
Beginning a presentation: how to create a gorgeous second slide
In a previous post I gave you great tips and advice on how to start your presentation with a powerful first slide . Now that you’re able to craft a great opening slide, you need to know what to do next: your second slide!
Let’s start diving into the second slide with a very common question:
Should your second slide be The Agenda?
I can hear a chorus of angelic voices shouting “nooooooooooo,” can you? The Agenda is not a necessary evil . It’s an evil we can dispense of for many reasons.
First of all, if your talk is so complex that it requires a slide to explain how it flows, maybe you really need to simplify it. Moreover the agenda slide shifts the focus from you … to a bulleted list , setting the mood for a slow, boring, badly delivered presentation.
Doesn’t your audience need an agenda?
By all means they do need an agenda! The best talks are the ones where the audience gets to know the exact structure beforehand . It makes them feel like they’re in control of what’s happening. It calms them down when the presentation is slow and boring and it energizes them when the talk is entertaining. Knowing the structure of a talk makes it easier to follow along . For instance, your audience will think that your first two points were great and eagerly await the third if you tell them it’s coming.
So how do we deliver the agenda to our audience? The answer is easy. We make a pause, look them in the eye and spend 20 to 40 seconds explaining how our talk is structured: we are going to tell 3 stories, we have 2 important themes, we are going to talk about topic x by performing 3 experiments together with the audience.
You don’t need a slide . This is the moment you are making an agreement with your audience about how you are going to spend the next few minutes together. It’s best that you step forward, look at them with an open and honest gaze, and tell them how you’re going to use their time.
This is also a great time to tell your audience how much time you will spend talking and when you want to field questions.
In the meantime your perfectly crafted first slide remains on screen. It’s gorgeous isn’t it? It deserves a little more screen time.
Great. But how about the second slide?
If it’s not the agenda what do you feature there?
There’s not one single answer, but if your conferences are like my conferences I would use the second slide to reinforce a point made before . Let me elaborate on that.
At the beginning of a presentation you share two facts with your audience: who you are and what you’re going to talk about . I suggest that the second slide of your presentation reinforce either of these two points.
If you’re at a conference where there is a skilled M.C. that has clearly talked about your bio and has introduced you properly, you can use the second slide to reinforce the topic you are going to talk about.
One thing you can do is to reveal – if it’s not known – what your relationship is to the topic (you’re the world expert, you became the world expert but you were ignorant about it only 1 year ago, etc.), so as to reinforce both your bio and the theme of your presentation.
You should do this also in a less formal setting if everybody doesn’t know who you are. In this case place a nice picture of yourself in the second slide and give not only a brief bio to your audience (and when I say brief it means you are allowed to use between 10 and 20 words), but also – as above – your relationship with the topic.
Regarding your portrait, when I talk about a nice picture I mean – whenever possible – something shot by a professional. If you can’t afford a photographer, you can shoot great pictures with smartphones nowadays. So go out on a sunny morning wearing something not too flashy (avoid any clothing that has brands on it), choose some neutral background and have a friend take a few head shots of you .
To summarize
No agenda : agendas are for G20 meetings, not for entertaining and informative talks.
Reveal your structure : by verbalizing the structure of your talk your audience becomes your accomplice
Introduce yourself : don’t let your audience discover who you are at the end of the presentation. Tell them beforehand, but be quick.
Reinforce the topic : if everyone knows who you are, reinforce the topic. Answer the question, why am I going to talk about x?
Pin It on Pinterest
You’re using an older browser version. Update to the latest version of Google Chrome , Safari , Mozilla Firefox , or Microsoft Edge for the best site experience.
- Corporate Training
- Course Selling
- Academic Learning
- Learning Basics
- Instructional Design
- Online Training Tools
- Manufacturing
- Products iSpring Suite iSpring Learn
- Use Cases Onboarding Compliance Training Induction Training Product Training Channel Partner Training Sales Training Microlearning Mobile Learning
- Company About Us Case Studies Customers Partnership Course Development Contact Us
- Knowledge Hub Knowledge Hub Academy Webinars Articles Guides Experts on iSpring
- Language EN English Français Deutsch Español Italiano Nederlands Português Polski 中文 日本語 العربية Indonesia
- Shopping Cart
How to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation

content creator
Helen Colman See full bio →

Think of a movie that has breathtaking special effects but no storyline. Does it have any chances of becoming a blockbuster? Of course not. The same is true with a PowerPoint presentation. No matter how beautiful the visuals of your slide deck are, it will never be a success if it doesn’t follow a logically sound structure.
In this post, we’ll cover the typical presentation structure in PowerPoint – what sections it should include – and provide some practical tips on how to arrange the slides and implement these ideas technically. Use these practical guidelines to organize your slides in a clear and simple way and save time on their development. But first, let’s see why your PPT deck needs to be guided by a structure.
Why Is Structuring a PowerPoint Presentation Important?
A sound deck structure is crucial for audience understanding. When the information is presented logically, it’s much easier for a viewer to get the message. The research supports this idea – it shows that people are 40% more likely to retain structured information than unstructured information.
If you’re going to accompany your slideshow with an oral presentation, a good structure is also important for you as a speaker. It will help you feel confident, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences, so you’re more likely to win your audience over.
What Is the Typical PowerPoint Presentation Structure?
A good PowerPoint presentation always has a story to tell and, like any narration, it consists of three basic parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Let’s look at each part in greater detail with some examples.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for the entire presentation and explains what the audience will come away with after viewing it. Here are the multiple slides you may need to add in the intro:

This is the main part of your presentation, which should keep the promises you made in the introduction. This is where you explain your topic and present all your information.
Depending on the nature of your presentation, divide it into segments/points. Arrange your points in a logical order and then provide information to support each of them. There are many different ways to organize your key points, for example:
- Number your points according to their priority (1, 2, 3, …)
- Place the points in a time frame (past, present, future)
- Use narration (tell a story from beginning to end)
- Present the points with a problem-solution dynamic (state a problem, describe its impact, offer ways to solve the issue)
A good conclusion summarizes the key points you made or highlights what the audience should have learned. It clarifies the general purpose of your presentation and reinforces the reason for viewing it. Here are the slides you may want to include:
- Summary. List what goals your audience have achieved, what knowledge they got, and how this information can help them in the future.
- Conclusion. Here you can thank your audience for viewing the presentation.
Tips for Structuring a Presentation in PowerPoint
Now that you know which parts a typical presentation should consist of, let’s see how to structure it in PowerPoint.
1. Combine slides into sections
When working with a large PowerPoint presentation (PPT), you can create sections that can be collapsed and expanded. This will help you keep presentation slides organized and facilitate navigation in editing mode. To do that, follow these steps:

- To shift a section, right-click on its name and use the Move Section Up and Move Section Down options.
- To collapse or expand a certain section, click on the collapse icon to the left of the section name. You can also minimize and maximize all sections at once by right-clicking on the section name and choosing Collapse All or Expand All .
As well, you can access these settings by choosing Slide Sorter under the VIEW tab.

This kind of segmentation is a great way to overview the logical flow of your slides all at once and see if there are any changes required. For example, you may decide to break one slide into two or three, or the other way around.
2. Use the Outline View
One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View . You can choose it from the VIEW tab.

This view doesn’t display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents. Here you can go through the entire text and edit it instantly. You can also work with text (on the left) and slides (on the right) simultaneously, as the latter is shown on the right side of your screen.
Note that, to be displayed in an outline, text needs to be typed in a text placeholder, not a text box . A text placeholder is a box with the words “Click to add text” or “Click to add title”, and it appears when you choose a standard layout.
You can also use Outline View to promote bullet text to titles and the other way around. To do that, right-click on a relevant title or text and select the Promote or Demote options.

Be attentive about demoting a title, as this will delete the original slide and move its title and text to the adjacent slide.
PowerPoint only allows users to promote and demote text, not entire slides. Therefore, there’s no possibility to change the hierarchical order of slides.
3. Create a table of contents
All the aforementioned tips help you organize a presentation when formatting it. However, it’s crucial that your viewers can easily navigate through entire presentation too. One sure way to provide them with this opportunity is to create an interactive and structured table of contents.
Though there’s no native automatic outline in PowerPoint, it can be created manually:

- Press Ctrl+A to select all the names, and Ctrl+C to copy them.
- Then Press Ctrl+V to paste the copied titles on the desired slide. In case there are too many titles and they don’t fit onto a single page, you can divide the table of contents into two columns or place it on two slides.

You’ll need to repeat this procedure to link all the chapters to corresponding slides. For more information, read this step-by-step guide on how to add a hyperlink in PowerPoint .
Now all the chapters can be accessed from a single table of contents, which is very convenient. However, you will also need to link them back to that unifying page. You can do this by inserting an Action Button on every slide of your presentation in Slide Master mode:

Now there is a single page from which all the other pages can be easily accessed. As well, it’s possible to go back to the table of contents at any time with the intuitive Home button.
Depending on the size of your presentation, the time it takes to create an interactive outline may vary, as you will need to add hyperlinks to every chapter manually. Be aware that if you rename a slide or simply delete it, these changes will not be automatically registered in the table of contents. For example, if you delete a slide, its title will still be displayed in the table of contents, but clicking on it won’t lead the viewer to another point in the presentation.
This is what our sample presentation looks like:

A Better Way to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation
Creating a table of contents manually might be fine for a small presentation, but if you have 122 slides, it would require too much time and energy to do so. That’s why, instead of manually creating a table of contents, we took advantage of iSpring Suite and simply enabled the automatic outline.
iSpring Suite
Fully-stocked eLearning authoring toolkit for PowerPoint. No training required to start!

Note: iSpring Suite turns slides into HTML5 format, so your audience can view them online, right in their browsers.

As you can see, the new presentation has a pop-up outline and a navigation panel, which make it possible to move to any slide at any time without leaving the slide show mode.
How to set up navigation
To create navigation in your presentation, follow these simple steps:
- Get a free trial of iSpring Suite.

- When you’ve configured the Slide Properties settings, click on Save & Close in the upper-left corner.
How to configure an outline
Whereas PowerPoint requires the outline to be designed manually, iSpring Suite has already prepared it for you. At the same time, you don’t have to stick with the standard outline template, as you can easily customize the player’s final look and feel:

We recommend leaving Enable Search marked, as this will allow viewers to search for any content at any time, including the texts on the slides. This is especially useful for large presentations with a lot of text.
If you have previously arranged slides into multiple levels in the Slide Properties, then leave Multilevel outline marked. That way, the outline will display the nesting structure of the presentation, facilitating navigation. You can learn more about the other outline options here .

