
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay

A character analysis essay is a challenging type of essay students usually write for literature or English courses. In this article, we will explain the definition of character analysis and how to approach it. We will also touch on how to analyze characters and guide you through writing character analysis essays.
Typically, this kind of writing requires students to describe the character in the story's context. This can be fulfilled by analyzing the relationship between the character in question and other personas. Although, sometimes, giving your personal opinion and analysis of a specific character is also appropriate.
Let's explain the specifics of how to do a character analysis by getting straight to defining what is a character analysis. Our term paper writers will have you covered with a thorough guide!
What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
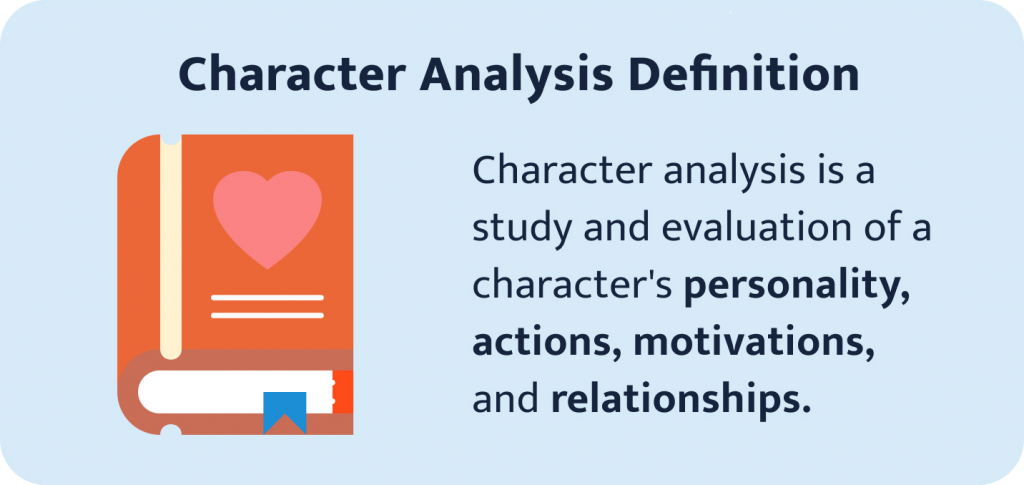
The character analysis definition explains the in-depth personality traits and analyzes characteristics of a certain hero. Mostly, the characters are from literature, but sometimes other art forms, such as cinematography. In a character analysis essay, your main job is to tell the reader who the character is and what role they play in the story. Therefore, despite your personal opinion and preferences, it is really important to use your critical thinking skills and be objective toward the character you are analyzing. A character analysis essay usually involves the character's relationship with others, their behavior, manner of speaking, how they look, and many other characteristics.
Although it's not a section about your job experience or education on a resume, sometimes it is appropriate to give your personal opinion and analysis of a particular character.
What Is the Purpose of a Character Analysis Essay
More than fulfilling a requirement, this type of essay mainly helps the reader understand the character and their world. One of the essential purposes of a character analysis essay is to look at the anatomy of a character in the story and dissect who they are. We must be able to study how the character was shaped and then learn from their life.
A good example of a character for a character analysis essay is Daisy Buchanan from 'The Great Gatsby.' The essay starts off by explaining who Daisy is and how she relates to the main character, Jay Gatsby. Depending on your audience, you need to decide how much of the plot should be included. If the entire class writes an essay on Daisy Buchanan, it is logical to assume everyone has read the book. Although, if you know for certain that your audience has little to no knowledge of who she is, it is crucial to include as much background information as possible.
After that, you must explain the character through certain situations involving her and what she said or did. Make sure to explain to the reader why you included certain episodes and how they have showcased the character. Finally, summarize everything by clearly stating the character's purpose and role in the story.
We also highly recommend reading how to write a hook for an essay .
Still Need Help with Your Character Analysis Essay?
Different types of characters.
To make it clear how a reader learns about a character in the story, you should note that several characters are based on their behaviors, traits, and roles within a story. We have gathered some of them, along with vivid examples from famous literature and cinema pieces:

Types of Characters
- Major : These are the main characters; they run the story. Regularly, there are only one or two major characters. Major characters are usually of two types: the protagonist – the good guy, and the antagonist: the bad guy or the villain.
- Protagonist (s) (heroes): The main character around whom most of the plot revolves.
For example, Othello from Shakespeare's play, Frodo from The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien, Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, and Elizabeth Bennet from 'Pride and Prejudice' by Jane Austen.
- Antagonist (s): This is the person that is in opposition to the protagonist. This is usually the villain, but it could also be a natural power, set of circumstances, majestic being, etc.
For example, Darth Vader from the Star Wars series by George Lucas, King Joffrey from Game of Thrones, or the Wicked Queen from 'Snow White and Seven Dwarfs.'
- Minor : These characters help tell the major character's tale by letting them interact and reveal their personalities, situations, and/or stories. They are commonly static (unchanging). The minor characters in The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien would be the whole Fellowship of the ring. In their own way, each member of the Fellowship helps Frodo get the ring to Mordor; without them, the protagonist would not be a protagonist and would not be able to succeed. In the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, minor characters are Ronald Weasley and Hermione Granger. They consistently help Harry Potter on his quests against Voldemort, and, like Frodo, he wouldn't have succeeded without them.
On top of being categorized as a protagonist, antagonist, or minor character, a character can also be dynamic, static, or foil.
- Dynamic (changing): Very often, the main character is dynamic.
An example would also be Harry Potter from the book series by J.K. Rowling. Throughout the series, we see Harry Potter noticing his likeness to Voldemort. Nevertheless, Harry resists these traits because, unlike Voldemort, he is a good person and resists any desire to become a dark wizard.
- Static (unchanging): Someone who does not change throughout the story is static.
A good example of a static character is Atticus Finch from “How to Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee. His character and views do not change throughout the book. He is firm and steady in his beliefs despite controversial circumstances.
- Foils : These characters' job is to draw attention to the main character(s) to enhance the protagonist's role.
A great example of a foil charact e r is Dr. Watson from the Sherlock Holmes series by Arthur Conan Doyle.
How to Analyze a Character
While preparing to analyze your character, make sure to read the story carefully.
- Pay attention to the situations where the character is involved, their dialogues, and their role in the plot.
- Make sure you include information about what your character achieves on a big scale and how they influence other characters.
- Despite the categories above, try thinking outside the box and explore your character from around.
- Avoid general statements and being too basic. Instead, focus on exploring the complexities and details of your character(s).
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
To learn how to write a character analysis essay and gather a more profound sense of truly understanding these characters, one must completely immerse themself in the story or literary piece.
- Take note of the setting, climax, and other important academic parts.
- You must be able to feel and see through the characters. Observe how analysis essay writer shaped these characters into life.
- Notice how little or how vast the character identities were described.
- Look at the characters' morals and behaviors and how they have affected situations and other characters throughout the story.
- Finally, observe the characters whom you find interesting.
Meanwhile, if you need help writing a paper, leave us a message ' write my paper .'
How Do You Start a Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, first, you have to choose a character you'd like to write about. Sometimes a character will be readily assigned to you. It's wise to consider characters who play a dynamic role in the story. This will captivate the reader as there will be much information about these personas.
Read the Story
You might think that if you already have read the book, there is no need to do so again; however, now that you know the character you would like to focus on, reading it again will have plenty of benefits. It will give you an opportunity to be more precise while reading the scenes that relate directly to your character and are important for his/her analysis. While reading the book, pay attention to every tiny detail to make sure you grasp the whole array of your character's traits.
Consider the following things:
- What specific descriptions does the author provide for each character?
For example, when J.K. Rowling describes Harry Potter for the first time, she describes his clothes as old and oversized, his hair untidy, and his glasses as broken. It might seem just like a simple description, but she expresses compassion and pity for an orphan neglected by his only relatives.
- What kinds of relationships does your character have with others?
Think about how Harry builds up his friendships with others. First, he and Ron do not like Hermione because she acts like a know-it-all, but when she gets stuck in the dungeons with a horrendous troll, he rushes to save her regardless.
- How do the actions of the character move the plot forward?
In 'The Philosopher's Stone,' Harry is very observant of any events taking place at school. He analyzes people's actions, which builds up the plot around the stone and its importance for the magical world.
Get help with your character analysis from our experts.
Choose a Dynamic Character
Choosing a dynamic character is a great idea. This does not necessarily have to be the protagonist, but a character that undergoes many changes has grown throughout the story and is not boring and/or static. This gives you a perfect advantage to fully show the character and make your paper entertaining and engaging for the reader. If you choose a character that is not very dynamic, your essay might seem monotonous because your character will not end up doing much and will not be very involved in the story.
While you are reading, it is useful to take notes or highlight/underline any of the critical elements of the story. This will add depth to your character description(s). By providing vivid and specific examples, you connect your reader to the character, and the character comes alive in their eyes. Review your notes and formulate the main idea about your character when you're finished reading with your character in mind.
Make an initial draft while taking note of the character analysis essay outline provided by your instructor. You may follow the recommended character analysis essay format if you have not been provided with a sample.
Choose a Main Idea
While reading the story, make sure you keep track of your notes. It is a good idea to look at them, choose the ones that are the most representative of your character and find patterns. This will be your thesis. Then, you must support this idea with examples and situations involving your character.
If your character were Jem Finch from 'To Kill a Mockingbird' by Harper Lee, the main idea would be how his personal character is shaped through racial conflicts, social inequalities, and internal struggles between public opinion, his own views, and what is actually right. Essaypro offers you history essay help. Leave us a notice if you need to proofread, edit, or write your essay.
Character Analysis Questions
Now that you have jotted down some main concepts about your character, here is a list of questions that can help you fill in the blanks you might still have:
.webp)
- Where do the events involving your character take place?
- What are the relationships between your character and other significant characters?
- What is the primary change your character has gone through throughout the story?
- What is your character's background?
- What is your character's occupation?
- What kind of emotions does your character go through?
- What are your character's values?
- What is your character's value?
- Does your character have friends?
- Is there a lesson your character has learned by the end of the story?
- Does the character achieve the goals he/she has set for himself/herself?
Make a Character Analysis Essay Outline
When you're unsure how to write a character synopsis, remember that creating a literary analysis outline is one of the most critical steps. A well-constructed character analysis outline will keep your thoughts and ideas organized.
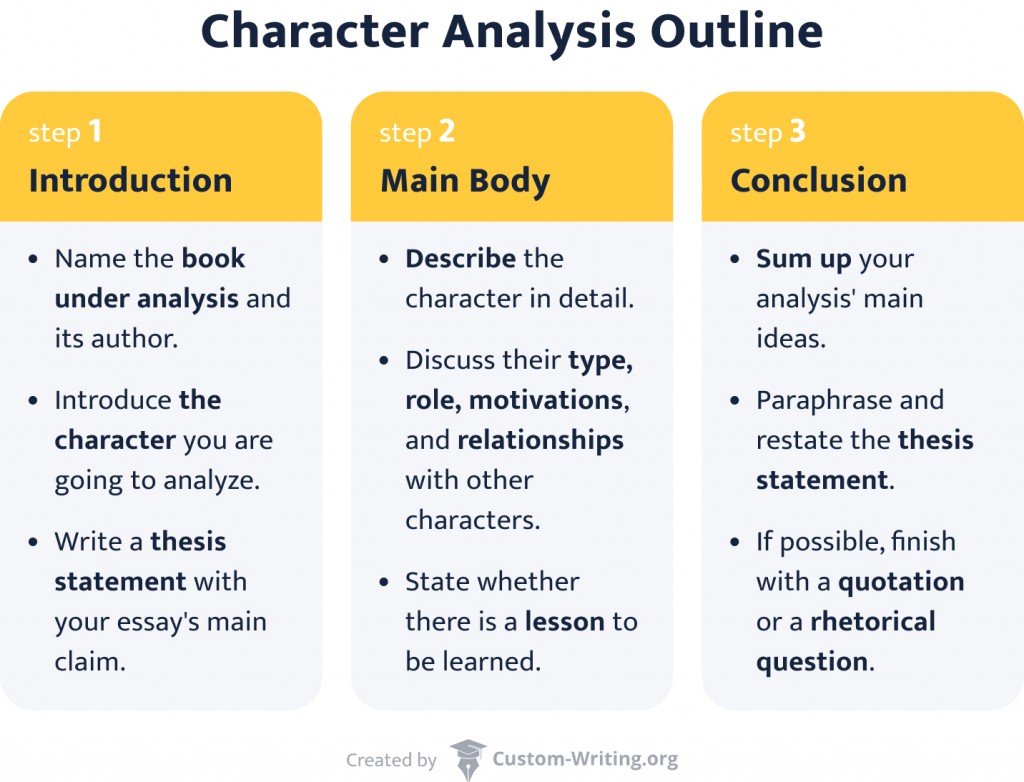
Character Analysis Essay Introduction:
Make the introduction to your paper brief and meaningful. It should hold together your entire essay and spark your audience's interest. Write a short description of the character in question. Don't forget to include a character analysis thesis statement which should make a case for the character's relevance within the narrative context.
Character Analysis Essay Body:
Subdivide your body paragraphs into different ideas or areas regarding the character. Look at your professor's rubric and ensure you'll be able to tackle all the requirements. You should also be provided with questions to be answered to formulate your analysis better. The body should answer the following questions:
- What is the character's physical appearance, personality, and background?
- What are the conflicts the character experiences, and how did he/she overcome them?
- What can we learn from this character?
- What is the meaning behind the character's actions? What motivates him/her?
- What does the character do? How does he/she treat others? Is he/she fair or unjust?
- What does the character say? What is his/her choice of words? Does he/she have a rich vocabulary?
- How does the character describe themself? How do others describe him/her?
- What words do you associate with the character? Perhaps a word like 'hope,' 'bravery,' or maybe even 'freedom'?
Character Analysis Essay Conclusion:
It's time to master the secrets of how to write character analysis essay conclusions. Your ending should also hold your ideas together and shape a final analysis statement. Mention things about the character's conflicts that we could experience in real life. Additionally, you can write about how a character should've reacted to a certain situation.
Character Analysis Essay Example
Read our blogs ‘Character Analysis of Jem Finch', 'The Great Gatsby Book Through Daisy Buchanan Character,' 'Analysis of Characters in Beowulf,' or simply use these character analysis essay examples to reference your paper. You might also be interested in a synthesis essay example .
Now that you know what is character analysis, it might be time to choose a character to write about. If you find yourself in a situation where you need to type ' do my homework for me ,' you should contact our writers. You also get a free plagiarism report, formatting, and citing when buying an essay from us!
STRUGGLE with Writing an Essay?
Address to our professional writers and get help asap!
How To Write A Character Analysis Essay?
How to start a character analysis essay, how to write an introduction for a character analysis essay.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
.webp)
Writing a Character Analysis Essay | Step-by-Step Guide
I’m also going to give you a ton of examples.
This post is split into four parts for easy navigation:
- What is a Character Analysis Essay?
- What is the best Format to Use?
- 11 Character Analysis Example Ideas
- Template, Checklist and Outline for Your own Piece

In this post, I’m going to explain to you clearly and in a step-by-step way how to conduct a character analysis.
1. What is a Character Analysis Essay?
Let’s get you started with some really simple details about what a character analysis is:
- A Quick Definition: A character analysis essay zooms-in on a character in a book, movie or even real life. It provides what we sometimes call a ‘sketch’ of a character.
- The Purpose of a Character Analysis: The purpose of a character analysis is to reveal interesting details about the character that might contain a broader moral message about the human condition. For example, Atticus Finch is not just a lawyer in To Kill a Mockingbird. Rather, he provides us with a moral message about the importance of doing what you believe is right even though you know you will likely fail.
2. What is the best Character Analysis Essay Format?
Character analysis essays do not have just one format.
However, let me offer some advice that might act as a character analysis essay outline or ‘checklist’ of possible things you could discuss:
1. Start with the Simple Details.
You can start a character analysis by providing a simple, clear description of who your character is. Look at some basic identity traits such as:
- Race (if relevant)
- Social class (if relevant)
- Protagonist or Antagonist? A protagonist is the character who is our central character in the plot; the antagonist is often the protagonist’s opponent or challenger.
- Major or minor character?
2. What are the character’s distinctive personality features?
Your character might have some really clearly identifiable character traits. It’s best to highlight in your character analysis the exact traits that this character possesses. Some common character traits include:
I recommend you take a moment to write down what you think the top 3 to 5 words are that you’d use to explain your character’s personality traits. These will be important to discuss throughout your character analysis.
Sometimes a character may start out with some personality traits, but change over the course of the text. This is quite common; and one clear example of this is Lady Macbeth she deteriorates from a cutthroat power player to a guilt ridden shell of a person roaming the halls of the castle. This dramatic character change is something that makes her very interesting, and is worthy of discussion!
3. What are the character’s key relationships?
Does your character have a close relationship with a certain person in the storyline?
You might want to discuss the character’s relationships as a part of your character analysis. These relationships may reveal some key personality traits of your character.
For example, in Shakespeare’s play Hamlet, Horatio is the loyal offsider to Hamlet. Through his actions in staying by Hamlet through thick and thin, we learn that he is a deeply loyal character.
Examining the character’s relationships with their friends and foes therefore is very useful for digging deeper into who this character actually is, and what personality traits they have when they are put to the test within the narrative.
4. What are the character’s motivations?
Another thing you might want to examine are the character’s motivations . What do they desire most in the world? Some common motivations for characters in stories are:
- A simple life
- To serve others
This list really could be endless, but I hope the above examples give you a bit of an idea of the sorts of traits to look out for. By mentioning and examining the motivations of the character, we will come closer and closer to learning exactly what moral message this character might be able to tell us.
5. What are the character’s key conflicts?
Stories tend to have a beginning, a complication, and a resolution.
The complication involves conflicts and challenges that need to be overcome. For Edmund in Narnia, it’s cowardice. For Romeo and Juliet, it’s the conflict between love and family loyalty. Here’s some other common conflicts for characters:
- Whether to stay loyal to a friend;
- To overcome obstacles to love;
- To seek a way out of a challenging situation;
- To escape war or poverty;
- To persevere through imprisonment;
- To overcome personal fear
Again, this list is endless.
Knowing the character’s core conflict gets us even closer to knowing the moral that the character is trying to teach us.
For example, in Romeo and Juliet, the challenge of Romeo and Juliet being together despite their families’ objections teaches us something. Personally, I believe it teaches us the importance of letting go of old grudges in order to let love bloom.
This moral lesson was taught to us through conflict: namely, the conflict that Romeo and Juliet were right in the center of.
6. What are the character’s epiphanies?
Sometimes a character has an epiphany. This often happens towards the end of the story and helps the character overcome the challenge or conflict that we discussed in the point above.
Here’s an example of an epiphany:
- In the Lion King, Simba runs away from his tribe to live in exile. After a chance encounter with his childhood friend Nala, he has an epiphany that he has a duty to his tribe. This leads him back home to fight Scar and return freedom to Pride Rock.
Not all characters have an epiphany. But, if they do, I strongly encourage you to write about it in your character analysis.
7. Examine the moral message the character teaches us.
Finally, conclude by examining the moral message behind the character. Nearly every character has something to teach the reader. Authors put a lot of thought into creating complex characters with whom we can relate. We relate to the character and say “wow, they taught me a lesson about something!”
The lesson might be something like:
- Money doesn’t buy happiness;
- Loyalty to family comes above all else;
- Love gives life meaning;
- Honesty is always the best policy
This is the core of your character analysis essay. If you can pick out exactly what moral message the character teaches you, you’ll be well on your way to writing a strong character analysis.
Below I’m going to give you some examples to help you out. I know it can be hard to really get your head around a character, so sometimes the best thing is to look at some samples!
3. Here’s 13 Example Character Analysis Essay Ideas.
Most times when we create a character analysis, we’re exploring the deeper moral stories / aspects of humanity. Here’s some example ideas. I’ve tried to outline in less than a paragraph exactly what your key point will be about each character:
- Atticus Finch from To Kill a Mockingbird: A character who teaches us a lesson about standing up for what’s right, even if you know you’re likely to lose.
- Huckleberry Finn from Huckleberry Finn: A character who reveals our inner desire for freedom from the elements of society that constrain us.
- Dudley from Harry Potter: A character whose personality tells us a cautionary tale of the perils of middle-class narcissism, parents’ desire to wrap their children in cotton wool, and the lack of discipline we perceive in contemporary childhoods.
- Jack from Lord of the Flies: A character who represents the innate desire for power that seems to lurk not too far from the surface of the human condition. When social structures are stripped away, he quickly reverts to violence and superstition to assert control over his peers.
- Lady Macbeth from Macbeth: Lady Macbeth teaches us a valuable lesson about the perils of contravening our own morality. She starts out a cutthroat killer but is increasingly consumed by the guilt of her own actions. While we may be able to escape full punishment from outside forces, it is the inner guilt that might eat us away to our last.
- The Boy who Cried Wolf: The boy who cried wolf is a character whose fatal flaw is his desire for attention and adulation. His repeated attempts at gaining the attention of others leads the townspeople to no longer take him seriously, which causes him harm when he actually needs the villagers to take him seriously to save his life. He teaches us the virtue of honest and humility.
- Nick Carraway from the Great Gatsby: Nick shows us all the inner conflict between the trappings of wealth, glamor and spectacle; and the desire for simplicity, honesty and community. He is drawn by the dazzling world of East Egg, New York, but by the end of the novel sees live in East Egg as shallow and lacking the moral depth of his former life in small town Minnesota.
- Alice from Alice in Wonderland: In many ways, Alice represents the child within all of us. She is a character of goodwill to all and who looks upon the world (or, rather, Wonderland) with awe. Travelling with a cadre of flawed characters, she learns with them the importance of seeking strength from within.
- The Nurse in Romeo and Juliet: Like many Shakespearian characters, the nurse’s role is both as loyal confidante to a central character and comic relief. Shakespeare uses minor characters to regale his crowd and sustain viewer interest between scenes.
- Lucy in The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe: Lucy represents a surprising character whose youthfulness and small stature make her an underrated character by all around her. Nonetheless, she possesses within the bravery and loyalty necessary to carry out the quest for Aslan. Lucy represents the goodness in children and, by extension, all of mankind.
- Anne in Anne of Green Gables: Anne occupies the typical literary role of young girls in many classical novels: she represents innocence and wonder, and her contraventions of rules are seen through a prism of childhood innocence. This frames Anne not as a deviant but as a precious soul.
- Simba from The Lion King: Simba’s story follows his struggle with growing up, embracing his destiny and duty to his family, or fleeing towards freedom and a ‘no worries’ lifestyle. Simba flees Pride Rock and goes through an existential crisis with his existentialist friends Timon and Pumba. When he runs into an old childhood friend, he realizes how shallow his new carefree life has become and reflects upon his obligation to his community back home.
- Woody from Toy Story: Woody starts out Andy’s favorite toy, but when Andy gets a new flashier toy, Woody’s status amongst the toys falls apart. Woody’s key character challenge is to learn to be humble and inclusive living within the group. By the end of the movie, Woody realizes his duty to love and serve Andy is more important than his own status within the group.
4. Here’s an Example Template for your own Character Analysis Essay
Feel free to use this brainstorming template to get you started with your character analysis essay. I recommend filling out as many of these key points as you can, but remember sometimes you might have to skip some of these points if they’re not relevant to your character.
Once you’ve brainstormed the ideas in Table 1, follow the character analysis essay outline in Table 2 to stay on track for your character analysis essay. Do remember though that each assignment will be different and you should adjust it based on your teacher’s requirements.
Here’s Table 1, which is a brainstorming template for your character analysis essay:
And here’s Table 2, which is an example character analysis essay outline. This is for a 1500 word character analysis essay. Change the word count according to how long your essay should be:
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
Character analyses can be really tough. You need to know your character really well. You might even need to re-read (or watch) your book or movie a few times over to get to know the character really well.
I recommend when you re-read or re-watch the text before you write your character analysis, have the checklist I provided above handy and take notes. Then, use the essay outline I provided above to put all of those notes together into a clear and thorough final character analysis essay.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay: Guide with Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A character analysis is a type of essay that requires you to analyze and evaluate the characteristics, traits, motivations, and decisions of a literary character. It involves closely examining such aspects as their personality, thoughts, behavior, and development. You should further explain how a character contributes to the overall meaning of the work.
When writing a character analysis essay, it is important to think critically and look beyond basic understanding of the character. For example, instead of simply describing their physical traits or explaining what happens in the plot, focus on how the characters think, feel, and interact with other characters. Examine the motivations behind their decisions and actions, as well as how they reflect a larger theme or idea in the work.
In this blog, we will explain how to write a character analysis essay. You will find a strtucture, outline and step-by-step guidelines along with examples.
If you don’t have much time for reading, we’ve got an easy solution for you. Entrust your assignment to essay writing services by StudyCrumb and get a custom paper tailored to your specific requirements.
What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
The main task of a character analysis essay is showing in detail key characteristics and certain person’s traits. Essay includes not just ordinary situations. It shows possible occasions for describing fictives fully and circumstantial. This type of essay helps understand how a hero will act in this or that situation, why would he do so, what were his reasons for these deeds? Analysis helps in figuring out what role a person plays in a story: great one or just secondary. Moreover, knowing the needed words of an analysis essay will enlarge students’ spoken literature.
What Is a Purpose of Character Analysis Essay?
Main purpose of a character analysis essay is helping the reader understand who's the bad one and who is among the good guys. This helps catch the idea of the story from the beginning. Knowing how a hero acts in this or that separate case, speaks a lot about his point of view. Essay divides all characters into main and minor ones. Detailed character analysis essay helps readers understand the nature of personages from an early beginning. Very often the story has several chapters, so the reader could discover much about a certain person from his doings/opinions.
Types of Character Using in Character Analysis Essay
While writing a character analysis essay, students have to remember two central personages: protagonist (key person) and antagonist. These are the main ones. The most striking roles are divided between them. Additional (minor) figures:
- confidante.
Each hero has special traits and behaviors. The round one is described as a person of passion having depth in feelings. Foil one is opposite one to positive, main one. Flat one is another side of round one: no vivid emotions, no changes while the story is being told. Use our college essay writing service to turn in the best character analysis your instructor has ever seen.
Protagonist — The Main Character
Protagonist in character analysis essays is the main story’s hero. This is a person all situations revolve around. They are the bearer of truth, the spokesman for the author's ideas, the main drive behind the plot. They don't have to even be a positive hero. After all, there is also an antihero - a protagonist with morally ambiguous or straight-up negative traits. Protagonist is a key figure, all other personages are considered minor ones. For better understanding of the protagonist, consider these examples: Romeo and Juliet, Katniss («Hunger Games»), Harry Potter, MacBeth. You can also consider Walter White («Breaking Bad»), Dexter Morgan («Dexter») and Hannibal Lecter («The Silence of the Lambs») to be antiheroes. All these examples are dynamic.
Antagonist — Character in the Opposite Position
Antagonist in character analysis essays is an opposite one to the protagonist. This type of character belongs to the dark side. Often, this can be a jealous, envious, bad, villain gossip person. They don't have to be the one ruining good protagonist’s plans, but they alway get in hero's way. Actually, there may even be more than one antagonist who may become hindrance for the protagonist. And if they are neutral in present, in the nearest future they will show their nature. Opposition between both protagonists and antagonists is clearly seen throughout the whole story. There is, of course, a catch. As with protagonists, there's more to know about antagonists' traits. After all, an anti-villain is also a thing! Basically it's when an antagonist has some heroic traits or can be sympathized with. One can also say that it's that type of person who has good intentions or their goal is pretty good, but their methods took a very wrong turn at some point. Othello, Captain Hook and Lord Voldemort — great antagonists’ examples. And those like John Silver, Khan («Star Trek») and Erik Lensherr («The X-Man») can be called anti-villain basically.
Major Characters
Major characters in character analysis essays are those who create a story. They play main (and clearly - important) parts, and have key roles. They make a so-called key set of personages. They are close confidants to the protagonist. If some conflict appears, major figures are mentioned first. Robinson Crusoe is a bright example.
Minor Characters
Minor characters in character analysis essays are often called supporting. They are important, but rarely are described in the story as key ones. This kind of fictives is represented by Yoda, Samwise Gamgee, Jabba the Hutt. They don’t remarkably influence the actual plot. Why flat? Because of no vivid progression.
Dynamic Characters
Talking about dynamic characters in character analysis essays - Shrek is a fine example. He is a dynamic personage because he changes: becomes softer and opens his heart to people. Fictives like him influence the story and make changes in the course of events. Their main feature: they change and grow throughout the story, making the reader sympathize with them. Another good example: Aladdin, Merida, Simba, Anakin Skywalker.
Static Characters
Static characters in character analysis essays do not change throughout whole story. They remain the same with their thoughts and opinions. Static personages are best described with the likes of Indiana Jones, Robin Hood, Sherlock Holmes. These personages are positive ones - though, unchangeable. Their points of view and tastes remain identical until a story ends.
Foils in character analysis essays are based on stereotypes and are opposite of main heroes. They have several key characteristics: they are wicked, distracted, conniving and scrooge. At the same time main personages are principled, focused, generous, and well-meaning. Foils are depressed and pessimistic, while main heroes — optimistic, kind, and good.
How to Analyze Characters in Character Analysis Essay?
While writing a character analysis essay, you should give a hero a general picture. Description has to grab appearance peculiarities and traits. Students must depict whether personage is good or bad. Are they pessimists or optimists? Do they have negative or positive thoughts? There are 3 main steps for analysis:
- Describing personality.
- Determining type of protagonist.
- Defining role in story.
To explore tiny personage’s quirks, all characteristics are taken into account. Just like in any literary analysis essay , you will need to pay special attention to literary devices that help reveal the true nature of a character.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay Outline?
Character analysis essay outline includes 3 main parts: introduction, body, conclusion. Below you can find short description to understand some peculiarities:
- Introduction should be meaningful and brief. After reading this piece, essay’s idea should be understood.
- Main body is one that should be divided into paragraphs with described main heroes. It should give detailed answers to different questions concerning personality and appearance. Pay attention, separate paragraph depicts what we learn from hero or situation.
- Conclusion is the one where you should draw the final line of analysis. Summarize points you've given above, loop to your thesis statement or give your reader some food for thought. Just remember that this section should be brief.
Additionally, it will be good to write how a situation changed because of main hero's influence.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
Instruction for writing character analysis essays is based on several steps. First, read a story carefully to find a person whom you are interested in. After reading the book, students should be able to completely grasp a key idea. Next steps include:
- choosing dynamic hero ;
- taking notes;
- defining main idea;
- answering analysis questions.
Concerning last point, think over next questions:
- What is hero's value?
- What kind of emotions does your hero go through?
- Does personage have a profound impact on plot?
- What are relationships between heroes and other significant figures?
Understanding an effect that main hero has on plot, it is easy to grasp the meaning the author put in their work.
How to Begin a Character Analysis Essay?
Character analysis essay introduction is the first step to start. It should describe whole essay in miniature. It's kind of a catchy hook for readers to get interested and proceed to explore chosen book. Introduction shows a completely full story in several paragraphs. To show all necessary information, make use of the thesis statement. These are rounded with text. It is fine to describe some catchy scenes and episodes to fuel readers’ interest.
Character Analysis Essay Body Paragraphs?
While introduction is a grand way to actually introduce the hero, character analysis essay body goal is identification of main personages features. Body should depict:
- Hero’s personality and physical appearance.
- Conflicts and ways of overcoming them.
- Lessons readers should learn.
- Meaning behind hero's actions.
Dynamic figure is key personage. Separate attention is given especially to them. Additional paragraph should describe a reader's feelings: what words are associated with a hero? Brave, modest, lucky, confident? Answers are key points to create a comprehensive description.
How to End a Character Analysis Essay?
How to write a conclusion paragraph for an essay ? Character analysis essay conclusion contains author’s point of view on course of events. Main ideas should be described shortly and clearly. Final part is a kind of review but with student's opinion. Lessons learned are described. For example, a story might teach how to live honestly, help poor people, feel merciful to others, etc. Remember that sheets’ personages teach us how to behave in real life. Many situations shown will be useful in everyday life. Hero’ deeds teach us how to cope with problems and find ways from tangled situations.
Character Analysis Essays: Final Thoughts
A character analysis essay is used for composing lines between parallel personages. It shows the present course of events that will make sense in future. Important traits and characteristics that are depicted in the book. They have a hidden idea, some kind of lesson. Comprehensive analysis helps to understand the meaning the author wanted to shed light on. Knowing main heros’ personal characteristics helps to explain their behavior and world perception. Buy essays for college in case this assignment isn't what you wanted to do this evening.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

