Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology

Research Methods | Definition, Types, Examples
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analysing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design . When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make.
First, decide how you will collect data . Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question :
- Qualitative vs quantitative : Will your data take the form of words or numbers?
- Primary vs secondary : Will you collect original data yourself, or will you use data that have already been collected by someone else?
- Descriptive vs experimental : Will you take measurements of something as it is, or will you perform an experiment?
Second, decide how you will analyse the data .
- For quantitative data, you can use statistical analysis methods to test relationships between variables.
- For qualitative data, you can use methods such as thematic analysis to interpret patterns and meanings in the data.
Table of contents
Methods for collecting data, examples of data collection methods, methods for analysing data, examples of data analysis methods, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Data are the information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question . The type of data you need depends on the aims of your research.
Qualitative vs quantitative data
Your choice of qualitative or quantitative data collection depends on the type of knowledge you want to develop.
For questions about ideas, experiences and meanings, or to study something that can’t be described numerically, collect qualitative data .
If you want to develop a more mechanistic understanding of a topic, or your research involves hypothesis testing , collect quantitative data .
| Qualitative | ||
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | . |
You can also take a mixed methods approach, where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Primary vs secondary data
Primary data are any original information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys , observations and experiments ). Secondary data are information that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in a government census or previous scientific studies).
If you are exploring a novel research question, you’ll probably need to collect primary data. But if you want to synthesise existing knowledge, analyse historical trends, or identify patterns on a large scale, secondary data might be a better choice.
| Primary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Secondary |
Descriptive vs experimental data
In descriptive research , you collect data about your study subject without intervening. The validity of your research will depend on your sampling method .
In experimental research , you systematically intervene in a process and measure the outcome. The validity of your research will depend on your experimental design .
To conduct an experiment, you need to be able to vary your independent variable , precisely measure your dependent variable, and control for confounding variables . If it’s practically and ethically possible, this method is the best choice for answering questions about cause and effect.
| Descriptive | ||
|---|---|---|
| Experimental |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
| Research method | Primary or secondary? | Qualitative or quantitative? | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Quantitative | To test cause-and-effect relationships. | |
| Primary | Quantitative | To understand general characteristics of a population. | |
| Interview/focus group | Primary | Qualitative | To gain more in-depth understanding of a topic. |
| Observation | Primary | Either | To understand how something occurs in its natural setting. |
| Secondary | Either | To situate your research in an existing body of work, or to evaluate trends within a research topic. | |
| Either | Either | To gain an in-depth understanding of a specific group or context, or when you don’t have the resources for a large study. |
Your data analysis methods will depend on the type of data you collect and how you prepare them for analysis.
Data can often be analysed both quantitatively and qualitatively. For example, survey responses could be analysed qualitatively by studying the meanings of responses or quantitatively by studying the frequencies of responses.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative analysis is used to understand words, ideas, and experiences. You can use it to interpret data that were collected:
- From open-ended survey and interview questions, literature reviews, case studies, and other sources that use text rather than numbers.
- Using non-probability sampling methods .
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions.
Quantitative analysis methods
Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive studies) or cause-and-effect relationships (in experiments).
You can use quantitative analysis to interpret data that were collected either:
- During an experiment.
- Using probability sampling methods .
Because the data are collected and analysed in a statistically valid way, the results of quantitative analysis can be easily standardised and shared among researchers.
| Research method | Qualitative or quantitative? | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | To analyse data collected in a statistically valid manner (e.g. from experiments, surveys, and observations). | |
| Meta-analysis | Quantitative | To statistically analyse the results of a large collection of studies. Can only be applied to studies that collected data in a statistically valid manner. |
| Qualitative | To analyse data collected from interviews, focus groups or textual sources. To understand general themes in the data and how they are communicated. | |
| Either | To analyse large volumes of textual or visual data collected from surveys, literature reviews, or other sources. Can be quantitative (i.e. frequencies of words) or qualitative (i.e. meanings of words). |
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
Is this article helpful?
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to Experimental Design | 5 Steps & Examples
- Between-Subjects Design | Examples, Pros & Cons
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
- Cluster Sampling | A Simple Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Confounding Variables | Definition, Examples & Controls
- Construct Validity | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Control Groups and Treatment Groups | Uses & Examples
- Controlled Experiments | Methods & Examples of Control
- Correlation vs Causation | Differences, Designs & Examples
- Correlational Research | Guide, Design & Examples
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Cross-Sectional Study | Definitions, Uses & Examples
- Data Cleaning | A Guide with Examples & Steps
- Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
- Explanatory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Explanatory vs Response Variables | Definitions & Examples
- Exploratory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples
- Extraneous Variables | Examples, Types, Controls
- Face Validity | Guide with Definition & Examples
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | Examples & Definition
- Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
- Inductive Reasoning | Types, Examples, Explanation
- Inductive vs Deductive Research Approach (with Examples)
- Internal Validity | Definition, Threats & Examples
- Internal vs External Validity | Understanding Differences & Examples
- Longitudinal Study | Definition, Approaches & Examples
- Mediator vs Moderator Variables | Differences & Examples
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Multistage Sampling | An Introductory Guide with Examples
- Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Population vs Sample | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods
- Quasi-Experimental Design | Definition, Types & Examples
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
- Reliability vs Validity in Research | Differences, Types & Examples
- Reproducibility vs Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques, & Examples
- Semi-Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Simple Random Sampling | Definition, Steps & Examples
- Stratified Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Systematic Review | Definition, Examples & Guide
- Systematic Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
- The 4 Types of Reliability in Research | Definitions & Examples
- The 4 Types of Validity | Types, Definitions & Examples
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
- Triangulation in Research | Guide, Types, Examples
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Examples
- Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples
- Unstructured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Are Control Variables | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Case-Control Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
- What Is a Double-Barrelled Question?
- What Is a Double-Blind Study? | Introduction & Examples
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- What Is a Prospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Retrospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
- What Is Concurrent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Content Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convergent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Criterion Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Deductive Reasoning? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Discriminant Validity? | Definition & Example
- What Is Ecological Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Ethnography? | Meaning, Guide & Examples
- What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
- What Is Predictive Validity? | Examples & Definition
- What Is Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Purposive Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
- What Is Quota Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
- What Is Snowball Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- Within-Subjects Design | Explanation, Approaches, Examples

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Why is research methodology important?
Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.
Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with....
What Is Research Methodology? A Plain-Language Explanation & Definition (With Examples)
By Derek Jansen (MBA) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Last updated April 2023)
If you’re new to formal academic research, it’s quite likely that you’re feeling a little overwhelmed by all the technical lingo that gets thrown around. And who could blame you – “research methodology”, “research methods”, “sampling strategies”… it all seems never-ending!
In this post, we’ll demystify the landscape with plain-language explanations and loads of examples (including easy-to-follow videos), so that you can approach your dissertation, thesis or research project with confidence. Let’s get started.
Research Methodology 101
- What exactly research methodology means
- What qualitative , quantitative and mixed methods are
- What sampling strategy is
- What data collection methods are
- What data analysis methods are
- How to choose your research methodology
- Example of a research methodology

What is research methodology?
Research methodology simply refers to the practical “how” of a research study. More specifically, it’s about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions . Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
- What type of data to collect (e.g., qualitative or quantitative data )
- Who to collect it from (i.e., the sampling strategy )
- How to collect it (i.e., the data collection method )
- How to analyse it (i.e., the data analysis methods )
Within any formal piece of academic research (be it a dissertation, thesis or journal article), you’ll find a research methodology chapter or section which covers the aspects mentioned above. Importantly, a good methodology chapter explains not just what methodological choices were made, but also explains why they were made. In other words, the methodology chapter should justify the design choices, by showing that the chosen methods and techniques are the best fit for the research aims, objectives and research questions.
So, it’s the same as research design?
Not quite. As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you’ll collect, from who, how you’ll collect it and how you’ll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you’ll adopt in your study. For example, whether you’ll use an experimental design in which you manipulate one variable while controlling others. You can learn more about research design and the various design types here .
Need a helping hand?
What are qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods?
Qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods are different types of methodological approaches, distinguished by their focus on words , numbers or both . This is a bit of an oversimplification, but its a good starting point for understanding.
Let’s take a closer look.
Qualitative research refers to research which focuses on collecting and analysing words (written or spoken) and textual or visual data, whereas quantitative research focuses on measurement and testing using numerical data . Qualitative analysis can also focus on other “softer” data points, such as body language or visual elements.
It’s quite common for a qualitative methodology to be used when the research aims and research questions are exploratory in nature. For example, a qualitative methodology might be used to understand peoples’ perceptions about an event that took place, or a political candidate running for president.
Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and research questions are confirmatory in nature. For example, a quantitative methodology might be used to measure the relationship between two variables (e.g. personality type and likelihood to commit a crime) or to test a set of hypotheses .
As you’ve probably guessed, the mixed-method methodology attempts to combine the best of both qualitative and quantitative methodologies to integrate perspectives and create a rich picture. If you’d like to learn more about these three methodological approaches, be sure to watch our explainer video below.
What is sampling strategy?
Simply put, sampling is about deciding who (or where) you’re going to collect your data from . Why does this matter? Well, generally it’s not possible to collect data from every single person in your group of interest (this is called the “population”), so you’ll need to engage a smaller portion of that group that’s accessible and manageable (this is called the “sample”).
How you go about selecting the sample (i.e., your sampling strategy) will have a major impact on your study. There are many different sampling methods you can choose from, but the two overarching categories are probability sampling and non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling involves using a completely random sample from the group of people you’re interested in. This is comparable to throwing the names all potential participants into a hat, shaking it up, and picking out the “winners”. By using a completely random sample, you’ll minimise the risk of selection bias and the results of your study will be more generalisable to the entire population.
Non-probability sampling , on the other hand, doesn’t use a random sample . For example, it might involve using a convenience sample, which means you’d only interview or survey people that you have access to (perhaps your friends, family or work colleagues), rather than a truly random sample. With non-probability sampling, the results are typically not generalisable .
To learn more about sampling methods, be sure to check out the video below.
What are data collection methods?
As the name suggests, data collection methods simply refers to the way in which you go about collecting the data for your study. Some of the most common data collection methods include:
- Interviews (which can be unstructured, semi-structured or structured)
- Focus groups and group interviews
- Surveys (online or physical surveys)
- Observations (watching and recording activities)
- Biophysical measurements (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, etc.)
- Documents and records (e.g., financial reports, court records, etc.)
The choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and research questions , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. For example, if your research is exploratory in nature, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups would likely be a good fit. Conversely, if your research aims to measure specific variables or test hypotheses, large-scale surveys that produce large volumes of numerical data would likely be a better fit.
What are data analysis methods?
Data analysis methods refer to the methods and techniques that you’ll use to make sense of your data. These can be grouped according to whether the research is qualitative (words-based) or quantitative (numbers-based).
Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include:
- Qualitative content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA)
- Visual analysis (of photographs, videos, art, etc.)
Qualitative data analysis all begins with data coding , after which an analysis method is applied. In some cases, more than one analysis method is used, depending on the research aims and research questions . In the video below, we explore some common qualitative analysis methods, along with practical examples.
Moving on to the quantitative side of things, popular data analysis methods in this type of research include:
- Descriptive statistics (e.g. means, medians, modes )
- Inferential statistics (e.g. correlation, regression, structural equation modelling)
Again, the choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and objectives , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. In the video below, we explain some core concepts central to quantitative analysis.
How do I choose a research methodology?
As you’ve probably picked up by now, your research aims and objectives have a major influence on the research methodology . So, the starting point for developing your research methodology is to take a step back and look at the big picture of your research, before you make methodology decisions. The first question you need to ask yourself is whether your research is exploratory or confirmatory in nature.
If your research aims and objectives are primarily exploratory in nature, your research will likely be qualitative and therefore you might consider qualitative data collection methods (e.g. interviews) and analysis methods (e.g. qualitative content analysis).
Conversely, if your research aims and objective are looking to measure or test something (i.e. they’re confirmatory), then your research will quite likely be quantitative in nature, and you might consider quantitative data collection methods (e.g. surveys) and analyses (e.g. statistical analysis).
Designing your research and working out your methodology is a large topic, which we cover extensively on the blog . For now, however, the key takeaway is that you should always start with your research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread). Every methodological choice you make needs align with those three components.
Example of a research methodology chapter
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of a research methodology from an actual dissertation, as well as an overview of our free methodology template .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

199 Comments
Thank you for this simple yet comprehensive and easy to digest presentation. God Bless!
You’re most welcome, Leo. Best of luck with your research!
I found it very useful. many thanks
This is really directional. A make-easy research knowledge.
Thank you for this, I think will help my research proposal
Thanks for good interpretation,well understood.
Good morning sorry I want to the search topic
Thank u more
Thank you, your explanation is simple and very helpful.
Very educative a.nd exciting platform. A bigger thank you and I’ll like to always be with you
That’s the best analysis
So simple yet so insightful. Thank you.
This really easy to read as it is self-explanatory. Very much appreciated…
Thanks for this. It’s so helpful and explicit. For those elements highlighted in orange, they were good sources of referrals for concepts I didn’t understand. A million thanks for this.
Good morning, I have been reading your research lessons through out a period of times. They are important, impressive and clear. Want to subscribe and be and be active with you.
Thankyou So much Sir Derek…
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on it so that we’ll continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Beautiful presentation. I love it.
please provide a research mehodology example for zoology
It’s very educative and well explained
Thanks for the concise and informative data.
This is really good for students to be safe and well understand that research is all about
Thank you so much Derek sir🖤🙏🤗
Very simple and reliable
This is really helpful. Thanks alot. God bless you.
very useful, Thank you very much..
thanks a lot its really useful
in a nutshell..thank you!
Thanks for updating my understanding on this aspect of my Thesis writing.
thank you so much my through this video am competently going to do a good job my thesis
Thanks a lot. Very simple to understand. I appreciate 🙏
Very simple but yet insightful Thank you
This has been an eye opening experience. Thank you grad coach team.
Very useful message for research scholars
Really very helpful thank you
yes you are right and i’m left
Research methodology with a simplest way i have never seen before this article.
wow thank u so much
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on is so that we will continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Very precise and informative.
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciate it.
Thanks this has really helped me. It is very easy to understand.
I found the notes and the presentation assisting and opening my understanding on research methodology
Good presentation
Im so glad you clarified my misconceptions. Im now ready to fry my onions. Thank you so much. God bless
Thank you a lot.
thanks for the easy way of learning and desirable presentation.
Thanks a lot. I am inspired
Well written
I am writing a APA Format paper . I using questionnaire with 120 STDs teacher for my participant. Can you write me mthology for this research. Send it through email sent. Just need a sample as an example please. My topic is ” impacts of overcrowding on students learning
Thanks for your comment.
We can’t write your methodology for you. If you’re looking for samples, you should be able to find some sample methodologies on Google. Alternatively, you can download some previous dissertations from a dissertation directory and have a look at the methodology chapters therein.
All the best with your research.
Thank you so much for this!! God Bless
Thank you. Explicit explanation
Thank you, Derek and Kerryn, for making this simple to understand. I’m currently at the inception stage of my research.
Thnks a lot , this was very usefull on my assignment
excellent explanation
I’m currently working on my master’s thesis, thanks for this! I’m certain that I will use Qualitative methodology.
Thanks a lot for this concise piece, it was quite relieving and helpful. God bless you BIG…
I am currently doing my dissertation proposal and I am sure that I will do quantitative research. Thank you very much it was extremely helpful.
Very interesting and informative yet I would like to know about examples of Research Questions as well, if possible.
I’m about to submit a research presentation, I have come to understand from your simplification on understanding research methodology. My research will be mixed methodology, qualitative as well as quantitative. So aim and objective of mixed method would be both exploratory and confirmatory. Thanks you very much for your guidance.
OMG thanks for that, you’re a life saver. You covered all the points I needed. Thank you so much ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
Thank you immensely for this simple, easy to comprehend explanation of data collection methods. I have been stuck here for months 😩. Glad I found your piece. Super insightful.
I’m going to write synopsis which will be quantitative research method and I don’t know how to frame my topic, can I kindly get some ideas..
Thanks for this, I was really struggling.
This was really informative I was struggling but this helped me.
Thanks a lot for this information, simple and straightforward. I’m a last year student from the University of South Africa UNISA South Africa.
its very much informative and understandable. I have enlightened.
An interesting nice exploration of a topic.
Thank you. Accurate and simple🥰
This article was really helpful, it helped me understanding the basic concepts of the topic Research Methodology. The examples were very clear, and easy to understand. I would like to visit this website again. Thank you so much for such a great explanation of the subject.
Thanks dude
Thank you Doctor Derek for this wonderful piece, please help to provide your details for reference purpose. God bless.
Many compliments to you
Great work , thank you very much for the simple explanation
Thank you. I had to give a presentation on this topic. I have looked everywhere on the internet but this is the best and simple explanation.
thank you, its very informative.
Well explained. Now I know my research methodology will be qualitative and exploratory. Thank you so much, keep up the good work
Well explained, thank you very much.
This is good explanation, I have understood the different methods of research. Thanks a lot.
Great work…very well explanation
Thanks Derek. Kerryn was just fantastic!
Great to hear that, Hyacinth. Best of luck with your research!
Its a good templates very attractive and important to PhD students and lectuter
Thanks for the feedback, Matobela. Good luck with your research methodology.
Thank you. This is really helpful.
You’re very welcome, Elie. Good luck with your research methodology.
Well explained thanks
This is a very helpful site especially for young researchers at college. It provides sufficient information to guide students and equip them with the necessary foundation to ask any other questions aimed at deepening their understanding.
Thanks for the kind words, Edward. Good luck with your research!
Thank you. I have learned a lot.
Great to hear that, Ngwisa. Good luck with your research methodology!
Thank you for keeping your presentation simples and short and covering key information for research methodology. My key takeaway: Start with defining your research objective the other will depend on the aims of your research question.
My name is Zanele I would like to be assisted with my research , and the topic is shortage of nursing staff globally want are the causes , effects on health, patients and community and also globally
Thanks for making it simple and clear. It greatly helped in understanding research methodology. Regards.
This is well simplified and straight to the point
Thank you Dr
I was given an assignment to research 2 publications and describe their research methodology? I don’t know how to start this task can someone help me?
Sure. You’re welcome to book an initial consultation with one of our Research Coaches to discuss how we can assist – https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Thanks a lot I am relieved of a heavy burden.keep up with the good work
I’m very much grateful Dr Derek. I’m planning to pursue one of the careers that really needs one to be very much eager to know. There’s a lot of research to do and everything, but since I’ve gotten this information I will use it to the best of my potential.
Thank you so much, words are not enough to explain how helpful this session has been for me!
Thanks this has thought me alot.
Very concise and helpful. Thanks a lot
Thank Derek. This is very helpful. Your step by step explanation has made it easier for me to understand different concepts. Now i can get on with my research.
I wish i had come across this sooner. So simple but yet insightful
really nice explanation thank you so much
I’m so grateful finding this site, it’s really helpful…….every term well explained and provide accurate understanding especially to student going into an in-depth research for the very first time, even though my lecturer already explained this topic to the class, I think I got the clear and efficient explanation here, much thanks to the author.
It is very helpful material
I would like to be assisted with my research topic : Literature Review and research methodologies. My topic is : what is the relationship between unemployment and economic growth?
Its really nice and good for us.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR EXPLANATION, ITS VERY CLEAR TO ME WHAT I WILL BE DOING FROM NOW .GREAT READS.
Short but sweet.Thank you
Informative article. Thanks for your detailed information.
I’m currently working on my Ph.D. thesis. Thanks a lot, Derek and Kerryn, Well-organized sequences, facilitate the readers’ following.
great article for someone who does not have any background can even understand
I am a bit confused about research design and methodology. Are they the same? If not, what are the differences and how are they related?
Thanks in advance.
concise and informative.
Thank you very much
How can we site this article is Harvard style?
Very well written piece that afforded better understanding of the concept. Thank you!
Am a new researcher trying to learn how best to write a research proposal. I find your article spot on and want to download the free template but finding difficulties. Can u kindly send it to my email, the free download entitled, “Free Download: Research Proposal Template (with Examples)”.
Thank too much
Thank you very much for your comprehensive explanation about research methodology so I like to thank you again for giving us such great things.
Good very well explained.Thanks for sharing it.
Thank u sir, it is really a good guideline.
so helpful thank you very much.
Thanks for the video it was very explanatory and detailed, easy to comprehend and follow up. please, keep it up the good work
It was very helpful, a well-written document with precise information.
how do i reference this?
MLA Jansen, Derek, and Kerryn Warren. “What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology?” Grad Coach, June 2021, gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/.
APA Jansen, D., & Warren, K. (2021, June). What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology? Grad Coach. https://gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/
Your explanation is easily understood. Thank you
Very help article. Now I can go my methodology chapter in my thesis with ease
I feel guided ,Thank you
This simplification is very helpful. It is simple but very educative, thanks ever so much
The write up is informative and educative. It is an academic intellectual representation that every good researcher can find useful. Thanks
Wow, this is wonderful long live.
Nice initiative
thank you the video was helpful to me.
Thank you very much for your simple and clear explanations I’m really satisfied by the way you did it By now, I think I can realize a very good article by following your fastidious indications May God bless you
Thanks very much, it was very concise and informational for a beginner like me to gain an insight into what i am about to undertake. I really appreciate.
very informative sir, it is amazing to understand the meaning of question hidden behind that, and simple language is used other than legislature to understand easily. stay happy.
This one is really amazing. All content in your youtube channel is a very helpful guide for doing research. Thanks, GradCoach.
research methodologies
Please send me more information concerning dissertation research.
Nice piece of knowledge shared….. #Thump_UP
This is amazing, it has said it all. Thanks to Gradcoach
This is wonderful,very elaborate and clear.I hope to reach out for your assistance in my research very soon.
This is the answer I am searching about…
realy thanks a lot
Thank you very much for this awesome, to the point and inclusive article.
Thank you very much I need validity and reliability explanation I have exams
Thank you for a well explained piece. This will help me going forward.
Very simple and well detailed Many thanks
This is so very simple yet so very effective and comprehensive. An Excellent piece of work.
I wish I saw this earlier on! Great insights for a beginner(researcher) like me. Thanks a mil!
Thank you very much, for such a simplified, clear and practical step by step both for academic students and general research work. Holistic, effective to use and easy to read step by step. One can easily apply the steps in practical terms and produce a quality document/up-to standard
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciated.
Thanks for a great work. well understood .
This was very helpful. It was simple but profound and very easy to understand. Thank you so much!
Great and amazing research guidelines. Best site for learning research
hello sir/ma’am, i didn’t find yet that what type of research methodology i am using. because i am writing my report on CSR and collect all my data from websites and articles so which type of methodology i should write in dissertation report. please help me. i am from India.
how does this really work?
perfect content, thanks a lot
As a researcher, I commend you for the detailed and simplified information on the topic in question. I would like to remain in touch for the sharing of research ideas on other topics. Thank you
Impressive. Thank you, Grad Coach 😍
Thank you Grad Coach for this piece of information. I have at least learned about the different types of research methodologies.
Very useful content with easy way
Thank you very much for the presentation. I am an MPH student with the Adventist University of Africa. I have successfully completed my theory and starting on my research this July. My topic is “Factors associated with Dental Caries in (one District) in Botswana. I need help on how to go about this quantitative research
I am so grateful to run across something that was sooo helpful. I have been on my doctorate journey for quite some time. Your breakdown on methodology helped me to refresh my intent. Thank you.
thanks so much for this good lecture. student from university of science and technology, Wudil. Kano Nigeria.
It’s profound easy to understand I appreciate
Thanks a lot for sharing superb information in a detailed but concise manner. It was really helpful and helped a lot in getting into my own research methodology.
Comment * thanks very much
This was sooo helpful for me thank you so much i didn’t even know what i had to write thank you!
You’re most welcome 🙂
Simple and good. Very much helpful. Thank you so much.
This is very good work. I have benefited.
Thank you so much for sharing
This is powerful thank you so much guys
I am nkasa lizwi doing my research proposal on honors with the university of Walter Sisulu Komani I m on part 3 now can you assist me.my topic is: transitional challenges faced by educators in intermediate phase in the Alfred Nzo District.
Appreciate the presentation. Very useful step-by-step guidelines to follow.
I appreciate sir
wow! This is super insightful for me. Thank you!
Indeed this material is very helpful! Kudos writers/authors.
I want to say thank you very much, I got a lot of info and knowledge. Be blessed.
I want present a seminar paper on Optimisation of Deep learning-based models on vulnerability detection in digital transactions.
Need assistance
Dear Sir, I want to be assisted on my research on Sanitation and Water management in emergencies areas.
I am deeply grateful for the knowledge gained. I will be getting in touch shortly as I want to be assisted in my ongoing research.
The information shared is informative, crisp and clear. Kudos Team! And thanks a lot!
hello i want to study
Hello!! Grad coach teams. I am extremely happy in your tutorial or consultation. i am really benefited all material and briefing. Thank you very much for your generous helps. Please keep it up. If you add in your briefing, references for further reading, it will be very nice.
All I have to say is, thank u gyz.
Good, l thanks
thank you, it is very useful
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog,…
- Free Download: Research Proposal Template (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Research design (methodology) […]
- Dissertation vs Thesis: What's the difference? - Grad Coach - […] and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a good research topic to which…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Research methods--quantitative, qualitative, and more: overview.
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Data Science Methods (Machine Learning, AI, Big Data)
- Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Evidence Synthesis/Systematic Reviews
- Get Data, Get Help!
About Research Methods
This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley.
As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods , "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge. The accumulation of knowledge through research is by its nature a collective endeavor. Each well-designed study provides evidence that may support, amend, refute, or deepen the understanding of existing knowledge...Decisions are important throughout the practice of research and are designed to help researchers collect evidence that includes the full spectrum of the phenomenon under study, to maintain logical rules, and to mitigate or account for possible sources of bias. In many ways, learning research methods is learning how to see and make these decisions."
The choice of methods varies by discipline, by the kind of phenomenon being studied and the data being used to study it, by the technology available, and more. This guide is an introduction, but if you don't see what you need here, always contact your subject librarian, and/or take a look to see if there's a library research guide that will answer your question.
Suggestions for changes and additions to this guide are welcome!
START HERE: SAGE Research Methods
Without question, the most comprehensive resource available from the library is SAGE Research Methods. HERE IS THE ONLINE GUIDE to this one-stop shopping collection, and some helpful links are below:
- SAGE Research Methods
- Little Green Books (Quantitative Methods)
- Little Blue Books (Qualitative Methods)
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedias
- Case studies of real research projects
- Sample datasets for hands-on practice
- Streaming video--see methods come to life
- Methodspace- -a community for researchers
- SAGE Research Methods Course Mapping
Library Data Services at UC Berkeley
Library Data Services Program and Digital Scholarship Services
The LDSP offers a variety of services and tools ! From this link, check out pages for each of the following topics: discovering data, managing data, collecting data, GIS data, text data mining, publishing data, digital scholarship, open science, and the Research Data Management Program.
Be sure also to check out the visual guide to where to seek assistance on campus with any research question you may have!
Library GIS Services
Other Data Services at Berkeley
D-Lab Supports Berkeley faculty, staff, and graduate students with research in data intensive social science, including a wide range of training and workshop offerings Dryad Dryad is a simple self-service tool for researchers to use in publishing their datasets. It provides tools for the effective publication of and access to research data. Geospatial Innovation Facility (GIF) Provides leadership and training across a broad array of integrated mapping technologies on campu Research Data Management A UC Berkeley guide and consulting service for research data management issues
General Research Methods Resources
Here are some general resources for assistance:
- Assistance from ICPSR (must create an account to access): Getting Help with Data , and Resources for Students
- Wiley Stats Ref for background information on statistics topics
- Survey Documentation and Analysis (SDA) . Program for easy web-based analysis of survey data.
Consultants
- D-Lab/Data Science Discovery Consultants Request help with your research project from peer consultants.
- Research data (RDM) consulting Meet with RDM consultants before designing the data security, storage, and sharing aspects of your qualitative project.
- Statistics Department Consulting Services A service in which advanced graduate students, under faculty supervision, are available to consult during specified hours in the Fall and Spring semesters.
Related Resourcex
- IRB / CPHS Qualitative research projects with human subjects often require that you go through an ethics review.
- OURS (Office of Undergraduate Research and Scholarships) OURS supports undergraduates who want to embark on research projects and assistantships. In particular, check out their "Getting Started in Research" workshops
- Sponsored Projects Sponsored projects works with researchers applying for major external grants.
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/researchmethods
Research Methods: What are research methods?
- What are research methods?
- Searching specific databases
What are research methods
Research methods are the strategies, processes or techniques utilized in the collection of data or evidence for analysis in order to uncover new information or create better understanding of a topic.
There are different types of research methods which use different tools for data collection.
Types of research
- Qualitative Research
- Quantitative Research
- Mixed Methods Research
Qualitative Research gathers data about lived experiences, emotions or behaviours, and the meanings individuals attach to them. It assists in enabling researchers to gain a better understanding of complex concepts, social interactions or cultural phenomena. This type of research is useful in the exploration of how or why things have occurred, interpreting events and describing actions.
Quantitative Research gathers numerical data which can be ranked, measured or categorised through statistical analysis. It assists with uncovering patterns or relationships, and for making generalisations. This type of research is useful for finding out how many, how much, how often, or to what extent.
Mixed Methods Research integrates both Q ualitative and Quantitative Research . It provides a holistic approach combining and analysing the statistical data with deeper contextualised insights. Using Mixed Methods also enables Triangulation, or verification, of the data from two or more sources.
Finding Mixed Methods research in the Databases
“mixed model*” OR “mixed design*” OR “multiple method*” OR multimethod* OR triangulat*
Data collection tools
| Qualitative Techniques or Tools | Quantitative Techniques or Tools |
|---|---|
| : these can be structured, semi-structured or unstructured in-depth sessions with the researcher and a participant. | Surveys or questionnaires: which ask the same questions to large numbers of participants or use Likert scales which measure opinions as numerical data. |
| : with several participants discussing a particular topic or a set of questions. Researchers can be facilitators or observers. | Observation: which can either involve counting the number of times a specific phenomenon occurs, or the coding of observational data in order to translate it into numbers. |
| : On-site, in-context or role-play options. | Document screening: sourcing numerical data from financial reports or counting word occurrences. |
| : Interrogation of correspondence (letters, diaries, emails etc) or reports. | Experiments: testing hypotheses in laboratories, testing cause and effect relationships, through field experiments, or via quasi- or natural experiments. |
| : Remembrances or memories of experiences told to the researcher. |
SAGE research methods
- SAGE research methods online This link opens in a new window Research methods tool to help researchers gather full-text resources, design research projects, understand a particular method and write up their research. Includes access to collections of video, business cases and eBooks,
Help and Information

