks
Agoraki M-EK, Delis MD, Pasiouras F (2011) Regulations, competition and bank risk-taking in transition countries. J Financ Stab 7(1):38–48
Google Scholar
Ahmad NH, Ariff M (2007) Multi-country study of bank credit risk determinants. Int J Bank Financ 5(1):35–62
Allen B, Chan KK, Milne A, Thomas S (2012) Basel III: Is the cure worse than the disease? Int Rev Financ Anal 25:159–166
Altman EI (2018) A fifty-year retrospective on credit risk models, the Altman Z-score family of models, and their applications to financial markets and managerial strategies. J Credit Risk 14(4):1–34
Alvarez F, Jermann UJ (2000) Efficiency, equilibrium, and asset pricing with risk of default. Econometrica 68(4):775–797
Ariss RT (2010) On the implications of market power in banking: evidence from developing countries. J Bank Financ 34(4):765–775
Aznar-Sánchez JA, Piquer-Rodríguez M, Velasco-Muñoz JF, Manzano-Agugliaro F (2019) Worldwide research trends on sustainable land use in agriculture. Land Use Policy 87:104069
Balasubramaniam C (2012) Non-performing assets and profitability of commercial banks in India: assessment and emerging issues. Nat Mon Refereed J Res Commer Manag 1(1):41–52
Barra C, Zotti R (2017) On the relationship between bank market concentration and stability of financial institutions: evidence from the Italian banking sector, MPRA working Paper No 79900. Last Accessed on Jan 2021 https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/79900/1/MPRA_paper_79900.pdf
Barth JR, Caprio G, Levine R (2004) Bank regulation and supervision: what works best? J Financ Intermed 2(13):205–248
Barth JR, Caprio G, Levine R (2008) Bank regulations are changing: For better or worse? Comp Econ Stud 50(4):537–563
Barth JR, Dopico LG, Nolle DE, Wilcox JA (2002) Bank safety and soundness and the structure of bank supervision: a cross-country analysis. Int Rev Financ 3(3–4):163–188
Bartolini M, Bottani E, Grosse EH (2019) Green warehousing: systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. J Clean Prod 226:242–258
Baselga-Pascual L, Trujillo-Ponce A, Cardone-Riportella C (2015) Factors influencing bank risk in Europe: evidence from the financial crisis. N Am J Econ Financ 34(1):138–166
Beck T, Demirgüç-Kunt A, Levine R (2006) Bank concentration, competition, and crises: first results. J Bank Financ 30(5):1581–1603
Berger AN, Demsetz RS, Strahan PE (1999) The consolidation of the financial services industry: causes, consequences, and implications for the future. J Bank Financ 23(2–4):135–194
Berger AN, Deyoung R (1997) Problem loans and cost efficiency in commercial banks. J Bank Financ 21(6):849–870
Berger AN, Udell GF (1998) The economics of small business finance: the roles of private equity and debt markets in the financial growth cycle. J Bank Financ 22(6–8):613–673
Berger AN, Udell GF (2002) Small business credit availability and relationship lending: the importance of bank organisational structure. Econ J 112(477):F32–F53
Berger AN, Udell GF (2006) A more complete conceptual framework for SME finance. J Bank Financ 30(11):2945–2966
Besanko D, Kanatas G (1996) The regulation of bank capital: Do capital standards promote bank safety? J Financ Intermed 5(2):160–183
Beyer A, Cohen DA, Lys TZ, Walther BR (2010) The financial reporting environment: review of the recent literature. J Acc Econ 50(2–3):296–343
Bikker JA (2010) Measuring performance of banks: an assessment. J Appl Bus Econ 11(4):141–159
Bolt W, Tieman AF (2004) Banking competition, risk and regulation. Scand J Econ 106(4):783–804
Boudriga A, BoulilaTaktak N, Jellouli S (2009) Banking supervision and non-performing loans: a cross-country analysis. J Financ Econ Policy 1(4):286–318
Bouzon M, Miguel PAC, Rodriguez CMT (2014) Managing end of life products: a review of the literature on reverse logistics in Brazil. Manag Environ Qual Int J 25(5):564–584. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-04-2013-0027