FAQs' for Character Analysis Essay
1. what is a good thesis statement for a character analysis essay.
Character analysis essay is saturated with essential messages. It appears at the end (in last sentence) of introductory paragraph. Its task is to inform reader about information they will get acquainted with. Every sentence has hidden meaning concerning heroes. Remember, introduction must be brief but meaningful. Student’s thesis statements should be specific — include only points that will be discussed. Good thesis statement should grab readers’ attention, make them read whole story.
2. What kind of essay is character analysis?
A character analysis essay mostly deals with certain books’ personages, though, figures from cinematography are involved. Its task is to explain in-depth key features of personages. Antagonist and protagonist are main ones. There also exist additional ones. This kind of an essay explains behavior and state of mind. Personal traits and preferences also make up whole picture described.
3. How do you write a literary character analysis essay?
Character analysis essay demands describing chosen personage in detail. Firstly though, it is needed to determine personage’s type. Next step include turning to plot for showing examples. Students have to explain why personages decide do act that way, after all.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
14 August, 2020
14 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
A character analysis essay is one of the most complicated academic assignments that students usually write for Literature or English classes. Generally, this kind of essay writing requires you to describe the character in the context of the story. This can be done through the analysis of the relationship between the major and secondary characters or through your personal opinion of a particular character.
So, there is something you should learn before getting down to work. What is a character analysis and how to approach it? Let’s try to find the answers in the information below.
What is a Character Analysis?
A character analysis is a kind of essay where you examine behaviors, motivations, and actions of characters. Also, a character analysis is an in-depth assignment that makes you think critically about one or more characters and make judgements after analyzing the text. In most cases, it is used for the analysis of literary works. This form of academic writing involves personalities’ descriptions and conflicts with others they experience throughout a story. This analysis aims to provide a critical assessment of characters and build up conclusions based on the storyline. You may analyze a personality through his or her behavioral patterns or internal and external conflicts.

