Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
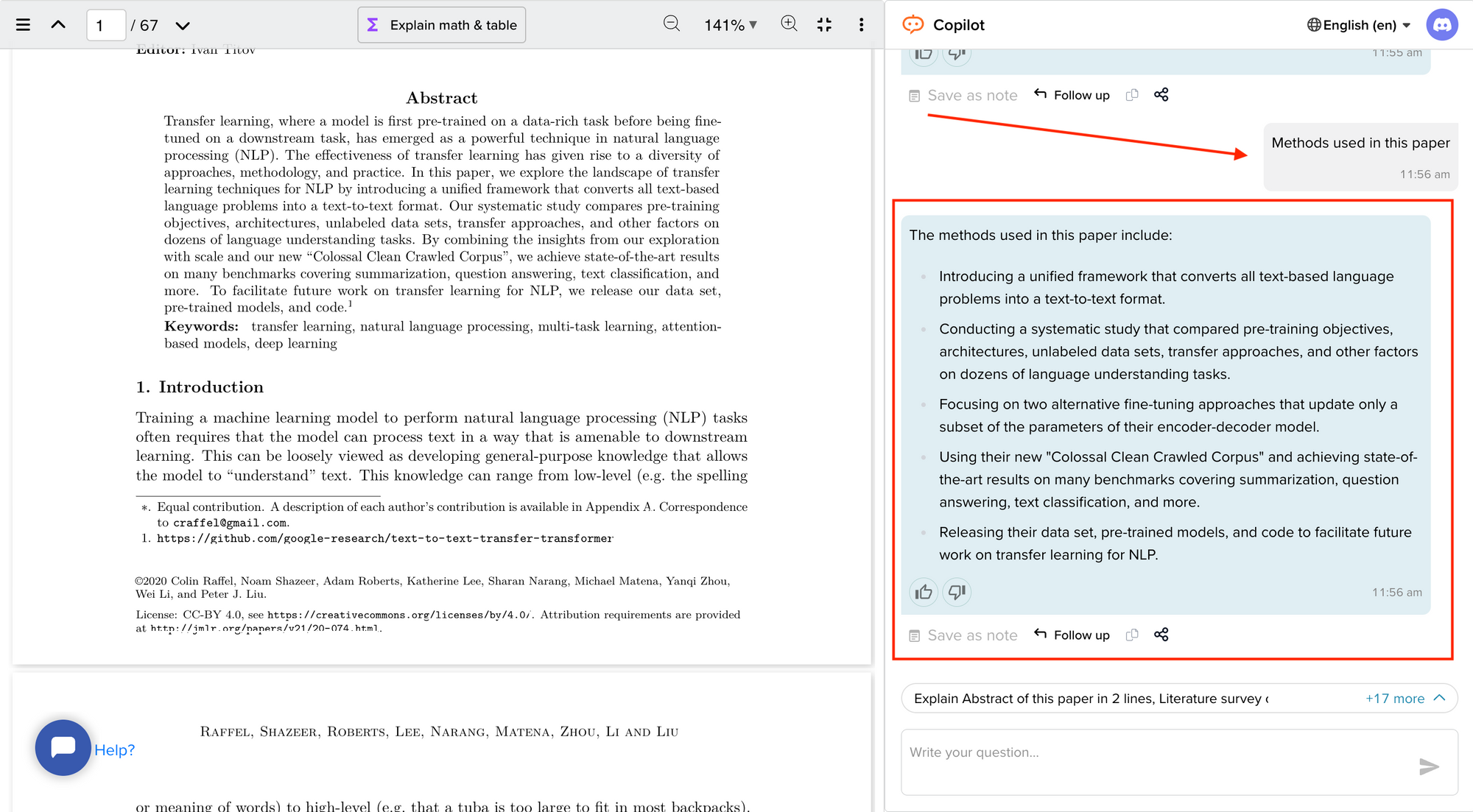
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 24 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
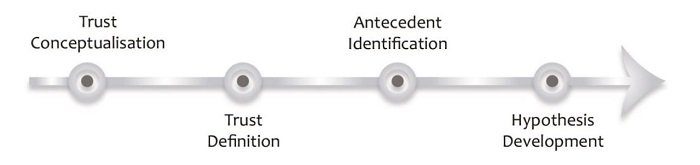
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., what’s the best chatgpt alternative for academic writing, how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding....

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.

2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- Reserve a study room
- Library Account
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
How to Conduct a Literature Review (Health Sciences and Beyond)
- What is a Literature Review?
- Developing a Research Question
Selection Criteria
Inclusion criteria, exclusion criteria.
- Database Search
- Documenting Your Search
- Organize Key Findings
- Reference Management
You may want to think about criteria that will be used to select articles for your literature review based on your research question. These are commonly known as inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria . Be aware that you may introduce bias into the final review if these are not used thoughtfully.
Inclusion criteria are the elements of an article that must be present in order for it to be eligible for inclusion in a literature review. Some examples are:
- Included studies must have compared certain treatments
- Included studies must be experimental
- Included studies must have been published in the last 5 years
Exclusion criteria are the elements of an article that disqualify the study from inclusion in a literature review. Some examples are:
- Study used an observational design
- Study used a qualitative methodology
- Study was published more than 5 years ago
- Study was published in a language other than English
- << Previous: Developing a Research Question
- Next: Databases >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 12:22 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.vcu.edu/health-sciences-lit-review

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
- Strategies to Find Sources
Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
Reading critically, tips to evaluate sources.
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
- A Closer Look at Evaluating Literature Reviews Excerpt from the book chapter, “Evaluating Introductions and Literature Reviews” in Fred Pyrczak’s Evaluating Research in Academic Journals: A Practical Guide to Realistic Evaluation , (Chapter 4 and 5). This PDF discusses and offers great advice on how to evaluate "Introductions" and "Literature Reviews" by listing questions and tips. First part focus on Introductions and in page 10 in the PDF, 37 in the text, it focus on "literature reviews".
- Tips for Evaluating Sources (Print vs. Internet Sources) Excellent page that will guide you on what to ask to determine if your source is a reliable one. Check the other topics in the guide: Evaluating Bibliographic Citations and Evaluation During Reading on the left side menu.
To be able to write a good Literature Review, you need to be able to read critically. Below are some tips that will help you evaluate the sources for your paper.
Reading critically (summary from How to Read Academic Texts Critically)
- Who is the author? What is his/her standing in the field.
- What is the author’s purpose? To offer advice, make practical suggestions, solve a specific problem, to critique or clarify?
- Note the experts in the field: are there specific names/labs that are frequently cited?
- Pay attention to methodology: is it sound? what testing procedures, subjects, materials were used?
- Note conflicting theories, methodologies and results. Are there any assumptions being made by most/some researchers?
- Theories: have they evolved overtime?
- Evaluate and synthesize the findings and conclusions. How does this study contribute to your project?
Useful links:
- How to Read a Paper (University of Waterloo, Canada) This is an excellent paper that teach you how to read an academic paper, how to determine if it is something to set aside, or something to read deeply. Good advice to organize your literature for the Literature Review or just reading for classes.
Criteria to evaluate sources:
- Authority : Who is the author? what is his/her credentials--what university he/she is affliliated? Is his/her area of expertise?
- Usefulness : How this source related to your topic? How current or relevant it is to your topic?
- Reliability : Does the information comes from a reliable, trusted source such as an academic journal?
Useful site - Critically Analyzing Information Sources (Cornell University Library)
- << Previous: Strategies to Find Sources
- Next: Tips for Writing Literature Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Jun 11, 2024 12:14 PM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Evaluating Sources (Print vs. Internet Sources) Excellent page that will guide you on what to ask to determine if your source is a reliable one. Check the other topics in the guide: Evaluating Bibliographic Citations and Evaluation During Reading on the left side menu.
Criteria to evaluate sources:
- Authority : Who is the author? What are the author's credentials and areas of expertise? Is he or she affiliated with a university?
- Usefulness : How this source related to your topic? How current or relevant it is to your topic?
- Reliability : Does the information comes from a reliable, trusted source such as an academic journal?
- Critically Analyzing Information Sources: Critical Appraisal and Analysis (Cornell University Library) Ten things to look for when you evaluate an information source.
Reading Critically
Reading critically (summary from how to read academic texts critically).
- Who is the author? What is his/her standing in the field?
- What is the author’s purpose? To offer advice, make practical suggestions, solve a specific problem, critique or clarify?
- Note the experts in the field: are there specific names/labs that are frequently cited?
- Pay attention to methodology: is it sound? what testing procedures, subjects, materials were used?
- Note conflicting theories, methodologies, and results. Are there any assumptions being made by most/some researchers?
- Theories: have they evolved over time?
- Evaluate and synthesize the findings and conclusions. How does this study contribute to your project?
- How to Read Academic Texts Critically Excellent document about how best to read critically academic articles and other texts.
- How to Read an Academic Article This is an excellent paper that teach you how to read an academic paper, how to determine if it is something to set aside, or something to read deeply. Good advice to organize your literature for the Literature Review or just reading for classes.
- << Previous: Keeping up with Research!
- Next: Organizing for Writing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
Penn State University Libraries
Soc 001: introductory sociology.
- Literature Reviews: Strategies for Writing
- Fake News and Evaluating Sources
Literature Reviews
What is a Literature Review? The literature review is a critical look at the existing research that is significant to the work that you are carrying out. This overview identifies prominent research trends in addition to assessing the overall strengths and weaknesses of the existing research.
Purpose of the Literature Review
- To provide background information about a research topic.
- To establish the importance of a topic.
- To demonstrate familiarity with a topic/problem.
- To “carve out a space” for further work and allow you to position yourself in a scholarly conversation.
Characteristics of an effective literature review In addition to fulfilling the purposes outlined above, an effective literature review provides a critical overview of existing research by
- Outlining important research trends.
- Assessing strengths and weaknesses (of individual studies as well the existing research as a whole).
- Identifying potential gaps in knowledge.
- Establishing a need for current and/or future research projects.
Steps of the Literature Review Process
1) Planning: identify the focus, type, scope and discipline of the review you intend to write. 2) Reading and Research: collect and read current research on your topic. Select only those sources that are most relevant to your project. 3) Analyzing: summarize, synthesize, critique, and compare your sources in order to assess the field of research as a whole. 4) Drafting: develop a thesis or claim to make about the existing research and decide how to organize your material. 5) Revising: revise and finalize the structural, stylistic, and grammatical issues of your paper.
This process is not always a linear process; depending on the size and scope of your literature review, you may find yourself returning to some of these steps repeatedly as you continue to focus your project.
These steps adapted from the full workshop offered by the Graduate Writing Center at Penn State.
Literature Review Format
Introduction
- Provide an overview of the topic, theme, or issue.
- Identify your specific area of focus.
- Describe your methodology and rationale. How did you decide which sources to include and which to exclude? Why? How is your review organized?
- Briefly discuss the overall trends in the published scholarship in this area.
- Establish your reason for writing the review.
- Find the best organizational method for your review.
- Summarize sources by providing the most relevant information.
- Respectfully and objectively critique and evaluate the studies.
- Use direct quotations sparingly and only if appropriate.
Conclusion
- Summarize the major findings of the sources that you reviewed, remembering to keep the focus on your topic.
- Evaluate the current state of scholarship in this area (ex. flaws or gaps in the research, inconsistencies in findings)
- Identify any areas for further research.
- Conclude by making a connection between your topic and some larger area of study such as the discipline.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Fake News and Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Oct 20, 2023 10:48 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/shenangosoc001
Literature reviews
- Introduction
- Conduct your search
- Store and organise the literature
Evaluate the information you have found
Critique the literature.
- Different subject areas
- Find literature reviews
When conducting your searches you may find many references that will not be suitable to use in your literature review.
- Skim through the resource. A quick read through the table of contents, the introductory paragraph or the abstract should indicate whether you need to read further or whether you can immediately discard the result.
- Evaluate the quality and reliability of the references you find. Our evaluating information page outlines what you need to consider when evaluating the books, journal articles, news and websites you find to ensure they are suitable for use in your literature review.
Critiquing the literature involves looking at the strength and weaknesses of the paper and evaluating the statements made by the author/s.
Books and resources on reading critically
- CASP Checklists Critical appraisal tools designed to be used when reading research. Includes tools for Qualitative studies, Systematic Reviews, Randomised Controlled Trials, Cohort Studies, Case Control Studies, Economic Evaluations, Diagnostic Studies and Clinical Prediction Rule.
- How to read critically - business and management From Postgraduate research in business - the aim of this chapter is to show you how to become a critical reader of typical academic literature in business and management.
- Learning to read critically in language and literacy Aims to develop skills of critical analysis and research design. It presents a series of examples of `best practice' in language and literacy education research.
- Critical appraisal in health sciences See tools for critically appraising health science research.
- << Previous: Store and organise the literature
- Next: Different subject areas >>
- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2024 2:56 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/research-techniques/literature-reviews
Literature reviews
A literature review is a research task that finds, evaluates and discusses information on a particular topic. You need to analyse multiple texts, and discuss key ideas that you find in the reading.
A literature review may also identify gaps for further research. It is not a process of summarising texts separately – that is done in an annotated bibliography .
A good literature review should:
- be well researched, planned and structured
- discuss a relevant issue, problem or practice that relates to your subject
- explain why your chosen topic is important
- identify key ideas or themes in the literature
- synthesise these findings into thematic paragraphs, using sufficient citations and correct referencing
- demonstrate your understanding of the topic and develop your knowledge and evidence-based practice.
Literature reviews differ across disciplines, so use your assessment instructions and marking criteria as your ultimate guide.
7 steps for writing a literature review
1. analyse the task.
Read the assessment instructions and marking rubric carefully. Note how many sources you need to include in your literature review and any guidelines on selecting the literature.
Choose a topic that interests you. A topic that is important to you will help you stay focused.
2. Establish a clear research question
A good research question will help you narrow down your topic so that it is manageable. If your question is too broad, you may be overwhelmed by the reading. If it is too narrow, you won’t find enough literature.
3. Search for relevant literature
Use keywords from your research question to begin searching .
In the research question "What factors impact student learning when on nursing placement?", the keywords are: student, learning, nursing and placement.
4. Read and review the literature, and take notes
When reading the literature, consider the following:
- Is the article relevant to your topic? For journal articles, read the abstract. For other sources, scan quickly and discard if you can’t see anything useful.
- Who is the author/s and what is their expertise?
- Is the source credible and scholarly ? Use any evaluation tools provided by your subject.
- What is the main topic and what themes are discussed?
Pay attention to important information, such as the abstract, introduction, headings/subheadings, graphs/tables and conclusion.
Take notes using the Cornell method or a note-taking grid. Keeping notes that help you remember the content and relevance of each source is vital for writing a literature review.
- Example note-taking grid for a literature review [Word - 14KB]
5. Identify common themes or areas for further research
It's important to understand the relationships between the sources you've read. Look out for:
- themes: what questions, ideas or topics recur across the literature? Where do authors agree or disagree?
- areas for further research: what is missing from the literature? Are there any weaknesses?
6. Plan the structure of the literature review
Before you start writing, plan how your literature review will be organised.
Literature reviews are usually organised thematically, meaning they discuss one theme after another. You can also organise your ideas chronologically (from past to present) or by methodology (e.g. comparing findings from qualitative and quantitative research).
7. Write, edit, proofread, submit
It's easy to get lost in the reading and not leave enough time for polishing your writing. Use the Assessment Planner to make a clear study plan that includes time for writing, editing and proofreading.
Structure of a literature review
Introduction.
The introduction should include:
- context or background : give a brief summary of the context for your research question and explain why it is important
- purpose (thesis statement): state the purpose of the literature review. This is a statement generated from the research question
- scope (roadmap): outline the specific themes the literature review will focus on and give the reader a sense of how your writing is organised.
Each body paragraph focuses on a specific theme and draws on several pieces of literature.
Paragraphs should include:
- topic sentence: start with the theme of the paragraph
- synthesis of evidence: make connections between multiple sources by comparing and contrasting their views. Use summaries, paraphrases and quotes , and don't forget to properly reference your sources
- analysis or evaluation: add your own interpretation of the findings and comment on any strengths, weaknesses, gaps or areas for further research in the literature
- link: end the paragraph by either linking back to your main topic or to the following paragraph.
Conclusions should include:
- restate the purpose of the review
- summary of the main findings : remind your reader of the main points. Make sure you paraphrase your ideas, so you don’t use the same wording as elsewhere in the literature review
- implications of the findings: suggest how the findings might be important for practice in your field
- areas for further research : provide suggestions for future research to address the problem, issue or question.
The conclusion is followed by a Reference list or Bibliography. Consult the Style notes page of the Academic Referencing Tool for examples.
For complete sample literature reviews with further annotations, see the Word and PDF documents below.
- Example Literature Review - Allied Health [PDF 245KB]
- Example Literature Review - Allied Health [Word 69KB]
- Example Literature Review - Education [PDF 283KB]
- Example Literature Review - Education [Word 104KB]
Further resources
- Using a reading to choose a research topic worksheet
- Manchester Academic Phrasebank - Phrases for academic writing and reporting on research
- Turn a stack of papers into a literature review: Useful tool for beginners (Journal article)
Pathfinder link
Still have questions? Do you want to talk to an expert? Peer Learning Advisors or Academic Skills and Language Advisors are available.
Cant R., Ryan, C., Hughes, L., Luders, E., & Cooper, S. (2021). What helps, what hinders? Undergraduate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical placements based on a thematic synthesis of literature. SAGE Open Nursing, 7, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1177/23779608211035845 Adapted and used under CC BY-NC 4.0 license
- << Previous: Annotated bibliographies
- Next: Presentations >>

Literature Reviews: Types of Reviews
- Types of Reviews
- Literature Search
- Evaluating Sources (If I Apply) This link opens in a new window
- Recommended Library Tools
- Citing Sources
What are Literature Reviews?
A literature review provides an overview of a topic, and is something most of you have encountered at one time or another. It is usually an article, or a section of an article,* that compiles and summarizes published materials (books, articles, etc.) which provide an examination of recent or current literature on a chosen topic.
Review articles can cover a wide range of subject matter at various levels of completeness and comprehensiveness based on analyses of literature that may include research findings. The review may reflect the state of the art. It also includes reviews as a literary form.
As a publication type, it is an article or book published after examination of previously published material on a subject. It may be comprehensive to various degrees, and the time range of material scrutinized may be broad or narrow, although the reviews most often desired are reviews of the current literature. The textual material examined may be equally broad and can encompass, in medicine specifically, clinical material as well as experimental research or case reports.
State-of-the-art reviews tend to address more current matters. A review of the literature must be differentiated from a HISTORICAL ARTICLE on the same subject, but a review of historical literature is also within the scope of this publication type.
* Lit reviews aren't always obviously labeled "literature review"; they may be embedded within sections such as the introduction or background.
Example Literature Review:
- Dance therapy for individuals with Parkinson’s disease: improving quality of life Notice how the introduction and subheadings provide background on the topic and describe way it's important. Some studies are grouped together that convey a similar idea. Limitations of some studies are addressed as a way of showing the significance of the research topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
- Systematic review
- Meta-analysis
- Integrative Review
- Scoping review
- Rapid review
- Umbrella review
- Systematized Review
A systematic review attempts to collate all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific research question. It uses explicit, systematic methods that are selected with a view to minimizing bias, thus providing more reliable findings from which conclusions can be drawn and decisions made (Antman 1992, Oxman 1993).
The key characteristics of a systematic review are:
- a clearly stated set of objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies;
- an explicit, reproducible methodology;
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies that would meet the eligibility criteria;
- an assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies, for example through the assessment of risk of bias; and
- a systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies.
From Cochrane Handbook, 1.2.2
- How to do a systematic review (NSU)
- Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach
Many, but not all, systematic reviews contain meta-analyses. Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarise the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analyses can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. Meta-analyses also facilitate investigations of the consistency of evidence across studies, and the exploration of differences across studies ( Cochrane Handbook, 1.2.2 ). More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analyses on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
An integrative review summarizes past research and draws overall conclusions from the body of literature on a particular topic. The body of literature comprises all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. In a properly executed integrative review, the effects of subjectivity are minimized through carefully applied criteria for evaluation. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor and replication.
"In general, scoping reviews are commonly used for ‘reconnaissance’ – to clarify working definitions and conceptual boundaries of a topic or field. Scoping reviews are therefore particularly useful when a body of literature has not yet been comprehensively reviewed, or exhibits a complex or heterogeneous nature not amenable to a more precise systematic review of the evidence. While scoping reviews may be conducted to determine the value and probable scope of a full systematic review, they may also be undertaken as exercises in and of themselves to summarize and disseminate research findings, to identify research gaps, and to make recommendations for the future research."
From Peters, MD, Godfrey, CM, Khalil, H, McInerney, P, Parker, D & Soares, CB 2015, 'Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews', International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 141-146 :
- Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews (methodology paper)
A rapid review is an assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue, by using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research. "Rapid reviews have emerged as a streamlined approach to synthesizing evidence in a timely manner -typically for the purpose of informing emergent decisions faced by decision makers in health care settings."
Khangura, S, Konnyu, K, Cushman, R, Grimshaw, J & Moher, D 2012, 'Evidence summaries: The evolution of a rapid review approach', Systematic Reviews, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 10.
An umbrella review is a synthesis of existing reviews, only including the highest level of evidence such as systematic reviews and meta-analyes. It specifically refers to review compiling evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document. Umbrella reviews focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address these interventions and their result.
Methodology paper: Aromataris, E, Fernandez, R, Godfrey, CM, Holly, C, Khalil, H & Tungpunkom, P 2015, 'Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach', Int J Evid Based Healthc , vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 132-140
A systematized review attempts to include elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of the systematic review. Systematized reviews are typically conducted as a postgraduate student assignment, in recognition that they are not able to draw upon the resources required for a full systematic review (such as two reviewers).
Hierarchy of Reviews: Most Common Types with Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis Considered the Highest Quality of Evidence

