Business Education

What is Intrapreneurship? Definition, Duties, and Examples
15 May, 2024

Intrapreneurship sparks innovation within an established company, empowering employees to launch new projects that push the business forward. It's about nurturing bold ideas and turning them into reality, using the company's resources to fuel growth.
Definition of Intrapreneurship
Intrapreneurship is the secret weapon of successful companies, where employees with an intrapreneurial mindset work within the existing framework to create innovations that secure the company's future. These employees, known as intrapreneurs, apply entrepreneurial skills to develop new ideas and projects that could turn into profitable ventures for the entire company. They operate like entrepreneurs but without the high personal costs, as they have the support and resources of the established company to bring their visions to life. This approach not only encourages growth but ensures the company remains competitive in a fast-moving business world.
The Evolution and History of Intrapreneurship
The journey of intrapreneurship began as a quiet revolution within the established organizations of the business world. It traces back to when forward-thinking companies recognized the need to encourage intrapreneurship to remain competitive and secure their future. The idea was simple: harness the entrepreneurial spirit within an organization, allowing employees to develop projects and ideas that could lead to major innovations and business growth.
In the past, a new venture within a company required significant investment and risk, often involving venture capital and extensive business plans. However, the concept of intrapreneurship shifted this dynamic, reducing the personal cost to employees and allowing them to act like entrepreneurs while leveraging the resources and support of their existing company. Paul Buchheit, while working at Google, developed Gmail, and Art Fry, in collaboration with 3M, invented the Post-it note — both products of intrapreneurial endeavors within their companies.
From creating small teams tasked with developing innovative solutions to setting up entire departments dedicated to nurturing new ideas, firms began to realize the benefits of fostering an intrapreneurial environment. This not only added value to the companies but also provided a framework within which intrapreneurs work, grow, and succeed.
The Intrapreneur: Role and Characteristics
The role of an intrapreneur within an organization goes beyond a mere job title—it's a mindset and a critical function.
- Innovative Mindset : An intrapreneur is responsible for developing fresh ideas that can enhance the company's innovation and help it remain competitive in the market.
- Entrepreneurial Skills : They possess entrepreneurial skills such as creativity, problem-solving, and strategic thinking, crucial for developing new ventures within a company.
- Initiative and Leadership : Intrapreneurs take charge and excel in roles where they can make a significant impact, often leading projects that contribute to the company's success.
- Resourcefulness : They are adept at locating and utilizing the company’s resources to bring ideas to life, balancing the risks and rewards with the support of the employer.
- Discipline and Commitment : Organization, dependability, and a strong work ethic are essential, as intrapreneurs follow through on their commitments to ensure project success.
By integrating these elements into their work, intrapreneurs play a pivotal role in propelling the company forward, aligning their innovative projects with the organization's strategic goals , and expanding the business's reach without incurring the full costs associated with entrepreneurship.
Intrapreneurship vs. Entrepreneurship: Understanding the Differences
In the dynamic world of business, intrapreneurship and entrepreneurship share common goals like innovation and value creation, but they differ in environment and approach.
- Risk and Investment : Entrepreneurs invest their own money and take significant financial risks to launch and grow their businesses, whereas intrapreneurs innovate within the safety net of an established organization, using company resources and support.
- Autonomy : Entrepreneurs enjoy complete autonomy in decision-making, crafting the business plan and strategy from scratch. In contrast, intrapreneurs must align their initiatives with the company's goals and often work within the parameters set by their employers.
- Resource Access : While entrepreneurs must secure funding, often through venture capital or loans, intrapreneurs have access to the existing company's resources, which can include a skilled workforce, capital, and a customer base.
- Impact on Company's Future : The success of an entrepreneur directly shapes their own future and that of their company. For intrapreneurs, their successful innovations contribute to the growth and competitive edge of the larger organization they work for.
- Job Security : Entrepreneurship comes with the risk of failure and personal financial loss. Intrapreneurs typically do not face the same level of personal financial jeopardy if their innovative projects do not succeed.
Understanding these differences is crucial for recognizing the unique contributions of intrapreneurs in driving forward the innovation and competitiveness of an established company, while also valuing the bold risks and independent spirit of entrepreneurs.
How Intrapreneurship Drives Business Growth and Innovation
Intrapreneurship is a driving force for business growth and innovation, transforming organizations from within.
- Fostering an Entrepreneurial Environment : Companies that cultivate an entrepreneurial environment encourage their employees to think and act like entrepreneurs. This mindset leads to the development of new ideas and projects that can evolve into significant revenue streams for the company.
- Leveraging Employee Skills and Leadership : Employees, especially those with strong leadership qualities and a broad skill set, can act as intrapreneurs. They are often in the best position to identify areas for innovation and growth within the company.
- Creating Value and Competition : Intrapreneurs help companies create value in new and existing markets. By fostering innovation, they ensure that firms remain competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
- Strategic Investment of Time and Resources : Intrapreneurship involves strategically investing the company's resources, such as money, time, and workforce, to turn an innovative idea into a profitable venture.
- Recognizing and Developing Potential : Successful intrapreneurs are recognized for their potential to develop projects that can significantly impact the brand and the organization's future.
- Building on the Company's Foundation : Instead of starting from zero, intrapreneurs build on the existing foundation of their company. They use the established system, brand recognition, and customer base to grow the business.
Intrapreneurship aligns the innovative drive of individual employees with the goals and resources of the company, leading to sustained growth and ensuring that the organization stays ahead in the game of innovation.
6 Steps for Implementing Intrapreneurship in Your Company
Implementing intrapreneurship within a company is a strategic process that unlocks innovation and drives growth.
- Cultivate the Right Environment : Creating an environment where employees feel empowered to act like entrepreneurs is the first step. Encourage the sharing of ideas and provide opportunities for workers to take ownership of projects.
- Identify and Nurture Skills : Look for employees who demonstrate the necessary skills to be successful intrapreneurs. These individuals often show initiative, are willing to take on risks, and have a knack for seeing projects through.
- Encourage Idea Generation : Establish systems that encourage employees to develop and share their ideas. Whether it's through brainstorming sessions or an internal idea submission platform, make it easy for employees to contribute.
- Provide Resources and Support : Once an idea is recognized, provide the intrapreneur with the necessary resources. This could include time away from their regular job, a budget, and access to mentors or advisors within the company.
- Develop a Framework for Execution : Help intrapreneurs by creating a clear process for developing their ideas. This might involve setting up a dedicated department or team and establishing a clear pathway from concept to execution.
- Measure and Adapt : Implement metrics to measure the success of intrapreneurial efforts. Use these insights to adapt strategies and processes, ensuring the ongoing success of the intrapreneurship program.
By following these steps, companies can foster a culture where intrapreneurs thrive, leading to continued innovation and a stronger competitive edge in the market.
Case Studies: Successful Intrapreneurship Examples
Intrapreneurship can lead to remarkable innovations within established companies. Here are just a few examples:
- 3M's Post-it Notes : Spencer Silver, a scientist at 3M, developed a repositionable adhesive, but it was Art Fry, another 3M employee, who saw the commercial application. Fry used the adhesive to anchor his bookmark in his hymnbook. This collaboration and intrapreneurial effort led to the creation of Post-it Notes, a staple office product worldwide.
- Nestlé's Soothe 'N' Chew : At Nestlé, Stéphanie Daru capitalized on her product development experience to create Soothe ‘N’ Chew, a product designed to address infant teething issues. It's an innovation born from Nestlé’s InGenius Intrapreneurs program, showcasing how intrapreneurs can solve real-world problems under a company's umbrella.
- Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works : Kelly Johnson, at Lockheed Martin, founded the Skunk Works project, an advanced development program that operates semi-autonomously within the larger organization. This program has been responsible for some of Lockheed's most innovative aircraft designs, demonstrating the value of allowing intrapreneurs to work independently within a firm.
- Google's Gmail : Developed by Paul Buchheit while at Google, Gmail revolutionized email services with its innovative features. It was a product of Google's policy allowing engineers to spend 20% of their time on side projects, which has resulted in multiple successful ventures for the company.
- Frito-Lay's Flamin' Hot Cheetos : Richard Montañez, who started as a janitor at Frito-Lay, developed Flamin' Hot Cheetos, which became one of the company's most successful products. His intrapreneurial drive and deep understanding of the company's customer base led to a new product line that significantly impacted Frito-Lay's sales and product offerings.
These case studies show that when organizations provide an environment where employees can channel their entrepreneurial spirit, it can result in innovations that redefine brands and drive significant business growth.
Overcoming Challenges: Best Practices for Fostering Intrapreneurship
Fostering intrapreneurship within a company can be challenging, but with the right practices, these hurdles can be overcome to create a thriving entrepreneurial environment.
- Empower Employees : Encourage employees to bring forward their ideas and give them the autonomy to pursue them like an entrepreneur within the organization.
- Provide Resources and Training : Allocate time and resources to help intrapreneurs develop their ideas. Offer training that sharpens their skills in innovation and project management.
- Cultivate a Supportive Culture : Create a company culture that values and supports intrapreneurship. Recognize efforts and celebrate successes to motivate intrapreneurs.
- Foster Collaboration : Encourage collaboration among employees, managers, and different departments. A collaborative effort can bring diverse perspectives and expertise to an intrapreneurial project.
- Address Failure Constructively : When efforts don’t lead to success, use these experiences as learning opportunities. Avoid penalizing failure to maintain a culture where employees are not afraid to take risks.
- Integrate Intrapreneurship into Business Strategy : Make intrapreneurship a part of the business strategy by setting clear objectives and expectations for innovation within the company.
Recognizing and Rewarding Intrapreneurs
Recognizing and rewarding intrapreneurs is crucial for sustaining an innovative culture within a company. Here are some strategies to effectively acknowledge their contributions:
- Acknowledgment Programs : Implement programs that publicly recognize the efforts of intrapreneurs. This can range from company-wide emails to awards ceremonies, highlighting their contributions and successes.
- Performance Incentives : Align incentives with intrapreneurial achievements. Whether it’s bonuses, stock options, or profit-sharing, providing financial rewards can motivate intrapreneurs to continue innovating.
- Career Advancement : Offer clear paths for career progression to intrapreneurs who demonstrate success. This could involve promotions, leadership roles, or opportunities to work on more significant projects.
- Resource Allocation : Reward successful intrapreneurs with increased resources for their next projects, such as larger teams, budgets, or access to advanced technology.
- Professional Development : Invest in the professional growth of intrapreneurs by sponsoring their attendance at conferences, workshops, or further education that can enhance their skills .
- Ownership and Autonomy : Allow intrapreneurs to have a stake in the projects they develop. This can include intellectual property rights or leadership roles in the project as it grows within the business.
By implementing these recognition and reward systems, companies can ensure that intrapreneurs feel valued and are motivated to continue driving innovation like an entrepreneur within the firm.
Why Intrapreneurship Matters More Than Ever
Embracing intrapreneurship is not just a strategy; it's a commitment to continuous innovation and a pledge to empower those who drive it. It's about creating a workspace where the entrepreneurial mindset flourishes, leading to breakthroughs that keep a company at the forefront of its industry. The presence of intrapreneurs within an organization signals a future-oriented mindset, ensuring that a company not only responds to the changes of today but actively shapes the trends of tomorrow.
Sign up for more content like this