When you’re asked to write a character analysis, you must look at that story from a different angle. How? This is not your average reading for fun. Your task is to focus on the character synopsis and everything that’s associated with the people involved in the story.
Aim of a Character Analysis
A character analysis aims to evaluate a character’s traits, their functions, and the conflicts they have to deal with throughout the story. During the analysis, you will need to think critically, ask questions, and make conclusions about the character. To make your analysis informative, you will have to go beyond available descriptions that are written by the author. To understand the meaning of every event, phrase, and action, you will have to read between the lines. Don’t be afraid of using some additional resources if you feel like knowing more about the epoch a character lives in. If you want to gain an alternative opinion about a character, do not hesitate to find out your friends’ or internet users’ thoughts. Thus, thorough research may help you develop some creative ideas that will add great value to your future paper.
General Types of Characters
You should have a deep understanding of a character before starting an in-depth analysis. While a good character has many sides, there are some standard features to be considered:
- Protagonist: Being the main figure in a story, this character has the whole plot based on their life, actions, events, and feelings.
- Antagonist: Being a villain in a story, this character is positioned as the opposite figure to the major hero. Their basic nature remains negative, which makes them even more interesting than the main character. An antagonist plays a significant role even in short stories.
- Major: This character dominates the story. While they are not the main one in the story, they are involved in all the events.
- Minor: This character appears in a story from time to time. Their role may be significant for the plot development, but then they may disappear for some time and pop up again.
- Dynamic and static characters: The existence of these two opposite characters is determined by their reflection of each other’s specifications. While one character of a story goes through an internal or external transformation, another one may have their basic characteristics unchanged. There is a common idea that an evolving character tends to be more interesting than a static one. However, you can also analyze a static character from the perspective that they are not sympathetic, smart, or deep enough to learn their lessons. Or on the contrary, they remain strong enough and can resist the system without going under it.
- Stereotypical: If you are familiar with stereotypes, you will know what type of character is meant here. Generally, this particular character serves as the representation of the social, national, as well as demographic background of the story.
- Foils: The main goal of this hero in the story is to stay in contrast with main characters and a protagonist in order to highlight the features of the main character.
- Multi-dimensional characters: This group of characters involves an unlimited number of personalities. They are one-dimensional characters in the story who usually are not particularly interesting for the reader or viewer and do not play a crucial role in the storyline.
How Do You Start a Character Analysis Essay?
Before you start writing, you may wonder how to do a character analysis. Of course, you need to select a character to describe. In some cases, your professor will give you a character to talk about. By reading a story several times, you may notice the tiniest details. Ideally, you can use a highlighter or marker to mark each spot where your character is mentioned. Here are some more details of how to start with a character analysis:
- Take notes while reading. Take notes by highlighting every significant element of the story.
- Introduce your character. Introduce your character by providing their detailed description.
- Describe your character. Provide a smooth transition from the general description of your character to the point of convergence of the story.
- Build up a thesis statement. Finish the presentation with your paper’s proposal.
Main Points of a Character Analysis
When you need to analyze one character, you can make it from the perspective of several types at once. The character’s ability to change can create an additional source of analysis. At the same time, the complex and changing personality will be more interesting for the detailed analysis. To make it easier to work with such characters, you should focus on their characteristics, namely their importance for a story, actions, events, and so on. In most cases, you have to cover three major points:
Personality
Reveal the main features of a character to provide the reader with a portrait. By adding some facts and descriptions of actions, you will enable a deeper understanding of the analyzed hero. There is no need to use some words with broad meanings like “bad,” “nice,” “honest,” etc.
Role in a story
Describe the importance of the particular character in the context of the general story. Also, you should pay attention to their actions and their ability to move the events forward.
Character development
Analyze the changes the character has gone through and what features they have now. You should focus on the progress of a person, even if it is regressive.
Character Analysis Outline
In the character analysis essay outline, you should describe two or maybe even three specific character categories. Your mission is to describe the personality of the character, their function in the story, and the value they have.
- Describe the personality of the character. The reader gets familiar with the characters of the story through the words the characters use, the emotions they express, and the actions they take. It is quite easy to build up an opinion about the personality of a character through the prism of their outward behaviors. Eventually, you will understand that the character fits into one of the character categories mentioned above.
- Explore the character’s role . While writing a character analysis, it is important to describe the role of that character in detail. Apart from expressing unique character traits, the character will also perform a specific function in the story. Whether it will be the major or minor role, the analysis should address all the aspects of the performed role.
- Outline the growth and development of the character . In order to write a professional analysis, you will explain how the character matures and transforms as the plot progresses.
The majority of characters will have to go through particular transformations until the end of the story. You should pay special attention to whether the character becomes better or worse, stronger or weaker, rich or poor. Mention any areas or scenes where these transformations occur. In the story, you will recognize them from the cues like “it was then that she understood…” or “for the first time in months, he…”
Do you need a more detailed analysis of your character?
To make your analysis essay correct, you need to explore your character deeply. If you set some points you will follow in your work, you will manage to be consequential in your analysis. So here are some crucial nuances you should remember to describe the character:
You should focus on the reasons that make the character in a story to make a particular decision or take a specific action. You have an opportunity to explore the rightfulness of those actions as well as their reasonability. While you are asked to express your thoughts about certain events and feelings, you should be objective by looking beyond the cover.
Every action taken by a character can say a lot about his/her personality. You should not skip any events because it can be important for the general story and reveal some info about the character, his/her attitude to things, etc.
You should pay attention to the words the person uses because they can say a lot about their personality. Their accents and phrases may provide you with valuable information about nationality, social status, education, or even age of a character.
Descriptions
There are two major sources of the description: from other people in a story and the author. The author can provide the reader with one attitude and description of the major character, while secondary heroes in a story may describe them from their own perspective. At that point, their conclusions may be totally different, yet they’ll provide you with an understanding of the person’s nature.
The way people refer to a person also determines the features of a character. They may have nicknames or other names that will demonstrate their background and the attitude of other characters toward them. You can also define the origin as well as other important nuances.
Character Analysis Examples
By using a readymade character analysis example, you can concentrate on the creative process itself. Here are some nice examples of written character analysis based on a couple of popular stories:
https://literatureessaysamples.com/joe-gargerys-character-analysis/
http://jmendelis.blogspot.com/p/sample-character-analysis-essay.html
Popular Topics for Character Analysis
- Hamlet Character Analysis
- The Crucible Character Analysis
- Macbeth Character Analysis
- Ophelia Character Analysis
- Iago Character Analysis
- 12 Angry Men Character Analysis
- The Great Gatsby Character Analysis
- Beowulf Character Analysis
- Lady Macbeth Character Analysis
- Atticus Finch Character Analysis
- Romeo Character Analysis
- Antigone Character Analysis
- Victor Frankenstein Character Analysis
- Pride And Prejudice Character Analysis
- Machinal By Sophie Treadwell Character Analysis
- Of Mice And Men Character Analysis
- Othello Character Analysis
- Macduff Character Analysis
- Lord Of The Flies Character Analysis
- To Kill A Mockingbird Character Analysis
- The Breakfast Club Character Analysis
- Charlie Brown Character Analysis
- Death Of A Salesman Character Analysis
- Hester Prynne Character Analysis
- Mr Darcy Character Analysis
- Desdemona Character Analysis
- Fahrenheit 451 Character Analysis
- Willy Loman Character Analysis
- A Raisin In The Sun Character Analysis
- The Things They Carried Character Analysis
- A Rose For Emily Character Analysis
- Nick Carraway Character Analysis
- Daisy Buchanan Character Analysis
- Boo Radley Character Analysis
- 13 Reasons Why Character Analysis
- King Lear Character Analysis
- Jay Gatsby Character Analysis
- Blanche Dubois Character Analysis
- Oedipus Character Analysis
- Claudius Character Analysis
Tips on Writing a Character Analysis from Handmadewriting Experts
Whether you follow a character analysis template yourself or ask a professional essay writer to complete this paper for you, you should not forget the common principles of work. Luckily, Handmadewriting’s specialists always follow the standard rules for character analysis writing:
- Support all your statements with evidence. Y ou should incorporate evidence for every single point you make, although it must be relevant to the story. By means of quotes taken from the story, you can easily support your ideas and increase your credibility.
- Point, illustrate, and explain. The so-called PIE method is a must for character analysis writing. Make sure to make a point, integrate quotations to support it, and explain how every quote creates the point.
- Use your own words to anchor the quote. A quotation should not be left alone in the sentence. You need to explain the eligibility of this quote and its meaning.
- Do not overuse quotes. You are allowed to use up to 10% of quotations in an academic paper, so remember this number. If you overuse quotes, you can hardly hope for a good grade.
Are you ready to proceed with your character analysis paper? Once you learn all writing rules and tips, you will be able to finish an excellent paper before the set deadline.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay: Examples & Outline
A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any other essay, your character analysis should contain an introduction, a conclusion, and a thesis.
Want to know how to write a character analysis essay? Not sure how to start? We understand. Whichever piece you choose – Lady Macbeth, A Rose for Emily, or something else, – analyzing a character for the first time might be challenging. No worries, we are here to help! In this guide by our custom writing experts, you will find a step-by-step guide, outlining and writing tips, as well as a number of character analysis examples.
- 📔 Character Analysis Definition
- 🧙 Types of Characters
- 📝 Writing Guide
- 🖥️ Formatting Tips
📑 Character Analysis Essay Examples
📔 what is a character analysis essay.
A character analysis essay is an assignment where you evaluate a character’s traits, behaviors, and motivations. It requires critical thinking and attention to detail. Unlike descriptions, analyses focus on a character’s personality and internal drives. It explains how those factors shape the narrated events.
So, what you need to do is to see the characters as if they were real people who feel and act just as we do. Ensure there are no baseless assumptions and interpretations: the ideas you present should be supported by quotes from the text.
Character: Definition (Literature)
How do you define a character? It is a person, a creature, or an animal that makes up the story’s world. A character can be based on a real-life person, or it can be entirely fictional. It is someone who thinks, feels, and acts.
We use the word “character” in many different contexts. For instance, it can denote someone eccentric or worthy of our admiration. In both contexts, the term “character” means a distinctive personality. Similarly, in an analysis, your task is to show what makes a character stand out.
Characterization: Literary Definition & Examples
Characterization is the process by which a character’s personality is revealed. It presents characters’ traits, feelings, and motives to the reader. For this reason, characterization is closely connected to character analysis. It helps us to understand the characters better throughout the reading process.
Characterization can be direct and indirect .
- Direct characterization is when the narrator directly tells the audience what the personality of a character is.
- In contrast, indirect characterization shows things that hint at a character’s nature.
Here are some examples of direct characterization taken from Patti Smith’s Just Kids :
“But he always suppressed his real feelings, mimicking the stoic nature of his father.”
Here we see a direct description of a character. The author straightforwardly talks about Robert’s feelings. In comparison, look at the description of a woman taken from John Steinbeck’s The Snake :
“He looked around at her again. Her dark eyes seemed veiled with dust. She looked without expression at the cat’s open throat.”
These lines don’t directly reveal anything about the woman, but the reader can understand that she is cold and dangerous. It’s an indirect characterization that focuses on looks and actions to convey the message to the reader.
🧙 Types of Characters for Your Essay
When it comes to characters, they can be divided into several groups. For example, characters can be:
- Protagonists or antagonists,
- Static or dynamic,
- Flat or round.
These types define how much the characters change through the course of the story and their role in it.
Character Type: Definition
In psychology, a character type is defined by a combination of personality traits that coexist in an individual. Authors incorporate different types of characters into their works to convey the message and make the story more exciting or relatable to the reader.
There are three ways to categorize a character type:
- by archetypes,
- by their role in the narrative,
- by their ability to change throughout the story.
If you are about to write a character analysis essay, being familiar with character archetypes is essential. They have been categorized by a generation of writers, including the Swiss psychologist Carl Jung and the American literary theorist Joseph Campbell. A lot of characters we see in today’s literary works are rooted in them.
Archetypes include the Trickster, the Ruler, the Lover, the Sage, and others. The Hero is one of the most notable archetypes. Hercules or Achilles can be good examples of heroic protagonists. They are strong and courageous; they meet challenges and save the day by helping others.
Main Character: Definition & Examples
The main character and the protagonist often get mixed up. Most narratives also have the figure of the antagonist , whose actions affect the plot and stimulate change. Let’s have a look at the similarities and differences between these types.
The main character is central in the narrative. We experience the story through their eyes. They don’t necessarily have to be protagonists, though it happens in many cases.
The crucial difference between the main character and the protagonist is that the protagonist goes through changes throughout the story. The main character, however, is there to guide the reader through the experience. Often they help to show a different, darker side of the protagonist.
To understand the difference better, let’s turn to some examples.
What’s a Static Character?
Now that we’ve learned about the main character and the protagonist, we will closely look at other types of character classifications. One of the ways to categorize a character is by their ability to change throughout the story.
A static or simple character is someone who undergoes little or no significant changes. They often exist for comedic purposes. Here are some examples:
Complex Character: Definition & Examples
Complex or dynamic characters are the opposite of static characters. Characters of this type change as the book progresses. They display different qualities, emotions, and motives. They become more complicated and interesting to the reader as the story unfolds.
Check out these examples of dynamic characters:
Other Kinds of Characters
You already know about several ways to define a type of character. Now, let’s go over some other types, starting with flat and round characters.
Similar to dynamic and static ones, round and flat characters represent two different ends of a spectrum. Round characters usually come with an in-depth background. They are traditionally protagonists, antagonists, or those close to them. In contrast, flat characters are two-dimensional, and there is not much depth to them.
For the examples, we will turn to the novel Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen.
Finally, here are some bonus character types for you:
- Stock characters have a fixed set of traits and are flat. Most of the time, they exist for comical relief.
- Symbolic characters represent a concept or a theme that goes beyond them. They can be round and flat as long as they symbolize a particular notion or phenomena.
- Sidekick is a secondary character who supports the protagonist.
- The love interest is someone with whom the main character is infatuated.
- Foil is someone who’s set in contrast with the protagonist, thus putting more emphasis on the latter’s qualities.
Characterization Essay: Which Character Type to Choose
Before you start writing a paper, it essential to decide on the character you’re going to analyze. There are different types of characters in every story, so you need to choose which one suits your essay topic the best.
Usually, it’s best to choose a dynamic and round character . With static and flat ones, there may not be enough substance for you to analyze. However, some such personalities can be interesting to work with. For instance, a flat character such as Mr. Collins can be symbolic of something. Then, you can talk about how it embodies a specific idea or notion. You can also look at how they affect other characters in the story.
📝 How to Write a Character Analysis Step by Step
Now, we’re going to discuss how to write your paper step-by-step. But first, here are some pre-writing steps for you to consider:
- Choose a character for analysis.
- Take notes while reading;
- Define the type of the character and their role in the story;
- Pay attention to their descriptions and actions.
How to Analyze a Character: Description Examples
Knowing how to organize your work is an essential skill. Certain things need special attention if you are describing a character:
- physical appearance,
- emotional state,
- how the character speaks,
- behavior and personality traits,
- relationships with other characters.
When you analyze a character, try to look at them as if they were a real-life person. You want to know their motive, learn about how they feel, and understand why they think in a certain way. Ask yourself:
- How did the character change throughout the story (if at all)?
- What do other characters say about them? Can their words be trusted?
- Where is the character physically and emotionally? What brought them here?
- What is the character ready to do to achieve their goal?
Now, let’s look at the character of Franklin from the short story Just Before the War with the Eskimos by J.D. Salinger:
Character Profile Template for Writing
When writing your essay, use this character analysis template:
In the following sections, we’ll discuss each step in detail.
Character Analysis Outline: How to Start a Character Analysis
The beginning of your essay is its crucial part. It sets the mood and grabs the reader’s attention. There are many different ways to write a character analysis introduction, but here are the most effective ones:
- Use a quotation. It’s a great way to make a catchy hook. If it relates to the character and reflects their nature, it can also help to set the tone for analysis. In case you are using a quotation from somewhere else, mention the source in parentheses.
- Talk about the book or story. Mention the author, the name of the story, and the genre. Briefly describe the main events that are taking place in the story.
- Introduce the character. State their role in the story (define whether they are a protagonist, an antagonist, etc.) Then, explain whether the character is static or dynamic. Finally, describe them in 2-3 sentences.
The final part of an introduction is a thesis statement.Read on to learn how to write one!
Character Analysis Thesis Statement & Examples
A thesis is the key component of every essay, and character analysis is not an exception. It’s crucial to develop a good and clear thesis statement that includes all the aspects of your paper. For instance, if you plan to write a 4-paragraph body, including 4 points in your thesis.
What should a character analysis thesis include? Well, try to think of any trait that the character possesses that has to do with their downfall or somehow influences the story. Think about how this trait affects the character’s relationship with others or how it contributes to their motive or aspiration.
Take a look at the following examples:
How to Write Character Analysis Paragraphs for the Main Body
The main body of your essay can include as many paragraphs as you need. In this part, you introduce the character and analyze them. We have already talked in this article about what kind of questions should be answered in these paragraphs. The most important points are:
- Describe the character and their role within the story.
- Give the audience an explanation of the character’s motives.
- Show what message the author wanted to convey through this character.
Keep in mind that every paragraph should have a topic sentence that captures its main idea.
Tsukuru Tazaki’s spiritual rebirth also affects his physical appearance.
Character Analysis Conclusion: How to Write
The conclusion part of your essay summarizes all the information you have mentioned and restates the thesis. Here is some advice for your conclusion paragraph:
🖥️ Character Analysis Essay Format
Most college assignments and essays are written according to the APA or MLA format. Both styles have the same formatting, which requires:
- a double-spaced paper with 1-inch margins,
- a page header with page numbers flush right,
- an 11-12-point font.
While writing an essay on characters, pay special attention to quotations. Here are some tips for APA in-text citations:
- When you summarize or paraphrase the information, mention the author’s name and publication date in brackets. Example: According to Collins (1997.)
- When you quote directly from the source, add the number of the page, as well. Example: “There is a view that…” (Collins, 1997, pp. 134-135.)
- If the source includes three or more authors, use the abbreviation “et al.” after the first author’s name. Example: (Collins et al., 1997)
As for MLA format:
- You can write the author’s name in the sentence. Example: As Collins mentions in his essay<…>.
- You can mention the author’s name in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. Example: (Collins, J.K.)
- The last option is to use either footnotes or endnotes.
Below you’ll find a collection of character analysis essay examples and a downloadable sample to inspire you even more.
- The Grandmother in A Good Man Is Hard to Find: Character Analysis
- Willy Loman in Death of a Salesman: Character Analysis
- Jay Gatsby and Nick Carraway: Character Analysis
- Prospero in The Tempest: Character Analysis
- Agamemnon in the Iliad: Character Analysis
- Lord Pococurante in Candide: Character Analysis
- Andromache in the Iliad: Character Analysis
- Character Analysis of the Knight from The Canterbury Tales
- Essay on Soldier’s Home: Analysis of the Characters
Character Analysis Example (Downloadable)
Roald Dahl’s Matilda is one of the most famous children’s novels of the 20th century. The protagonist of this tale is Matilda Wormwood, a five and a half-year-old girl with a brilliant and lively mind that distances her from the rest of the family. Matilda’s character is particularly interesting as she has a powerful personality with extraordinary mental abilities, and she manages to overcome all the obstacles that surround her.
Character Analysis Essay Topics
- Character analysis of Abbas from A.D.: New Orleans After the Deluge .
- Jay Gatsby in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- Beowulf and Hamlet: similarity and diversity of the characters.
- Personal and social failures of Willy Loman in Death of a Salesman by Arthur Miller.
- Character analysis of Othello.
- Analyze the characters of Stanley and Blanche from A Streetcar Named Desire .
- The tragedy of Mathilde Loisel from The Necklace by Guy de Maupassant.
- Character analysis of Huck Finn from Mark Twain’s The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn .
- Moral force of Kate Lipton from Double Helix by Nancy Parker.
- Character analysis of Thorvald and Nora in Henrik Ibsen’s A Doll’s House .
- Discuss the character of king Creon in Antigone .
- Analyze the personality of Lydia from Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice .
- Compare Nick Carraway and Tom Buchanan from The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- Describe the peculiarities of Lord Pococurante in Candide .
- Sarty Snopes in William Faulkner’s Barn Burning : character analysis.
- Analyze the character of Biff Loman in Death of a Salesman.
- Personality of Nora in A Doll House by Henrik Ibsen.
- Examine the main characters of The Yellow Paper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
- Personality change of the main character in Edgar Alan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Analyze the characters of E. Hemingway’s A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .
- Describe the main characters of the novel The Overstory by Richard Powers.
- Controversial personality of Vladek in Maus: A Survivor’s Tale by Art Spiegelman.
- Character analysis of Victor Frankenstein in Frankenstein by Mary Shelley.
- Discuss the character of Creon in Oedipus the King .
- The manipulative character of Iago in Willian Shakespeare’s Othello .
- Analyze the characters of Nil and Kristine in A Doll’s House .
- Eccentricity of Grendel’s character in Beowulf .
- Describe the main characters of Four Summers by Joyce Carol Oates.
- Examine the characters of Harold Krebs and his mother in Ernest Hemingway’s Soldier’s Home .
- Analyze common and different traits of the characters in The Monkey’s Paw .
- Character peculiarities of Rostam and Sohrab in Shahnameh by Ferdowsi Tousi.
- How does the character of Elizabeth Bennet in Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen differ from the rest of her family?
- The behavior and meaning of the characters in Nicholas Rowe’s The Tragedy of Jane Shore.
- Compare the characters of Victor Frankenstein and the monster in Frankenstein or the Modern Prometheus by Mary Shelley.
- Discuss the differences of main characters in Everyday Use by Alice Walker.
- Examine the character of Connie in Where Are You Going, Where Have You Been by Joyce Carol Oates.
- The influence of social pressure on the characters of Chopin’s Desirée’s Baby and Sedaris’ A Modest Proposal .
- Dynamic feminist characters of Delia and Jig in Sweat by Z. Hurston and Hills Like White Elephants by E. Hemingway.
- Analyze the personality traits of Emily in William Faulkner’s A Rose for Emily .
- Examine the characters of The Quiet American by Graham Greene.
- Henry ΙV by William Shakespeare : analysis of main characters.
Now you know everything necessary for writing an excellent character analysis. What character would you like to analyze? Let us know in the comments!
Further reading:
- How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay Step by Step
- Literature Review Outline: Examples, Approaches, & Templates
- Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]
- How to Write a Critique Paper: Tips + Critique Essay Examples
- 435 Literary Analysis Essay Topics and Prompts [2024 Upd]
- How to Write a Literature Review: Actionable Tips & Links
❓ Character Analysis FAQ
A character analysis involves:
1. description of a character; 2. explanation of how they change throughout the story; 3. their role in the narrative; 4. relationships with other characters; 5. what idea the author wanted to convey through the character.
A character analysis creates a description that contains their most important qualities. It provides a new perspective of a character that reveals more about what it’s like to be human. It can also point to a moral or a lesson.
Literary analysis uses the technique of tracing the character development. This technique is usually used to understand the theme of the work better. Through tracing a character’s development, we can learn more about the story’s message and how it’s conveyed.
A summary paragraph in a character study should include answers to the questions “what,” “who,” “where,” and “why.” You should mention who narrates the story, where the story is set, its theme, and the message it conveys.
- Critical Concepts: Character and Characterization: Kansas State University
- Analyzing Novels & Short Stories: Texas A&M University
- Guidelines for Writing a Character Analysis Essay: Tidewater Communite College
- Literary Criticism: Thesis Examples: The University of Texas at Arlington
- Writing a Literary Analysis Paper: Germanna Community College
- Flat and Round Characters: Encyclopedia Britannica
- Literature: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- How to Write a Book Analysis: Kean University
- Elements of Literary Analysis: Alamo Colleges District
- Defining Characterization: Read Write Think
- APA Style: General Format: Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![essay on the literary character Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![essay on the literary character How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![essay on the literary character How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![essay on the literary character How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![essay on the literary character How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay: Step-by-Step Guide
Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
- 2.1 Protagonist
- 2.2 Antagonist
- 2.5 Dynamic
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.3 Summary
- 4.1 Read up on the story
- 4.2 Decide on what character to choose
- 4.3 Outline your essay
- 4.4 Define the main idea
- 4.5 Make notes while reading
- 4.6 Compose a list of questions
- 5 Character Analysis Essay Example
Writing can be as interesting as communicating. You can provide your thoughts and in-depth analysis of a character you like. That’s why you can come across various writing assignments in high school or college, including an analysis essay . Preparing such a work enables you to reveal your creativity and develop your ability to analyze and systemize information.
Like any other essay types , a character analysis paper sticks to a particular structure and has a certain purpose. It also discloses a range of specific points you should take into account when putting words on paper. So, if you need help starting to write, you landed in the right place. Here, we uncover all you need to know on how to write a good character analysis article.
What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
A character analysis essay is worthy of putting effort into writing. This assignment involves a versatile description of a central character from a book, novel, or whatever storytelling. In such an essay, you must open the main personality traits you choose to write about.
Writing about a character, you should describe their inner world as well as their behavior, actions, and lifestyle. This is detailed work about a person you should study well. To be able to explain their particular behavioral line in the context of a story, you must turn on your imagination and thorough examination.
With this in mind, it is easy to understand the purpose of a character analysis essay. It involves evaluating a character’s pack of traits reflected in the context of the primary source. You might choose whether to disclose the positive or negative side of a character. This depends on the topics and the approach used for composing an analysis paper.
Also, it is possible to call this type of writing a process analysis essay because you are to disclose the character’s emotions along with how actions occur and change during the plot.
Common Types of Characters in Your Essay
When encountering characters’ analysis and defining an objective of your essay, you must know what types of characters exist. This might help you direct your analysis into the correct flow.
Protagonist
The protagonist is the story’s central figure on which the main focus is fixed. Not only one character can be a hero. You can find several of them through the narrative, expressing their experience and engaging scenes.
This character represents an opposite role to a protagonist in the context, bringing some worse experiences to the story. They always create an obstacle for a protagonist to reach a goal.
A major person in a story plays an important role, yet not the central one. These can be characters who are close in relationship with the main hero and accompany them throughout the book.
Minor characters, accordingly, play a minor role in the story. They can show up occasionally in a plot for a while and then disappear.
A dynamic character shows growth and brings some modifications throughout the story. Typically, a protagonist is dynamic, accepting challenges and learning to become better and stronger.
An opposite message to dynamic persons brings a static character. They don’t reflect any story changes and remain with the same traits and behaviors. Minor persons are usually static.
This type of character is specific as they draw a reader’s attention to crucial persons in a story. Their mission is to strengthen a protagonist’s role.
Understanding the role of your character is crucial. You will know how to explain particular actions and scene changes. If you still find it challenging to start writing a character analysis essay, contact our PapersOwl writing service and let professional writers bring you an excellent piece of copy.
Character Analysis Essay Format
In addition to the context you must provide, an essay should look elegant and meaningfully ordered. For this purpose, you should adhere to a particular character analysis paper format. Here is a sample of what compositional elements your work should include.
Introduction
As you deal with a literary composition in different volumes, you should provide a background of what a story is about. Also, you need to mention the author and the title of a book or novel you will describe characters from.
Furthermore, if you put on a character analysis thesis statement, it will be a brilliant idea to make your introductory part more enticing. So think about how to compose a meaningful statement in one or two phrases.
This main component in an essay’s format is the biggest one. You must write all you want to reveal about your characters at this stage. But keep in mind to order your train of thought and present it in a comprehensive way.
An overall description of your personality, specific traits, and influencing factors should be carefully covered in your body section. To confirm some unique characteristics or actions, you must cite a dialogue inside essays as an original reference. Information can be voluminous, so make sure you separate it into several meaningful paragraphs.
Concluding your main points about your protagonist is the final stage of your writing. Highlight the experience your character has gone through in the story.
Whatever question you have about character analysis writing, you can always address our helpful platform. We will help you do your essays in the best way to improve your academic performance.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
There needs to be more than just knowing how to arrange your essay. So, we’ve outlined some helpful steps you should take before getting started.
Read up on the story
If you want to demonstrate good knowledge of the characters and all episodes they were in, you should read the entire story more than once. Thus, you will be able to note some crucial details and cite them. Rereading a story will enhance your knowledge about each scene.
Decide on what character to choose
Your choice might depend on your preferences and the type of narrative you read. Think of whose personality you can easily reveal and build rich judgment around them. It’s up to you to write about a protagonist, major or static characters.
Outline your essay
This is one of the most important strategies in writing. You should create an outline of what you are going to uncover in your article. It is a good idea to draft a structure for your composition and note down the insights in each structural element. This will help you follow the presentation of the material and, at the same time, remind you of the next step.
Define the main idea
Once you select a character you want to analyze in your character analysis essay, you decide what part of a personality you will focus on.
Make notes while reading
To create a comprehensive picture of a character, you should know as much as possible about their traits and behavior. Your outline helps you follow the structure while referring to quotes and dialogues, allowing you to confirm specific situations that best show personalities.
Compose a list of questions
To make your character analysis less challenging, we recommend you make a list of lead-in questions. You can even create those questions for each structural part of your composition. This enables you to be precise in providing relevant information about a character.
In addition to general steps on how to write a character analysis essay, we’ve prepared a range of insightful tips. By following them, we believe you will bring up solid work. Here they are:
- Provide a catchy hook in the introductory part;
- Keep short and simple sentences;
- Split into paragraphs each idea you want to mention about a character;
- Use examples right from the primary source;
- Be concise and clear when estimating your characters.
One of the literary analysis papers is writing a poetry essay and describing a character analysis in poetry. Writing such an essay can be more challenging as students need help understanding this style. No worries. There is always a way out, and you can buy essays online from the best writers as an option.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Character Analysis Essay Example
Lady Macbeth is one of the most influential female characters in literature. She conveyed an entirely different figure of how a woman doesn’t need to look. Shakespeare created a sick-ambitious character burning to be queen.
Lady Macbeth was pretty rude to her husband. She judged him for not being as brave as she expected from him. We know about his bloody deeds on the battlefields, though. But in public, she acted like a real actress, conveying her best traits to respect her king.
In the scene when she loses consciousness after Duncan’s murder, the audience wonders whether she was playing another role at that very moment. Eventually, she fails each test coming into her life. After the follow-up blaming her husband during the banquet (Act III, Scene 4), the worst turns back into her life. She becomes nervous and unable to control her emotions. We can notice her strange behavior when murmuring in Act V, Scene 1, as she “confesses” her participation in the murder.
Her death became an event that made Macbeth contemplate deeper on the time of nature and mortality in the speech “Tomorrow and tomorrow and tomorrow” (Act V, Scene 5).
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Character Analysis Guide: Master Literature
What is character analysis, how to identify characteristics of a character, how to analyze character development, how to analyze character interactions, how to analyze character motivations, how to analyze character influence on plot, how to analyze character influence on theme, how to analyze character arc and transformation.
- How to write character analysis essay
Picture your favorite book. Now, think about the characters that brought that story to life. Their actions, thoughts, and words paint a vivid picture in our minds, don't they? Well, the secret to understanding those characters, as well as the heart of the story, lies in mastering the art of analyzing characterization in literature. It's like a fun detective game where you gather clues about characters to uncover the deeper layers of the story. Let's jump right in!
Character analysis is a fascinating journey into the heart of a story. It's about looking closely at each character and understanding their traits, roles, and experiences. Imagine you are a detective and the character is a puzzle waiting to be solved. You're not just reading about who they are on the surface, but you're digging into their actions, words, and thoughts to see what makes them tick. Here's how you do it:
- Identify the character's traits: These are the qualities that make a character who they are. It could be anything from being brave, clever, kind, or stubborn.
- Understand their role in the story: Every character plays a part in moving the story forward. They could be the hero, the sidekick, the villain, or even the comic relief.
- Examine the conflicts they experience: Characters often face challenges or conflicts. How they deal with these situations can reveal a lot about their personality and growth.
Remember, analyzing characterization in literature isn't just about listing facts about the character. It's about understanding them in a way that brings the story to life. It's about seeing how they change, how they interact with others, and how they influence the plot and themes of the story. There's a whole world to explore within each character, so let's get started!
So, you're ready to start analyzing characterization in literature, and the first step is to identify the characteristics of a character. But how do you do it? Here is a straightforward plan:
- Observe their actions: What a character does can tell you a lot about who they are. For example, if a character always stands up for others, they're likely brave and compassionate.
- Pay attention to their words: Dialogue can reveal a lot about a character's personality, beliefs, and relationships with others. For instance, a character who always speaks kindly to others is likely a nice person.
- Consider their thoughts and feelings: Sometimes, a character's inner world — their thoughts and feelings — can tell you more about them than their actions or words.
- Take into account their appearance: How a character dresses or looks can give you clues about their personality or their role in the story.
Identifying characteristics is like collecting puzzle pieces about a character. It's not just about noting what you see or read, but about putting those pieces together to get a fuller picture of who the character really is. So, keep those detective glasses on and let's continue our journey in analyzing characterization in literature.
Now that you've got the basics down, let's move on to analyzing character development. This involves observing how a character changes and grows throughout the story. Here's the scoop:
- Track the character's journey: Look at where the character started at the beginning of the story and where they end up. Have they grown? Have they learned something new? Have their beliefs or attitudes changed? This can give you a sense of their development.
- Analyze key events: Major events in the story often trigger changes in characters. Examine these closely and consider how the character reacted, what choices they made, and how it affected them.
- Consider relationships: Relationships can greatly influence a character's development. How a character interacts with others, their reactions, and the changes in their relationships can all signify growth or change.
Remember, not all characters will develop or change in a story—that's okay. Some characters are static, meaning they stay the same throughout the story. Others are dynamic, meaning they undergo significant changes. Both are important and understanding this is a key part of analyzing characterization in literature.
Let's dive into another important part of analyzing characterization in literature: examining character interactions. This is all about how characters relate to each other. Let's break this down:
- Observe dialogues: So much can be uncovered from the way characters talk to each other. Do they argue? Are they supportive? Do they joke around? Dialogues can reveal a lot about relationships between characters.
- Look at their actions: Actions can speak louder than words. If a character helps another in a tough situation, or perhaps the opposite, betrays them, it can tell you much about their relationship and interactions.
- Consider their influence: Characters often influence each other's decisions and behaviors. If a character changes because of another, it shows the power and effect of their interaction.
When analyzing character interactions, it's important to note that these interactions can change over time—just like in real life. Characters can start off as friends and end up as enemies, or vice versa. Understanding these changing dynamics can give you a deeper understanding of the characters and the story as a whole.
It's time to explore the driving forces behind characters' actions. Understanding character motivations is a key part of analyzing characterization in literature. Here's what you need to watch out for:
- Desires and Goals: What does the character want more than anything? This could be anything from a physical object, a relationship, a change in their life, or even the resolution of a mystery. Their ultimate goal will heavily influence their actions.
- Fears and Worries: On the flip side, what does the character want to avoid? Fears and worries can be as motivating as desires and goals. They can push the character to take risks or to make safe choices.
- Values and Beliefs: What does the character believe in? What are their morals? These deeply held values can guide a character's decisions, even when they conflict with their desires or fears.
Remember, motivations can evolve as the story progresses. Characters might change their minds, achieve their goals, or face new fears. Keeping track of these changes can help you understand not just the characters, but also the bigger themes and messages of the story.
The plot of a story isn't just something that happens—it's often driven by the actions and decisions of its characters. That's why analyzing characterization in literature includes understanding how characters influence the plot. Here's how you can do it:
- Actions: Look at the key events in the story. How many of them are caused directly by the character's actions? A character who frequently makes things happen is likely to have a significant influence on the plot.
- Decisions: Similarly, consider the character's decisions. How do they affect the story's direction? Remember, a decision isn't always about doing something—sometimes, the decision to do nothing can be equally impactful!
- Reactions: Even passive characters can influence the plot through their reactions. How do other characters and events in the story change as a result of this character's responses? This can give you clues about their indirect influence on the plot.
As you can see, a character's influence on the plot goes beyond their actions. It's about how they shape the world around them, and how the world, in turn, shapes them. This give-and-take is a vital part of analyzing characterization in literature, and it can reveal a lot about the story's deeper meanings.
When analyzing characterization in literature, one often overlooked aspect is how characters can embody and influence the theme of the story. Themes are the underlying messages or big ideas of a story, and characters play a crucial role in expressing these. So how do you analyze a character's influence on theme? Here's a simple guide:
- Beliefs: What does the character believe in? Their beliefs can often mirror the theme of the story. For instance, if a character strongly believes in forgiveness, the theme of the story may revolve around redemption.
- Speech: The way a character speaks can reflect the theme. For example, a character who frequently talks about freedom and independence might hint at a theme of personal liberty.
- Behavior: How does the character behave? Do they consistently act in a way that supports the theme? In a story themed around courage, you might find a character who consistently stands up for what they believe in, no matter the cost.
Remember, characters are often vehicles for the author's themes. By diving into a character's beliefs, speech, and behavior, you can gain a deeper understanding of the story's larger messages. And that's the beauty of analyzing characterization in literature—it's not just about understanding the characters, but also the world they inhabit and the ideas they represent.
Another fascinating aspect of analyzing characterization in literature is the character arc and transformation. A character's arc is the journey they go through, the changes they undergo from the start of the story to the end. This can provide a wealth of insight into not only the character but also the story's overall message. Let's take a look at how to analyze this aspect:
- Identify the starting point: Where does the character begin in the story? Are they timid, confident, naive, cynical? This initial characterization sets the stage for their journey.
- Track the changes: As the story progresses, how does the character change? Do they become more confident? Do they lose their innocence? Identifying these changes can help you understand the character arc.
- Understand the catalysts: What events or experiences prompt these changes in the character? The reasons behind a character's transformation can be as revealing as the changes themselves.
- Analyze the end point: Where does the character end up at the end of the story? How do they differ from the character we met at the beginning? Assessing the end point of the character's journey can provide insight into the overall theme of the story.
Character transformation is one of the most compelling aspects of a story. It's what makes us root for characters, mourn their losses, and celebrate their victories. By analyzing a character's arc, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of storytelling and the power of character development in literature.
How to write a character analysis essay
Now that we've covered the intricate process of analyzing characterization in literature, let's apply this knowledge to the final step: writing a character analysis essay. This task may seem daunting at first, but don't worry, we're in this together. Here's how you can approach it:
- Choose your character: Start by selecting the character you want to analyze. It could be a major character or a minor one—whatever sparks your interest!
- Identify key characteristics: Next, list down the key characteristics of your chosen character. Remember, these can include physical attributes, personality traits, and even their habits and quirks!
- Analyze character development: How does your character change over the course of the story? What experiences or events lead to these changes? This is where your understanding of character arcs comes into play.
- Consider character interactions: Look at how your character interacts with others. These interactions can reveal a lot about your character's motivations and their role in the story.
- Examine influence on plot and theme: How does your character influence the plot and the theme of the story? Their actions, decisions, and transformations can have significant impacts on the storyline and the underlying messages of the text.
- Organize your thoughts: Before you start writing, create an outline for your essay. This will help you structure your thoughts and ensure a smooth flow of ideas.
- Write, review, and revise: Now it's time to bring it all together! Write your essay, then take some time to review and revise it. Make sure your analysis is clear, your arguments are well-supported, and your writing is engaging.
And there you have it! With these steps, you're well on your way to writing a stellar character analysis essay. Remember, the goal is not to simply describe your character, but to delve into their personality, their changes, their motivations, and their impact on the story. So go ahead, flex those analytical muscles and dive into the wonderful world of character analysis!
If you enjoyed our Character Analysis Guide and want to dive deeper into the world of creating compelling characters, be sure to check out the workshop ' Creating Characters: The Design Process ' by Kit Buss. This workshop will provide you with valuable insights on how to design unique and memorable characters for your stories, further enhancing your understanding of literature.