- When you have finished configuring the player, click on Apply & Close in the upper-left corner.
- Now you can publish your enhanced presentation either to HTML5, to make it easily accessible via browser on any device, or MP4 video format. If you’re going to upload your presentation to an LMS, you can publish it to any eLearning format: SCORM, AICC, Tin Can, or cmi5.
While a standard PowerPoint slideshow is straightforward and limited, iSpring Suite saves viewers from having to follow a strict slide order. An interactive and searchable outline allows non-linear navigation, where any information can be accessed at any time at a glance.
Also read : → How to Convert PowerPoint to MP4 Video
Also read : → How To Record Presentations With Audio
Another perk
iSpring Suite comes with Content Library , which provides a great collection of presentation templates and allows you to create professional-looking presentations in a matter of minutes. Each template includes basic course elements: a title slide, a table of contents, chapters, a timeline, and info slides. Organize them in the order you prefer, populate them with your texts and images, and your presentation is ready to go.

We hope this article will help you develop an ideal structure for your PowerPoint presentation and do this quickly and easily. Captivate your audience with a powerful and persuasive presentation!
Do you have any other insights on how to simplify PowerPoint slides design? Please share them in the comment section. We’d like to hear from you.
Table of Contents
Create online courses and assessments in record time.

Content creator
Helen Colman
She enjoys combining in-depth research with expert knowledge of the industry. If you have eLearning insights that you’d like to share, please get in touch .

How to Create an eLearning Course – A Comprehensive Guide

9 Ways to Assess Student Learning Online
The 60+ Best Instructional Design Software Tools and Resources for 2024
Subscribe to our blog
Stay tuned to get our latest eLearning tips and tricks!
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to our Privacy Policy . All emails include an unsubscribe link, so that you can opt-out at any time.
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website and also for analytics and marketing purposes. You can enable or disable optional cookies as desired. See our Cookie Policy for more details.
Manage your cookies
Essential cookies are always on. You can turn off other cookies if you wish.
Essential cookies
Analytics cookies
Social media cookies

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
30 Presentation Terms & What They Mean
Delivering a captivating presentation is an art that requires more than just confidence and oratory skills. From the design of your slides to the way you carry yourself on stage, every little detail contributes to the overall effectiveness of your presentation. For those who wish to master this art, getting familiar with the associated terminology is a great place to start.
In this article, we’ll explore “30 Presentation Terms & What They Mean,” shedding light on the key terms and concepts in the world of presentations. Whether you’re a professional looking to refine your skills, a student aiming to ace your next presentation, or just someone curious about the subject, this guide is sure to provide you with valuable insights.
Dive in as we explore everything from slide decks and speaker notes to body language and Q&A sessions.
Each term is elaborated in depth, giving you a comprehensive understanding of their meanings and applications. This knowledge will not only make you more comfortable with presentations but will also empower you to deliver them more effectively.
2 Million+ PowerPoint Templates, Themes, Graphics + More
Download thousands of PowerPoint templates, and many other design elements, with a monthly Envato Elements membership. It starts at $16 per month, and gives you unlimited access to a growing library of over 2,000,000 presentation templates, fonts, photos, graphics, and more.

Mystify Presentation

Modern PPT Templates
New & innovative.

Maximus Template

Minimal PPT Templates
Clean & clear.

Pitch Deck Templates
Startup pitch deck.
Ciri Template
Explore PowerPoint Templates
Table of Contents
- Speaker Notes
- White Space
- Aspect Ratio
- Grid System
- Master Slide
- Infographic
- Data Visualization
- Call-to-Action (CTA)
- Color Palette
- Negative Space
- Storyboarding
- Bullet Points
- Eye Contact
- Body Language
- Q&A Session
1. Slide Deck
A slide deck, in its most basic sense, is a collection of slides that are presented in sequence to support a speech or presentation. The slides typically contain key points, graphics, and other visual aids that make the presentation more engaging and easier to understand.
Beyond merely displaying information, a well-crafted slide deck can tell a story, create an emotional connection, or illustrate complex concepts in a digestible way. Its design elements, including the choice of colors, fonts, and images, play a significant role in how the presentation is received by the audience.
2. Speaker Notes
Speaker notes are a feature in presentation software that allows presenters to add notes or cues to their slides. These notes are only visible to the presenter during the presentation. They can include additional information, reminders, prompts, or even the full script of the speech.
While the audience sees the slide deck, the speaker can use these notes as a guide to ensure they cover all necessary points without memorizing the entire speech. It’s essential to use speaker notes strategically – they should aid the presentation, not become a script that hinders natural delivery.
A template is a pre-designed layout for a slide deck. It typically includes a set design, color scheme, typefaces, and placeholders for content like text, images, and graphs. Templates can significantly reduce the time and effort required to create a professional-looking presentation.
While templates can be incredibly helpful, it’s important to choose one that aligns with the theme, purpose, and audience of the presentation. Customizing the template to match your brand or topic can further enhance its effectiveness.
4. Transition
In the realm of presentations, a transition refers to the visual effect that occurs when you move from one slide to the next. Simple transitions include fade-ins and fade-outs, while more complex ones might involve 3D effects, wipes, or spins.
Transitions can add a touch of professionalism and dynamism to a presentation when used correctly. However, overuse or choosing flashy transitions can be distracting and detract from the content. The key is to use transitions that complement the presentation’s tone and pace without overshadowing the message.
5. Animation
Animation is the process of making objects or text in your slide deck appear to move. This can involve anything from making bullet points appear one by one, to having graphics fly in or out, to creating a simulation of a complex process. Animation can add interest, emphasize points, and guide the audience’s attention throughout the presentation.
While animations can make a presentation more engaging, they must be used judiciously. Excessive or overly complex animations can distract the audience, complicate the message, and look unprofessional. As with transitions, animations should support the content, not detract from it.
6. Multimedia
Multimedia refers to the combination of different types of media — such as text, images, audio, video, and animation — within a single presentation. Incorporating multimedia elements can make a presentation more engaging, cater to different learning styles, and aid in explaining complex ideas.
However, it’s important to ensure that multimedia elements are relevant, high-quality, and appropriately scaled for the presentation. Additionally, depending on the presentation venue, technical considerations such as file sizes, internet speed, and audio quality need to be taken into account when using multimedia.
7. White Space
In the context of presentation design, white space (or negative space) refers to the unmarked portions of a slide, which are free of text, images, or other visual elements. Despite its name, white space doesn’t necessarily have to be white — it’s any area of a slide not filled with content.
White space can give a slide a clean, balanced look and can help draw attention to the most important elements. It can also reduce cognitive load, making it easier for the audience to process information. Good use of white space is often a key difference between professional and amateur designs.
8. Aspect Ratio
Aspect ratio is the proportional relationship between a slide’s width and height. It’s typically expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, such as 4:3 or 16:9. The first number represents the width, and the second represents the height.
The choice of aspect ratio can affect how content fits on the screen and how the presentation appears on different displays. For instance, a 16:9 aspect ratio is often used for widescreen displays, while a 4:3 ratio may be more suitable for traditional computer monitors and projectors.
9. Grid System
The grid system is a framework used to align and layout design elements in a slide. It’s comprised of horizontal and vertical lines that divide the slide into equal sections or grids.
The grid system aids in creating visual harmony, balance, and consistency across slides. It can guide the placement of text, images, and other elements, ensuring that they’re evenly spaced and aligned. It’s an important tool for maintaining a professional and organized appearance in a presentation.
10. Readability
Readability refers to how easy it is for an audience to read and understand the text on your slides. It involves factors such as font size, typeface, line length, spacing, and contrast with the background.
Ensuring good readability is crucial in presentations. If your audience can’t easily read and understand your text, they’ll be more likely to disengage. Large fonts, simple language, high-contrast color schemes, and ample white space can enhance readability.
11. Infographic
An infographic is a visual representation of information, data, or knowledge. They’re used in presentations to communicate complex data in a clear, concise, and engaging way. Infographics can include charts, graphs, icons, pictures, and text.
While infographics can effectively communicate complex ideas, they must be designed carefully. Too much information, confusing visuals, or a lack of a clear hierarchy can make an infographic difficult to understand. It’s important to keep the design simple and focus on the key message.
To embed in a presentation context means to incorporate external content, such as a video, a document, or a website, directly into a slide. When an object is embedded, it becomes part of the presentation file and can be viewed or played without leaving the presentation.
Embedding can be a useful tool to incorporate interactive or supplementary content into a presentation. However, it’s important to remember that it can increase the file size of the presentation and may require an internet connection or specific software to function correctly.
13. Palette
A palette, in terms of presentations, refers to the set of colors chosen to be used throughout the slide deck. This can include primary colors for backgrounds and text, as well as secondary colors for accents and highlights.
The right color palette can help convey the mood of a presentation, reinforce branding, and increase visual interest. It’s important to choose colors that work well together and provide enough contrast for readability. Tools like color wheel or color scheme generators can be helpful in choosing a harmonious palette.
14. Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are digital images created using mathematical formulas rather than pixels. This means they can be scaled up or down without losing quality, making them ideal for presentations that may be viewed on different screen sizes.
Vector graphics often have smaller file sizes than their pixel-based counterparts (raster graphics), which can help keep your presentation file manageable. Common types of vector graphics include logos, icons, and illustrations.
15. Mood Board
A mood board is a collection of images, text, colors, and other design elements that serve as visual inspiration for a presentation. It helps establish the aesthetic, mood, or theme of the presentation before the design process begins.
Creating a mood board can be a valuable step in the presentation design process. It can help you visualize how different elements will work together, communicate your design ideas to others, and maintain consistency across your slides.
16. Hierarchy
In design, hierarchy refers to the arrangement of elements in a way that implies importance. In presentations, visual hierarchy helps guide the viewer’s eye to the most important elements first.
Hierarchy can be created through the use of size, color, contrast, alignment, and whitespace. Effective use of hierarchy can make your slides easier to understand and keep your audience focused on the key points.
17. Stock Photos
Stock photos are professionally taken photographs that are bought and sold on a royalty-free basis. They can be used in presentations to add visual interest, convey emotions, or illustrate specific concepts.
While stock photos can enhance a presentation, it’s important to use them judiciously and choose images that align with your presentation’s tone and content. Overuse of generic or irrelevant stock photos can make a presentation feel impersonal or unprofessional.
18. Sans Serif
Sans serif refers to a category of typefaces that do not have small lines or strokes attached to the ends of larger strokes. Sans serif fonts are often used in presentations because they’re typically easier to read on screens than serif fonts, which have these small lines.
Some popular sans serif fonts for presentations include Helvetica, Arial, and Calibri. When choosing a font for your slides, readability should be a primary consideration.
19. Hyperlink
A hyperlink, or link, is a clickable element in a slide that directs the viewer to another slide in the deck, a different document, or a web page. Hyperlinks can be used in presentations to provide additional information or to navigate to specific slides.
While hyperlinks can be useful, they should be used sparingly and appropriately. Links that direct the viewer away from the presentation can be distracting and disrupt the flow of your talk.
PDF stands for Portable Document Format. It’s a file format that preserves the fonts, images, graphics, and layout of any source document, regardless of the computer or software used to create it. Presentations are often saved and shared as PDFs to ensure they look the same on any device.
While a PDF version of your presentation will maintain its appearance, it won’t include interactive elements like animations, transitions, and hyperlinks. Therefore, it’s best used for distributing slide handouts or when the presentation software used to create the deck isn’t available.
21. Raster Graphics
Raster graphics are digital images composed of individual pixels. These pixels, each a single point with its own color, come together to form the full image. Photographs are the most common type of raster graphics.
While raster graphics can provide detailed and vibrant images, they don’t scale well. Enlarging a raster image can lead to pixelation, where the individual pixels become visible and the image appears blurry. For this reason, raster images in presentations should be used at their original size or smaller.
22. Typeface
A typeface, often referred to as a font, is a set of characters with the same design. This includes letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and sometimes symbols. Typefaces can have different styles and weights, such as bold or italic.
The choice of typeface can significantly impact the readability and mood of a presentation. For example, serif typefaces can convey tradition and authority, while sans serif typefaces can appear modern and clean. The key is to choose a typeface that aligns with the purpose and audience of your presentation.
23. Visual Content
Visual content refers to the graphics, images, charts, infographics, animations, and other non-text elements in a presentation. These elements can help capture the audience’s attention, enhance understanding, and make the presentation more memorable.
While visual content can enhance a presentation, it’s important not to overload slides with too many visual elements, as this can confuse or overwhelm the audience. All visual content should be relevant, clear, and support the overall message of the presentation.
24. Call to Action
A call to action (CTA) in a presentation is a prompt that encourages the audience to take a specific action. This could be anything from visiting a website, signing up for a newsletter, participating in a discussion, or implementing a suggested strategy.
A strong CTA aligns with the goals of the presentation and is clear and compelling. It often comes at the end of the presentation, providing the audience with a next step or a way to apply what they’ve learned.
25. Thumbnails
In presentations, thumbnails are small versions of the slides that are used to navigate through the deck during the design process. They provide an overview of the presentation’s flow and can help identify inconsistencies in design.
Thumbnails are typically displayed in the sidebar of presentation software. They allow you to easily move, delete, or duplicate slides, and can provide a visual check for overall consistency and flow.
26. Aspect Ratio
27. interactive elements.
Interactive elements are components in a presentation that the audience can interact with. These could include hyperlinks, embedded quizzes, interactive infographics, or multimedia elements like audio and video.
Interactive elements can make a presentation more engaging and memorable. However, they require careful planning and should always be tested before the presentation to ensure they work as intended.
28. Placeholders
In the context of presentations, placeholders are boxes that are included in a slide layout to hold specific types of content, such as text, images, or charts. They guide the placement of content and can help ensure consistency across slides.
Placeholders can be especially useful when working with templates, as they provide a predefined layout to follow. However, they should be used flexibly – not every placeholder needs to be used, and additional elements can be added if necessary.
29. Master Slide
The master slide is the top slide in a hierarchy of slides that stores information about the theme and slide layouts of a presentation. Changes made to the master slide, such as modifying the background, fonts, or color scheme, are applied to all other slides in the presentation.
Master slides can help ensure consistency across a presentation and save time when making global changes. However, it’s important to note that individual slides can still be modified independently if necessary.
In presentations, a layout refers to the arrangement of elements on a slide. This includes the placement of text, images, shapes, and other elements, as well as the use of space and alignment.
Choosing the right layout can make your slides look organized and professional, guide the viewer’s eye, and enhance your message. Most presentation software offers a variety of pre-defined layouts, but these can usually be modified to better suit your content and design preferences.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
PowerPoint 2010 - Slide Basics
Powerpoint 2010 -, slide basics, powerpoint 2010 slide basics.