Article Google Scholar
Boyd JH, De Nicolo G (2005) The theory of bank risk taking and competition revisited. J Financ 60(3):1329–1343
Brealey RA, Myers SC, Allen F, Mohanty P (2012) Principles of corporate finance. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
Buston CS (2016) Active risk management and banking stability. J Bank Financ 72:S203–S215
Casu B, Girardone C (2006) Bank competition, concentration and efficiency in the single European market. Manch Sch 74(4):441–468
Charumathi B, Ramesh L (2020) Impact of voluntary disclosure on valuation of firms: evidence from Indian companies. Vision 24(2):194–203
Chen X (2007) Banking deregulation and credit risk: evidence from the EU. J Financ Stab 2(4):356–390
Chen H-J, Lin K-T (2016) How do banks make the trade-offs among risks? The role of corporate governance. J Bank Financ 72(1):S39–S69
Chen M, Wu J, Jeon BN, Wang R (2017) Do foreign banks take more risk? Evidence from emerging economies. J Bank Financ 82(1):20–39
Claessens S, Laeven L (2003) Financial development, property rights, and growth. J Financ 58(6):2401–2436. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1540-6261.2003.00610.x
Claessens S, Laeven L (2004) What drives bank competition? Some international evidence. J Money Credit Bank 36(3):563–583
Cnaan RA, Moodithaya M, Handy F (2012) Financial inclusion: lessons from rural South India. J Soc Policy 41(1):183–205
Core JE, Holthausen RW, Larcker DF (1999) Corporate governance, chief executive officer compensation, and firm performance. J Financ Econ 51(3):371–406
Dahir AM, Mahat FB, Ali NAB (2018) Funding liquidity risk and bank risk-taking in BRICS countries: an application of system GMM approach. Int J Emerg Mark 13(1):231–248
Dechow P, Ge W, Schrand C (2010) Understanding earnings quality: a review of the proxies, their determinants, and their consequences. J Acc Econ 50(2–3):344–401
Delis MD, Molyneux P, Pasiouras F (2011) Regulations and productivity growth in banking: evidence from transition economies. J Money Credit Bank 43(4):735–764
Demirguc-Kunt A, Laeven L, Levine R (2003) Regulations, market structure, institutions, and the cost of financial intermediation (No. w9890). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Deyoung R, Jang KY (2016) Do banks actively manage their liquidity? J Bank Financ 66:143–161
Ding Y, Cronin B (2011) Popularand/orprestigious? Measures of scholarly esteem. Inf Process Manag 47(1):80–96
Eastburn RW, Sharland A (2017) Risk management and managerial mindset. J Risk Financ 18(1):21–47
Erfani GR, Vasigh B (2018) The impact of the global financial crisis on profitability of the banking industry: a comparative analysis. Economies 6(4):66
Erkens DH, Hung M, Matos P (2012) Corporate governance in the 2007–2008 financial crisis: evidence from financial institutions worldwide. J Corp Finan 18(2):389–411
Fahimnia B, Sarkis J, Davarzani H (2015) Green supply chain management: a review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Econ 162:101–114
Financial Stability Report (2019) Financial stability report (20), December 2019. https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/PublicationReportDetails.aspx?UrlPage=&ID=946 Accesses on March 2020
Fink A (2005) Conducting Research Literature Reviews:From the Internet to Paper, 2nd edn. SAGE Publications
Ghosh A (2015) Banking-industry specific and regional economic determinants of non-performing loans: evidence from US states. J Financ Stab 20:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfs.2015.08.004
Gonzalez F (2005) Bank regulation and risk-taking incentives: an international comparison of bank risk. J Bank Financ 29(5):1153–1184
Goyal K, Kumar S (2021) Financial literacy: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Consum Stud 45(1):80–105