Special Thanks
Special Thanks to Dr. Julie Sarpy, PhD, MSLS, MA, AHIP, for permission to reuse content from her Medical Sciences guide . Dr. Sarpy is a Reference and Instruction Librarian at the Martin and Gail Press Health Professions Division Library, and a Liaison to the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Allopathic Medicine, as well as an Adjunct Assistant Professor with the Department of Medical Education at the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University in Ft. Lauderdale, Florida.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Literature Search >>
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 10:34 AM
- URL: https://libguides.marshall.edu/litreview

How are guidelines developed?
Vol. 55 No. 5
- Psychotherapy
APA’s clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) and professional practice guidelines (PPGs) are the result of a complex and lively process of decision-making, interdisciplinary discussion, literature review, public comment, APA approval, and more. Here’s a quick rundown of how they come together:
Clinical practice guidelines
An advisory committee of 9 to 10 APA members identifies an area or domain that needs a guideline based on various criteria and health equity considerations. Next, to dive into that topic, the board recruits a diverse, multidisciplinary panel of 7 to 12 members, usually including health care providers and researchers from a range of clinical and theoretical perspectives. Each panel also includes one or two patient representatives with lived experience as full members of the panel, said John McQuaid, PhD, ABPP, a member of the CPG advisory steering committee and former chair of the CPG on depression across three age cohorts.
“APA is really committed to that diversity because we need a variety of different perspectives as we review the literature,” he said.
[ Related: A powerful way to recharge your practice ]
Panelists then use a clinical research framework known as PICOTS (patient, intervention, comparison, outcome, timing, and setting) to determine the scope of a given guideline—which populations and what treatments it will cover, for example. Next, they carefully examine relevant systematic reviews of the literature, either by compiling existing quality reviews or nominating new ones. This initial framework is then put out for public comment.
After considering the public’s suggestions, panelists work to determine which treatments to recommend. They consider four factors: the overall strength of the evidence, the balance of benefits to potential harms, patients’ values and preferences, and the applicability or generalizability of the evidence. They parse their recommendations into specific statements that become part of the full guideline document, which also includes an in-depth discussion of the topic and supporting materials. The guideline is then submitted for another round of public comments, edits are made accordingly, and the guideline is ready for a vote by APA’s Council of Representatives.
Professional practice guidelines
PPGs cover a wide and diverse range of topics, and for now, development of these guidelines is initiated by a variety of entities including APA divisions and APA’s Board of Professional Affairs (BPA).
Sometimes groups start drafting PPGs and then BPA and the Committee on Professional Practice and Standards (COPPS) work together to create a panel of relevant experts from different perspectives who determine what should be covered in the guideline. That team holds discussions and gathers and summarizes information, research, and resources. APA staff and other stakeholders provide input, draft guidelines documents undergo a public comment period and review by APA’s Office of General Counsel, comments are reviewed and addressed; once finalized, it goes to the Council of Representatives for approval. As BPA and COPPS focus on identifying current and future needs of practitioners for guidance, the development process could change to help meet those needs more effectively.
Six Things Psychologists are Talking About
The APA Monitor on Psychology ® sister e-newsletter offers fresh articles on psychology trends, new research, and more.
Welcome! Thank you for subscribing.
Speaking of Psychology
Subscribe to APA’s audio podcast series highlighting some of the most important and relevant psychological research being conducted today.
Subscribe to Speaking of Psychology and download via:

Contact APA
You may also like.
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Department of Brain Sciences, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Behavioural Brain Sciences Unit, Population Policy Practice Programme, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- Max L. Y. Chang,
- Irene O. Lee