PowerPoint 2010: Slide Basics
Lesson 2: slide basics.
/en/powerpoint2010/getting-started-with-powerpoint/content/
Introduction
PowerPoint includes all of the features you need to produce professional-looking presentations. When you create a PowerPoint presentation, it is made up of a series of slides . The slides contain the information you want to communicate with your audience. This information can include text, pictures, charts, video, and sound. Before you begin adding information to slides, you'll need to know the basics of working with slides. In this lesson, you will learn how to insert new slides, modify a layout , and change your presentation view .

Slide basics
Every PowerPoint presentation is composed of a series of slides . To begin creating a slide show, you'll need to know the basics of working with slides. You'll need to feel comfortable with tasks such as inserting a new slide, changing the layout of a slide, arranging existing slides, changing slide view , and adding notes to a slide.
Optional: You can download this example for extra practice.
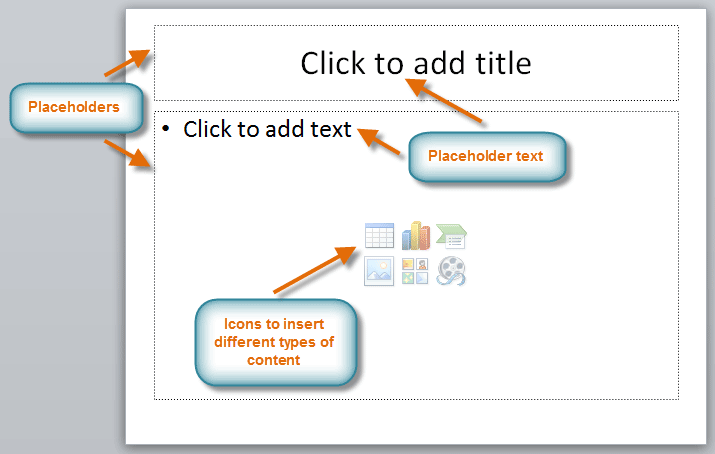
About slides
Slides contain placeholders , which are areas on the slide that are enclosed by dotted borders. Placeholders can contain many different items, including text, pictures, and charts. Some placeholders have placeholder text , or text you can replace. They also have thumbnail-sized icons that represent specific commands such as Insert Picture , Insert Chart , and Insert ClipArt . In PowerPoint, hover over each icon to see the type of content you can insert in a placeholder.
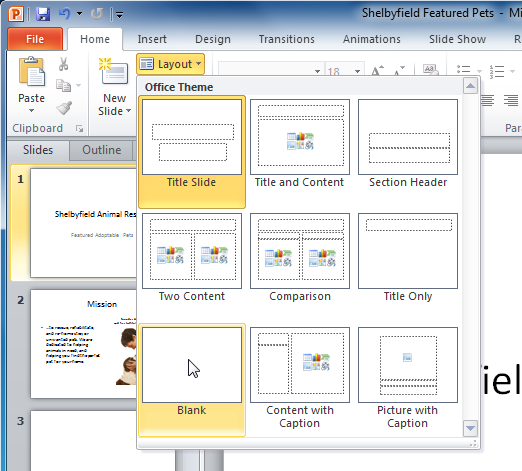
About slide layouts
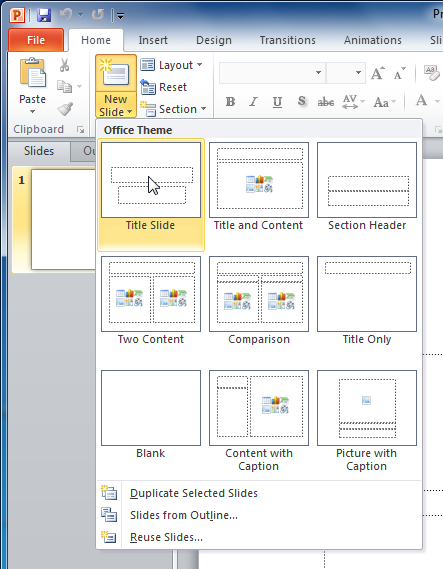
Placeholders are arranged in different layouts that can be applied to existing slides or chosen when you insert a new slide . A slide layout arranges your content using different types of placeholders, depending on what information you might want to include in your presentation.
In the example above, the layout is called Title and Content and includes title and content placeholders. While each layout has a descriptive name, you can also tell from the image of the layout how the placeholders will be arranged.
Customizing slide layouts
To change the layout of an existing slide:.
To delete a placeholder:
You can easily customize your layout by deleting unwanted—or extra—placeholders from any slide.
- Press Backspace or Delete on your keyboard. The placeholder will be removed from the slide.
To add a text box:
Text boxes allow you to add to your current layout, so you can place text wherever you want on your slide.
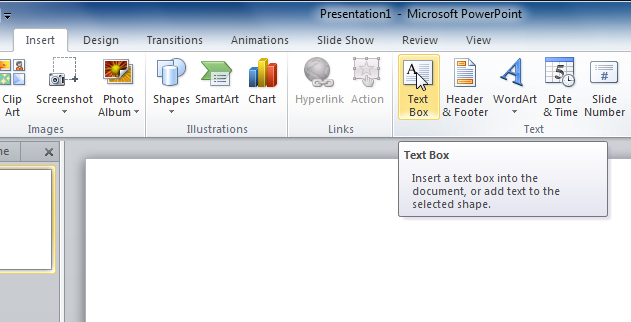
Explore our Text Basics lesson to learn more about inserting and using text boxes in PowerPoint 2010.
To use a blank slide:
For more control over your content, you may prefer a blank slide—a slide without placeholders—over one of the existing layouts. Blank slides can be customized by adding your own text boxes, pictures, charts, and more.
Working with slides
To insert a new slide:.
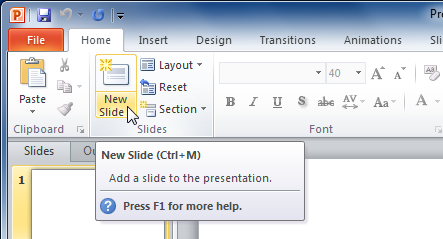
- A new slide will be added your presentation.
To instantly add a slide that uses the same layout as the one you have selected, click the top half of the New Slide command.
To copy and paste a slide:
- On the Slides tab in the left pane, select the slide you want to copy.
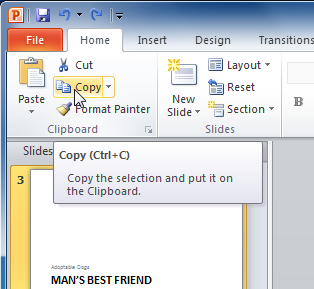
To select multiple slides, press and hold Ctrl on your keyboard and click the slides you want to select.
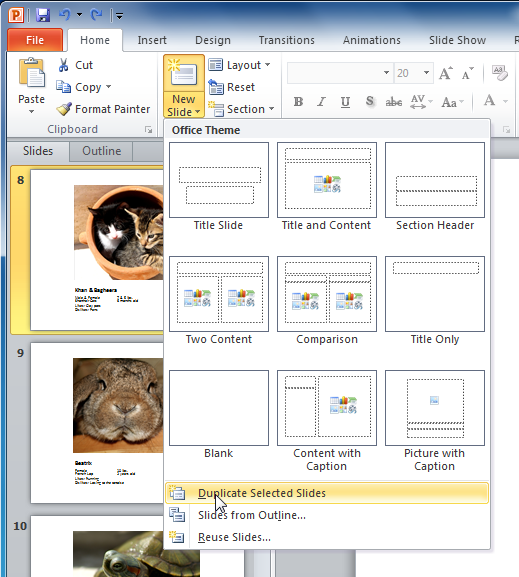
To duplicate a slide:
An alternative to copying and pasting, duplicating slides copies the selected slide and—in one step—pastes it directly underneath. This feature does not allow you to choose the location of the copied slide, nor does it offer Paste Options for advanced users, so it's more convenient for quickly inserting similar slides.
- Select the slide you want to duplicate.
- Click the New Slide command.
To delete a slide:
- Select the slide you want to delete.
- Press the Delete or Backspace key on your keyboard.
To move a slide:
- Select the slide you want to move.
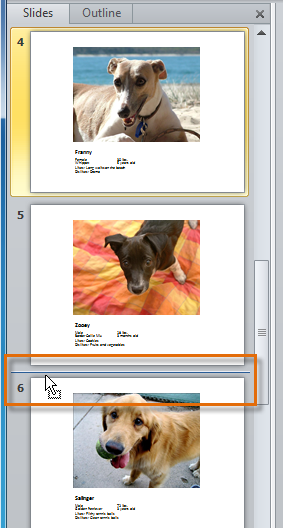
- Release the mouse button. The slide will appear in the new location.
Managing slides and presentations
As you add slides to your presentation, PowerPoint offers a variety of views and tools to help you organize and prepare your slide show.
About slide views
It's important to be able to access the different slide views and use them for various tasks. The slide view commands are located on the bottom-right of the PowerPoint window in Normal view.
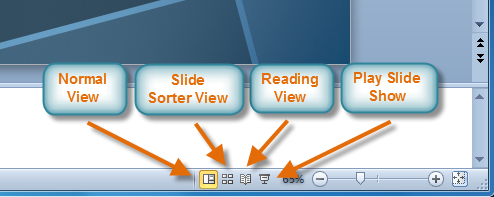
Normal view : This is the default view where you create and edit your slides. You can also move slides in the Slides tab in the pane on the left.
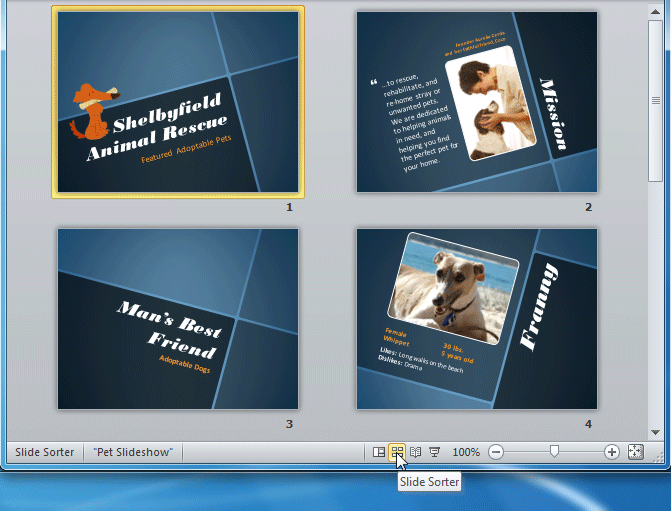
Slide Sorter view : In this view, miniature slides are arranged on the screen. You can drag and drop slides to easily reorder them and to see more slides at one time. This is a good view to use to confirm that you have all the needed slides and that none have been deleted.
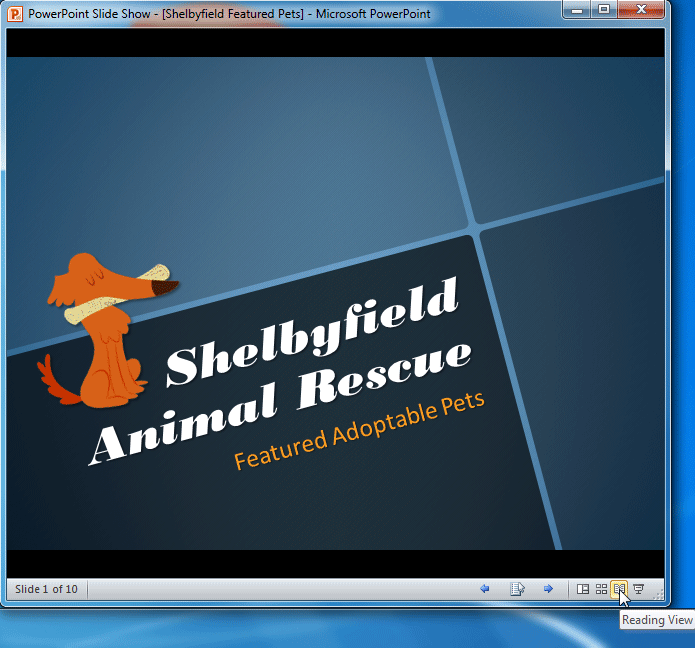
Reading view : This view fills most of the computer screen with a preview of your presentation. Unlike Slide Show view, it includes easily accessible buttons for navigation, located at the bottom-right.
Slide Show view : This view completely fills the computer screen and is what the audience will see when they view the presentation. Slide Show view has an additional menu that appears when you hover over it, allowing you to navigate slides and access other features you can use during a presentation.
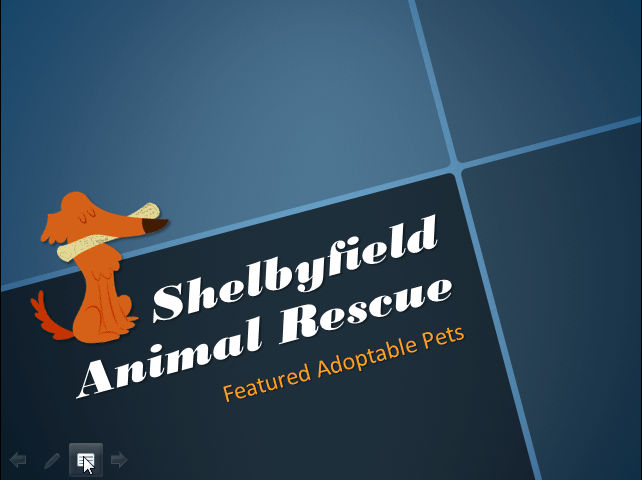