Definition of Equity in Accounting: How Does it Work?
2 Jul, 2024
Equity in accounting is a critical measure of a company's financial health. A key component on any balance sheet, it offers insights into a ...

What is a Liability Account? Definition, Types, and Examples
1 Jul, 2024
Liability accounts are crucial in understanding a company's financial health, mapping out obligations like accounts payable, long-term debts...

Asset Accounts: Definition, Types, and Examples
30 Jun, 2024
Asset accounts are the backbone of a company's financial position, holding the key to understanding its resources and economic value.
Book a Call
Submit your information, and we will contact you to schedule a call with our program director..
Our content is reader-supported. Things you buy through links on our site may earn us a commission
Join our newsletter
Never miss out on well-researched articles in your field of interest with our weekly newsletter.
- Project Management
- Starting a business
Get the latest Business News
Intrapreneurial business plans.

Entrepreneurship is as invaluable to large organizations as it is to small ones, perhaps more so. While big companies often can provide the resources start-up businesses lack, they also typically provide all sorts of bureaucracy, slow decision-making and red tape that can stifle entrepreneurial spirits. This can apply to for profits or nonprofits, or for that matter, some departments of government agencies, such as driver’s ed programs, or gift shops at national parks.
The flip side of that is an entrepreneurial person or a group (sometimes called a “skunk works” team) that uses innovative and risk-taking strategies to convert an idea into a profitable finished product in a large organization. Those people are sometimes described as “intrapreneurs” as in entrepreneurs “inside” a big company. They pursue the goals of the organization, working hard to break through the innovation gridlock that prevents many large companies from taking best advantage of their resources.