- Next: Finding qualitative research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 11:16 AM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/researchmethods

- Research Process
Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers
- 3 minute read
- 41.3K views
Table of Contents
Choosing an optimal research methodology is crucial for the success of any research project. The methodology you select will determine the type of data you collect, how you collect it, and how you analyse it. Understanding the different types of research methods available along with their strengths and weaknesses, is thus imperative to make an informed decision.
Understanding different research methods:
There are several research methods available depending on the type of study you are conducting, i.e., whether it is laboratory-based, clinical, epidemiological, or survey based . Some common methodologies include qualitative research, quantitative research, experimental research, survey-based research, and action research. Each method can be opted for and modified, depending on the type of research hypotheses and objectives.
Qualitative vs quantitative research:
When deciding on a research methodology, one of the key factors to consider is whether your research will be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative research is used to understand people’s experiences, concepts, thoughts, or behaviours . Quantitative research, on the contrary, deals with numbers, graphs, and charts, and is used to test or confirm hypotheses, assumptions, and theories.
Qualitative research methodology:
Qualitative research is often used to examine issues that are not well understood, and to gather additional insights on these topics. Qualitative research methods include open-ended survey questions, observations of behaviours described through words, and reviews of literature that has explored similar theories and ideas. These methods are used to understand how language is used in real-world situations, identify common themes or overarching ideas, and describe and interpret various texts. Data analysis for qualitative research typically includes discourse analysis, thematic analysis, and textual analysis.
Quantitative research methodology:
The goal of quantitative research is to test hypotheses, confirm assumptions and theories, and determine cause-and-effect relationships. Quantitative research methods include experiments, close-ended survey questions, and countable and numbered observations. Data analysis for quantitative research relies heavily on statistical methods.
Analysing qualitative vs quantitative data:
The methods used for data analysis also differ for qualitative and quantitative research. As mentioned earlier, quantitative data is generally analysed using statistical methods and does not leave much room for speculation. It is more structured and follows a predetermined plan. In quantitative research, the researcher starts with a hypothesis and uses statistical methods to test it. Contrarily, methods used for qualitative data analysis can identify patterns and themes within the data, rather than provide statistical measures of the data. It is an iterative process, where the researcher goes back and forth trying to gauge the larger implications of the data through different perspectives and revising the analysis if required.
When to use qualitative vs quantitative research:
The choice between qualitative and quantitative research will depend on the gap that the research project aims to address, and specific objectives of the study. If the goal is to establish facts about a subject or topic, quantitative research is an appropriate choice. However, if the goal is to understand people’s experiences or perspectives, qualitative research may be more suitable.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an understanding of the different research methods available, their applicability, advantages, and disadvantages is essential for making an informed decision on the best methodology for your project. If you need any additional guidance on which research methodology to opt for, you can head over to Elsevier Author Services (EAS). EAS experts will guide you throughout the process and help you choose the perfect methodology for your research goals.

Why is data validation important in research?

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

Writing a good review article

Scholarly Sources: What are They and Where can You Find Them?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Research Design & Method
Research Methods Guide: Research Design & Method
- Introduction
- Survey Research
- Interview Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Research Design & Method
Research Methods (sociology-focused)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (intro)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (advanced)

FAQ: Research Design & Method
What is the difference between Research Design and Research Method?
Research design is a plan to answer your research question. A research method is a strategy used to implement that plan. Research design and methods are different but closely related, because good research design ensures that the data you obtain will help you answer your research question more effectively.
Which research method should I choose ?
It depends on your research goal. It depends on what subjects (and who) you want to study. Let's say you are interested in studying what makes people happy, or why some students are more conscious about recycling on campus. To answer these questions, you need to make a decision about how to collect your data. Most frequently used methods include:
- Observation / Participant Observation
- Focus Groups
- Experiments
- Secondary Data Analysis / Archival Study
- Mixed Methods (combination of some of the above)
One particular method could be better suited to your research goal than others, because the data you collect from different methods will be different in quality and quantity. For instance, surveys are usually designed to produce relatively short answers, rather than the extensive responses expected in qualitative interviews.
What other factors should I consider when choosing one method over another?
Time for data collection and analysis is something you want to consider. An observation or interview method, so-called qualitative approach, helps you collect richer information, but it takes time. Using a survey helps you collect more data quickly, yet it may lack details. So, you will need to consider the time you have for research and the balance between strengths and weaknesses associated with each method (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative).
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Survey Research >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
What is Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Examples

The search for knowledge is closely linked to the object of study; that is, to the reconstruction of the facts that will provide an explanation to an observed event and that at first sight can be considered as a problem. It is very human to seek answers and satisfy our curiosity. Let’s talk about research.
Content Index
What is Research?
What are the characteristics of research.
- Comparative analysis chart
Qualitative methods
Quantitative methods, 8 tips for conducting accurate research.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, “research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.”
Inductive methods analyze an observed event, while deductive methods verify the observed event. Inductive approaches are associated with qualitative research , and deductive methods are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis .
Research is conducted with a purpose to:
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions. Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research. The information must be accurate and correct. For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
What is the purpose of research?
There are three main purposes:
- Exploratory: As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions. The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem. It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before. This exploratory data analysis process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Descriptive Analysis
- Descriptive: It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection. Descriptive research describe the behavior of a sample population. Only one variable is required to conduct the study. The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings. For example, a study conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company profit.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Explanatory: Causal research or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures. Running experiments is the most popular form. For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Here is a comparative analysis chart for a better understanding:
| Approach used | Unstructured | Structured | Highly structured |
| Conducted through | Asking questions | Asking questions | By using hypotheses. |
| Time | Early stages of decision making | Later stages of decision making | Later stages of decision making |
It begins by asking the right questions and choosing an appropriate method to investigate the problem. After collecting answers to your questions, you can analyze the findings or observations to draw reasonable conclusions.
When it comes to customers and market studies, the more thorough your questions, the better the analysis. You get essential insights into brand perception and product needs by thoroughly collecting customer data through surveys and questionnaires . You can use this data to make smart decisions about your marketing strategies to position your business effectively.
To make sense of your study and get insights faster, it helps to use a research repository as a single source of truth in your organization and manage your research data in one centralized data repository .
Types of research methods and Examples

Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative .
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods .
Qualitative research is a method that collects data using conversational methods, usually open-ended questions . The responses collected are essentially non-numerical. This method helps a researcher understand what participants think and why they think in a particular way.
Types of qualitative methods include:
- One-to-one Interview
- Focus Groups
- Ethnographic studies
- Text Analysis
Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable forms . It uses a systematic way of investigating events or data. It answers questions to justify relationships with measurable variables to either explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
Types of quantitative methods include:
- Survey research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
Remember, it is only valuable and useful when it is valid, accurate, and reliable. Incorrect results can lead to customer churn and a decrease in sales.
It is essential to ensure that your data is:
- Valid – founded, logical, rigorous, and impartial.
- Accurate – free of errors and including required details.
- Reliable – other people who investigate in the same way can produce similar results.
- Timely – current and collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Complete – includes all the data you need to support your business decisions.
Gather insights

- Identify the main trends and issues, opportunities, and problems you observe. Write a sentence describing each one.
- Keep track of the frequency with which each of the main findings appears.
- Make a list of your findings from the most common to the least common.
- Evaluate a list of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats identified in a SWOT analysis .
- Prepare conclusions and recommendations about your study.
- Act on your strategies
- Look for gaps in the information, and consider doing additional inquiry if necessary
- Plan to review the results and consider efficient methods to analyze and interpret results.
Review your goals before making any conclusions about your study. Remember how the process you have completed and the data you have gathered help answer your questions. Ask yourself if what your analysis revealed facilitates the identification of your conclusions and recommendations.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Exploring Types of Correlation for Patterns and Relationship
Jun 10, 2024

Life@QuestionPro: The Journey of Kristie Lawrence
Jun 7, 2024

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is research methodology?

The basics of research methodology
Why do you need a research methodology, what needs to be included, why do you need to document your research method, what are the different types of research instruments, qualitative / quantitative / mixed research methodologies, how do you choose the best research methodology for you, frequently asked questions about research methodology, related articles.
When you’re working on your first piece of academic research, there are many different things to focus on, and it can be overwhelming to stay on top of everything. This is especially true of budding or inexperienced researchers.
If you’ve never put together a research proposal before or find yourself in a position where you need to explain your research methodology decisions, there are a few things you need to be aware of.
Once you understand the ins and outs, handling academic research in the future will be less intimidating. We break down the basics below:
A research methodology encompasses the way in which you intend to carry out your research. This includes how you plan to tackle things like collection methods, statistical analysis, participant observations, and more.
You can think of your research methodology as being a formula. One part will be how you plan on putting your research into practice, and another will be why you feel this is the best way to approach it. Your research methodology is ultimately a methodological and systematic plan to resolve your research problem.
In short, you are explaining how you will take your idea and turn it into a study, which in turn will produce valid and reliable results that are in accordance with the aims and objectives of your research. This is true whether your paper plans to make use of qualitative methods or quantitative methods.
The purpose of a research methodology is to explain the reasoning behind your approach to your research - you'll need to support your collection methods, methods of analysis, and other key points of your work.
Think of it like writing a plan or an outline for you what you intend to do.
When carrying out research, it can be easy to go off-track or depart from your standard methodology.
Tip: Having a methodology keeps you accountable and on track with your original aims and objectives, and gives you a suitable and sound plan to keep your project manageable, smooth, and effective.
With all that said, how do you write out your standard approach to a research methodology?
As a general plan, your methodology should include the following information:
- Your research method. You need to state whether you plan to use quantitative analysis, qualitative analysis, or mixed-method research methods. This will often be determined by what you hope to achieve with your research.
- Explain your reasoning. Why are you taking this methodological approach? Why is this particular methodology the best way to answer your research problem and achieve your objectives?
- Explain your instruments. This will mainly be about your collection methods. There are varying instruments to use such as interviews, physical surveys, questionnaires, for example. Your methodology will need to detail your reasoning in choosing a particular instrument for your research.
- What will you do with your results? How are you going to analyze the data once you have gathered it?
- Advise your reader. If there is anything in your research methodology that your reader might be unfamiliar with, you should explain it in more detail. For example, you should give any background information to your methods that might be relevant or provide your reasoning if you are conducting your research in a non-standard way.
- How will your sampling process go? What will your sampling procedure be and why? For example, if you will collect data by carrying out semi-structured or unstructured interviews, how will you choose your interviewees and how will you conduct the interviews themselves?
- Any practical limitations? You should discuss any limitations you foresee being an issue when you’re carrying out your research.
In any dissertation, thesis, or academic journal, you will always find a chapter dedicated to explaining the research methodology of the person who carried out the study, also referred to as the methodology section of the work.
A good research methodology will explain what you are going to do and why, while a poor methodology will lead to a messy or disorganized approach.
You should also be able to justify in this section your reasoning for why you intend to carry out your research in a particular way, especially if it might be a particularly unique method.
Having a sound methodology in place can also help you with the following:
- When another researcher at a later date wishes to try and replicate your research, they will need your explanations and guidelines.
- In the event that you receive any criticism or questioning on the research you carried out at a later point, you will be able to refer back to it and succinctly explain the how and why of your approach.
- It provides you with a plan to follow throughout your research. When you are drafting your methodology approach, you need to be sure that the method you are using is the right one for your goal. This will help you with both explaining and understanding your method.
- It affords you the opportunity to document from the outset what you intend to achieve with your research, from start to finish.
A research instrument is a tool you will use to help you collect, measure and analyze the data you use as part of your research.
The choice of research instrument will usually be yours to make as the researcher and will be whichever best suits your methodology.
There are many different research instruments you can use in collecting data for your research.
Generally, they can be grouped as follows:
- Interviews (either as a group or one-on-one). You can carry out interviews in many different ways. For example, your interview can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. The difference between them is how formal the set of questions is that is asked of the interviewee. In a group interview, you may choose to ask the interviewees to give you their opinions or perceptions on certain topics.
- Surveys (online or in-person). In survey research, you are posing questions in which you ask for a response from the person taking the survey. You may wish to have either free-answer questions such as essay-style questions, or you may wish to use closed questions such as multiple choice. You may even wish to make the survey a mixture of both.
- Focus Groups. Similar to the group interview above, you may wish to ask a focus group to discuss a particular topic or opinion while you make a note of the answers given.
- Observations. This is a good research instrument to use if you are looking into human behaviors. Different ways of researching this include studying the spontaneous behavior of participants in their everyday life, or something more structured. A structured observation is research conducted at a set time and place where researchers observe behavior as planned and agreed upon with participants.
These are the most common ways of carrying out research, but it is really dependent on your needs as a researcher and what approach you think is best to take.
It is also possible to combine a number of research instruments if this is necessary and appropriate in answering your research problem.
There are three different types of methodologies, and they are distinguished by whether they focus on words, numbers, or both.
| Data type | What is it? | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
Quantitative | This methodology focuses more on measuring and testing numerical data. What is the aim of quantitative research? | Surveys, tests, existing databases. |
Qualitative | Qualitative research is a process of collecting and analyzing both words and textual data. | Observations, interviews, focus groups. |
Mixed-method | A mixed-method approach combines both of the above approaches. | Where you can use a mixed method of research, this can produce some incredibly interesting results. This is due to testing in a way that provides data that is both proven to be exact while also being exploratory at the same time. |
➡️ Want to learn more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative research, and how to use both methods? Check out our guide for that!
If you've done your due diligence, you'll have an idea of which methodology approach is best suited to your research.
It’s likely that you will have carried out considerable reading and homework before you reach this point and you may have taken inspiration from other similar studies that have yielded good results.
Still, it is important to consider different options before setting your research in stone. Exploring different options available will help you to explain why the choice you ultimately make is preferable to other methods.
If proving your research problem requires you to gather large volumes of numerical data to test hypotheses, a quantitative research method is likely to provide you with the most usable results.
If instead you’re looking to try and learn more about people, and their perception of events, your methodology is more exploratory in nature and would therefore probably be better served using a qualitative research methodology.
It helps to always bring things back to the question: what do I want to achieve with my research?
Once you have conducted your research, you need to analyze it. Here are some helpful guides for qualitative data analysis:
➡️ How to do a content analysis
➡️ How to do a thematic analysis
➡️ How to do a rhetorical analysis
Research methodology refers to the techniques used to find and analyze information for a study, ensuring that the results are valid, reliable and that they address the research objective.
Data can typically be organized into four different categories or methods: observational, experimental, simulation, and derived.
Writing a methodology section is a process of introducing your methods and instruments, discussing your analysis, providing more background information, addressing your research limitations, and more.
Your research methodology section will need a clear research question and proposed research approach. You'll need to add a background, introduce your research question, write your methodology and add the works you cited during your data collecting phase.
The research methodology section of your study will indicate how valid your findings are and how well-informed your paper is. It also assists future researchers planning to use the same methodology, who want to cite your study or replicate it.