Live classes every day
Learn from industry-leading creators
Get useful feedback from experts and peers
Best deal of the year
* billed annually after the trial ends.
*Billed monthly after the trial ends.
beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”

Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.
Start Writing a Character Analysis Essay with Us
- Essay Writing Guides

Characters are the cornerstones of stories in the broad world of literature; they are individuals with unique intricacies, motivations, and travels. But taking characters at their value only goes so far in revealing their significance. Exploring character analysis in depth reveals a wealth of knowledge that enhances reading and promotes a comprehensive comprehension of the story’s overall structure. In this article, we set out to discover the fundamentals of a character analysis essay , delving into its definition, significance, and constituent parts.
Understand Character Analysis Essay
What is a character analysis essay? Character analysis is a critical process that involves examining the traits, motivations, and development of characters in a literary work. It goes beyond mere observation, requiring readers to delve into the intricacies of characters’ personalities, actions, and relationships. Characters serve as conduits through which readers explore the depths of human nature, embodying universal themes and aspects of behavior.
Characters analysis offers profound insights into the human condition and enhances comprehension by enabling readers to grasp the underlying messages, themes, and conflicts within a story. Character analysis fosters critical thinking by encouraging readers to interpret evidence, form connections, and form informed opinions about the text.
Key components of the character analysis essay include personality traits, character development, motivations and goals, relationships, and symbolism and archetypes. Personality traits provide insights into the character’s strengths, weaknesses, virtues, and flaws, while character development examines how the character evolves and changes throughout the story. Understanding these components enhances the reading experience and instills a deeper appreciation for the artistry of storytelling.
Selecting the Character
What is a character analysis selection process? Selecting a character for analysis is crucial for crafting a compelling and insightful essay about a character . Some tips to guide in choosing the most suitable character include considering their significance, complexity, contrasts, personal interest, availability of textual evidence, and relevance.
Choosing a character integral to the plot is essential for conducting a meaningful character analysis essay that sheds light on the central themes and conflicts of the story. Characters are the driving force behind the plot, shaping events and conflicts that unfold within the story. Analyzing a character central to the plot allows for a deeper understanding of the story’s progression and thematic significance. They often embody the central themes and motifs of the narrative, allowing readers to uncover deeper layers of symbolism embedded within the text.
Analyzing a character central to the plot provides context for understanding the motivations, conflicts, and relationships that drive the narrative forward. Characters who play pivotal roles in the plot are often more compelling and memorable to readers, engaging them deeper and encouraging deeper engagement with the text.
Analyzing a character that resonates with the writer on a personal level can greatly enhance the depth and authenticity of the analysis. The benefits of choosing a character that resonates with the writer include emotional investment, empathy and understanding, authenticity, and insightful reflection.
Emotional investment allows for a deeper level of engagement with the text, fueling the passion for the analysis and inspiring insightful observations. Empathy and understanding enable readers to empathize with the character’s experiences, motivations, and struggles, leading to a more nuanced analysis.
Authenticity lends authenticity to the analysis, as it reflects genuine thoughts and feelings about the character. Insightful reflection prompts insights into one’s own experiences, beliefs, and values, enriching the analysis and adding depth to understanding both the character and oneself.
By choosing an essay about a character that resonates with the writer personally, one can infuse their analysis with authenticity, empathy, and emotional depth, resulting in a more compelling and insightful exploration of the text.
Gathering Evidence
Character analysis is a crucial process in understanding a character’s personality and behavior. To learn how to write a character analysis essay correctly, it is essential to gather textual evidence, such as close reading, note-taking, annotation, character profiles, comparative analysis, and archetypal analysis. These methods help extract relevant information from the text, providing a foundation for your analysis.
Archetypal analysis can explore how the character embodies archetypal traits or roles commonly found in literature, such as the hero, villain, mentor, or trickster. By carefully identifying and documenting the various traits exhibited by the character, you can develop a nuanced understanding of their personality and behavior.
Supporting details play a crucial role in bolstering your character analysis essay , providing concrete evidence to support your interpretations and arguments. To effectively utilize specific examples from the text to support your analysis, select relevant examples that directly relate to the traits, motivations, and actions you are analyzing.
Provide context by introducing each example with a brief explanation or summary of its significance within the larger narrative. Analyze the example in detail, pointing out specific details or language choices that illuminate the character’s traits or motivations. Incorporate quotations from the text whenever possible, using quotation marks to indicate the exact words spoken or written by the character.
When analyzing supporting details, consider multiple perspectives: Acknowledge alternative interpretations and perspectives, but provide reasons why your analysis is the most valid or persuasive. By effectively utilizing specific examples from the text to support your character analysis essay , you can strengthen your arguments and provide readers with a deeper understanding of the character’s role within the story.
Character Analysis Essay Outline
Let’s have a look at the character analysis essay outline and how to write it perfectly.
- Start with a hook or question about the character.
- Provide background information and the thesis statement.
- Describe the character’s role, appearance, and initial impressions.
- Identify and discuss the primary traits of the character.
- Explore the character’s desires, fears, and motivations.
- Analyze the character’s evolution throughout the story.
- Discuss key events or turning points that shape the character’s development.
- Examine the character’s interactions with other characters.
- Discuss the character’s role in the plot.
- Explore how the character embodies or reflects the story’s themes and symbols.
- Analyze how the character’s actions affect the plot’s progression.
- Provide specific quotes or passages from the text.
- Illustrate key character traits with examples of their actions or dialogue.
- Interpret symbols or imagery associated with the character.
- Restate the thesis.
- Recap key points
- End with a thought-provoking statement.
By following this outline for a character analysis essay , you can structure your essay effectively, providing a comprehensive analysis of the chosen character while engaging the reader from start to finish.
Character Analysis Essay Structure
Character analysis essay format typically follows a three-part format: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. The introduction serves to introduce the character being analysed and provide context for the analysis. Create a compelling introduction, start with a hook, write background information, and introduce the thesis statement. End the introduction with a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose and focus of the essay. This will set the stage for a compelling and engaging character analysis essay.
The body paragraphs delve into the analysis of the character, each focusing on a specific aspect or trait. Each essay paragraph should begin with a topic sentence, followed by supporting evidence from the text and an analysis that explores the significance of the evidence in relation to the character’s development and role in the story. Organizing the analysis into coherent paragraphs is essential for presenting a logical and persuasive argument.
The conclusion of the character analysis essay summarises the analysis’s main points and reinforces the character’s significance within the narrative. It restates the thesis statement in different words, provides a brief recap of the main arguments presented in the essay, and offers final insights or reflections on the character’s importance and impact on the story.
By following these guidelines, you can craft a conclusion that reinforces the significance of the character and provides a satisfying conclusion to the essay.
Process of Analyzing a Character
Character Development:
- Initial Impression: Discuss the character’s introduction and personality traits.
- Growth and Change: Analyze how the character evolves and changes over the story.
- Internal Conflict: Explore internal struggles or conflicts the character faces.
- Relationships: Examine the character’s relationships with other characters and how they evolve.
- Resolution: Evaluate the character’s development at the end of the story.
Motivations and Actions:
- Identify Core Motivations: Understand what drives the character to act and the underlying reasons behind their behavior.
- External Influences: Analyze the external factors that influence the character’s motivations and actions.
- Internal Conflicts: Explore any internal conflicts or contradictions within the character that influence their motivations and actions.
- Character Consistency: Evaluate the consistency of the character’s motivations and actions throughout the text.
- Consequences of Actions: Discuss the consequences of the character’s actions and decisions within the narrative.
Impact on the Narrative:
- Plot Development: Examine the character’s role in advancing the plot and driving the story forward.
- Theme Exploration: Analyze how the character embodies or reflects the story’s central themes and motifs.
- Symbolic Significance: Explore any symbolic significance associated with the character and their role in the story.
- Influence on Other Characters: Discuss how their relationships, actions, and decisions impact the development and behavior of other characters.
- Resolution and Conclusion: Evaluate the character’s ultimate role in the resolution and conclusion of the story.
By discussing what is character analysis significance in shaping the story, you can provide a comprehensive analysis of their role and impact within the narrative, highlighting their contribution to the overall meaning and interpretation of the text.
Polishing and Refining
Proofreading is an important step in the editing process, ensuring your writing is free from errors and effectively communicates your ideas. To correct errors in grammar, punctuation, and syntax, take a break, read aloud, use editing tools, focus on one element at a time, print and review, and seek feedback from peers or instructors.
Polishing involves refining language, strengthening arguments, and enhancing the overall clarity and coherence of your work. Techniques for polishing your writing include clarifying your thesis, tightening your writing, strengthening your arguments, enhancing transitions, checking for consistency in tone, style, and formatting, and proofreading carefully.
Afterthoughts on Character Analysis Essay
A profound character analysis essay offers a profound understanding of the human psyche, storytelling, and the timeless relevance of literature. By examining character traits, motivations, and impact on the narrative, students gain a deeper understanding of universal themes, conflicts, and complexities of the human experience.
- Academic Writing Guides
- Citation Guides
- Research Paper Writing Guides
- Study Tips and Tricks
Featured articles

How to Title an Essay? Everything an Essay Guru Should Know
As soon as you sit down to compose an academic paper, you may be troubled by how to name your essay so that it reveals the essence of your text and grabs the audience’s attention at first sight. Ideally, that’s what a good title should achieve – informing and engaging. So, what’s the secret recipe […]
Author: Marina Kean

Strategies for Writing a Great Problem Solution Essay
Composing an assignment on a problem and solution essay topic allows you to demonstrate your ability to resolve human challenges. It helps you understand human problems and how to be a part of the solution instead of allocating blame and pointing fingers. So, how do you compose a great problem solutions essay? This post has […]
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay With Examples and Tips
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 4453 words
- Icon Clock 20 min read
Essay writing is an exciting and valuable academic exercise for students at all levels of learning. Basically, the practice helps in developing students’ critical thinking skills. For example, when writing a character analysis essay, students use these skills to cover a specific character’s personality and mannerisms objectively. Moreover, this type of essay aims to analyze a character in a story in such a way that readers can develop a mental picture of them. In this case, the secret of writing a good character analysis essay involves choosing a dynamic character, such as a protagonist or an antagonist. Then, another tip is to write the first draft and read it at least twice to identify and correct errors and mistakes. In turn, the final draft should reflect a perfect document. Hence, students need to learn how to write a good character analysis essay with its features.
Definition of a Character Analysis Essay
Among many different types of essays is a character analysis essay, a text that describes a particular character in a story. When writing this essay, students analyze relationships between characters in question and other characters, paying particular attention to their mannerisms. Also, these mannerisms are exemplified by their behaviors, styles of speaking, physical appearances, and many other characteristics. Even though students may offer their personal opinions when analyzing specific characters, they must employ critical thinking and be objective. In essence, what matters in a character analysis essay is factual information about a character in question. In this case, the writer’s opinion should support rather than challenge the specific traits and characteristics of a character. Hence, a student writes this type of essay when instructions require them to discuss how a particular character is shaped in a story.

Types of Characters
When analyzing a character in a story, writers must first understand what kinds of characters are their subjects. Typically, there are different types of characters whose distinctions are based on particular behaviors, traits, and roles that they exemplify within a story. In turn, the main character types fall under five categories: major, minor, dynamic, static, and stoic.
1. Major Characters
In a story, major characters run a storyline, and they define a plot of this story. For example, there are two types of major characters: protagonists and antagonists. In this case, the former represents typical heroes, those characters that the audience is likely to admire. Then, the latter represents characters that take the role of a villain. Basically, the audience is likely to despise this type of character. Moreover, it is easier to spot protagonists because a story’s plot revolves around them. In literature, examples of protagonists include Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, Othello from the tragedy Othello by William Shakespeare, Elizabeth Bennet from “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen, and Frodo from The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien. On the other hand, examples of antagonists from the literature include King Joffrey from Game of Thrones , Darth Vader from the Star Wars series by George Lucas, and the Wicked Queen from “Snow White and Seven Dwarfs.”
2. Minor Characters
As opposed to major characters, minor characters do not run stories. However, they are ones that help major characters to shine through storylines. In other words, minor characters in the course of their activities help main characters to create situations and circumstances that reveal the central characters’ personalities. As explained, this personality is defined by mannerism. Then, examples of minor characters in the literature include the whole Fellowship of the Ring in J.R.R Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings. Individually, these characters help Frodo, a protagonist, to deliver the Ring to Mordor. In turn, another example of minor characters in literature is the duo Ronald Weasley and Hermione Granger in J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series. On several occasions, they help Harry Potter, a protagonist, in his battle against Voldemort.
3. Dynamic, Static, and Stoic Characters
Dynamic characters are those characters that change the course of a story in certain respects. In many cases, a protagonist is a dynamic character. Moreover, an example in the literature is Harry Potter from J.K. Rowling’s book series, who notices that he is similar to Voldemort in many ways throughout a storyline. Nevertheless, he resists “dark” traits that define Voldemort because he is a good person. As such, he resists any temptation to become a dark wizard. On the other hand, static characters never change in a story. Also, an excellent example in the literature is Atticus Finch from “How to Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee. Despite finding himself in controversial circumstances, he remains firm in character and worldview throughout a story. Further on, stoic characters draw attention to the main character(s), and their role in a story is to fortify the protagonist’s role and image. In turn, a great example of a stoic character in literature is Dr. Watson from Sherlock Holmes by Arthur Conan Doyle.
Step 1: Preparation
Preparation is the starting step in writing a critical analysis essay. In essence, this step involves planning how to go about writing. Basically, a student reads a story, chooses a character, defines a topic, prepares ideas, and considers the audience and its needs. In this case, the essence of preparation is that it enables students to “get it right” from the beginning. Moreover, it is by preparing that students take into consideration requirements and seek clarification as necessary.
A. Reading a Story
In most instances, instructors guide students on which story to read and a character to analyze. However, if such guidance is not provided, a student should – as a matter of priority – choose a story and a character in this story to write about. About a story, writers should read it at least twice to have a good understanding of a plot and each character’s role.
B. Choosing a Character
The standard practice is that a character analysis essay focuses on major characters (protagonist and antagonist) as subjects of analysis. However, as indicated, an instructor may require students to analyze a specific character. In this case, instructions can require students to explore how a minor character enhances a major character’s image in a story. Also, the writer’s issue is to identify characters for analysis and read all about them in an assigned story.
C. Defining a Topic
Like any essay, a character analysis essay should have a topic. Basically, even though the goal is to analyze a specific character, writers must have a topic that underscores their work. When defining a topic, students may follow the instructor’s prompt or develop their own approach. Ultimately, a character analysis essay topic should align with the paper’s goal, which is to analyze a specific character.
D. Preparing Ideas
Typically, students get ideas about their work as soon as they read prompt requirements given by their instructors. When writing a character analysis essay, a student should generate ideas after reading instructions and reading through them. However, it is the latter exercise that serves as the foundation of ideas for writing a text. Indeed, this aspect exemplifies the essence of a character analysis essay, focusing on how a character emerges from a story. As discussed, a character can only be a protagonist, antagonist, minor, dynamic, or stoic. Understanding where characters fit helps a writer to generate ideas about effects of their roles in a story. Here, students should apply critical thinking to dissect characters objectively.
E. Considering an Audience
Every form of writing has an audience – readers that writers have in mind when writing their texts. In essay writing, the main audience is the instructor. However, in an application essay for college, the audience is the admission board of a college or university. Since instructors determine the quality of a character analysis essay, students should consider their requirements. Ideally, these requirements reflect what instructors, as the audience, need regarding a character analysis essay.
Step 2: Setting Up the Stage
The second step in writing a character analysis essay is setting the stage for the actual writing of a text. Here, students engage in several activities, including finding credible sources, making notes, creating an essay outline, and creating an annotated bibliography. As an academic text, a character analysis essay should satisfy all academic writing conventions, including backing up claims and arguments with evidence. Although a learner can write about a character in a story by simply reading a story, a character analysis reflects an in-depth discussion about a specific character. Hence, students should write about what others (scholars) have said about a story and a character.
A. Finding Sources
Reliable sources are external texts that writers rely on to find evidence supporting what they intend to write. Basically, when writers make claims or observations when composing a text, they must back it up with evidence to avoid making what they write seems like a personal opinion. Notably, subjective opinion is not encouraged in academic writing, unless writers are using it objectively. Moreover, the only way that students can demonstrate that their essays are free of bias is by providing evidence for their claims, arguments, opinions, and observations. In turn, this evidence comes from external academic sources – books and journal articles.
B. Making Notes
After finding sources, a student should read through them while making notes. Basically, these notes should be relevant to a task at hand. Therefore, when authors of a character analysis essay find sources pertinent to their mission, they should make notes as they read through them and write down what they find interesting about their characters. Given that the task at hand involves analyzing a character in question, students’ notes should reflect a deeper understanding of this character, such as what others say about their manner of speaking or effect in a story.
C. Creating an Outline and an Annotated Bibliography
Like any other academic text, such as a research paper, a term paper, a Master’s thesis, or a dissertation, essays have outlines that provide a structure. Typically, this outline involves having three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. When writing a character analysis essay, a student should stick to this essay structure. Then, an annotated bibliography summarizes study sources that writers intend to use to get evidence that backs up their claims and arguments. Although it is not needed in an essay, students who write a character analysis essay can develop one based on credible sources that they identified in the second step of essay writing. In this case, annotated bibliographies would provide quick access to evidence that learners need to strengthen their papers.
Step 3: Actual Writing of a Character Analysis Essay
After preparing and setting the stage, authors of a character analysis essay begin the actual writing of a paper. Here, students begin with the first draft, which provides an opportunity to organize thoughts, make mistakes, come up with new ideas, find new sources that back them up, and alter a critical analysis essay outline. Basically, this stage is about putting everything together to develop an essay that addresses the instructor’s requirements.
A. Writing a First Draft of a Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, students are likely to make numerous spelling and grammatical errors and other mistakes, such as inconsistent arguments and illogical conclusions. As such, writing the first draft provides writers with this allowance since they would have an opportunity to perfect their work. Nonetheless, the first draft’s content should mirror the expected work, which is dissecting a character’s personality.
Step 4: Wrapping Up
After writing the first draft of a character analysis essay, students must read and reread their work to identify all mistakes and errors. As discussed above, the chances of the first draft having spelling and grammatical errors, illogical conclusions, and inconsistent arguments are high. In turn, this fourth step in writing a character analysis essay provides students with an opportunity to perfect their work. Here, learners revise and edit the first draft to eliminate all errors and mistakes and ensure that their papers reflect a format of an academic text in all aspects. Also, body paragraphs should have topic and concluding sentences, transitions, and right formatting. Additionally, writers should subject their work to peer review and then write the final draft.
A. Revising and Editing the First Draft
The purpose of reading the first draft at least twice is to identify all errors and mistakes, as explained above. Basically, once writers note them down, they should revise their papers accordingly, ensuring that all inconsistencies are corrected. Moreover, students should edit all spelling and grammatical mistakes to give a written document to look like a professional appeal.
B. Topic Sentences
The first statement that a student writes in every paragraph in the main text (body) should reflect a topic sentence. Basically, this sentence aims to introduce a single idea that a writer intends to develop in a paragraph. By considering a character analysis essay, this idea can be a claim or an observation about a subject under analysis. In this case, the standard practice is that a single idea that a writer expresses in a topic sentence should align with a paper’s thesis statement, as it is developed in the introduction part of a character analysis essay.
C. Concluding Sentences
While a topic sentence introduces a paragraph, a concluding sentence brings it to a close. For example, a reason why a student writes a concluding sentence is to finalize an intended message captured in a section. As such, it provides the writer’s concluding thoughts about a topic sentence and how it advances a thesis statement. Also, the content that comes between topic sentences and concluding sentences reinforces a sandwich rule: making a claim, backing it up with supporting facts, elaborating on it, and indicating its relevance in a context of a thesis.
D. Transitions
In writing a character analysis essay, students need to create a document with a natural flow from a beginning to an end. Basically, the aspect that enhances this flow is the use of transitions, which involve words and phrases, like “consequently,” “hence,” “thus,” “nonetheless,” “as such,” and “put differently.” In this case, a writer can use these words and phrases in any part of a text. However, using them in the main text is more appropriate as it is where writers need to create linkages between claims, evidence, and elaborations. Hence, transitions make such connections flawless and logical.
E. Formatting
When writing an academic text, it is critical for students to observe all academic writing rules. For example, one of these rules is writing a character analysis essay according to assigned rules that guide a paper format that learners are using to write their work. In this case, the main paper formats are APA 7, MLA 9, Harvard, and Chicago/Turabian, all of which differ in certain ways. For instance, they all have different requirements for citations and paragraph formation. Therefore, when writing a character analysis essay, a student should format a paper according to the appropriate writing format. Although learners may observe this rule when writing the first draft, they should certainly do so when creating the final draft.
F. Peer Reviewing
When writing a character analysis essay, students should ensure that their work is of high quality. Basically, what makes an academic text of high quality is peer review, which means subjecting a written work to a critical review by a friend, tutor, or mentor. For example, journal articles are regarded as peer-reviewed scholarly sources for a simple reason that they have been reviewed and made perfect. In turn, this perfection entails ensuring the absence of errors and mistakes and the use of credible and reliable sources.
Step 5: Writing a Final Draft of a Character Analysis Essay
The final draft represents the final work of a student in writing a character analysis essay. Basically, it is a document that students hand over to the audience by way of submission or publication. As such, writers must ensure that their texts are of the highest standard to eliminate the possibility of attracting penalties, such as a low grade or lousy review, in case they publish their work on online platforms. Also, to be clear that what students have is of the highest quality, they should read and reread their papers. In turn, it is the only way in which they can be sure that there are no errors or mistakes.
Simple Outline Example of a Character Analysis Essay
As indicated in the previous section, students should take time and create an outline for their work when writing an essay. This outline comprises three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion as below.
I. Introduction Paragraph II. Body Section (this part may include several paragraphs) III. Conclusion Paragraph
While most academic texts follow this outline, some papers differ on features that writers address in each section. Basically, when writing a character analysis essay, students should ensure that the introduction section highlights its thesis. In turn, this statement guides the entire writing, meaning that it is the central claim or idea in a paper. In body paragraphs, writers should ensure that topic sentences open each paragraph while concluding sentences end them. Moreover, learners should ensure sufficient and appropriate use of transitions and observance of a sandwich rule. In the conclusion section, students should restate the thesis and summarize the paper’s main points.
How Students Know That They Write a Character Analysis Essay
Generally, the purpose of a character analysis essay is to provide an in-depth analysis of a specific character. As such, writers know that they write a character analysis essay if their texts describe a given character’s personality and mannerisms. In turn, the latter entails how a character in question behaves, speaks, looks like (physical features), and their familial and social relationships, as it is covered in a story.
How a Character Analysis Essay Differs From Other Papers
When it comes to an outline, a character analysis essay is similar to other types of papers. However, regarding the content, this type of essay differs from other papers significantly. For example, an argumentative essay focuses on making the writer’s argument acceptable to the audience, meaning that the content revolves around the writer’s perspective regarding an issue. In contrast, a character analysis essay focuses on providing the audience with a detailed picture of a specific character in a story, meaning that the content revolves around a subject (character). In an informative essay, the writer’s goal is to educate the audience about a topic or an issue, meaning that the content revolves around explaining concepts relating to a specific theme in question. Therefore, the point of difference between a character analysis essay and other essay types is content more than structure.
Easy Strategies for Writing Each Section of a Character Analysis Essay
When it comes to the introduction, authors of a character analysis essay should provide a hook, which can be a statement, quote, or a joke. Basically, a hook sentence aims to grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading the entire paper. Then, if students know how to write a hook, they provide a brief background of a text after it. Also, it is where they introduce a story and a character under investigation. In turn, writers should conclude this section with a thesis, thus outlining the purpose of writing. About the main text (body), if learners are familiar with the rules of how to write a topic sentence, they begin each paragraph with it, which establishes a claim. Further on, the feature that follows is evidence (supporting facts) and then an explanation. As a result, the last element is a concluding sentence.
1. Paying an Attention
Based on the above information, it is evident that authors of a character analysis essay must pay attention to several things. In the introduction, writers should pay attention to the thesis, and, in the body paragraphs, they should follow a sandwich rule. Basically, this rule reinforces the claim-evidence-explanation approach. In the conclusion section, students should pay attention to the main points’ summary to make sure no new information is captured in this paragraph. Additionally, learners should ensure that they provide closing remarks, which emphasize their objective opinions about subjects matter.
2. Major Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Besides spelling, grammatical and other mistakes, writers of essays make other mistakes, leading to the fact that their work becomes less than high-quality. In writing a character analysis essay, one mistake that students make is to focus on a single aspect, such as personality, thereby undermining the subject’s full image. In this case, the solution to this mistake for a writer is to focus on the character’s mannerisms – behavior, speaking style, and appearance. Then, another mistake that learners make is to focus on aspects that do not advance an in-depth analysis of a subject, such as a story’s plot. In turn, the solution to this mistake for students is to focus on the subject’s roles in a plot’s context.
An Example of Writing a Character Analysis Essay
Topic: Frodo and His Heroic Weakness
I. Sample Introduction of a Character Analysis Essay
In literature, characters play an essential role in enhancing the plot of a story. Basically, they do this through their actions, behaviors, relationships, and other aspects of personality. Moreover, their mannerisms define who they are within the context of a story. In The Lord of the Ring , J.R.R. Tolkien captures a heroic conscience that characterizes human existence. Then, the author reveals the destructive power of greed and envy, mainly where promises are concerned. Nonetheless, Tolkien shows how friendship and courage overcome these vices. At the center of a story , The Lord of the Ring, is Frodo Baggins, a protagonist, who, despite undergoing a series of challenging adventures, emerges as a hero.
II. Example of a Body in a Character Analysis Essay
A. frodo as a hero.
Tolkien develops Frodo as a young hobbit with a remarkable character. As a ring-bearer of a fellowship, Frodo has the Ring that belongs to Sauron, the Lord of the Rings. As such, Sauron is an antagonist in a story. For example, he is “a dark lord who lost the one Ring that held much of his power” (Tolkien, 2003, p. 54). Then, the author describes the Ring as precious and powerful enough to enslave Middle Earth. While everybody is scared of the Ring and no one wants to lead its destruction, Frodo courageously overcomes such fear. Despite a myth that absolute evil and frightening dark forces are likely to victimize anyone who attempts to destroy the Ring, the young hobbit is keen to prove everybody wrong. In turn, it is the anger toward myths and oppressions that they seemed to cause people that motivate Frodo to act to restore safety in Middle Earth.
B. Frodo’s Weakness
The first indication of Frodo’s inexperience comes when he faces his initial challenges in his quest. Basically, how he deals with them reveals his weak points. For example, when Frodo delays his departure from the Shire, in spite of the urgency of the task ahead, he comes out as an indecisive character (Tolkien, 2003). Although a protagonist has common sense, he lacks wisdom, which is evident when he chooses to face the Old Forest’s dangers. Besides getting himself into harm’s way, Frodo also endangers the lives of his friends. In this case, he comes out as a fool in Bree when he draws unnecessary attention to himself. At Weathertop, the main character gives in to the temptation of putting on the Ring, thus exposing himself to an attack by the Ringwraiths (Tolkien, 2003). Despite all these shortcomings, Frodo survives the dangers of his own mistakes and those of his quest. Moreover, the novel attributes this success to the fact that hobbits are tougher than they look and can endure hardships. More importantly, Frodo himself is not interested in possessing the Ring, which makes him avoid the dark forces it represents. In this respect, he emerges as a hero in the end.
III. Conclusion Example of a Character Analysis Essay
Frodo’s adventure in The Lord of the Ring is a selfless quest to bring good to society despite powerful myths that undermine people’s courage to act when needed. In this case, Tolkien describes specific events that characterize the protagonist’s quest to destroy Sauron’s Ring. Moreover, what is clear is that Frodo is a courageous hobbit who refuses to be defined by his weaknesses. Eventually, his actions display his heroic character, one that defies all odds against him. In turn, a lesson from a story is that people do not need to be perfect to be heroes, but they need to aspire to do what is right.
Arthur, S. (2003). Walking with Frodo: A devotional journey through the Lord of the Rings . Carol Stream, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, Inc.
Summing Up on How to Write a Good Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, students must understand that this type of paper is different from all others. While an argumentative essay focuses on convincing the audience about an issue, a character analysis essay covers telling the audience about a specific character’s personality and mannerisms within the context of a story’s plot. As such, it also differs from an informative essay that focuses on educating the audience about a topic or an issue. Nonetheless, all these essays assume the same outline, which entails three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. In turn, when writing a character analysis essay, a student must note the following tips:
- Read the instructions carefully.
- Read a story.
- If there is no instruction about a character, choose a dynamic character, who is either a protagonist or antagonist.
- Reread a story and make notes that are specific to a chosen character.
- Develop a thesis statement.
- Draft an outline.
- Write the first draft.
- Read and reread the first draft to identify and correct errors and mistakes.
- Subject the first draft to a peer review.
- Write the final draft.
- Read and reread the final draft.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Write a Critical Response Essay With Examples and Tips
- 7 September 2020