Certainly the most well-known person who took that approach was Steve Jobs, yet many employees with much less authority have used these strategies successfully. In other words, you don’t need to be the boss or senior manager to be an intrepreneur: you just need to be innovative and smart (so you don’t get fired!) to get the job done.
And you often need a business plan, whether it be formal or informal, long or short. As always, a business plan lays out how you’re going to get from where you are now to where you want to be, based on solid research and analysis of things like markets, competitors, pricing, marketing, and credible financial projections, along with an innovation strategy — how to work inside (and sometimes outside) the organizational culture to reach the desired result.
Here’s a structure for an intrapeurial business plan, from Gifford Pinchot, a leader in this area. This structure pretty similar to any other business plan. Good business planning is good business planning, regardless of the sector or size of organization.
http://company.pinchot.com/PDFs/BusPlan-1.pdf
What do you think?
- Copyright © 2013 Rolfe Larson Associates
- Social Impact App , find social enterprises nearby and online
- Venture Forth! endorsed by Paul Newman of Newman’s Own

Rolfe Larson

Resources for Starting a Business
Legal Structures of Organizations Legal Forms and Traditional Structures of Organizations Market Research — Inbound Marketing Planning Your Research Market Research Find and Feed the Feeling Strategizing Understanding Strategy and Strategic Thinking Competitor Analysis Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part I) Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part 2) Competitive Intelligence Product Planning Product Management E-Commerce Sales and …

Ultimate Business Planning Guide with Updated Resources
Complete Business Planning Guide with Extensive Resources Copyright Carter McNamara, MBA, PhD. NOTE: Your business plan should be highly customized to your current organizational situation. Thus, using a generic business plan template could completely misrepresent the needed focus of your business plan. (This step-by-step manual is a complement to the topic How to Start Your …

Learn Strategic Thinking from Napoleon
Biographers of Napoleon Bonaparte talk about his ability to size up a situation with a single coup d’oeil,(pronounced koo-DOY), meaning “a stroke of the eye” or “glance.” Napoleon was so knowledgeable about his strategic situation—the landscape, the enemy, available technology, similar situations from the past—that he could understand and respond quickly to ever- changing circumstances. …

Strategic Planning Facilitator: Guiding the Planning Process
Strategic Planning: The Crucial Role of a Facilitator The goal of strategic planning should be to produce a Plan that is 1) relevant, realistic, and flexible; 2) with a very high likelihood of being implemented; 3) in order to achieve the purpose of the planning, e.g., a purpose to evolve to the next stage of …

Mistakes Made by Strategic Planning Facilitators
Here’s a list of the biggest mistakes that I have seen made by strategic planning facilitators over the years: 1. Not getting sufficiently trained on how to do facilitating, e.g., planning the meeting, goals, ground rules, which techniques to cultivate complete participation, doing interventions, managing conflict 2. Not learning a variety of strategic planning models, …

Strategic Thinking in the Age of LinkedIn
LinkedIn founder and triple billionaire Reid Hoffman has two endearing mannerisms that reveal the way he sees–and reasons with–the strategic environment. First, he peppers his statements with the word so. Almost a verbal tic that would grate on a speaking coach like the overuse of the dreaded uh … but he uses it more like …
Avoid the Silicon Valley Syndrome!
Guest blog from my colleague, Adam Brock, Director of Social Enterprise at Joining Vision and Action (formerly JVA Consulting): How can a well-meaning startup avoid “Silicon Valley Syndrome” and actually use a social startup to create real value for society? Every era has an industry that epitomizes its values. At the turn of the 20th …

Develop Your Strategic Intuition
The best decision-makers in chaotic “fog of war” conditions seem able to call on intuition – knowing what to do without knowing why or how they know.

Free Online Program to Learn Strategic Planning Facilitation

Moneyball: The Role of the Chief Strategy Officer
Paul DePodesta – role of the Chief Strategy Officer for the Cleveland BrownsPaul DePodesta was recently named the Chief Strategy Officer by the Cleveland Browns of the National Football League. This is significant because, as any fan of Moneyball knows, Mr. DePodesta has spent his career in the sport of baseball, not football. This matters …

50 Tips and Tools for Effective Strategic Thinking Skills
To engage in strategic thought, you must think and reflect on the big picture—on the diverse players and forces in your competitive environment. Anticipate the future. Use your right brain for intuition and wisdom, and your left for planning. As Isaac Newton said, “Truth is the offspring of silence and meditation.” Here are 50 tips …

To Learn Strategy, Know History
When you are faced with the most important and strategic decision of your life, where can you go for wisdom? Can you find insight in a book of history? Facing a world in crisis, John F. Kennedy did just that. Generally, we learn skills by trying something, failing, and trying again until we get it …

Execution Trumps Strategy
The results are in – Execution trumps strategy. Your business plan may have great strategies, but it will be a great failure if executed poorly. So just hire the right people, right? Turns out the answer is not what you think. At least according to a recent Harvard Business Review Article. Five Myths About Effective …

Is Balance Possible?
Now here’s a frank perspective: Balance doesn’t work. So don’t even try. Accept the fact that the only way to really make something happen is to go “full out” at it, with everything you have.

B Corp As A Competitive Edge?
Last week, I attended a celebration for B corps in Colorado. These are for-profit companies certified by a nonprofit called B Lab for achieving social and environmental goals along with business ones. What I noticed differently from other discussions among B Corps in the past, was a stronger focus not only on this vibrant community …
Privacy Overview
- Best Countries for a Business
- How to Do Market Research
- Define Your Target Market
- How to Write a Business Plan
- Key Elements of a Business Plan
- How to Buy a Business
- What is a Pitch Deck?
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Best Business Opportunities
- Best Small Business Ideas
- Lucrative Online Business Ideas
- Side Ideas for Women
- Small Scale Business Ideas
- Best Tech Startup Ideas
- App Ideas for Start-Ups
- Small Business Ideas in India
- Business Tycoons to Learn From
- Most Innovative Entrepreneurs
- Successful Women Entrepreneurs
- Best Business Books of All Time
- Startup Pitch Deck Examples
- Successful Social Entrepreneurs
- Top Entrepreneurs of India
- Best Online Legal Services
- Small Business Software
- Apps for Daily Operations
- Business Name Generators
- Mission Statement Generators
- Privacy Policy Generators
- Start a Profitable Online Store
- Start a Dropshipping Business
- Start a Consulting Business
- Start a Podcast: 10-Step Tutorial
- Create a Successful Online Course
- How to Sell on Etsy
12 Examples of Successful Intrapreneurs
Imagine a world where the status quo is never challenged, and innovation is left to chance. Luckily, we don't live in that world today, thanks to a group of individuals known as intrapreneurs.
These bold thinkers disrupt the norm, challenge the system, and bring new and great ideas to life within their organizations.