- Published: June 4, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Internet usage has seen a stark global rise over the last few decades, particularly among adolescents and young people, who have also been diagnosed increasingly with internet addiction (IA). IA impacts several neural networks that influence an adolescent’s behaviour and development. This article issued a literature review on the resting-state and task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies to inspect the consequences of IA on the functional connectivity (FC) in the adolescent brain and its subsequent effects on their behaviour and development. A systematic search was conducted from two databases, PubMed and PsycINFO, to select eligible articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Eligibility criteria was especially stringent regarding the adolescent age range (10–19) and formal diagnosis of IA. Bias and quality of individual studies were evaluated. The fMRI results from 12 articles demonstrated that the effects of IA were seen throughout multiple neural networks: a mix of increases/decreases in FC in the default mode network; an overall decrease in FC in the executive control network; and no clear increase or decrease in FC within the salience network and reward pathway. The FC changes led to addictive behaviour and tendencies in adolescents. The subsequent behavioural changes are associated with the mechanisms relating to the areas of cognitive control, reward valuation, motor coordination, and the developing adolescent brain. Our results presented the FC alterations in numerous brain regions of adolescents with IA leading to the behavioural and developmental changes. Research on this topic had a low frequency with adolescent samples and were primarily produced in Asian countries. Future research studies of comparing results from Western adolescent samples provide more insight on therapeutic intervention.
Citation: Chang MLY, Lee IO (2024) Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies. PLOS Ment Health 1(1): e0000022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
Editor: Kizito Omona, Uganda Martyrs University, UGANDA
Received: December 29, 2023; Accepted: March 18, 2024; Published: June 4, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Chang, Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information files.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The behavioural addiction brought on by excessive internet use has become a rising source of concern [ 1 ] since the last decade. According to clinical studies, individuals with Internet Addiction (IA) or Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) may have a range of biopsychosocial effects and is classified as an impulse-control disorder owing to its resemblance to pathological gambling and substance addiction [ 2 , 3 ]. IA has been defined by researchers as a person’s inability to resist the urge to use the internet, which has negative effects on their psychological well-being as well as their social, academic, and professional lives [ 4 ]. The symptoms can have serious physical and interpersonal repercussions and are linked to mood modification, salience, tolerance, impulsivity, and conflict [ 5 ]. In severe circumstances, people may experience severe pain in their bodies or health issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, dry eyes, irregular eating and disrupted sleep [ 6 ]. Additionally, IA is significantly linked to comorbidities with other psychiatric disorders [ 7 ].
Stevens et al (2021) reviewed 53 studies including 17 countries and reported the global prevalence of IA was 3.05% [ 8 ]. Asian countries had a higher prevalence (5.1%) than European countries (2.7%) [ 8 ]. Strikingly, adolescents and young adults had a global IGD prevalence rate of 9.9% which matches previous literature that reported historically higher prevalence among adolescent populations compared to adults [ 8 , 9 ]. Over 80% of adolescent population in the UK, the USA, and Asia have direct access to the internet [ 10 ]. Children and adolescents frequently spend more time on media (possibly 7 hours and 22 minutes per day) than at school or sleeping [ 11 ]. Developing nations have also shown a sharp rise in teenage internet usage despite having lower internet penetration rates [ 10 ]. Concerns regarding the possible harms that overt internet use could do to adolescents and their development have arisen because of this surge, especially the significant impacts by the COVID-19 pandemic [ 12 ]. The growing prevalence and neurocognitive consequences of IA among adolescents makes this population a vital area of study [ 13 ].
Adolescence is a crucial developmental stage during which people go through significant changes in their biology, cognition, and personalities [ 14 ]. Adolescents’ emotional-behavioural functioning is hyperactivated, which creates risk of psychopathological vulnerability [ 15 ]. In accordance with clinical study results [ 16 ], this emotional hyperactivity is supported by a high level of neuronal plasticity. This plasticity enables teenagers to adapt to the numerous physical and emotional changes that occur during puberty as well as develop communication techniques and gain independence [ 16 ]. However, the strong neuronal plasticity is also associated with risk-taking and sensation seeking [ 17 ] which may lead to IA.
Despite the fact that the precise neuronal mechanisms underlying IA are still largely unclear, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) method has been used by scientists as an important framework to examine the neuropathological changes occurring in IA, particularly in the form of functional connectivity (FC) [ 18 ]. fMRI research study has shown that IA alters both the functional and structural makeup of the brain [ 3 ].
We hypothesise that IA has widespread neurological alteration effects rather than being limited to a few specific brain regions. Further hypothesis holds that according to these alterations of FC between the brain regions or certain neural networks, adolescents with IA would experience behavioural changes. An investigation of these domains could be useful for creating better procedures and standards as well as minimising the negative effects of overt internet use. This literature review aims to summarise and analyse the evidence of various imaging studies that have investigated the effects of IA on the FC in adolescents. This will be addressed through two research questions:
- How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
- How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The review protocol was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see S1 Checklist ).
Search strategy and selection process
A systematic search was conducted up until April 2023 from two sources of database, PubMed and PsycINFO, using a range of terms relevant to the title and research questions (see full list of search terms in S1 Appendix ). All the searched articles can be accessed in the S1 Data . The eligible articles were selected according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria used for the present review were: (i) participants in the studies with clinical diagnosis of IA; (ii) participants between the ages of 10 and 19; (iii) imaging research investigations; (iv) works published between January 2013 and April 2023; (v) written in English language; (vi) peer-reviewed papers and (vii) full text. The numbers of articles excluded due to not meeting the inclusion criteria are shown in Fig 1 . Each study’s title and abstract were screened for eligibility.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g001
Quality appraisal
Full texts of all potentially relevant studies were then retrieved and further appraised for eligibility. Furthermore, articles were critically appraised based on the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations) framework to evaluate the individual study for both quality and bias. The subsequent quality levels were then appraised to each article and listed as either low, moderate, or high.
Data collection process
Data that satisfied the inclusion requirements was entered into an excel sheet for data extraction and further selection. An article’s author, publication year, country, age range, participant sample size, sex, area of interest, measures, outcome and article quality were all included in the data extraction spreadsheet. Studies looking at FC, for instance, were grouped, while studies looking at FC in specific area were further divided into sub-groups.
Data synthesis and analysis
Articles were classified according to their location in the brain as well as the network or pathway they were a part of to create a coherent narrative between the selected studies. Conclusions concerning various research trends relevant to particular groupings were drawn from these groupings and subgroupings. To maintain the offered information in a prominent manner, these assertions were entered into the data extraction excel spreadsheet.
With the search performed on the selected databases, 238 articles in total were identified (see Fig 1 ). 15 duplicated articles were eliminated, and another 6 items were removed for various other reasons. Title and abstract screening eliminated 184 articles because they were not in English (number of article, n, = 7), did not include imaging components (n = 47), had adult participants (n = 53), did not have a clinical diagnosis of IA (n = 19), did not address FC in the brain (n = 20), and were published outside the desired timeframe (n = 38). A further 21 papers were eliminated for failing to meet inclusion requirements after the remaining 33 articles underwent full-text eligibility screening. A total of 12 papers were deemed eligible for this review analysis.
Characteristics of the included studies, as depicted in the data extraction sheet in Table 1 provide information of the author(s), publication year, sample size, study location, age range, gender, area of interest, outcome, measures used and quality appraisal. Most of the studies in this review utilised resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging techniques (n = 7), with several studies demonstrating task-based fMRI procedures (n = 3), and the remaining studies utilising whole-brain imaging measures (n = 2). The studies were all conducted in Asiatic countries, specifically coming from China (8), Korea (3), and Indonesia (1). Sample sizes ranged from 12 to 31 participants with most of the imaging studies having comparable sample sizes. Majority of the studies included a mix of male and female participants (n = 8) with several studies having a male only participant pool (n = 3). All except one of the mixed gender studies had a majority male participant pool. One study did not disclose their data on the gender demographics of their experiment. Study years ranged from 2013–2022, with 2 studies in 2013, 3 studies in 2014, 3 studies in 2015, 1 study in 2017, 1 study in 2020, 1 study in 2021, and 1 study in 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t001
(1) How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
The included studies were organised according to the brain region or network that they were observing. The specific networks affected by IA were the default mode network, executive control system, salience network and reward pathway. These networks are vital components of adolescent behaviour and development [ 31 ]. The studies in each section were then grouped into subsections according to their specific brain regions within their network.
Default mode network (DMN)/reward network.
Out of the 12 studies, 3 have specifically studied the default mode network (DMN), and 3 observed whole-brain FC that partially included components of the DMN. The effect of IA on the various centres of the DMN was not unilaterally the same. The findings illustrate a complex mix of increases and decreases in FC depending on the specific region in the DMN (see Table 2 and Fig 2 ). The alteration of FC in posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) in the DMN was the most frequently reported area in adolescents with IA, which involved in attentional processes [ 32 ], but Lee et al. (2020) additionally found alterations of FC in other brain regions, such as anterior insula cortex, a node in the DMN that controls the integration of motivational and cognitive processes [ 20 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g002
The overall changes of functional connectivity in the brain network including default mode network (DMN), executive control network (ECN), salience network (SN) and reward network. IA = Internet Addiction, FC = Functional Connectivity.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t002
Ding et al. (2013) revealed altered FC in the cerebellum, the middle temporal gyrus, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) [ 22 ]. They found that the bilateral inferior parietal lobule, left superior parietal lobule, and right inferior temporal gyrus had decreased FC, while the bilateral posterior lobe of the cerebellum and the medial temporal gyrus had increased FC [ 22 ]. The right middle temporal gyrus was found to have 111 cluster voxels (t = 3.52, p<0.05) and the right inferior parietal lobule was found to have 324 cluster voxels (t = -4.07, p<0.05) with an extent threshold of 54 voxels (figures above this threshold are deemed significant) [ 22 ]. Additionally, there was a negative correlation, with 95 cluster voxels (p<0.05) between the FC of the left superior parietal lobule and the PCC with the Chen Internet Addiction Scores (CIAS) which are used to determine the severity of IA [ 22 ]. On the other hand, in regions of the reward system, connection with the PCC was positively connected with CIAS scores [ 22 ]. The most significant was the right praecuneus with 219 cluster voxels (p<0.05) [ 22 ]. Wang et al. (2017) also discovered that adolescents with IA had 33% less FC in the left inferior parietal lobule and 20% less FC in the dorsal mPFC [ 24 ]. A potential connection between the effects of substance use and overt internet use is revealed by the generally decreased FC in these areas of the DMN of teenagers with drug addiction and IA [ 35 ].
The putamen was one of the main regions of reduced FC in adolescents with IA [ 19 ]. The putamen and the insula-operculum demonstrated significant group differences regarding functional connectivity with a cluster size of 251 and an extent threshold of 250 (Z = 3.40, p<0.05) [ 19 ]. The molecular mechanisms behind addiction disorders have been intimately connected to decreased striatal dopaminergic function [ 19 ], making this function crucial.
Executive Control Network (ECN).
5 studies out of 12 have specifically viewed parts of the executive control network (ECN) and 3 studies observed whole-brain FC. The effects of IA on the ECN’s constituent parts were consistent across all the studies examined for this analysis (see Table 2 and Fig 3 ). The results showed a notable decline in all the ECN’s major centres. Li et al. (2014) used fMRI imaging and a behavioural task to study response inhibition in adolescents with IA [ 25 ] and found decreased activation at the striatum and frontal gyrus, particularly a reduction in FC at inferior frontal gyrus, in the IA group compared to controls [ 25 ]. The inferior frontal gyrus showed a reduction in FC in comparison to the controls with a cluster size of 71 (t = 4.18, p<0.05) [ 25 ]. In addition, the frontal-basal ganglia pathways in the adolescents with IA showed little effective connection between areas and increased degrees of response inhibition [ 25 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g003
Lin et al. (2015) found that adolescents with IA demonstrated disrupted corticostriatal FC compared to controls [ 33 ]. The corticostriatal circuitry experienced decreased connectivity with the caudate, bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), as well as the striatum and frontal gyrus [ 33 ]. The inferior ventral striatum showed significantly reduced FC with the subcallosal ACC and caudate head with cluster size of 101 (t = -4.64, p<0.05) [ 33 ]. Decreased FC in the caudate implies dysfunction of the corticostriatal-limbic circuitry involved in cognitive and emotional control [ 36 ]. The decrease in FC in both the striatum and frontal gyrus is related to inhibitory control, a common deficit seen with disruptions with the ECN [ 33 ].
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), ACC, and right supplementary motor area (SMA) of the prefrontal cortex were all found to have significantly decreased grey matter volume [ 29 ]. In addition, the DLPFC, insula, temporal cortices, as well as significant subcortical regions like the striatum and thalamus, showed decreased FC [ 29 ]. According to Tremblay (2009), the striatum plays a significant role in the processing of rewards, decision-making, and motivation [ 37 ]. Chen et al. (2020) reported that the IA group demonstrated increased impulsivity as well as decreased reaction inhibition using a Stroop colour-word task [ 26 ]. Furthermore, Chen et al. (2020) observed that the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum experienced a negative connection efficiency value, specifically demonstrating that the dorsal striatum activity suppressed the left DLPFC [ 27 ].
Salience network (SN).
Out of the 12 chosen studies, 3 studies specifically looked at the salience network (SN) and 3 studies have observed whole-brain FC. Relative to the DMN and ECN, the findings on the SN were slightly sparser. Despite this, adolescents with IA demonstrated a moderate decrease in FC, as well as other measures like fibre connectivity and cognitive control, when compared to healthy control (see Table 2 and Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g004
Xing et al. (2014) used both dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and insula to test FC changes in the SN of adolescents with IA and found decreased structural connectivity in the SN as well as decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) that correlated to behaviour performance in the Stroop colour word-task [ 21 ]. They examined the dACC and insula to determine whether the SN’s disrupted connectivity may be linked to the SN’s disruption of regulation, which would explain the impaired cognitive control seen in adolescents with IA. However, researchers did not find significant FC differences in the SN when compared to the controls [ 21 ]. These results provided evidence for the structural changes in the interconnectivity within SN in adolescents with IA.
Wang et al. (2017) investigated network interactions between the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway in IA subjects [ 24 ] (see Fig 5 ), and found 40% reduction of FC between the DMN and specific regions of the SN, such as the insula, in comparison to the controls (p = 0.008) [ 24 ]. The anterior insula and dACC are two areas that are impacted by this altered FC [ 24 ]. This finding supports the idea that IA has similar neurobiological abnormalities with other addictive illnesses, which is in line with a study that discovered disruptive changes in the SN and DMN’s interaction in cocaine addiction [ 38 ]. The insula has also been linked to the intensity of symptoms and has been implicated in the development of IA [ 39 ].
“+” indicates an increase in behaivour; “-”indicates a decrease in behaviour; solid arrows indicate a direct network interaction; and the dotted arrows indicates a reduction in network interaction. This diagram depicts network interactions juxtaposed with engaging in internet related behaviours. Through the neural interactions, the diagram illustrates how the networks inhibit or amplify internet usage and vice versa. Furthermore, it demonstrates how the SN mediates both the DMN and ECN.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g005
(2) How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The findings that IA individuals demonstrate an overall decrease in FC in the DMN is supported by numerous research [ 24 ]. Drug addict populations also exhibited similar decline in FC in the DMN [ 40 ]. The disruption of attentional orientation and self-referential processing for both substance and behavioural addiction was then hypothesised to be caused by DMN anomalies in FC [ 41 ].
In adolescents with IA, decline of FC in the parietal lobule affects visuospatial task-related behaviour [ 22 ], short-term memory [ 42 ], and the ability of controlling attention or restraining motor responses during response inhibition tests [ 42 ]. Cue-induced gaming cravings are influenced by the DMN [ 43 ]. A visual processing area called the praecuneus links gaming cues to internal information [ 22 ]. A meta-analysis found that the posterior cingulate cortex activity of individuals with IA during cue-reactivity tasks was connected with their gaming time [ 44 ], suggesting that excessive gaming may impair DMN function and that individuals with IA exert more cognitive effort to control it. Findings for the behavioural consequences of FC changes in the DMN illustrate its underlying role in regulating impulsivity, self-monitoring, and cognitive control.
Furthermore, Ding et al. (2013) reported an activation of components of the reward pathway, including areas like the nucleus accumbens, praecuneus, SMA, caudate, and thalamus, in connection to the DMN [ 22 ]. The increased FC of the limbic and reward networks have been confirmed to be a major biomarker for IA [ 45 , 46 ]. The increased reinforcement in these networks increases the strength of reward stimuli and makes it more difficult for other networks, namely the ECN, to down-regulate the increased attention [ 29 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Executive control network (ECN).
The numerous IA-affected components in the ECN have a role in a variety of behaviours that are connected to both response inhibition and emotional regulation [ 47 ]. For instance, brain regions like the striatum, which are linked to impulsivity and the reward system, are heavily involved in the act of playing online games [ 47 ]. Online game play activates the striatum, which suppresses the left DLPFC in ECN [ 48 ]. As a result, people with IA may find it difficult to control their want to play online games [ 48 ]. This system thus causes impulsive and protracted gaming conduct, lack of inhibitory control leading to the continued use of internet in an overt manner despite a variety of negative effects, personal distress, and signs of psychological dependence [ 33 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Wang et al. (2017) report that disruptions in cognitive control networks within the ECN are frequently linked to characteristics of substance addiction [ 24 ]. With samples that were addicted to heroin and cocaine, previous studies discovered abnormal FC in the ECN and the PFC [ 49 ]. Electronic gaming is known to promote striatal dopamine release, similar to drug addiction [ 50 ]. According to Drgonova and Walther (2016), it is hypothesised that dopamine could stimulate the reward system of the striatum in the brain, leading to a loss of impulse control and a failure of prefrontal lobe executive inhibitory control [ 51 ]. In the end, IA’s resemblance to drug use disorders may point to vital biomarkers or underlying mechanisms that explain how cognitive control and impulsive behaviour are related.
A task-related fMRI study found that the decrease in FC between the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum was congruent with an increase in impulsivity in adolescents with IA [ 26 ]. The lack of response inhibition from the ECN results in a loss of control over internet usage and a reduced capacity to display goal-directed behaviour [ 33 ]. Previous studies have linked the alteration of the ECN in IA with higher cue reactivity and impaired ability to self-regulate internet specific stimuli [ 52 ].
Salience network (SN)/ other networks.
Xing et al. (2014) investigated the significance of the SN regarding cognitive control in teenagers with IA [ 21 ]. The SN, which is composed of the ACC and insula, has been demonstrated to control dynamic changes in other networks to modify cognitive performance [ 21 ]. The ACC is engaged in conflict monitoring and cognitive control, according to previous neuroimaging research [ 53 ]. The insula is a region that integrates interoceptive states into conscious feelings [ 54 ]. The results from Xing et al. (2014) showed declines in the SN regarding its structural connectivity and fractional anisotropy, even though they did not observe any appreciable change in FC in the IA participants [ 21 ]. Due to the small sample size, the results may have indicated that FC methods are not sensitive enough to detect the significant functional changes [ 21 ]. However, task performance behaviours associated with impaired cognitive control in adolescents with IA were correlated with these findings [ 21 ]. Our comprehension of the SN’s broader function in IA can be enhanced by this relationship.
Research study supports the idea that different psychological issues are caused by the functional reorganisation of expansive brain networks, such that strong association between SN and DMN may provide neurological underpinnings at the system level for the uncontrollable character of internet-using behaviours [ 24 ]. In the study by Wang et al. (2017), the decreased interconnectivity between the SN and DMN, comprising regions such the DLPFC and the insula, suggests that adolescents with IA may struggle to effectively inhibit DMN activity during internally focused processing, leading to poorly managed desires or preoccupations to use the internet [ 24 ] (See Fig 5 ). Subsequently, this may cause a failure to inhibit DMN activity as well as a restriction of ECN functionality [ 55 ]. As a result, the adolescent experiences an increased salience and sensitivity towards internet addicting cues making it difficult to avoid these triggers [ 56 ].
The primary aim of this review was to present a summary of how internet addiction impacts on the functional connectivity of adolescent brain. Subsequently, the influence of IA on the adolescent brain was compartmentalised into three sections: alterations of FC at various brain regions, specific FC relationships, and behavioural/developmental changes. Overall, the specific effects of IA on the adolescent brain were not completely clear, given the variety of FC changes. However, there were overarching behavioural, network and developmental trends that were supported that provided insight on adolescent development.
The first hypothesis that was held about this question was that IA was widespread and would be regionally similar to substance-use and gambling addiction. After conducting a review of the information in the chosen articles, the hypothesis was predictably supported. The regions of the brain affected by IA are widespread and influence multiple networks, mainly DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway. In the DMN, there was a complex mix of increases and decreases within the network. However, in the ECN, the alterations of FC were more unilaterally decreased, but the findings of SN and reward pathway were not quite clear. Overall, the FC changes within adolescents with IA are very much network specific and lay a solid foundation from which to understand the subsequent behaviour changes that arise from the disorder.
The second hypothesis placed emphasis on the importance of between network interactions and within network interactions in the continuation of IA and the development of its behavioural symptoms. The results from the findings involving the networks, DMN, SN, ECN and reward system, support this hypothesis (see Fig 5 ). Studies confirm the influence of all these neural networks on reward valuation, impulsivity, salience to stimuli, cue reactivity and other changes that alter behaviour towards the internet use. Many of these changes are connected to the inherent nature of the adolescent brain.
There are multiple explanations that underlie the vulnerability of the adolescent brain towards IA related urges. Several of them have to do with the inherent nature and underlying mechanisms of the adolescent brain. Children’s emotional, social, and cognitive capacities grow exponentially during childhood and adolescence [ 57 ]. Early teenagers go through a process called “social reorientation” that is characterised by heightened sensitivity to social cues and peer connections [ 58 ]. Adolescents’ improvements in their social skills coincide with changes in their brains’ anatomical and functional organisation [ 59 ]. Functional hubs exhibit growing connectivity strength [ 60 ], suggesting increased functional integration during development. During this time, the brain’s functional networks change from an anatomically dominant structure to a scattered architecture [ 60 ].
The adolescent brain is very responsive to synaptic reorganisation and experience cues [ 61 ]. As a result, one of the distinguishing traits of the maturation of adolescent brains is the variation in neural network trajectory [ 62 ]. Important weaknesses of the adolescent brain that may explain the neurobiological change brought on by external stimuli are illustrated by features like the functional gaps between networks and the inadequate segregation of networks [ 62 ].
The implications of these findings towards adolescent behaviour are significant. Although the exact changes and mechanisms are not fully clear, the observed changes in functional connectivity have the capacity of influencing several aspects of adolescent development. For example, functional connectivity has been utilised to investigate attachment styles in adolescents [ 63 ]. It was observed that adolescent attachment styles were negatively associated with caudate-prefrontal connectivity, but positively with the putamen-visual area connectivity [ 63 ]. Both named areas were also influenced by the onset of internet addiction, possibly providing a connection between the two. Another study associated neighbourhood/socioeconomic disadvantage with functional connectivity alterations in the DMN and dorsal attention network [ 64 ]. The study also found multivariate brain behaviour relationships between the altered/disadvantaged functional connectivity and mental health and cognition [ 64 ]. This conclusion supports the notion that the functional connectivity alterations observed in IA are associated with specific adolescent behaviours as well as the fact that functional connectivity can be utilised as a platform onto which to compare various neurologic conditions.
Limitations/strengths
There were several limitations that were related to the conduction of the review as well as the data extracted from the articles. Firstly, the study followed a systematic literature review design when analysing the fMRI studies. The data pulled from these imaging studies were namely qualitative and were subject to bias contrasting the quantitative nature of statistical analysis. Components of the study, such as sample sizes, effect sizes, and demographics were not weighted or controlled. The second limitation brought up by a similar review was the lack of a universal consensus of terminology given IA [ 47 ]. Globally, authors writing about this topic use an array of terminology including online gaming addiction, internet addiction, internet gaming disorder, and problematic internet use. Often, authors use multiple terms interchangeably which makes it difficult to depict the subtle similarities and differences between the terms.
Reviewing the explicit limitations in each of the included studies, two major limitations were brought up in many of the articles. One was relating to the cross-sectional nature of the included studies. Due to the inherent qualities of a cross-sectional study, the studies did not provide clear evidence that IA played a causal role towards the development of the adolescent brain. While several biopsychosocial factors mediate these interactions, task-based measures that combine executive functions with imaging results reinforce the assumed connection between the two that is utilised by the papers studying IA. Another limitation regarded the small sample size of the included studies, which averaged to around 20 participants. The small sample size can influence the generalisation of the results as well as the effectiveness of statistical analyses. Ultimately, both included study specific limitations illustrate the need for future studies to clarify the causal relationship between the alterations of FC and the development of IA.
Another vital limitation was the limited number of studies applying imaging techniques for investigations on IA in adolescents were a uniformly Far East collection of studies. The reason for this was because the studies included in this review were the only fMRI studies that were found that adhered to the strict adolescent age restriction. The adolescent age range given by the WHO (10–19 years old) [ 65 ] was strictly followed. It is important to note that a multitude of studies found in the initial search utilised an older adolescent demographic that was slightly higher than the WHO age range and had a mean age that was outside of the limitations. As a result, the results of this review are biased and based on the 12 studies that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Regarding the global nature of the research, although the journals that the studies were published in were all established western journals, the collection of studies were found to all originate from Asian countries, namely China and Korea. Subsequently, it pulls into question if the results and measures from these studies are generalisable towards a western population. As stated previously, Asian countries have a higher prevalence of IA, which may be the reasoning to why the majority of studies are from there [ 8 ]. However, in an additional search including other age groups, it was found that a high majority of all FC studies on IA were done in Asian countries. Interestingly, western papers studying fMRI FC were primarily focused on gambling and substance-use addiction disorders. The western papers on IA were less focused on fMRI FC but more on other components of IA such as sleep, game-genre, and other non-imaging related factors. This demonstrated an overall lack of western fMRI studies on IA. It is important to note that both western and eastern fMRI studies on IA presented an overall lack on children and adolescents in general.
Despite the several limitations, this review provided a clear reflection on the state of the data. The strengths of the review include the strict inclusion/exclusion criteria that filtered through studies and only included ones that contained a purely adolescent sample. As a result, the information presented in this review was specific to the review’s aims. Given the sparse nature of adolescent specific fMRI studies on the FC changes in IA, this review successfully provided a much-needed niche representation of adolescent specific results. Furthermore, the review provided a thorough functional explanation of the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway making it accessible to readers new to the topic.
Future directions and implications
Through the search process of the review, there were more imaging studies focused on older adolescence and adulthood. Furthermore, finding a review that covered a strictly adolescent population, focused on FC changes, and was specifically depicting IA, was proven difficult. Many related reviews, such as Tereshchenko and Kasparov (2019), looked at risk factors related to the biopsychosocial model, but did not tackle specific alterations in specific structural or functional changes in the brain [ 66 ]. Weinstein (2017) found similar structural and functional results as well as the role IA has in altering response inhibition and reward valuation in adolescents with IA [ 47 ]. Overall, the accumulated findings only paint an emerging pattern which aligns with similar substance-use and gambling disorders. Future studies require more specificity in depicting the interactions between neural networks, as well as more literature on adolescent and comorbid populations. One future field of interest is the incorporation of more task-based fMRI data. Advances in resting-state fMRI methods have yet to be reflected or confirmed in task-based fMRI methods [ 62 ]. Due to the fact that network connectivity is shaped by different tasks, it is critical to confirm that the findings of the resting state fMRI studies also apply to the task based ones [ 62 ]. Subsequently, work in this area will confirm if intrinsic connectivity networks function in resting state will function similarly during goal directed behaviour [ 62 ]. An elevated focus on adolescent populations as well as task-based fMRI methodology will help uncover to what extent adolescent network connectivity maturation facilitates behavioural and cognitive development [ 62 ].
A treatment implication is the potential usage of bupropion for the treatment of IA. Bupropion has been previously used to treat patients with gambling disorder and has been effective in decreasing overall gambling behaviour as well as money spent while gambling [ 67 ]. Bae et al. (2018) found a decrease in clinical symptoms of IA in line with a 12-week bupropion treatment [ 31 ]. The study found that bupropion altered the FC of both the DMN and ECN which in turn decreased impulsivity and attentional deficits for the individuals with IA [ 31 ]. Interventions like bupropion illustrate the importance of understanding the fundamental mechanisms that underlie disorders like IA.
The goal for this review was to summarise the current literature on functional connectivity changes in adolescents with internet addiction. The findings answered the primary research questions that were directed at FC alterations within several networks of the adolescent brain and how that influenced their behaviour and development. Overall, the research demonstrated several wide-ranging effects that influenced the DMN, SN, ECN, and reward centres. Additionally, the findings gave ground to important details such as the maturation of the adolescent brain, the high prevalence of Asian originated studies, and the importance of task-based studies in this field. The process of making this review allowed for a thorough understanding IA and adolescent brain interactions.
Given the influx of technology and media in the lives and education of children and adolescents, an increase in prevalence and focus on internet related behavioural changes is imperative towards future children/adolescent mental health. Events such as COVID-19 act to expose the consequences of extended internet usage on the development and lifestyle of specifically young people. While it is important for parents and older generations to be wary of these changes, it is important for them to develop a base understanding of the issue and not dismiss it as an all-bad or all-good scenario. Future research on IA will aim to better understand the causal relationship between IA and psychological symptoms that coincide with it. The current literature regarding functional connectivity changes in adolescents is limited and requires future studies to test with larger sample sizes, comorbid populations, and populations outside Far East Asia.
This review aimed to demonstrate the inner workings of how IA alters the connection between the primary behavioural networks in the adolescent brain. Predictably, the present answers merely paint an unfinished picture that does not necessarily depict internet usage as overwhelmingly positive or negative. Alternatively, the research points towards emerging patterns that can direct individuals on the consequences of certain variables or risk factors. A clearer depiction of the mechanisms of IA would allow physicians to screen and treat the onset of IA more effectively. Clinically, this could be in the form of more streamlined and accurate sessions of CBT or family therapy, targeting key symptoms of IA. Alternatively clinicians could potentially prescribe treatment such as bupropion to target FC in certain regions of the brain. Furthermore, parental education on IA is another possible avenue of prevention from a public health standpoint. Parents who are aware of the early signs and onset of IA will more effectively handle screen time, impulsivity, and minimize the risk factors surrounding IA.
Additionally, an increased attention towards internet related fMRI research is needed in the West, as mentioned previously. Despite cultural differences, Western countries may hold similarities to the eastern countries with a high prevalence of IA, like China and Korea, regarding the implications of the internet and IA. The increasing influence of the internet on the world may contribute to an overall increase in the global prevalence of IA. Nonetheless, the high saturation of eastern studies in this field should be replicated with a Western sample to determine if the same FC alterations occur. A growing interest in internet related research and education within the West will hopefully lead to the knowledge of healthier internet habits and coping strategies among parents with children and adolescents. Furthermore, IA research has the potential to become a crucial proxy for which to study adolescent brain maturation and development.
Supporting information
S1 checklist. prisma checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s001
S1 Appendix. Search strategies with all the terms.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s002
S1 Data. Article screening records with details of categorized content.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s003
Acknowledgments
The authors thank https://www.stockio.com/free-clipart/brain-01 (with attribution to Stockio.com); and https://www.rawpixel.com/image/6442258/png-sticker-vintage for the free images used to create Figs 2 – 4 .
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 2. Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5 ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
- 10. Stats IW. World Internet Users Statistics and World Population Stats 2013 [ http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm .
- 11. Rideout VJR M. B. The common sense census: media use by tweens and teens. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense Media; 2019.
- 37. Tremblay L. The Ventral Striatum. Handbook of Reward and Decision Making: Academic Press; 2009.
- 57. Bhana A. Middle childhood and pre-adolescence. Promoting mental health in scarce-resource contexts: emerging evidence and practice. Cape Town: HSRC Press; 2010. p. 124–42.
- 65. Organization WH. Adolescent Health 2023 [ https://www.who.int/health-topics/adolescent-health#tab=tab_1 .
- Open access
- Published: 22 June 2024
BETTER LIFE- guidelines for chronic disease preventive care for people aged 18–39 years: a literature review
- Nasheed Moqueet 1 ,
- Sylvie D. Cornacchi 2 ,
- Jesmin Antony 3 ,
- Ielaf Khalil 4 ,
- Donna Manca 5 ,
- Carolina Fernandes 5 ,
- Lawrence Paszat 6 ,
- Kris Aubrey-Bassler 7 ,
- Eva Grunfeld 8 , 13 ,
- Nicolette Sopcak 5 ,
- Andrew Pinto 9 ,
- Jill Konkin 5 ,
- Candace Nykiforuk 10 ,
- Linda Rabeneck 11 ,
- Peter Selby 12 , 13 ,
- Becky Wall 14 ,
- Mary Ann O’Brien 13 na1 &
- Aisha Lofters 3 , 13 na1
BMC Primary Care volume 25 , Article number: 224 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
The original ‘BETTER’ (Building on Existing Tools To Improve Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Primary Care) approach consisted of a prevention-focused visit between participants aged 40–65 years and a “Prevention Practitioner” (PP), who empowered the participant to set achievable prevention and screening goals for cancers and chronic diseases. BETTER was successfully adapted for economically deprived communities (BETTER HEALTH) in Canada. Our objective was to conduct a review of guidelines in preparation for adapting the ‘BETTER HEALTH’ approach for younger adults aged 18–39 years living with lower income, a group known to have earlier mortality due to a higher prevalence of preventable chronic diseases than their peers with higher income.
We searched multiple electronic databases and grey literature for clinical practice guidelines on prevention/screening and included those that met the following criteria: published in English from 2008–2020 in Canada or any of the following countries (Australia, Ireland, New Zealand, Scotland, United States and England); and addressed prevention or screening. We assessed quality using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE) II tool and extracted data (publication details, recommendations, and Quality/Level of evidence as reported by authors) from sources with overall scores of 5 or higher. Final recommendations were compiled after harmonization with input from diverse stakeholders (co-investigators, PPs, and the Community Advisory Committee).
We included a total of 85 guidelines, and developed a final list of 42 recommendations for 18–39 year-olds across 21 topics. Specific recommendations fell under the following topics: cancers, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, lifestyle (alcohol; healthy nutrition/physical activity); healthy relationships and healthy sexuality, immunization, oral health, social determinants of health, and substance use .
We identified evidence-based guidelines on individual-level prevention/screening actions for adults 18–39 years old and relevant for those living with lower income which will directly inform development and implementation of the BETTER LIFE intervention.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Despite the existence of strong evidence for lifestyle modifications and for screening and preventive actions to improve health outcomes, an implementation gap exists due to limited physician time [ 1 ], conflicting/unclear guidelines, and difficulties inherent to sustained behaviour change [ 2 ]. The original BETTER (Building on Existing Tools To Improve Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Primary Care) intervention was designed to address this gap by providing an integrated approach to increasing uptake of chronic disease prevention and screening (CDPS) actions using a framework of shared decision-making between patient and practitioner. In a pragmatic cluster randomised control trial (RCT), the BETTER approach improved the uptake of CDPS actions against heart disease, diabetes and several cancers (colorectal, breast and cervical cancers) by 32.5% in urban primary care settings in Alberta and Ontario, Canada [ 2 , 3 ]. The intervention consisted of an individual prevention-focussed visit between participants aged 40–65 years and a “Prevention Practitioner” (PP), who used principles of motivational interviewing to empower the participant to set achievable prevention and screening goals, based on the harmonization of evidence, which were then recorded in a goals sheet and a personalized ‘prevention prescription’.
There have been subsequent modifications of the BETTER approach with similar positive results. ‘BETTER 2’ targeted the same age group as the original BETTER but modified the approach for different populations due to equity concerns, including individuals from rural, lower income, or historically marginalized backgrounds in Newfoundland and Labrador and the Northwest Territories, Canada [ 4 ]. Subsequently, BETTER WISE (Building on Existing Tools to Improve Cancer and Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Primary Care for Wellness of Cancer Survivors and Patients) tailored the BETTER approach for cancer survivors (breast, colorectal, prostate) aged 40–65 and also included screening for poverty, as well as an updated literature review to recommend specific prevention and screening actions [ 5 ]. Another modified version, BETTER HEALTH: Durham used a public health-led model with public health nurses serving as PPs for 40–64 year-olds living with lower income in Durham, Ontario, and found a 53% increase in completed health actions (immediate intervention, n = 60 vs. wait-listed arm, n = 66) [ 6 , 7 ]. Although there were positive results for this age group, the community advisory group for BETTER HEALTH: Durham suggested that starting the intervention at 40 years of age was too late for people living with low income, where evidence shows an earlier onset of chronic diseases [ 8 ]. We aimed to adapt the BETTER HEALTH: Durham intervention to a new population of adults aged 18–39 years living with low income, a group known to have earlier mortality due to, and higher prevalence of, preventable chronic diseases than their peers with higher income.
To support the adaptation, we conducted a review of guidelines to identify and assess prevention and screening actions for health issues and risk factors amenable to individual change for the 18–39 year age group. This paper describes the methods and results of the literature review.
Overview of search strategy
First, we assessed the data sources (clinical practice guidelines) from the most recent BETTER WISE study [ 9 ], which had entailed a rigorous evidence review process to recommend specific prevention and screening actions, for applicability to adults aged 18–39 years.Then, we used a structured grey literature search of specific repositories and websites to find relevant clinical practice guidelines for new topics suggested by the research team. If guidelines were unavailable for these topics, we performed a systematic literature search in the databases Ovid Medline, CINAHL (Cumulated Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews to identify systematic reviews/meta-analyses. Thus, our search and eligibility criteria for new sources was restricted to clinical practice guidelines (i.e. excluding systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and review of reviews when guidelines were found) and expanded to allow systematic reviews and meta-analyses when guidelines were not available (See Fig. 1 ).