Grassa R, Moumen N, Hussainey K (2020) Do ownership structures affect risk disclosure in Islamic banks? International evidence. J Financ Rep Acc 19(3):369–391
Haque F, Shahid R (2016) Ownership, risk-taking and performance of banks in emerging economies: evidence from India. J Financ Econ Policy 8(3):282–297
Hellmann TF, Murdock KC, Stiglitz JE (2000) Liberalization, moral hazard in banking, and prudential regulation: Are capital requirements enough? Am Econ Rev 90(1):147–165
Hirshleifer D (2001) Investor psychology and asset pricing. J Financ 56(4):1533–1597
Huang J, You JX, Liu HC, Song MS (2020) Failure mode and effect analysis improvement: a systematic literature review and future research agenda. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 199:106885
Ibáñez Zapata A (2017) Bibliometric analysis of the regulatory compliance function within the banking sector (Doctoral dissertation). Last Accessed on Jan 2021 https://riunet.upv.es/bitstream/handle/10251/85952/Bibliometric%20analysis_AIZ_v4.pdf?sequence=1
Ibrahim MS (2010) Performance evaluation of regional rural banks in India. Int Bus Res 3(4):203–211
Jayadev M, Singh H, Kumar P (2017) Small finance banks: challenges. IIMB Manag Rev 29(4):311–325
Jin JY, Kanagaretnam K, Lobo GJ, Mathieu R (2013) Impact of FDICIA internal controls on bank risk taking. J Bank Financ 37(2):614–624
Joshi MK (2020) Financial performance analysis of select Indian Public Sector Banks using Altman’s Z-Score model. SMART J Bus Manag Stud 16(2):74–87
Kanoujiya J, Bhimavarapu VM, Rastogi S (2021) Banks in India: a balancing act between profitability, regulation and NPA. Vision, 09722629211034417
Karyani E, Dewo SA, Santoso W, Frensidy B (2020) Risk governance and bank profitability in ASEAN-5: a comparative and empirical study. Int J Emerg Mark 15(5):949–969
Kasman S, Kasman A (2015) Bank competition, concentration and financial stability in the Turkish banking industry. Econ Syst 39(3):502–517
Keeley MC (1990) Deposit insurance, risk, and market power in banking. Am Econ Rev 1:1183–1200
Khaddafi M, Heikal M, Nandari A (2017) Analysis Z-score to predict bankruptcy in banks listed in indonesia stock exchange. Int J Econ Financ Issues 7(3):326–330
Khanna T, Yafeh Y (2007) Business groups in emerging markets: Paragons or parasites? J Econ Lit 45(2):331–372
King RG, Levine R (1993) Finance and growth: schumpeter might be right. Q J Econ 108(3):717–737
Kiran KP, Jones TM (2016) Effect of non performing assets on the profitability of banks–a selective study. Int J Bus Gen Manag 5(2):53–60
Klomp J, De Haan J (2015) Banking risk and regulation: Does one size fit all? J Bank Financ 36(12):3197–3212
Koehn M, Santomero AM (1980) Regulation of bank capital and portfolio risk. J Financ 35(5):1235–1244
Köhler M (2015) Which banks are more risky? The impact of business models on bank stability. J Financ Stab 16(1):195–212
Kothari SP (2001) Capital markets research in accounting. J Account Econ 31(1–3):105–231
Kumar S, Goyal N (2015) Behavioural biases in investment decision making – a systematic literature review. Qual Res Financ Mark 7(1):88–108
Kumar S, Kamble S, Roy MH (2020) Twenty-five years of Benchmarking: an International Journal (BIJ): a bibliometric overview. Benchmarking Int J 27(2):760–780. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-07-2019-0314
Kumar S, Sureka R, Colombage S (2020) Capital structure of SMEs: a systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Manag Rev Q 70(4):535–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00175-4
Kwan SH, Laderman ES (1999) On the portfolio effects of financial convergence-a review of the literature. Econ Rev 2:18–31
Lado AA, Boyd NG, Hanlon SC (1997) Competition, cooperation, and the search for economic rents: a syncretic model. Acad Manag Rev 22(1):110–141