Use the keys on your keyboard—including the arrow keys, Page Up and Page Down keys, spacebar, and Enter key—to move through the slides in Slide Show view. Press the Esc key to end the slide show.
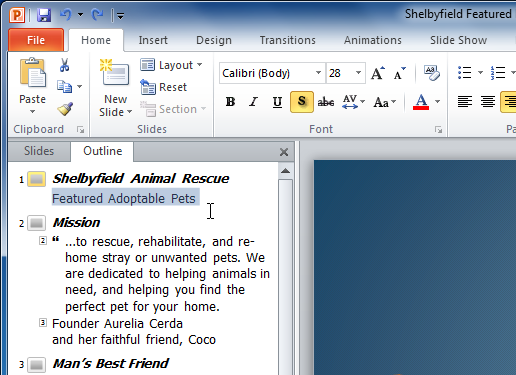
To view an outline of your presentation:
The Outline tab shows your slide text in outline form. This allows you to quickly edit your slide text and view the contents of multiple slides at once.
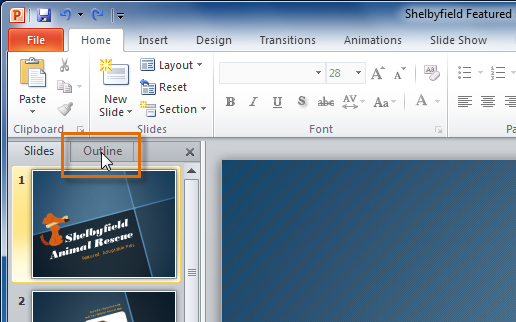
- An outline of your slide text appears.
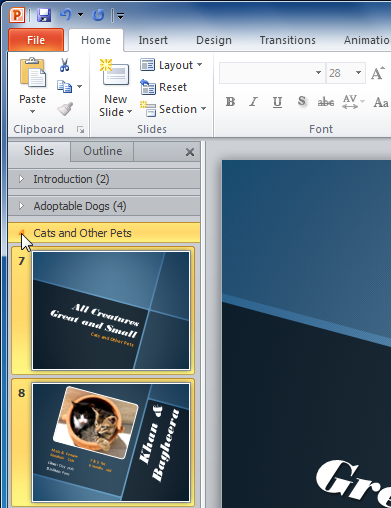
To organize slides into sections:
You can organize your slides into sections to make your presentation easier to navigate. Sections can be collapsed or expanded in the left pane and named for easy reference. In this example, we will add two sections: one for dogs that are available for adoption, and another for cats and other pets.
- Select the slide you want to begin your first section.
- From the Home tab, click the Section command.
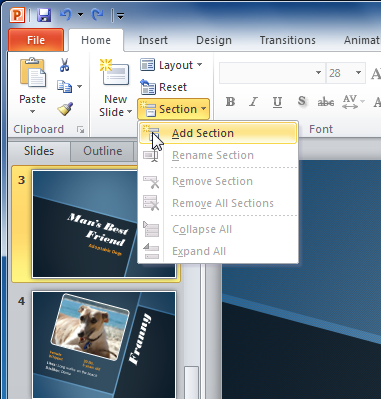
- Repeat to add as many sections as you want.
Adding notes to slides
PowerPoint gives you the ability to add notes to your slides—often called speaker notes —to help you deliver or prepare for your presentation. You can enter and view your speaker notes using the Notes pane or the Notes Page view.
To use the Notes pane:
- Locate the Notes pane at the bottom of the screen, directly below the Slide pane.
To use Notes Page view:
- Go to the View tab.
- Open an existing PowerPoint presentation . If you want, you can use this example .
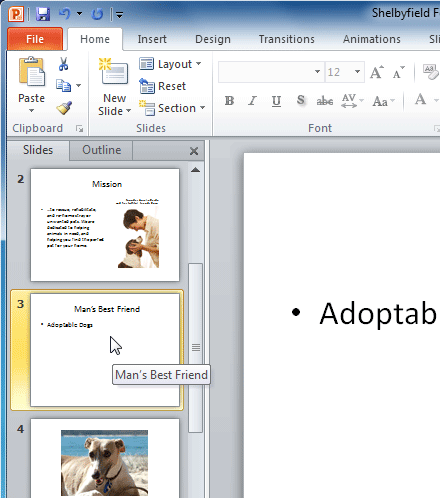
- Change the layout of a slide. If you are using the example, change the layout of slide 3 to Section Header .
- Add a new blank slide, then insert a text box .
- Copy and paste a slide, then move it to a new location.
- View your presentation in Normal view, Slide Sorter view, Reading view, and Slide Show view.
- View an outline of your presentation in the left pane.
- Divide your presentation into at least two sections , and try collapsing and expanding them. If you are using the example, create one section for dogs and another for cats and other pets.
- Experiment with adding speaker notes to your presentation using the Notes pane and the Notes Page view .
/en/powerpoint2010/text-basics/content/
- I Tried Both: Apple Watch 9 vs Fitbit Charge 6
- Best Places to Print Photos Online
The Definition of a Slide (or Slides) in a PowerPoint Presentation
- Brock University
Presentation software such as PowerPoint generates a series of slides to accompany a human presenter or to be recorded as a stand-alone presentation. A slide is a single screen of a presentation, and every presentation is composed of several slides. Depending on the subject matter, the best presentations may consist of 10 to 12 slides to get a message across, but more may be needed for complex subjects.
Slides keep an audience's attention during a presentation and provide additional supporting information in textual or graphic format.
Selecting Slide Formats in PowerPoint
When you open a new PowerPoint presentation file, you are presented with a large selection of slide templates that you can choose from to set the tone for your presentation. Each template has a series of related slides in the same theme, color, and font choice for different purposes. You can choose a template and use only the additional slides that work for your presentation.
The first slide of a presentation is usually a title or introductory slide. It typically consists of text only, but it can include graphic elements or images as well. Subsequent slides are chosen based on the information to be transmitted. Some slides contain images, or charts and graphs.
Transitions Between Slides
Slides follow one after another during a presentation, either at a set time or when the presenter advances the slides manually. PowerPoint includes a large number of transitions you can apply to slides. A transition controls the appearance of one slide as it transitions to the next. Transitions include one slide morphing into another, a fade of one to another, and all sorts of special effects such as page curls or animated motion.
Although transitions add extra interest to a slide presentation, overdoing them by applying a different spectacular effect to each slide tends to look unprofessional and may even distract the audience from what the speaker is saying, so use transitions judiciously.
Enhancing a Slide
Slides can have sound effects attached to them. The sound effects list includes cash register, crowd laughing, drum roll, whoosh, typewriter and many more.
Adding motion to an element on a slide – a line of text or an image – is called animation. PowerPoint comes with a large selection of stock animations you can use to generate movement on a slide. For example, you can choose a headline and have it zoom in from the margin, spin around 360 degrees, flip in one letter at a time, bounce into position or one of many other stock animation effects .
As with transitions, don't use so many special effects that the audience is distracted from the content of the slide.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- The 8 Best Slideshow Apps of 2024
- Beyond the Basics in PowerPoint
- The 8 Best Google Drive Add-ons for 2024
- Different Ways to View Slides in PowerPoint
- How to Use Google Duet in Slides
- The 10 Most Common PowerPoint Terms
- What Is an Animation in Presentation Software?
- Make the Most of PowerPoint's Slide Transition Options
- Create a Wedding PowerPoint Presentation
- PowerPoint Master Slide
- Tips for Memorial PowerPoint Presentations
- How to Use Google Slide Animations and Transitions
- 10 Free PowerPoint Game Templates
- Converting PowerPoint Slides to Word Documents
- How to Hide and Unhide a Slide in PowerPoint
- An Introduction to PowerPoint
, .
, .
, .
, .
, .
, , , , , , .