Search strategy for guidelines for BETTER LIFE
Search strategy for topics of interest
To create the overall search strategy, we consulted an experienced information specialist (CZ). We used different combinations of key words such as ‘guidelines’, ‘chronic disease prevention’, ‘prevention’, ‘clinical practice guidelines’, and ‘screening’ with terms from topics of interest from previous versions of BETTER ( cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, obesity, diet and nutrition, physical activity, smoking/tobacco and alcohol use) and new topics suggested by the wider research team (co-investigators, PPs, Community Advisory Committee (CAC)) due to their importance for our target population (See Supp Table 1 ).
Search sources
We conducted a structured search in repositories of guidelines at the provincial level (Ontario, Alberta, Newfoundland & Labrador): Cancer Care Ontario; Cancer Control Alberta; Eastern Health Cancer Care Program; and national level: Health Canada; Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC); and the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care (CTFPHC). (Details in Fig. 1 ).
We did not find guidelines for four topics recommended by our study team for our target population ( speeding, texting & driving, seat belts, bullying & cyberbullying). Therefore, we then conducted a systematic search on select databases (Ovid Medline, CINAHL, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews) for systematic reviews and meta-analyses published from 2008-August 2020 on these topics.
Inclusion & exclusion criteria
When screening abstracts obtained from our searches, we included articles for full-text review if they met the following criteria: clinical practice guidelines in English only; published from 2008–2020; country of publication was Australia, Canada, England, Ireland, New Zealand, Scotland, or US; included at least one of the identified topics in title or abstract; and addressed prevention or screening.
At full-text screening, we excluded articles if they met any of the following: exclusively focused on management or treatment; exclusively targeted ages not 18–39 years old (i.e., under 18, 40 or older); lacked individual-level recommendations (i.e. contained only macro-level data (e.g. legal, policy)); or lacked evidence of synthesis. With the exception of the four topics covered during the systematic search, we also excluded full-texts if they were systematic reviews, review of reviews, or meta-analyses.
During full-text screening, if multiple eligible sources existed, we used a hierarchical approach to determine inclusion: preference for most recent Canadian guideline/ review and if not available, relevant guidelines from any of 6 aforementioned primarily English-speaking countries of interest. If there were discrepancies or disagreements among guidelines, we searched for and extracted information from primary or common references.
All abstracts and full-texts were uploaded and screened using Covidence [ 10 ].
Quality assessment
We chose AGREE-II for quality assessment since it was developed specifically for assessing quality of existing practice guidelines, unlike GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations), which is most suited for developing guidelines de novo and for rating primary sources of evidence for specific outcomes, which was outside the scope of our study. We used a two-step process to assess guideline quality. For the first step, two trained reviewers (NM and SC) independently used a shorter 2-item AGREE-II [ 11 ] rating system to assess the “Rigour of development” (items 7 and 12—‘ Systematic methods were used to search for evidence’ and ‘There is an explicit link between the recommendations and the supporting evidence’ , respectively) on all references. If methodological details were missing from guidelines, we emailed authors or guideline developers to request more information. Both reviewers had to assign a score of 4 or higher (out of 7) on both AGREE-II items for the article to move to full quality assessment with the 23-item AGREE-II tool.
Specifically, the reviewers examined the ‘ Methods ’ section of each guideline to assess the details of systematic methods (Item #7) that were used and consulted any methods papers that governed the overall initiative when available [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. If the guideline developer did not report any evidence of an independent synthesis as per the first step in the AGREE–II screening process, the guideline was not assessed further. If no Canadian reference met the criteria for the 2-item AGREE-II screening tool on a given topic, the reviewers then assessed the quality of the non-Canadian documents. Disagreement over scores was discussed and a final decision was determined by consensus.
For step 2, two reviewers independently applied the full AGREE-II instrument on all guidelines that passed the 2-item screening. Overall scores of 5 and above (out of 7) by both reviewers were used to move to full data extraction phase. To ensure consistent interpretation of data quality, we pilot tested the full AGREE-II tool on 5 articles that had previously been included in BETTER WISE and that also met the eligibility criteria for BETTER LIFE.
Data extraction
Two reviewers also pilot tested the data extraction form on 5 articles and resolved differences by consensus. Each reviewer independently extracted data from half the included articles and then checked a subset from the other reviewer for consistency, resolving differences by discussion. Extracted data included publication details (issuing body/author, year and country of publication), participant characteristics (target population, age, ethnicity, socioeconomic metrics, identified risk factors, clinical context) and guideline details (individual-level recommendations, quality of supporting evidence, and whether conflict of interest was declared or not).
Harmonization and synthesis of extracted data
The extracted data were grouped by topics. Each article was assigned to two reviewers who independently either categorized recommendations for inclusion in BETTER LIFE or excluded them if they were duplicative, out of scope, or not actionable (See Fig. 2 ).

Harmonization process for BETTER LIFE
The reviewers met to discuss and assign a final primary categorization to each recommendation with the overall team meeting to resolve differences if there was no agreement between reviewers. The senior co-authors (AL and MAO) reviewed the categorizations, clarified unclear recommendations and identified specific recommendations for further review from content experts/co-investigators in the BETTER team.
Harmonization and synthesis
We followed a similar harmonization process to Campbell-Sherer et al [ 9 ] within an overarching ADAPT-ITT framework [ 21 ].
All the co-investigators and PPs in the BETTER team were invited to provide input on topics in which they had expertise and asked to rank the newly included recommendations in an online survey (Qualtrics, Provo, UT), with the goal of reaching consensus on the top ranked (most relevant) recommendations. Recommendations ranked with a mean of 90% or above were included, while those that were that consistently ranked low (mean of less than 75%) were removed. For topics with multiple individual recommendations with mean scores of 80–89%, we combined, summarized and simplified the multiple recommendations where it seemed appropriate to do so and included them.
After the harmonization process, we compiled the final list of recommendations and topics into a table and also grouped all related included topics into existing or new ‘domains’ for data visualization.
There were 864 abstracts, of which 762 were unique. Of these, 435 were moved to the full-text phase and assessed for inclusion. One hundred and eighty-five guidelines met the inclusion criteria for quality assessment (Fig. 3 a).