Research Methodologies
- What are research designs?
- What are research methodologies?
What are research methods?
Quantitative research methods, qualitative research methods, mixed method approach, selecting the best research method.
- Additional Sources
Research methods are different from research methodologies because they are the ways in which you will collect the data for your research project. The best method for your project largely depends on your topic, the type of data you will need, and the people or items from which you will be collecting data. The following boxes below contain a list of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methods.
- Closed-ended questionnaires/survey: These types of questionnaires or surveys are like "multiple choice" tests, where participants must select from a list of premade answers. According to the content of the question, they must select the one that they agree with the most. This approach is the simplest form of quantitative research because the data is easy to combine and quantify.
- Structured interviews: These are a common research method in market research because the data can be quantified. They are strictly designed for little "wiggle room" in the interview process so that the data will not be skewed. You can conduct structured interviews in-person, online, or over the phone (Dawson, 2019).
Constructing Questionnaires
When constructing your questions for a survey or questionnaire, there are things you can do to ensure that your questions are accurate and easy to understand (Dawson, 2019):
- Keep the questions brief and simple.
- Eliminate any potential bias from your questions. Make sure that they do not word things in a way that favor one perspective over another.
- If your topic is very sensitive, you may want to ask indirect questions rather than direct ones. This prevents participants from being intimidated and becoming unwilling to share their true responses.
- If you are using a closed-ended question, try to offer every possible answer that a participant could give to that question.
- Do not ask questions that assume something of the participant. The question "How often do you exercise?" assumes that the participant exercises (when they may not), so you would want to include a question that asks if they exercise at all before asking them how often.
- Try and keep the questionnaire as short as possible. The longer a questionnaire takes, the more likely the participant will not complete it or get too tired to put truthful answers.
- Promise confidentiality to your participants at the beginning of the questionnaire.
Quantitative Research Measures
When you are considering a quantitative approach to your research, you need to identify why types of measures you will use in your study. This will determine what type of numbers you will be using to collect your data. There are four levels of measurement:
- Nominal: These are numbers where the order of the numbers do not matter. They aim to identify separate information. One example is collecting zip codes from research participants. The order of the numbers does not matter, but the series of numbers in each zip code indicate different information (Adamson and Prion, 2013).
- Ordinal: Also known as rankings because the order of these numbers matter. This is when items are given a specific rank according to specific criteria. A common example of ordinal measurements include ranking-based questionnaires, where participants are asked to rank items from least favorite to most favorite. Another common example is a pain scale, where a patient is asked to rank their pain on a scale from 1 to 10 (Adamson and Prion, 2013).
- Interval: This is when the data are ordered and the distance between the numbers matters to the researcher (Adamson and Prion, 2013). The distance between each number is the same. An example of interval data is test grades.
- Ratio: This is when the data are ordered and have a consistent distance between numbers, but has a "zero point." This means that there could be a measurement of zero of whatever you are measuring in your study (Adamson and Prion, 2013). An example of ratio data is measuring the height of something because the "zero point" remains constant in all measurements. The height of something could also be zero.
Focus Groups
This is when a select group of people gather to talk about a particular topic. They can also be called discussion groups or group interviews (Dawson, 2019). They are usually lead by a moderator to help guide the discussion and ask certain questions. It is critical that a moderator allows everyone in the group to get a chance to speak so that no one dominates the discussion. The data that are gathered from focus groups tend to be thoughts, opinions, and perspectives about an issue.
Advantages of Focus Groups
- Only requires one meeting to get different types of responses.
- Less researcher bias due to participants being able to speak openly.
- Helps participants overcome insecurities or fears about a topic.
- The researcher can also consider the impact of participant interaction.
Disadvantages of Focus Groups
- Participants may feel uncomfortable to speak in front of an audience, especially if the topic is sensitive or controversial.
- Since participation is voluntary, not every participant may contribute equally to the discussion.
- Participants may impact what others say or think.
- A researcher may feel intimidated by running a focus group on their own.
- A researcher may need extra funds/resources to provide a safe space to host the focus group.
- Because the data is collective, it may be difficult to determine a participant's individual thoughts about the research topic.
Observation
There are two ways to conduct research observations:
- Direct Observation: The researcher observes a participant in an environment. The researcher often takes notes or uses technology to gather data, such as a voice recorder or video camera. The researcher does not interact or interfere with the participants. This approach is often used in psychology and health studies (Dawson, 2019).
- Participant Observation: The researcher interacts directly with the participants to get a better understanding of the research topic. This is a common research method when trying to understand another culture or community. It is important to decide if you will conduct a covert (participants do not know they are part of the research) or overt (participants know the researcher is observing them) observation because it can be unethical in some situations (Dawson, 2019).
Open-Ended Questionnaires
These types of questionnaires are the opposite of "multiple choice" questionnaires because the answer boxes are left open for the participant to complete. This means that participants can write short or extended answers to the questions. Upon gathering the responses, researchers will often "quantify" the data by organizing the responses into different categories. This can be time consuming because the researcher needs to read all responses carefully.
Semi-structured Interviews
This is the most common type of interview where researchers aim to get specific information so they can compare it to other interview data. This requires asking the same questions for each interview, but keeping their responses flexible. This means including follow-up questions if a subject answers a certain way. Interview schedules are commonly used to aid the interviewers, which list topics or questions that will be discussed at each interview (Dawson, 2019).
Theoretical Analysis
Often used for nonhuman research, theoretical analysis is a qualitative approach where the researcher applies a theoretical framework to analyze something about their topic. A theoretical framework gives the researcher a specific "lens" to view the topic and think about it critically. it also serves as context to guide the entire study. This is a popular research method for analyzing works of literature, films, and other forms of media. You can implement more than one theoretical framework with this method, as many theories complement one another.
Common theoretical frameworks for qualitative research are (Grant and Osanloo, 2014):
- Behavioral theory
- Change theory
- Cognitive theory
- Content analysis
- Cross-sectional analysis
- Developmental theory
- Feminist theory
- Gender theory
- Marxist theory
- Queer theory
- Systems theory
- Transformational theory
Unstructured Interviews
These are in-depth interviews where the researcher tries to understand an interviewee's perspective on a situation or issue. They are sometimes called life history interviews. It is important not to bombard the interviewee with too many questions so they can freely disclose their thoughts (Dawson, 2019).
- Open-ended and closed-ended questionnaires: This approach means implementing elements of both questionnaire types into your data collection. Participants may answer some questions with premade answers and write their own answers to other questions. The advantage to this method is that you benefit from both types of data collection to get a broader understanding of you participants. However, you must think carefully about how you will analyze this data to arrive at a conclusion.
Other mixed method approaches that incorporate quantitative and qualitative research methods depend heavily on the research topic. It is strongly recommended that you collaborate with your academic advisor before finalizing a mixed method approach.
How do you determine which research method would be best for your proposal? This heavily depends on your research objective. According to Dawson (2019), there are several questions to ask yourself when determining the best research method for your project:
- Are you good with numbers and mathematics?
- Would you be interested in conducting interviews with human subjects?
- Would you enjoy creating a questionnaire for participants to complete?
- Do you prefer written communication or face-to-face interaction?
- What skills or experiences do you have that might help you with your research? Do you have any experiences from past research projects that can help with this one?
- How much time do you have to complete the research? Some methods take longer to collect data than others.
- What is your budget? Do you have adequate funding to conduct the research in the method you want?
- How much data do you need? Some research topics need only a small amount of data while others may need significantly larger amounts.
- What is the purpose of your research? This can provide a good indicator as to what research method will be most appropriate.
- << Previous: What are research methodologies?
- Next: Additional Sources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 2, 2022 2:36 PM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

A tutorial on methodological studies: the what, when, how and why
Lawrence mbuagbaw.
1 Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Canada
2 Biostatistics Unit/FSORC, 50 Charlton Avenue East, St Joseph’s Healthcare—Hamilton, 3rd Floor Martha Wing, Room H321, Hamilton, Ontario L8N 4A6 Canada
3 Centre for the Development of Best Practices in Health, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Daeria O. Lawson
Livia puljak.
4 Center for Evidence-Based Medicine and Health Care, Catholic University of Croatia, Ilica 242, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia
David B. Allison
5 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health – Bloomington, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 USA
Lehana Thabane
6 Departments of Paediatrics and Anaesthesia, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Canada
7 Centre for Evaluation of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Healthcare-Hamilton, Hamilton, ON Canada
8 Population Health Research Institute, Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton, ON Canada
Associated Data
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Methodological studies – studies that evaluate the design, analysis or reporting of other research-related reports – play an important role in health research. They help to highlight issues in the conduct of research with the aim of improving health research methodology, and ultimately reducing research waste.
We provide an overview of some of the key aspects of methodological studies such as what they are, and when, how and why they are done. We adopt a “frequently asked questions” format to facilitate reading this paper and provide multiple examples to help guide researchers interested in conducting methodological studies. Some of the topics addressed include: is it necessary to publish a study protocol? How to select relevant research reports and databases for a methodological study? What approaches to data extraction and statistical analysis should be considered when conducting a methodological study? What are potential threats to validity and is there a way to appraise the quality of methodological studies?
Appropriate reflection and application of basic principles of epidemiology and biostatistics are required in the design and analysis of methodological studies. This paper provides an introduction for further discussion about the conduct of methodological studies.
The field of meta-research (or research-on-research) has proliferated in recent years in response to issues with research quality and conduct [ 1 – 3 ]. As the name suggests, this field targets issues with research design, conduct, analysis and reporting. Various types of research reports are often examined as the unit of analysis in these studies (e.g. abstracts, full manuscripts, trial registry entries). Like many other novel fields of research, meta-research has seen a proliferation of use before the development of reporting guidance. For example, this was the case with randomized trials for which risk of bias tools and reporting guidelines were only developed much later – after many trials had been published and noted to have limitations [ 4 , 5 ]; and for systematic reviews as well [ 6 – 8 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, studies that report on research differ substantially in how they are named, conducted and reported [ 9 , 10 ]. This creates challenges in identifying, summarizing and comparing them. In this tutorial paper, we will use the term methodological study to refer to any study that reports on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary or secondary research-related reports (such as trial registry entries and conference abstracts).
In the past 10 years, there has been an increase in the use of terms related to methodological studies (based on records retrieved with a keyword search [in the title and abstract] for “methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study” in PubMed up to December 2019), suggesting that these studies may be appearing more frequently in the literature. See Fig. 1 .

Trends in the number studies that mention “methodological review” or “meta-
epidemiological study” in PubMed.
The methods used in many methodological studies have been borrowed from systematic and scoping reviews. This practice has influenced the direction of the field, with many methodological studies including searches of electronic databases, screening of records, duplicate data extraction and assessments of risk of bias in the included studies. However, the research questions posed in methodological studies do not always require the approaches listed above, and guidance is needed on when and how to apply these methods to a methodological study. Even though methodological studies can be conducted on qualitative or mixed methods research, this paper focuses on and draws examples exclusively from quantitative research.
The objectives of this paper are to provide some insights on how to conduct methodological studies so that there is greater consistency between the research questions posed, and the design, analysis and reporting of findings. We provide multiple examples to illustrate concepts and a proposed framework for categorizing methodological studies in quantitative research.
What is a methodological study?
Any study that describes or analyzes methods (design, conduct, analysis or reporting) in published (or unpublished) literature is a methodological study. Consequently, the scope of methodological studies is quite extensive and includes, but is not limited to, topics as diverse as: research question formulation [ 11 ]; adherence to reporting guidelines [ 12 – 14 ] and consistency in reporting [ 15 ]; approaches to study analysis [ 16 ]; investigating the credibility of analyses [ 17 ]; and studies that synthesize these methodological studies [ 18 ]. While the nomenclature of methodological studies is not uniform, the intents and purposes of these studies remain fairly consistent – to describe or analyze methods in primary or secondary studies. As such, methodological studies may also be classified as a subtype of observational studies.
Parallel to this are experimental studies that compare different methods. Even though they play an important role in informing optimal research methods, experimental methodological studies are beyond the scope of this paper. Examples of such studies include the randomized trials by Buscemi et al., comparing single data extraction to double data extraction [ 19 ], and Carrasco-Labra et al., comparing approaches to presenting findings in Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) summary of findings tables [ 20 ]. In these studies, the unit of analysis is the person or groups of individuals applying the methods. We also direct readers to the Studies Within a Trial (SWAT) and Studies Within a Review (SWAR) programme operated through the Hub for Trials Methodology Research, for further reading as a potential useful resource for these types of experimental studies [ 21 ]. Lastly, this paper is not meant to inform the conduct of research using computational simulation and mathematical modeling for which some guidance already exists [ 22 ], or studies on the development of methods using consensus-based approaches.
When should we conduct a methodological study?
Methodological studies occupy a unique niche in health research that allows them to inform methodological advances. Methodological studies should also be conducted as pre-cursors to reporting guideline development, as they provide an opportunity to understand current practices, and help to identify the need for guidance and gaps in methodological or reporting quality. For example, the development of the popular Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were preceded by methodological studies identifying poor reporting practices [ 23 , 24 ]. In these instances, after the reporting guidelines are published, methodological studies can also be used to monitor uptake of the guidelines.
These studies can also be conducted to inform the state of the art for design, analysis and reporting practices across different types of health research fields, with the aim of improving research practices, and preventing or reducing research waste. For example, Samaan et al. conducted a scoping review of adherence to different reporting guidelines in health care literature [ 18 ]. Methodological studies can also be used to determine the factors associated with reporting practices. For example, Abbade et al. investigated journal characteristics associated with the use of the Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (PICOT) format in framing research questions in trials of venous ulcer disease [ 11 ].
How often are methodological studies conducted?
There is no clear answer to this question. Based on a search of PubMed, the use of related terms (“methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study”) – and therefore, the number of methodological studies – is on the rise. However, many other terms are used to describe methodological studies. There are also many studies that explore design, conduct, analysis or reporting of research reports, but that do not use any specific terms to describe or label their study design in terms of “methodology”. This diversity in nomenclature makes a census of methodological studies elusive. Appropriate terminology and key words for methodological studies are needed to facilitate improved accessibility for end-users.
Why do we conduct methodological studies?
Methodological studies provide information on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary and secondary research and can be used to appraise quality, quantity, completeness, accuracy and consistency of health research. These issues can be explored in specific fields, journals, databases, geographical regions and time periods. For example, Areia et al. explored the quality of reporting of endoscopic diagnostic studies in gastroenterology [ 25 ]; Knol et al. investigated the reporting of p -values in baseline tables in randomized trial published in high impact journals [ 26 ]; Chen et al. describe adherence to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement in Chinese Journals [ 27 ]; and Hopewell et al. describe the effect of editors’ implementation of CONSORT guidelines on reporting of abstracts over time [ 28 ]. Methodological studies provide useful information to researchers, clinicians, editors, publishers and users of health literature. As a result, these studies have been at the cornerstone of important methodological developments in the past two decades and have informed the development of many health research guidelines including the highly cited CONSORT statement [ 5 ].
Where can we find methodological studies?
Methodological studies can be found in most common biomedical bibliographic databases (e.g. Embase, MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science). However, the biggest caveat is that methodological studies are hard to identify in the literature due to the wide variety of names used and the lack of comprehensive databases dedicated to them. A handful can be found in the Cochrane Library as “Cochrane Methodology Reviews”, but these studies only cover methodological issues related to systematic reviews. Previous attempts to catalogue all empirical studies of methods used in reviews were abandoned 10 years ago [ 29 ]. In other databases, a variety of search terms may be applied with different levels of sensitivity and specificity.
Some frequently asked questions about methodological studies
In this section, we have outlined responses to questions that might help inform the conduct of methodological studies.
Q: How should I select research reports for my methodological study?
A: Selection of research reports for a methodological study depends on the research question and eligibility criteria. Once a clear research question is set and the nature of literature one desires to review is known, one can then begin the selection process. Selection may begin with a broad search, especially if the eligibility criteria are not apparent. For example, a methodological study of Cochrane Reviews of HIV would not require a complex search as all eligible studies can easily be retrieved from the Cochrane Library after checking a few boxes [ 30 ]. On the other hand, a methodological study of subgroup analyses in trials of gastrointestinal oncology would require a search to find such trials, and further screening to identify trials that conducted a subgroup analysis [ 31 ].
The strategies used for identifying participants in observational studies can apply here. One may use a systematic search to identify all eligible studies. If the number of eligible studies is unmanageable, a random sample of articles can be expected to provide comparable results if it is sufficiently large [ 32 ]. For example, Wilson et al. used a random sample of trials from the Cochrane Stroke Group’s Trial Register to investigate completeness of reporting [ 33 ]. It is possible that a simple random sample would lead to underrepresentation of units (i.e. research reports) that are smaller in number. This is relevant if the investigators wish to compare multiple groups but have too few units in one group. In this case a stratified sample would help to create equal groups. For example, in a methodological study comparing Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews, Kahale et al. drew random samples from both groups [ 34 ]. Alternatively, systematic or purposeful sampling strategies can be used and we encourage researchers to justify their selected approaches based on the study objective.
Q: How many databases should I search?
A: The number of databases one should search would depend on the approach to sampling, which can include targeting the entire “population” of interest or a sample of that population. If you are interested in including the entire target population for your research question, or drawing a random or systematic sample from it, then a comprehensive and exhaustive search for relevant articles is required. In this case, we recommend using systematic approaches for searching electronic databases (i.e. at least 2 databases with a replicable and time stamped search strategy). The results of your search will constitute a sampling frame from which eligible studies can be drawn.
Alternatively, if your approach to sampling is purposeful, then we recommend targeting the database(s) or data sources (e.g. journals, registries) that include the information you need. For example, if you are conducting a methodological study of high impact journals in plastic surgery and they are all indexed in PubMed, you likely do not need to search any other databases. You may also have a comprehensive list of all journals of interest and can approach your search using the journal names in your database search (or by accessing the journal archives directly from the journal’s website). Even though one could also search journals’ web pages directly, using a database such as PubMed has multiple advantages, such as the use of filters, so the search can be narrowed down to a certain period, or study types of interest. Furthermore, individual journals’ web sites may have different search functionalities, which do not necessarily yield a consistent output.
Q: Should I publish a protocol for my methodological study?
A: A protocol is a description of intended research methods. Currently, only protocols for clinical trials require registration [ 35 ]. Protocols for systematic reviews are encouraged but no formal recommendation exists. The scientific community welcomes the publication of protocols because they help protect against selective outcome reporting, the use of post hoc methodologies to embellish results, and to help avoid duplication of efforts [ 36 ]. While the latter two risks exist in methodological research, the negative consequences may be substantially less than for clinical outcomes. In a sample of 31 methodological studies, 7 (22.6%) referenced a published protocol [ 9 ]. In the Cochrane Library, there are 15 protocols for methodological reviews (21 July 2020). This suggests that publishing protocols for methodological studies is not uncommon.
Authors can consider publishing their study protocol in a scholarly journal as a manuscript. Advantages of such publication include obtaining peer-review feedback about the planned study, and easy retrieval by searching databases such as PubMed. The disadvantages in trying to publish protocols includes delays associated with manuscript handling and peer review, as well as costs, as few journals publish study protocols, and those journals mostly charge article-processing fees [ 37 ]. Authors who would like to make their protocol publicly available without publishing it in scholarly journals, could deposit their study protocols in publicly available repositories, such as the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ).
Q: How to appraise the quality of a methodological study?
A: To date, there is no published tool for appraising the risk of bias in a methodological study, but in principle, a methodological study could be considered as a type of observational study. Therefore, during conduct or appraisal, care should be taken to avoid the biases common in observational studies [ 38 ]. These biases include selection bias, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of exposure or outcome. In other words, to generate a representative sample, a comprehensive reproducible search may be necessary to build a sampling frame. Additionally, random sampling may be necessary to ensure that all the included research reports have the same probability of being selected, and the screening and selection processes should be transparent and reproducible. To ensure that the groups compared are similar in all characteristics, matching, random sampling or stratified sampling can be used. Statistical adjustments for between-group differences can also be applied at the analysis stage. Finally, duplicate data extraction can reduce errors in assessment of exposures or outcomes.
Q: Should I justify a sample size?
A: In all instances where one is not using the target population (i.e. the group to which inferences from the research report are directed) [ 39 ], a sample size justification is good practice. The sample size justification may take the form of a description of what is expected to be achieved with the number of articles selected, or a formal sample size estimation that outlines the number of articles required to answer the research question with a certain precision and power. Sample size justifications in methodological studies are reasonable in the following instances:
- Comparing two groups
- Determining a proportion, mean or another quantifier
- Determining factors associated with an outcome using regression-based analyses
For example, El Dib et al. computed a sample size requirement for a methodological study of diagnostic strategies in randomized trials, based on a confidence interval approach [ 40 ].
Q: What should I call my study?
A: Other terms which have been used to describe/label methodological studies include “ methodological review ”, “methodological survey” , “meta-epidemiological study” , “systematic review” , “systematic survey”, “meta-research”, “research-on-research” and many others. We recommend that the study nomenclature be clear, unambiguous, informative and allow for appropriate indexing. Methodological study nomenclature that should be avoided includes “ systematic review” – as this will likely be confused with a systematic review of a clinical question. “ Systematic survey” may also lead to confusion about whether the survey was systematic (i.e. using a preplanned methodology) or a survey using “ systematic” sampling (i.e. a sampling approach using specific intervals to determine who is selected) [ 32 ]. Any of the above meanings of the words “ systematic” may be true for methodological studies and could be potentially misleading. “ Meta-epidemiological study” is ideal for indexing, but not very informative as it describes an entire field. The term “ review ” may point towards an appraisal or “review” of the design, conduct, analysis or reporting (or methodological components) of the targeted research reports, yet it has also been used to describe narrative reviews [ 41 , 42 ]. The term “ survey ” is also in line with the approaches used in many methodological studies [ 9 ], and would be indicative of the sampling procedures of this study design. However, in the absence of guidelines on nomenclature, the term “ methodological study ” is broad enough to capture most of the scenarios of such studies.
Q: Should I account for clustering in my methodological study?
A: Data from methodological studies are often clustered. For example, articles coming from a specific source may have different reporting standards (e.g. the Cochrane Library). Articles within the same journal may be similar due to editorial practices and policies, reporting requirements and endorsement of guidelines. There is emerging evidence that these are real concerns that should be accounted for in analyses [ 43 ]. Some cluster variables are described in the section: “ What variables are relevant to methodological studies?”
A variety of modelling approaches can be used to account for correlated data, including the use of marginal, fixed or mixed effects regression models with appropriate computation of standard errors [ 44 ]. For example, Kosa et al. used generalized estimation equations to account for correlation of articles within journals [ 15 ]. Not accounting for clustering could lead to incorrect p -values, unduly narrow confidence intervals, and biased estimates [ 45 ].
Q: Should I extract data in duplicate?
A: Yes. Duplicate data extraction takes more time but results in less errors [ 19 ]. Data extraction errors in turn affect the effect estimate [ 46 ], and therefore should be mitigated. Duplicate data extraction should be considered in the absence of other approaches to minimize extraction errors. However, much like systematic reviews, this area will likely see rapid new advances with machine learning and natural language processing technologies to support researchers with screening and data extraction [ 47 , 48 ]. However, experience plays an important role in the quality of extracted data and inexperienced extractors should be paired with experienced extractors [ 46 , 49 ].
Q: Should I assess the risk of bias of research reports included in my methodological study?
A : Risk of bias is most useful in determining the certainty that can be placed in the effect measure from a study. In methodological studies, risk of bias may not serve the purpose of determining the trustworthiness of results, as effect measures are often not the primary goal of methodological studies. Determining risk of bias in methodological studies is likely a practice borrowed from systematic review methodology, but whose intrinsic value is not obvious in methodological studies. When it is part of the research question, investigators often focus on one aspect of risk of bias. For example, Speich investigated how blinding was reported in surgical trials [ 50 ], and Abraha et al., investigated the application of intention-to-treat analyses in systematic reviews and trials [ 51 ].
Q: What variables are relevant to methodological studies?
A: There is empirical evidence that certain variables may inform the findings in a methodological study. We outline some of these and provide a brief overview below:
- Country: Countries and regions differ in their research cultures, and the resources available to conduct research. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that there may be differences in methodological features across countries. Methodological studies have reported loco-regional differences in reporting quality [ 52 , 53 ]. This may also be related to challenges non-English speakers face in publishing papers in English.
- Authors’ expertise: The inclusion of authors with expertise in research methodology, biostatistics, and scientific writing is likely to influence the end-product. Oltean et al. found that among randomized trials in orthopaedic surgery, the use of analyses that accounted for clustering was more likely when specialists (e.g. statistician, epidemiologist or clinical trials methodologist) were included on the study team [ 54 ]. Fleming et al. found that including methodologists in the review team was associated with appropriate use of reporting guidelines [ 55 ].
- Source of funding and conflicts of interest: Some studies have found that funded studies report better [ 56 , 57 ], while others do not [ 53 , 58 ]. The presence of funding would indicate the availability of resources deployed to ensure optimal design, conduct, analysis and reporting. However, the source of funding may introduce conflicts of interest and warrant assessment. For example, Kaiser et al. investigated the effect of industry funding on obesity or nutrition randomized trials and found that reporting quality was similar [ 59 ]. Thomas et al. looked at reporting quality of long-term weight loss trials and found that industry funded studies were better [ 60 ]. Kan et al. examined the association between industry funding and “positive trials” (trials reporting a significant intervention effect) and found that industry funding was highly predictive of a positive trial [ 61 ]. This finding is similar to that of a recent Cochrane Methodology Review by Hansen et al. [ 62 ]
- Journal characteristics: Certain journals’ characteristics may influence the study design, analysis or reporting. Characteristics such as journal endorsement of guidelines [ 63 , 64 ], and Journal Impact Factor (JIF) have been shown to be associated with reporting [ 63 , 65 – 67 ].
- Study size (sample size/number of sites): Some studies have shown that reporting is better in larger studies [ 53 , 56 , 58 ].
- Year of publication: It is reasonable to assume that design, conduct, analysis and reporting of research will change over time. Many studies have demonstrated improvements in reporting over time or after the publication of reporting guidelines [ 68 , 69 ].
- Type of intervention: In a methodological study of reporting quality of weight loss intervention studies, Thabane et al. found that trials of pharmacologic interventions were reported better than trials of non-pharmacologic interventions [ 70 ].
- Interactions between variables: Complex interactions between the previously listed variables are possible. High income countries with more resources may be more likely to conduct larger studies and incorporate a variety of experts. Authors in certain countries may prefer certain journals, and journal endorsement of guidelines and editorial policies may change over time.
Q: Should I focus only on high impact journals?
A: Investigators may choose to investigate only high impact journals because they are more likely to influence practice and policy, or because they assume that methodological standards would be higher. However, the JIF may severely limit the scope of articles included and may skew the sample towards articles with positive findings. The generalizability and applicability of findings from a handful of journals must be examined carefully, especially since the JIF varies over time. Even among journals that are all “high impact”, variations exist in methodological standards.
Q: Can I conduct a methodological study of qualitative research?
A: Yes. Even though a lot of methodological research has been conducted in the quantitative research field, methodological studies of qualitative studies are feasible. Certain databases that catalogue qualitative research including the Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) have defined subject headings that are specific to methodological research (e.g. “research methodology”). Alternatively, one could also conduct a qualitative methodological review; that is, use qualitative approaches to synthesize methodological issues in qualitative studies.
Q: What reporting guidelines should I use for my methodological study?
A: There is no guideline that covers the entire scope of methodological studies. One adaptation of the PRISMA guidelines has been published, which works well for studies that aim to use the entire target population of research reports [ 71 ]. However, it is not widely used (40 citations in 2 years as of 09 December 2019), and methodological studies that are designed as cross-sectional or before-after studies require a more fit-for purpose guideline. A more encompassing reporting guideline for a broad range of methodological studies is currently under development [ 72 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, the requirements for scientific reporting should be respected, and authors of methodological studies should focus on transparency and reproducibility.
Q: What are the potential threats to validity and how can I avoid them?
A: Methodological studies may be compromised by a lack of internal or external validity. The main threats to internal validity in methodological studies are selection and confounding bias. Investigators must ensure that the methods used to select articles does not make them differ systematically from the set of articles to which they would like to make inferences. For example, attempting to make extrapolations to all journals after analyzing high-impact journals would be misleading.
Many factors (confounders) may distort the association between the exposure and outcome if the included research reports differ with respect to these factors [ 73 ]. For example, when examining the association between source of funding and completeness of reporting, it may be necessary to account for journals that endorse the guidelines. Confounding bias can be addressed by restriction, matching and statistical adjustment [ 73 ]. Restriction appears to be the method of choice for many investigators who choose to include only high impact journals or articles in a specific field. For example, Knol et al. examined the reporting of p -values in baseline tables of high impact journals [ 26 ]. Matching is also sometimes used. In the methodological study of non-randomized interventional studies of elective ventral hernia repair, Parker et al. matched prospective studies with retrospective studies and compared reporting standards [ 74 ]. Some other methodological studies use statistical adjustments. For example, Zhang et al. used regression techniques to determine the factors associated with missing participant data in trials [ 16 ].
With regard to external validity, researchers interested in conducting methodological studies must consider how generalizable or applicable their findings are. This should tie in closely with the research question and should be explicit. For example. Findings from methodological studies on trials published in high impact cardiology journals cannot be assumed to be applicable to trials in other fields. However, investigators must ensure that their sample truly represents the target sample either by a) conducting a comprehensive and exhaustive search, or b) using an appropriate and justified, randomly selected sample of research reports.
Even applicability to high impact journals may vary based on the investigators’ definition, and over time. For example, for high impact journals in the field of general medicine, Bouwmeester et al. included the Annals of Internal Medicine (AIM), BMJ, the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Lancet, the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), and PLoS Medicine ( n = 6) [ 75 ]. In contrast, the high impact journals selected in the methodological study by Schiller et al. were BMJ, JAMA, Lancet, and NEJM ( n = 4) [ 76 ]. Another methodological study by Kosa et al. included AIM, BMJ, JAMA, Lancet and NEJM ( n = 5). In the methodological study by Thabut et al., journals with a JIF greater than 5 were considered to be high impact. Riado Minguez et al. used first quartile journals in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) for a specific year to determine “high impact” [ 77 ]. Ultimately, the definition of high impact will be based on the number of journals the investigators are willing to include, the year of impact and the JIF cut-off [ 78 ]. We acknowledge that the term “generalizability” may apply differently for methodological studies, especially when in many instances it is possible to include the entire target population in the sample studied.
Finally, methodological studies are not exempt from information bias which may stem from discrepancies in the included research reports [ 79 ], errors in data extraction, or inappropriate interpretation of the information extracted. Likewise, publication bias may also be a concern in methodological studies, but such concepts have not yet been explored.
A proposed framework
In order to inform discussions about methodological studies, the development of guidance for what should be reported, we have outlined some key features of methodological studies that can be used to classify them. For each of the categories outlined below, we provide an example. In our experience, the choice of approach to completing a methodological study can be informed by asking the following four questions:
- What is the aim?
A methodological study may be focused on exploring sources of bias in primary or secondary studies (meta-bias), or how bias is analyzed. We have taken care to distinguish bias (i.e. systematic deviations from the truth irrespective of the source) from reporting quality or completeness (i.e. not adhering to a specific reporting guideline or norm). An example of where this distinction would be important is in the case of a randomized trial with no blinding. This study (depending on the nature of the intervention) would be at risk of performance bias. However, if the authors report that their study was not blinded, they would have reported adequately. In fact, some methodological studies attempt to capture both “quality of conduct” and “quality of reporting”, such as Richie et al., who reported on the risk of bias in randomized trials of pharmacy practice interventions [ 80 ]. Babic et al. investigated how risk of bias was used to inform sensitivity analyses in Cochrane reviews [ 81 ]. Further, biases related to choice of outcomes can also be explored. For example, Tan et al investigated differences in treatment effect size based on the outcome reported [ 82 ].
Methodological studies may report quality of reporting against a reporting checklist (i.e. adherence to guidelines) or against expected norms. For example, Croituro et al. report on the quality of reporting in systematic reviews published in dermatology journals based on their adherence to the PRISMA statement [ 83 ], and Khan et al. described the quality of reporting of harms in randomized controlled trials published in high impact cardiovascular journals based on the CONSORT extension for harms [ 84 ]. Other methodological studies investigate reporting of certain features of interest that may not be part of formally published checklists or guidelines. For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described how often the implications for research are elaborated using the Evidence, Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (EPICOT) format [ 30 ].
Sometimes investigators may be interested in how consistent reports of the same research are, as it is expected that there should be consistency between: conference abstracts and published manuscripts; manuscript abstracts and manuscript main text; and trial registration and published manuscript. For example, Rosmarakis et al. investigated consistency between conference abstracts and full text manuscripts [ 85 ].
In addition to identifying issues with reporting in primary and secondary studies, authors of methodological studies may be interested in determining the factors that are associated with certain reporting practices. Many methodological studies incorporate this, albeit as a secondary outcome. For example, Farrokhyar et al. investigated the factors associated with reporting quality in randomized trials of coronary artery bypass grafting surgery [ 53 ].
Methodological studies may also be used to describe methods or compare methods, and the factors associated with methods. Muller et al. described the methods used for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies [ 86 ].
Some methodological studies synthesize results from other methodological studies. For example, Li et al. conducted a scoping review of methodological reviews that investigated consistency between full text and abstracts in primary biomedical research [ 87 ].
Some methodological studies may investigate the use of names and terms in health research. For example, Martinic et al. investigated the definitions of systematic reviews used in overviews of systematic reviews (OSRs), meta-epidemiological studies and epidemiology textbooks [ 88 ].
In addition to the previously mentioned experimental methodological studies, there may exist other types of methodological studies not captured here.
- 2. What is the design?
Most methodological studies are purely descriptive and report their findings as counts (percent) and means (standard deviation) or medians (interquartile range). For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described the reporting of research recommendations in Cochrane HIV systematic reviews [ 30 ]. Gohari et al. described the quality of reporting of randomized trials in diabetes in Iran [ 12 ].
Some methodological studies are analytical wherein “analytical studies identify and quantify associations, test hypotheses, identify causes and determine whether an association exists between variables, such as between an exposure and a disease.” [ 89 ] In the case of methodological studies all these investigations are possible. For example, Kosa et al. investigated the association between agreement in primary outcome from trial registry to published manuscript and study covariates. They found that larger and more recent studies were more likely to have agreement [ 15 ]. Tricco et al. compared the conclusion statements from Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews with a meta-analysis of the primary outcome and found that non-Cochrane reviews were more likely to report positive findings. These results are a test of the null hypothesis that the proportions of Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews that report positive results are equal [ 90 ].
- 3. What is the sampling strategy?
Methodological reviews with narrow research questions may be able to include the entire target population. For example, in the methodological study of Cochrane HIV systematic reviews, Mbuagbaw et al. included all of the available studies ( n = 103) [ 30 ].
Many methodological studies use random samples of the target population [ 33 , 91 , 92 ]. Alternatively, purposeful sampling may be used, limiting the sample to a subset of research-related reports published within a certain time period, or in journals with a certain ranking or on a topic. Systematic sampling can also be used when random sampling may be challenging to implement.
- 4. What is the unit of analysis?
Many methodological studies use a research report (e.g. full manuscript of study, abstract portion of the study) as the unit of analysis, and inferences can be made at the study-level. However, both published and unpublished research-related reports can be studied. These may include articles, conference abstracts, registry entries etc.
Some methodological studies report on items which may occur more than once per article. For example, Paquette et al. report on subgroup analyses in Cochrane reviews of atrial fibrillation in which 17 systematic reviews planned 56 subgroup analyses [ 93 ].
This framework is outlined in Fig. 2 .