Free Personal Narrative Examples: Basic Guidelines With Tips
- 5 September 2020

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.14: Sample Student Literary Analysis Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40514

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
While reading these examples, ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the essay's thesis statement, and how do you know it is the thesis statement?
- What is the main idea or topic sentence of each body paragraph, and how does it relate back to the thesis statement?
- Where and how does each essay use evidence (quotes or paraphrase from the literature)?
- What are some of the literary devices or structures the essays analyze or discuss?
- How does each author structure their conclusion, and how does their conclusion differ from their introduction?
Example 1: Poetry
Victoria Morillo
Instructor Heather Ringo
3 August 2022
How Nguyen’s Structure Solidifies the Impact of Sexual Violence in “The Study”
Stripped of innocence, your body taken from you. No matter how much you try to block out the instance in which these two things occurred, memories surface and come back to haunt you. How does a person, a young boy , cope with an event that forever changes his life? Hieu Minh Nguyen deconstructs this very way in which an act of sexual violence affects a survivor. In his poem, “The Study,” the poem's speaker recounts the year in which his molestation took place, describing how his memory filters in and out. Throughout the poem, Nguyen writes in free verse, permitting a structural liberation to become the foundation for his message to shine through. While he moves the readers with this poignant narrative, Nguyen effectively conveys the resulting internal struggles of feeling alone and unseen.
The speaker recalls his experience with such painful memory through the use of specific punctuation choices. Just by looking at the poem, we see that the first period doesn’t appear until line 14. It finally comes after the speaker reveals to his readers the possible, central purpose for writing this poem: the speaker's molestation. In the first half, the poem makes use of commas, em dashes, and colons, which lends itself to the idea of the speaker stringing along all of these details to make sense of this time in his life. If reading the poem following the conventions of punctuation, a sense of urgency is present here, as well. This is exemplified by the lack of periods to finalize a thought; and instead, Nguyen uses other punctuation marks to connect them. Serving as another connector of thoughts, the two em dashes give emphasis to the role memory plays when the speaker discusses how “no one [had] a face” during that time (Nguyen 9-11). He speaks in this urgent manner until the 14th line, and when he finally gets it off his chest, the pace of the poem changes, as does the more frequent use of the period. This stream-of-consciousness-like section when juxtaposed with the latter half of the poem, causes readers to slow down and pay attention to the details. It also splits the poem in two: a section that talks of the fogginess of memory then transitions into one that remembers it all.
In tandem with the fluctuating nature of memory, the utilization of line breaks and word choice help reflect the damage the molestation has had. Within the first couple of lines of the poem, the poem demands the readers’ attention when the line breaks from “floating” to “dead” as the speaker describes his memory of Little Billy (Nguyen 1-4). This line break averts the readers’ expectation of the direction of the narrative and immediately shifts the tone of the poem. The break also speaks to the effect his trauma has ingrained in him and how “[f]or the longest time,” his only memory of that year revolves around an image of a boy’s death. In a way, the speaker sees himself in Little Billy; or perhaps, he’s representative of the tragic death of his boyhood, how the speaker felt so “dead” after enduring such a traumatic experience, even referring to himself as a “ghost” that he tries to evict from his conscience (Nguyen 24). The feeling that a part of him has died is solidified at the very end of the poem when the speaker describes himself as a nine-year-old boy who’s been “fossilized,” forever changed by this act (Nguyen 29). By choosing words associated with permanence and death, the speaker tries to recreate the atmosphere (for which he felt trapped in) in order for readers to understand the loneliness that came as a result of his trauma. With the assistance of line breaks, more attention is drawn to the speaker's words, intensifying their importance, and demanding to be felt by the readers.
Most importantly, the speaker expresses eloquently, and so heartbreakingly, about the effect sexual violence has on a person. Perhaps what seems to be the most frustrating are the people who fail to believe survivors of these types of crimes. This is evident when he describes “how angry” the tenants were when they filled the pool with cement (Nguyen 4). They seem to represent how people in the speaker's life were dismissive of his assault and who viewed his tragedy as a nuisance of some sorts. This sentiment is bookended when he says, “They say, give us details , so I give them my body. / They say, give us proof , so I give them my body,” (Nguyen 25-26). The repetition of these two lines reinforces the feeling many feel in these scenarios, as they’re often left to deal with trying to make people believe them, or to even see them.
It’s important to recognize how the structure of this poem gives the speaker space to express the pain he’s had to carry for so long. As a characteristic of free verse, the poem doesn’t follow any structured rhyme scheme or meter; which in turn, allows him to not have any constraints in telling his story the way he wants to. The speaker has the freedom to display his experience in a way that evades predictability and engenders authenticity of a story very personal to him. As readers, we abandon anticipating the next rhyme, and instead focus our attention to the other ways, like his punctuation or word choice, in which he effectively tells his story. The speaker recognizes that some part of him no longer belongs to himself, but by writing “The Study,” he shows other survivors that they’re not alone and encourages hope that eventually, they will be freed from the shackles of sexual violence.
Works Cited
Nguyen, Hieu Minh. “The Study” Poets.Org. Academy of American Poets, Coffee House Press, 2018, https://poets.org/poem/study-0 .
Example 2: Fiction
Todd Goodwin
Professor Stan Matyshak
Advanced Expository Writing
Sept. 17, 20—
Poe’s “Usher”: A Mirror of the Fall of the House of Humanity
Right from the outset of the grim story, “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Edgar Allan Poe enmeshes us in a dark, gloomy, hopeless world, alienating his characters and the reader from any sort of physical or psychological norm where such values as hope and happiness could possibly exist. He fatalistically tells the story of how a man (the narrator) comes from the outside world of hope, religion, and everyday society and tries to bring some kind of redeeming happiness to his boyhood friend, Roderick Usher, who not only has physically and psychologically wasted away but is entrapped in a dilapidated house of ever-looming terror with an emaciated and deranged twin sister. Roderick Usher embodies the wasting away of what once was vibrant and alive, and his house of “insufferable gloom” (273), which contains his morbid sister, seems to mirror or reflect this fear of death and annihilation that he most horribly endures. A close reading of the story reveals that Poe uses mirror images, or reflections, to contribute to the fatalistic theme of “Usher”: each reflection serves to intensify an already prevalent tone of hopelessness, darkness, and fatalism.
It could be argued that the house of Roderick Usher is a “house of mirrors,” whose unpleasant and grim reflections create a dark and hopeless setting. For example, the narrator first approaches “the melancholy house of Usher on a dark and soundless day,” and finds a building which causes him a “sense of insufferable gloom,” which “pervades his spirit and causes an iciness, a sinking, a sickening of the heart, an undiscerned dreariness of thought” (273). The narrator then optimistically states: “I reflected that a mere different arrangement of the scene, of the details of the picture, would be sufficient to modify, or perhaps annihilate its capacity for sorrowful impression” (274). But the narrator then sees the reflection of the house in the tarn and experiences a “shudder even more thrilling than before” (274). Thus the reader begins to realize that the narrator cannot change or stop the impending doom that will befall the house of Usher, and maybe humanity. The story cleverly plays with the word reflection : the narrator sees a physical reflection that leads him to a mental reflection about Usher’s surroundings.
The narrator’s disillusionment by such grim reflection continues in the story. For example, he describes Roderick Usher’s face as distinct with signs of old strength but lost vigor: the remains of what used to be. He describes the house as a once happy and vibrant place, which, like Roderick, lost its vitality. Also, the narrator describes Usher’s hair as growing wild on his rather obtrusive head, which directly mirrors the eerie moss and straw covering the outside of the house. The narrator continually longs to see these bleak reflections as a dream, for he states: “Shaking off from my spirit what must have been a dream, I scanned more narrowly the real aspect of the building” (276). He does not want to face the reality that Usher and his home are doomed to fall, regardless of what he does.
Although there are almost countless examples of these mirror images, two others stand out as important. First, Roderick and his sister, Madeline, are twins. The narrator aptly states just as he and Roderick are entombing Madeline that there is “a striking similitude between brother and sister” (288). Indeed, they are mirror images of each other. Madeline is fading away psychologically and physically, and Roderick is not too far behind! The reflection of “doom” that these two share helps intensify and symbolize the hopelessness of the entire situation; thus, they further develop the fatalistic theme. Second, in the climactic scene where Madeline has been mistakenly entombed alive, there is a pairing of images and sounds as the narrator tries to calm Roderick by reading him a romance story. Events in the story simultaneously unfold with events of the sister escaping her tomb. In the story, the hero breaks out of the coffin. Then, in the story, the dragon’s shriek as he is slain parallels Madeline’s shriek. Finally, the story tells of the clangor of a shield, matched by the sister’s clanging along a metal passageway. As the suspense reaches its climax, Roderick shrieks his last words to his “friend,” the narrator: “Madman! I tell you that she now stands without the door” (296).
Roderick, who slowly falls into insanity, ironically calls the narrator the “Madman.” We are left to reflect on what Poe means by this ironic twist. Poe’s bleak and dark imagery, and his use of mirror reflections, seem only to intensify the hopelessness of “Usher.” We can plausibly conclude that, indeed, the narrator is the “Madman,” for he comes from everyday society, which is a place where hope and faith exist. Poe would probably argue that such a place is opposite to the world of Usher because a world where death is inevitable could not possibly hold such positive values. Therefore, just as Roderick mirrors his sister, the reflection in the tarn mirrors the dilapidation of the house, and the story mirrors the final actions before the death of Usher. “The Fall of the House of Usher” reflects Poe’s view that humanity is hopelessly doomed.
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Fall of the House of Usher.” 1839. Electronic Text Center, University of Virginia Library . 1995. Web. 1 July 2012. < http://etext.virginia.edu/toc/modeng/public/PoeFall.html >.
Example 3: Poetry
Amy Chisnell
Professor Laura Neary
Writing and Literature
April 17, 20—
Don’t Listen to the Egg!: A Close Reading of Lewis Carroll’s “Jabberwocky”
“You seem very clever at explaining words, Sir,” said Alice. “Would you kindly tell me the meaning of the poem called ‘Jabberwocky’?”
“Let’s hear it,” said Humpty Dumpty. “I can explain all the poems that ever were invented—and a good many that haven’t been invented just yet.” (Carroll 164)
In Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking-Glass , Humpty Dumpty confidently translates (to a not so confident Alice) the complicated language of the poem “Jabberwocky.” The words of the poem, though nonsense, aptly tell the story of the slaying of the Jabberwock. Upon finding “Jabberwocky” on a table in the looking-glass room, Alice is confused by the strange words. She is quite certain that “ somebody killed something ,” but she does not understand much more than that. When later she encounters Humpty Dumpty, she seizes the opportunity at having the knowledgeable egg interpret—or translate—the poem. Since Humpty Dumpty professes to be able to “make a word work” for him, he is quick to agree. Thus he acts like a New Critic who interprets the poem by performing a close reading of it. Through Humpty’s interpretation of the first stanza, however, we see the poem’s deeper comment concerning the practice of interpreting poetry and literature in general—that strict analytical translation destroys the beauty of a poem. In fact, Humpty Dumpty commits the “heresy of paraphrase,” for he fails to understand that meaning cannot be separated from the form or structure of the literary work.
Of the 71 words found in “Jabberwocky,” 43 have no known meaning. They are simply nonsense. Yet through this nonsensical language, the poem manages not only to tell a story but also gives the reader a sense of setting and characterization. One feels, rather than concretely knows, that the setting is dark, wooded, and frightening. The characters, such as the Jubjub bird, the Bandersnatch, and the doomed Jabberwock, also appear in the reader’s head, even though they will not be found in the local zoo. Even though most of the words are not real, the reader is able to understand what goes on because he or she is given free license to imagine what the words denote and connote. Simply, the poem’s nonsense words are the meaning.
Therefore, when Humpty interprets “Jabberwocky” for Alice, he is not doing her any favors, for he actually misreads the poem. Although the poem in its original is constructed from nonsense words, by the time Humpty is done interpreting it, it truly does not make any sense. The first stanza of the original poem is as follows:
’Twas brillig, and the slithy toves
Did gyre and gimble in the wabe;
All mimsy were the borogroves,
An the mome raths outgrabe. (Carroll 164)
If we replace, however, the nonsense words of “Jabberwocky” with Humpty’s translated words, the effect would be something like this:
’Twas four o’clock in the afternoon, and the lithe and slimy badger-lizard-corkscrew creatures
Did go round and round and make holes in the grass-plot round the sun-dial:
All flimsy and miserable were the shabby-looking birds
with mop feathers,
And the lost green pigs bellowed-sneezed-whistled.
By translating the poem in such a way, Humpty removes the charm or essence—and the beauty, grace, and rhythm—from the poem. The poetry is sacrificed for meaning. Humpty Dumpty commits the heresy of paraphrase. As Cleanth Brooks argues, “The structure of a poem resembles that of a ballet or musical composition. It is a pattern of resolutions and balances and harmonizations” (203). When the poem is left as nonsense, the reader can easily imagine what a “slithy tove” might be, but when Humpty tells us what it is, he takes that imaginative license away from the reader. The beauty (if that is the proper word) of “Jabberwocky” is in not knowing what the words mean, and yet understanding. By translating the poem, Humpty takes that privilege from the reader. In addition, Humpty fails to recognize that meaning cannot be separated from the structure itself: the nonsense poem reflects this literally—it means “nothing” and achieves this meaning by using “nonsense” words.
Furthermore, the nonsense words Carroll chooses to use in “Jabberwocky” have a magical effect upon the reader; the shadowy sound of the words create the atmosphere, which may be described as a trance-like mood. When Alice first reads the poem, she says it seems to fill her head “with ideas.” The strange-sounding words in the original poem do give one ideas. Why is this? Even though the reader has never heard these words before, he or she is instantly aware of the murky, mysterious mood they set. In other words, diction operates not on the denotative level (the dictionary meaning) but on the connotative level (the emotion(s) they evoke). Thus “Jabberwocky” creates a shadowy mood, and the nonsense words are instrumental in creating this mood. Carroll could not have simply used any nonsense words.
For example, let us change the “dark,” “ominous” words of the first stanza to “lighter,” more “comic” words:
’Twas mearly, and the churly pells
Did bimble and ringle in the tink;
All timpy were the brimbledimps,
And the bip plips outlink.
Shifting the sounds of the words from dark to light merely takes a shift in thought. To create a specific mood using nonsense words, one must create new words from old words that convey the desired mood. In “Jabberwocky,” Carroll mixes “slimy,” a grim idea, “lithe,” a pliable image, to get a new adjective: “slithy” (a portmanteau word). In this translation, brighter words were used to get a lighter effect. “Mearly” is a combination of “morning” and “early,” and “ringle” is a blend of “ring” and "dingle.” The point is that “Jabberwocky’s” nonsense words are created specifically to convey this shadowy or mysterious mood and are integral to the “meaning.”
Consequently, Humpty’s rendering of the poem leaves the reader with a completely different feeling than does the original poem, which provided us with a sense of ethereal mystery, of a dark and foreign land with exotic creatures and fantastic settings. The mysteriousness is destroyed by Humpty’s literal paraphrase of the creatures and the setting; by doing so, he has taken the beauty away from the poem in his attempt to understand it. He has committed the heresy of paraphrase: “If we allow ourselves to be misled by it [this heresy], we distort the relation of the poem to its ‘truth’… we split the poem between its ‘form’ and its ‘content’” (Brooks 201). Humpty Dumpty’s ultimate demise might be seen to symbolize the heretical split between form and content: as a literary creation, Humpty Dumpty is an egg, a well-wrought urn of nonsense. His fall from the wall cracks him and separates the contents from the container, and not even all the King’s men can put the scrambled egg back together again!
Through the odd characters of a little girl and a foolish egg, “Jabberwocky” suggests a bit of sage advice about reading poetry, advice that the New Critics built their theories on. The importance lies not solely within strict analytical translation or interpretation, but in the overall effect of the imagery and word choice that evokes a meaning inseparable from those literary devices. As Archibald MacLeish so aptly writes: “A poem should not mean / But be.” Sometimes it takes a little nonsense to show us the sense in something.
Brooks, Cleanth. The Well-Wrought Urn: Studies in the Structure of Poetry . 1942. San Diego: Harcourt Brace, 1956. Print.
Carroll, Lewis. Through the Looking-Glass. Alice in Wonderland . 2nd ed. Ed. Donald J. Gray. New York: Norton, 1992. Print.
MacLeish, Archibald. “Ars Poetica.” The Oxford Book of American Poetry . Ed. David Lehman. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2006. 385–86. Print.
Attribution
- Sample Essay 1 received permission from Victoria Morillo to publish, licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International ( CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 )
- Sample Essays 2 and 3 adapted from Cordell, Ryan and John Pennington. "2.5: Student Sample Papers" from Creating Literary Analysis. 2012. Licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported ( CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 )

10 Literary Analysis Essay Examples
To write a literary analysis essay always understand the assignment thoroughly and identify the key elements e.g. plot, characters, and themes. Select a central theme to focus on and put together evidence to support your analysis.