Laeven L, Majnoni G (2003) Loan loss provisioning and economic slowdowns: Too much, too late? J Financ Intermed 12(2):178–197
Laeven L, Ratnovski L, Tong H (2016) Bank size, capital, and systemic risk: Some international evidence. J Bank Finance 69(1):S25–S34
Lee C-C, Hsieh M-F (2013) The impact of bank capital on profitability and risk in Asian banking. J Int Money Financ 32(1):251–281
Leech D, Leahy J (1991) Ownership structure, control type classifications and the performance of large British companies. Econ J 101(409):1418–1437
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35(2):688–726
Lim CY, Woods M, Humphrey C, Seow JL (2017) The paradoxes of risk management in the banking sector. Br Acc Rev 49(1):75–90
Lo AW (2009) Regulatory reform in the wake of the financial crisis of 2007–2008. J Financ Econ Policy 1(1):4–43
Louzis DP, Vouldis AT, Metaxas VL (2012) Macroeconomic and bank-specific determinants of non-performing loans in Greece: a comparative study of mortgage, business and consumer loan portfolios. J Bank Financ 36(4):1012–1027
Maddaloni A, Peydró J-L (2011) Bank risk-taking, securitization, supervision, and low interest rates: evidence from the Euro-area and the U.S. lending standards. Rev Financ Stud 24(6):2121–2165. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhr015
Maji SG, De UK (2015) Regulatory capital and risk of Indian banks: a simultaneous equation approach. J Financ Econ Policy 7(2):140–156
Maji SG, Hazarika P (2018) Capital regulation, competition and risk-taking behavior of Indian banks in a simultaneous approach. Manag Financ 44(4):459–477
Messai AS, Jouini F (2013) Micro and macro determinants of non-performing loans. Int J Econ Financ Issues 3(4):852–860
Mitra S, Karathanasopoulos A, Sermpinis G, Dunis C, Hood J (2015) Operational risk: emerging markets, sectors and measurement. Eur J Oper Res 241(1):122–132
Mohsni S, Otchere I (2018) Does regulatory regime matter for bank risk-taking? A comparative analysis of US and Canada, d/Seas Working Papers-ISSN 2611-0172 1(1):28–28
Nguyen TPT, Nghiem SH (2015) The interrelationships among default risk, capital ratio and efficiency: evidence from Indian banks. Manag Financ 41(5):507–525
Niinimäki J-P (2004) The effects of competition on banks’ risk taking. J Econ 81(3):199–222
Page L, Brin S, Motwani R, Winograd T (1999) The PageRank citation ranking: bringing order to the web. Stanford InfoLab
Pakravan K (2014) Bank capital: the case against Basel. J Financ Regul Compl 22(3):208–218
Palacios-Callender M, Roberts SA, Roth-Berghofer T (2016) Evaluating patterns of national and international collaboration in Cuban science using bibliometric tools. J Doc 72(2):362–390. https://doi.org/10.1108/JD-11-2014-0164
Pinto G, Rastogi S, Kadam S, Sharma A (2019) Bibliometric study on dividend policy. Qual Res Financ Mark 12(1):72–95
Polizzi S, Scannella E (2020) An empirical investigation into market risk disclosure: Is there room to improve for Italian banks? J Financ Regul Compl 28(3):465–483
Prasad P, Narayanasamy S, Paul S, Chattopadhyay S, Saravanan P (2019) Review of literature on working capital management and future research agenda. J Econ Surv 33(3):827–861
Rahman MM, Zheng C, Ashraf BN, Rahman MM (2018) Capital requirements, the cost of financial intermediation and bank risk-taking: empirical evidence from Bangladesh. Res Int Bus Financ 44(1):488–503
Rajan RG (1994) Why bank credit policies fluctuate: a theory and some evidence. Q J Econ 109(2):399–441
Rastogi S, Gupte R, Meenakshi R (2021) A holistic perspective on bank performance using regulation, profitability, and risk-taking with a view on ownership concentration. J Risk Financ Manag 14(3):111
Rastogi S, Kanoujiya J (2022) Does transparency and disclosure (T&D) improve the performance of banks in India? Int J Product Perform Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-10-2021-0613