A proposed framework for methodological studies
Conclusions
Methodological studies have examined different aspects of reporting such as quality, completeness, consistency and adherence to reporting guidelines. As such, many of the methodological study examples cited in this tutorial are related to reporting. However, as an evolving field, the scope of research questions that can be addressed by methodological studies is expected to increase.
In this paper we have outlined the scope and purpose of methodological studies, along with examples of instances in which various approaches have been used. In the absence of formal guidance on the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of methodological studies, we have provided some advice to help make methodological studies consistent. This advice is grounded in good contemporary scientific practice. Generally, the research question should tie in with the sampling approach and planned analysis. We have also highlighted the variables that may inform findings from methodological studies. Lastly, we have provided suggestions for ways in which authors can categorize their methodological studies to inform their design and analysis.
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations.
| CONSORT | Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials |
| EPICOT | Evidence, Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations |
| PICOT | Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| SWAR | Studies Within a Review |
| SWAT | Studies Within a Trial |
Authors’ contributions
LM conceived the idea and drafted the outline and paper. DOL and LT commented on the idea and draft outline. LM, LP and DOL performed literature searches and data extraction. All authors (LM, DOL, LT, LP, DBA) reviewed several draft versions of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
This work did not receive any dedicated funding.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
DOL, DBA, LM, LP and LT are involved in the development of a reporting guideline for methodological studies.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
2.2 Research Methods
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you should be able to:
- Recall the 6 Steps of the Scientific Method
- Differentiate between four kinds of research methods: surveys, field research, experiments, and secondary data analysis.
- Explain the appropriateness of specific research approaches for specific topics.
Sociologists examine the social world, see a problem or interesting pattern, and set out to study it. They use research methods to design a study. Planning the research design is a key step in any sociological study. Sociologists generally choose from widely used methods of social investigation: primary source data collection such as survey, participant observation, ethnography, case study, unobtrusive observations, experiment, and secondary data analysis , or use of existing sources. Every research method comes with plusses and minuses, and the topic of study strongly influences which method or methods are put to use. When you are conducting research think about the best way to gather or obtain knowledge about your topic, think of yourself as an architect. An architect needs a blueprint to build a house, as a sociologist your blueprint is your research design including your data collection method.
When entering a particular social environment, a researcher must be careful. There are times to remain anonymous and times to be overt. There are times to conduct interviews and times to simply observe. Some participants need to be thoroughly informed; others should not know they are being observed. A researcher wouldn’t stroll into a crime-ridden neighborhood at midnight, calling out, “Any gang members around?”
Making sociologists’ presence invisible is not always realistic for other reasons. That option is not available to a researcher studying prison behaviors, early education, or the Ku Klux Klan. Researchers can’t just stroll into prisons, kindergarten classrooms, or Klan meetings and unobtrusively observe behaviors or attract attention. In situations like these, other methods are needed. Researchers choose methods that best suit their study topics, protect research participants or subjects, and that fit with their overall approaches to research.
As a research method, a survey collects data from subjects who respond to a series of questions about behaviors and opinions, often in the form of a questionnaire or an interview. The survey is one of the most widely used scientific research methods. The standard survey format allows individuals a level of anonymity in which they can express personal ideas.
At some point, most people in the United States respond to some type of survey. The 2020 U.S. Census is an excellent example of a large-scale survey intended to gather sociological data. Since 1790, United States has conducted a survey consisting of six questions to received demographical data pertaining to residents. The questions pertain to the demographics of the residents who live in the United States. Currently, the Census is received by residents in the United Stated and five territories and consists of 12 questions.
Not all surveys are considered sociological research, however, and many surveys people commonly encounter focus on identifying marketing needs and strategies rather than testing a hypothesis or contributing to social science knowledge. Questions such as, “How many hot dogs do you eat in a month?” or “Were the staff helpful?” are not usually designed as scientific research. The Nielsen Ratings determine the popularity of television programming through scientific market research. However, polls conducted by television programs such as American Idol or So You Think You Can Dance cannot be generalized, because they are administered to an unrepresentative population, a specific show’s audience. You might receive polls through your cell phones or emails, from grocery stores, restaurants, and retail stores. They often provide you incentives for completing the survey.
Sociologists conduct surveys under controlled conditions for specific purposes. Surveys gather different types of information from people. While surveys are not great at capturing the ways people really behave in social situations, they are a great method for discovering how people feel, think, and act—or at least how they say they feel, think, and act. Surveys can track preferences for presidential candidates or reported individual behaviors (such as sleeping, driving, or texting habits) or information such as employment status, income, and education levels.
A survey targets a specific population , people who are the focus of a study, such as college athletes, international students, or teenagers living with type 1 (juvenile-onset) diabetes. Most researchers choose to survey a small sector of the population, or a sample , a manageable number of subjects who represent a larger population. The success of a study depends on how well a population is represented by the sample. In a random sample , every person in a population has the same chance of being chosen for the study. As a result, a Gallup Poll, if conducted as a nationwide random sampling, should be able to provide an accurate estimate of public opinion whether it contacts 2,000 or 10,000 people.
After selecting subjects, the researcher develops a specific plan to ask questions and record responses. It is important to inform subjects of the nature and purpose of the survey up front. If they agree to participate, researchers thank subjects and offer them a chance to see the results of the study if they are interested. The researcher presents the subjects with an instrument, which is a means of gathering the information.
A common instrument is a questionnaire. Subjects often answer a series of closed-ended questions . The researcher might ask yes-or-no or multiple-choice questions, allowing subjects to choose possible responses to each question. This kind of questionnaire collects quantitative data —data in numerical form that can be counted and statistically analyzed. Just count up the number of “yes” and “no” responses or correct answers, and chart them into percentages.
Questionnaires can also ask more complex questions with more complex answers—beyond “yes,” “no,” or checkbox options. These types of inquiries use open-ended questions that require short essay responses. Participants willing to take the time to write those answers might convey personal religious beliefs, political views, goals, or morals. The answers are subjective and vary from person to person. How do you plan to use your college education?
Some topics that investigate internal thought processes are impossible to observe directly and are difficult to discuss honestly in a public forum. People are more likely to share honest answers if they can respond to questions anonymously. This type of personal explanation is qualitative data —conveyed through words. Qualitative information is harder to organize and tabulate. The researcher will end up with a wide range of responses, some of which may be surprising. The benefit of written opinions, though, is the wealth of in-depth material that they provide.
An interview is a one-on-one conversation between the researcher and the subject, and it is a way of conducting surveys on a topic. However, participants are free to respond as they wish, without being limited by predetermined choices. In the back-and-forth conversation of an interview, a researcher can ask for clarification, spend more time on a subtopic, or ask additional questions. In an interview, a subject will ideally feel free to open up and answer questions that are often complex. There are no right or wrong answers. The subject might not even know how to answer the questions honestly.
Questions such as “How does society’s view of alcohol consumption influence your decision whether or not to take your first sip of alcohol?” or “Did you feel that the divorce of your parents would put a social stigma on your family?” involve so many factors that the answers are difficult to categorize. A researcher needs to avoid steering or prompting the subject to respond in a specific way; otherwise, the results will prove to be unreliable. The researcher will also benefit from gaining a subject’s trust, from empathizing or commiserating with a subject, and from listening without judgment.
Surveys often collect both quantitative and qualitative data. For example, a researcher interviewing people who are incarcerated might receive quantitative data, such as demographics – race, age, sex, that can be analyzed statistically. For example, the researcher might discover that 20 percent of incarcerated people are above the age of 50. The researcher might also collect qualitative data, such as why people take advantage of educational opportunities during their sentence and other explanatory information.
The survey can be carried out online, over the phone, by mail, or face-to-face. When researchers collect data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting, they are conducting field research, which is our next topic.
Field Research
The work of sociology rarely happens in limited, confined spaces. Rather, sociologists go out into the world. They meet subjects where they live, work, and play. Field research refers to gathering primary data from a natural environment. To conduct field research, the sociologist must be willing to step into new environments and observe, participate, or experience those worlds. In field work, the sociologists, rather than the subjects, are the ones out of their element.
The researcher interacts with or observes people and gathers data along the way. The key point in field research is that it takes place in the subject’s natural environment, whether it’s a coffee shop or tribal village, a homeless shelter or the DMV, a hospital, airport, mall, or beach resort.
While field research often begins in a specific setting , the study’s purpose is to observe specific behaviors in that setting. Field work is optimal for observing how people think and behave. It seeks to understand why they behave that way. However, researchers may struggle to narrow down cause and effect when there are so many variables floating around in a natural environment. And while field research looks for correlation, its small sample size does not allow for establishing a causal relationship between two variables. Indeed, much of the data gathered in sociology do not identify a cause and effect but a correlation .