Fredrick Eghosa
May 20, 2024

Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
How to structure a literary analysis essay, the introduction, start with an attention-grabbing hook:, provide context and background information., explain the significance of the work:, include your thesis statement., preview your main points:, body paragraphs, always start with a topic sentence:, provide textual evidence., identify and analyze the literary devices:, link back to the thesis statement:, use transitions:, restate your thesis statement:, summarize key points:, emphasize the importance of your analysis:, avoid introducing new information:, example conclusion:, how to write a literary analysis essay with a co-writer, analyze the assignment thoroughly., engage in active reading:, identify key elements, analyze narrative techniques, choose a theme to focus on using cowriter, identify potential themes in the literary work:, evaluate the significance and depth of the themes in the work:, tap into personal interest and interpretation:, examples of themes:, collect and interpret the evidence., write a thesis statement, develop your argument, refer back to your thesis statement, organize your essay structure, support your argument with evidence, use cowriter to write a rough draft., refine and review your essay, types of literary analysis essay, close reading analysis, character analysis, thematic analysis, comparative analysis, symbolism and allegory analysis, historical or cultural analysis, narrative or structural analysis, literary analysis essay examples pdf free download, wrapping up.

- A literary analysis essay extensively evaluates specific aspects of a literary work or the work as a whole and thoroughly examines elements such as character development, plot intricacies, and setting.
- A literary analysis essay follows the structure of a typical academic essay, including an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- To write a literary analysis essay, begin by thoroughly understanding your assignment and analyzing the chosen literary work. Identify critical elements in the literary work, such as plot, characters, and themes. Choose a central theme to focus on and gather evidence to support your analysis. Craft a strong thesis statement and develop a coherent argument. Proceed to write your essay and edit it to ensure it's error-free.
- You can use CoWriter to streamline and improve the writing process.
- There are different types of literary analysis essays, such as:
- Author's name
- Title of the work
- Any relevant context (historical, cultural, or biographical).
- For every theme you state and intend to explore, you must present specific quotes, passages, or scenes from the literary work(s) to support your argument.
- Explain how the textual evidence supports your argument and contributes to the thematic analysis.
- Reflect on your reading and note any recurring ideas, emotions, or messages the text conveys.
- Consider broader concepts explored in the work, such as love, power, identity, justice, freedom, or morality.
- Analyze characters' motivations and conflicts to uncover underlying thematic concerns.
- Choose a theme central to the narrative that plays a substantial role in shaping the characters or plot.
- Select a theme that allows for in-depth analysis and invites multiple interpretations. Avoid overly simplistic or superficial themes.
- Choose a theme that resonates with you or sparks curiosity. When you are genuinely interested in the theme, you can conduct thorough research and develop a compelling essay.

- Start by choosing specific quotes that are relevant to your analysis. Look for passages that contain vivid language, symbolism, or thematic significance.
- Pay attention to descriptive details, imagery, and figurative language used by the author to convey thematic messages.
- Proceed by providing the context for each quote to explain its significance within the narrative. Consider the surrounding events or character actions that give meaning to the quoted passage.
- Analyze and note how literary devices (e.g., metaphor, symbolism, foreshadowing) contribute to the thematic development in the quoted passages.
- Clearly state the connection between the selected evidence and your broader argument about the text.
- Acknowledge contradictory viewpoints and explain why your interpretation is more compelling or supported by the text.
- Group related pieces of evidence together based on thematic connections or arguments in your essay outline.

- Create a clear outline that outlines the main points and supporting evidence you will present in your essay. Organize your ideas logically to build a coherent argument.
- Create an outline and decide where each piece of evidence fits within your overarching argument. At this stage, you may need more supporting points.
- Use specific quotes, passages, or examples from the literary work(s) to support your interpretations and claims.
- After presenting evidence, analyze how it relates to your argument and thesis statement. Explain the significance of the evidence in the context of the broader themes or ideas you are discussing.

- Review the organization of your essay. Ensure each paragraph flows logically from one to the next, supporting your thesis statement.
- Confirm that each body paragraph begins with a clear topic sentence that relates directly to your thesis and sets the focus for the paragraph.
- Revisit your thesis statement. Ensure it presents your main argument and provides a roadmap for the reader to understand the scope of your analysis.
- Evaluate the textual evidence you've provided. Ensure each quote or example directly supports your points about the theme or argument.
- Throughout the essay, maintain a consistent focus on the chosen theme. Avoid tangential discussions that do not directly contribute to your central argument.
- Edit for grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure errors. Pay attention to spelling and word choice.
- Focuses on analyzing a specific passage, scene, or excerpt from a literary work in detail.
- Examines language, style, imagery, and literary devices to uncover deeper meanings and themes.
- Example: Analyzing the symbolism of the green light in F. Scott Fitzgerald's "The Great Gatsby" and its thematic significance.
- Analyze a specific character's development, motivations, and significance in a literary work.
- Explores how characters contribute to the overall themes and messages of the text.
- Example: Examining the character of Hamlet in William Shakespeare's "Hamlet" to understand his internal conflicts and role in the play's exploration of revenge and mortality.
- Focuses on exploring and interpreting a literary work's central themes or ideas.
- Examines how recurring themes contribute to the overall meaning and impact of the text.
- Example**: Analyzing the theme of isolation in Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein" and its implications for the characters' development and societal critique.
- Compares and contrasts two or more literary works, characters, themes, or authors.
- Highlights similarities and differences to deepen understanding of literary techniques, themes, or cultural contexts.
- Example: Comparing the depiction of women in Charlotte Bront's "Jane Eyre" and Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice" to explore differing perspectives on gender roles.
- Analyzes symbolic elements and figurative representations within a literary work.
- reveals hidden meanings and underlying messages conveyed through symbols, motifs, or symbolic narratives.
- Examines a literary work's historical, cultural, or social context.
- Investigate how historical or cultural factors influence the author's themes, characters, and narrative techniques.
- Focuses on analyzing a literary work's narrative techniques, structure, and form.
- Examines how narrative choices impact the reader's experience and contribute to thematic development.
Join other 3200+ writers now!
Ready to take the next big step for your writing?
Lead engineering teams at Figma, Pitch, and Protocol Labs.
Related posts

Apr 16, 2024
The Best Free AI MLA Citation Generator
The best free AI MLA citation generators are CoWriter, Opendemia, Scribbr MLA Citation Generator, MyBib, Citefast, Cite This For Me's MLA Citation Generator, and QuillBot M.L.A. Citation Generator. They stay updated on the latest MLA guidelines and can handle various source types like books, articles, and websites.

The Best Free Outline Generator for Essays
The best free outline generators for essay writing are CoWriter, Ahrefs Free AI Outline Generator, ClickUp, Jenni AI Essay Outline Generator, GitMind, Rytr, and Simplified. They streamline the process by generating structured outlines based on prompts and parameters.

Apr 12, 2024
The 7 Best AI Bibliography Generator
The best AI bibliography generators are CoWriter, Zotero, EndNote, Cite This For Me, Citation Machine, CiteMaker, and KnightCite. These tools streamline the citation process by supporting various citation styles, source types, and formatting options, ensuring accuracy and adherence to academic standards.

30 AI Prompts to Humanize Your Essay
AI prompts to humanize your essay are invaluable tools for students who want to humanize their AI-generated essays. With prompts for different writing styles and objectives, you can add personality, storytelling, humor, and clarity to their content.

The Best Free AI APA Citation Generator
The best free AI APA citation generators are CoWriter, Grammarly, SciSpace APA Citation Generator, Scribbr AI Citation Generators, Quillbot AI Citation Generators, Junia.ai, and Simplified. These generators use intelligent algorithms to automatically create citations for different sources, saving time and ensuring formatting and APA citation style accuracy.

How to Write a Biography Essay With Examples
To write a biography essay, choose an exciting subject, research extensively, and develop a thesis statement. Then, structure your essay chronologically or thematically, starting with a captivating introduction, exploring the subject's life in the body paragraphs, and concluding with its contemporary significance.

How is a narrative essay organized?
A narrative essay tells a story chronologically, beginning with an introduction, moving into a body where events build to a climax, and finishing with a resolution or final reflection.

Mar 27, 2024
How to Write a Biography Essay and Biography Essay Examples

Mar 25, 2024
The Good AI Review and Best Alternatives
Good AI is a handy platform that uses smart technology to assist with writing tasks. Its AI essay writer lets users quickly create 1,500-word, well-structured, and informative essays.

Jenni AI Review and Best Alternatives
Jenni.AI is an AI writer designed to assist with academic research and writing. It offers a great selection of features for academic purposes, including a built-in research engine. The best alternatives for Jenni AI you can try are CoWriter, Jasper AI, Copy AI, Frase.io, and Writesonic.

Mar 24, 2024
10 Steps to Writing an Informative Essay with an Outline
To write an informative essay with an outline, pick a topic, research it, and create an outline. Write an introduction with a hook and thesis, followed by body paragraphs with evidence. Conclude by summarizing the main points and restating the thesis. Finally, edit, cite sources, and submit.

Mar 11, 2024
5 Best AI Writer for Research Papers
The best AI writers for research papers are CoWriter, SciSpace Literature Review, Wordtune, Trinka, and Paperpal. These AI writers offer different functionalities, from grammar and citation checking to plagiarism detection and content generation.

Mar 16, 2024
The 5 Best AI Writer for Students
The best AI writers for students are CoWriter, Jasper, AI-Writer, Rytr, and Article Forge. Choosing the best AI writer for students depends on their needs. Some prioritize grammar and clarity assistance, while others focus on paraphrasing and summarizing.

10 Best AI Co-Writers
The best AI co-writers are CoWriter, HIX.AI, Copy.ai, Wordtune, Scalenut, Rytr, HyperWrite, Texta, TextCortex, and Writesonic. They can help generate ideas, overcome writer's block, and improve the flow of your writing.

Mar 18, 2024
How to Edit an Essay Written by AI to Perfection
To edit an AI-written essay perfectly, carefully read the text to ensure it makes sense and conveys your ideas. Please review the entire piece to grasp its tone, purpose, and quality, as AI-generated content often lacks logical progression and may have gaps, awkward transitions, or readability issues.

Best Free AI Paper Writer
The best free AI paper writers are CoWriter, Rytr, Simplified, CopyAI, Writesonic, Grammarly, and Paperpal. These tools can help you brainstorm or start and polish your paper.

How To Write A Research Paper With AI
To write a research paper, ensure you understand the assignment, choose an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, develop a clear thesis statement, and create a structured outline. Write while integrating research findings, then revise for clarity and coherence. Finally, edit for accuracy and adhere to formatting guidelines to present a polished and professional paper. You can use an A.I. writing assistant to optimize and streamline entire writing.

How To Write A Research Proposal With AI
To write a research paper using A.I., define your research topic and formulate straightforward, specific research questions, use A.I. to streamline the literature reviews, refine methodologies, and create a structured proposal outline, draft your proposal using the outline you created. Use an A.I. writing assistant for revision, correcting errors, and enhancing clarity; incorporate visual aids to show critical concepts effectively. As such, define your research topic and formulate straightforward, specific research questions. Use AI to streamline the literature reviews, refine methodologies, and create a structured proposal outline. Draft your proposal using the outline you created. Use an AI writing assistant for revision, correcting errors, and enhancing clarity.

Can AI Write An Annotated Bibliography
A.I. can write an annotated bibliography by curating and organizing relevant sources. It can generate concise summaries that outline each source's content, relevance, and significance to your research. A.I. writing assistant streamlines the process of compiling an annotated bibliography, saving time and effort while ensuring the inclusion of informative annotations for each source.

How To Write A Historical Essay Introduction
To write a historical essay introduction, begin with an engaging hook, like a thought-provoking quote or a question. Follow this with background details about your topic and conclude with a clear thesis statement. Utilize CoWriter to assist in composing your introduction.
.jpg%3Ftable%3Dblock%26id%3D011c22f2-6b48-44a5-a3ab-00a65e117aee%26cache%3Dv2&optimizer=image&quality=80&width=280)
How To Write a 4-Paragraph Essay
To write a 4-paragraph essay effectively, start by thoroughly researching your topic. This step is crucial for gathering supporting information. Next, create a structured outline that divides your essay into four clear paragraphs. Draft your thesis statement to convey the topic of your essay. With the outline in place, draft your essay following the outlined structure. Finally, take time to edit and proofread your essay.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Character
I. What is Character?
A character is a person, animal, being, creature, or thing in a story. Writers use characters to perform the actions and speak dialogue, moving the story along a plot line. A story can have only one character (protagonist) and still be a complete story. This character’s conflict may be an inner one (within him/herself), or a conflict with something natural, such as climbing a mountain. Most stories have multiple characters interacting, with one of them as the antagonist, causing a conflict for the protagonist.
II. Examples of Character
A popular television series that just ended is the show “Glee.” Each season had popular characters who had to learn to work together to create a good musical production. Various characters underwent a change, making them a dynamic character, such as Noah Puckerman. He appears to carry out the stereotype of a jock (strong but not so smart), but his character changes as it’s revealed that he can be hard working and intelligent.
A movie that features one character throughout most of it is “Castaway” with Tom Hanks. His character is on board a shipping plane when it crashes. He’s the only survivor, trapped on an island for four years. This movie focuses on his psychological (mental) and physical condition as he slowly adapts to a life of isolation, living alone on an island that is off all regular sea and airplane routes. It’s a great example of how a story can work with only one character, although many minor characters appear in the beginning and end.
III. Types of Character
A. major characters.
These are the most important characters in the story. There are two types, of which there may be a couple for each.
- Protagonist – This is the main character, around which the whole story revolves. The decisions made by this character will be affected by a conflict from within, or externally through another character, nature, technology, society, or the fates/God.
- Antagonist – This character, or group of characters, causes the conflict for the protagonist. However, the antagonist could be the protagonist, who is torn by a problem within. Most times, something external is causing the problem. A group of people causing the conflict would be considered society, perhaps the members of a team, community, or institution. Additionally, the antagonist could be a part of nature, such as an animal, the weather, a mountain or lake. A different kind of antagonist would be an item such as a pen, car, phone, carpet, etc. These are all considered technology, since they are instruments or tools to complete a job. Finally, if the conflict comes from something out of the character’s control, the antagonist is fate or God.
b. Minor characters
These are the other characters in a story. They are not as important as the major characters, but still play a large part in the story. Their actions help drive the story forward. They may impact the decisions the protagonist or antagonist make, either helping or interfering with the conflict.
Characters can have different traits. Major characters will usually be more dynamic, changing and growing through the story while minor characters may be more static.
- Foil – A foil is a character that has opposite character traits from another, meant to help highlight or bring out another’s positive or negative side. Many times, the antagonist is the foil for the protagonist.
- Static – Characters who are static do not change throughout the story. Their use may simply be to create or relieve tension, or they were not meant to change. A major character can remain static through the whole story.
- Dynamic – Dynamic characters change throughout the story. They may learn a lesson, become bad, or change in complex ways.
- Flat – A flat character has one or two main traits, usually only all positive or negative. They are the opposite of a round character. The flaw or strength has its use in the story.
- Round – These are the opposite of the flat character. These characters have many different traits, good and bad, making them more interesting.
- Stock – These are the stereotypical characters, such as the boy genius, ambitious career person, faithful sidekick, mad scientist, etc.
IV. The Importance of Character
Characters are what make stories. Without a character, there is no story to tell, only a lot of scenery. Many characters in literature, television series, and movies have a huge impact on people. Some people like to live their lives through these characters, who appear to have more exciting lives. Also, these characters may seem so real and inspirational, that people forget they are fictional.
Characters become so important to the audience, that cities across the country hold conventions in which people pay a lot of money to dress and act as their favorite characters from multiple types of shows, particularly of the comic magazine genre (type of literature).
V. Examples of Character in Pop Culture
The Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles have been keeping the city safe since the 1980s, but are still just as popular today. They each have their own special fighting method as well as personality. Originally simple, small turtles, they became super human, err turtle, after an accident in which the fish bowl of water they were in got knocked out of their owner’s hands and fell down a sewer grate, along with a canister of radioactive material. The rest is history. Nickelodeon has brought the characters back to fame, as can be seen on the channel and in the Nickelodeon Hotel in Orlando, Florida. The hotel features suites based on characters from the Nickelodeon shows for kids, and kids can interact with their favorite characters, including the Turtles, during breakfast and fun events. It’s clear that characters are an important part of our culture.
The characters are named after famous painters, and each turtle has his own personality to which different kids may relate. For example, Leonardo is the wise leader, the one who can keep the group focused. Raphael is the hothead. His temper wants to get the best of him, just as most of us would like to jump into things! Michaelangelo is the comedian. Like our class clowns in school, he’s the group clown. Finally, no group is complete without the geeky nerd. Donatello is always inventing things to help our turtle heroes in their adventures .
VI. Examples of Character in Literature
A book whose character was inspired by a real teenage girl is “The Fault in Our Stars” by John Green. The protagonist is 16-year-old Hazel, who meets Gus, a fellow 16-year-old cancer patient, at a camp. Their young romance is doomed as they are fighting a losing battle with cancer. Their strong spirits overcome their parents’ fears as the determined Hazel gets her wish to go overseas to meet an author she has long admired. The book has both characters undergoing change, very dynamic, as they struggle to adapt to their fate. The minor characters are impacted by the decisions Hazel and Gus make, giving depth to the story line. This book is an example of how authors take real life situations to create believable and interesting characters. Green’s inspiration for the story, Esther Earl, was a young fan with cancer who had wanted to meet him. He became friends with her and her family. She was diagnosed with cancer at 12 and died at 16.

VII. Related Terms
Archetype: A standard or stock type of character that appears in fiction, such as the villain, the hero, the damsel-in-distress, or the sidekick. Each archetype has more categories within, as well. For example, the villain could be a tyrant, devil, schemer, etc. The hero could be the warrior, proto-female, scapegoat, etc. These are especially common in fairy and folk tales.
VIII. Conclusion
Characters are the whole reason for any story. They can be used to help teach a lesson, to entertain, to educate, and even to persuade, depending on the author’s goal for the story line. Characters can be based on real people and events, or be totally unrealistic, such as space aliens. People become attached to characters as if they are real, may develop favorites, and relate to those that have faced similar situations.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
- Collections
- Support PDR
Search The Public Domain Review
Professor Megalow’s Dinosaur Bones Richard Owen and Victorian Literature
By Richard Fallon
Richard Owen, the Victorian scientist who first named the “dinosaurs”, claimed that he could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from inspecting a single bone. Richard Fallon revisits other Owen-inspired fictions — by R. D. Blackmore, William Makepeace Thackeray, and Charles Kingsley — and finds literature layered with scientific, religious, and political interventions, spurred by the discovery of prehistoric life.
May 2, 2024

“Professor Owen—On his Favourite Hobby”, colour zincograph by F. Gillot from the cover of an 1870 issue of The Period: An Illustrated Review of What Is Going On — Source .
Richard Owen, known today for coining the term “dinosaur” and founding London’s Natural History Museum, was Victorian Britain’s most celebrated comparative anatomist. He was also — to put it diplomatically — a divisive figure. Writing in 1851, one of his various scientific nemeses, Thomas Henry Huxley, considered it “astonishing with what an intense feeling of hatred Owen is regarded by the majority of his contemporaries”. 1 Yet, when one of his chief admirers, Richard Doddridge (R. D.) Blackmore, based a character in his latest novel on Owen, that character was intended to epitomize the famous naturalist’s “common sense, kindness and humility”. 2 Huxley and Blackmore were evidently seeing very different Owens.
We will return to Blackmore’s intriguing but now largely forgotten novel, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore, Bart., M.P., Formerly Known as “Tommy Upmore” (1884), in which Owen is transmuted into the kindly “Professor Megalow”. First, however, it must be asked why the man attracted such variety, and intensity, of feeling. In other words, why did so many fellow naturalists hate his guts? And why did so many titans of literary culture — including not just Blackmore but also Charles Dickens, William Makepeace Thackeray, and many others — find his recondite investigations into zoology and palaeontology so profoundly inspiring?

“Dinner in the Iguanodon ”. On New Year’s Eve, 1853, Owen presides over a meal celebrating the construction of model prehistoric animals at the Crystal Palace in Sydenham. Illustration after Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins from an issue of Illustrated London News that same year — Source .
Owen rose up from relatively unglamorous family roots in Lancaster, becoming curator, professor, and finally — in 1842 — conservator of London’s well-stocked Hunterian Museum of the Royal College of Surgeons. Superintendency of the natural history collections of the British Museum followed in 1856. Across both spaces, Owen had access to the finest zoological and palaeontological treasures of the ever-growing and ever-acquisitive British Empire. In addition to providing us with the dinosaurs, Owen’s accomplishments included the reconstruction of the New Zealand moa and the giant South American ground sloth Mylodon , pioneering work on the gorilla, and — both before and after the publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species (1859) — he postulated innovative if arcane theories of life’s natural development through time. 3 Museums were his speciality: Owen’s orchestration of the opening of the Natural History Museum in 1881, absorbing scientific collections formerly housed at the British Museum, capped an illustrious career.
Nonetheless, Owen’s egotism and inscrutability made him enemies in the scientific world from the start. This habit of acquiring adversaries eventually became a serious problem. In the late 1850s, tensions with the rising star Huxley were already foreboding future ill; in 1864, a powerful group calling itself the X Club formed to take charge of science’s role in society and stuck a more persistent thorn in Owen’s side. This influential group of secular scientific naturalists, whose members included Huxley as well as Herbert Spencer, stood for much that Owen detested. Their agnosticism and naturalistic interpretation of evolutionary processes — sometimes understood as driven by what Spencer termed “survival of the fittest”, or what Darwin called “natural selection” — were anathema to Owen’s theistic evolutionism, in which humans represent the apex of God’s providentially unfolding plan. Charles Kingsley’s classic children’s story The Water-Babies (1863) memorably satirized one of the most public clashes between Owen and Huxley, in which the former attempted to distance humans biologically from apes, while the latter, stressing our humble animal descent, did just the reverse.

Linley Sambourne depicts opponents Owen (left) and Huxley (right) in an 1885 edition of Charles Kingsley’s The Water-Babies — Source .

Owen dines at the Palaeontographical Society, accompanied by those prehistoric creatures whose fossil bones he knew so intimately. 19th-century lithograph by A. Orton after E. C. Rye — Source .
In addition to espousing a more compartmentalized view of the relationship between science and religion than Owen, and a less compartmentalized view of the relationship between humanity and other animals, those naturalists who came to form the X Club distrusted his pervasive influence over scientific culture. As such, many opposed his ambitious proposals for a separate Natural History Museum. Although he got his museum in the end, acolytes of Darwin and Huxley wrote much of the subsequent history, creating a caricature of Owen as a bigoted obscurantist. Notably, Darwin’s statue currently holds pride of place over Owen’s in the latter’s own museum.
Owen, however, enjoyed propagandistic powers of his own. He came to number leading politicians and members of the royal family among his intimate friends and whipped up excitement for his work in lectures and publications for general readers. Particularly integral to his reputation was the notion that Owen could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from a single bone. His most sensational feat concerned a broken femur found in New Zealand. When it was presented to Owen in 1839, he declared that this femur belonged to a then-unidentified ostrich-like bird. In 1843, further specimens vindicated his apparently audacious prediction and revealed that New Zealand had, indeed, once been infested by these giant, flightless moa birds, which Owen dubbed Dinornis . Contemporaries found this story of scientific wizardry utterly enchanting. The reality, which Owen’s media machine smothered with increasing severity, was slightly more mundane: John Rule, the surgeon who presented Owen with the femur, had already provided evidence for its avian origin.