In this article, we'll shine a light on 12 remarkable intrapreneurship examples and the innovations they brought to the world.
What is Intrapreneurship?
You've heard widely about entrepreneurship. But what is intrapreneurship that we're talking about? It's like entrepreneurship, but instead of starting your own business, you innovate and drive change from within an existing organization.
But what exactly is the difference between an intrapreneur and an entrepreneur ? Intrapreneurs and entrepreneurs are all rebels, disruptors, and dreamers who refuse to settle for the status quo. They are the ones who think outside the box and are not afraid to take risks.
The main difference lies in whether they become an employee or an employer. But who exactly prefers a job or business ? Intrapreneurs go for a job, while entrepreneurs settle for their own businesses.

Intrapreneurship is about embracing a culture of innovation and empowering employees to bring new ideas to the table. It's about creating a workplace where creativity and entrepreneurship can thrive.
Let's now explore our examples of intrapreneurship in the workplace of individuals who improved our world.
Examples of Successful Intrapreneurs
Spencer silver’s & art fry's post-it-note.

The Innovator
In the late 1960s, Spencer Silver worked as a scientist at 3M, trying to develop a strong adhesive for aircraft construction. However, he stumbled upon a low-tack, reusable adhesive that stuck to surfaces but could be easily removed without leaving a residue.
The Innovation
Despite his colleagues' skepticism, Spencer recognized his discovery's potential and began experimenting with different applications. He even tried to market it as a super-strong bookmark but didn't have much success. It wasn't until several years later, when Spencer's colleague, Art Fry, had an idea for a new type of bookmark, that he realized the true potential of the adhesive.
The result was the Post-it Note, which has become one of the most ubiquitous office supplies in the world. This intrapreneurial example of Post-it Notes highlights the value of being open to experimentation and iteration. It also emphasizes the potential benefits of collaboration between individuals with different skill sets and perspectives.
Ken Kutaragi's Sony Playstation

In the early 1990s, Ken Kutaragi, an engineer at Sony Computer Entertainment, worked on developing sound chips for the company's electronic products. He devised a game-changing idea: a dedicated video game console that could rival the Nintendo game console and Sega.
Ken Kutaragi proposed creating a gaming console that could play high-quality 3D games. At the time, video games were primarily played on computers or low-quality consoles with limited graphics. Sony executives resisted his idea, but he persisted and eventually convinced them to fund the project.
The Sony PlayStation was launched in 1994 and became an instant success. It revolutionized the gaming industry by introducing 3D graphics and immersive gameplay, setting a new standard for consoles, and exhibiting true corporate innovation. It also helped Sony become a major player in the electronics industry, paving the way for future innovations like the PlayStation 2, 3, and 4.
Kutaragi's success with the Playstation demonstrated that an intrapreneur requires creativity, innovation, and the ability to identify and seize opportunities outside the company's traditional areas of expertise.
Paul Buchheit’s Gmail

Paul Buchheit was an engineer at Google who had previously worked at Intel and Compaq. In 2001, he was assigned to work on a new email service, which was initially intended to be a competitor to Hotmail.
Buchheit came up with the idea of providing users with massive storage, which was unheard of then. He also introduced the concept of threading emails, which made it easier for users to keep track of conversations. In addition, he implemented a powerful search function that allowed users to easily find specific emails.
Gmail was released to the public in 2004 and quickly became one of the successful launches of Google. Gmail's innovative features and user-friendly interface made it a popular choice among email users, and it helped cement Google's reputation as a company focused on user experience. Gmail’s success underscores the importance of being willing to take calculated risks and invest in promising project ideas, even if there is no immediate profit.
Richard Montañez’s Flamin' Hot Cheetos

In the 1980s, Richard Montañez was a janitor at Frito-Lay, a subsidiary of PepsiCo, in Rancho Cucamonga, California. His humble background did not deter him from showing his entrepreneurial mindset . He noticed that the company had no spicy snack options for the Latino market, a significant segment of the population in Southern California. He pitched his idea to the CEO.
Montañez's idea for Flamin' Hot Cheetos significantly departed from the company's usual products. He added a homemade spice mix as a flavoring to the Cheetos and did its community promotions as a snack that would appeal to Latino consumers. He also developed a unique packaging design featuring flames, which helped the product stand out on store shelves.
Flamin' Hot Cheetos quickly became Frito-Lay's best seller in multicultural sales, and Montañez was eventually promoted to a position in the company's executive team. The success of Flamin' Hot highlights the importance of taking risks and being persistent in pursuing your innovative ideas. Montañez's idea was unconventional and went against the company's usual processes, but his consistent efforts turned Flamin' Hot Cheetos into a cultural phenomenon.
Bob Bernstein's McDonald's Happy Meal

Bob Bernstein was a marketing executive at McDonald's in the 1970s, where he was tasked with finding a way to make the fast-food chain more appealing to families with children. At the time, McDonald's was primarily a destination for adults, but it lacked a menu item that catered specifically to children.
Bob came up with the ingenious idea of the Happy Meal, a small meal for kids that would include a burger or chicken nuggets, fries, and a toy. The toy was the game-changer. It transformed the Happy Meal from just another meal option to a fun, interactive experience that kids looked forward to. The toys often tie in with popular movies or TV shows, creating a sense of excitement and anticipation for children.
Introduced in 1979, the Happy Meal quickly became a massive success. It is a perfect example of how intrapreneurship can drive business success by identifying customer needs, taking risks, and constantly innovating to stay ahead of the competition.
Kelly Johnson's Skunk Works

Kelly Johnson was an aeronautical engineer who worked at Lockheed Martin during the Cold War. In 1943, Johnson established a small, secret research and development team called “Skunk Works” that was tasked with creating advanced aircraft designs ahead of their time.
Under Johnson's leadership, the Skunk Works team created some of the most advanced and groundbreaking aircraft of the 20th century, including the U-2 spy plane and the SR-71 Blackbird. These planes were designed to fly higher and faster than any other planes then, and they revolutionized the fields of intelligence gathering and surveillance.
The Skunk Works approach demonstrates the importance of empowering and trusting talented employees to work independently without fear of failure or micromanagement. This allows for more agile decision-making and encourages innovative thinking and risk-taking. Today, “Skunk Works” has become synonymous with innovative and secret projects in various industries.
Mark Zuckerberg's Like Button