Sociology in the Real World
Beyoncé and lady gaga as sociological subjects.
Sociologists have studied Lady Gaga and Beyoncé and their impact on music, movies, social media, fan participation, and social equality. In their studies, researchers have used several research methods including secondary analysis, participant observation, and surveys from concert participants.
In their study, Click, Lee & Holiday (2013) interviewed 45 Lady Gaga fans who utilized social media to communicate with the artist. These fans viewed Lady Gaga as a mirror of themselves and a source of inspiration. Like her, they embrace not being a part of mainstream culture. Many of Lady Gaga’s fans are members of the LGBTQ community. They see the “song “Born This Way” as a rallying cry and answer her calls for “Paws Up” with a physical expression of solidarity—outstretched arms and fingers bent and curled to resemble monster claws.”
Sascha Buchanan (2019) made use of participant observation to study the relationship between two fan groups, that of Beyoncé and that of Rihanna. She observed award shows sponsored by iHeartRadio, MTV EMA, and BET that pit one group against another as they competed for Best Fan Army, Biggest Fans, and FANdemonium. Buchanan argues that the media thus sustains a myth of rivalry between the two most commercially successful Black women vocal artists.
Participant Observation
In 2000, a comic writer named Rodney Rothman wanted an insider’s view of white-collar work. He slipped into the sterile, high-rise offices of a New York “dot com” agency. Every day for two weeks, he pretended to work there. His main purpose was simply to see whether anyone would notice him or challenge his presence. No one did. The receptionist greeted him. The employees smiled and said good morning. Rothman was accepted as part of the team. He even went so far as to claim a desk, inform the receptionist of his whereabouts, and attend a meeting. He published an article about his experience in The New Yorker called “My Fake Job” (2000). Later, he was discredited for allegedly fabricating some details of the story and The New Yorker issued an apology. However, Rothman’s entertaining article still offered fascinating descriptions of the inside workings of a “dot com” company and exemplified the lengths to which a writer, or a sociologist, will go to uncover material.
Rothman had conducted a form of study called participant observation , in which researchers join people and participate in a group’s routine activities for the purpose of observing them within that context. This method lets researchers experience a specific aspect of social life. A researcher might go to great lengths to get a firsthand look into a trend, institution, or behavior. A researcher might work as a waitress in a diner, experience homelessness for several weeks, or ride along with police officers as they patrol their regular beat. Often, these researchers try to blend in seamlessly with the population they study, and they may not disclose their true identity or purpose if they feel it would compromise the results of their research.
At the beginning of a field study, researchers might have a question: “What really goes on in the kitchen of the most popular diner on campus?” or “What is it like to be homeless?” Participant observation is a useful method if the researcher wants to explore a certain environment from the inside.
Field researchers simply want to observe and learn. In such a setting, the researcher will be alert and open minded to whatever happens, recording all observations accurately. Soon, as patterns emerge, questions will become more specific, observations will lead to hypotheses, and hypotheses will guide the researcher in analyzing data and generating results.
In a study of small towns in the United States conducted by sociological researchers John S. Lynd and Helen Merrell Lynd, the team altered their purpose as they gathered data. They initially planned to focus their study on the role of religion in U.S. towns. As they gathered observations, they realized that the effect of industrialization and urbanization was the more relevant topic of this social group. The Lynds did not change their methods, but they revised the purpose of their study.
This shaped the structure of Middletown: A Study in Modern American Culture , their published results (Lynd & Lynd, 1929).
The Lynds were upfront about their mission. The townspeople of Muncie, Indiana, knew why the researchers were in their midst. But some sociologists prefer not to alert people to their presence. The main advantage of covert participant observation is that it allows the researcher access to authentic, natural behaviors of a group’s members. The challenge, however, is gaining access to a setting without disrupting the pattern of others’ behavior. Becoming an inside member of a group, organization, or subculture takes time and effort. Researchers must pretend to be something they are not. The process could involve role playing, making contacts, networking, or applying for a job.
Once inside a group, some researchers spend months or even years pretending to be one of the people they are observing. However, as observers, they cannot get too involved. They must keep their purpose in mind and apply the sociological perspective. That way, they illuminate social patterns that are often unrecognized. Because information gathered during participant observation is mostly qualitative, rather than quantitative, the end results are often descriptive or interpretive. The researcher might present findings in an article or book and describe what he or she witnessed and experienced.
This type of research is what journalist Barbara Ehrenreich conducted for her book Nickel and Dimed . One day over lunch with her editor, Ehrenreich mentioned an idea. How can people exist on minimum-wage work? How do low-income workers get by? she wondered. Someone should do a study . To her surprise, her editor responded, Why don’t you do it?
That’s how Ehrenreich found herself joining the ranks of the working class. For several months, she left her comfortable home and lived and worked among people who lacked, for the most part, higher education and marketable job skills. Undercover, she applied for and worked minimum wage jobs as a waitress, a cleaning woman, a nursing home aide, and a retail chain employee. During her participant observation, she used only her income from those jobs to pay for food, clothing, transportation, and shelter.
She discovered the obvious, that it’s almost impossible to get by on minimum wage work. She also experienced and observed attitudes many middle and upper-class people never think about. She witnessed firsthand the treatment of working class employees. She saw the extreme measures people take to make ends meet and to survive. She described fellow employees who held two or three jobs, worked seven days a week, lived in cars, could not pay to treat chronic health conditions, got randomly fired, submitted to drug tests, and moved in and out of homeless shelters. She brought aspects of that life to light, describing difficult working conditions and the poor treatment that low-wage workers suffer.
The book she wrote upon her return to her real life as a well-paid writer, has been widely read and used in many college classrooms.
Ethnography
Ethnography is the immersion of the researcher in the natural setting of an entire social community to observe and experience their everyday life and culture. The heart of an ethnographic study focuses on how subjects view their own social standing and how they understand themselves in relation to a social group.
An ethnographic study might observe, for example, a small U.S. fishing town, an Inuit community, a village in Thailand, a Buddhist monastery, a private boarding school, or an amusement park. These places all have borders. People live, work, study, or vacation within those borders. People are there for a certain reason and therefore behave in certain ways and respect certain cultural norms. An ethnographer would commit to spending a determined amount of time studying every aspect of the chosen place, taking in as much as possible.
A sociologist studying a tribe in the Amazon might watch the way villagers go about their daily lives and then write a paper about it. To observe a spiritual retreat center, an ethnographer might sign up for a retreat and attend as a guest for an extended stay, observe and record data, and collate the material into results.
Institutional Ethnography
Institutional ethnography is an extension of basic ethnographic research principles that focuses intentionally on everyday concrete social relationships. Developed by Canadian sociologist Dorothy E. Smith (1990), institutional ethnography is often considered a feminist-inspired approach to social analysis and primarily considers women’s experiences within male- dominated societies and power structures. Smith’s work is seen to challenge sociology’s exclusion of women, both academically and in the study of women’s lives (Fenstermaker, n.d.).
Historically, social science research tended to objectify women and ignore their experiences except as viewed from the male perspective. Modern feminists note that describing women, and other marginalized groups, as subordinates helps those in authority maintain their own dominant positions (Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada n.d.). Smith’s three major works explored what she called “the conceptual practices of power” and are still considered seminal works in feminist theory and ethnography (Fensternmaker n.d.).
Sociological Research
The making of middletown: a study in modern u.s. culture.
In 1924, a young married couple named Robert and Helen Lynd undertook an unprecedented ethnography: to apply sociological methods to the study of one U.S. city in order to discover what “ordinary” people in the United States did and believed. Choosing Muncie, Indiana (population about 30,000) as their subject, they moved to the small town and lived there for eighteen months.
Ethnographers had been examining other cultures for decades—groups considered minorities or outsiders—like gangs, immigrants, and the poor. But no one had studied the so-called average American.
Recording interviews and using surveys to gather data, the Lynds objectively described what they observed. Researching existing sources, they compared Muncie in 1890 to the Muncie they observed in 1924. Most Muncie adults, they found, had grown up on farms but now lived in homes inside the city. As a result, the Lynds focused their study on the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
They observed that Muncie was divided into business and working class groups. They defined business class as dealing with abstract concepts and symbols, while working class people used tools to create concrete objects. The two classes led different lives with different goals and hopes. However, the Lynds observed, mass production offered both classes the same amenities. Like wealthy families, the working class was now able to own radios, cars, washing machines, telephones, vacuum cleaners, and refrigerators. This was an emerging material reality of the 1920s.
As the Lynds worked, they divided their manuscript into six chapters: Getting a Living, Making a Home, Training the Young, Using Leisure, Engaging in Religious Practices, and Engaging in Community Activities.
When the study was completed, the Lynds encountered a big problem. The Rockefeller Foundation, which had commissioned the book, claimed it was useless and refused to publish it. The Lynds asked if they could seek a publisher themselves.
Middletown: A Study in Modern American Culture was not only published in 1929 but also became an instant bestseller, a status unheard of for a sociological study. The book sold out six printings in its first year of publication, and has never gone out of print (Caplow, Hicks, & Wattenberg. 2000).
Nothing like it had ever been done before. Middletown was reviewed on the front page of the New York Times. Readers in the 1920s and 1930s identified with the citizens of Muncie, Indiana, but they were equally fascinated by the sociological methods and the use of scientific data to define ordinary people in the United States. The book was proof that social data was important—and interesting—to the U.S. public.
Sometimes a researcher wants to study one specific person or event. A case study is an in-depth analysis of a single event, situation, or individual. To conduct a case study, a researcher examines existing sources like documents and archival records, conducts interviews, engages in direct observation and even participant observation, if possible.
Researchers might use this method to study a single case of a foster child, drug lord, cancer patient, criminal, or rape victim. However, a major criticism of the case study as a method is that while offering depth on a topic, it does not provide enough evidence to form a generalized conclusion. In other words, it is difficult to make universal claims based on just one person, since one person does not verify a pattern. This is why most sociologists do not use case studies as a primary research method.
However, case studies are useful when the single case is unique. In these instances, a single case study can contribute tremendous insight. For example, a feral child, also called “wild child,” is one who grows up isolated from human beings. Feral children grow up without social contact and language, which are elements crucial to a “civilized” child’s development. These children mimic the behaviors and movements of animals, and often invent their own language. There are only about one hundred cases of “feral children” in the world.
As you may imagine, a feral child is a subject of great interest to researchers. Feral children provide unique information about child development because they have grown up outside of the parameters of “normal” growth and nurturing. And since there are very few feral children, the case study is the most appropriate method for researchers to use in studying the subject.
At age three, a Ukranian girl named Oxana Malaya suffered severe parental neglect. She lived in a shed with dogs, and she ate raw meat and scraps. Five years later, a neighbor called authorities and reported seeing a girl who ran on all fours, barking. Officials brought Oxana into society, where she was cared for and taught some human behaviors, but she never became fully socialized. She has been designated as unable to support herself and now lives in a mental institution (Grice 2011). Case studies like this offer a way for sociologists to collect data that may not be obtained by any other method.
Experiments
You have probably tested some of your own personal social theories. “If I study at night and review in the morning, I’ll improve my retention skills.” Or, “If I stop drinking soda, I’ll feel better.” Cause and effect. If this, then that. When you test the theory, your results either prove or disprove your hypothesis.
One way researchers test social theories is by conducting an experiment , meaning they investigate relationships to test a hypothesis—a scientific approach.
There are two main types of experiments: lab-based experiments and natural or field experiments. In a lab setting, the research can be controlled so that more data can be recorded in a limited amount of time. In a natural or field- based experiment, the time it takes to gather the data cannot be controlled but the information might be considered more accurate since it was collected without interference or intervention by the researcher.
As a research method, either type of sociological experiment is useful for testing if-then statements: if a particular thing happens (cause), then another particular thing will result (effect). To set up a lab-based experiment, sociologists create artificial situations that allow them to manipulate variables.
Classically, the sociologist selects a set of people with similar characteristics, such as age, class, race, or education. Those people are divided into two groups. One is the experimental group and the other is the control group. The experimental group is exposed to the independent variable(s) and the control group is not. To test the benefits of tutoring, for example, the sociologist might provide tutoring to the experimental group of students but not to the control group. Then both groups would be tested for differences in performance to see if tutoring had an effect on the experimental group of students. As you can imagine, in a case like this, the researcher would not want to jeopardize the accomplishments of either group of students, so the setting would be somewhat artificial. The test would not be for a grade reflected on their permanent record of a student, for example.
And if a researcher told the students they would be observed as part of a study on measuring the effectiveness of tutoring, the students might not behave naturally. This is called the Hawthorne effect —which occurs when people change their behavior because they know they are being watched as part of a study. The Hawthorne effect is unavoidable in some research studies because sociologists have to make the purpose of the study known. Subjects must be aware that they are being observed, and a certain amount of artificiality may result (Sonnenfeld 1985).
A real-life example will help illustrate the process. In 1971, Frances Heussenstamm, a sociology professor at California State University at Los Angeles, had a theory about police prejudice. To test her theory, she conducted research. She chose fifteen students from three ethnic backgrounds: Black, White, and Hispanic. She chose students who routinely drove to and from campus along Los Angeles freeway routes, and who had had perfect driving records for longer than a year.
Next, she placed a Black Panther bumper sticker on each car. That sticker, a representation of a social value, was the independent variable. In the 1970s, the Black Panthers were a revolutionary group actively fighting racism. Heussenstamm asked the students to follow their normal driving patterns. She wanted to see whether seeming support for the Black Panthers would change how these good drivers were treated by the police patrolling the highways. The dependent variable would be the number of traffic stops/citations.
The first arrest, for an incorrect lane change, was made two hours after the experiment began. One participant was pulled over three times in three days. He quit the study. After seventeen days, the fifteen drivers had collected a total of thirty-three traffic citations. The research was halted. The funding to pay traffic fines had run out, and so had the enthusiasm of the participants (Heussenstamm, 1971).
Secondary Data Analysis
While sociologists often engage in original research studies, they also contribute knowledge to the discipline through secondary data analysis . Secondary data does not result from firsthand research collected from primary sources, but are the already completed work of other researchers or data collected by an agency or organization. Sociologists might study works written by historians, economists, teachers, or early sociologists. They might search through periodicals, newspapers, or magazines, or organizational data from any period in history.
Using available information not only saves time and money but can also add depth to a study. Sociologists often interpret findings in a new way, a way that was not part of an author’s original purpose or intention. To study how women were encouraged to act and behave in the 1960s, for example, a researcher might watch movies, televisions shows, and situation comedies from that period. Or to research changes in behavior and attitudes due to the emergence of television in the late 1950s and early 1960s, a sociologist would rely on new interpretations of secondary data. Decades from now, researchers will most likely conduct similar studies on the advent of mobile phones, the Internet, or social media.
Social scientists also learn by analyzing the research of a variety of agencies. Governmental departments and global groups, like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics or the World Health Organization (WHO), publish studies with findings that are useful to sociologists. A public statistic like the foreclosure rate might be useful for studying the effects of a recession. A racial demographic profile might be compared with data on education funding to examine the resources accessible by different groups.
One of the advantages of secondary data like old movies or WHO statistics is that it is nonreactive research (or unobtrusive research), meaning that it does not involve direct contact with subjects and will not alter or influence people’s behaviors. Unlike studies requiring direct contact with people, using previously published data does not require entering a population and the investment and risks inherent in that research process.
Using available data does have its challenges. Public records are not always easy to access. A researcher will need to do some legwork to track them down and gain access to records. To guide the search through a vast library of materials and avoid wasting time reading unrelated sources, sociologists employ content analysis , applying a systematic approach to record and value information gleaned from secondary data as they relate to the study at hand.
Also, in some cases, there is no way to verify the accuracy of existing data. It is easy to count how many drunk drivers, for example, are pulled over by the police. But how many are not? While it’s possible to discover the percentage of teenage students who drop out of high school, it might be more challenging to determine the number who return to school or get their GED later.
Another problem arises when data are unavailable in the exact form needed or do not survey the topic from the precise angle the researcher seeks. For example, the average salaries paid to professors at a public school is public record. But these figures do not necessarily reveal how long it took each professor to reach the salary range, what their educational backgrounds are, or how long they’ve been teaching.
When conducting content analysis, it is important to consider the date of publication of an existing source and to take into account attitudes and common cultural ideals that may have influenced the research. For example, when Robert S. Lynd and Helen Merrell Lynd gathered research in the 1920s, attitudes and cultural norms were vastly different then than they are now. Beliefs about gender roles, race, education, and work have changed significantly since then. At the time, the study’s purpose was to reveal insights about small U.S. communities. Today, it is an illustration of 1920s attitudes and values.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Tonja R. Conerly, Kathleen Holmes, Asha Lal Tamang
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Sociology 3e
- Publication date: Jun 3, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/2-2-research-methods
© Jan 18, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Science and the scientific method: Definitions and examples
Here's a look at the foundation of doing science — the scientific method.

The scientific method
Hypothesis, theory and law, a brief history of science, additional resources, bibliography.
Science is a systematic and logical approach to discovering how things in the universe work. It is also the body of knowledge accumulated through the discoveries about all the things in the universe.
The word "science" is derived from the Latin word "scientia," which means knowledge based on demonstrable and reproducible data, according to the Merriam-Webster dictionary . True to this definition, science aims for measurable results through testing and analysis, a process known as the scientific method. Science is based on fact, not opinion or preferences. The process of science is designed to challenge ideas through research. One important aspect of the scientific process is that it focuses only on the natural world, according to the University of California, Berkeley . Anything that is considered supernatural, or beyond physical reality, does not fit into the definition of science.
When conducting research, scientists use the scientific method to collect measurable, empirical evidence in an experiment related to a hypothesis (often in the form of an if/then statement) that is designed to support or contradict a scientific theory .
"As a field biologist, my favorite part of the scientific method is being in the field collecting the data," Jaime Tanner, a professor of biology at Marlboro College, told Live Science. "But what really makes that fun is knowing that you are trying to answer an interesting question. So the first step in identifying questions and generating possible answers (hypotheses) is also very important and is a creative process. Then once you collect the data you analyze it to see if your hypothesis is supported or not."

The steps of the scientific method go something like this, according to Highline College :
- Make an observation or observations.
- Form a hypothesis — a tentative description of what's been observed, and make predictions based on that hypothesis.
- Test the hypothesis and predictions in an experiment that can be reproduced.
- Analyze the data and draw conclusions; accept or reject the hypothesis or modify the hypothesis if necessary.
- Reproduce the experiment until there are no discrepancies between observations and theory. "Replication of methods and results is my favorite step in the scientific method," Moshe Pritsker, a former post-doctoral researcher at Harvard Medical School and CEO of JoVE, told Live Science. "The reproducibility of published experiments is the foundation of science. No reproducibility — no science."
Some key underpinnings to the scientific method:
- The hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable, according to North Carolina State University . Falsifiable means that there must be a possible negative answer to the hypothesis.
- Research must involve deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning . Deductive reasoning is the process of using true premises to reach a logical true conclusion while inductive reasoning uses observations to infer an explanation for those observations.
- An experiment should include a dependent variable (which does not change) and an independent variable (which does change), according to the University of California, Santa Barbara .
- An experiment should include an experimental group and a control group. The control group is what the experimental group is compared against, according to Britannica .
The process of generating and testing a hypothesis forms the backbone of the scientific method. When an idea has been confirmed over many experiments, it can be called a scientific theory. While a theory provides an explanation for a phenomenon, a scientific law provides a description of a phenomenon, according to The University of Waikato . One example would be the law of conservation of energy, which is the first law of thermodynamics that says that energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
A law describes an observed phenomenon, but it doesn't explain why the phenomenon exists or what causes it. "In science, laws are a starting place," said Peter Coppinger, an associate professor of biology and biomedical engineering at the Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology. "From there, scientists can then ask the questions, 'Why and how?'"
Laws are generally considered to be without exception, though some laws have been modified over time after further testing found discrepancies. For instance, Newton's laws of motion describe everything we've observed in the macroscopic world, but they break down at the subatomic level.
This does not mean theories are not meaningful. For a hypothesis to become a theory, scientists must conduct rigorous testing, typically across multiple disciplines by separate groups of scientists. Saying something is "just a theory" confuses the scientific definition of "theory" with the layperson's definition. To most people a theory is a hunch. In science, a theory is the framework for observations and facts, Tanner told Live Science.