7 slides you should have in your PowerPoint presentation
We really hope you enjoyed: “7 Slides you should have in your PowerPoint Presentation”. This list is by no means exhaustive but if more presenters added just some of these techniques to their presentations the world would be a lot less cluttered with death-by-PowerPoint and we’d have more alive audiences. Now that’s an idea worth spreading!
Along the way we have discovered and developed strategies to give our client’s presentations the WOW FACTOR . This page has been made so we can share some of what we have learnt with you, to help you with your presentations. This is by no means an exhaustive tips list but it is a good start to get you on your way with designing.
We are sure you will be impressed so to hire us please contact us as we are always happy to help your company with our amazing presentation design skills!
1. Logo Animation
Your logo or brand is a critical part of your communication. So why put it in the corner of your slides? Your logo or brand should be displayed front and centre at the start of your presentation and well animated to convey the essence of your brand. Your logo style and colors should then be reflected in the presentation template you are using.
Take a look at these examples:
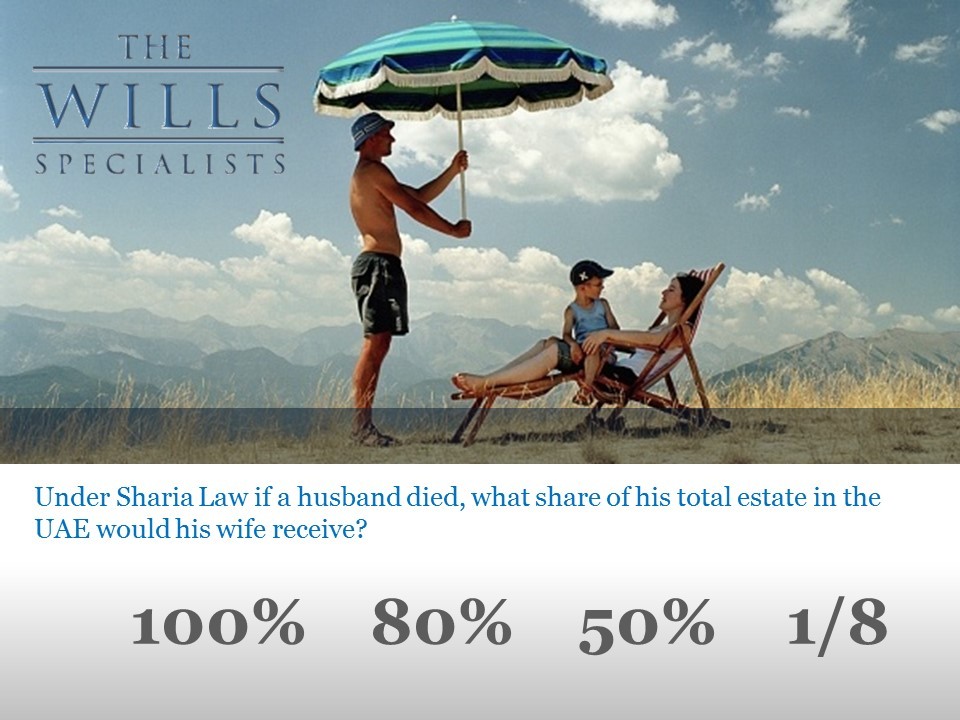
2. Problem & Solution
From the outset you want to engage the audience by asking them a question. The question should stimulate the audience into thinking – yes why is that so – why does that happen – how can we solve that? Once the issue is defined – offer your solution.
Here’s a great example of this:
This client posed several of these types of questions at the start of the presentation and then revealed the answer – thus defining the need for their service!
3. Timeline
How long have you been doing what you’re doing? What services do you offer & over what period have you been doing this? Audiences love to see a visual representation of the time you’ve invested in your solution. Timeline slides can be animated or interactive – touch a year on the timeline ribbon to go to that year.
Here’s a few examples:
4. Interaction
Presentations are getting shorter. Have you heard of the 10, 20 ,30 rule of presenting? Average pitch decks are now just 10-15 slides so how can you get more interaction with your audience in the same time? Interactivity that’s how! Your presentation should have a buttons which link to different sections of your presentations.
Below is an example of one presentation which has over 1800 slides! The client never presents them all just uses interaction as a way of presenting. And with the increase usage of touchscreen laptops this will make for a very interactive sales meeting.
5. Multi-Lingual
If you are communicating to a multilingual audience then please consider getting some of your text translated into the relevant language. There’s nothing that an audience loves more than if you’ve considered them in your pitch. The onscreen text should be in both languages so that you can refer to the subject while they read the highlights.
Here’s some creative Arabic examples which work well:
6. Infographics
Still using bullet points? Come on – be bulletproof! There’s enough bullets in the world and nothing says amateur than reading a screen full of bullets. We recommend replacing the bullets with infographics and if possible animating the.
Here’s some recent examples:
7. Amazing Factoids
Take something normal about your offering and make it amazing with an onscreen amazing factoid animation.
Checkout these examples:
Tell Us What You Need - Only Takes 2 Minutes!
Fill in the brief form for a FREE quote

Explore all our presentation design services
Presentation design, audience engagement, presentation training, data visualization, master powerpoint animator, visual presentation, advance public speaking, kids training.

How to easily make an AWESOME first slide in PowerPoint?
By: Author Shrot Katewa

A good first impression can have a lasting impact. Thus, having a good design for your first slide is important. We’ve seen that people often simply put the title of the presentation as a first slide. I personally dislike this the most. It just shows that the person creating the presentation was simply not interested in it (even though that may not necessarily be true).
Thus, knowing how to create a good first slide is as important if not more as knowing how to create the rest of the presentation. The best part is – you can easily create an awesome first slide for your presentation in minutes in a few quick and easy steps. Obviously, if you have the time at hand, you can easily spend an hour or two making that perfect first slide! In this post, we take a look at how to easily create a first slide with a few examples of actual designs that we have created for our clients.
1. What is the first slide of a PPT presentation called?
The first slide of a presentation is called a “Title slide” or a “Cover slide” . This slide often contains the title of the presentation and hence the name title slide. It is also often referred to as the “Opening slide” of the presentation. The title slide is often the slide that is displayed on the screen before you start your presentation. Thus, it is important to have a title slide that not only looks good but also shares relevant information about your presentation.
2. What content should be included on the first slide of the PPT presentation?
A title slide or the cover slide does not need too much content. The purpose of the title slide is really to give an indication of what the presentation is all about. Thus, an ideal title slide should contain nothing more than –
- Presentation title
- Date of the presentation
- Presenter’s name and designation
It is not necessary to have all the above three pieces of information on a cover slide. Do keep in mind that not all cover slides are the same and what content is displayed on the cover slide can be organisation specific. An organisation may have a preference or a fixed structure for the content that needs to be put on a cover slide. This may vary from the above structure.
3. How to easily design a beautiful first slide in minutes?
As I mentioned earlier, having a good first slide can have a lasting positive impact on your audience. Thus, it is important to create a good design for your first slide. There are several ways you can design the cover slide. Let’s look at some of the easiest ways you can create a beautiful cover slide –
Method 1 – Using PowerPoint’s “Design Ideas” functionality (for beginners)
I must admit, PowerPoint’s “Design Ideas” functionality has great potential. In fact, we at OwlScape were planning on creating a similar plugin for PowerPoint users before Microsoft introduced this feature. This functionality is not just great for beginners, but also at least a must try for intermediate level users too. Designers from OwlScape also at least check out the functionality every once in a while especially when we hit a creative bloq.
It is really easy to work with. In just a couple of clicks and a few minutes, you can make your title slide look completely different –