Mark Zuckerberg, the co-founder and CEO of Facebook, and his team introduced the “Awesome Button” on Facebook in 2009. The Awesome Button, now known as the “Like” button, was designed to increase user engagement on the platform and make it more user-friendly by allowing users to appreciate a post or comment without leaving a written response.
The Awesome Button was groundbreaking because it innovated the traditional way of interacting on social media platforms. Before its introduction, users were limited to commenting or reading posts. The Like button gave users a quick and easy way to show their support or approval for a post without leaving a comment.
Zuckerberg's vision for the Like button was to enhance the platform's user experience, collect data, and increase engagement. Furthermore, this shows us that intrapreneurs must understand and identify gaps in the consumer market and address them through innovative solutions, ultimately leading to the company's success. Different platforms also copied the concept, but all the credit goes to Facebook.
Davide Costello's Fast & Green

Fast & Green is a project led by Davide Costello at Nestle. Davide noticed that many customers needed more Nespresso pods before they could restock, leaving them without coffee at home. He had an idea to deliver pods to customers quickly while also considering the environmental impact.
To make the service more sustainable, Davide proposed making deliveries via bicycle. With the help of Nestlé's resources and infrastructure, Davide's idea was brought to life within just eight weeks. Fast & Green offers customers a faster and more eco-friendly delivery option today.
David's idea was not only innovative but also had a focus on sustainability. This shows that intrapreneurial thinking can lead to solutions that not only benefit the company but also have a positive impact on society and the environment. The success of Fast & Green also demonstrates that intrapreneurship can bring a competitive advantage to a company by staying ahead of the curve with innovative projects and encouraging personal creative projects of employees.
Stéphanie Daru’s Soothe ‘N' Chew

Stéphanie Daru is one of the most recent intrapreneurs who impacted the world. She worked as a product development expert at Nestle. When her seven-month-old daughter began teething and biting on everything around the house, she had a brilliant idea. She realized that creating an all-natural and edible teething treat would be an excellent solution for babies to chew on and alleviate pain during the teething process.
Stéphanie submitted her concept, and within no time, it was produced as “Soothe ‘N' Chew.” The soft banana-flavored treat is a natural product that soothes babies' gums and satisfies the urge to chew without causing harm or pain. Despite the pandemic, Soothe ‘N' Chew was a great addition to Nestle's product line.
One key takeaway from Stephanie Daru's story is the importance of identifying a problem or need and creating a solution that fills that gap in the consumer market. Stephanie noticed a problem in her own life as a parent. She used her knowledge and experience to create a new product that not only helped her own family but also had the potential to benefit others.
Steve Jobs’ Macintosh

Steve Jobs is synonymous with innovation, and the Apple Macintosh exemplifies his intrapreneurial spirit within his company. Jobs co-founded Apple in 1976 and was ousted from the company in 1985. However, he returned to the organization in 1996 and started work on a new computer, the Macintosh.
The Macintosh was a game-changer for the personal computer industry. It featured a graphical user interface, a mouse, and a range of software programs, making it easier to use and understand than other computers on the market.
An important takeaway is the value of investing in research and development to stay ahead of the competition. The Macintosh was a game-changing product in the personal computer industry, and Apple's investment in research and development helped them to achieve this breakthrough. This investment allowed the company to develop new technologies, set market trends, and innovate in ways competitors could not match.
Jeff Bezos’ Amazon Prime

Jeff Bezos is one of the most innovative entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs. After Jeff Bezos founded Amazon in 1994 as an online bookstore, he kept expanding it into different horizons. Amazon VP Greg Greeley and Bezos saw an opportunity to create a loyalty program that would retain existing customers and attract new ones.
With the launch of Amazon Prime in 2005, Bezos altered the traditional retail model by offering customers the convenience of fast, free shipping and access to exclusive content. In addition, the streaming of movies, TV shows, and music has also become a major draw for customers. This also helped Amazon become a major player in the entertainment industry.
The success of Amazon Prime highlights the importance of customer loyalty and the value of offering added benefits to retain and attract customers. Amazon has increased customer loyalty and set a new standard for e-commerce and entertainment by focusing on customer needs and investing in research and development.
Larry Hornbeck’s Digital Micromirror Device

Larry Hornbeck, a researcher at Texas Instruments, was tinkering with technology using tiny mirrors to redirect photons for almost a decade. In 1987, the tinkering paid, and Hornbeck and his team developed the Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). These micromirrors were initially used for printing airline tickets.
Hornbeck realized that the technology could significantly decrease the size and cost of a digital projector which was very costly. Soon after, TI launched an internal venture called the Digital Imaging Venture Project to expand on the efforts, paving the way for video projectors. The DMD became an industry standard, and Hornbeck received an Emmy Award for outstanding achievement in engineering development.
This story is a great example of a successful intrapreneurship showing that intrapreneurs can leverage their knowledge and expertise to develop disruptive technologies and improve existing products through creative ideas. In this case, Hornbeck's experimentation with mirrors using company resources led to a digital projector technology breakthrough, revolutionizing the industry.
Conclusion: What You Can Learn From These Intrapreneur Examples
Intrapreneurship is all about harnessing the entrepreneurial spirit within an established organization. The examples of intrapreneurs we have explored demonstrate that innovation and creativity can come from anyone, regardless of their position or title within a company.
It's all about having the right mindset, being willing to take risks, and having the courage to pursue new ideas. Companies that embrace intrapreneurship can tap into the collective talent of their workforce and create a dynamic environment where innovation and growth are encouraged.
Intrapreneurs show us there are no limits to what can be achieved when creativity is given free rein. These examples are a testament to the power of innovative thinking, and they inspire anyone looking to steer change and make a positive impact within their organization. So, let's celebrate the intrapreneurs of the world and continue to support their endeavors!
Explore Further
- 10 Most Successful Social Entrepreneurs
- Are Successful Entrepreneurs Born Or Made?
- 13 Different Types of Entrepreneurs
- 12 Most Successful Women Entrepreneurs
- 4 Key Elements of Entrepreneurship
- Essential Characteristics and Skills of Successful Entrepreneurs
Was This Article Helpful?
Anastasia belyh.
Anastasia has been a professional blogger and researcher since 2014. She loves to perform in-depth software reviews to help software buyers make informed decisions when choosing project management software, CRM tools, website builders, and everything around growing a startup business.
Anastasia worked in management consulting and tech startups, so she has lots of experience in helping professionals choosing the right business software.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Why You Should Become an “Intrapreneur”
- Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic

You’ll be more engaged, and more productive.
Most organizations — especially large corporations — are awash in creative ideas that never get executed. Entrepreneurship is the process that turns those ideas into actual innovations, and when it occurs in large corporations we tend to refer to it as intra preneurship or corporate innovation. In essence, this means acting like an innovative entrepreneur, but within the ecosystem of a larger, more traditional, organization. Research shows that being intrapreneurial tends to elevate both employee engagement and productivity scores, and that short redesigns — and even a simple reframing — of your role can make your work more intrapreneurial and meaningful.
Do you try to learn new things at work?
- Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic is the Chief Innovation Officer at ManpowerGroup, a professor of business psychology at University College London and at Columbia University, co-founder of deepersignals.com , and an associate at Harvard’s Entrepreneurial Finance Lab. He is the author of Why Do So Many Incompetent Men Become Leaders? (and How to Fix It ) , upon which his TEDx talk was based. His latest book is I, Human: AI, Automation, and the Quest to Reclaim What Makes Us Unique. Find him at www.drtomas.com . drtcp
Partner Center
Importance of Business Plan to an Entrepreneur – A business plan is an essential road map that entrepreneurs use to navigate the difficult process of starting and expanding a profitable firm. It performs as a strategic instrument for outlining the goals. Also, serve as a financial prediction of a company.
Whether you’re just starting or an experienced entrepreneur looking to sharpen your strategies, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and instructions you need to harness the power of a well-structured business plan.
Importance of a Business Plan to an Entrepreneurs
A strong business plan’s importance cannot be overstated since it provides entrepreneurs with a comprehensive framework for making decisions, attracting investors , securing funding, and navigating the dynamic business world. This article will cover the significance of a business plan. Also, offer practical guidance on how entrepreneurs can utilize it to advance their ventures. Let’s discuss what are the importance of a business plan to an entrepreneur.
A Business Plan Provides a Roadmap for a Business
A business plan may be compared to a road map that directs businesses toward commercial success. It acts as a strategy document that explains the objectives, strategies, and activities necessary to establish and expand a successful company. A business plan offers entrepreneurs a clear path to follow to accomplish their business goals. It is just like a roadmap that aids travelers in navigating new roads and arriving at their destination.
Picture you are going on a road trip to a dream destination. Before setting off, you would carefully plan your route, mark critical milestones, estimate travel time, and consider alternative paths in case of detours. Similarly, a business plan helps entrepreneurs chart their course by defining their vision, identifying target markets, assessing competition, setting financial goals, and mapping out strategies to overcome challenges.
Read – Can Anyone Be an Entrepreneur
Helps Entrepreneurs to Define Their Objectives
A business plan is a valuable tool that helps entrepreneurs in defining their objectives clearly. It offers business owners a well-organized framework for expressing their vision and establishing clear objectives. Entrepreneurs that go through the process of writing a business plan find clarity and concentration in their goals.
Imagine that an entrepreneur wishes to launch a sustainable clothing line. They would specify their goals through the business planning process, such as advancing ethical fashion, minimizing environmental effects, and making a good social impact. The business plan would outline these objectives and establish strategies and action steps to align the business activities with these goals.
Defined objectives in a business plan help entrepreneurs think critically, establish purpose, and guide decision-making. By setting SMART objectives, entrepreneurs can track performance, evaluate strategies, and make necessary adjustments to achieve desired outcomes. For example, an e-commerce business can increase online sales by 50% within a year, allowing regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustments to achieve its target.
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Identifying Their Target Market
When determining the target market for their goods or services, businesses place a lot of weight on their business plans. A business plan aids entrepreneurs in comprehending their potential clients, their demands, and their preferences by doing in-depth market research and analysis. This knowledge is essential for creating efficient marketing plans and modifying the company’s product offerings to satisfy the needs of the target market.
Let’s use the example of an entrepreneur who wants to launch a line of fitness clothes to demonstrate the significance of this. They would do market research as part of the process of writing a business plan to pinpoint their target consumers, such as fitness fanatics, gym visitors, or athletes. The business plan would include insightful information on the target market’s demographics, hobbies, and purchase patterns. With this knowledge, the business owner may carefully coordinate their product offering, price, and marketing messaging to appeal to the determined target demographic.
Entrepreneurs may focus on the appropriate audience, avoid one-size-fits-all techniques, and customize their products, services, and marketing strategies to their consumers’ needs by determining their target market. This aids in comprehending the competitive landscape, spotting gaps, and creating distinctive value propositions that appeal to the target market.
Read – Qualities of a Good Businessman
Helps Entrepreneurs to Assesses Competition
A business plan is a valuable tool that helps entrepreneurs assess their competition and gain a deeper understanding of the market landscape in which they operate. By following a structured approach, a business plan guides entrepreneurs on how to effectively analyze and evaluate their competitors.
A business plan helps entrepreneurs identify their key competitors by conducting research and gathering information about their products or services, pricing strategies, target market, marketing tactics, distribution channels, and customer reviews. This helps entrepreneurs understand their unique selling points and position themselves in the market. Entrepreneurs can compare their strengths and weaknesses to those of their competitors, identifying areas for differentiation. They also analyze market demand and customer preferences to identify gaps or underserved segments, tailoring their products or services to cater to these needs. A business plan guides entrepreneurs in positioning themselves against their competition, developing a unique value proposition that resonates with the target market. This roadmap helps entrepreneurs stay agile and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Importance to Evaluate Feasibility
When assessing the viability of their business idea, entrepreneurs must give the highest priority to their business plans. It acts as a helpful road map for business owners as they determine whether their idea is workable and has the potential to succeed.
Entrepreneurs should undertake in-depth market research and analysis, create financial predictions, perform a SWOT analysis, examine operational factors, and seek professional guidance to determine whether a company strategy is feasible. These steps help determine the feasibility of the business idea, identify potential blind spots, and develop contingency plans. By addressing factors such as resource availability, skills, expertise, infrastructure requirements, and operational processes, entrepreneurs can develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate risks and ensure the venture’s success.
Read – Benefits of Being an Entrepreneur
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Attract Investors
A business plan holds immense importance for entrepreneurs when it comes to attracting investors to support their venture. A well-crafted business plan serves as a persuasive tool that demonstrates the potential of the business and convinces investors to provide financial backing.
To attract investors, entrepreneurs should create a compelling executive summary, detailed business description, market analysis, competitive advantage, financial projections, marketing and sales strategy, management team, risk assessment and mitigation, and clear exit strategy. These elements help investors understand the business’s growth potential, market potential, and competitive advantage.
Helps Entrepreneurs to Secures Their Funding
A business plan is essential for assisting entrepreneurs in obtaining finance for their projects. It acts as a roadmap that details the company’s potential, financial estimates, and growth plans. Entrepreneurs should write a succinct executive summary, thorough business description, market and competitive analysis, financial projections, funding requirements, marketing and sales strategy, management team, risk assessment, and mitigation, and supporting documents to obtain funding through a business plan.
These elements help investors and lenders understand the business’s unique value proposition, target market, revenue potential, and funding requirements. By presenting realistic financial projections, well-supported financial projections, and a well-thought-out marketing and sales strategy, entrepreneurs can secure funding and attract investors and lenders.
Read – Common Myths about Entrepreneurs
Business Plan Guides Entrepreneurs to Resource Allocation
A business plan serves as a valuable tool that guides entrepreneurs in allocating their resources effectively. It provides a clear roadmap for resource allocation by outlining the key areas of the business that require attention and investment.
To effectively allocate resources in a business plan, entrepreneurs should identify resource needs, set priorities, allocate financial resources based on projections and budget, allocate human resources based on skills and expertise, optimize time management, monitor and adjust resource allocation, seek efficiency and optimization, and regularly review and update the plan to reflect changes in resource needs. By doing so, entrepreneurs can optimize their resources and maximize the value derived from available resources. Regularly reviewing and updating the business plan ensures that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.