The earliest evidence of science can be found as far back as records exist. Early tablets contain numerals and information about the solar system , which were derived by using careful observation, prediction and testing of those predictions. Science became decidedly more "scientific" over time, however.
1200s: Robert Grosseteste developed the framework for the proper methods of modern scientific experimentation, according to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. His works included the principle that an inquiry must be based on measurable evidence that is confirmed through testing.
1400s: Leonardo da Vinci began his notebooks in pursuit of evidence that the human body is microcosmic. The artist, scientist and mathematician also gathered information about optics and hydrodynamics.
1500s: Nicolaus Copernicus advanced the understanding of the solar system with his discovery of heliocentrism. This is a model in which Earth and the other planets revolve around the sun, which is the center of the solar system.
1600s: Johannes Kepler built upon those observations with his laws of planetary motion. Galileo Galilei improved on a new invention, the telescope, and used it to study the sun and planets. The 1600s also saw advancements in the study of physics as Isaac Newton developed his laws of motion.
1700s: Benjamin Franklin discovered that lightning is electrical. He also contributed to the study of oceanography and meteorology. The understanding of chemistry also evolved during this century as Antoine Lavoisier, dubbed the father of modern chemistry , developed the law of conservation of mass.
1800s: Milestones included Alessandro Volta's discoveries regarding electrochemical series, which led to the invention of the battery. John Dalton also introduced atomic theory, which stated that all matter is composed of atoms that combine to form molecules. The basis of modern study of genetics advanced as Gregor Mendel unveiled his laws of inheritance. Later in the century, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays , while George Ohm's law provided the basis for understanding how to harness electrical charges.
1900s: The discoveries of Albert Einstein , who is best known for his theory of relativity, dominated the beginning of the 20th century. Einstein's theory of relativity is actually two separate theories. His special theory of relativity, which he outlined in a 1905 paper, " The Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies ," concluded that time must change according to the speed of a moving object relative to the frame of reference of an observer. His second theory of general relativity, which he published as " The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity ," advanced the idea that matter causes space to curve.
In 1952, Jonas Salk developed the polio vaccine , which reduced the incidence of polio in the United States by nearly 90%, according to Britannica . The following year, James D. Watson and Francis Crick discovered the structure of DNA , which is a double helix formed by base pairs attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute .
2000s: The 21st century saw the first draft of the human genome completed, leading to a greater understanding of DNA. This advanced the study of genetics, its role in human biology and its use as a predictor of diseases and other disorders, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute .
- This video from City University of New York delves into the basics of what defines science.
- Learn about what makes science science in this book excerpt from Washington State University .
- This resource from the University of Michigan — Flint explains how to design your own scientific study.
Merriam-Webster Dictionary, Scientia. 2022. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/scientia
University of California, Berkeley, "Understanding Science: An Overview." 2022. https://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/0_0_0/intro_01
Highline College, "Scientific method." July 12, 2015. https://people.highline.edu/iglozman/classes/astronotes/scimeth.htm
North Carolina State University, "Science Scripts." https://projects.ncsu.edu/project/bio183de/Black/science/science_scripts.html
University of California, Santa Barbara. "What is an Independent variable?" October 31,2017. http://scienceline.ucsb.edu/getkey.php?key=6045
Encyclopedia Britannica, "Control group." May 14, 2020. https://www.britannica.com/science/control-group
The University of Waikato, "Scientific Hypothesis, Theories and Laws." https://sci.waikato.ac.nz/evolution/Theories.shtml
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Robert Grosseteste. May 3, 2019. https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/grosseteste/
Encyclopedia Britannica, "Jonas Salk." October 21, 2021. https://www.britannica.com/ biography /Jonas-Salk
National Human Genome Research Institute, "Phosphate Backbone." https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Phosphate-Backbone
National Human Genome Research Institute, "What is the Human Genome Project?" https://www.genome.gov/human-genome-project/What
Live Science contributor Ashley Hamer updated this article on Jan. 16, 2022.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
'The difference between alarming and catastrophic': Cascadia megafault has 1 especially deadly section, new map reveals
Arctic 'zombie fires' rising from the dead could unleash vicious cycle of warming
Epidurals may lower risk of complications after birth, study hints
Most Popular
- 2 100-foot 'walking tree' in New Zealand looks like an Ent from Lord of the Rings — and is the lone survivor of a lost forest
- 3 A 'new star' could appear in the sky any night now. Here's how to see the Blaze Star ignite.
- 4 Why did Homo sapiens emerge in Africa?
- 5 Blood Falls: Antarctica's crimson waterfall forged from an ancient hidden heart
- 2 James Webb telescope finds carbon at the dawn of the universe, challenging our understanding of when life could have emerged
- 3 Shigir Idol: World's oldest wood sculpture has mysterious carved faces and once stood 17 feet tall
- 4 What could aliens look like?
- 5 Humans didn't domesticate horses until 4,200 years ago — a millennium later than thought
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded .
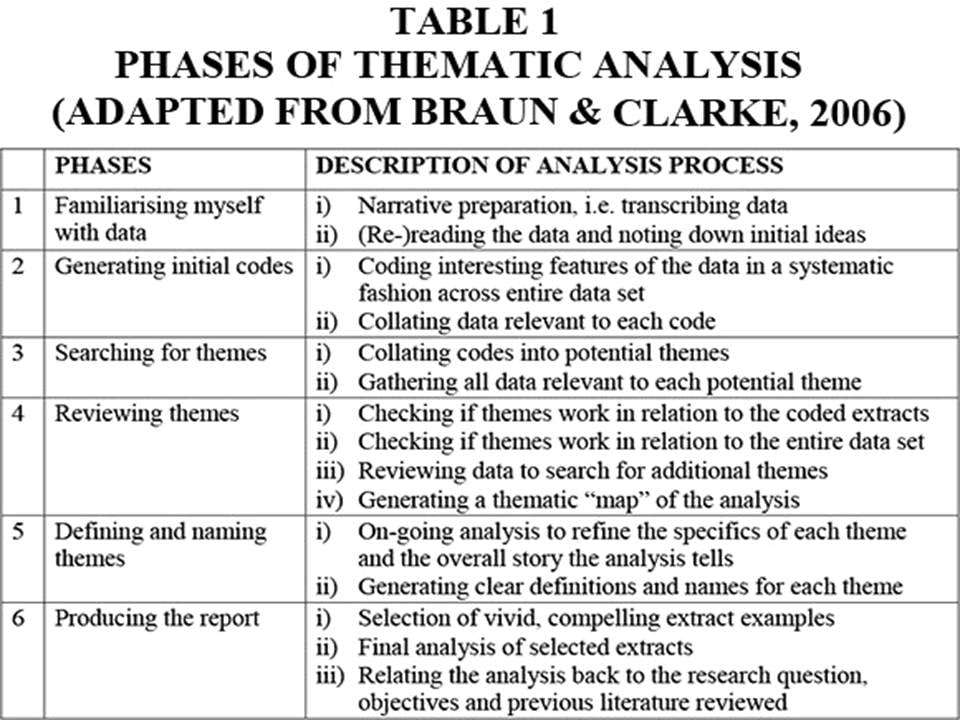
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Is Data Analysis? (With Examples)
Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions.
![what is the research method used [Featured image] A female data analyst takes notes on her laptop at a standing desk in a modern office space](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/2CUbULaq9mEfSSIq6lsCUu/b8ec58abf5106bf9bf75b17da09c39c0/What_is_data_analysis.png?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
"It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock Holme's proclaims in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's A Scandal in Bohemia.
This idea lies at the root of data analysis. When we can extract meaning from data, it empowers us to make better decisions. And we’re living in a time when we have more data than ever at our fingertips.
Companies are wisening up to the benefits of leveraging data. Data analysis can help a bank to personalize customer interactions, a health care system to predict future health needs, or an entertainment company to create the next big streaming hit.
The World Economic Forum Future of Jobs Report 2023 listed data analysts and scientists as one of the most in-demand jobs, alongside AI and machine learning specialists and big data specialists [ 1 ]. In this article, you'll learn more about the data analysis process, different types of data analysis, and recommended courses to help you get started in this exciting field.
Read more: How to Become a Data Analyst (with or Without a Degree)
Beginner-friendly data analysis courses
Interested in building your knowledge of data analysis today? Consider enrolling in one of these popular courses on Coursera:
In Google's Foundations: Data, Data, Everywhere course, you'll explore key data analysis concepts, tools, and jobs.
In Duke University's Data Analysis and Visualization course, you'll learn how to identify key components for data analytics projects, explore data visualization, and find out how to create a compelling data story.
Data analysis process
As the data available to companies continues to grow both in amount and complexity, so too does the need for an effective and efficient process by which to harness the value of that data. The data analysis process typically moves through several iterative phases. Let’s take a closer look at each.
Identify the business question you’d like to answer. What problem is the company trying to solve? What do you need to measure, and how will you measure it?
Collect the raw data sets you’ll need to help you answer the identified question. Data collection might come from internal sources, like a company’s client relationship management (CRM) software, or from secondary sources, like government records or social media application programming interfaces (APIs).
Clean the data to prepare it for analysis. This often involves purging duplicate and anomalous data, reconciling inconsistencies, standardizing data structure and format, and dealing with white spaces and other syntax errors.
Analyze the data. By manipulating the data using various data analysis techniques and tools, you can begin to find trends, correlations, outliers, and variations that tell a story. During this stage, you might use data mining to discover patterns within databases or data visualization software to help transform data into an easy-to-understand graphical format.
Interpret the results of your analysis to see how well the data answered your original question. What recommendations can you make based on the data? What are the limitations to your conclusions?
You can complete hands-on projects for your portfolio while practicing statistical analysis, data management, and programming with Meta's beginner-friendly Data Analyst Professional Certificate . Designed to prepare you for an entry-level role, this self-paced program can be completed in just 5 months.
Or, L earn more about data analysis in this lecture by Kevin, Director of Data Analytics at Google, from Google's Data Analytics Professional Certificate :
Read more: What Does a Data Analyst Do? A Career Guide
Types of data analysis (with examples)
Data can be used to answer questions and support decisions in many different ways. To identify the best way to analyze your date, it can help to familiarize yourself with the four types of data analysis commonly used in the field.
In this section, we’ll take a look at each of these data analysis methods, along with an example of how each might be applied in the real world.
Descriptive analysis
Descriptive analysis tells us what happened. This type of analysis helps describe or summarize quantitative data by presenting statistics. For example, descriptive statistical analysis could show the distribution of sales across a group of employees and the average sales figure per employee.
Descriptive analysis answers the question, “what happened?”
Diagnostic analysis
If the descriptive analysis determines the “what,” diagnostic analysis determines the “why.” Let’s say a descriptive analysis shows an unusual influx of patients in a hospital. Drilling into the data further might reveal that many of these patients shared symptoms of a particular virus. This diagnostic analysis can help you determine that an infectious agent—the “why”—led to the influx of patients.
Diagnostic analysis answers the question, “why did it happen?”
Predictive analysis
So far, we’ve looked at types of analysis that examine and draw conclusions about the past. Predictive analytics uses data to form projections about the future. Using predictive analysis, you might notice that a given product has had its best sales during the months of September and October each year, leading you to predict a similar high point during the upcoming year.
Predictive analysis answers the question, “what might happen in the future?”
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis takes all the insights gathered from the first three types of analysis and uses them to form recommendations for how a company should act. Using our previous example, this type of analysis might suggest a market plan to build on the success of the high sales months and harness new growth opportunities in the slower months.
Prescriptive analysis answers the question, “what should we do about it?”
This last type is where the concept of data-driven decision-making comes into play.
Read more : Advanced Analytics: Definition, Benefits, and Use Cases
What is data-driven decision-making (DDDM)?
Data-driven decision-making, sometimes abbreviated to DDDM), can be defined as the process of making strategic business decisions based on facts, data, and metrics instead of intuition, emotion, or observation.
This might sound obvious, but in practice, not all organizations are as data-driven as they could be. According to global management consulting firm McKinsey Global Institute, data-driven companies are better at acquiring new customers, maintaining customer loyalty, and achieving above-average profitability [ 2 ].
Get started with Coursera
If you’re interested in a career in the high-growth field of data analytics, consider these top-rated courses on Coursera:
Begin building job-ready skills with the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate . Prepare for an entry-level job as you learn from Google employees—no experience or degree required.
Practice working with data with Macquarie University's Excel Skills for Business Specialization . Learn how to use Microsoft Excel to analyze data and make data-informed business decisions.
Deepen your skill set with Google's Advanced Data Analytics Professional Certificate . In this advanced program, you'll continue exploring the concepts introduced in the beginner-level courses, plus learn Python, statistics, and Machine Learning concepts.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Where is data analytics used .
Just about any business or organization can use data analytics to help inform their decisions and boost their performance. Some of the most successful companies across a range of industries — from Amazon and Netflix to Starbucks and General Electric — integrate data into their business plans to improve their overall business performance.
What are the top skills for a data analyst?
Data analysis makes use of a range of analysis tools and technologies. Some of the top skills for data analysts include SQL, data visualization, statistical programming languages (like R and Python), machine learning, and spreadsheets.
Read : 7 In-Demand Data Analyst Skills to Get Hired in 2022
What is a data analyst job salary?
Data from Glassdoor indicates that the average base salary for a data analyst in the United States is $75,349 as of March 2024 [ 3 ]. How much you make will depend on factors like your qualifications, experience, and location.
Do data analysts need to be good at math?
Data analytics tends to be less math-intensive than data science. While you probably won’t need to master any advanced mathematics, a foundation in basic math and statistical analysis can help set you up for success.
Learn more: Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: What’s the Difference?
Article sources
World Economic Forum. " The Future of Jobs Report 2023 , https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2023.pdf." Accessed March 19, 2024.
McKinsey & Company. " Five facts: How customer analytics boosts corporate performance , https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/five-facts-how-customer-analytics-boosts-corporate-performance." Accessed March 19, 2024.
Glassdoor. " Data Analyst Salaries , https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/data-analyst-salary-SRCH_KO0,12.htm" Accessed March 19, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
- Open access
- Published: 29 May 2024
Exploring the use of body worn cameras in acute mental health wards: a mixed-method evaluation of a pilot intervention
- Una Foye 1 , 2 ,
- Keiran Wilson 1 , 2 ,
- Jessica Jepps 1 , 2 ,
- James Blease 1 ,
- Ellen Thomas 3 ,
- Leroy McAnuff 3 ,
- Sharon McKenzie 3 ,
- Katherine Barrett 3 ,
- Lilli Underwood 3 ,
- Geoff Brennan 1 , 2 &
- Alan Simpson 1 , 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 681 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
344 Accesses
12 Altmetric
Metrics details
Body worn cameras (BWC) are mobile audio and video capture devices that can be secured to clothing allowing the wearer to record some of what they see and hear. This technology is being introduced in a range of healthcare settings as part of larger violence reduction strategies aimed at reducing incidents of aggression and violence on inpatient wards, however limited evidence exists to understand if this technology achieves such goals.
This study aimed to evaluate the implementation of BWCs on two inpatient mental health wards, including the impact on incidents, the acceptability to staff and patients, the sustainability of the resource use and ability to manage the use of BWCs on these wards.
The study used a mixed-methods design comparing quantitative measures including ward activity and routinely collected incident data at three time-points before during and after the pilot implementation of BWCs on one acute ward and one psychiatric intensive care unit, alongside pre and post pilot qualitative interviews with patients and staff, analysed using a framework based on the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research.
Results showed no clear relationship between the use of BWCs and rates or severity of incidents on either ward, with limited impact of using BWCs on levels of incidents. Qualitative findings noted mixed perceptions about the use of BWCs and highlighted the complexity of implementing such technology as a violence reduction method within a busy healthcare setting Furthermore, the qualitative data collected during this pilot period highlighted the potential systemic and contextual factors such as low staffing that may impact on the incident data presented.
This study sheds light on the complexities of using such BWCs as a tool for ‘maximising safety’ on mental health settings. The findings suggest that BWCs have a limited impact on levels of incidents on wards, something that is likely to be largely influenced by the process of implementation as well as a range of contextual factors. As a result, it is likely that while BWCs may see successes in one hospital site this is not guaranteed for another site as such factors will have a considerable impact on efficacy, acceptability, and feasibility.
Peer Review reports
Body worn cameras (BWC) are mobile audio and video capture devices that can be secured to clothing allowing the wearer to record some of what they see and hear. In England, these have been introduced in the National Health Service (NHS) as part of a violence reduction strategy [ 1 ] which emphasises the reduction of aggression and violence against staff. The NHS Staff Survey 2022 found that 14.7% of NHS staff had experienced at least one incident of physical violence from patients, relatives or other members of the public in the previous 12 months. Violent attacks on staff were found to contribute to almost half of staff illness [ 2 ]. Levels of violence against staff working in mental health trusts remain much higher than other types of healthcare providers [ 3 ]. Numerous reports internationally highlight the increased risks faced by staff working in psychiatric care [ 4 ], though studies have reported that both ward staff and mental health patients experience violence and feeling unsafe on inpatient wards [ 5 , 6 ].
Body worn cameras have been in use for over a decade within law enforcement, where they hoped to provide transparency and accountability within use-of-force incidents and in the event of citizen complaints against police [ 7 ]. It was believed that video surveillance would help identify integral problems within the organisation, improve documentation of evidence, reduce use-of-force incidents, improve police-community relations, and provide training opportunities for officers [ 8 ]. However, a recent extensive international systematic review by Lum et al. [ 9 ], found that despite the successes noted in early evaluations, the way BWCs are currently used by police may not substantially affect most officer or citizen behaviours. Irrespective of these findings, other public services such as train operators have been implementing BWCs for security purposes, with reductions reported in the number of assaults on railway staff [ 10 ].
A recent systematic review of BWC use in public sector services established that there is a poor evidence base supporting the use of BWCs in the reduction of violence and aggression [ 11 ]. Yet, we are seeing a swift increase in the use of BWCs in mental health settings with that aim, with few studies conducted on the use of BWC technology in inpatient mental health wards, and even fewer studies exploring staff or patients’ views. Two evaluations conducted in England reported mixed results with both increases and decreases in violence and aggression found, and variation between types of wards. There is some suggestion of a reduction in more serious incidents and the use of restraint, but quality of evidence is low [ 12 , 13 ].
The use of BWCs in mental healthcare settings for safety and security remains a contentious topic due to the lack of evidence regarding the influence that such technology has on preventing violence and aggression and the complex philosophical and ethical issues raised, particularly where many patients may lack capacity and/or are detained under mental health legislation [ 14 ]. Additionally, there are concerns that BWCs may be used as a ‘quick fix’ for staff shortages rather than addressing the wider systemic and resourcing issues facing services [ 15 ]. With little independent evaluation of body-worn cameras in mental health settings, many of these concerns remain unanswered. There is also limited understanding of this technology from an implementation perspective. Therefore, in this study we aimed to conduct an independent evaluation of the introduction of BWCs as a violence reduction intervention on two inpatient mental health wards during a six-month pilot period to explore the impact of using the technology, alongside an exploration of the facilitators and barriers to implementation.
Research aim(s)
To evaluate the implementation of BWCs on two inpatient mental health wards, including the impact on incidents, the acceptability to staff and patients, the sustainability of the resource use and ability to manage the use of BWCs on these wards.
Patient and public involvement
The research team included a researcher and independent consultant, each with lived experience of mental health inpatient care. In addition, we recruited and facilitated a six member Lived Experience Advisory Panel (LEAP). This group was made up of patients and carers, some of whom had experienced the use of BWCs. Members were of diverse ethnic backgrounds and included four women and two men. The LEAP provided guidance and support for the research team in developing an understanding of the various potential impacts of the use of BWCs on inpatient mental health wards. Members contributed to the design of the study, development of the interview schedule, practice interviews prior to data collection on the wards, and supported the analysis and interpretation of the data, taking part in coding sessions to identify themes in the interview transcripts. The LEAP met once a month for two hours and was chaired by the Lived Experience Research Assistant and Lived Experience Consultant. Participants in the LEAP were provided with training and paid for their time.
The pilot introduction of the body worn cameras was conducted within a London mental health Trust consisting of four hospital sites with 17 acute wards. The research team were made aware of extensive preparatory work and planning that was conducted at a directorate and senior management level prior to camera implementation, including lived experience involvement and consultation, and the development of relevant policies and protocols inclusive of a human rights assessment and legal consultation.
The pilot period ran from 25th April to 25th October 2022. Reveal (a company who supply BWCs nationally across the UK) provided the Trust with 12 Calla BWCs for a flat fee that covered use of the cameras, cloud-based storage of footage, management software, and any support/maintenance required during the pilot period. Cameras were introduced to two wards based on two hospital sites, with six cameras provided to each of the wards on the same date. Training on using the BWCs was provided by the BWC company to staff working on both wards prior to starting the pilot period. Ward one was a 20-bed male acute inpatient ward, representing the most common ward setting where cameras have been introduced. Ward two was a ten-bed male Psychiatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU), representing smaller and more secure wards in which patients are likely to present as more unwell and where there are higher staff to patient ratios.
To answer our research questions, we used a mixed-methods design [ 16 ]. Using this design allowed us to investigate the impact of implementing BWCs in mental health settings on a range of quantitative and qualitative outcomes. This mixed methods design allows the study to statistically evaluate the effectiveness of using BWCs in these settings on key dependent variables (i.e., rates of violence and aggression, and incidents of conflict and containment) alongside qualitatively exploring the impact that the implementation of such technology has on patients and staff.
To ensure that the study was able to capture the impact and effect of implementation of the cameras, a repeated measures design was utilised to capture data at three phases on these wards:
Pre-pilot data: data prior of the implementation of the BWCs (quantitative and qualitative data).
Pilot period data: data collected during the six-month pilot period when BWCs were implemented on the wards (quantitative and qualitative data).
Post-pilot: data collected after the pilot period ended and cameras had been removed from the wards (quantitative data only).
Quantitative methods
Quantitative data was collected at all three data collection periods:
Pre-period: Data spanning six months prior to the implementation of BWCs (Nov 21 to May 22).
Pilot period: Data spanning the six months of the Trusts pilot period of using BWCs on the wards (June 22 to Nov 22).
Post-pilot: Data spanning the six months following the pilot period, when BWCs had been removed (Dec 22 to May 23).
Quantitative measures
To analyse the impact of BWC implementation, we collected two types of incident data related to violence and aggression and use of containment measures, including BWCs. Combined, these data provide a view of a wide range of incidents and events happening across the wards prior to, during, and after the implementation and removal of the BWCs.
The patient-staff conflict checklist
The Patient-staff Conflict Checklist (PCC-SR) [ 17 ] is an end of shift report that is completed by nurses to collate the frequency of conflict and containment events. This measure has been used successfully in several studies on inpatient wards [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].The checklist consists of 21 conflict behaviour items, including physical and verbal aggression, general rule breaking (e.g., smoking, refusing to attend to personal hygiene), eight containment measures (e.g., special observation, seclusion, physical restraint, time out), and staffing levels. In tests based on use with case note material, the PCC-SR has demonstrated an interrater reliability of 0.69 [ 21 ] and has shown a significant association with rates of officially reported incidents [ 22 ].
The checklist was revised for this study to include questions related to the use of BWCs ( e.g., how many uses of BWCs happened during the shift when a warning was given and the BWC was not used; when a warning was given and the BWC was used; when the BWC was switched on with no warning given ) in order to provide insight into how the cameras were being used on each ward (see appendix 1). Ward staff were asked to complete the checklist online at the end of each shift.
Routinely collected incident data (via datix system)
To supplement the PCC-SR-R, we also used routinely collected incident data from both wards for all three data collection phases. This data is gathered as part of routine practice by ward staff members via the Datix system Datix [ 23 ] is a risk management system used widely across mental health wards and Trusts in the UK to gather information on processes and errors. Previous studies have utilised routinely collect data via this system [ 24 , 25 ]. Incidents recorded in various Datix categories were included in this study (see Table 1 ). Incidents were anonymised before being provided to the research team to ensure confidentiality.
Routinely collected data included:
Recorded incidents of violence and aggression.
Recorded use of restrictive practices including seclusion, restraint, and intra-muscular medication/rapid tranquilisations.
Patient numbers.
Staffing levels.
Numbers of staff attending BWC training.
Quantitative data analysis
Incident reports.
Incident reports retrieved from Datix were binary coded into aggregate variables to examine violence and aggression, self-harm, and other conflict as outlined in Table 1 . Multivariate analyses of variance (MANOVA) were used to identify differences in type of incident (violence against person, violence against object, verbal aggression, self-harm, conflict) for each ward. MANOVA was also used to examine differences in incident outcomes (severity, use of restrictive practice, police involvement) across pre-trial, trial, and post-trial periods for each ward. Incident severity was scored by ward staff on a four-point scale (1 = No adverse outcome, 2 = Low severity, 3 = Moderate severity, 4 = Severe). Use of restrictive practice and police involvement were binary coded for presence or absence. Analyses were conducted using SPSS [ 26 ].
Patient-staff conflict checklist shift-report – revised (PCC-SR-R; )
Data were condensed into weeks for analysis rather than shifts to account for variability in PCC-SR-R submission by shift. Linear regressions assessed the relationship between BWC use and incident outcome (severity, use of restrictive practice, police involvement).
Qualitative methods
We used semi-structured qualitative interviews to explore participants’ experiences of BWCs on the ward to understand the impact of their use as well as to identify any salient issues for patients, staff and visitors that align with the measures utilised within the quantitative aspect of this study. These interviews were conducted at two time points: pre-pilot and at the end of the six-month pilot period.
Sample selection, eligibility, and recruitment
Convenience sampling was used to recruit staff and patients on wards. Researchers approached ward managers to distribute information sheets to staff, who shared that information with patients. Staff self-selected to participate in the study by liaising directly with the research team. Patients that were identified as close to discharge and having capacity to consent were approached by a clinical member of the team who was briefed on the study inclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). The staff member spoke with the patient about the study and provided them with a copy of the information sheet to consider. If patients consented, a member of the research team approached the participant to provide more information on the study and answer questions. After initial contact with the research team, participants were given a 24-hour period to consider whether they wanted to participate before being invited for an interview.
Participants were invited to take part in an interview within a private space on the ward. Interviews were scheduled for one hour with an additional 15 min before and after to obtain informed consent and answer any questions. Participation was voluntary and participants were free to withdraw at any time. To thank patients for their time, we offered a £10 voucher following the interview. Interviews were audio-recorded and saved to an encrypted server. Interview recordings were transcribed by an external company, and the research team checked the transcripts for accuracy and pseudonymised all participants. All transcripts were allocated a unique ID number and imported to MicroSoft Excel [ 27 ] for analysis.
Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data were analysed using a framework analysis [ 28 ] informed by implementation science frameworks. Our coding framework used the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 29 ], which is comprised of five major domains including: Intervention Characteristics, Implementation Processes, Outer Setting, Inner Setting, and Characteristics of the Individual. Each domain consists of several constructs that reflect the evidence base of the types of factors that are most likely to influence implementation of interventions. The CFIR is frequently used to design and conduct implementation evaluations and is commonly used for complex health care delivery interventions to understand barriers and facilitators to implementation. Based on its description, the CFIR is an effective model to address our research question, particularly given the complexity of the implementation of surveillance technology such as BWCs in this acute care setting.
The initial analytic stage was undertaken by eight members of the study team with each researcher charting data summaries onto the framework for each of the interviews they had conducted on MicroSoft Excel [ 27 ]. Sub-themes within each broad deductive theme from our initial framework were then derived inductively through further coding and collaborative discussion within the research team, inclusive of Lived Experience Researcher colleagues. Pseudonyms were assigned to each participant during the anonymisation of transcripts along with key identifiers to provide context for illustrative quotes (e.g., P = patient, S = staff, A = acute ward, I = Intensive Care, Pre = pre-BWC implementation interview, Post = Post BWC implementation interview).
All participants gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Health Research Authority: London - Camden & Kings Cross Research Ethics Committee (IRAS Project ID 322,268, REC Reference 23/LO/0337).
Quantitative results
Exploring how body worn cameras were used during the pilot period.
Analysis of the PCC-SR-R provides information about how the BWCs were used on a day-to-day basis during the pilot period. Out of 543 total shift reports completed, BWC use was reported 50 times, indicating that BWCs were used on less than 10% of shifts overall; 78% of those deployments were on the Acute ward (see Figure 1 ). Overall, the majority of deployments happened as activations without a warning being given ( n = 30, 60% of activations), 19 times the BWC was deployed with a warning but the camera was not activated (38%), and only one was the camera activated without a warning being given (2%).
BWC use by ward per week of pilot (no data available before week 6 on Ward 1)
According to the PCC-SR-R, a total of 227 incidents of aggression occurred during the pilot period across both wards (see Table 3 ). Overall, there were small statistically significant correlations between BWC usage and certain types of conflict, aggression, and restrictive practice. Results found that BWC use was positively correlated with verbal aggression and use of physical restraint. BWC use was moderately positively correlated with verbal aggression ( r = .37, p < .001). This indicates that BWCs were more likely to be used in incidents involving verbal aggression, which do not tend to be documented in Datix. Similarly, BWC use was moderately positively correlated with physical restraint ( r = .31, p < .001) indicating that they were also more likely to be used alongside physical restraint.
Exploring the impact of BWCs utilising routinely collected ward data
Acute ward results.
Routine data collected via Datix records were used to examine differences in frequency of conflict and aggression, incident severity, and use of containment measures before, during, and after introduction of BWCs on each trial ward (see Table 4 ).
There was no effect of trial period on incident type ( F (10, 592) = 1.703, p = .077, Wilk’s Λ = 0.945), meaning there was no discernible difference in the type of incidents that occurred (E.g., verbal aggression, physical aggression) before, during, and after the pilot phase.
Incident outcomes
There was an effect of trial period on incident outcomes ( F (6, 596) = 10.900, p < .001, Wilk’s Λ = 0.812). Incident severity was statistically significantly higher in the trial and post-trial periods compared to the pre-trial period. Use of restrictive practice was significantly lower in the post-trial period compared to the pre-trial and trial period. Police involvement was also lower in the post-trial period compared to the pre-trial and trial periods (see Table 5 ).
Results for the psychiatric intensive care unit
There was an effect of trial period on incident type ( F (10, 490) = 4.252, p < .001, Wilk’s Λ = 0.847). Verbal aggression was statistically significantly higher in the post-trial period compared to the pre and trial periods. Self-harm was statistically significantly higher in the trial period compared to the pre-trial and post-trial periods. There were no differences in violence against a person ( p = .162), violence against an object or conflict behaviour (see Table 4 ).
There was a statistically significant difference in incident outcome across the trial periods ( F (6, 494) = 12.907, p < .001, Wilk’s Λ = 0.747). There was no difference in incident severity or police involvement. However, use of restrictive practice was statistically significantly higher in the pre-trial period, reducing in the test period, and reducing further in the post-trial period (see Table 5 ).
Qualitative findings
A total of 22 participants took part in interviews: five patients and 16 staff members. During the pre-pilot interviews a total of nine staff took part (five in the acute ward, four in the PICU ward) and two patients (both from the acute ward). After the pilot period, a total of eight staff took part (four from each ward) and three patients (all from the acute ward). Table 6 includes a full description of participants.
Below we have presented the key themes aligning to the five core CFIR categories of Intervention Characteristics, Characteristics of Individuals, The Process of Implementation, the Inner Setting, and The Outer Setting (see Table 7 ).
Intervention characteristics
Design and usability of wearing a bwc on the ward.
When discussing the use of the BWCs, staff noted a range of design issues related to the cameras that they said impacted on their use and acceptance of the cameras. This included the nature of the camera pulling on clothing necklines (a particular issue for female staff working on male wards), and overheating causing discomfort and irritation to skin, challenges with infection control, as well as the issue of cameras in a mental health setting where they can be easily grabbed, thrown and broken during an incident. Staff often cited these design issues as related to the lack of proactive use of the cameras on the wards.
There were issues around the devices getting overheated or about it going on your clothing, it pulls down the top… we had one person who was leading on it, whenever he was around, of course, the camera was being used, but if he wasn’t there, people weren’t as proactive in using the camera. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
There were also issues with staff forgetting to wear the cameras, forgetting to switch them on during incidents, and forgetting to charge them at the end of the shift, reducing the potential use of the cameras by other staff. These were perceived as key logistical issues prior to the pilot and were reported as issues at the end of the pilot by several staff on the wards.
The practicalities of will they actually turn it on in those sorts of incidents, I don’t know. Just little stuff as well, like if they don’t put it back on the docking station, so you think you’re charging it for next shift but then it’s not charged and the battery is dead, that’s one less camera to use, so little stuff. Jamal (m), Staff, A, Pre.
In relation to usability, staff noted that the cameras were small and easy to use given their simple single switch interface. It was felt that not having to upload and manage the data themselves made cameras more user friendly and usable by staff members. Protocols put into place such as signing the cameras in and out, and allocation for use during shifts were likened to procedures in place for other security measures therefore the implementation of this for the BWCs was viewed as easy for many staff.
It’s just like the ASCOM alarms that we wear. There’s a system to sign in and sign out, and that’s it. Alice (f), Staff, A, Pre.
While staff were generally positive about the usability of the cameras, some were cautious of with concerns for those less confident with technology.
… you have to be conscious that there’s some people – it’s quite easy to use, but I can say that because I’m alright using devices and all that but there’s some that are older age or not that familiar with using devices that may struggle with using it… they’re feeling a bit anxious and a bit scared, if they’re not familiar with it then they won’t use it. Jamal (m), Staff, A, Pre.
Evidence strength and quality: do BWCs change anything?
There were conflicting reports regarding the potential benefits of using BWCs on the wards, with both staff and patients reporting mixed perceptions as to whether the cameras might reduce violence and aggression. In the pre-pilot interviews, some staff reported feeling that the BWCs may have a positive impact on reducing physical violence.
I think it’s going to reduce violence and aggression on the ward…I don’t think they’ll want to punch you…they might be verbally abusive but in terms of physical that might reduce. Sarah (f), Staff, I, Pre.
Patients however noted that the cameras might hold staff to account of their own behaviours and therefore may improve care, however they felt that this impact would wear off after the first few months after which people might forget about the cameras being there.
Now they’ve got the body cams, it’s going to be a lot of changes. They’ll think, ‘Ooh well he’s on tape’. So, it might do something to their conscience, they actually start to listen to patients… until the novelty wears off and it might go back to square one again. Ian (m), Patient, A, Pre.
One staff member suggested that incident rates had reduced following introduction of the BWCs, but they remained unsure as to whether this was due to the cameras, reflecting that violence and aggression on wards can be related to many factors.
I know our violence and aggression has reduced significantly since the start of the cameras pilot… I don’t know, because obviously wearing the camera’s one thing, but if they weren’t in use, I don’t know maybe just the presence of the camera made a difference. But yeah, it’s hard to tell. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
In contrast, several staff reported that they had seen limited evidence for such changes.
I used it yesterday. He was aggressive and I used it, but he even when I was using [it] he doesn’t care about the camera… it didn’t make any difference… It doesn’t stop them to do anything, this camera does not stop them to do anything. Abraham (m), Staff, I, Post.
Some staff suggested that in some circumstances the cameras increased patient agitation and created incidents, so there was a need to consider whether the BWCs were going to instigate aggression in some circumstances.
There has been with a few patients because they will threaten you. They will tell you, ‘if you turn it on, I’m gonna smash your head in’. So incidents like that, I will not turn it on… Yeah, or some of them will just tell you, ‘if you come close by, I’m going to pull that off your chest’. So things like that, I just stay back. Ada (f), Staff, A, Post.
One rationale for a potential lack of effectiveness was noted by both staff and patients and was related to the levels of acute illness being experienced by patients which meant that for many they were too unwell to have insight into their own actions or those of staff switching on the cameras.
We’ve had instances where patients are so unwell that they just don’t care. You switch on the camera, whether you switch it on or not, it doesn’t really change the behaviour. ‘All right, okay, whatever switch it on’. They’re so unwell, they’re not really understanding. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post. It might make [staff] feel safer as a placebo effect, but I don’t think it would necessarily make them safer… I think the people that are likely to attack a member of staff are crazy enough that they’re not gonna even consider the camera as a factor. Harry (m), Patient, A, Pre.
This lack of evidence that the cameras were necessarily effective in reducing incident rates or severity of incidents may have had an impact on staff buy-in and the use of the cameras as a result. One staff member reflected that having feedback from senior management about the impact and evidence would have been useful during the pilot period to inform ward staff whether the cameras were influencing things or not.
Staff want feedback. I don’t think we’ve had any since we’ve had the cameras… it would be nice to get feedback from, I don’t know, whoever is watching it, and stuff like that. Ada (f), Staff, A, Post.
Relative advantage: are BWCs effective and efficient for the ward?
Due to a combination of personal beliefs related to BWCs, the lack of evidence of their impact on violence and aggression, and other elements of care and culture on the wards, a number of staff and patients explored alternative interventions and approaches that may be more beneficial than BWCs. Both staff and patients suggested that Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) as an intervention that provided the transparency of using cameras and video footage but with an independent perspective. This was felt by many to remove the bias that could be introduced in BWC use as the video capture didn’t require staff control of the filming.
I feel like [BWCs] puts all the power and trust into the hands of the staff and I feel that it would be better to have CCTV on the ward because CCTV is neutral. Harry (m), Patient, A, Pre. I have control over that [BWC recording] … It kind of gives that split as well between staff and patients. You can tell me or I can tell you when to switch it on. Whereas I feel like a CCTV camera is there all the time. Nobody’s asking to switch it on. It’s there. If you wanted to review the footage you can request it, anyone can request to view the footage for a legitimate reason. Whereas the camera can come across as if you’re threatening. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
In addition, some participants reflected that the nature and design of BWCs meant that unless staff were present for an incident it wouldn’t be captured, whereas CCTV has the advantage of being always present.
If there’s CCTV, then it’s the same thing, you get me. Like, if its body worn cameras that people can always do things away from staff. They can always go down to that corridor to have their fight or go to the side where staff ain’t gonna see them to have their fight, but with CCTV you can’t do that. Elijah (m), Patient, A, Post.
In addition to exploring technological and video-based interventions, many staff noted that the key tool to violence reduction had to be the use of de-escalation skills, noting that the use of communication and positive relationships had to be the primary tool before other interventions such as BWCs or CCTV.
We do a lot of verbal de-escalation. So we got our destress room now still open. That has a punch bag, and it’s got sensory tiles, and the aim and hope is that when people do get frustrated, because we’re all human. We all get annoyed at anything or many little things in life. There is the aim that they go into that room and start punching the bag instead of property and damaging furniture. But we also are working really hard on verbal de-escalation and actually trying to listen to patients and talk to them before anything else. And that’s helped a lot. And between this kind of shared, or role modelling, where while we’re showing staff, actually even spending an extra 20 min is okay. If it means you’re not going to end up having to restrain a patient. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
By using communication skills and de-escalation techniques skilfully, some staff felt there was no need to utilise the BWCs. One concern with the introduction of the BWCs for staff was that the use of this technology may negatively impact on trust and relationships and the use of de-escalation.
Some situations I feel like it can make a situation worse sometimes… I think a lot of situations can be avoided if you just talk with people…. Trying to find out why they’re angry, trying to just kind of see it from their point of view, understand them… I think maybe additional training for verbal de-escalation is needed first. Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
Characteristics of individuals
Staff and patients’ knowledge and beliefs about the intervention.
Overall, there were mixed views among both staff and patients as to whether cameras would reduce incidents, prior to and after the pilot period. When considering the possible impact on violence and aggressive incidents there was a view among staff that there was the need for a nuanced and person-centred view.
All the patients that come in, they’re different you know. They have different perceptions; they like different things… everyone is different. So, it just depends. We might go live, and then we have good feedback because the patients they are open and the understand why we have it, and then as they get discharged and new patients come in it might not go as well. It just depends. Serene (f), Staff, A, Pre.
As a result of the desire to be person-centred in the use of such interventions, one staff member noted that they weighed-up such consequences for the patient before using the BWC and would make decisions not to use the camera where they thought it may have a negative impact.
Actually, with this body worn camera, as I did mention, if a patient is unwell, that doesn’t, the patient will not have the capacity to I mean, say yes, you cannot just put it on like that. Yeah, I know it’s for evidence, but when something happens, you first have to attend to the patient. You first have to attend to the patient before this camera is, for me. Ruby (f), Staff, I, Post.
Some staff questioned the existing evidence and theories as to why BWCs work to reduce incidents, and instead noted that for some people it will instigate an incident, while others may be triggered by a camera.
I’m on the fence of how that is going to work because I know the evidence is that by telling a patient ‘look if you keep escalating I’m gonna have to turn this on’, but I know several of our patients would kind of take that as a dare and escalate just to spite so that you would turn it on. Diana (f), Staff, A, Pre.
In contrast, some staff felt the cameras helped them feel safer on wards due to transparency of footage as evidence for both staff and patients.
They [staff] need to use it for protection, for recording evidence, that type of thing… They can record instances for later evidence. Yeah, for them as well. Safer for them and for patients because you can also have the right to get them to record, because a patient might be in the wrong but sometimes it may be the staff is in the wrong position. And that’s achieving safety for patients as well. Yeah, I think it works both ways. Dylan (m), Patient, A, Post.
Positive buy-in was also related to the potential use of the intervention as a training, learning or reflective tool for staff to improve practice and care and promote positive staff behaviour.
If you know that your actions might be filmed one way or the other, that would make me to step up your behaviour to patients… if you know that your actions can be viewed, if the authority wants to, then you behave properly with patients so I think that will improve the quality of the care to patient. Davide (m), Staff, I, Pre.
While there were some positive attitudes towards the cameras, there remained considerable concerns among participants regarding the transparency of camera use to collate evidence in relation to incidents as it was widely noted that the cameras remain in staff control therefore there is an issue in relation to bias and power.
I do think my gut would say that it wouldn’t necessarily be well received. Because also I think people feel like prisoners in here, that’s how some of the patients have described their experience, so in terms of the power dynamic and also just – I think that can make one feel a bit, even worse, basically, you know? Leslie (m), Staff, A, Pre.
These issues lead to staff reporting they didn’t want to wear the camera.
I’d feel quite uncomfortable wearing one to be honest. Leslie (m), Staff, A, Pre.
The staff control of the cameras had a particular impact on patient acceptability of the intervention as it led to some patients viewing BWCs as being an intervention for staff advantage and staff safety, thus increasing a ‘them and us’ culture and leading to patient resistance to the cameras. This was particularly salient for those with prior negative experiences of police use of cameras or mistrust in staff.
I feel like the fact that the body worn cameras is gonna be similar to how the police use them, if a staff member has negative intent toward a patient, they would be able to instigate an incident and then turn the camera on and use the consequences of what they’ve instigated to expect restraint or injection or whatever else might happen. So, I feel like it would be putting all the power and trust into the hands of the staff and I feel that it would be better to have CCTV on the ward because CCTV is neutral. Whereas, the body worn camera, especially with some of the personality conflicts/bad attitudes, impressions I’ve had from certain members of staff since I’ve been here, I feel like body worn cameras might be abused in that way possible. Harry (m), Patient, A, Pre.
Perceived unintended consequences and impact on care
Prior to the implementation there were concerns from staff that the introduction of BWCs could have consequences beyond the intended use of reducing violence and aggression, unintentionally affecting a range of factors that may impact on the overall delivery of care. There was a key concern regarding the potential negative impact that cameras may have for patients who have paranoia or psychosis as well as for those who may have prior traumatic experiences of being filmed.
It might have negative impacts on these patients because I’m thinking about kind of patients with schizophrenia and things like that who already have paranoid delusions, thinking that people are after them, thinking that people are spying on them, people are watching them, and then seeing kind of cameras around. It might have negative impacts on them. Tayla (f), Staff, I, Pre. When I was admitted I was going through psychosis… I don’t want to be filmed and things like that. So you just see a camera, a guy with a camera on, you are like, are you filming me? Elijah (m), Patient, A, Post.
There was also a considerable concern among both staff and patients that the use of cameras would have a negative impact on the therapeutic relationship between staff and patients. This was felt to be related to the implication that the cameras enhanced a ‘them and us’ dynamic due to the power differential that staff controlling the cameras can create, likened to policing and criminalisation of patients. With the potential of a negative impact on relationships between staff and patients, staff suggested they may be disinclined to use BWCs if it would stop patients speaking to them or approaching them if they needed support.
Yeah, I think it would probably damage [the therapeutic relationship] because I think what’s probably quite helpful is things that maybe create less of a power difference. I think to some extent, [the BWC] might hinder that ability. Like for example imagine going to a therapist and them just like ‘I’ve got this camera in the corner of the room and it’s gonna be filming our session and just in case – or like, just in case I feel that you might get aggressive with me’. Um, I don’t think that’s going to help the therapeutic relationship! Jamal (m), Staff, A, Pre. When you get body worn cameras on there, the relationship as well between staff and patients, is just gonna instantly change because you’re looking like police! Elijah (m), Patient, A, Post.
In contrast, a minority of staff felt that the presence of cameras may improve relationships as they provide transparency of staff behaviour and would encourage staff to behave well and provide high quality care for patients.
It will also help how, improve the way we look at the patients… because if you know that your actions might be filmed one way or the other, that would make me to step up your behaviour you know… you behave properly with patients so I think that will improve the quality of the care to patient. More efficiently, more caring to patient. Davide (m), Staff, I, Pre.
The process of implementation
Planning: top-down implementation.
Staff perceived that BWC implementation directives had been given by senior management or policy stakeholders whom they felt viewed the process from a position of limited understanding due to a lack of ‘frontline’ mental health service experience. This led to a lack of faith amongst staff, and a perception that funds were being misspent.
They sit up there, they just roll it out and see how it works, how it goes. They waste a whole lot of money, millions or whatever, thousands of pounds in it, and then they see that ‘Oh, it’s not gonna work’. They take it back and all of that. Before coming out with it, you need to come speak to us… they just sit up there drinking tea and coffee, and then they’re just like, Oh, yeah, well, let’s do it this way…come stay with these people, work with them, for just I give you a 12 h shift, stay with them. Richard (m), Staff, I, Post.
This was exacerbated when staff felt there was a lack of consultation or explanation.
we don’t always get the ins and outs of certain things…We know that the cameras are coming in and stuff like that, but you know, and obviously it’s gone through every avenue to make sure that it’s fine. But then sometimes we don’t always know the ins and outs to then explain to people why we have the cameras. Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
It was also highlighted that due to multiple initiatives being implemented and directives handed down in parallel, staff felt negative towards interventions more widely, with the BWCs being ‘ just another thing to do’ , adding to workload for staff and reducing enthusiasm to use the cameras.
it’s not just to do with the camera, I just think there’s lots of changes happening at once, and there’s loads of new things being constantly introduced that people are just thinking oh it’s another thing. I think that’s what it is more than the camera itself. Alice (f), Staff, A, Pre.
Execution: training, Use and Ward Visibility
Overall, there was a lack of consistency amongst staff in their understanding of the purpose and processes of using the BWCs on the wards.
What do you do, do you record every single thing or, I don’t know. Do you record like, if a patient said, I want to talk to you, confidential, you go sit in a room, do you record things like those or is it just violence and aggression? Ada (f), Staff, A, Post.
The lack of clarity regarding the purpose of the intervention and the appropriate use of the cameras was felt to impact staffs’ attitudes and acceptance of using them and contributed to a lack of transparency or perhaps trust regarding the use of any subsequent video footage.
I think if the importance of the recording was explained a bit more…and how it would improve things, I think people would use it more… that’s why I don’t think it’s always used sometimes… if you’re not sure why some of it’s important, then you’re not going to see the value…I think if you’re gonna keep with them, it’s about updating the training, teaching staff when to use it, then where does that information go? How does that look in terms of improving? Just a bit of transparency, I think. But when you don’t know certain things it’s a bit hard to get behind something or back it, you know? Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
The lack of information about the purpose and processes related to the intervention was also seen among patients, with most patients noting that they hadn’t received information about the cameras during their admissions.
No information at all. I don’t think any of the patients know about it. Toby (m), Patient, A, Post.
While training was provided it was widely felt that it was insufficient to provide understanding about the purpose of the cameras or the more in-depth processes beyond operational aspects such as charging and docking. Several staff interviewed were unaware of the training, while others noted that they had an informal run-through by colleagues rather than anything formal.
What training are you talking about?… I wasn’t here, so I was taught by my colleague. I mean, from what I was taught, to operate the camera, and to give a warning to the patient that you’re going to use the camera. Nevis (f), Staff, A, Post.
Longer training with further details beyond operational use was felt to be needed by staff.
I think the training should have to be longer, even if it’s like an hour or something… Like what situations deem the camera to be… more information on the cameras, when to use it, why it’s used, and I think if the importance of the recording was explained a bit more and what it was doing and how that recording would go and how it would improve things. Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
Furthermore, there was a need for training to be on a rolling basis given the use of bank staff who were not trained to use the cameras or to understand the proper processes or purpose of using the BWCs, which could leave them vulnerable to misuse or abuse.
We have bank staff [who aren’t trained] so they say ‘I don’t know how to use that camera you are giving me’. Nevis (f), Staff, A, Post.
The inner setting
Ward context: acceptance of violence and aggression is part of the job.
It was widely believed by staff that the nature of working on a mental health ward included accepting that violence and aggression was part of the job. This was not seen as an acceptance of violence but more that the job was providing care for individuals who are mentally unwell, and confusion, fear, frustration and aggression can be part of that. As a result, there was an ambivalence among some staff that the introduction of cameras would change this.
I think like in this line of work, there’s always that potential for like risky behaviours to happen. I’m not sure if putting the camera on will make much difference. Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
Staff noted that because of the nature of the job, staff are used to managing these situations and they understood that it was part of the job; therefore, it was unlikely that they would record everything that on paper might be considered an incident.
There’s also enough things that happen here, so I don’t think they would record [the incidents] because it’s just another day here. You know what I’m saying… [staff] can just say, ‘Stop, go back to your room and leave it at that and that kind of be the end of it’. Dylan (m), Patient, A, Post. We are trained for it. Eveline (f), Staff, I, Pre.
This acceptance that incidents are a hazard of mental healthcare was linked to staff’s acknowledgment that many factors make up the complexity of violence and aggression including the nature of individual patients, acuity levels, ward atmosphere, staffing levels, access to activities, leave and outside space. The interplay of multiple factors creates a context in which frustrations and incidents are likely, thus become part of the everyday and ‘normal’ life on the ward for staff and patients alike.
I feel like, you know, how in GP services you say, zero tolerance to abusive language, or any kind of harassment. I don’t think there is that on a psychiatric ward you are kind of expected to take all the abuse and just get on with it. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
With staff reported having a higher threshold for these behaviours it was perceived that this was likely to impact on the efficiency of the intervention as staff would be less likely to consider a situation as violent but more ‘ part of the job’ .
Reactive nature of the ward and incidents
Most participants noted that the ward context is always changing with people being admitted and discharged, with daily staff changes and wider turnover of staff, so things are never static and can change at any point. This reflects the dynamic nature of the ward which creates a complex moving picture that staff need to consider and react to.
[the atmosphere] it’s very good at the moment. If you had asked me this two weeks ago, I would say, ‘Oh, my gosh’. But it changes… The type of patient can make your whole ward change… it depends on the client group we have at the time. Nevis (f), Staff, A, Post.
Staff noted that a key limitation of using the cameras to reduce incidents was the reactive nature of the environment and care being provided. This was felt to impact on the feasibility and use of the cameras as staff noted that they often react to what is happening rather than thinking to ‘ put the camera on first ’. It was felt by staff with experience of reacting to incidents that the failure to use BWCs during these processes were linked to staff’s instincts and training to focus on patients as a priority.
Say for instance, you’re in the office, and two patients start fighting, or a patient attacks someone and, all you’re thinking about is to go there to stop the person. You’re not thinking about putting on any camera. You understand? So sometimes it’s halfway through it, somebody might say, ‘Has anybody switched the camera on’? And that’s the time you start recording… If something happens immediately, you’re not thinking about the camera at that time, you’re just thinking to just go, so yeah. Nevis (f), Staff, A, Post.
Incidents happen quickly and often surprise staff, therefore staff react instantly so are not thinking about new processes such as recording on the cameras as this would slow things down or is not in the reactive nature needed by staff during such incidents.
When you’re in the middle of an incident and your adrenaline’s high, you’re focusing on the incident itself. It’s very difficult for you to now remember, remind yourself to switch on the camera because you’re thinking, patient safety, staff safety, who’s coming to relieve you? What’s going on? Who’s at the door? Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
In addition, the need for an immediate response meant that it was felt that by the time staff remember to, or have the chance to, switch the camera on it was often too late.
Sometimes in the heat of moments and stuff like that, or if the situation’s happening, sometimes you don’t always think to, you know, put your camera on. Patrick (m), Staff, A, Post.
Outer setting
Resources: staffing.
Issues related to staffing were highlighted by several participants as a key problem facing mental health wards thus leading to staff having higher workloads, and higher rates of bank and agency staff being used on shift and feeling burnt-out.
Out of all the wards I’ve been on I’d say this is the worst. It’s primarily because the staff are overworked…it seems like they spend more time doing paperwork than they do interacting with the patients. Harry (m), Patient, A, Pre. We’re in a bit of a crisis at the minute, we’re really, really understaffed. We’re struggling to cover shifts, so the staff are generally quite burnt out. We’ve had a number of people that have just left all at once, so that had an impact… Staff do get frustrated if they’re burnt out from lack of staff and what have you. Alice (f), Staff, A, Pre.
It was noted by one participant that the link of a new intervention with extra workload was likely to have a negative impact on its acceptability due to these increasing demands.
People automatically link the camera to then the additional paperwork that goes alongside it. It’s like, ‘Oh god, if we do this, we’ve got to do that’, and that could play a part. Petra (f), Staff, A, Post.
One staff member noted that the staffing issue meant there were more likely to be bank staff on wards so the care of patients may be affected as temporary staff may be less able to build meaningful therapeutic relationships.
So obviously there is the basic impact on safety of not having adequate staffing, but then there’s the impact of having a lot of bank staff. So obviously when you have permanent staff they get to know the patients more, we’re able to give them the more individualised care that we ideally should be giving them, but we can’t do that with bank staff. Diana (f), Staff, A, Pre.
It was also suggested that staffing levels and mix often made it more difficult to provide activities or facilitate escorted leave which can lead to patients feeling frustrated and becoming more aggressive.
So you know there is enough staff to facilitate the actual shift, so you know when there’s less staff like you say you’ve got people knocking at the door, but then you don’t have staff to take people out on leave straight away, that all has a rippling effect! Serene (f), Staff, A, Pre.
Wider systemic issues
Overall, there was a concern that the introduction of BWCs would not impact on wider, underlying factors that may contribute to frustration, aggression and incidents on wards. Providing a more enhanced level of care and better addressing the needs of patients was felt to be central to helping people but also reducing the frustration that patients feel when on the ward.
… for violence and aggression, [focus on] the mental health side of things like therapy and psychology should be compulsory. It shouldn’t be something you apply for and have to wait three or four weeks for. I think every person should, more than three or four weeks even, months even… we need psychology and therapists. That’s what will stop most violence, because psychologists and a therapist can edit the way that they speak to people because they’ve been given that skill depending on the way the person behaves. So that’s what we need regularly… not like all this dancing therapy, yoga therapy. That’s a person, that you come and you actually sit down and talk through your shit with them. That will help! Elijah (m), Patient, A, Post. There’s a lack of routine and I think there’s a lack of positive interaction between the patient and the staff as well. The only time you interact with a member of staff is if you’re hassling them for something, you have to hassle for every little thing, and it becomes a sort of, frustration inducing and like I’m a very calm person, but I found myself getting very fucking angry, to be honest, on this ward just because out of pure frustration… there’s bigger problems than body worn cameras going on. Harry (m), Patient, A, Pre.
Staff agreed that there was a need to invest in staff and training rather than new technologies or innovations as it is staff and their skills behind the camera.
It’s not the camera that will do all of that. It’s not making the difference. It’s a very good, very beautiful device, probably doing its job in its own way. But it’s more about investing in the staff, giving them that training and making them reflect on every day-to-day shift. Richard (m), Staff, I, Post.
There was felt to be a need to support staff more in delivering care within wards that can be challenging and where patients are unwell to ensure that staff feel safe. While in some circumstances the cameras made some staff feel safer, greater support from management would be more beneficial in making staff feel valued.
In this study exploring the implementation and use of body-worn cameras on mental health wards, we employed two methods for collecting and comparing data on incidents and use of containment measures, including BWCs, on one acute ward and one psychiatric intensive care unit. We found no clear relationship between the use of BWCs and rates or severity of incidents on either ward. While BWCs may be used when there are incidents of both physical and verbal aggression, results indicate that they may also provoke verbal aggression, as was suggested during some interviews within this study. This should be a concern, as strong evidence that being repeatedly subject to verbal aggression and abuse can lead to burnout and withdrawal of care by staff [ 30 ]. These mixed findings reflect results that were reported in two earlier studies of BWCs on mental health wards [ 12 , 13 ]. However, the very low use of the cameras, on just 10 per cent of the shifts where data was obtained, makes it even more difficult to draw any conclusions.
While the data shows limited impact of using BWCs on levels of incidents, we did find that during the pilot period BWC use tended to occur alongside physical restraint, but the direction of relationship is unclear as staff were asked to use BWCs when planning an intervention such as restraint. This relationship with restraint reflected the findings on several wards in a previous study [ 13 ], while contrasting with those reported in a second study that found reductions in incidents involving restraint during the evaluation period [ 12 ]. Such a mix of findings highlights the complexity of using BWCs as a violence reduction method within a busy healthcare setting in which several interacting components and contextual factors, and behaviours by staff and patients can affect outcomes [ 31 ]. The qualitative data collected during this pilot period highlighted the potential systemic and contextual factors such as low staffing that may have a confounding impact on the incident data presented in this simple form.
The findings presented within this evaluation provide some insights into the process of implementing BWCs as a safety intervention in mental health services and highlight some of the challenges and barriers faced. The use of implementation science to evaluate the piloting of BWCs on wards helps to demonstrate how multiple elements including a variety of contextual and systemic factors can have a considerable impact and thus change how a technology may vary not only between hospitals, but even across wards in the same hospital. By understanding the elements that may and do occur during the process of implementing such interventions, we can better understand if and how BWCs might be used in the future.
Within this pilot, extensive preparatory work conducted at a directorate and senior management level did not translate during the process of implementation at a ward level, which appeared to impact on the use of BWCs by individuals on the wards. This highlights that there is a need to utilise implementation science approaches in planning the implementation of new technologies or interventions and to investigate elements related to behavioural change and context rather than just the desired and actual effects of the intervention itself.
While ward staff and patients identified the potential for BWCs to enhance safety on the wards, participants distrusted their deployment and expressed concerns about ethical issues and possible harmful consequences of their use on therapeutic relationships, care provided and patient wellbeing. These themes reflect previous findings from a national interview study of patient and staff perspectives and experiences of BWCs in inpatient mental health wards [ 14 ]. Given these issues, alternatives such as increasing de-escalation skills were identified by staff as possible routes that may be more beneficial in these settings. Furthermore, other approaches such as safety huddles have also been highlighted within the literature as potential means to improve patient safety by looking ahead at what can be attended to or averted [ 32 ].
Furthermore, it is important to consider that the presence of power imbalances and the pre-existing culture on the ward have considerable implications for safety approaches and must be considered, as exemplified by the preferences by both staff and patients in this evaluation for more perceived ‘impartial’ interventions such as CCTV. As identified within previous studies [ 14 ], BWCs can have different implications for psychological safety, particularly for vulnerable patients who already feel criminalised in an environment with asymmetrical power imbalances between staff and patients. This is particularly salient when considering aspects of identity such as race, ethnicity, and gender both in terms of the identities of the patient group but also in terms of the staff/patient relationship.
While preferences in this study note CCTV as more ‘impartial’, work by Desai [ 33 ] draws on the literature about the use of surveillance cameras in other settings (such as public streets) as well as on psychiatric wards and concludes that CCTV monitoring is fraught with difficulties and challenges, and that ‘watching’ patients and staff through the lens of a camera can distort the reality of what is happening within a ward environment. In her recently published book, Desai [ 34 ] develops this theme to explore the impacts of being watched on both patients and staff through her ethnographic research in psychiatric intensive care units. She highlights concerns over the criminalisation of patient behaviour, safeguarding concerns in relation to the way women’s bodies and behaviours are viewed and judged, and the undermining by CCTV of ethical mental health practice by staff who attempt to engage in thoughtful, constructive, therapeutic interactions with patients in face-to-face encounters. Appenzeller et al.’s [ 35 ] review found that whilst the presence of CCTV appeared to increase subjective feelings of safety amongst patients and visitors, there was no objective evidence that video surveillance increases security, and that staff may develop an over-reliance on the technology.
In addition, our findings add to the existing literature which notes that alternative interventions and approaches that address underlying contextual and systemic issues related to improving care on inpatient wards require attention to address the underlying factors related to incidents, e.g., flashpoints [ 36 ]. Evidence suggests that factors leading to incidents can be predicted; therefore, there is a need to enable staff to work in a proactive way to anticipate and prevent incidents rather than view incidents as purely reactive [ 37 , 38 , 39 ]. Such skills-based and relational approaches are likely to impact more on improving safety and reducing incidents by addressing the complex and multi-faceted issue of incidents on inpatient mental health wards [ 40 ].
These findings highlight that interventions such as BWCs are not used within a vacuum, and that hospitals are complex contexts in which there are a range of unique populations, processes, and microsystems that are multi-faceted [ 41 ]. As a result, interventions will encounter both universal, specific, and local barriers that will impact on its functioning in the real world. This is salient because research suggests that camera use inside mental health wards is based on a perception of the violent nature of the mental health patient, a perception that not only influences practice but also impacts how patients experience the ward [ 33 ]. As a result, there needs to be careful consideration of the use of any new and innovative intervention aimed at improving safety within mental health settings that have limited research supporting their efficacy.
Limitations
While the study provides important insights into the efficacy and acceptability of introducing BWCs onto inpatient mental health wards, there were several limitations. Firstly, the analysis of incident data is limited in its nature as it only presents surface level information about incidents without wider contextual information. Results using such data should be cautiously interpreted as they do not account for confounding factors, such as staffing, acuity, ward culture or ward atmosphere, that are likely to contribute to incidents of violence and aggression. For example, while there was a statistically significant decrease in restrictive practice on the PICU across the study period, we know that BWCs were not widely used on that ward, so this is likely due to a confounding variable that was not accounted for in the study design.
Secondly, the study faced limitations in relation to recruitment, particularly with patients. Researchers’ access to wards was challenging due to high staff turnover and high rates of acuity, meaning many patients were not deemed well enough to be able to consent to take part in the study. In addition, the low use of the cameras on wards meant that many patients, and some staff, had not seen the BWCs in use. Similarly, patients had been provided limited information about the pilot, so their ability to engage in the research and describe their own experiences with BWCs was restricted.
Thirdly, analysis captures the active use of the BWC, however it does not fully capture the impact of staff wearing the cameras even where they do not actively use them. While our qualitative analysis provides insight into the limitation of such passive use, it is likely that the presence of the cameras being worn by staff, even when turned off, may have an impact on both staff and patient behaviours. This may explain trends in the data that did not reach significance but warrant further investigation in relation to the presence of BWCs, nonetheless.
Finally, researchers had planned to collect quantitative surveys from staff and patients in relation to their experiences of the ward atmosphere and climate, views related to therapeutic relationships on the ward, levels of burnout among staff, views on care, and attitudes to containment measures. Due to issues related to staff time, patient acuity, and poor engagement from staff leading to challenges accessing the wards, the collection of such survey data was unfeasible, and this element of the study was discontinued. As a result, we have not reported this aspect in our paper. This limitation reflects the busy nature of inpatient mental health wards with pressures on staff and high levels of ill health among patients. As such, traditional methodologies for evaluation are unlikely to elicit data that is comprehensive and meaningful. Alternative approaches may need to be considered.
Future directions
With BWCs being increasingly used across inpatient mental health services [ 14 ], it is important that further research and evaluation is conducted. To date, there is limited data regarding the effectiveness of this technology in relation to violence reduction; however, there may be other beneficial uses in relation to safeguarding and training [ 13 ]. Future research should consider alternative methods that ensure contextual factors are accounted for and that patient voices can be maximised. For example, focus groups with patients currently admitted to a mental health ward or interviews with those who have recently been on a ward that has used the cameras, would bypass problems encountered with capacity to consent in the present study. Furthermore, ethnographic approaches may provide a deeper understanding of the implementation, deployment and impact that BWCs have on wards.
Overall, this research sheds light on the complexities of using BWCs as a tool for ‘maximising safety’ in mental health settings. The findings suggest that BWCs have a limited impact on levels of incidents on wards, something that is likely to be largely influenced by the process of implementation as well as a range of contextual factors, including the staff and patient populations on the wards. As a result, it is likely that while BWCs may see successes in one hospital site this is not guaranteed for another site as such factors will have a considerable impact on efficacy, acceptability, and feasibility. Furthermore, the findings point towards the need for more consideration to be placed on processes of implementation and the complex ethical discussions regarding BWC use from both a patient and a staff perspective.
In conclusion, while there have been advances in digital applications and immersive technologies showing promise of therapeutic benefits for patients and staff more widely, whether BWCs and other surveillance approaches are to be part of that picture remains to be seen and needs to be informed by high-quality, co-produced research that focuses on wider therapeutic aspects of mental healthcare.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Department of Health and Social Care. The NHS Long Term Plan. 2019. https://www.longtermplan.nhs.uk/about/ . [Accessed on 01/11/2021].
NHS England. Violence prevention and safety. 2023. https://www.england.nhs.uk/supporting-our-nhs-people/health-and-wellbeing-programmes/violence-prevention-and-safety/#:~:text=The%20impact%20on%20staff%20is,thinking%20about%20leaving%20the%20organisation . [Accessed on 06/07/23].
Royal College of Nursing. Violence and aggression in the NHS: estimating the size and the impact of the problem. London: Royal College of Nursing; 2018.
Google Scholar
Iozzino L, Ferrari C, Large M, Nielssen O, de Girolamo G. Prevalence and risk factors of violence by psychiatric acute inpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0128536. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128536 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cranage K, Foster K. Mental health nurses’ experience of challenging workplace situations: a qualitative descriptive study. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2020;31(3):665–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.12986 .
Article Google Scholar
Jenkin G, Quigg S, Paap H, Cooney E, Peterson D, Every-Palmer S. Places of safety? Fear and violence in acute mental health facilities: a large qualitative study of staff and service user perspectives. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(5):e0266935. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0266935 .
Gaub JE, Choate DE, Todak N, Katz CM, White MD. Officer perceptions of body-worn cameras before and after deployment: a study of three departments. Police Q. 2016;19(3):275–302.
Cubitt TI, Lesic R, Myers GL, Corry R. Body-worn video: a systematic review of literature. Australian New Z J Criminol. 2017;50(3):379–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004865816638909 .
Lum C, Koper CS, Wilson DB, Stoltz M, Goodier M, Eggins E et al. Body-worn cameras’ effects on police officers and citizen behavior: A systemitic review. Campbell Syst Reviews. 2020;16(3), e1112.
Ariel B, Newton M, McEwan L, Ashbridge GA, Weinborn C, Brants HS. Reducing assaults against Staff using body-worn cameras (BWCs) in Railway stations. Criminal Justice Rev. 2019;44(1):76–93.
Wilson K, Eaton J, Foye U, Ellis M, Thomas E, Simpson A. What evidence supports the use of body worn Cameras in mental health inpatient wards? A systematic review and narrative synthesis of the effects of body worn Cameras in public sector services. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.12954 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ellis T, Shurmer DL, Badham-May S, Ellis-Nee C. The use of body worn video cameras on mental health wards: results and implications from a pilot study. Mental Health Family Med. 2019;15:859–68.
Hardy S, Bennett L, Rosen P, Carroll S, White P, Palmer-Hill S. The feasibility of using body-worn cameras in an inpatient mental health setting. Mental Health Family Med. 2017;13:393–400.
Wilson K, Foye U, Thomas E, Chadwick M, Dodhia S, Allen J, Lynn J, Brennan G, Simpson A. Exploring the use of body-worn cameras in acute mental health wards: a qualitative interview study with mental health patients and staff. Int J Nurs Stud. 2023;140:104456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2023.104456 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Baker J, Pryjmachuk S. Will safe staffing in Mental Health nursing become a reality? J Psychiatry Mental Health Nurs. 2016;23(2):75–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpm.12282 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Piano VL, Creswell JW. Understanding Research: A Consumer Guide. 2nd edition. 2015. Boston: Pearson Education, INC.
Bowers L, Simpson A, Alexander J. Patient-staff conflict: results of a survey on acute psychiatric wards. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2013;38(7):402–8.
Bowers L. The City-128 study of observation and outcomes. BMC Psychiatry. 2007;7(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-7-S1-S122 . S122.
Bowers L, Flood C, Brennan G, Allan T. A replication study of the City nurse intervention: reducing conflict and containment on three acute psychiatric wards. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2008;15:737–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2850.2008.01294.x .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bowers L, James K, Quirk A, Simpson A, Stewart D, Hodsoll J, SUGAR. Reducing conflict and containment rates on acute psychiatric wards: the safewards cluster randomised controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52(9):1412–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2015.05.001 . Erratum in: Int J Nurs Stud. 2016;58:102. PMID: 26166187; PMCID: PMC4518134.
Bowers L, Douzenis A, Galeazzi G et al. Disruptive and dangerous behaviour by patients on acute psychiatric wards in three European centres. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 2005;40, 822–828. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00127-005-0967-1 .
Bowers L, Flood C, Brennan G, LiPang M, Oladapo P. Preliminary outcomes of a trial to reduce conflict and containment on acute psychiatric wards: City nurses. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2006;13:165–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2850.2006.00931.x .
Datix. (2019). Products. Retrieved from https://www.rldatix.com/en-uk/products .
Fazel S, Toynbee M, Ryland H, et al. Modifiable risk factors for inpatient violence in psychiatric hospital: prospective study and prediction model. Psychol Med. 2023;53(2):590–6. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721002063 .
Mushcab H, Bunting D, Yami S, Abandi A, Hunt C. An evaluation of Datix implementation for incident reporting at Johns Hopkins Aramco Healthcare. J Patient Saf Risk Manage. 2020;25(2):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/2516043520905481 .
SPSS. IBM SPSS statistics for Windows. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp; 2023.
Microsoft Corporation. (2018). Microsoft Excel . Retrieved from https://office.microsoft.com/excel .
Ritchie J, Lewis J. Qualitative. Research Practice. London: Sage; 2003.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, et al. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-4-50 .
Porath CL, Pearson CM. Emotional and behavioral responses to workplace incivility and the impact of hierarchical status. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2009;42(Suppl 1):E326–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2012.01020.x .
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, et al. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2008;337. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.a1655 .
Taylor-Watt J, Cruickshank A, Innes J, Brome B, Shah A. Reducing physical violence and developing a safety culture across wards in East London. Br J Mental Health Nurs. 2017. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjmh.2017.6.1.35 .
Desai S. The new stars of CCTV: what is the purpose of monitoring patients in communal areas of psychiatric hospital wards, bedrooms and seclusion rooms? Divers Equality Health Care. 2009;6(1):12. [Google Scholar].
Desai S. Surveillance Practices and Mental Health: the impact of CCTV inside mental health wards. Routledge; 2022.
Appenzeller YE, Appelbaum PS, Trachsel M. Ethical and practical issues in Video Surveillance of Psychiatric Units. Psychiatric Serv. 2020;71(5):480–6. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201900397 .
Bowers L. Safewards: a new model of conflict and containment on psychiatric wards. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2014;21(6):499–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpm.12129 . PMID: 24548312; PMCID: PMC4237187.
Goodman H, Papastavrou Brooks C, Price O, Barley EA. Barriers and facilitators to the effective de-escalation of conflict behaviours in forensic high-secure settings: a qualitative study. Int J Mental Health Syst. 2020;14:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-020-00392-5 .
Johnson ME, Delaney KR. Keeping the unit safe: the anatomy of escalation. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2007;13:42–52.
Johnson ME, Hauser PM. The practice of expert nurses: accompanying the patient to a calmer space. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2001;22:651–68.
Hamrin V, Iennaco J, Olsen D. A review of ecological factors affecting inpatient psychiatric unit violence: implications for relational and unit cultural improvements. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2009;30(4):214 – 26. doi: 10.1080/01612840802701083. PMID: 19363726.
Squires JE, Estabrooks CA, Scott SD, Cummings GG, Hayduk L. The influence of organizational context on the use of research by nurses in Canadian pediatric hospitals. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-351 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank The Burdett Trust for Nursing for funding this work. We would also like to acknowledge our wider Lived Experience Advisory Panel and Project Advisory Panel for their contributions and support and would like to thank the staff and service users on the wards we attended for their warmth and participation.
Funding was provided by The Burdett Trust of Nursing. Funders were independent of the research and did not impact findings.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mental Health Nursing, Health Service and Population Research Department, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience, King’s College London, Denmark Hill, London, SE5 8AF, UK
Una Foye, Keiran Wilson, Jessica Jepps, James Blease, Geoff Brennan & Alan Simpson
Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery & Palliative Care, Mental Health Nursing, King’s College London, London, UK
Una Foye, Keiran Wilson, Jessica Jepps, Geoff Brennan & Alan Simpson
Lived Experience Advisor, London, UK
Ellen Thomas, Leroy McAnuff, Sharon McKenzie, Katherine Barrett & Lilli Underwood
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript. Authors AS, UF, KW, GB created the protocol for the study. KW, JJ, UF conducted the recruitment for the study, and conducted the interviews. UF, JJ, JB, LMA, LU, SMK, KB, ET coded data, and contributed to the analysis. All authors supported drafting and development of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Una Foye .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical. Ethical approval was granted by the Health Research Authority: London - Camden & Kings Cross Research Ethics Committee (IRAS PROJECT ID 322268, REC Reference 23/LO/0337). All participants provided informed consent prior to enrolment in the study, including consent for publication of anonymised quotes.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, supplementary material 6, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Foye, U., Wilson, K., Jepps, J. et al. Exploring the use of body worn cameras in acute mental health wards: a mixed-method evaluation of a pilot intervention. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 681 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11085-x
Download citation
Received : 03 January 2024
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 29 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11085-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Implementation
- Body worn cameras
- Qualitative
- Mental health
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organizations to understand their cultures. | |
| Action research | Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorize common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
What is peer review?
Reviewers play a pivotal role in scholarly publishing. The peer review system exists to validate academic work, helps to improve the quality of published research, and increases networking possibilities within research communities. Despite criticisms, peer review is still the only widely accepted method for research validation and has continued successfully with relatively minor changes for some 350 years.
Elsevier relies on the peer review process to uphold the quality and validity of individual articles and the journals that publish them.
Peer review has been a formal part of scientific communication since the first scientific journals appeared more than 300 years ago. The Philosophical Transactions opens in new tab/window of the Royal Society is thought to be the first journal to formalize the peer review process opens in new tab/window under the editorship of Henry Oldenburg (1618- 1677).
Despite many criticisms about the integrity of peer review, the majority of the research community still believes peer review is the best form of scientific evaluation. This opinion was endorsed by the outcome of a survey Elsevier and Sense About Science conducted in 2009 opens in new tab/window and has since been further confirmed by other publisher and scholarly organization surveys. Furthermore, a 2015 survey by the Publishing Research Consortium opens in new tab/window , saw 82% of researchers agreeing that “without peer review there is no control in scientific communication.”
To learn more about peer review, visit Elsevier’s free e-learning platform Researcher Academy opens in new tab/window and see our resources below.