Rastogi S, Ragabiruntha E (2018) Financial inclusion and socioeconomic development: gaps and solution. Int J Soc Econ 45(7):1122–1140
RBI (2001) Prudential Norms on income recognition, asset classification, and provisioning -pertaining to advances. Accessed on Apr 2020. https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/23068.pdf
Reddy S (2018) Announcement of payment banks and stock performance of commercial banks in India. J Internet Bank Commer 23(1):1–12
Repullo R (2004) Capital requirements, market power, and risk-taking in banking. J Financ Intermed 13(2):156–182
Rowley J, Slack F (2004) Conducting a literature review. Manag Res News 27(6):31–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/01409170410784185
Salas V, Saurina J (2003) Deregulation, market power and risk behaviour in Spanish banks. Eur Econ Rev 47(6):1061–1075
Samitas A, Polyzos S (2015) To Basel or not to Basel? Banking crises and contagion. Journal of Financial Regulation and Compliance 23(3):298–318
Sarmiento M, Galán JE (2017) The influence of risk-taking on bank efficiency: evidence from Colombia. Emerg Mark Rev 32:52–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ememar.2017.05.007
Schaeck K, Cihak M, Wolfe S (2009) Are competitive banking systems more stable? J Money Credit Bank 41(4):711–734
Schwerter S (2011) Basel III’s ability to mitigate systemic risk. J Financ Regul Compl 19(4):337–354
Sen S, Sen RL (2014) Impact of NPAs on bank profitability: an empirical study. In: Ray N, Chakraborty K (eds) Handbook of research on strategic business infrastructure development and contemporary issues in finance. IGI Global, pp 124–134. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-5154-8.ch010
Chapter Google Scholar
Shajahan K (1998) Non-performing assets of banks: Have they really declined? And on whose account? Econ Pol Wkly 33(12):671–674
Sharifi S, Haldar A, Rao SN (2016) Relationship between operational risk management, size, and ownership of Indian banks. Manag Financ 42(10):930–942
Sharma A, Theresa L, Mhatre J, Sajid M (2019) Application of altman Z-Score to RBI defaulters: Indian case. Asian J Res Bus Econ Manag 9(4):1–11
Shehzad CT, De Haan J (2015) Supervisory powers and bank risk taking. J Int Finan Markets Inst Money 39(1):15–24
Shen L, Xiong B, Hu J (2017) Research status, hotspotsandtrends forinformation behavior in China using bibliometric and co-word analysis. J Doc 73(4):618–633
Shleifer A, Vishny RW (1997) A survey of corporate governance. J Financ 52(2):737–783
Singh HP, Kumar S (2014) Working capital management: a literature review and research agenda. Qual Res Financ Mark 6(2):173–197
Tabak BM, Fazio DM, Cajueiro DO (2013) Systemically important banks and financial stability: the case of Latin America. J Bank Financ 37(10):3855–3866
Tahamtan I, SafipourAfshar A, Ahamdzadeh K (2016) Factors affecting number of citations: a comprehensive review of the literature. Scientometrics 107(3):1195–1225
Thakor AV (2018) Post-crisis regulatory reform in banking: Address insolvency risk, not illiquidity! J Financ Stab 37(1):107–111
Thomsen S, Pedersen T (2000) Ownership structure and economic performance in the largest European companies. Strategic Manag J 21(6):689–705
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
Triki T, Kouki I, Dhaou MB, Calice P (2017) Bank regulation and efficiency: What works for Africa? Res Int Bus Financ 39(1):183–205
Tsay M, Shu Z (2011) Journal bibliometric analysis: a case study on the journal of documentation. J Doc 67(5):806–822
Vento GA, La Ganga P (2009) Bank liquidity risk management and supervision: which lessons from recent market turmoil. J Money Invest Bank 10(10):78–125
Wahid ANM (1994) The grameen bank and poverty alleviation in Bangladesh: theory, evidence and limitations. Am J Econ Sociol 53(1):1–15