Late in life, holding the famous femur in one hand and caressing a moa in another, Owen relives the high point of his career. Halftone after J. Smit after a photograph, ca. 1877 — Source .
Most of Owen’s contemporaries, however, knew nothing of John Rule. As his career thrived in the 1840s, Owen befriended more and more star-studded litterateurs, many of whose works he voraciously consumed in snatches of spare time. This was an era when palaeontological reconstruction, geological time, and extinction were thrilling and still relatively novel notions. Pre-Darwinian controversies over “development” (or, to use a more recognisable term, evolution) raged, while the largely Christian community of British naturalists continued to construct sophisticated ways of making sense of Earth’s history via liberal interpretation of the Book of Genesis — and vice versa. Owen, for his part, was happy to frame his work (or have others frame it) as confirming that even the most apparently monstrous prehistoric creatures were the products of God’s benign design, mysteriously unfolding over sublime aeons of deep time.
Owen’s ability to resurrect these strange animals from inadequate materials struck several leading novelists as an apt analogy for their own literary methods. “How can I tell the feelings in a young lady’s mind; the thoughts in a young gentleman’s bosom?” asks the narrator of William Makepeace Thackeray’s The Newcomes (1854–55). His justification is palaeontological: “As Professor Owen . . . takes a fragment of a bone, and builds an enormous forgotten monster out of it, wallowing in primæval quagmires . . . so the novelist puts this and that together: from the footprint finds the foot; from the foot, the brute who trod on it; from the brute, the plant he browsed on, the marsh in which he swam”. 4 For Thackeray, this quasi-scientific pedigree — not entirely proposed in jest — was gratifying, implying as it did that his gigantic works were painstakingly researched and planned.
Dickens was even closer to Owen. His periodicals, including Household Words , published Owen’s articles and promoted the naturalist’s ideas, from his moa mythmaking to his esoteric concept of the ideal “archetype” underlying all vertebrate forms. Nor did Dickens’ novels escape his friend’s osseous influence. Direct reference to Owen in Our Mutual Friend (1864–65) is admittedly limited to a droll description of the complacent Mrs Podsnap, a “fine woman for Professor Owen” possessing “quantity of bone, neck and nostrils like a rocking-horse”; nonetheless, as literary scholars like Gowan Dawson have shown, an Owenian language of palaeontological reassembly pervades this last of Dickens’ completed novels. 5 Not least in scenes including the bone collector Mr Venus and the wooden-legged Silas Wegg, the question of conjuring the whole from the part comes to symbolize, as in Thackeray’s The Newcomes , the task of the Victorian serial novelist, who must prove that isolated fragments are all integral contributions to a harmonious and insightful end product.

Satirical lithograph dating roughly to the 1840s: in a parody of the dagger scene in Macbeth , the dreaming palaeontologist is visited by creatures that he has perhaps, in waking life, striven to reconstruct — Source .
Thackeray and Dickens were just two of the famous authors who extolled Owen in his glory days. In 1884, R. D. Blackmore — to return, as promised, to Sir Thomas Upmore — gave Owen, in the form of “Professor Megalow”, a more prominent role than any author of fiction had ever attempted before, and at a time when the man himself was passing out of fashion. Although he only retired from the Natural History Museum the previous year, Owen’s scientific authority had been besieged for decades. Alienating Darwin and X Clubbers like Huxley had resulted in him being sidelined from many cutting-edge evolutionary discussions of later Victorian science, even if Owen continued to publish elaborate, lavishly illustrated zoological and palaeontological “memoirs” and monographs.
The two Richards — Owen and Blackmore — were fast friends (and fellow chess aficionados), living not far from each other in what is now the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames. Blackmore had previously shot to fame with Lorna Doone: A Romance of Exmoor (1869), a historical romance set in the seventeenth century which remains in print today. 6 Sir Thomas Upmore , which stands out among the author’s otherwise substantially rural literary oeuvre, has not enjoyed similar success, and the reasons are not far to seek. The Saturday Review ’s critic called it “neither allegory nor novel, neither satire nor romance, but a mixture – not altogether a successful mixture – of all four”. 7 Despite, or because of, this generic confusion, it is highly interesting to a present-day reader.
The titular character of Blackmore’s allegorico-romantico-satirico novel, like many fellow Victorian narrators, undertakes an upwardly mobile journey to gentlemanliness. The son of a soap manufacturer, young Tommy Upmore courts Laura, the beautiful daughter of Lady Twentifold of Twentifold Towers. To win the respect of the aristocratic Laura’s politically-obsessed brother, Roland, he must also win a seat as Conservative MP and fight off the onslaughts of Liberals pursuing a dramatic reform agenda. What distinguishes this novel from comparable realist works is its highly fantastic element: due to his body’s abnormal density, Tommy can fly, or rather float. At the end of the novel, he literally rises up above the party-political din in the House of Commons to unite Britain’s politicians in nationalistic fervour.

Watercolour by Ernest Griset depicting Richard Owen (seated) and the mineralogist Bryce Wright, ca. 1873 — Source .
Despite its protagonist’s ability to float above divisions, Sir Thomas Upmore is hardly a conciliatory novel. Although not as diehard a Tory as Roland, Tommy is shocked at the radical progressive reforms proposed by their Liberal foes (led by the smooth-talking Panclast): “grand measures were being prepared, for a fine subversion of established things; Liberal statesmen being quite convinced by their own condition, that the universe was wrong”. 8 Their nefarious plans include the abolition of land ownership, the secession of Britain’s strategic and colonial territories, and even the restitution of plundered artefacts. In addition to swiping at socialists and anarchists, Blackmore caricatured the reforming aims of prime minister W. E. Gladstone’s Liberal government, in power since 1880. In the eyes of the Saturday Review , the novel’s Panclast was “as like Mr. Gladstone as one pea is like another”. 9
Science is central to the novel’s conservative political intervention. Blackmore skewers “Professor Brachipod” and the collective of evolutionists brought in to investigate Tommy’s remarkable floating abilities. Insensitive to the boy’s feelings and quick to speculate baselessly about the origin of his powers, these “scientists” — a neologism Blackmore accompanies with scare quotes to indicate his distaste — are impious champions of scientific naturalism, like those men comprising the X Club. Blackmore’s targets are indicated not just by the scientists’ menacing association with vivisection, but also when they help overthrow the traditional classical curriculum of Tommy’s school, replacing it with a new, scientistic syllabus. Both the necessity of vivisection and the need for scientific instruction to accompany — or even replace — classical education, were standard talking points for men such as Huxley.
If Tommy mocks his scientific teachers’ incompetence in the field of ancient Greek and Latin, patrician Lady Twentifold is concerned by something deeper: the apparent atheism of the modern approaches to science they promulgate. “Who brought up this tree?” she asks, gesturing to a grand oak. While some, Tommy observes, would say “Nature”, “Science”, or “Accident”, she prefers to say “that the Almighty made it so”. 10 Luckily for both, a more positive model for the scientific practitioner is at hand: Professor Megalow, “whose name shall never be out-rubbed by time”, and whose face, when Tommy first encounters it, appears “the kindest and grandest I had ever seen”. 11

Photomechanical portrait of Richard Owen, ca. 1880s — Source .
Megalow is nothing like Brachipod (or their equally oddly named colleagues Jargoon, Chocolous, and Mullicles). A devout Christian, softly spoken, reluctant to construct premature hypotheses, and uninterested in fame or lucre, he dispenses wisdom to Tommy throughout the latter’s career. That Blackmore intended to flatter his friend is undeniable: he even wrote to Owen, asking permission to do so. Megalow was meant to be so recognisable “that the public . . . will exclaim at once ‘this must be Professor Owen’”. 12
As the title of an early chapter indicates, Megalow understands “True Science”. He is Blackmore’s ideal scientific practitioner, albeit one at odds with the times. “Even upon subjects, he understands more thoroughly than any other man yet born”, Tommy observes, Megalow “speaks (when he does speak at all) with more doubt, and diffidence, and humility, than a school-girl does, who knows nothing about it, except from one of his own books”. 13 Tommy’s old schoolmaster, the classics-obsessed Dr Rumbelow, calls him “a genuine acolyte of that glorious sage, Pythagoras”. 14 Himself an enthusiast and one-time tutor of classical literature, as well as a conservative in both politics and religion, Blackmore represented Owen as a reassuring and responsible steward of the era’s dramatic scientific advances.
Megalow’s standout scene takes place when Tommy and Laura help him to excavate a “Deino-Saurian” from a cliff face. It is tempting to suggest that this set piece reflects a growing interest in dinosaurs, catalysed by fossils unearthed in the United States during the 1870s and 1880s, including Brontosaurus and Stegosaurus . Owen himself, after all, had coined “dinosaur” back in 1842 and Megalosaurus was even one of the creatures included in his definition. For most of the nineteenth century, however, general audiences were surprisingly indifferent to the term “dinosaur” and Blackmore’s pedantic spelling suggests that the fossil is to be understood as some rather obscure animal. An arguably more pertinent reference point here is the moa: just as Owen had, according to the myth, predicted the form of the moa and been vindicated years later, the “Deino-Saurian” discovery acts as “tangible proof” of Megalow’s “inductions, published in a treatise ten years ago”. 15
Owen’s life-like restoration of Megalosaurus , one of the gigantic extinct creatures he included in his category “Dinosauria” and the origin of the name of Blackmore’s “Professor Megalow”. Illustration from Owen’s Geology and Inhabitants of the Ancient World (1854) — Source .

Detail from an 1863 engraving by C. G. Lewis after T. J. Barker of notables gathered at Buckingham Palace. Gladstone (left, seated) gestures to a military treaty, while Owen (right, with Dickens at his left shoulder), examines an invention — Source .
Strikingly, Megalow’s method is presented as a third way not just in science but also in the era’s polarized politics. In an otherwise polemical and reactionary novel, Megalow’s Liberal — and worse, “Rad” (Radical) — allegiance is repeatedly stressed. As the ultra-Tory Roland thunders, “[how] can such a great man as the Professor ever have become a Liberal?” 16 Indeed, while far from being a revolutionary, the real Owen’s early career had been steeped in the liberal Conservatism of reformist prime minister Robert Peel, who even commissioned a painting of Owen to hang in his country seat, Drayton Manor. In later decades, the Liberal doyen Gladstone himself became a major ally in Owen’s quest to establish the Natural History Museum, as well as supplementing the ageing anatomist’s pension and array of titles.
Admittedly, Tommy’s tolerance for his mentor’s inconvenient political beliefs is enabled by the latter’s reluctance to act upon them: Megalow “was not at all a partisan, or active politician, but quietly held his opinions, upon reasons which satisfied him, and therefore cannot have been weak ones”. 17 Attempting conciliation, Tommy concludes that the party governing Britain, “[w]hether it be Radical, or Tory, matters little to the average Englishman; so long as it acts with courage, candour, common sense, and consistency”. 18 (And, presumably, doesn’t meddle with landowners or the country’s colonial possessions.)
Sir Thomas Upmore is a fascinating and bizarre text (and, as readers will have noticed, an excellent repository of Victorian character names, including those of Tommy’s father Bucephalus, his friend Bill Chumps, and the formidable Lord Grando Crushbill). Far more so than its young leads and their somewhat perfunctory romance, Professor Megalow lingers with us as the novel’s most compelling character. A modest master of rarefied induction, and unwilling to pursue scientific theories with disruptive social consequences, he represents a safe pair of hands to usher in scientific modernity. This was something of the impression Blackmore absorbed in conversation with his accomplished friend, Owen, making Sir Thomas Upmore one of the century’s greatest love letters to one of its most controversial men of science.
Notes Show Notes
- Leonard Huxley, Life and Letters of Thomas Henry Huxley , 2 vols (London: Macmillan, 1900), I, 93.
- Letter quoted in undated catalogue of manuscript material for sale by Maggs Bros of London, “English Literature of the 19th and 20th Centuries … Part I”, no. 443, 30. Available here .
- For a classic study of Owen’s complex relationship with evolutionary thought, see Evelleen Richards, “A Question of Property Rights: Richard Owen’s Evolutionism Reassessed”, British Journal for the History of Science , vol. 20 (1987): 129–171.
- William Makepeace Thackeray, The Newcomes: Memoirs of a Most Respectable Family , 2 vols (London: Bradbury and Evans, 1855), II, 81.
- Gowan Dawson, “Dickens, Dinosaurs, and Design”, Victorian Literature and Culture , vol. 44 (2016): 761–778.
- For a concise modern biography of Blackmore, see Charlotte Mitchell, “Blackmore, Richard Doddridge (1825–1900), Novelist and Fruit Farmer”, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography , 23 Sep., 2004. Available here .
- “Two Novels”, Saturday Review , vol. 57 (1884): 755.
- R. D. Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore, Bart., M.P., Formerly Known as “Tommy Upmore” (London: Sampson Low, Marston, 1894 [1884]), 386.
- “Two Novels”, 755–756.
- Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore , 392.
- Ibid., 30–31.
- Maggs Bros, “English Literature of the 19th and 20th Centuries”, 30.
- Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore , 257.
- Ibid., 254.
- Ibid., 245.
- Ibid., 352.
- Ibid., 440.
Public Domain Works
- Internet Archive
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Google Books
- Internet Archive (volume 1)
- Internet Archive (volume 2)
Further Reading
For twenty years, the X Club was the most powerful network in Victorian science -- the men succeeded each other in the presidency of the Royal Society for a dozen years. Barton's group biography traces the roots of their success and the lasting effects of their championing of science against those who attempted to limit or control it, along the way shedding light on the social organization of science, the interactions of science and the state, and the places of science and scientific men in elite culture in the Victorian era.

Nineteenth-century palaeontologists boasted that, shown a single bone, they could identify or even reconstruct the extinct creature it came from with infallible certainty ― “Show me the bone, and I will describe the animal!” Show Me the Bone tells the story of the rise and fall of this famous claim. In so doing, Gowan Dawson reveals how decisively the practices of the scientific elite were ― and still are ― shaped by their interactions with the general public.

When the term “dinosaur” was coined in 1842, it referred to fragmentary British fossils. In subsequent decades, American discoveries — including Brontosaurus and Triceratops — proved that these so-called “terrible lizards” were in fact hardly lizards at all. Unlike previous scholars, who have focused on displays in American museums, Richard Fallon argues that literature was critical in turning these extinct creatures into cultural icons. Popular authors skillfully related dinosaurs to wider concerns about empire, progress, and faith; some of the most prominent, like Arthur Conan Doyle and Henry Neville Hutchinson, also disparaged elite scientists, undermining distinctions between scientific and imaginative writing. The rise of the dinosaurs thus accompanied fascinating transatlantic controversies about scientific authority.

In the mid-1850s, no scientist in the British Empire was more visible than Richard Owen. But, a century and a half later, Owen remains largely obscured by the shadow of the most famous Victorian naturalist of all, Charles Darwin. With this innovative biography, Nicolaas A. Rupke resuscitates Owen's reputation. Arguing that Owen should no longer be judged by the evolution dispute that figured in only a minor part of his work, Rupke stresses context, emphasizing the importance of places and practices in the production and reception of scientific knowledge.
The Public Domain Review receives a small percentage commission from sales made via the links to Bookshop.org (10%) and Amazon (4.5%). Thanks for supporting the project! For more recommended books, see all our “ Further Reading ” books, and browse our dedicated Bookshop.org stores for US and UK readers.
Richard Fallon is a postdoctoral researcher at the Natural History Museum and a knowledge exchange fellow at the University of Nottingham. His research focuses on literary culture’s relationship with geology and palaeontology. Richard received his doctorate in English from the University of Leicester in 2019 and completed a Leverhulme Trust Early Career Fellowship at the University of Birmingham in 2023. His books Reimagining Dinosaurs in Late Victorian and Edwardian Literature (Cambridge University Press) and Creatures of Another Age (Richmond, VA: Valancourt Books) were published in 2021.
The text of this essay is published under a CC BY-SA license, see here for details.
- Science & Medicine
If You Liked This…

Get Our Newsletter
Our latest content, your inbox, every fortnight

Prints for Your Walls
Explore our selection of fine art prints, all custom made to the highest standards, framed or unframed, and shipped to your door.
Start Exploring
{{ $localize("payment.title") }}
{{ $localize('payment.no_payment') }}
Pay by Credit Card
Pay with PayPal
{{ $localize('cart.summary') }}
Click for Delivery Estimates
Sorry, we cannot ship to P.O. Boxes.
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Lit Century
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

The Poetry of Chinese Names
Wendy chen on generation poems and the stories hidden in names.
My mother named me Wendy, after the character in Peter Pan . She had come across the animated film on the television one day and had been struck by the character’s creativity, imagination, and kindness. But that was not the only reason she settled on my name.
“Wendy” also converted easily into Chinese, where it became two characters: “wen” and “di.” The first character, “wen,” was the same as the first character of my sister’s name, thus emphasizing our sibling relationship and the fact that we were part of the same generation. “Wen” by itself was associated with the image of clouds forming different shapes, shapes my mother used to love gazing at in the sky as a child. When the two characters of my name were put together, the meaning was a reference to a part of a flower. This also matched my sister’s name, which had a similar floral meaning. Names related to flowers are common for daughters, as they are suggestive of beauty and sweetness.
Thus, the name my mother gave me had several stories to tell, as Chinese names often do. Chinese parents often choose names that reflect the hopes of the family—whether for their child’s personality or future. My name was chosen for its meaning, and also for its ability to signify my relationship with my sister and the specific generation I would be born into. Furthermore, my name with its bilingual nature reveals something about our family history: my parent’s choice to immigrate to America and embrace their new country.
When I was deciding on names of characters for my novel, Their Divine Fires , I wanted to choose names that held significance in terms of meaning and their relationship to generational and familial history. In order to do so, I looked to my family’s names for inspiration. This was a particularly useful strategy as Their Divine Fires is an intergenerational family epic, spanning a century in China and America.
For example, the names of my grandparents who were born in the 1930s in China reflects the vast social changes that were happening at the time. My grandmother’s name includes the character “ming,” meaning “bright,” a character typically reserved for sons. From what I’ve heard, my grandmother’s mother was a progressive woman for her time who had refused to bind her feet. I like to think that she chose “ming” for her daughter in the hopes she would lead a more liberated life. Over the course of my grandmother’s lifetime, gender expectations for women underwent a sea change. My grandmother ended up pursuing an education and becoming a doctor, leading an independent life that made her mother proud.
My grandfather, on the other hand, was born into a more traditional, wealthy family. One of the characters in his name had the character for “gold” within it. During the Communist Revolution, my grandfather, like many others, decided to change his name to one without such bourgeois decadence. He ended up choosing the character for “spring” as his new name, a name that represented a hopeful optimism for the future of the country.
The names of my parents’ generation—those born in the 60s—were heavily influenced by the nationalistic fervor of the time, the kind of fervor that would eventually drive the Cultural Revolution in China. Names reflected the interests of the nation, rather than the family. For example, names might include the character for “red” (a color associated with revolution), “army,” or even “peasant.”
Sometimes, names made references to Mao Zedong directly, such as the name “Weidong,” meaning “protect Dong” (as in Ze dong ). During this time period, one’s love for the nation could break even the strongest family bonds. It wasn’t uncommon for children to denounce their parents or students their teachers as antirevolutionary to the Red Guards, who might then humiliate, torture, and even kill these “enemies” of the state. Looking back on the names of my parents’ generation, I am better able to understand the pervasiveness of this fervor.
In Their Divine Fires , I also wanted to pay homage to the concept of a “generation poem.” This was inspired by my father’s family, who has a generation poem they have used for centuries. A generation poem is a poem that a clan agrees to use when naming their descendants. The first word of the poem would be used in the names of the first generation of the family clan. The second word of the poem would be used in the names of the second generation, and so on. When the family reaches the last word of the poem, they will start again at the very beginning.
A generation poem would typically be composed by important progenitors of the family; sometimes, a generation poem might even have been composed by the emperor himself and gifted to a noble family to honor them. In my novel, one of the families is more conservative and traditional, and using a generation poem for that family is a shorthand way to demonstrate those qualities.
When I reflect on the names of my family and each successive generation, I see glimmers of the history we’ve experienced. Our names illuminate our place in the family, and our place in history. Although the many wars, civil wars, and revolutions over the last century in China have destroyed most of my family’s paper records, our names are an inheritance that can never be confiscated or burned. The stories of our names can be passed down, generation to generation, and in that act alone, they hold great power. Choosing the right Chinese name is an act of love. More than that, it is an art.
_________________________________________

Their Divine Fires by Wendy Chen is available now via Algonquin Books.
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Google+ (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)

Previous Article
Next article, support lit hub..

Join our community of readers.
to the Lithub Daily
Popular posts.

Follow us on Twitter

Pulitzer Prize-Winner Ilyon Woo on Craft Lessons From the Late Filmmaker Dai Sil Kim Gibson
- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month

Writing Psychologically-Realistic Characters in Fiction
A psychiatrist-novelist reveals her writing methods..
Posted May 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- As readers, we usually want fictional characters to be both unique and psychologically realistic.
- Psychiatrist-novelists have a well of clinical experience teaching them how people feel, behave, and grow.
- Novelists have sometimes-unconscious reasons for choosing certain themes and characters to write about.

Good novelists create characters who are complex. unique, and have relatable human needs and feelings. Joyce Carol Oates is one of our best contemporary novelists, and has created a host of memorable characters. including a hippie, an imagined Marilyn Monroe, and a teenage boy. When she and I met and exchanged novels, she said: “You’re a psychiatrist and a novelist. What a great combination!”
There certainly are superb novelists who are also psychiatrists. Dr. Daniel Mason, for example, is both an inpatient psychiatrist and one of our finest contemporary writers of fiction. However, non- psychiatric physicians have also written psychologically rich characters. Dr. Abraham Verghese, for example, specializes in internal medicine. And many of the greatest novelists of all time who created complex characters: Dickens, Tolstoy, and Dostoevsky were neither psychiatrists nor physicians.
So how, then, are psychiatrist novelists “a great combination"?
The advantages of being a psychiatrist-novelist
Humans are fascinated by other people and their behaviors. From earliest childhood , we listen to and read stories to show how people face challenging situations. We psychiatrists have an added advantage. In our clinical work, we are privileged to hear the most private thoughts and feelings of many people: their fears, the different ways they have tried to protect themselves in difficult and often traumatizing relationships and situations. We also see how they change and grow. When creating fictional characters, we have access to this well of knowledge to write imaginary but psychologically realistic people.
The challenges
When it comes down to the writing, though, physicians have a disadvantage. We're trained to write clinical case histories in a rigid format: presenting problem, history of present illness, past medical history, family history, and so on. This is totally unlike the process fiction authors must master to write characters that come alive on the page. We physicians must put aside that ingrained pattern of straightforward reporting if we are to write good fiction.
One psychiatrist-novelist’s process of writing
Is our process of writing fiction different from that of other novelists? What follows is my own method. I tend to think it is not; readers here may hazard their own guess.
Finding a topic gripping to the novelist
A novelist will spend countless hours in his/her imagination , even more writing sentences, paragraphs, and chapters, then even more rewriting. Because of this heavy expenditure of energy and time, we must find a topic that fascinates us so much we are willing (or needing) to invest the months and years necessary to write about it.
In my case, the idea for my novel of psychological suspense, The End of Miracles , came directly from my clinical work as a psychiatrist. Over a period of a few months, I was asked to see three women, each with an extended false pregnancy , a condition technically named pseudocyesis.
In addition to my clinical interest in evaluating and treating them, and my scientific interest in studying their hormone levels, I also thought: wouldn’t it be fascinating to write a novel in which, at some point, the main character develops pseudocyesis?
Why was this topic so appealing? Only during the course of writing did the realization of the likely roots of my fascination become apparent.
Having an overarching goal
I'd long harbored a creative need to write a novel. I also wanted to add an engrossing book to the world of literature in return for the pleasure I’ve received from reading fiction since my childhood. As a psychiatrist, I set myself additional goals . I wanted to show psychiatrists as they really are, not as the devious or incompetent stereotypes so often portrayed in books or films. I wanted to show that people who develop a serious mental illness are not that different from the rest of us.
Creating the characters
One method I used was to become an actor. I'd pretend to be a particular character and then "listen to" their inner monologue and dialogue. Probably the easiest chapters to write were about the psychiatrist in the novel. I simply imagined myself in my own office, sitting across from the main character, Margo, and having a therapeutic session with her.
Writing the psychological roots of behaviors
It was very important to me to make Margo’s thoughts and actions grow out of her psychology. Once I'd written enough to know her feelings and behaviors in the present, I added to prior chapters instances of thoughts and experiences that were roots of the current ones.