a Summary flow from literature search to full-text review for quality assessment. b Quality assessment of guidelines using the AGREE-II instrument to the data extraction stage
From the 150 guidelines included in BETTER WISE that were published in 2008 or later, 40 guidelines were applicable to the 18–39 year age group, of which 14 had been updated since inclusion in BETTER WISE. Newer versions were available for the following 8 topics: cancers (breast, cervical, colorectal), CVD, diabetes, obesity, lifestyle (alcohol; healthy nutrition/physical activity) .
From the search for topics for which there were no identified guidelines (speeding, texting and driving, seat belts, bullying and cyberbullying) , 213 papers were uploaded into Covidence after removing duplicates. However, all the papers on these topics were excluded at various stages.
One hundred and eighty-five guidelines were eligible for quality screening (Fig. 3 b). After exclusion at various stages, 93 guidelines were rated with the 2-item AGREE-II. Of these, 75 were rated with the full AGREE-II tool and 58 papers (77%, 58/75) were scored 5 or higher by both reviewers.
We extracted data from 85 guidelines (58 were new guidelines and 27 were from previous versions of BETTER). Of the 38 new topics (Supp Table 1 ), 22 were relevant to the 18–39 year age group (Supp Table 2).
Of the 19 colleagues invited, 9 responded, reporting expertise on atleast one of the topics on the list (between 1–8 respondents provided ranking on each of the various new recommendations). At the harmonization stage, the team removed the topic ‘ falls/injury prevention’ as the recommendation was deemed not in scope for the 18–39 age group.
Due to low ranking scores from Co-investigators, we removed 6 topics from inclusion in the final BETTER LIFE recommendations ( intimate partner violence, sexual health, skin cancer, sleep, violence, vitamins ). We also excluded hepatitis C as only one co-investigator provided a ranking for this recommendation, and the recommendation was to not screen for hepatitis C. On the advice of the research team, we also included screening for Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) [ 22 , 23 ].
Based on the results of the data extraction and harmonization, the final list of topics contained 42 recommendations for 18–39 year-olds across 21 total topics (Table 1 ). We grouped the final list of topics into existing or new domains (See Supp Fig. 1 ).
The CDPS recommendations for heart disease and colorectal and breast cancers were only targeted to those deemed ‘high-risk’ (based on various clinical criteria such as family history) in the 18–39 age group. For most of the new topics, we also identified specific maneuvers or screening questions/tools that could be incorporated into the BETTER visits or into BETTER tools.
We used a structured search of published and grey literature, and a systematic search of specific databases to compile recent evidence from clinical practice guidelines on risk factors and individual prevention and screening actions relevant to adults aged 18–39 years, particularly those living with low income, in Canada. We also obtained input from our co-investigators, a team of experts in primary care, public health, the social determinants of health, and the BETTER program. Through this process, we were able to identify 42 recommendations within 21 total topics that will be applied in the BETTER LIFE approach for younger adults living with low income.
Some topics and health recommendations from previous BETTER versions were updated or included, such as those addressing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, smoking, alcohol, nutrition, and exercise . Risk assessments for diabetes, cardiovascular disease and most cancers were similar for those aged 18–39 years old as with previous versions of BETTER, though routine screening was only recommended for those deemed high risk (with the exception of cervical cancer screening). We found evidence-based guidelines addressing new topics relevant specifically to 18–39 year olds grouped into the following new domains: healthy relationships and healthy sexuality, immunization, oral health, social determinants of health, and substance use . Some recommendations in BETTER LIFE were similar to those published by others [ 97 , 98 , 99 ], though the recency, diversity, and sources of our search; our harmonization and implementation process, as well as the definition of our target population were different. For example, Persaud et. al. developed 15 preventive care recommendations and 1 policy recommendation that promote health equity in Canada. Although their work and ours both prioritize health equity in primary care, Persaud et al. did not have any age restrictions on their target population nor a primary focus on uptake of individual-level preventive actions. They also utilized systematic reviews, primary research articles and randomized controlled trials to develop recommendations using a GRADE approach. Because we prioritized recommendations that were individually actionable, supported by evidence that met our criteria, and ranked highly by content experts, topics like vitamins and skin cancer prevention were eventually omitted. Although we ultimately excluded skin cancer , this topic is an important one in many countries such as Australia [ 100 ].
Taking specific contexts into account is important when determining how best to implement and support uptake of the recommendations. For some new topics, we found stronger evidence for resources and screening tools for PPs than for specific recommendations (e.g. the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Quick Screen or the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) for substance use ). PPs identified local community resources for some new health topics ( parenting; substance use; oral health ) which could help to support participants achieve recommended actions. They also suggested considering social contexts as opportunities for engagement, e.g. by focusing conversations in BETTER LIFE visits on the concepts of health promotion or meaningful overall health and social well-being rather than explicit chronic disease prevention; by using different media for sharing health information (e.g. mobile apps, social media or online resources); by considering social contexts as barriers or enablers of behaviour change, especially regarding physical activity, alcohol, substance use ; or by taking life stage into account (single adult vs. parenting).
Our study had several strengths and limitations. Our strengths include a rigorous critical appraisal of the literature with a two-step quality assessment process and independent review that ensured that only guidelines that met high methodological rigour and transparency were included for data extraction and harmonization; focus on actionable recommendations (e.g. goal-setting, access/referral to community resources); and meaningful collaborations with diverse community, public health, and clinical experts. However, all the guidelines were published prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, so did not take pandemic-related disruptions and health impact into account. COVID-19 has exacerbated health and economic inequities and disproportionately affected racialized and low income groups with a higher risk of exposure due to living and working conditions; higher prevalence of co-morbidities; inequitable access to testing and treatment; and disruption of health services [ 101 , 102 ]. We also relied on consensus to resolve disagreements during the screening process and to formulate the final recommendations as well as on voluntary responses during harmonization which led to varied numbers of reviewers for each recommendation, and which may be subject to bias. However, we used AGREE-II to ensure transparency and careful documentation, and also consulted a wide and diverse range of experts (in primary care, public health, the social determinants of health, Prevention Practitioners, and the Community Advisory Committee) at many stages of the project. Finally, we may have missed guidelines because we targeted our search to specific criteria, repositories, and databases.
Adults living with low income are at increased risk of chronic disease. Through critical literature review and guideline harmonization, we have curated a list of individual-level actionable recommendations relevant to prevention and screening for people aged 18–39 living with low income in English-speaking countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
Adverse Childhood Experiences
Assessment, Decision, Adaptation, Production, Topical Experts, Integration, Training, Testing
Appraisal of Guidelines for Research & Evaluation II
Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test
Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test
Building on Existing Tools To Improve Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Primary Care
Building on Existing Tools to Improve Cancer and Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Primary Care for Wellness of Cancer Survivors and Patients
Body mass index
Blood pressure
Community Advisory Committee
Chronic disease prevention and screening
Cumulated Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature
Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care
Coronavirus disease 2019
Cardiovascular disease
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
Electronic nicotine delivery systems
Generalized Anxiety Disorder 2-item
Human papillomavirus
Manual office blood pressure device
National Institute on Drug Abuse
Public Health Agency of Canada
Primary care provider
Prevention Practitioner
Randomised control trial
Sexually transmitted infection
United States
Yarnall KSH, Pollak KI, Østbye T, Krause KM, Michener JL. Primary Care: Is There Enough Time for Prevention? Am J Public Health. 2003;93(4):635–41. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.93.4.635 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Grunfeld E, Manca D, Moineddin R, et al. Improving chronic disease prevention and screening in primary care: results of the BETTER pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-14-175 .
BETTER. BETTER website. http://better-program.ca/evidence/ . Accessed Jan 23, 2022.
Aubrey-Bassler K, Fernandes C, Penney C, et al. The effectiveness of a proven chronic disease prevention and screening intervention in diverse and remote primary care settings: an implementation study on the BETTER 2 Program. BJGP Open. 2019;3(3):bjgpopen19X101656 https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgpopen19X101656 .
Manca DP, Fernandes C, Grunfeld E, et al. The BETTER WISE protocol: building on existing tools to improve cancer and chronic disease prevention and screening in primary care for wellness of cancer survivors and patients – a cluster randomized controlled trial embedded in a mixed methods design. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):927. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4839-y .
Paszat L, Sutradhar R, O’Brien MA, et al. BETTER HEALTH: Durham – protocol for a cluster randomized trial of BETTER in community and public health settings. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):754. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4797-3 .
Lofters AK, O’Brien MA, Sutradhar R, et al. Building on existing tools to improve chronic disease prevention and screening in public health: a cluster randomized trial. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1496. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11452-x .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Roberts KC, Rao DP, Bennett TL, Loukine L, Jayaraman GC. Prevalence and patterns of chronic disease multimorbidity and associated determinants in Canada. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2015;35(6):87–94. https://doi.org/10.24095/hpcdp.35.6.01 .
Campbell-Scherer D, Rogers J, Manca D, et al. Guideline harmonization and implementation plan for the BETTER trial: Building on Existing Tools to Improve Chronic Disease Prevention and Screening in Family Practice. CMAJ Open. 2014;2(1):E1–10. https://doi.org/10.9778/cmajo.20130040 .
Covidence systematic review software. https://www.covidence.org . Melbourne, Australia. Computer program
Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, et al. AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care. Can Med Assoc J. 2010;182(18):E839–42. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.090449 .
Article Google Scholar
BC Guidelines. Guidelines and Protocols Advisory Committee Handbook: How our “Made in BC” Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols are Developed . Vancouver: British Columbia Ministry of Health;2017. gpachandbook2017.pdf (gov.bc.ca); Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Alberta Health Services CancerControl Alberta. Guideline Methodology Handbook – Version 5 . 2020. GURU Handbook (albertahealthservices.ca) Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care (CTFPHC). Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care Procedure Manual . Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC);2014. https://canadiantaskforce.ca/methods/ Accessed Jan 23, 2022.
Davino-Ramaya C, Krause LK, Robbins CW, et al. Transparency Matters: Kaiser Permanente’s National Guideline Program Methodological Processes. Perm J. 2012;16(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.7812/TPP/11-134 .
Michigan Quality Improvement Consortium (MQIC). MQIC Guideline Development Criteria . 2013. Clinical Care Guidelines | University of Michigan Health (uofmhealth.org) Accessed Jan 23, 2022.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Developing NICE guidelines: the manual. Manchester: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2014.
Toward Optimized Practice (TOP). Toward Optimized Practice Clinical Practice Guideline Development Methodology. 2016. https://actt.albertadoctors.org/cpgs Accessed May 25, 2020.
University of Michigan. Michigan Medicine Quality Department Clinical Care Guidelines: Purpose and Methods. 2019. https://www.uofmhealth.org/provider/clinical-care-guidelines . Accessed May 25 2020. Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO handbook for guideline development, 2nd Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data; 2014.
Wingood GM, DiClemente RJ. The ADAPT-ITT Model. JAIDS J Acqu Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2008;47(Supplement 1):S40–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181605df1 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Watson P. How to screen for ACEs in an efficient, sensitive, and effective manner. Paediatr Child Health. 2019;24(1):37–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/pxy146 .
California Surgeon General’s Clinical Advisory Committee. Adverse Childhood Experience Questionnaire for Adults. California: Office of the Surgeon General/California Department of Health Care Services; 2020.
BC Guidelines. Problem Drinking. 2013. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/problem-drinking . Accessed May 29, 2020.
Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Screening and Behavioral Counseling Interventions to Reduce Unhealthy Alcohol Use in Adolescents and Adults. JAMA. 2018;320(18):1899. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.16789 .
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). [CG115] Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking (high-risk drinking) and alcohol dependence 2011. Overview | Alcohol-use disorders: diagnosis, assessment and management of harmful drinking (high-risk drinking) and alcohol dependence | Guidance | NICE, Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse and Addiction (CCSA). Guidelines for Healthcare Providers to Promote Low-Risk Drinking Among Patients . 2013. www.ccsa.ca/Resource Library/2012-Canada-Low-Risk-AlcoholDrinking-Guidelines-Poster-en.pdf . Accessed May 25, 2020.
UK Chief Medical Officers (CMO). UK Chief Medical Officers’ Low Risk Drinking Guidelines 2016. https://www.gov.uk/government/consultations/health-risks-from-alcohol-new-guidelines . Accessed May 28, 2020
Katzman MA, Bleau P, Blier P, Chokka P, Kjernisted K, Van Ameringen M. Canadian clinical practice guidelines for the management of anxiety, posttraumatic stress and obsessive-compulsive disorders. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14(Suppl 1):S1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-14-S1-S1 .
Gregory KD, Chelmow D, Nelson HD, et al. Screening for Anxiety in Adolescent and Adult Women: A Recommendation From the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.7326/M20-0580 .
Cancer Care Ontario. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Screening of Women at High Risk for Breast Cancer. 2018. https://www.cancercareontario.ca/en/guidelines-advice/cancer-continuum/screening/breast-cancer-high-risk-women/faqs-for-healthcare-providers . 2018. Accessed May 25, 2020.
Towards Optimized Practice. Breast Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Guideline. 2013. https://actt.albertadoctors.org/CPGs/Lists/CPGDocumentList/Breast-Cancer-Screening-CPG.pdf . Accesses May 29, 2020
Eastern Health. Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and High Risk Hereditary Breast Cancer. 2017 https://www.easternhealth.ca/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/06/Breast-Magnetic-Resonance-MRI-and-High-Risk-Guideline_2017.pdf Accessed May 25, 2020.
Eastern Health. Indications for Use of Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). 2018. https://www.easternhealth.ca/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/06/Indications_for_Use_of_Breast_Magnetic_Imaging_MRI_Jan_2018.pdf Accessed May 25, 2020.
Fischer B, Russell C, Sabioni P, et al. Lower-Risk Cannabis Use Guidelines: A Comprehensive Update of Evidence and Recommendations. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(8):e1–12. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2017.303818 .
Toward Optimized P. Cervical Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Guideline. 2016. cervical-cancer-screening-cpg.pdf (albertadoctors.org) Accessed May 25, 2020.
Dickinson J, Tsakonas E, Conner Gorber S, et al. Recommendations on screening for cervical cancer. CMAJ. 2013;185(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.121505 .
Cancer Care Ontario. Ontario Cervical Screening Guidelines Summary. Toronto: Cancer Care Ontario; 2016.
Toward Optimized Practice (TOP) Working Group for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Colorectal Cancer Screening Clinical Practice Practice Guideline. Edmonton: Accelerating Change Transformation Team (ACCT) Alberta Medical Association; 2013.
Provenzale D, Ness RM, Llor X, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Colorectal Cancer Screening, Version 2.2020. J Nat Comprehen Cancer Net. 2020;18(10):1312–1320. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.0048 .
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). SIGN 126 Diagnosis and management of colorectal cancer. 2016. https://www.sign.ac.uk/media/1064/sign126.pdf Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Leddin D, Lieberman DA, Tse F, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline on Screening for Colorectal Cancer in Individuals With a Family History of Nonhereditary Colorectal Cancer or Adenoma: The Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Banff Consensus. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(5):1325-1347.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.017 .
Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Recommendations on screening for colorectal cancer in primary care. CMAJ. 2016;188(5):340–8. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.151125 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cancer Care Ontario. Colorectal Cancer. 2019 https://www.cancercareontario.ca/en/guidelines-advice/cancer-continuum/screening/resources-healthcare-providers Accessed Mar 20, 2024
U. S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 2016;315(23):2564–2575. Recommendation: Colorectal Cancer: Screening | United States Preventive Services Taskforce ( uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org ). Accessed 20 Mar 2024.
Black A, Guilbert E, Costescu D, et al. Canadian Contraception Consensus. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015;37(11):1033–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1701-2163(16)30054-8 .
BC Guidelines. Hypertension – Diagnosis and Management. 2020. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/hypertension . Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Lindsay P, Connor Gorber S, Joffres M, et al. Recommendations on screening for high blood pressure in Canadian adults. Can Fam Physician . 2013;59(9):927–933, e393–400.
Siu AL, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for high blood pressure in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(10):778–86 https://doi.org/10.7326/M15-2223 .
Rabi DM, McBrien KA, Sapir-Pichhadze R, et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2020 Comprehensive Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults and Children. Can J Cardiol. 2020;36(5):596–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.086 .
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Depression in adults: recognition and management : guidance (CG90). National Institute for Health and Care Excellence - NICE; 2009/10/28 2009. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng222 . Accessed May 25, 2020.
Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for Depression in Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2016;315(4):380–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.18392 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Joffres M, Jaramillo A, Dickinson J et al. Canadian Task Force for Preventive Health Care (CTFPHC). Recommendations on screeming for depression in adults . CMAJ 2013; 185(9):775–782. https://doi.oorg/ https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj . 130403
Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI). A dult Depression in Primary Care. 2016. https://www.icsi.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Depr.pdf Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Diabetes Canada Clinical Prractice Guidelines Expert Committee. Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Prractice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabates in Canada. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(Suppl1):S1–325.
Google Scholar
Pottie K, Jaramillo A, Lewin G, et al. Recommendations on screening for type 2 diabetes in adults. CMAJ. 2012;184(15):1687–96. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.120732 .
Siu AL, U S Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Abnormal Blood Glucose and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(11):861–8 https://doi.org/10.7326/M15-2345 .
ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(2):e49–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000002501 .
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S14–31 https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-S002 .
Wilson RD, Genetics Committee, Wilson RD, et al. Pre-conception Folic Acid and Multivitamin Supplementation for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Neural Tube Defects and Other Folic Acid-Sensitive Congenital Anomalies. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015;37(6):534–52 https://doi.org/10.1016/s1701-2163(15)30230-9 .
US Preventive Services Task Force, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Folic Acid Supplementation for the Prevention of Neural Tube Defects: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2017;317(2):183–9 https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.19438 .
Health Canada. Canada’s Dietary Guidelines. 2018. CDG-EN-2018.pdf (canada.ca) Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Nutrition Working Group, O’Connor DL, Blake J, et al. Canadian Consensus on Female Nutrition: Adolescence, Reproduction, Menopause, and Beyond. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2016;38(6):508-554.e18 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogc.2016.01.001 .
Anderson TJ, Grégoire J, Pearson GJ, et al. 2016 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the Adult. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(11):1263–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2016.07.510 .
Toward Optimized Practice. Prevention and Risk Management of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Primary Care Clinical Practice Guideline . 2015. https://actt.albertadoctors.org/media/b21chzfk/cvd-risk-cpg.pdf . Accessed Man 20, 2024.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF). Behavioral Counseling to Promote a Healthful Diet and Physical Activity for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Adults Without Cardiovascular Risk Factors: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA :J Am Med Assoc. 2017;318(2):167–74 https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.7171 .
Ross R, Chaput JP, Giangregorio LM, et al. Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Adults aged 18–64 years and Adults aged 65 years or older: an integration of physical activity, sedentary behaviour, and sleep. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(10 (Suppl. 2)):S57-S102. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2020-0467
Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(29):2315–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw106 .
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Cardiovascular disease: risk assessment and reduction, including lipid modification – NICE guideline . Royal College of Physicians of London - RCP; 2014/07/01 2016. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng238 . Accessed May 25, 2020.
Allan GM, Lindblad AJ, Comeau A, et al. Simplified lipid guidelines: Prevention and management of cardiovascular disease in primary care. Can Fam Phys. 2015;61(10):857–67 e439–50.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast Cancer Risk Reduction version 1.2020. https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category 1. Accessed May 25, 2020.
Public Health Agency of Canada. Rubella vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide. 2016; https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-4-active-vaccines/page-20-rubella-vaccine.html . Accessed June 4, 2020.
Public Health Agency of Canada. Amendment to the 2015 “Update on the recommended Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine immunization schedule.” Ottawa, Ontario: Public Health Agency of Canada; 2015.
Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian immunization guide. Part 3. Vaccination of specific populations. 2016. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-3-vaccination-specific-populations.html . Accessed 4 June 2020.
Wharton S, Lau DCW, Vallis M, et al. Obesity in adults: a clinical practice guideline. Can Med Assoc J. 2020;192(31):E875–91. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.191707 .
Brauer P, Gorber SC, Shaw E, et al. Recommendations for prevention of weight gain and use of behavioural and pharmacologic interventions to manage overweight and obesity in adults in primary care. CMAJ. 2015;187(3):184–95. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.140887 .
US Preventive Services Task Force, Curry SJ, Krist AH, et al. Behavioral Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;320(11):1163–71 https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.13022 .
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation. 2014;129(25 Suppl 2):S102–38. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000437739.71477.ee .
Fitch A, Everling L, Fox C, et al. Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement. Prevention and Management of Obesity for Adults . . Updated May 2013. https://1library.net/document/y69pmp7y-prevention-and-management-of-obesity-for-adults.html . Accessed 20 Mar 2024.
LeFevre ML. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Behavioral counseling to promote a healthful diet and physical activity for cardiovascular disease prevention in adults with cardiovascular risk factors: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(8):587–93 https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-1796 .
Public Health England (PHE). Delivering better oral health: an evidence-based toolkit for prevention. 2017. Delivering better oral health: an evidence-based toolkit for prevention - GOV.UK (www.gov.uk ) Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Kavan MG, Saxena SK, Rafiq N. General Parenting Strategies: Practical Suggestions for Common Child Behavior Issues. Am Fam Physician. 2018;97(10):642–8.
PubMed Google Scholar
Alberta Health Services. Nutrition Guideline Household Food Insecurity . 2013. https://www.albertahealthservices.ca/assets/info/nutrition/if-nfs-ng-household-food-insecurity.pdf Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Pottie K, Kendall CE, Aubry T, et al. Clinical guideline for homeless and vulnerably housed people, and people with lived homelessness experience. CMAJ. 2020;192(10):E240–54. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.190777 .
Moser A, Stuck AE, Silliman RA, Ganz PA, Clough-Gorr KM. The eight-item modified Medical Outcomes Study Social Support Survey: psychometric evaluation showed excellent performance. J Clin Epidemiol. 2012;65(10):1107–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.04.007 .
Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC). Sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections: guides for health professionals. Canadian Guidelines on Sexually Transmitted Infections. Ottawa: Public Health Agency of Canada; 2020.
LeFevre ML, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Chlamydia and gonorrhea: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(12):902–910. https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-1981
Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1–137.
Kaiser P. Sexually Transmitted Infection: Screening, Testing and Treatment Guideline . 2019. https://wa-provider.kaiserpermanente.org/provider-manual/patient-care/clinical-guidelines Accessed May 25, 2020.
Siu AL. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Interventions for Tobacco Smoking Cessation in Adults, Including Pregnant Women: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(8):622–34 https://doi.org/10.7326/M15-2023 .
Thombs BD, Jaramillo Garcia A, Reid D, et al. Recommendations on behavioural interventions for the prevention and treatment of cigarette smoking among school-aged children and youth. CMAJ. 2017;189(8):E310–6. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.161242 .
CAN-ADAPTT. Canadian Smoking Cessation Clinical Practice Guideline . Toronto, Canada: Canadian Action Network for the Advancement, Dissemination and Adoption of Practice-informed Tabacco Treatment, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health. 2011. The first Canadian Guidelines for Tobacco Control was developed in 2010 (utoronto.ca) Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario. Engaging Clients Who Use Substances . 2015. https://rnao.ca/sites/rnao-ca/files/Engaging_Clients_Who_Use_Substances_WEB.pdf Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Unhealthy Drug Use: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2020;323(22):2301–9 https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.8020 .
Ontario Health Cancer Care Ontario. Vaping products including e-cigarettes: Evidence summary . Ontario, Canada: Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario); 2020. https://www.cancercareontario.ca/en/content/vaping-products-including-e-cigarettes . Accessed Mar 20, 2024.
Livingston CJ, Freeman RJ, Costales VC, et al. Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems or E-cigarettes: American College of Preventive Medicine’s Practice Statement. Am J Prev Med. 2019;56(1):167–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2018.09.010 .
Shimizu T, Bouchard M, Mavriplis C. Update on age-appropriate preventive measures and screening for Canadian primary care providers. Can Fam Physician. 2016;62(2):131–8.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ridley J, Ischayek A, Dubey V, Iglar K. Adult health checkup: Update on the Preventive Care Checklist Form©. Can Fam Physician. 2016;62(4):307–13.
Persaud N, Sabir A, Woods H, et al. Preventive care recommendations to promote health equity. Can Med Assoc J. 2023;195(37):E1250–73. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.230237 .
Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Guidelines for preventive activities in general practice (Red Book). Melbourne: Royal Australian College of General Practitioners; 2021. http://Guidelinesfor-preventive-activities-in-general-practice.pdf ( http://racgp.org.au ). Accessed 20 Mar 2024.
Sundaram ME, Calzavara A, Mishra S, et al. Individual and social determinants of SARS-CoV-2 testing and positivity in Ontario, Canada: a population-wide study. Can Med Assoc J. 2021;193(20):E723–34. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.202608 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Toronto Public Health. COVID-19 and the Social Determinants of Health: What do we know? 2020. 96e0-SDOHandCOVID19_Summary_2020May14.pdf (toronto.ca). Accessed 20 Mar 2024.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Carolyn Ziegler for the systematic search. Jane Ebreo for all administrative support. Kimberly Devotta for project management support. Tutsirai Makuwaza for feedback on the qualitative work on BETTER LIFE. Mary-Anne Pietrusiak for subject matter expertise. Ranya Mistry for Qualtrics survey development support.
This study was funded by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Catalyst Grant: Disease Prevention and Risk Factor Modification – Non-Communicable Diseases (#428589).
Author information
Mary Ann O’Brien and Aisha Lofters are co-senior authors.
Authors and Affiliations
Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Nasheed Moqueet
McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Sylvie D. Cornacchi
Women’s College Hospital, 76 Grenville St, Toronto, ON, M5S 1B2, Canada
Jesmin Antony & Aisha Lofters
Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Sinai Health System, Toronto, ON, Canada
Ielaf Khalil
Department of Family Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Donna Manca, Carolina Fernandes, Nicolette Sopcak & Jill Konkin
Sunnybrook Research Institute, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada
Lawrence Paszat
Primary Healthcare Research Unit, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL, Canada
Kris Aubrey-Bassler
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, Toronto, ON, Canada
Eva Grunfeld
Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada
Andrew Pinto
School of Public Health, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Candace Nykiforuk
Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Linda Rabeneck
Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, ON, Canada
Peter Selby
Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Eva Grunfeld, Peter Selby, Mary Ann O’Brien & Aisha Lofters
Durham Region Health Department, Whitby, ON, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
NM, SDC, JA, IK, MAO, AL provided substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work (review, data synthesis, data extraction, quality assessment, harmonization); NM, SDC, JA, IK, DM, CF, LP, PS, MAO, AL acquired, analyzed, and interpreted data; NM, SDC, IK, MAO, AL wrote the manuscript;NM, SDC, JA, IK, DM, CF, LP, KAB, EG, NS, AP, JK, CN, LR, PS, BW, MAO, AL (i.e. all authors) reviewed the manuscript critically for important intellectual content; NM, SDC, JA, IK, DM, CF, LP, KAB, EG, NS, AP, JK, CN, LR, PS, BW, MAO, AL (i.e. all authors) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Aisha Lofters .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., supplementary material 4., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Moqueet, N., Cornacchi, S.D., Antony, J. et al. BETTER LIFE- guidelines for chronic disease preventive care for people aged 18–39 years: a literature review. BMC Prim. Care 25 , 224 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-024-02471-9
Download citation
Received : 06 September 2023
Accepted : 10 June 2024
Published : 22 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-024-02471-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health promotion
BMC Primary Care
ISSN: 2731-4553
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Submit a Manuscript
- Advanced search

American Journal of Neuroradiology
Advanced Search
Does Long-term Surveillance Imaging Improve Survival in Patients Treated for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review of the Current Evidence
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- Info & Metrics
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
BACKGROUND: Long-term post-treatment surveillance imaging algorithms for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are not standardized due to debates over optimal surveillance strategy and efficacy. Consequently, current guidelines do not provide long-term surveillance imaging recommendations beyond 6 months.
PURPOSE: We performed a systematic review to evaluate the impact of long-term imaging surveillance (i.e., imaging beyond 6 months following treatment completion) on survival in patients treated definitively for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
DATA SOURCES: A search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, Scopus, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science for English literature published between 2003 and 2024 evaluating the impact of long-term surveillance imaging on survival in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
STUDY SELECTION: 718 abstracts were screened and 9 5 underwent full-text review, with 2 articles meeting inclusion criteria. The Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies of Interventions assessment tool was used.
DATA ANALYSIS: A qualitative assessment without a pooled analysis was performed for the two studies meeting inclusion criteria.
DATA SYNTHESIS: No randomized prospective controlled trials were identified. Two retrospective two-arm studies were included comparing long-term surveillance imaging with clinical surveillance and were each rated as having moderate risk of bias. Each study included heterogeneous populations with variable risk profiles and imaging surveillance protocols. Both studies investigated the impact of long-term surveillance imaging on overall survival and came to a different conclusion with one study reporting a survival benefit for long-term surveillance imaging with FDG PET/CT in patients with stage III or IV disease or an oropharyngeal primary tumor and the other study demonstrating no survival benefit.
LIMITATIONS: Limited heterogeneous retrospective data available precludes definitive conclusions on the impact of long-term surveillance imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
CONCLUSIONS: There is insufficient quality evidence regarding the impact of long-term surveillance imaging on survival in patients treated definitively for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. There is a lack of standardized definition of long-term surveillance, variable surveillance protocols, and inconsistencies in results reporting, underscoring the need for a prospective multi-center registry assessing outcomes.
ABBREVIATIONS: HNSCC = Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma; RT= radiotherapy; NCCN = National Comprehensive Cancer Network; MPC = metachronous primary cancer; CR = complete response; OS = overall survival; CRT = chemoradiotherapy; HPV = human papillomavirus; PFS = progression-free survival; CFU = clinical follow up; NI-RADS = Neck Imaging Reporting and Data System.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the content of this article.
- © 2024 by American Journal of Neuroradiology
Log in using your username and password
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word on American Journal of Neuroradiology.
NOTE: We only request your email address so that the person you are recommending the page to knows that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not junk mail. We do not capture any email address.
Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager

- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Jump to section
Related articles.
- No related articles found.
- Google Scholar
Cited By...
- No citing articles found.
This article has not yet been cited by articles in journals that are participating in Crossref Cited-by Linking.
More in this TOC Section
- Endovascular Thrombectomy for Carotid Pseudo-occlusion in the Setting of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Double stent-retriever technique for mechanical thrombectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Similar Articles
Advertisement
Intrinsic Capacity and Its Biological Basis: A Scoping Review
- Open access
- Published: 10 April 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Melkamu Bedimo Beyene ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4349-9887 1 , 2 ,
- Renuka Visvanathan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1303-9479 2 , 3 &
- Azmeraw T. Amare ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7940-0335 1 , 2 , 4
962 Accesses
5 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) introduced the concept of intrinsic capacity (IC) to define healthy aging based on functional capacity. In this scoping review, we summarized available evidence on the development and validation of IC index scores, the association of IC with health-related factors, and its biological basis. The review specifically focused on identifying current research gaps, proposed strategies to leverage biobank datasets, and opportunities to study the genetic mechanisms and gene-environment interactions underlying IC.
The literature search was conducted across six databases, including PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Scopus, AgeLine, and PsycINFO, using keywords related to IC.
This review included 84 articles, and most of them (n=38) adopted the 5-domains approach to operationalize IC, utilizing correlated five factors or bifactor structures. Intrinsic capacity has consistently shown significant associations with socio-demographic and health-related outcomes, including age, sex, wealth index, nutrition, exercise, smoking, alcohol use, ADL, IADL, frailty, multimorbidity, and mortality. While studies on the biological basis of the composite IC are limited, with only one study finding a significant association with the ApoE gene variants, studies on specific IC domains — locomotor, vitality, cognitive, psychological, and sensory suggest a heritability of 20–85% of IC and several genetic variants associated with these subdomains have been identified. However, evidence on how genetic and environmental factors influence IC is still lacking, with no available study to date.
Our review found that there was inconsistency in the use of standardized IC measurement tools and indicators, but the IC indices had shown good construct and predictive validity. Research into the genetic and gene-to-environment interactions underlying IC is still lacking, which calls for the use of resources from large biobank datasets in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference centiles for intrinsic capacity throughout adulthood and their association with clinical outcomes: a cross-sectional analysis from the INSPIRE-T cohort
Healthy aging meta-analyses and scoping review of risk factors across Latin America reveal large heterogeneity and weak predictive models
Development and validation of an intrinsic capacity composite score in the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam: a formative approach
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
I n 2020, one billion of the world’s population was 60 years or older, with an increase of 400 million expected between 2021 and 2030 ( 1 – 3 ). As this demographic shift continues, exploring innovative mechanisms to promote healthy aging is an important global health and economic policy agenda. Advocacy for improved health across the lifespan to increase the likelihood of older people being functionally able and capable of doing what they value in older age is increasing.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) redefined Healthy Aging in 2015, taking a life-course approach in preparation for the predicted demographic shift globally. It was redefined as the life-long process of developing and maintaining functional ability ( 1 ), determined by intrinsic capacity (IC), the environment, and the interaction between these two factors ( 1 ). Intrinsic capacity refers to the composite of an individual’s physical and mental capacities across the five domains: locomotor, vitality, cognitive, psychological, and sensory ( 4 ). Higher IC levels are associated with decreased disability risk and better overall quality of life ( 5 – 7 ).
In the last two years, four scoping reviews relating to IC have been published ( 8 – 11 ). These reviews have focused on the sensitivity and specificity of WHO’s Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) step 1 tool in detecting loss of IC ( 11 ), demonstrated that IC predicts physical function, frailty, falls and quality of life over time ( 10 ), highlighted that there was a lack of consistency in terms of the domains and metrics used across studies ( 9 ), and queried if IC was as an underlying latent trait of all capacities rather than an aggregate summary measure of the sub-domain capacities ( 8 ). The scoping reviews thus far are yet to address IC’s biological (genetic) underpinnings. Intrinsic capacity is influenced by the person’s underlying genetic as well as the interaction between the person’s genetic make-up and their environment (including lifestyle). Also, research on IC is rapidly increasing, providing a basis for more recent reviews.
Our research group is researching to understand IC genetics better, leveraging existing cohorts where genetic data were collected. Within that context, the primary aim of this scoping review was to explore the existing literature to identify factors (especially genetics) relating to IC and to provide a current overview of knowledge regarding the measurement of IC, along with its predictive and construct validities.
Scoping Review Framework
We used the Joanna Brigs Institute’s (JBI’s) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) and Arksey and O’Malley methodological framework ( 12 – 14 ). The process involved five stages, including defining the purpose, the research question, and the search terms (Stage 1); identifying relevant studies (stage 2); selecting studies that met the predetermined inclusion criteria (stage 3); mapping and charting the data obtained from the selected studies (stage 4); and collating, summarizing, and reporting of the review findings (stage 5).
Stage 1: Defining the research questions and search terms
This initial phase involved refining the scope and direction of the review based on a preliminary search conducted on Google Scholar. Through this step, we had background information on studies and search terms related to IC measurement, IC measures’ validity, health and health-related functional outcomes associated with IC, and its underlying biologic(genetic) basis.
“Generally, the research questions for this review were:
What are the IC measurement tools in literature? What are the approaches to computing composite IC scores and assessing the validity of the scores? This question aims to summarize research findings on IC domains used/found, their indicators, approach to developing composite scores, and the validation of indexes.
What are the different sociodemographic, health, and health-related factors associated with intrinsic capacity?
Does IC have a biological/genetic basis? What are the biomarkers associated with IC?
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The Participant, Concept, Context (PCC) approach was employed to develop the eligibility criteria for study inclusion. The inclusion criteria were; studies conducted on human subjects of all ages (populations), focusing on the measurement of IC, its validation, association with socio-economic and health outcomes (concept), and in any setting – whether the studies were conducted in the community or institutional setting (context), published in the English language and published between 01/01/2015 – 20/10/2023. However, abstracts, conference proceedings, commentary, editorials, reviews, and personal opinions were excluded. No research records were available until WHO experts released the initial article operationalizing IC measurement ( 15 ).
Stage 2: Identifying relevant studies (Search strategy)
The literature search was conducted across Six Databases: PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Scopus, AgeLine, and PsycINFO using the mesh terms and keywords “intrinsic capacity”, “intrinsic capacity decline”, “intrinsic capacity domains”, “intrinsic capacity impairment”, “intrinsic capacity index”, “intrinsic capacity model”, and “intrinsic capacity score” in the context of Aging. Each database’s detailed search string is presented in Supplementary Table 1 (Supplementary Table- 1).
Stage 3: Selection of relevant articles
Identified articles were imported into Clarivate Analytics EndNote 20 after the completion of the search, and duplicates were removed. Following this, two researchers (MB and AT) independently evaluated the titles and abstracts of the articles against the inclusion criteria. The two assessors thoroughly reviewed the full text of the selected articles. Articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded, and the reasons for their exclusion were documented and reported. Disagreements that arose during the selection process were resolved through discussion. The search outcomes and procedure for selecting or excluding studies can be observed in the PRISMA-ScR flowchart (Figure 1 ).
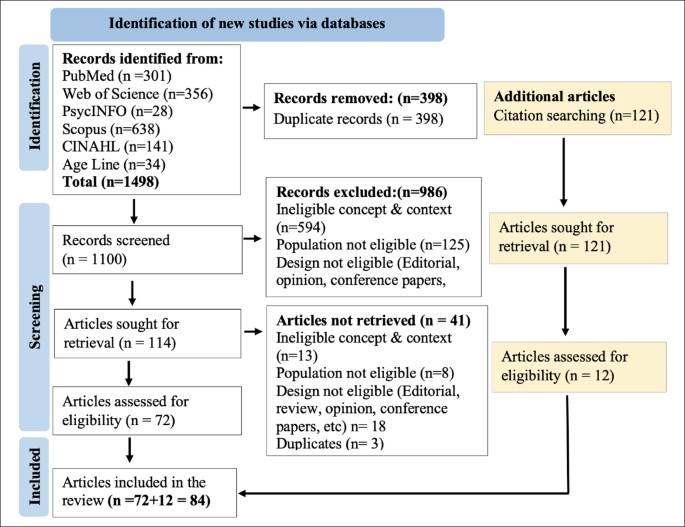
PRISMA flow chart showing the steps of the literature search
Stage 4: Data extraction and synthesis
Using a data extraction tool, MB and AT collected various information from selected articles, including name of authors, publication year, characteristics of study participants, design and setting of the study, domains of IC measured, method used to calculate composite IC scores, validation approaches, and other relevant information. Supplementary Table 2 provides the data extraction form and the summary of information collected from the articles (Supplementary Table 2). The results collected from these selected articles were presented primarily using narrative descriptions and tables.
Descriptive Summary
Our search strategy yielded 1498 articles, of which 398 were identified as duplicates and, thus, removed. After screening titles and abstracts (Figure 1 ), 986 publications were excluded, and full-text screening of 114 articles was conducted, resulting in 72 publications for full-text review. With a targeted citation search strategy, we found 12 additional articles relevant to our topic, and the final list for this scoping review was 84 articles.
Of the total 84 articles reviewed, the majority, 77 articles (92%), were published in the last two years, between 2021 and 2023.
The majority (51 articles, 61%) of the publications were carried out using samples sourced from Asia, of which 33 were from China. The remaining studies utilized study participants distributed across other geographical regions, including 20 (24%) studies in Europe (France (n=9), UK (n=4), Belgium (n=3), Spain (n=2), and Netherlands (n=1), and Norway (n=1)), North America (n=3), South America (n=5), New Zealand (n=1) (Supplementary Table-2). Four articles involving study samples from multiple continents. Out of the 84 reviewed articles, 33 were cross-sectional studies, 43 had a longitudinal approach (involving cohort, case-control, or longitudinal designs), and 8 were randomized control trials (Supplementary Table- 2).
Most (64 studies) have explored the validity of IC measurement in different ways. Some studies assessed the predictive validity ( 16 – 20 ) by assessing if IC predicts future health outcomes, whereas others assessed construct validity through the cross-sectional association of IC with socio-demographic variables ( 21 – 23 ), health and health-related functional outcomes ( 7 , 20 , 24 , 25 ), mortality ( 26 – 29 ), and quality of life ( 7 ).
Some of the studies have inquired into the structural validity of IC ( 30 , 31 ), sensitivity and specificity analyses ( 23 , 32 – 34 ), tested internal consistency using Cronbach alpha ( 20 , 35 ), performed ROC curve analysis ( 19 ), assessed criterion validity through logistic regression analysis ( 28 ), and conducted validation analysis by dividing the population into two as 70% for training and 30% validation cohort ( 26 ). The WHO has also published an expert consensus article on the measurement and validation of IC, providing a comprehensive working definition of vitality capacity ( 36 ).
The association of biological and environmental factors with IC
Biological markers with ic.
Eight studies explored the association of IC with aging-related biomarkers. While specific studies estimating the heritability of IC are currently lacking, evidence based on the five IC domains suggests a heritability estimate of 20–85% ( 37 – 54 ). Thus far, only one candidate gene study has been conducted, and this study showed a significant association of IC with ApoE carriage ( 26 ).
Research conducted by Lu WH, et al. (2023) showed an increased level of inflammatory markers such as Plasma C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (TNFR-1), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) in individuals with lower IC ( 55 ). Another study by Lee WJ, et al. (2023) found that high serum levels of IL-6, CRP, hyperglycemia, and low dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) were associated with low IC ( 26 , 56 ). Lower levels of serum albumin and folate ( 26 ), high homocysteine ( 55 ), Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 level (TNFR1) ( 57 ), Plasma N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide level ( 58 ), or E-selectin ( 26 ) and increased allostatic load ( 26 ) were significantly associated with low IC. Recent studies have also reported associations between IC and plasma biomarkers reflecting inflammation (such as CRP, IL-6, TNFR-1, and MCP-1) and mitochondrial impairment (such as GDF-15, IF1) such that elevated levels of plasma interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (TNFR-1), CRP, growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) and IF1 were associated with lower IC or faster decline in IC ( 59 – 61 ). Details of all factors associated with intrinsic capacity are presented in Table 1 (Table 1 ).
Lifestyle and socio-economic factors with IC
Exercise and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in IC, with studies revealing significant associations. Smoking is linked to lower IC ( 23 , 64 , 68 , 70 – 73 ), as is alcohol consumption ( 23 , 71 ), and reduced meat intake ( 64 ). Interventional and cohort studies, respectively, underscore the positive impact of healthy eating ( 77 ) and fruits and vegetables and protein-rich diets on IC ( 96 ). A multidomain intervention has also been shown to enhance IC ( 102 ).
The exploration of socio-economic factors demonstrates noteworthy associations with IC. Age is inversely correlated, with lower IC found in older age ( 7 , 20 – 23 , 32 , 57 , 62 – 69 ), and women tend to exhibit lower IC (7, 20–23, 62, 63, 66, 67). Lower educational status ( 7 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 32 , 64 , 66 – 68 ), low economic status ( 20 – 22 , 62 , 64 , 65 , 67 , 91 ), unmarried status ( 21 , 23 , 32 , 64 , 68 ), and urban residence are associated with lower IC.; however, being white race was associated with a higher IC ( 23 , 64 ), and higher IC was observed in Chinese individuals compared to non- Chinese in Singapore ( 23 , 97 ).
Social factors also play a role in IC. Lower social engagement, lower subjective social status, fewer social activities, and lower housing index are linked to lower IC ( 7 , 32 , 66 ).
Mortality and morbidity with IC
IC is a significant predictor of various health outcomes. It predicts multimorbidity ( 20 , 65 ), mortality ( 10 , 27 , 28 , 35 , 56 , 65 , 74 , 81 , 93 – 95 ), quality of life ( 5 , 6 , 10 , 76 ), risk of dementia ( 87 ), cardiovascular diseases mortality ( 17 ), respiratory disease mortality ( 16 ), hospitalization ( 27 ), and complications related to hospitalization ( 95 ). Conversely, multimorbidity predicts declines in IC ( 68 ). In addition to predictive relationships, IC index has shown cross-sectional associations with quality of life ( 7 ), medication adherence ( 89 ), sleep health ( 21 ), nursing home-acquired pneumonia ( 90 ), polypharmacy ( 82 ), hypertension status ( 32 ), hospitalization ( 90 ), presence of chronic neurological illness ( 69 ), low self-rated health ( 82 ) and various health conditions, such as insomnia, memory loss, constipation, slowness, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and osteoarthritis ( 64 ).
Functional ability with IC
IC predicted functional difficulty parameters, including the future incidence of ADL ( 20 , 24 , 27 , 35 , 74 – 81 ), IADL (20, 24, 27, 31, 66, 74, 76, 78, 82, 83), Frailty ( 24 , 84 – 88 ), disability/functional decline/dependence ( 6 , 28 , 65 , 75 ), and have shown cross-sectional associations with ADL ( 7 , 23 , 25 , 69 ), frailty ( 7 , 25 , 63 ) and IADL ( 7 , 23 , 25 , 63 ). Moreover, IC was associated with fragility fracture ( 99 ), nursing home stay ( 35 ), life-space mobility ( 30 ), falls ( 24 ), incontinence ( 64 , 82 ), and sarcopenia ( 18 ).
Measurement and validation of IC and its domains
Various approaches have been utilized in the process of constructing IC, each involving a different number and type of domain. Although most studies (n=38; 45%) utilized the five domains methodology ( 6 , 7 , 24 , 26 – 28 , 30 , 31 , 55 – 57 , 62 , 64 , 71 , 74 , 79 , 81 , 84 , 85 , 94 , 96 , 98 , 103 – 107 ), seven studies utilized the bifactor structure (with one general domain (IC) and five sub-domains) ( 20 , 22 , 23 , 35 , 66 , 67 , 86 ). Five of these studies ( 20 , 23 , 35 , 66 , 67 ) comparing the goodness of fit when the bifactor approach was applied instead of the correlated factors and hierarchical model options found that the bifactor structure has better model fit statistics. Eight other studies adopted the six domains construct by dividing the sensory domain into two components, namely hearing and vision ( 21 , 33 , 75 , 83 , 87 , 89 , 91 , 108 ), whereas eleven studies considered only four domains by excluding the sensory domain ( 34 , 59 – 61 , 70 , 73 , 77 , 88 , 90 , 93 , 102 ) and another two studies used four domains excluding the cognition domain ( 16 , 17 ). Three studies utilized other methods, including seven domains ( 65 ), eight domains ( 78 ), and no domain but summing up indicators directly ( 5 ).
Studies comparing the traditional (correlated factors) method, the bifactor method, and the hierarchical method consistently demonstrate that the bifactor model provides a superior fit compared to both the hierarchical model and the correlated factors models ( 20 , 23 , 35 , 66 , 67 ). In measuring IC, various methods have been used, ranging from simple approaches involving a single variable to complex composite assessments. Details of all methods used to operationalize each domain under the reviewed articles are shown in Table 2 (Table 2 ).
Computation of IC scores
Sixty-seven articles have created IC composite scores. Standard methods for constructing IC composite scores involve using factor analysis or principal component analysis ( 7 , 25 , 73 ), in line with original research relating to IC ( 20 ). Out of the nine studies utilizing factor analysis methods, two employed the traditional correlated five-factors approach ( 30 , 98 ), while the remaining seven utilized the bifactor method, incorporating five specific factors and one general factor ( 20 , 22 , 23 , 35 , 66 , 67 , 86 ).
However, the majority 32 (47.8%) papers calculated the IC score by summing individual IC domains scores without weighting, using either a two-point scale (0-impaired/bad and 1-unimpaired/good) or a three-point scale (0-impaired, 1-slightly impaired, or 2-unimpaired) ( 18 , 19 , 21 , 24 , 32 , 33 , 55 – 58 , 61 – 64 , 68 , 69 , 71 , 74 , 75 , 80 , 82 – 85 , 94 , 95 , 97 , 100 , 106 , 109 , 113 , 114 ). Other ways employed to compute IC were averaging the z-scores of the domains ( 70 , 72 , 81 , 90 , 93 , 96 , 102 ), direct summation of the values of indicators ( 5 , 16 , 17 , 88 , 101 , 115 ), the latent growth modeling (LGM) method ( 31 ), weighted linear combination of indicators with loading greater than 0.3 ( 78 ), direct summation of indicators associated with domains in the regression model ( 26 , 65 , 79 ), averaging the domains’ average values ( 28 , 59 , 60 ), and a 2-parameter domains item response theory (IRT) which refers to direct categorization of IC as “0” for impairment in any domain and “1” for no impairment in any of the domains ( 6 , 27 ).
Some eight years since the WHO redefined Healthy Aging, there has been an exponential growth in research relating to IC, with almost all publications in the last 2 years and the majority (61%) leveraging data from Asia. Whilst studies have explored the association and predictive ability of IC with inflammatory, lifestyle, health, and socio-economic factors, research relating to genes and IC is rare. Many methods have been used to assess and score IC, making it vital that a consensus is reached globally.
While specific studies estimating the heritability of IC are currently lacking, evidence based on the five IC domains suggests a heritability range of 20–85%; specifically, genetic factors contribute to the variability in cognitive 50–70% ( 37 – 39 ), sensory 20–30% ( 40 – 43 ), locomotor 30–85% ( 44 – 47 ), vitality 25– 65% ( 48 – 50 ) and psychological 35–70% ( 51 – 54 ) domains. There has been one attempt, through a candidate gene study approach, to identify genes associated with the broader IC domain. This particular study showed a significant association of IC with ApoE carriage ( 26 ). Understanding the interaction between genes and environment (including lifestyle factors) and IC is important. Before this, it is essential to identify genetic markers associated with IC. Such research may confirm the benefits of lifestyle or behavioral changes in helping people age well, including allowing the personalization of this intervention to the individual.
As outlined in the results section, our scoping review introduces new elements beyond those explored in the initial review addressing adverse health outcomes associated with IC. In addition to investigating biological and inflammatory biomarkers which are new, this review also identifies additional factors previously unexplored, which are related to socioeconomic (such as educational status, economic standing, marital status, ethnicity, residence, housing index, and social engagement); functional ability (such as fragility fracture, life-space mobility, nursing home stay, incontinence, and sarcopenia are also assessed); morbidity and mortality (such as multimorbidity, medication adherence, polypharmacy, hospitalization and its associated complications, sleep health, cardiovascular diseases mortality, and respiratory diseases mortality which were not addressed in the previous review) and behavioral and lifestyle-related factors (such as exercise, alcohol consumption, smoking, eating habits, and dietary patterns).
In the context of developing IC indices, no consistent method has been used thus far. New indicators for IC domains continue to be used, often without goodness of fit testing. Goodness of fit tests must be done while new indicators are used to determine whether those indicators are appropriate ( 118 ). Similarly, some studies used quick and direct tools, and others employed more complex and time-consuming composite measures. Balancing the precision of variable measurement with tool simplicity is crucial, and in the realm of measurement science, it is recommended to utilize straightforward yet robust instruments to assess variables like IC ( 119 , 120 ). Studies also reveal that the bifactor method correlates with the five factors method and performs better than the correlated factors and hierarchical methods ( 20 , 23 , 35 , 66 , 67 ). There is also evidence of better explanatory power of the bifactor model when compared to the other two methods ( 121 – 123 ). Whilst evidence supports that the bifactor method results have better conceptual clarity and fit than the other structures, the lack of standardization may introduce bias (128).
Furthermore, there needs to be an effort to reach a consensus in defining indicators for individual domains. Consensus about the indicators and methods is necessary to inform the planning of future cohort studies. Planned cohort studies, as opposed to leveraging already collected data, may have the advantage of enabling the collection of appropriate indicators to measure IC. Two primary approaches are being applied to compute the IC composite score: the CFA ( 20 , 22 , 23 , 30 , 66 , 67 , 86 , 96 ) and the arithmetic sum/average of the values of the domains ( 19 , 24 , 32 , 55 – 58 , 62 – 64 , 71 , 74 , 75 , 82 , 84 , 85 , 94 , 106 , 114 ). Both have demonstrated good construct and predictive validity. Concerning the approaches for measurement, the reflective versus formative nature of the IC measurement (i.e. whether IC should be considered as an underlying latent trait of all capacities or an aggregate summary measure of the subdomain capacities) shall also be considered in future studies ( 124 ).
Limitations and Strengths
The major strength of this review is that we followed a rigorous and stepwise screening process with the involvement of independent assessors. The findings were reported following the JBI’s PRISMA guideline extension for scoping review (PRISMA-ScR). The scope of the literature search was limited to peer-reviewed articles, and as a result, unpublished studies and organizational reports were not included. Due to logistic limitations, only articles published in the English language were reviewed, although studies published in other languages may have provided information on the external validity of IC tools in a multicultural setting.
Conclusion and recommendations
Since the introduction of IC for defining healthy aging and functional capacity, extensive research has been conducted to measure these indices and validate them, as well as to assess their relevance in medical, social, and behavioral sciences. This review identifies that there is a knowledge gap (no evidence) when it comes to our understanding of the genetics of IC. Such understanding can be improved by leveraging existing longitudinal studies but there is also a need for planned cohort studies where IC measurements are collected prospectively, and genetic data is also available. This review highlights the current difficulties in comparing existing studies given the lack of standardization in defining indicators that ought to be collected for each IC domain and how best to assess and score IC. Reaching such consensus is imperative because it will not only define the approach for the use of already collected data but will also support the planning and conduct of new longitudinal studies focused on IC and functional ability. The pooling of data globally to advance our understanding collectively would also be more likely through a standardized approach.
WHO. Decade of Healthy Ageing: Baseline Report. WHO; 2020.
WHO: Ageing and health. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (2022). Accessed 10/04 2023.
Nations U. Leaving No One Behind In An Ageing World. World Social Report 2023
Organization WH. World report on ageing and health. World Health Organization; 2015.
Stephens C, Allen J, Keating N, Szabó Á, Alpass F. Neighborhood environments and intrinsic capacity interact to affect the health-related quality of life of older people in New Zealand. Maturitas. 2020;139:1–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.05.008 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Salinas-Rodríguez A, González-Bautista E, Rivera-Almaraz A, Manrique-Espinoza B. Longitudinal trajectories of intrinsic capacity and their association with quality of life and disability. Maturitas. 2022;161:49–54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2022.02.005 .
Cheong CY, Yap P, Nyunt MSZ, Qi G, Gwee X, Wee SL, et al. Functional health index of intrinsic capacity: multi-domain operationalisation and validation in the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Study (SLAS2). Age & Ageing. 2022;51(3):1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afac011 .
Article Google Scholar
Koivunen K, Schaap LA, Hoogendijk EO, Schoonmade LJ, Huisman M, van Schoor NM. Exploring the conceptual framework and measurement model of intrinsic capacity defined by the World Health Organization: A scoping review. AGEING RESEARCH REVIEWS. 2022;80. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2022.101685 .
Liang Y, Shang S, Gao Y, Zhai J, Cheng X, Yang C, et al. Measurements of Intrinsic Capacity in Older Adults: A Scoping Review and Quality Assessment. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2023;24(3):267-. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2022.09.011 .
Zhou J, Chang H, Leng M, Wang Z. Intrinsic Capacity to Predict Future Adverse Health Outcomes in Older Adults: A Scoping Review. Healthcare (2227-9032). 2023;11(4):450. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11040450 .
de Oliveira VP, Ferriolli E, Lourenço RA, González-Bautista E, Barreto PD, de Mello RGB. The sensitivity and specificity of the WHO’s ICOPE screening tool, and the prevalence of loss of intrinsic capacity in older adults: A scoping review. MATURITAS. 2023;177. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2023.107818 .
Aromataris E MZE: JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. https://synthesismanual.jbi.global/ Accessed 23/11 2022.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Annals of internal medicine. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International journal of social research methodology. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Cesari M, Araujo de Carvalho I, Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan J, Cooper C, Martin FC, Reginster JY, et al. Evidence for the Domains Supporting the Construct of Intrinsic Capacity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018;73(12):1653–60.
Ramírez-Vélez R, Iriarte-Fernandez M, Santafé G, Malanda A, Beard JR, Garcia-Hermoso A, et al. Association of intrinsic capacity with respiratory disease mortality. Respiratory Medicine. 2023;212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2023.107243 .
Ramírez-Vélez R, Iriarte-Fernández M, Santafé G, Malanda A, Beard JR, Garcia-Hermoso A, et al. Association of intrinsic capacity with incidence and mortality of cardiovascular disease: Prospective study in UK Biobank. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle. 2023;14(5):2054–63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13283 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhu L, Zong X, Shi X, Ouyang X. Association between Intrinsic Capacity and Sarcopenia in Hospitalized Older Patients. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2023;27(7):542–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1946-5 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lu F, Liu S, Liu X, Li J, Jiang S, Sun X, et al. Comparison of the predictive value of intrinsic capacity and comorbidity on adverse health outcome in community-dwelling older adults. Geriatric Nursing. 2023;50:222–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.02.001 .