To do this, all you need to do is put some text on your cover slide and use the “Design Ideas” functionality of PowerPoint. For example, you can write the title and subtitle of your presentation.
Next, click on the “Design” tab on your Menu bar. On the ribbon under the design tab, look for “Design Ideas” feature. It is normally on the far right of the screen on the ribbon. Click on it, and wait for a bit.
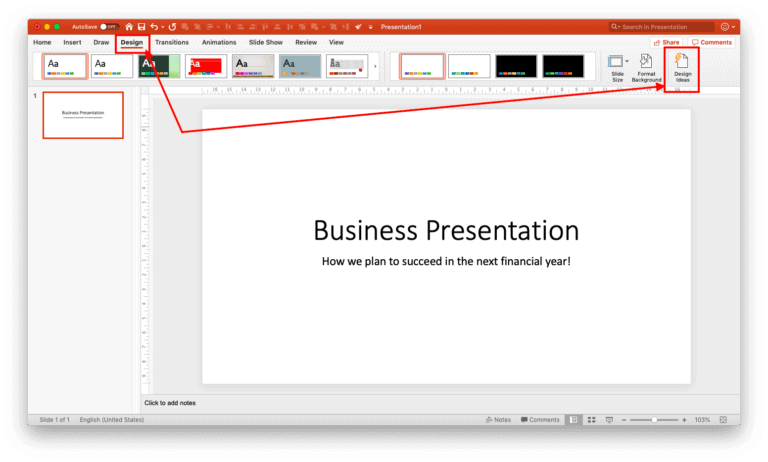
In a few seconds, PowerPoint will automatically throw a few ways in which you can design your title slide. You can choose the design you like, and repeat the process to get more results.
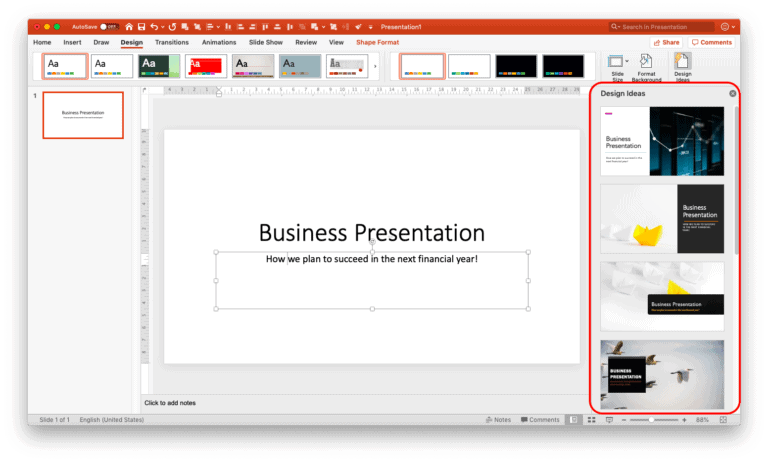
If you are unable to see any design ideas or you get an error, you could close the error result by clicking on the close button marked with “X” next to Design Ideas. Then, try clicking in any of the text box on the slide and click on “Design Ideas” again. A few attempts will surely give you some interesting results.
There are a few drawbacks though. These are as follows –
- The results are not consistent . If you happen to delete the slide and try to recreate using the exact same process, the result may be different. This can be both good and bad 🙂
- Editing the design of the suggested slide may not be easy for beginners – when you need to make some changes to the chosen design option, it doesn’t happen directly. You will need to work with the master slides in order to make the design changes. This may seem daunting especially if you are a beginner.
- Sometimes, it just doesn’t work – Even though you may have created a slide using the same content before, sometimes when you try to recreate using the same content, it may simply fail to showcase any ideas. In such an event, we would advise you to click on the text box or an image on your slide and try again by clicking on the Design Ideas option.
- Available for Office 2016 onwards – If you are a PowerPoint user using an older version of Microsoft Office, you may not be able to easily access this functionality. Having the latest PowerPoint version can be of great help!
One thing to note is that the “Design Ideas” option can be used not just for the cover slide, but also for other slides. However, I would advise resisting the temptation of using it for every single slide. 🙂
Method 2 – Using shapes to create an interesting cover slide (for intermediate users)
One other way of having an interesting cover slide is by using the shapes in PowerPoint. Let’s look at the following example –

If you look at the above example carefully, you’ll notice that we’ve only added a shape to the already existing title and the subtitle in the “After” slide. Simply adding a shape, a logo and aligning the text can alter the look of the slide drastically.
There are many ways you can add a shape to the slide. My favourite method is to add a horizontal or a vertical “Trapezoid/ trapezium” (a quadrilateral shape with one pair of parallel sides). A trapezoid shape allows me to have enough space to write the title of the slide and some more content.
To create this shape, you can follow the below steps –
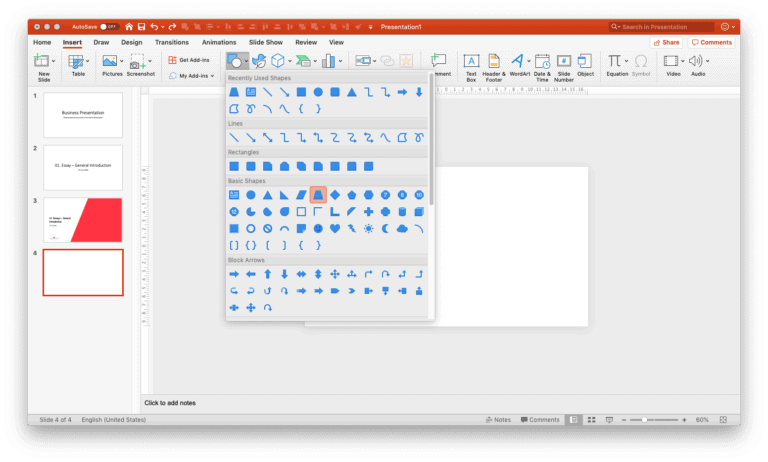
On the menu bar, click on “Insert” and then click on “Shapes”. Under the basic shapes option, select the trapezium shape. Next, create the shape on your slide.
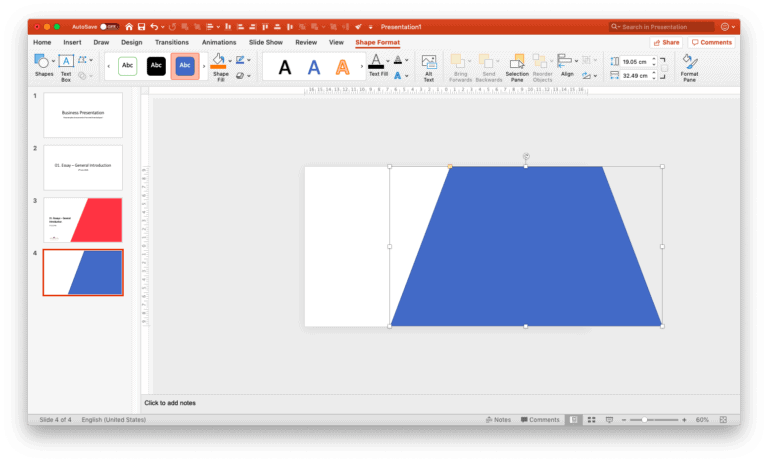
Make sure that the size of the trapezium is good enough to cover about ⅔ parts of the slide. Also ensure that the parallel sides of the trapezium touch the top and bottom part of the slide. Now all you need to do is add the title and subtitle, along with the logo to create your cover slide.

Similarly, you can also use the trapezium vertically. You can also use various types of shapes on your cover slide. The possibilities are literally endless!
Method 3 – Using shapes with images to create an awesome cover slide! (for advanced users)
If you are still not satisfied with your cover slide, there are several other ways you can make it look even more impressive. The easiest way to take it to the next level is to use images in combination with the shapes.
Let’s look at a few examples –
Combination cover slide design example – 1

In the above design, a shape has been created in the background using a freeform tool. Next, two appropriate images have been identified and put in front of the shape. All this has been kept predominantly to the right side of the slide allowing space to write the title, subtitle and the other relevant information on the left.
Combination cover slide design example – 2
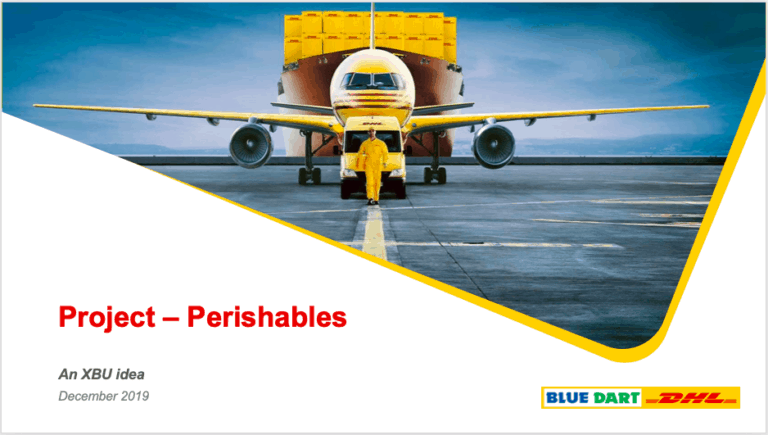

In this example, we’ve used one corner of curved rectangle shape to create an interesting design. Two copies of the same shape have been considered. The one below is filled with a colour and tilted at a slight angle. The one above has an image inserted in the shape.
Combination cover slide design example – 3

In the above example, a combination of several shapes and images are used to create a visually pleasing design. Obviously, this may not be something that a beginner can create right of the bat. But the reason we put this design as an example is because barring the design skills (knowing what shape to include and where), creating this slide is not as advanced as you might think. This slide has been created by only using shapes and image elements along with the logo and text. The purpose of using this as an example was to showcase the endless possibilities on how a seemingly complex cover slide can be made by merely using basic shapes and images.
4. How to find images for the first slide of your presentation?
Whether you are using a combination of images and shapes or simply using an image on your title slide, it is important to identify a good image that resembles the topic of your presentation. Consider the following example –