In the process of writing this way, I discovered a possible clue as to why I was so attracted to the theme of a false pregnancy. A memory came to mind: 5-year-old me seeing my mother very pregnant, seeing babies in fancy carriages, seeing women nursing their babies. Likely I wanted a baby then, too—yet never got to have one. But these women who’d developed false pregnancies with distended abdomens had found a solution to that problem! Why hadn’t I thought of that? Well, now I had.
Writing suspensefully
I’ve read many thrillers, and now used the techniques I’d observed in them to create tension and a page-turning experience for my own readers. In the most suspenseful sections, I kept chapter lengths short and hinted in their last sentences that something crucial was about to happen,
Sending the book out into the world
Publication was a joy mixed with an unexpected momentary sense of loss. In a way, it resembled what it’s like when a baby is born: for many months, you’ve had a private, intimate relationship, and then it ends. Similarly, when my novel was published, there was a brief sadness about sending it out into the world to make new relationships with its readers.
The audiobook re-creation
When we read a book, we're not actually reading the same book as its other readers. We filter what we see on the page through our own experiences and understanding of the world. With an audiobook, the narrator voices the story and the characters through their own response to the text.
For The End of Miracle 's Audible audiobook, I listened to many of their narrators read aloud sections of other books and of my own before choosing the one whose voice resonated best with the story. I would be entrusting this person to be a kind of co-creator with me. It’s been gratifying to read comments of those who’ve both read and listened, writing they very much liked the print version and loved the audiobook. Then, I am reassured that I made the right choice.
The effect on one listener, though, was unexpected and humorous. My teenage grandson wrote on his Facebook page: “After reading the novel I listened to the audiobook and it was a relief to hear the phrase ‘egg showered in sperm’ in someone else’s voice instead of my grandmother’s.”
Starkman, M. (2016) The End of Miracles: A Novel, She Writes Press.

Monica Starkman, MD is a professor of psychiatry emerita at the University of Michigan. Her novel The End of Miracles is a suspenseful story about a woman who unravels psychologically after harrowing infertility and a tragic miscarriage, the shocking choices she makes, and the psychiatrists and close ones who try to save her.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Jump to navigation
War and Trauma Literature
We seek papers/article-length write-ups/essays/commentaries/causeries on war and representations in literature and allied subjects, exploring the trauma of psychological, physiological, socio-emotional, somatic, eco-environmental, financial, fiscal consequences on the subjects, economies. Papers across disciplines, dealing with the trauma/post-trauma in war literature will be undertaken for consideration. The twentieth-century war climate will particularly be the case in point. Articles/papers on novel ideations, unheard dimensions of wars of the past, in the nineteenth century or the troubled or strained nationalities/borders of the current world order, will also be considered. Battle-field horrors, fear-mongering, policy negotiations, imaginary lands, utopias/dystopias, failed social architecture, distorted political visions, destructive civil or military actions, revolutions, falling stocks, crippling economies, troubled poetic psyche, expansive prose critique etc are some of the thematic ambits for deliberation and review. For the summer issue 1.1, we encourage praxis-based, pragmatic, conceptual manuscripts from scholars and practitioners across social sciences and humanities. Prospective submitting authors should consult the manuscript guidelines below and submit a proposal that includes:
· An abstract of 250 words with 1-2 sentences on each of the following:
- Essential points of literature review (which underline the introduction to the study)
- Problem or research questions and research objectives clearly stated
- Brief description of (research) methods/Methodology
- Praxis, Concept, or Results/findings
- Implications/Relevance in Future
Manuscript Guidelines:
00001. Manuscripts must be in both Microsoft Word.Doc. Do not send your files as pdf.
00002. Manuscripts should not exceed 3500-5000 words, including abstracts and work cited
00003. Manuscripts should be written in English, should be single- spaced, including quotations and references and in 12-point Times New Roman font. Follow MLA ninth style formatting. More can be read from- https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formattin...
00004. Titles must be in bold, 14-point Times New Roman font while sub-titles remain 12-point, bold, and initial letter cap. All abbreviations and acronyms should be written in full at first appearance in the manuscript text.
00005. All manuscripts must include a brief but captivating abstract which should not exceed 200 words and should describe the scope of the work, methodology, theoretical framework, and the findings. The abstract should also include a set of 5 keywords (preferably in pairs) listed in order of importance to assist in indexing the article.
00006. Manuscripts must not have been published or submitted for publication elsewhere.

'The Office' gets new life. Instead of selling paper — the characters sell papers
MICHEL MARTIN, HOST:
The hit show "The Office" is getting new life in a new setting. Creators of the project say in this version, instead of selling paper, the characters in this mockumentary sitcom will sell papers. The show starts production this summer. The setting is, according to the producers, a dying historic Midwestern newsroom. I mean, ouch. So we called up a few small town newspapers for their thoughts on what the show should include. Art Cullen is editor and publisher of the Storm Lake Times Pilot in Iowa.
ART CULLEN: We're a locally owned hometown newspaper owned by two brothers. So we're just a rural community county seat newspaper.
STEVE INSKEEP, HOST:
This twice-weekly paper serves a small city of about 12,000 with an equally small newsroom. Cullen says about a dozen people work there.
CULLEN: Including me, my son, my brother, my wife, my sister-in-law (laughter), our dog, Peach. So it's pretty down-home. It's a busy little place. We're in a metal shed. We call it Storm Lake's nicest machine shed.
MARTIN: Cullen sees the comic potential outside the shed.
CULLEN: If they'd like to get some - what I think are funny storylines (laughter) that actually are ripped from real headlines, they should give me a call. You know, a guy getting picked up for drunk driving on a lawnmower - that's funny. That has all sorts of possibilities.
INSKEEP: (Laughter) I'm still thinking about the dog, Peach - a newshound, I assume. Papers like the Times Pilot survive with reader donations or even volunteers, like in the new sitcom. These are real-life struggles that Jessie Opoien would like to see given a new spin.
JESSIE OPOIEN: I guess my immediate reaction to the premise was cautious optimism.
MARTIN: Opoien covers state politics for a bigger newspaper, the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
OPOIEN: If this case of this publisher looking for volunteer reporters gives people outside of the industry some insight into that and reminds them of the importance of local journalism, maybe that will be a helpful plot device.
INSKEEP: You know, Michel, I wonder if you've had the same experience. When you go to a town, if there's a good paper, the place just feels more accessible. It feels more alive. You feel the difference in a community.
MARTIN: You absolutely do. And, I mean, this - look. This is a real - it's supposed to be a sitcom, but it's not funny. Losing small newspapers, losing local journalism is a really serious crisis in this country. If this little show can make that better, I'm for it.
INSKEEP: All right. All right.
(SOUNDBITE OF JAY FERGUSON'S "THE OFFICE THEME") Transcript provided by NPR, Copyright NPR.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
‘They Have Established the Backbone of the Case’: Three Lawyers Dissect the Trump Trial

By David French , Rebecca Roiphe and Ken White
Mr. French is a Times columnist. Ms. Roiphe is a former assistant district attorney in the Manhattan district attorney’s office. Mr. White is a former federal prosecutor.
David French, a Times columnist, hosted a written online conversation with Rebecca Roiphe, a former assistant district attorney in the Manhattan district attorney’s office, and Ken White, a former federal prosecutor, to discuss Donald Trump’s Manhattan trial and Michael Cohen’s testimony.
David French: Let’s start with a big-picture question. I have less trial experience than either of you, but this deep into a trial, I always had a sense of the momentum of the case, of who is winning and who is losing. Who is more pleased with the course of the trial so far — the prosecution or the defense?
Rebecca Roiphe: In my view, the prosecution is happier about how things are going than the defense. They have established the backbone of the case, which is the false records, and they have provided a great deal of circumstantial evidence tying Donald Trump to those records and establishing his intent.
Ken White: When you ask who is more pleased with the course of the trial, remember that Trump is usually pursuing a public relations and political strategy at the expense of good courtroom strategy. In that sense, I suspect Team Trump is happy that he’s getting lots of airtime to push his narrative that he’s a victim of the elites and that the trial doesn’t seem to have had much of an impact on his polling numbers.
If you ask me as a trial lawyer, I agree with Rebecca that the D.A. is doing a solid job proving the elements of its case and telling the story in a way likely to grab the jury. So far, they are hitting all the necessary points.
French: Stormy Daniels’s testimony was far more riveting and disturbing than I anticipated. She described a sexual encounter that was fundamentally exploitive and potentially even predatory. In the aftermath, Trump’s lawyer moved for a mistrial, claiming that the details of that testimony could prejudice the jury. What was your assessment of her testimony? Did the prosecution make a mistake in asking her to describe the details of the encounter?
White: This is all on Trump. He’s the one who decided, for ego reasons, to make repeated claims that the sexual encounter never happened. He could have rendered the details irrelevant by keeping his mouth shut, but he had to call her a liar. That makes it relevant. Yes, her description was skin-crawling. She wasn’t a great witness — she was argumentative and had trouble answering questions directly — but she did what the prosecution needed her to do.
Roiphe: The prosecution was in a difficult position. It needed to establish that this story would have been disturbing, so much so that Trump would find it necessary to suppress it. But the judge had admonished them not to bring out too many details. The media got caught up in the sex scene at the expense of the real point of the testimony, and it’s possible that the jury did as well. But I don’t think it will ultimately undermine the case.
French: Is the judge’s decision to deny the motion for mistrial a reversible error?
Roiphe: I don’t think this will cause a huge legal problem for the prosecution on appeal. Defense lawyers call for mistrials all the time, and judges have a great deal of latitude in dealing with moments like these when testimony slips out that should not have.
French: Let’s talk about Michael Cohen for a moment. His testimony is obviously crucial for the prosecution, but as is often the case, the prosecution is using the testimony of a criminal to try to convict the defendant. How vulnerable are criminal informants to impeachment, and how do juries tend to process their testimony?
White: It’s a rookie mistake for a prosecutor to try to argue, “Actually, our cooperator isn’t that bad.” Cohen is that bad. Redemption tour and podcast or not, he’s a convicted liar. Fortunately the D.A. isn’t making him out to be an angel.
Roiphe: The prosecution has done a great job in setting up Cohen’s testimony. They have used other witnesses to paint him as a misfit, a liar, a bully. You don’t have to like Cohen to believe him. There are so many dots that have already been connected that Cohen is simply going over ground that has already been paved.
White: And prosecutors seem to be using the classic move of using Cohen’s dishonesty against Trump, by showing to the jury that Trump chose Cohen precisely because he’s a crook. Watch for them to lean into that theme in closing: Cohen is a dishonest person who does dishonest things, and that’s why Trump needed him.
Roiphe: There are a few key pieces of his testimony beyond what has already been established that the prosecution hopes the jury will believe. Namely, that Trump led this scheme and was directly involved in the cover-up.
French: I want to share my chief concern about the case. Readers may recall that to secure a conviction for a felony, the prosecution doesn’t just have to prove that Trump falsified business records but that he did so in furtherance of another crime. In your judgment, is the prosecution doing enough to establish that crucial element of the case? And is that element of the case legally robust enough to survive an appeal?
Roiphe: I am not as concerned about the vulnerability of this case as others have been. There has been a lot of testimony about Trump’s concern about these women’s stories and how they would affect the election. This testimony has come from pretty uncontroversial witnesses like Hope Hicks. In a way, it’s just common sense: Why were all these people involved in such a coordinated and intricate effort to make these payments and then lie about them? There are very few plausible reasons other than the one the prosecution has set forth.
White: The jury will be less worried about the nuances of the “furtherance of another crime” element than we commenters are. Juries tend to absorb things on a big-picture story level. The D.A. has done a very solid job connecting Trump’s deceit and hush-money payments to campaign concerns, not to family embarrassment.
French: It would be a dreadful outcome for the country if Trump is convicted before the election, only to have that conviction reversed afterward. It would provide rocket fuel for the argument that the prosecution was little more than partisan election interference.
Roiphe: For the D.A.’s office, in terms of the legal question, this just doesn’t look all that different from other cases that it regularly prosecutes. Sure, the means are different. But I think the New York courts will see this as consistent with the very broad interpretation they have given to this statute.
French: Has the defense scored any obvious points? My perception, much like yours, is that the prosecution has done a solid job of building its case. But are there any surprising weak points? What’s the defense’s best moment so far?
Roiphe: I thought the defense scored some points with Stormy Daniels, even though overall her testimony was solid. Trump’s lawyer Susan Necheles argued that Daniels had a vendetta, that she hates Trump and that she has been inconsistent in telling this story. But the jury doesn’t really have to think her motives are innocent, as long as they believe the basic story. And I don’t think the defense managed to blow up her testimony in any important way.
White: The defense’s attempts to shame Stormy Daniels for being an adult film performer fell flat, as they should. I think the defense’s best opportunity to really shine will come during the cross-examination of Michael Cohen.
French: Justice Juan Merchan has one of the most challenging jobs in trial judge history. He’s presiding over the prosecution of a former president, and Trump is an extraordinarily defiant defendant. How’s he doing?
Roiphe: One of the hardest things for the judge is whether and to what extent to take into account the identity of the defendant in making decisions. For the most part, the judge has treated this like any other trial and in that way has done a solid job and appeared impartial.
White: Justice Merchan has a thankless job. The defense is treating him extremely disrespectfully, and the prosecution is being impatient. When he is cautious and methodical, as he has been in taking the gag order and contempt issues slowly and carefully, half the country is frustrated that he hasn’t thrown Trump in jail, and half is furious that he’s persecuting Trump.
Roiphe: The gag order has really been a test. It would be such a spectacle to throw a former president in jail for contempt. It would have played right into Trump’s victim narrative.
White: Overall, he seems to be doing a thoughtful, patient job.
French: My understanding is that the defense wasn’t necessarily planning on calling a large number of witnesses, and I certainly don’t expect Trump to testify. When their turn comes to make their case, what do you expect? How much will the defense tell its own story, as opposed to resting mainly on cross-examination of prosecution witnesses?
Roiphe: Some of that might depend on how well Cohen holds up on cross-examination. If the prosecution looks as strong as it does now at the time the government rests its case, I think the defense will feel a lot of pressure to put on some sort of case.
It’s hard to know what sort of defense they would put on, given that they never really settled on one theory. They went in with the sweeping argument that Trump did nothing at all wrong. They would have a hard time establishing that his conduct was perfect. But they may be able to buttress some of the smaller arguments they have raised if they can call witnesses who could undermine the prosecution’s argument about his intent.
White: The Trump team will make the decision based largely on political strategy, not courtroom strategy. They may offer some witnesses who will advance the campaign narrative of Trump the victim.
French: In normal circumstances, applying a political strategy to a criminal prosecution would be foolish. You could make yourself popular but still go to jail.
Roiphe: The defense essentially shifted the burden to themselves to prove their client is perfect, when all they had to do was show that the prosecution failed to prove its case. But from a political perspective, that’s so Trump, and it has worked for him.
French: In this circumstance, how much could a political victory help Trump legally? This would be a state conviction, not federal, so his control over the Department of Justice doesn’t matter, and he would not have the power to pardon himself. But would a political victory make a conviction fundamentally irrelevant?
Roiphe: Practically, the appeals process will inevitably take time, and I doubt if Trump wins the election, he would be sent to state prison. So maybe in the long run, it’s not a terrible miscalculation.
White: Since the Mueller investigation, Trump has consistently done things that are foolish legally but promote his narrative — his brand. We saw that recently in the E. Jean Carroll trials, we saw it throughout the investigations leading up to the four criminal cases against him, and we’re seeing it in court now. The smart play here, for instance, would have been to say it doesn’t matter whether or not he had a relationship with Stormy Daniels, because that renders big chunks of the case irrelevant. But character is destiny, and Trump’s character is egotistical and combative.
French: Let’s end with some lightning round questions. First, since the trial has started, in your view has the chance of conviction gone up or down?
Roiphe: Up.
White: Up significantly.
French: Trump is supremely irritated by the judge’s gag order, and while gag orders are infrequent, they’re not all that unusual. Is the gag order in this case justified?
Roiphe: Yes, although I think there should be an exception when witnesses like Michael Cohen have been so public and vocal.
White: We should thank Trump for making law on gag orders. We have a very detailed D.C. Circuit opinion now that will be extremely helpful in a First Amendment area that was previously not well charted. By being so willing to antagonize the judge and by being able to afford lawyers to brief and appeal the gag order, Trump’s helping clarify the law.
French: One last question: J.D. Vance has been mentioned as a potential Trump vice-presidential pick, and he showed up at court on Monday to support Trump. Who is the next V.P. hopeful to make an appearance?
Roiphe: The ghost of Kristi Noem’s dog?
White: It’s going to be Alex Jones or any cop who has pepper-sprayed at least five student protesters.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Rebecca Roiphe, a former assistant district attorney in the Manhattan district attorney’s office, is a law professor at New York Law School. Ken White, a former federal prosecutor, is a partner at Brown White & Osborn in Los Angeles.
Source photographs by Charly Triballeau, MediaNews Group/Reading Eagle, Michael M. Santiago, and The Washington Post via Getty Images.
David French is an Opinion columnist, writing about law, culture, religion and armed conflict. He is a veteran of Operation Iraqi Freedom and a former constitutional litigator. His most recent book is “Divided We Fall: America’s Secession Threat and How to Restore Our Nation .” You can follow him on Threads ( @davidfrenchjag ).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To write a character analysis essay, start by selecting a character from a literary work or film. Then, gather evidence from the text or film to support your analysis, including direct quotes, actions, dialogue, and descriptions. Analyze the character's traits, motivations, conflicts, and relationships with other characters.
Character analysis essays do not have just one format. However, let me offer some advice that might act as a character analysis essay outline or 'checklist' of possible things you could discuss: 1. Start with the Simple Details. You can start a character analysis by providing a simple, clear description of who your character is.
Introduction: Introduce the character you are writing about using a good hook to get your reader curious. Body: In this section, use a few paragraphs to describe the character's traits, their role, and the transformation they undergo (you could write one paragraph for each of the sections outlined above). Conclusion: Summarize your essay in ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
A character analysis is a type of essay that requires you to analyze and evaluate the characteristics, traits, motivations, and decisions of a literary character. It involves closely examining such aspects as their personality, thoughts, behavior, and development. You should further explain how a character contributes to the overall meaning of ...
A character analysis is a kind of essay where you examine behaviors, motivations, and actions of characters. Also, a character analysis is an in-depth assignment that makes you think critically about one or more characters and make judgements after analyzing the text. In most cases, it is used for the analysis of literary works.
Step 1: Choose Your Individual for Analysis. Character evaluation is the first step to a great analysis. The role or persona you choose for your analysis is crucial to its success. Primary characters are sometimes easier to write since they have well-defined personalities, and their motivations may be evident.
If the source includes three or more authors, use the abbreviation "et al." after the first author's name. Example: (Collins et al., 1997) As for MLA format: You can write the author's name in the sentence. Example: As Collins mentions in his essay<…>.
4.2 Decide on what character to choose. 4.3 Outline your essay. 4.4 Define the main idea. 4.5 Make notes while reading. 4.6 Compose a list of questions. 5 Character Analysis Essay Example. Writing can be as interesting as communicating. You can provide your thoughts and in-depth analysis of a character you like.
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
A character study essay is a written character analysis that examines a character from a literary work. Like every other type of character analysis, it is used when an individual wants to analyze ...
How to write a character analysis essay. Now that we've covered the intricate process of analyzing characterization in literature, let's apply this knowledge to the final step: writing a character analysis essay. This task may seem daunting at first, but don't worry, we're in this together. Here's how you can approach it: Choose your character ...
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis . There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include: Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work.
Understand Character Analysis Essay. What is a character analysis essay? Character analysis is a critical process that involves examining the traits, motivations, and development of characters in a literary work. It goes beyond mere observation, requiring readers to delve into the intricacies of characters' personalities, actions, and ...
Step 2: Setting Up the Stage. The second step in writing a character analysis essay is setting the stage for the actual writing of a text. Here, students engage in several activities, including finding credible sources, making notes, creating an essay outline, and creating an annotated bibliography.
ANALYZING a literary character (as found in a character analysis) and merely DESCRIBING ... when necessary, but do not structure the entire essay around the retelling of the story. Questions to Ask Yourself: If plot is the "what and the what" of a story, then character analysis is the "how" and the "why." ...
Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
To write a literary analysis essay always understand the assignment thoroughly and identify the key elements e.g. plot, characters, and themes. ... You've been asked to conduct a literary analysis—study the characters, setting, tone, and imagery to understand how the author uses these elements to convey their message. It helps you gain a ...
Character analysis essay example #1: Character Analysis of Anders in Bullet in the Brain, a Book by Tobias Wolff. The first essay is a brief analysis. It focuses on how readers see the character of Anders in the short story "Bullet in the Brain" develops. *Click images below to enlarge. In the above character analysis essay example, I noted ...
A character is a person, animal, being, creature, or thing in a story. Writers use characters to perform the actions and speak dialogue, moving the story along a plot line. A story can have only one character (protagonist) and still be a complete story. This character's conflict may be an inner one (within him/herself), or a conflict with ...
At TellTale Heart, literary learners not only have a deeper understanding of the essence of the story through the five elements but also a deeper understanding of why Edgar Allan Poe created the story. By spending time and energy digging into the details, setting, relevant historical background, and author biography, people begin to see the ...
Richard Owen, the Victorian scientist who first named the "dinosaurs", claimed that he could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from inspecting a single bone. Richard Fallon revisits other Owen-inspired fictions — by R. D. Blackmore, William Makepeace Thackeray, and Charles Kingsley — and finds literature layered with scientific, religious, and political interventions, spurred by ...
Wendy Chen Wendy Chen is the author of the award-winning poetry collection Unearthings.Her short stories, creative nonfiction, translations, and reviews have appeared widely including Freeman's, A Public Space, North American Review, and American Poets.Her work has been translated into multiple languages and has been adapted into musical compositions.
When creating fictional characters, we have access to this well of knowledge to write imaginary but psychologically realistic people. The challenges When it comes down to the writing, though ...
The Trans- Phenomenon in Language, Literature, and Culture. November 15-16, 2024. Organized by the Department of English and Humanities. ... Selected papers will be published in an edited volume. IMPORTANT DATES: Abstract Submission: July 23, 2024. Acceptance Notification: August 23, 2024.
In Stephen King's world, "It" is a loaded word. It's hard not to picture Pennywise the Clown haunting the sewers of Derry, Maine, of course, but in the horror writer's newest collection ...
Papers across disciplines, dealing with the trauma/post-trauma in war literature will be undertaken for consideration. The twentieth-century war climate will particularly be the case in point. Articles/papers on novel ideations, unheard dimensions of wars of the past, in the nineteenth century or the troubled or strained nationalities/borders ...
A small newspaper in the Midwest is the setting for a new version of the hit TV show The Office. We asked the editor of a tiny newsroom in rural Iowa about what the show should focus on.
But character is destiny, and Trump's character is egotistical and combative. French: Let's end with some lightning round questions. First, since the trial has started, in your view has the ...