The peer review process
Types of peer review.
Peer review comes in different flavours. Each model has its own advantages and disadvantages, and often one type of review will be preferred by a subject community. Before submitting or reviewing a paper, you must therefore check which type is employed by the journal so you are aware of the respective rules. In case of questions regarding the peer review model employed by the journal for which you have been invited to review, consult the journal’s homepage or contact the editorial office directly.
Single anonymized review
In this type of review, the names of the reviewers are hidden from the author. This is the traditional method of reviewing and is the most common type by far. Points to consider regarding single anonymized review include:
Reviewer anonymity allows for impartial decisions , as the reviewers will not be influenced by potential criticism from the authors.
Authors may be concerned that reviewers in their field could delay publication, giving the reviewers a chance to publish first.
Reviewers may use their anonymity as justification for being unnecessarily critical or harsh when commenting on the authors’ work.
Double anonymized review
Both the reviewer and the author are anonymous in this model. Some advantages of this model are listed below.
Author anonymity limits reviewer bias, such as on author's gender, country of origin, academic status, or previous publication history.
Articles written by prestigious or renowned authors are considered based on the content of their papers, rather than their reputation.
But bear in mind that despite the above, reviewers can often identify the author through their writing style, subject matter, or self-citation – it is exceedingly difficult to guarantee total author anonymity. More information for authors can be found in our double-anonymized peer review guidelines .
Triple anonymized review
With triple anonymized review, reviewers are anonymous to the author, and the author's identity is unknown to both the reviewers and the editor. Articles are anonymized at the submission stage and are handled in a way to minimize any potential bias towards the authors. However, it should be noted that:
The complexities involved with anonymizing articles/authors to this level are considerable.
As with double anonymized review, there is still a possibility for the editor and/or reviewers to correctly identify the author(s) from their writing style, subject matter, citation patterns, or other methodologies.
Open review
Open peer review is an umbrella term for many different models aiming at greater transparency during and after the peer review process. The most common definition of open review is when both the reviewer and author are known to each other during the peer review process. Other types of open peer review consist of:
Publication of reviewers’ names on the article page
Publication of peer review reports alongside the article, either signed or anonymous
Publication of peer review reports (signed or anonymous) with authors’ and editors’ responses alongside the article
Publication of the paper after pre-checks and opening a discussion forum to the community who can then comment (named or anonymous) on the article
Many believe this is the best way to prevent malicious comments, stop plagiarism, prevent reviewers from following their own agenda, and encourage open, honest reviewing. Others see open review as a less honest process, in which politeness or fear of retribution may cause a reviewer to withhold or tone down criticism. For three years, five Elsevier journals experimented with publication of peer review reports (signed or anonymous) as articles alongside the accepted paper on ScienceDirect ( example opens in new tab/window ).
Read more about the experiment
More transparent peer review
Transparency is the key to trust in peer review and as such there is an increasing call towards more transparency around the peer review process . In an effort to promote transparency in the peer review process, many Elsevier journals therefore publish the name of the handling editor of the published paper on ScienceDirect. Some journals also provide details about the number of reviewers who reviewed the article before acceptance. Furthermore, in order to provide updates and feedback to reviewers, most Elsevier journals inform reviewers about the editor’s decision and their peers’ recommendations.
Article transfer service: sharing reviewer comments
Elsevier authors may be invited to transfer their article submission from one journal to another for free if their initial submission was not successful.
As a referee, your review report (including all comments to the author and editor) will be transferred to the destination journal, along with the manuscript. The main benefit is that reviewers are not asked to review the same manuscript several times for different journals.
Tools and resources
Interesting reads.
Chapter 2 of Academic and Professional Publishing, 2012, by Irene Hames in 2012 opens in new tab/window
"Is Peer Review in Crisis?" Perspectives in Publishing No 2, August 2004, by Adrian Mulligan opens in new tab/window
“The history of the peer-review process” Trends in Biotechnology, 2002, by Ray Spier opens in new tab/window
Reviewers’ Update articles
Peer review using today’s technology
Lifting the lid on publishing peer review reports: an interview with Bahar Mehmani and Flaminio Squazzoni
How face-to-face peer review can benefit authors and journals alike
Innovation in peer review: introducing “volunpeers”
Results masked review: peer review without publication bias
Elsevier Researcher Academy modules
The certified peer reviewer course opens in new tab/window
Transparency in peer review opens in new tab/window
Heroin Research Report What is heroin and how is it used?
Heroin is an illegal, highly addictive drug processed from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seed pod of certain varieties of poppy plants. It is typically sold as a white or brownish powder that is "cut" with sugars, starch, powdered milk, or quinine. Pure heroin is a white powder with a bitter taste that predominantly originates in South America and, to a lesser extent, from Southeast Asia, and dominates U.S. markets east of the Mississippi River. 3 Highly pure heroin can be snorted or smoked and may be more appealing to new users because it eliminates the stigma associated with injection drug use. "Black tar" heroin is sticky like roofing tar or hard like coal and is predominantly produced in Mexico and sold in U.S. areas west of the Mississippi River. 3 The dark color associated with black tar heroin results from crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Impure heroin is usually dissolved, diluted, and injected into veins, muscles, or under the skin.