Importance to Facilitate Decision-Making
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs in facilitating effective decision-making throughout their entrepreneurial journey. It provides a framework that helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions by considering various factors and evaluating potential outcomes.
To effectively use a business plan for decision-making, entrepreneurs should define goals and objectives, gather relevant information, evaluate alternatives, consider financial implications, analyze risks and mitigation strategies, seek input from experts, regularly review and update the plan, and trust intuition and vision. This balances analytical thinking with an entrepreneurial instinct, ensuring long-term sustainability and informed decisions.
Read – Entrepreneur Mindset Books
Identifies Risks and Mitigation Strategies
A business plan plays a vital role in helping entrepreneurs identify risks and develop effective mitigation strategies. By carefully considering potential challenges and uncertainties, entrepreneurs can proactively address them and minimize their impact on the business.
To identify risks and develop mitigation strategies in a business plan, conduct a comprehensive risk assessment, analyze the impact and likelihood of risks, and develop specific strategies. Allocate resources, including financial, personnel, and time, to support the implementation of these strategies. Regularly monitor and update the business plan, seeking external expertise or consulting with industry professionals to gain insights. Communicate the identified risks and mitigation strategies clearly to stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and partners, to demonstrate professionalism and confidence in the business.
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Assists in Team Building
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs in assisting them with team building, as it provides a clear framework for recruiting, developing, and managing their team effectively.
Entrepreneurs can use a business plan to aid in team building by defining roles and responsibilities, establishing recruitment criteria, developing a training and development plan, fostering a collaborative culture, setting performance goals and metrics, regularly evaluating and providing feedback, and fostering leadership and empowerment. These steps help attract and select the right individuals, align with the business plan’s objectives, and promote a supportive environment for innovation and creativity.
Read – Entrepreneurship Books for Students
Business Plan Supports Marketing and Sales Efforts
A business plan holds significant importance in supporting marketing and sales efforts for entrepreneurs. It provides a strategic roadmap for effectively promoting products or services and attracting customers. A business plan helps understand the target market, define the unique selling proposition (USP), develop marketing strategies, allocate budgets, monitor and measure results, and adapt and evolve.
By conducting thorough market research, defining the USP, and focusing on channels and tactics, entrepreneurs can effectively reach and engage their target audience. Regularly updating the business plan to reflect market trends and competitors can help entrepreneurs stay competitive and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Guides Product or Service Development
A business plan is essential for directing entrepreneurs as they create their goods or services. It offers a methodical way to determine consumer demands, specify product characteristics, and create a schedule for product development.
A business plan can guide product or service development by identifying customer needs, defining product or service features, setting development milestones, determining resource requirements, conducting testing and iteration, and integrating marketing and launch strategies. This helps entrepreneurs stay focused, track progress, and ensure the timely completion of activities. The plan should also outline the necessary funding, collaborations, and resources needed for the development process. By incorporating continuous improvement and iterative development, entrepreneurs can create a high-quality offering that meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Read – Green Innovation
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Manage Finances Effectively
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs when it comes to managing finances effectively. It offers a thorough foundation for comprehending the financial facets of the firm and aids business owners in making defensible choices to maximize financial resources.
Entrepreneurs should construct a financial overview, define financial goals and objectives, develop a budget, track financial performance, plan for managing cash flow, and seek expert financial assistance to manage their money efficiently. This helps entrepreneurs forecast future financial needs, allocate resources effectively, and identify potential issues early on. By implementing these strategies, entrepreneurs can ensure the sustainability of their businesses and make informed decisions about their financial future.
Business Plan Measures Progress and Success
A business plan holds significant importance for entrepreneurs in measuring their progress and success. They may compare their accomplishments to it as a standard to see if they are progressing in the correct path.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are in line with the goals of the business’s plan to successfully measure the growth and success of entrepreneurs. Regularly track and monitor KPIs to assess progress and make informed decisions. Conduct periodic reviews to evaluate progress against the plan, identify areas for adjustments or course corrections, and celebrate milestones and successes. Continuously update and evolve the business plan to reflect evolving goals, strategies, and market conditions.
Read – Difference Between Entrepreneur and Intrapreneur
Business Plan Importance to Enhance Credibility
A business plan plays a crucial role in enhancing the credibility of entrepreneurs and their ventures. It demonstrates to stakeholders, including potential investors, lenders, partners, and even customers, that entrepreneurs have a well-thought-out and strategic approach to their business.
To enhance entrepreneurs’ credibility, a well-presented business plan should present a professional image, conduct thorough market research, highlight the unique selling proposition, provide detailed financial projections, incorporate risk analysis and mitigation strategies, seek third-party validation, and regularly update and refine the plan. This shows credibility and commitment to continuous improvement, demonstrating the business’s ability to adapt and thrive in the ever-changing landscape.
Business Plan Provides a Basis for Partnerships
When forming partnerships, entrepreneurs place a lot of weight on their business plans. It offers a strong platform for prospective partners to comprehend the company. Also, its objectives, and the value it brings.
To successfully attract and establish partnerships, entrepreneurs should clearly define their business, highlight their target customers, market opportunities, and competitive advantages, outline partnership opportunities, develop partnership plans, and use the business plan as a communication tool. This aids potential partners in comprehending the goals and potential of the company as well as the growth potential of the market. Entrepreneurs may successfully convey their vision, ambitions, and potential to potential partners by emphasizing the advantages of collaboration, promoting development and success for both parties.
Read – Imitative Entrepreneurship
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Do Business Expansion
A business plan plays a crucial role for entrepreneurs when it comes to business expansion. It provides a strategic framework and guidance for expanding operations, entering new markets, or launching new products or services.
Entrepreneurs can use a business plan to facilitate expansion by evaluating current performance, defining expansion goals and objectives, conducting market research, developing a strategic expansion plan, assessing financial requirements, monitoring and adjusting the plan as needed, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the plan to ensure success. This approach helps businesses navigate market dynamics, identify strengths and weaknesses, and adapt to unforeseen challenges or opportunities.
Guides Entrepreneurs to Succession Planning
A business plan is of significant importance when it comes to guiding entrepreneurs in succession planning, which involves preparing for the future transition of leadership and ownership within a business.
To effectively use a business plan for succession planning, assess current leadership and ownership, identify potential successors, define succession goals and timeline, develop a succession plan, communicate with stakeholders, and regularly review and update the plan. This process ensures alignment with the long-term vision and aspirations of the business and its stakeholders. Regularly assess the progress of potential successors and provide development opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Importance to Increases Self-Awareness
A business plan is crucial for entrepreneurs because it may help them become more self-aware and better grasp their advantages, disadvantages, and possibilities for growth.
Entrepreneurs should consider their objectives and values, perform a SWOT analysis, create reasonable company goals, ask for criticism and mentoring, constantly evaluate their success, and change to improve their self-awareness. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, entrepreneurs can create a clear vision and align their business plans with their values. By seeking feedback and mentoring, entrepreneurs can develop a stronger self-awareness and improve their business strategies.