If you’ve been following along, I’m sure you would have noticed by now that the above title slide has been created using a combination of images and shapes. Again, the design can be easily created using shapes and image elements. However, part of the reason that makes this slide look good and relevant to the presentation is the choice of image. Since the presentation is for a corporate organisation, choosing an image that resembles a corporate environment would be relevant.
Take a moment to scroll up and notice the other cover slide examples that I shared above.
The cover slide example 1 was designed for a presentation on education. Thus, choosing an image that represents education effectively communicates to the audience that the presentation is something to do with education even without the word “education” in the title or the subtitle or anywhere on the slide (Don’t resist, go ahead and have a look at the slide again! 🙂 )
Likewise, example 3 uses a mobile device in the title slide giving an indication that the product being talked about in the presentation is likely going to be an app.
Thus, choosing an appropriate image is important as it subtly communicates the message to the audience.
Finding the images for your presentation can take some time. You can use Google to see a few references on what type of images can be used. Avoid the temptation of using Google images directly on your presentation as this can violate copyright laws. We wrote a detailed post on where to find and how to use images for your presentation (link – https://owlscape.in/can-i-use-google-images-for-my-presentation/ ). Be sure to check it out!
I’m sure by now you’ve noticed a few different ways you can create a good title slide for your presentation. I hope this post helps you to think out of the box while creating the title slide of your next presentation. I also hope that going forward you will surely give enough focus on creating an impressive first slide even if you only have a few minutes.
If you’re struggling while creating your next title slide or your presentation, simply drop us an email on [email protected]
Home Blog PowerPoint Tutorials PowerPoint Slide Size: What is the Best Size for a Presentation
PowerPoint Slide Size: What is the Best Size for a Presentation
Whether you’re a business professional, educator, or public speaker, understanding what are the optimal slide dimensions can enhance the impact of your presentation. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the size of your PowerPoint presentation, from the basics to advanced tips.
What is the PowerPoint Slide Size?
PowerPoint slide size refers to the dimensions of the slides within your PowerPoint presentation. These dimensions determine how your content is displayed in a monitor or projector, and can significantly affect the overall look and feel of your presentation.
The most common slide sizes in PowerPoint are 16:9 (widescreen) and 4:3 (standard).
Choosing the right slide size is essential as it impacts how your content is perceived and ensures compatibility with various display devices. Once you define the optimal slide size for your next presentation, you can change the slide dimensions in PowerPoint following the steps described in our article.
It is important to understand the differences between Aspect Ratio and Pixel Dimensions.
The specific pixel dimensions for a standard 16:9 slide are 1920 pixels in width by 1080 pixels in height.
Understanding Aspect Ratio vs. Pixel Dimensions
Aspect ratio vs. pixel dimensions: what’s the difference.
When defining the optimal slide size for your presentation, it’s important to understand the difference between aspect ratio and pixel dimensions, as these terms often cause confusion but are critical for creating well-designed presentations.
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio refers to the proportional relationship between the width and height of your slide. It’s expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, such as 4:3 or 16:9. The aspect ratio defines the shape of your slide and how it will appear on different screens.
Pixel Dimensions:
Pixel dimensions, on the other hand, specify the total number of pixels in the width and height of your slide. This measurement determines the resolution and quality of your images and text in your PowerPoint slide size. For example:
- 1920 x 1080 pixels: This is a common dimension for a 16:9 aspect ratio, known as Full HD. It provides high clarity and detail, making it suitable for large screens and high-resolution displays.
- 1024 x 768 pixels: This dimension matches a 4:3 aspect ratio and is often used for smaller screens or lower resolution displays. It’s less detailed than 1920 x 1080 but can be effective for standard printouts or older projectors.
Why both slide size definitions matter? Understanding both aspect ratio and pixel dimensions is important because they impact how your PowerPoint slide size is viewed across different devices and formats. Here’s why:
- Consistency Across Devices: Ensuring your aspect ratio is compatible with the display device prevents issues like black bars on the sides (letterboxing) or content being cut off (cropping).
- Clarity and Detail: Choosing appropriate pixel dimensions ensures that your images and text appear sharp and clear, avoiding pixelation or blurriness.
- Professional Appearance: Matching the right aspect ratio and pixel dimensions helps maintain a polished and professional look, whether you’re presenting on a large screen, sharing a PDF handout (as we will see later), or displaying your slides online.
The Impact of Slide Size on Different Industries
Different industries have unique needs when it comes to presentation slide sizes. For instance:
- Business: Corporate presentations often require widescreen formats (16:9 slide size) to showcase detailed charts and data on modern projectors and screens. However, in some environments there are still projectors using the traditional 4:3 aspect ratio format for slide sizes.
- Education: Lectures and workshops benefit from both 16:9 and 4:3 formats, depending on the teaching aids and screen setups used.
- Design: Creative professionals need to create visually appealing slides that may require custom dimensions to stand out and effectively communicate their ideas.
Best Practices for Choosing a Proper Slide Size for your Presentation
When selecting an optimal PowerPoint slide size, consider the following:
- Audience and Venue: Tailor your slide size to the screen size and setup of your presentation venue. Widescreen (16:9) is typically best for large screens, while standard (4:3) works well for print distributions.
- Presentation Type: Webinars and online presentations held via Zoom or Teams , for example, often benefit from widescreen formats, while in-person meetings might require flexibility.
- Aesthetics vs. Functionality: Balance visual appeal with readability and content integrity.
When creating PDF handouts from your PowerPoint presentation, it’s also important to choose a convenient slide size that ensures readability and clarity in print.
The 4:3 aspect ratio is generally preferred for printed handouts as it aligns well with standard paper sizes such as A4 or Letter. This format ensures that your content fits neatly onto the page without excessive margins or cropping.
Additionally, using 4:3 for print ensures that text and graphics are appropriately scaled, maintaining the legibility and professional appearance of your handouts. This consideration is essential for creating effective printed materials that complement your live presentations.
Overcoming Challenges with Slide Size
Adapting content for different slide sizes.
Resizing images and adjusting layouts can be challenging. Here are some tips:
- Resizing Images: Ensure that images maintain their aspect ratio to avoid distortion.
- Text Adjustments: Modify font sizes and text boxes to fit the new slide dimensions without compromising readability.
- Consistency: Keep a consistent layout throughout your presentation to maintain a professional look.
Dealing with Mixed Slide Sizes in a Presentation
Sometimes, you may need to integrate slides with different dimensions. Here’s how:
- Transition Techniques: Use smooth transitions to blend slides of varying sizes seamlessly.
- Tools and Add-Ins: You can use PowerPoint add-ins that help manage and standardize slide sizes across your presentation.
Advanced Tips for Custom Slide Sizes
When it is time to innovate, the PowerPoint slide size can also play an important role. If you are considering to create a presentation for digital signage, or non traditional devices, choosing a custom PowerPoint slide size can help to achieve this. Here are some ideas and ways you can innovate by choosing a different slide size:
- Unique Dimensions: Create custom slide sizes for branding or special events.
- Custom Branding: Use non-standard slide sizes to align with your brand identity and marketing materials.
- Innovative Uses: Experiment with different dimensions to create unique visual experiences.
For example, to create high-quality digital signage content, you’d need to set the PowerPoint slides to a 1920×1080 resolution in vertical (portrait) or horizontal (landscape) mode, which are the typical digital sign screen sizes.
Understanding what is the optimal slide size and how to configure it is essential for creating effective and engaging presentations. By optimizing your slides, and overcoming common challenges, you can ensure your visual aids are impactful and professional. Keep experimenting with different sizes and formats to find what works best for your needs. Remember, the key to a successful presentation lies in the details—choosing the right slide size is one of them.

Like this article? Please share
Presentation Tips Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • May 17th, 2024
How to Import Google Slides Themes
Importing Google Slides Themes is an easy task that can bring life into your presentations. Learn how to reuse old slides to create new cool themes here.
Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • May 17th, 2024
How to Edit Background Graphics in PowerPoint
You don’t have to stick with template designs that don’t appeal to your intended message. Learn how to edit background graphics in PowerPoint to become a master user.
How to Make Google Slides Vertical
Power up your presentation skills by learning how to make google slides go vertical. Step-by-step instructions with examples.
Leave a Reply
Press Herald
Account Subscription: ACTIVE
Questions about your account? Our customer service team can be reached at [email protected] during business hours at (207) 791-6000 .
- Local & State
Observe Memorial Day with these events in southern Maine
Tons of towns have parades and ceremonies happening Monday.

You are able to gift 5 more articles this month.
Anyone can access the link you share with no account required. Learn more .
With a Press Herald subscription, you can gift 5 articles each month.
It looks like you do not have any active subscriptions. To get one, go to the subscriptions page .
Loading....

Kids and adults gather at a Memorial Day parade to honor and celebrate veterans in South Portland. Sofia Aldinio/ Staff Photographer
BATH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at 200 Congress Ave. and concludes at Library Park and will be followed by a wreath-laying service at 11 a.m.
BERWICK 11 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at Berwick Town Hall/Sullivan Square and proceeds to Lord’s Cemetery by way of Wilson and Allen streets. After a ceremony there, the parade will continue down Saw Mill Hill Street with a pause at the Somersworth-Berwick Bridge for a brief memorial service for those lost at sea. The parade ends at Sullivan Square with a memorial service honoring area veterans.
BIDDEFORD-SACO Opening ceremony at 9:55 a.m. Monday at Saco City Hall. Parade starts at 10 a.m. from Saco City Hall and proceeds along Main Street and down York Hill into Biddeford, continues along Main Street, onto Alfred Street and finishes at Veteran’s Memorial Park with a closing ceremony at 10:45 a.m.
BRUNSWICK-TOPSHAM 9 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from Topsham Town Hall, pauses for observances while crossing the Brunswick-Topsham bridge, and concludes at the Brunswick Mall.
CAPE ELIZABETH 9 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at the middle school parking lot, turns right on Scott Dyer Road, right onto Route 77 and ends at the village green adjacent to the town hall. A brief ceremony and laying of the wreath will be held at the Village Green after the parade.
CUMBERLAND 8 a.m. Monday. Kids run at Greely High School followed by 5K Run and Remember race at 8:30 a.m. Parade starts at 10 a.m. at Mabel I. Wilson School and ends at the veterans’ monument in Moss Side Cemetery in Cumberland Center, where a ceremony will be held at 10:30 a.m. Advertisement
FALMOUTH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from 65 Depot Road (Falmouth American Legion) to Pine Grove Park, where a ceremony will be held.
FREEPORT 9:30 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from Holbrook Street, heads north on Main and makes a right onto School Street, then right onto Park Street, ending in Memorial Park. There will be a small ceremony in Memorial Park starting at 10 a.m.
GORHAM 11 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Village School (12 Robie St.) and ends at Eastern Cemetery on Johnson Road.
GRAY 11:30 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves the Russell School (8 Gray Park), proceeds to Shaker Road and continues to the Soldiers Monument at the intersection of Routes 26 and 3 for a wreath-laying ceremony. Parade continues north to the American Legion Post (15 Lewiston Road) for a closing ceremony.
LYMAN 1 p.m. Monday. Parade starts at Waterhouse Road/Mill Pond in Goodwins Mills and ends at the Lyman Town Hall on South Waterboro Road.
NEW GLOUCESTER 9 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves from Memorial Elementary School (86 Intervale Road) and heads down Intervale Road to Route 100/202 to Veterans Park for a memorial service. The parade will reconvene and go down Peacock Hill Road, then take a left on Gilmore Road. Advertisement
OLD ORCHARD BEACH 1 p.m. Monday. Parade starts at the corner of Ballpark Way and E. Emerson Cumming Boulevard and proceeds down Saco Avenue, Old Orchard Beach Street to First Street and ends at Veteran’s Memorial Park.
PORTLAND 2 p.m. Monday. The procession starts at Longfellow School (432 Stevens Ave.) and ends at Evergreen Cemetery for a commemoration ceremony.
SANFORD 10 a.m. Monday. The parade starts at the Sanford Armory (88 William Oscar Emery Drive), proceeds up Gowen Park Drive and ends at Central Park.
SCARBOROUGH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Scarborough High School, turns onto Route 114 and then Route 1, past town offices to the Maine Veterans Home and concludes with a ceremony there.
SOUTH PORTLAND 10:30 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Southern Maine Community College parking lot, proceeds down Broadway to the Veterans Monument for a short Memorial Day recognition service.
WELLS 9 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Wells High School (200 Sanford Road) and proceeds to Ocean View Cemetery for a ceremony and musical performances. Advertisement
WESTBROOK 10 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds down Main Street and will be followed by a ceremony in Riverbank Park.
WINDHAM 9 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Windham Town Hall and proceeds onto Route 202 toward Windham High School. At 10 a.m., there will be a ceremony in front of Windham’s Veterans Memorial Flagpole at Windham High School.
YARMOUTH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves from Yarmouth High School (286 West Elm St.) and proceeds to the Memorial Green at Town Hall for a ceremony.
YORK 10 a.m. Monday. Parade starts near St. Christopher’s Church (4 Barrell Lane) and proceeds down York Street to York Town Hall.
Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Forgot Password?
Don't have a commenting profile? Create one.
Hi, to comment on stories you must create a commenting profile . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login. Already have a commenting profile? Login .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Create a commenting profile by providing an email address, password and display name. You will receive an email to complete the registration. Please note the display name will appear on screen when you participate.
Already registered? Log in to join the discussion.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why .
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.
Send questions/comments to the editors.
« Previous
Third candidate challenges Angus King for U.S. Senate seat
Next »
Girl hospitalized with ‘serious’ injuries after jumping down embankment by Waterville RiverWalk
In Camden, a story of wealthy neighbors, ocean views and over $1.7 million in fines
More than half of food-insecure mainers can’t get food stamps, skowhegan woman learns to heal from nearly 20 years of stepfather’s ‘cult-like’ abuse, for better burgers, up your bun game with these maine-made rolls, james pak, biddeford landlord convicted of killing 2 teenage tenants, dies in prison, daily headlines.
- Email address
- Hidden Untitled
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Member Log In
Please enter your username and password below. Already a subscriber but don't have one? Click here .
Not a subscriber? Click here to see your options
Iowa baseball interference call: What umpire coordinator said of controversial play