Beard JR, Jotheeswaran AT, Cesari M, Araujo De Carvalho I. The structure and predictive value of intrinsic capacity in a longitudinal study of ageing. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11). doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026119 .
Chang YH, Chen YC, Ku LE, Chou YT, Chen HY, Su HC, et al. Association between sleep health and intrinsic capacity among older adults in Taiwan. Sleep Med. 2023;109:98–103. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2023.06.016 .
Yu R, Lai D, Leung G, Woo J. Trajectories of Intrinsic Capacity: Determinants and Associations with Disability. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2023;27(3):174–81. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1881-5 .
Aliberti Márlon JR, Bertola L, Szlejf C, Oliveira Db, Piovezan Ronaldo D, Cesari M, et al. Validating intrinsic capacity to measure healthy aging in an upper middle-income country: Findings from the ELSI-Brazil. The Lancet Regional Health - Americas. 2022;12:100284.
Tay L, Tay EL, Mah SM, Latib A, Koh C, Ng YS. Association of Intrinsic Capacity with Frailty, Physical Fitness and Adverse Health Outcomes in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. JOURNAL OF FRAILTY & AGING. 2023;12(1):7–15. doi: https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2022.28 .
CAS Google Scholar
Gutiérrez-Robledo LM, García-Chanes RE, González-Bautista E, Rosas-Carrasco O. Validation of Two Intrinsic Capacity Scales and Its Relationship with Frailty and Other Outcomes in Mexican Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2021;25(1):33–40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1555-5 .
Meng LC, Huang ST, Peng LN, Chen LK, Hsiao FY. Biological Features of the Outcome-Based Intrinsic Capacity Composite Scores From a Population-Based Cohort Study: Pas de Deux of Biological and Functional Aging. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:851882.
Campbell CL, Cadar D, McMunn A, Zaninotto P. Operationalization of Intrinsic Capacity in Older People and Its Association With Subsequent Disability, Hospital Admission and Mortality: Results From The English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences. 2023;78(4):698–703. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glac250 .
Koivunen K, Hoogendijk Emiel O, Schaap Laura A, Huisman M, Heymans Martijn W, van Schoor Natasja M. Development and validation of an intrinsic capacity composite score in the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam: a formative approach. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research. 2023.
Charles A, Buckinx F, Locquet M, Reginster J-Y, Petermans J, Gruslin B, et al. Prediction of Adverse Outcomes in Nursing Home Residents According to Intrinsic Capacity Proposed by the World Health Organization. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences. 2020;75(8):1594–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glz218 .
Lee JQ, Ding YY, Latib A, Tay L, Ng YS. INtrinsic Capacity and its RElAtionship With Life-SpacE Mobility (INCREASE): a cross-sectional study of community-dwelling older adults in Singapore. BMJ OPEN. 2021;11(12). doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054705 .
Lu SY, Liu YQ, Guo YQ, Ho HC, Song YM, Cheng W, et al. Neighbourhood physical environment, intrinsic capacity, and 4-year late-life functional ability trajectories of low-income Chinese older population: A longitudinal study with the parallel process of latent growth curve modelling. ECLINICALMEDICINE. 2021;36. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100927 .
Leung AYM, Su JJ, Lee ESH, Fung JTS, Molassiotis A. Intrinsic capacity of older people in the community using WHO Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) framework: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatrics. 2022;22(1):1–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-02980-1 .
Lu F, Li J, Liu X, Liu S, Sun X, Wang X. Diagnostic performance analysis of the Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) screening tool for identifying decline in intrinsic capacity. BMC Geriatr. 2023;23(1):509. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04180-x .
Sanchez-Rodriguez D, Demonceau C, Bruyère O, Cavalier E, Reginster JY, Beaudart C. Intrinsic capacity and risk of death: Focus on the impact of using different diagnostic criteria for the nutritional domain. MATURITAS. 2023;176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2023.107817 .
Stolz E, Mayerl H, Freidl W, Roller-Wirnsberger R, Gill TM. Intrinsic Capacity Predicts Negative Health Outcomes in Older Adults. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences. 2022;77(1):101–5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glab279 .
Bautmans I, Knoop V, Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan J, Maier AB, Beard JR, Freiberger E, et al. WHO working definition of vitality capacity for healthy longevity monitoring. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022;3(11):e789–e96.
Tucker-Drob EM, Briley DA, Harden KP. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Cognition Across Development and Context. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2013;22(5):349–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721413485087 .
Reynolds CA, Finkel D. A Meta-analysis of Heritability of Cognitive Aging: Minding the “Missing Heritability” Gap. Neuropsychology Review. 2015;25(1):97–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-015-9280-2 .
McGue M, Christensen K. The heritability of cognitive functioning in very old adults: evidence from Danish twins aged 75 years and older. Psychology and aging. 2001;16(2):272–80. doi: https://doi.org/10.1037//0882-7974.16.2.272 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Vuckovic D, Dawson S, Scheffer DI, Rantanen T, Morgan A, Di Stazio M, et al. Genome-wide association analysis on normal hearing function identifies PCDH20 and SLC28A3 as candidates for hearing function and loss. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(19):5655–64. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv279 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kvestad E, Czajkowski N, Krog NH, Engdahl B, Tambs K. Heritability of hearing loss. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass). 2012;23(2):328–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e318245996e .
Hogg RE, Dimitrov PN, Dirani M, Varsamidis M, Chamberlain MD, Baird PN, et al. Gene–Environment Interactions and Aging Visual Function: A Classical Twin Study. Ophthalmology. 2009;116(2):263–9.e1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.09.002 .
Hammond CJ, Duncan DD, Snieder H, de Lange M, West SK, Spector TD, et al. The heritability of age-related cortical cataract: the twin eye study. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 2001;42(3):601–5.
Roth SM. Genetic aspects of skeletal muscle strength and mass with relevance to sarcopenia. Bonekey Rep. 2012;1:58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/bonekey.2012.58 .
Zempo H, Miyamoto-Mikami E, Kikuchi N, Fuku N, Miyachi M, Murakami H. Heritability estimates of muscle strength-related phenotypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports. 2017;27(12):1537–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12804 .
Peter I, Papandonatos GD, Belalcazar LM, Yang Y, Erar B, Jakicic JM, et al. Genetic modifiers of cardiorespiratory fitness response to lifestyle intervention. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(2):302–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182a66155 .
Willems SM, Wright DJ, Day FR, Trajanoska K, Joshi PK, Morris JA, et al. Large-scale GWAS identifies multiple loci for hand grip strength providing biological insights into muscular fitness. Nature Communications. 2017;8(1):16015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms16015 .
Hanscombe KB, Persyn E, Traylor M, Glanville KP, Hamer M, Coleman JRI, et al. The genetic case for cardiorespiratory fitness as a clinical vital sign and the routine prescription of physical activity in healthcare. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):180. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-021-00994-9 .
Doris PA. The genetics of blood pressure and hypertension: the role of rare variation. Cardiovasc Ther. 2011;29(1):37–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00246.x .
Robinson MR, English G, Moser G, Lloyd-Jones LR, Triplett MA, Zhu Z, et al. Genotype–covariate interaction effects and the heritability of adult body mass index. Nature Genetics. 2017;49(8):1174–81. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3912 .
Polderman TJ, Benyamin B, de Leeuw CA, Sullivan PF, van Bochoven A, Visscher PM, et al. Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies. Nat Genet. 2015;47(7):702–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3285 .
Amare AT, Vaez A, Hsu Y-H, Direk N, Kamali Z, Howard DM, et al. Bivariate genome-wide association analyses of the broad depression phenotype combined with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder or schizophrenia reveal eight novel genetic loci for depression. Molecular Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1420–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0336-6 .
Mullins N, Forstner AJ, O’Connell KS, Coombes B, Coleman JRI, Qiao Z, et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nature Genetics. 2021;53(6):817–29. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00857-4 .
Cardno AG, Marshall EJ, Coid B, Macdonald AM, Ribchester TR, Davies NJ, et al. Heritability estimates for psychotic disorders: the Maudsley twin psychosis series. Archives of general psychiatry. 1999;56(2):162–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.56.2.162 .
Lin S, Wang F, Zheng J, Yuan Y, Huang F, Zhu P. Intrinsic Capacity Declines with Elevated Homocysteine in Community-Dwelling Chinese Older Adults. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2022;17:1057–68. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S370930 .
Lee WJ, Peng LN, Lin MH, Loh CH, Hsiao FY, Chen LK. Intrinsic capacity differs from functional ability in predicting 10-year mortality and biological features in healthy aging: results from the I-Lan longitudinal aging study. AGING-US. 2023;15(3):748–64.
Ma L, Liu P, Zhang Y, Sha G, Zhang L, Li Y. High Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 Levels Are Related to Risk of Low Intrinsic Capacity in Elderly Adults. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2021;25(4):416–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1533-y .
Ma L, Zhang Y, Liu P, Li S, Li Y, Ji T, et al. Plasma N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide is Associated with Intrinsic Capacity Decline in an Older Population. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2021;25(2):271–7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1468-3 .
Lu WH, Guyonnet S, Martinez LO, Lucas A, Parini A, Vellas B, et al. Association between aging-related biomarkers and longitudinal trajectories of intrinsic capacity in older adults. GEROSCIENCE. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-023-00906-2 .
Lu WH, Gonzalez-Bautista E, Guyonnet S, Lucas A, Parini A, Walston JD, et al. Plasma inflammation-related biomarkers are associated with intrinsic capacity in community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle. 2023;14(2):930–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13163 .
da Silva JA, Martinez LO, Rolland Y, Najib S, Croyal M, Perret B, et al. Plasma Level of ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1 and Intrinsic Capacity in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Prospective Data From the MAPT Study. JOURNALS OF GERONTOLOGY SERIES A-BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES AND MEDICAL SCIENCES. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glad142 .
Gutiérrez-Robledo LM, García-Chanes RE, Pérez-Zepeda MU. Allostatic Load as a Biological Substrate to Intrinsic Capacity: A Secondary Analysis of CRELES. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2019;23(9):788–95. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1251-5 .
Ma L, Chhetri JK, Zhang Y, Liu P, Chen Y, Li Y, et al. Integrated Care for Older People Screening Tool for Measuring Intrinsic Capacity: Preliminary Findings From ICOPE Pilot in China. Frontiers in Medicine. 2020;7. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.576079 .
Ma L, Chhetri JK, Zhang L, Sun F, Li Y, Tang Z. Cross-sectional study examining the status of intrinsic capacity decline in community-dwelling older adults in China: prevalence, associated factors and implications for clinical care. BMJ Open. 2021;11(1):e043062.
Prince MJ, Acosta D, Guerra M, Huang Y, Jacob KS, Jimenez-Velazquez IZ, et al. Intrinsic capacity and its associations with incident dependence and mortality in 10/66 Dementia Research Group studies in Latin America, India, and China: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2021;18(9):e1003097.
Yu R, Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan J, Leung J, Lu Z, Kwok T, Woo J. Validation of the Construct of Intrinsic Capacity in a Longitudinal Chinese Cohort. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(6):808–15.
Beard JR, Si Y, Liu Z, Chenoweth L, Hanewald K. Intrinsic Capacity: Validation of a New WHO Concept for Healthy Aging in a Longitudinal Chinese Study. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences. 2022;77(1):94–100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glab226 .
Jiang X, Chen F, Yang X, Yang M, Zhang X, Ma X, et al. Effects of personal and health characteristics on the intrinsic capacity of older adults in the community: a cross-sectional study using the healthy aging framework. BMC Geriatrics. 2023;23(1):1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04362-7 .
Rarajam Rao A, Waris M, Saini M, Thakral M, Hegde K, Bhagwasia M, et al. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Impairment in Intrinsic Capacity among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: An Observational Study from South India. Current Gerontology & Geratrics Research. 2023;2023:1–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/4386415 .
Huang CH, Umegaki H, Makino T, Uemura K, Hayashi T, Kitada T, et al. Effect of Various Exercises on Intrinsic Capacity in Older Adults With Subjective Cognitive Concerns. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2021;22(4):780-. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.06.048 .
Muneera K, Muhammad T, Althaf S. Socio-demographic and lifestyle factors associated with intrinsic capacity among older adults: evidence from India. BMC Geriatrics. 2022;22(1):1–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-03558-7 .
Zhou M, Kuang L, Hu N. The Association between Physical Activity and Intrinsic Capacity in Chinese Older Adults and Its Connection to Primary Care: China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023;20(7). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20075361 .
Yu R, Lai D, Leung G, Tam LY, Cheng C, Kong S, et al. Moving towards the ICOPE Approach: Evaluation of Community-Based Intervention Activities on Improving Intrinsic Capacity. JOURNAL OF NUTRITION HEALTH & AGING. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-2003-0 .
Zeng X, Shen S, Xu L, Wang Y, Yang Y, Chen L, et al. The Impact of Intrinsic Capacity on Adverse Outcomes in Older Hospitalized Patients: A One-Year Follow-Up Study. Gerontology. 2021;67(3):267–75. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000512794 .
Chen JJ, Liu LF, Chang SM. Approaching person-centered long-term care: The trajectories of intrinsic capacity and functional decline in Taiwan. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2022;22(7):516–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.14391 .
Yu J, Si H, Jin Y, Qiao X, Ji L, Bian Y, et al. Patterns of intrinsic capacity among community-dwelling older adults: Identification by latent class analysis and association with one-year adverse outcomes. Geriatric Nursing. 2022;45:223–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2022.04.021 .
Lim K-Y, Lo H-C, Cheong I-F, Wang Y-Y, Jian Z-R, Chen IC, et al. Healthy Eating Enhances Intrinsic Capacity, Thus Promoting Functional Ability of Retirement Home Residents in Northern Taiwan. Nutrients. 2022;14(11):2225-. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112225 .
Waris M, Upadhyay AD, Chatterjee P, Chakrawarty A, Kumar P, Dey AB. Establishment of Clinical Construct of Intrinsic Capacity in Older Adults and Its Prediction of Functional Decline. Clin Interv Aging. 2022;17:1569–80.
Zhao J, Chhetri Jagadish K, Chang Y, Zheng Z, Ma L, Chan P. Intrinsic Capacity vs. Multimorbidity: A Function-Centered Construct Predicts Disability Better Than a Disease-Based Approach in a Community-Dwelling Older Population Cohort. Frontiers in Medicine. 2021;8.
Jiang YS, Shi H, Kang YT, Shen J, Li J, Cui J, et al. Impact of age-friendly living environment and intrinsic capacity on functional ability in older adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC GERIATRICS. 2023;23(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04089-5 .
Sánchez-Sánchez JL, Rolland Y, Cesari M, de Souto Barreto P. Associations Between Intrinsic Capacity and Adverse Events Among Nursing Home Residents: The INCUR Study. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2022;23(5):872-. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2021.08.035 .
Yu R, Leung G, Leung J, Cheng C, Kong S, Tam LY, et al. Prevalence and Distribution of Intrinsic Capacity and Its Associations with Health Outcomes in Older People: The Jockey Club Community eHealth Care Project in Hong Kong. J Frailty Aging. 2022;11(3):302–8.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Yu J, Jin Y, Si H, Bian Y, Liu Q, Qiao X, et al. How does social support interact with intrinsic capacity to affect the trajectory of functional ability among older adults? Findings of a population-based longitudinal study. Maturitas. 2023;171:33–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2023.03.005 .
Liu S, Kang L, Liu X, Zhao S, Wang X, Li J, et al. Trajectory and Correlation of Intrinsic Capacity and Frailty in a Beijing Elderly Community. Frontiers in Medicine. 2021;8.
Tay L, Tay EL, Mah SM, Latib A, Ng YS. Intrinsic capacity rather than intervention exposure influences reversal to robustness among prefrail community-dwelling older adults: A non-randomized controlled study of a multidomain exercise and nutrition intervention. FRONTIERS IN MEDICINE. 2022;9. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.971497 .
Yu R, Leung J, Leung G, Woo J. Towards Healthy Ageing: Using the Concept of Intrinsic Capacity in Frailty Prevention. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2022;26(1):30–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-021-1715-2 .
Gonzalez-Bautista E, Llibre-Guerra JJ, Sosa AL, Acosta I, Andrieu S, Acosta D, et al. Exploring the natural history of intrinsic capacity impairments: longitudinal patterns in the 10/66 study. Age and Ageing. 2023;52(7):1–9.
Chew J, Lim JP, Yew S, Yeo A, Ismail NH, Ding YY, et al. Disentangling the Relationship between Frailty and Intrinsic Capacity in Healthy Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cluster Analysis. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2021;25(9):1112–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-021-1679-2 .
Meng LC, Hsiao FY, Huang ST, Lu WH, Peng L-N, Chen LK. Intrinsic Capacity Impairment Patterns and their Associations with Unfavorable Medication Utilization: A Nationwide Population-Based Study of 37,993 Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2022;26(10):918–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-022-1847-z .
Sanchez-Sánchez JL, Rolland Y, Cesari M, de Souto Barreto P. Impact of nursing home-acquired pneumonia on the domains of the novel construct of intrinsic capacity: The INCUR study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2022;70(12):3436–46.
Pages A, Costa N, Gonzalez-Bautista E, Mouni M, Juillard-Condat B, Molinier L, et al. Screening for deficits on intrinsic capacity domains and associated healthcare costs. ARCHIVES OF GERONTOLOGY AND GERIATRICS. 2022;100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2022.104654 .
Liao X, Shen J, Li M. Effects of multi-domain intervention on intrinsic capacity in older adults: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Experimental Gerontology. 2023;174. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2023.112112 .
Locquet M, Sanchez-Rodriguez D, Bruyère O, Geerinck A, Lengelé L, Reginster JY, et al. Intrinsic Capacity Defined Using Four Domains and Mortality Risk: A 5-Year Follow-Up of the SarcoPhAge Cohort. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2022;26(1):23–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-021-1702-7 .
Yu R, Lai ETC, Leung G, Ho SC, Woo J. Intrinsic capacity and 10-year mortality: Findings from a cohort of older people. EXPERIMENTAL GERONTOLOGY. 2022;167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2022.111926 .
Nagae M, Umegaki H, Komiya H, Nakashima H, Fujisawa C, Watanabe K, et al. Intrinsic capacity in acutely hospitalized older adults. Experimental Gerontology. 2023;179. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2023.112247 .
Huang CH, Okada K, Matsushita E, Uno C, Satake S, Martins BA, et al. Dietary patterns and intrinsic capacity among community-dwelling older adults: a 3-year prospective cohort study. European Journal of Nutrition. 2021;60(6):3303–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02505-3 .
Plácido J, Marinho V, Ferreira JV, Teixeira IA, Costa EC, Deslandes AC. Association among race/color, gender, and intrinsic capacity: results from the ELSI-Brazil study. Revista de Saude Publica. 2023;57(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.11606/S1518-8787.2023057004548 .
Yeung SSY, Sin D, Yu R, Leung J, Woo J. Dietary Patterns and Intrinsic Capacity in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging. 2022;26(2):174–82. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-022-1742-7 .
Astrone P, Perracini MR, Martin FC, Marsh DR, Cesari M. The potential of assessment based on the WHO framework of intrinsic capacity in fragility fracture prevention. Aging Clinical & Experimental Research. 2022;34(11):2635–43. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-022-02186-w .
Lin S, Huang M, Yang L, Chen S, Huang X, Zheng J, et al. Dietary diversity and overweight are associated with high intrinsic capacity among Chinese urban older adults (2020-2021). Experimental Gerontology. 2023;177. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2023.112194 .
Su H, Xu L, Yu H, Zhou Y, Li Y. Social isolation and intrinsic capacity among left-behind older adults in rural China: The chain mediating effect of perceived stress and health-promoting behavior. Frontiers in Public Health. 2023;11. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1155999 .
Giudici KV, Barreto PD, Beard J, Cantet C, de Carvalho IA, Rolland Y, et al. Effect of long-term omega-3 supplementation and a lifestyle multidomain intervention on intrinsic capacity among community-dwelling older adults: Secondary analysis of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (MAPT study). MATURITAS. 2020;141:39–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.06.012 .
Ramirez-Velez R, Correa-Bautista JE, Garcia-Hermoso A, Cano CA, Izquierdo M. Reference values for handgrip strength and their association with intrinsic capacity domains among older adults. JOURNAL OF CACHEXIA SARCOPENIA AND MUSCLE. 2019;10(2):278–86. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12373 .
Arokiasamy P, Selvamani Y, Jotheeswaran AT, Sadana R. Socioeconomic differences in handgrip strength and its association with measures of intrinsic capacity among older adults in six middle-income countries. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):19494.
Nascimento LMD, Cruz TGCD, Silva JFDLE, Silva LP, Inácio BB, Sadamitsu CMO, et al. Use of Intrinsic Capacity Domains as a Screening Tool in Public Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023;20(5). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054227 .
Jia S, Zhao W, Ge M, Xia X, Hu F, Hao Q, et al. Associations between transitions of intrinsic capacity and frailty status, and 3-year disability. BMC Geriatrics. 2023;23(1):1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-03795-4 .
Luque XRI, Blancafort-Alias S, Casanovas SP, Forne S, Vergara NM, Povill PF, et al. Identification of decreased intrinsic capacity: Performance of diagnostic measures of the ICOPE Screening tool in community dwelling older people in the VIMCI study. BMC GERIATRICS. 2023;23(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-03799-0 .
Mathur A, Bhardwaj P, Joshi NK, Jain YK, Singh K. Intrinsic Capacity of Rural Elderly in Thar Desert using World Health Organization Integrated Care for Older Persons Screening Tool: A Pilot Study. Indian Journal of Public Health. 2022;66(3):337–40. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijph.ijph_731_22 .
Muneera K, Muhammad T, Pai M, Ahmed W, Althaf S. Associations between intrinsic capacity, functional difficulty, and fall outcomes among older adults in India. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-37097-x .
Yu J, Si H, Qiao X, Jin Y, Ji L, Liu Q, et al. Predictive value of intrinsic capacity on adverse outcomes among community-dwelling older adults. Geriatric Nursing. 2021;42(6):1257–63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2021.08.010 .
Langballe EM, Skirbekk V, Strand BH. Subjective age and the association with intrinsic capacity, functional ability, and health among older adults in Norway. European Journal of Ageing. 2023;20(1):1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10433-023-00753-2 .
Google Scholar
Hu XH, Ruan J, Zhang WB, Chen J, Bao ZJ, Ruan QW, et al. The overall and domain-specific quality of life of Chinese community-dwelling older adults: the role of intrinsic capacity and disease burden. FRONTIERS IN PSYCHOLOGY. 2023;14. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1190800 .
Zhang N, Zhang H, Sun M-Z, Zhu Y-S, Shi G-P, Wang Z-D, et al. Intrinsic capacity and 5-year late-life functional ability trajectories of Chinese older population using ICOPE tool: the Rugao Longevity and Ageing Study. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research. 2023;35(10):2061–8.
Gonzalez-Bautista E, de Souto Barreto P, Andrieu S, Rolland Y, Vellas B. Screening for intrinsic capacity impairments as markers of increased risk of frailty and disability in the context of integrated care for older people: Secondary analysis of MAPT. Maturitas. 2021;150:1–6.
Liu S, Yu X, Wang X, Li J, Jiang S, Kang L, et al. Intrinsic Capacity predicts adverse outcomes using Integrated Care for Older People screening tool in a senior community in Beijing. Archives of Gerontology & Geriatrics. 2021;94:N.PAG–N.PAG. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2021.104358 .
Gonzalez-Bautista E, de Souto Barreto P, Virecoulon Giudici K, Andrieu S, Rolland Y, Vellas B. Frequency of Conditions Associated with Declines in Intrinsic Capacity According to a Screening Tool in the Context of Integrated Care for Older People. J Frailty Aging. 2021;10(2):94–102.
Rodríguez-Laso A, García-García FJ, Rodríguez-Mañas L. The ICOPE Intrinsic Capacity Screening Tool: Measurement Structure and Predictive Validity of Dependence and Hospitalization. JOURNAL OF NUTRITION HEALTH & AGING. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1985 .
Schermelleh-Engel K, Moosbrugger H, Müller H. Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods of psychological research online. 2003;8(2):23–74.
Thorndike RM. Book review: psychometric theory by Jum Nunnally and Ira Bernstein New York: McGraw-hill, 1994, xxiv+ 752 pp. Applied psychological measurement. 1995;19(3):303–5.
DeVellis RF, Thorpe CT. Scale development: Theory and applications. Sage publications; 2021.
Markon KE. Bifactor and hierarchical models: Specification, inference, and interpretation. Annual review of clinical psychology. 2019;15:51–69.
Chen FF, Hayes A, Carver CS, Laurenceau JP, Zhang Z. Modeling general and specific variance in multifaceted constructs: A comparison of the bifactor model to other approaches. Journal of personality. 2012;80(1):219–51.
Zhang B, Sun T, Cao M, Drasgow F. Using bifactor models to examine the predictive validity of hierarchical constructs: Pros, cons, and solutions. Organizational Research Methods. 2021;24(3):530–71.
Koivunen K, Schaap LA, Hoogendijk EO, Schoonmade LJ, Huisman M, van Schoor NM. Exploring the conceptual framework and measurement model of intrinsic capacity defined by the World Health Organization: A scoping review. Ageing Research Reviews. 2022;80:101685. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2022.101685 .
Download references
Acknowledgments
MB Beyene is Ph.D. student with scholarship support from University of Adelaide (The University Adelaide Research Scholarship).
Funding: AT Amare is currently supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Emerging Leadership (EL1) Investigator Grant (APP2008000). Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and The University of Adelaide.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Discipline of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Melkamu Bedimo Beyene & Azmeraw T. Amare
Adelaide Geriatrics Training and Research with Aged Care Centre (GTRAC), Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Adelaide, Woodville, SA, 5011, Australia
Melkamu Bedimo Beyene, Renuka Visvanathan & Azmeraw T. Amare
Aged and Extended Care Services, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Central Adelaide Local Health Network, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Renuka Visvanathan
Adelaide Medical School, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, 5000, Australia
Azmeraw T. Amare
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Azmeraw T. Amare .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest: Professor Renuka Visvanathan is a member of the WHO Clinical Consortium in Healthy Aging, but the work presented in this manuscript does not represent the views of the consortium.
Ethical standards: This review was conducted in accordance with established ethical procedures and standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary table 1:.
Article search string
Supplementary Table 2: Study Characteristics (Intrinsic capacity and its biological basis: A scoping review)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Beyene, M.B., Visvanathan, R. & Amare, A.T. Intrinsic Capacity and Its Biological Basis: A Scoping Review. J Frailty Aging (2024). https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2024.30
Download citation
Received : 15 January 2023
Accepted : 23 February 2024
Published : 10 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2024.30
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Intrinsic capacity
- healthy aging
- functional ability
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Foxy’s Kitchen + Bar
Hours updated 3 weeks ago