Xiao Y, Watson M (2019) Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res 39(1):93–112
Xu X, Chen X, Jia F, Brown S, Gong Y, Xu Y (2018) Supply chain finance: a systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Econ 204:160–173
Yadav M (2011) Impact of non performing assets on profitability and productivity of public sector banks in India. AFBE J 4(1):232–239
Yong-Hak J (2013), Web of Science, Thomson Reuters
Zheng C, Rahman MM, Begum M, Ashraf BN (2017) Capital regulation, the cost of financial intermediation and bank profitability: evidence from Bangladesh. J Risk Financ Manag 10(2):9
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, India
Shailesh Rastogi, Arpita Sharma & Venkata Mrudula Bhimavarapu
SIES School of Business Studies, Navi Mumbai, India
Geetanjali Pinto
School of Commerce and Management, D Y Patil International University, Akurdi, Pune, India
Venkata Mrudula Bhimavarapu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
‘SR’ performed Abstract, Introduction, and Data methodology sections and was the major contributor; ‘AS’ performed Bibliometric and Network analysis and conceptual framework; ‘GP’ performed citation analysis and discussion section; ‘VMB’ collated data from the database and concluded the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Venkata Mrudula Bhimavarapu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rastogi, S., Sharma, A., Pinto, G. et al. A literature review of risk, regulation, and profitability of banks using a scientometric study. Futur Bus J 8 , 28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-022-00146-4
Download citation
Received : 11 March 2022
Accepted : 16 August 2022
Published : 03 September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-022-00146-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bank performance
- Profitability
- Bibliometric analysis
- Scientometric analysis

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The present paper is designed to study the implementation of the Credit Risk Management Framework by Commercial Banks in India. To achieve the above mentioned objective a primary survey was conducted.
(Singh., 2015) this paper examines the effect of credit risk management on private and public sector banks in India. Credit risk comes when customers default or failed to comply with their obstacles to service debt, pushing a total or partial loss. The primary cause of credit risk is poor credit risk management. When
The present research paper provides empirical evidence on the interconnection between credit risk and bank-specific/internal factors on FP commercial banks. To analyze the data set, first, the study applies the descriptive analysis to identify the big picture of the data, then the correlation section and at the end, regression results are ...
Research however faults some of the credit risk management policies in place the broad framework ... (Campbell, 2007). This paper investigates the relationship between the two major sources of bank default risk: liquidity risk and credit risk. We use a sample of virtually all U.S. commercial banks during the period 1998 to 2010 to ...
Abstract. The primary objective of this paper is to examine the risk management techniques and practices of credit risk management followed by Indian commercial banks for the period from 2021-17 to 2020-21. The other objective is to compare risk management practices followed by the public sector banks (PSBs) and private sector of banks (PVBs).
Book Reviews: K. Vaidyanathan, Credit Risk Management for Indian Banks. Show details Hide details. Mirza Allim Baig. South Asia Economic Journal. Dec 2014. Free access. ... A Study of Banks in India. Show details Hide details. Deepak Tandon and more ... Global Business Review. Apr 2017. ... Sage Research Methods Supercharging research opens in ...