Iowa baseball was on the short end of a controversial call in Thursday's Big Ten Tournament loss to Illinois.
The Hawkeyes fell 4-2 in 10 innings on Thursday's likely season-ending elimination game, despite having the bases loaded with no outs in the bottom of the 10th. Controversy struck when Michael Seegers grounded out to the Fighting Illini first baseman, who tried a double play, but runner Kyle Huckstorf was called for interference on his slide at second, despite beating the late throw to the base.
REQUIRED READING: Iowa baseball's season ends amid controversy against Illinois at Big Ten Tournament
It initially seemed the Hawkeyes would be down 4-3 with runners on first and third with one out, but the interference call resulted in another out while bringing the runner back to third base. With two outs in the bottom of the 10th, Ben Wilmes struck out to end the game.
Iowa coach Rick Heller was ejected for protesting the call.
After the game, umpires explained their reasoning for the call, which was reviewed during the game and confirmed.
Here's the umpires' explanation for how the call was made in Iowa's loss to Illinois on Thursday:
Iowa baseball interference call explanation
Here's the explanation of the Iowa baseball interference call, according to a pool report response from umpire coordinator Mark Uhl:
"There are three elements to what's called the force play slide rule and it's rule 8-4, it's on pages 77 and 78 of the NCAA Rule Book," Uhl told On3's Kyle Huesmann, the on-site pool reporter. "The two requirements which were applicable to this play, as the rule says it's a force play, the runner must slide in a direct line between the two bases. The rule then goes on to define directly into a base means the runner's entire body, feet, legs, trunk and arms must stay in a straight line between the bases. His legs, trunk and arms were not in a straight line between the bases, so the original call was interference.
"This is a reviewable play under NCAA rules. The umpiring crew went to video review. Once in a review room they confirmed the call because the video showed one, the runner did not slide in a direct line between the two bases and the runner's entire body was not in a straight line between the two bases."
Iowa baseball's Rick Heller on interference call
Note: Rick Heller was ejected for protesting the play.
Here's what Iowa baseball coach Rick Heller said about the interference call in Thursday's game:
“How it all went down, I don’t even really understand,” Heller told reporters after the game. “I still don’t even know what they saw on the double play. I’ve watched it 20 times. I’m still confused. To have it end like that — yeah, we still had a chance — but I don’t really know what to say.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this case place a nice picture of yourself in the second slide and give not only a brief bio to your audience (and when I say brief it means you are allowed to use between 10 and 20 words), but also - as above - your relationship with the topic. Regarding your portrait, when I talk about a nice picture I mean - whenever possible ...
2. Use the Outline View. One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View. You can choose it from the VIEW tab. This view doesn't display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents.
Step-1: Select the Slide first. At first, you have to go to the slide you want to change the layout of and then click on the 'Layout' button in the 'Slides' section of the 'Home' tab. This will open a drop-down menu of all the slide layouts in your presentation. Step-2: Click on Layout and Select a Different Layout.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
3. Template. A template is a pre-designed layout for a slide deck. It typically includes a set design, color scheme, typefaces, and placeholders for content like text, images, and graphs. Templates can significantly reduce the time and effort required to create a professional-looking presentation.
Let me elaborate on that. At the beginning of a presentation you share two facts with your audience: who you are and what you're going to talk about. I suggest that the second slide of your ...
From the Home tab, click the bottom half of the New Slide command. Choose the desired slide layout from the menu that appears. The new slide will appear. Click any placeholder and begin typing to add text. You can also click an icon to add other types of content, like a picture or chart.
Slide Pane: Each page of a presentation is called a slide. New presentations open with a Title slide in Normal view. The Slide Pane is where you'll add the text, images, and other screen-show elements that are a part of your presentation. Slides Tab: This area toggles between Slides view and Outline view. Slides view shows a tiny picture of all ...
Slide basics. Every PowerPoint presentation is composed of a series of slides. To begin creating a slide show, you'll need to know the basics of working with slides. You'll need to feel comfortable with tasks such as inserting a new slide, changing the layout of a slide, arranging existing slides, changing slide view, and adding notes to a slide.
A slide is a single screen of a presentation, and every presentation is composed of several slides. Depending on the subject matter, the best presentations may consist of 10 to 12 slides to get a message across, but more may be needed for complex subjects. Slides keep an audience's attention during a presentation and provide additional ...
1. Do keep your slides simple and succinct. "The most common mistake I see is slides that are overcrowded. People tend to want to spell everything out and cover too much information," says Jurczynski. Not only are these everything-but-the-kitchen-sink slides unattractive and amateurish, they also divert your audience's attention away from ...
Key Points: Summarize the main points covered in a clear, easy-to-read format. Visual Recap: Use simple graphics, charts, or callouts to represent significant data or conclusions visually. Concluding Remark: A sentence or two that encapsulates the overarching message or conclusion of the presentation.
Pecha Kucha, chit-chat in Japanese, is a unique presentation style. These presentations are known for telling stories through images rather than text and are typically brief. They use the 20x20 rule, where each presentation consists of 20 slides, and each slide is displayed for only 20 seconds, automatically progressing to the next one.
The main difference between a presentation and a slide is that a slide is just a single page of a presentation document whereas a presentation is an actual process of sharing and presenting the information present on the slides. There are several other similar terms that are used when referring to presentations.
Here's how to automatically advance slides in PowerPoint -. Step-1: Select the slide to add the effect. The first step is to select the slide that you want to modify or add the effect to. Step-2: Locate the "Advance slide" option. Next, click on the " Transitions " tab and locate the " Advance Slide " options.
From your first paragraph, it looks like you mean a dry slide with the list of section names (which can be generated automatically by, e.g., Beamer's \tableofcontents). @Jakebeal in his answer seems to understand it as a handwritten slide with an introduction/synopsis (which is maybe what you called "motivation slide").
Two weeks ago I gave you great tips and advice to start your presentation with a powerful first slide. Now that you're able to craft a great opening slide, you need to know what to do next: your…
1. Logo Animation. Your logo or brand is a critical part of your communication. So why put it in the corner of your slides? Your logo or brand should be displayed front and centre at the start of your presentation and well animated to convey the essence of your brand. Your logo style and colors should then be reflected in the presentation ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A typical presentation contains what type of content in the first and second slides? p. 371-72, What view appears when you start PowerPoint? p. 372, When might you want to create a new presentation using a template? p. 374 and more.
a title. PowerPoint assumes every new slide, except for a blank slide, has ____. landscape. By default, slides in a new presentation are in ____ orientation. quick access toolbar. The Undo button is located on the ____. enter. Pressing the ____ key when entering title text in a placeholder creates a new paragraph. backspace.
PechaKucha ( Japanese: ぺちゃくちゃ, IPA: [petɕa kɯ̥tɕa], [1] chit-chat) is a storytelling format in which a presenter shows 20 slides for 20 seconds of commentary each. At a PechaKucha Night, individuals gather at a venue to share personal presentations about their work. The PechaKucha format can be used, for example, in business ...
When a second slide is added to a presentation, a _____ __ appears on the right side of the Slide Pane to allow the users to move forward or backward through the presentation. ... In the accompanying Figure, the eight colorful slide thumbnails are called _____/ 20. The default setting for the Undo command reverses up o the last _ changed.
To create this shape, you can follow the below steps -. On the menu bar, click on "Insert" and then click on "Shapes". Under the basic shapes option, select the trapezium shape. Next, create the shape on your slide. Make sure that the size of the trapezium is good enough to cover about ⅔ parts of the slide.
PowerPoint slide size refers to the dimensions of the slides within your PowerPoint presentation. These dimensions determine how your content is displayed in a monitor or projector, and can significantly affect the overall look and feel of your presentation. The most common slide sizes in PowerPoint are 16:9 (widescreen) and 4:3 (standard).
The life of Saint Rita of Cascia the Play | 17th May 2024 | 8pm
Our Public Safety Committee is scheduled to meet at 12.30pm. Find the agenda here: https://grandrapidscity.primegov.com/Portal/Meeting?meetingTemplateId=3255
Kids and adults gather at a Memorial Day parade to honor and celebrate veterans in South Portland. Sofia Aldinio/ Staff Photographer. BATH. 10 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at 200 Congress Ave. and ...
Here's the explanation of the Iowa baseball interference call, according to a pool report response from umpire coordinator Mark Uhl: "There are three elements to what's called the force play slide rule and it's rule 8-4, it's on pages 77 and 78 of the NCAA Rule Book," Uhl told On3's Kyle Huesmann, the on-site pool reporter.