COMMENTS
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question. If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods. If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data.
Quantitative research methods are used to collect and analyze numerical data. This type of research is useful when the objective is to test a hypothesis, determine cause-and-effect relationships, and measure the prevalence of certain phenomena. Quantitative research methods include surveys, experiments, and secondary data analysis.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question. If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods. If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data.
Definition, Types, and Examples. Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of ...
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
Data analysis methods refer to the methods and techniques that you'll use to make sense of your data. These can be grouped according to whether the research is qualitative (words-based) or quantitative (numbers-based). Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include: Qualitative content analysis; Thematic analysis; Discourse ...
About Research Methods. This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods, "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge.
What are research methods. Research methods are the strategies, processes or techniques utilized in the collection of data or evidence for analysis in order to uncover new information or create better understanding of a topic. There are different types of research methods which use different tools for data collection.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Other interesting articles. If you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. Statistics. Normal distribution. Skewness. Kurtosis. Degrees of freedom. Variance. Null hypothesis.
Choosing an optimal research methodology is crucial for the success of any research project. The methodology you select will determine the type of data you collect, how you collect it, and how you analyse it. Understanding the different types of research methods available along with their strengths and weaknesses, is thus imperative to make an ...
Research design is a plan to answer your research question. A research method is a strategy used to implement that plan. Research design and methods are different but closely related, because good research design ensures that the data you obtain will help you answer your research question more effectively.
Research design: Research design refers to the overall plan and structure of the study, including the type of study (e.g., observational, experimental), the sampling strategy, and the data collection and analysis methods. Sampling strategy: Sampling strategy refers to the method used to select a representative sample of participants or units ...
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
A research methodology encompasses the way in which you intend to carry out your research. This includes how you plan to tackle things like collection methods, statistical analysis, participant observations, and more. You can think of your research methodology as being a formula. One part will be how you plan on putting your research into ...
Types of Research Methods. Research methods refer to the specific approaches and techniques used to collect and analyze data in a research study. There are various types of research methods, and researchers often choose the most appropriate method based on their research question, the nature of the data they want to collect, and the resources ...
Research methods are different from research methodologies because they are the ways in which you will collect the data for your research project. The best method for your project largely depends on your topic, the type of data you will need, and the people or items from which you will be collecting data. The following boxes below contain a ...
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if ...
The methods used in many methodological studies have been borrowed from systematic and scoping reviews. This practice has influenced the direction of the field, with many methodological studies including searches of electronic databases, screening of records, duplicate data extraction and assessments of risk of bias in the included studies.
They use research methods to design a study. Planning the research design is a key step in any sociological study. Sociologists generally choose from widely used methods of social investigation: primary source data collection such as survey, participant observation, ethnography, case study, unobtrusive observations, experiment, and secondary ...
Science is a systematic and logical approach to discovering how things in the universe work. Scientists use the scientific method to make observations, form hypotheses and gather evidence in an ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it. Quantitative Methods. Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires, can produce both quantitative information.
Quantitative research design is defined as a research method used in various disciplines, including social sciences, psychology, economics, and market research. It aims to collect and analyze numerical data to answer research questions and test hypotheses. Quantitative research design offers several advantages, including the ability to ...
Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Apr 19, 2024. Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions. "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock ...
To answer our research questions, we used a mixed-methods design . Using this design allowed us to investigate the impact of implementing BWCs in mental health settings on a range of quantitative and qualitative outcomes. This mixed methods design allows the study to statistically evaluate the effectiveness of using BWCs in these settings on ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Reviewers play a pivotal role in scholarly publishing. The peer review system exists to validate academic work, helps to improve the quality of published research, and increases networking possibilities within research communities. Despite criticisms, peer review is still the only widely accepted method for research validation and has continued ...
Heroin is an illegal, highly addictive drug processed from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seed pod of certain varieties of poppy plants. It is typically sold as a white or brownish powder that is "cut" with sugars, starch, powdered milk, or quinine. Pure heroin is a white powder with a bitter taste that predominantly originates in South America and, to a lesser ...