This research study assesses the impact of credit risk management on Indian public and private banks during the 2009-2012 period. Using pooled OLS, fixed effects and random effects, the study examines credit risk management in seven private banks and seven public banks.
The pre-dominance of credit risk is the main component in the capital allocation. As per their estimate credit risk takes the major part of the Risk Management apparatus accounting for over 70 per cent of all Risks. As per them the Market Risk and Operational Risk are important, but more attention needs to be paid to the Credit Risk Management ...
Indian banks Key words: Credit Risk, Liquidity Risk, Bank Performance JEL Classification Number: G20, G30, L14 Arindam Bandyopadhyay (Corresponding Author) National Institute of Bank Management, India E-mail: [email protected] Mayuri Saxena Accenture, INDIA E-mail: [email protected]
The effective management of credit risk is a critical component of comprehensive risk management and essential for the long term success of a banking organization. This study is divided into two parts (1) To analyze and compare the financial performance of selected Private and Public sector Banks and (2) To identifying the factors contributing ...
Credit risk management is becoming increasingly important element in Indian banks as its regulatory framework by BASEL II makes banks compulsory to implement cr ... Sophia, Sharon, Credit Risk Management in Indian Banking System (April 18, 2013). Available at SSRN: ... Research Paper Series; Conference Papers; Partners in Publishing; Jobs ...
Importance of credit risk management in banking operations Credit risk management plays a crucial role in banking operations for several reasons: Risk Mitigation: Credit risk refers to the potential loss that a bank may incur if borrowers fail to repay their loans or meet their financial obligations. Effective credit risk management helps banks ...
A Study of Credit Risk Management Practices and its Impact on the Indian Banking Industry Post Basel II Implementation: Researcher: Rashmy Moray: Guide(s): Ravi Chitnis: Keywords: Credit Risk Management , Indian Banking Industry , Implementation: University: Symbiosis International University: Completed Date: 2015: Abstract: newline: Pagination ...
including credit risk management, market risk management, operational risk management, liquidity risk management, legal and regulatory risk management, stress testing, risk-based supervision, corporate governance, Basel III regulations, and cyber security risk management. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
operation. One of the risks that affects its financial condition to a large extent is credit risk. This research paper aims to analyse the impact of credit risk on financial Performance of the top 13 commercial banks of India. The main objective is to determine whether there is a significant impact of CAR and NPA on the ROE of the banks.
This involves a decision either (A) to extend credit, which provides a reward but entails a risk, or (B) to refuse credit. The situation facing the credit manager is shown as a decision tree diagram. The requirement is to balance the gain from taking the credit risk by extending credit against the potential loss.
Asst. Professor Jaywant Institute of Management Wathar, Tal. Karad, Dist. Satara, (Maharashtra) India. Abstract: Credit risk is the most common cause of bank failures. With the changing dynamics of banking business brings new kind of risk exposure. Credit risk is the possibility of losses associated with diminution in the credit quality of ...
In this liberalization period, credit Risk Management has got much importance in the Indian Economy. The main challenges faced by the banking sector today are the challenge of identifying the risk and managing it. The risk is imbibed nature of the banking business. The main role of a bank is of intermediate for those having resources and requiring resources. For risk management various risks ...
Abstract: This paper examines the effect of credit risk management on private and public sector banks in India. Credit risk occurs when customers default or fail to comply with their obligation to service debt, triggering a total or partial loss. The primary cause of credit risk is poor credit risk management.
This study presents a systematic literature review of regulation, profitability, and risk in the banking industry and explores the relationship between them. It proposes a policy initiative using a model that offers guidelines to establish the right mix among these variables. This is a systematic literature review study. Firstly, the necessary data are extracted using the relevant keywords ...
Banks ", Research Journal of Management Sciences, 2(7), ... Re serve Bank of India Occasiona l Papers, 24(3), 81- ... in banking sector credit risk management is being most important task of all ...