Review Highlights

“ First, throughout the planning process, Tim and Teri listened to all my requests and exceeded each request. ” in 3 reviews

“ The space has all the ambience of its former occupant - Shame in the Moon - but the food is substantially upgraded. ” in 4 reviews

“ Foxy 's should be on the list of every desert resident who seeks high quality food at affordable prices. ” in 2 reviews
Location & Hours
Suggest an edit
69-950 Frank Sinatra Dr
Rancho Mirage, CA 92270
| Closed now | |
Amenities and More
Ask the community.
Ask a question
Yelp users haven’t asked any questions yet about Foxy’s Kitchen + Bar .
Recommended Reviews

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
This article is organized as follows: The next section presents the methodology adopted by this research, followed by a section that discusses the typology of literature reviews and provides empirical examples; the subsequent section summarizes the process of literature review; and the last section concludes the paper with suggestions on how to improve the quality and rigor of literature ...
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A GOOD LITERATURE REVIEW SHOULD… • Be organized around a thesis statement or research question(s) • Develop your understanding of the literature in a field(s) of study • Synthesize results into a narrative summary of what is known and not known on your topic • Identify areas of controversy • Formulate questions for future research
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
3. Evaluate and select literature. 4. Analyze the literature. 5. Plan the structure of your literature review. 6. Write your literature review. Other resources to help you write a successful literature review.
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
How to write a literature review in 6 steps. How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
at each of these in turn.IntroductionThe first part of any literature review is a way of inviting your read. into the topic and orientating them. A good introduction tells the reader what the review is about - its s. pe—and what you are going to cover. It may also specifically tell you.
Literature Review and Research Design by Dave Harris This book looks at literature review in the process of research design, and how to develop a research practice that will build skills in reading and writing about research literature--skills that remain valuable in both academic and professional careers. Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
Exclusion criteria are the elements of an article that disqualify the study from inclusion in a literature review. Some examples are: Study used an observational design; Study used a qualitative methodology; Study was published more than 5 years ago; Study was published in a language other than English
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
Purpose of the Literature Review. To provide background information about a research topic. To establish the importance of a topic. To demonstrate familiarity with a topic/problem. To "carve out a space" for further work and allow you to position yourself in a scholarly conversation. Characteristics of an effective literature review
When conducting your searches you may find many references that will not be suitable to use in your literature review. Skim through the resource. A quick read through the table of contents, the introductory paragraph or the abstract should indicate whether you need to read further or whether you can immediately discard the result.
Literature review is the process of examining research that has been conducted in a particular flied of study. Is an act of selecting available documents and evaluate those documents in relation ...
Steps in tiie literature review process Given the particular processes involved in systematic reviews, meta-anaiysis and meta-synthesis, the focus of the remainder of this article is on the steps involved in undertaking a traditional or narrative review of the Table 2. The literature review process • Selecting a review topic • Searching the ...
A literature review is a research task that finds, evaluates and discusses information on a particular topic. You need to analyse multiple texts, and discuss key ideas that you find in the reading. A literature review may also identify gaps for further research. It is not a process of summarising texts separately - that is done in an ...
An integrative review summarizes past research and draws overall conclusions from the body of literature on a particular topic.The body of literature comprises all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. In a properly executed integrative review, the effects of subjectivity are minimized through carefully applied criteria for evaluation.
APA's clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) and professional practice guidelines (PPGs) are the result of a complex and lively process of decision-making, interdisciplinary discussion, literature review, public comment, APA approval, and more. Here's a quick rundown of how they come together: Clinical practice guidelines
Internet usage has seen a stark global rise over the last few decades, particularly among adolescents and young people, who have also been diagnosed increasingly with internet addiction (IA). IA impacts several neural networks that influence an adolescent's behaviour and development. This article issued a literature review on the resting-state and task-based functional magnetic resonance ...
Overview of search strategy. First, we assessed the data sources (clinical practice guidelines) from the most recent BETTER WISE study [], which had entailed a rigorous evidence review process to recommend specific prevention and screening actions, for applicability to adults aged 18-39 years.Then, we used a structured grey literature search of specific repositories and websites to find ...
BACKGROUND: Long-term post-treatment surveillance imaging algorithms for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are not standardized due to debates over optimal surveillance strategy and efficacy. Consequently, current guidelines do not provide long-term surveillance imaging recommendations beyond 6 months. PURPOSE: We performed a systematic review to evaluate the impact of long-term imaging ...
Background In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) introduced the concept of intrinsic capacity (IC) to define healthy aging based on functional capacity. In this scoping review, we summarized available evidence on the development and validation of IC index scores, the association of IC with health-related factors, and its biological basis. The review specifically focused on identifying ...
19 reviews and 32 photos of FOXY'S KITCHEN + BAR "Remarkable Evening!! Tim and Teri organized my Birthday Celebration on Saturday. My 12 guests were greeted and seated by the Fabulous Danny. First, throughout the planning process, Tim and Teri listened to all my requests and exceeded each request. Appetizers, Cocktails and Entrees were all served promptly and with great presentation!!!