An effective business plan is a crucial tool for entrepreneurs . It gives them a path to success. A successful business plan may help entrepreneurs define clear goals. Also, identify their target market, analyze the competition, determine whether their idea is feasible, draw in investors, manage funds, and track their progress. It functions as a manual to assist business owners make wise decisions, manage resources effectively, and adjust to changing conditions.
A solid business plan is crucial for entrepreneurs to navigate the complex commercial world, guiding their companies toward expansion, profitability, and long-term success. It should be evaluated and revised regularly to reflect company demands, serving as a compass for entrepreneurs.
FAQ about the Importance of Business Plans to Entrepreneurs
Why is a business plan important.
Because it gives business owners a clear road map for their venture, a business plan is crucial. It aids in establishing goals, locating target markets, evaluating rivalry, obtaining finance, and coming to wise conclusions. Describing their vision and plans, it functions as a strategic instrument that leads business owners toward success.
When is the Best Time to Write a Business Plan?
Typically, before launching a new firm. It is the ideal time to draft a business plan. Likewise, when a current firm is expected to undergo significant adjustments. Be sure you have a solid strategy in place before approaching investors, looking for finance. Especially, starting a business. Making a business plan, though, is never too late, and you can always change it as your company grows.
What is a Business Plan’s Main Objective?
A business plan’s main objective is to outline an organization’s goals, strategies, and financial predictions. It helps business owners communicate their vision, pinpoint their target market, assess the profitability of their endeavor, entice investors, and allocate their resources effectively. It serves as a compass for monitoring growth and making adjustments as needed.
What are the Typical Challenges of Writing a Business Plan?
Entrepreneurs face hurdles while drafting a business plan, such as limited time and resources, writing skills, market research, financial predictions, and strategic planning. The complexity of the process may be increased by using accurate market data, reasonable estimates, strategic planning, clear writing, and managing other elements of the firm.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

More From Forbes
Five ways you can become an intrapreneur in your organization.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
If you want to position yourself for advancement and make a large impact, you don’t need to leave your current role and start your own company. I have been able to make significant change inside a very traditional, very operational organization as a CMO in the financial space. You can make a big difference right where you are by leveraging intrapreneurial behaviors.
Like their namesake entrepreneurs, intrapreneurs are innovative thinkers who use the combined power of creative problem solving and risk tolerance when they approach business challenges. But unlike entrepreneurs who launch startups to meet customer and market needs, intrapreneurs are employees in existing companies who develop projects and explore new ideas using an entrepreneurial mindset.
"Most new products are launched by small, focused teams,” Josh Millet, CEO of Criteria Corp, told me. “When these small teams are embedded in bigger organizations, there's a different set of challenges than with startups. Getting buy-in from leadership and being clear about how the new product aligns with the larger company goals is critical.”
Interested in becoming more intrapreneurial? Try out these five strategies to become an intrapreneur within your current organization:
Understand your own company.
The value of intrapreneurs begins with a deep understanding of the unique challenges that their companies face. To become more intrapreneurial, the first step is to spend ample time researching a specific problem within your area of expertise so that you will have insight into what needs fixing.
Spend time getting to know your department’s unique pain points and how those might impact customers, as well as colleagues in other functional areas. Build your user knowledge and insider relationships to gain allies, resources and support for your ideas.
Smart intrapreneurs become experts at quickly unearthing the most agile ways to add value to their companies. After beginning in their own backyard, they extend a hand to cross-functional peers and management to elevate the design and delivery of products and services for the ultimate benefit of all involved.
Focus on evolving your organization from the inside out.
To uncover what makes intrapreneurs tick, it helps to better understand the best traits of entrepreneurs— but it’s also important to recognize a key difference between these roles. Both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs apply qualities like passion, empathy, critical thinking and collaboration to help their organizations compete and evolve.
Yet although they use similar approaches to creatively solve problems, an intrapreneur’s focus is on transforming the company from the inside out . This means looking within their own areas of expertise as a starting point and tackling a specific challenge. If successful in implementing change at this level, intrapreneurs might stretch and scale their initiative cross-functionally to create new opportunities companywide.
“The entrepreneurial spirit isn’t confined by an official role or title,” said Carolyn Rodz, founder and CEO of Circular Board. “Great intrapreneurs have the same tenacity, openness to risk and creativity that make successful entrepreneurs tick. Both intrapreneurs and entrepreneurs constantly seek innovative solutions to the problems they see around them.”
Don’t be afraid to experiment.
If you want to be intrapreneurial, you can’t be afraid to fail. A love of experimentation is another way that intrapreneurs mirror entrepreneurs. Both recognize that exploring many different potential paths is necessary to produce innovative breakthroughs, but failure often results from experimentation. As an intrapreneur, you can't see a failed experiment as permanent “Failure” with a capital “F.” Instead, understand that it’s an important and unavoidable stepping stone on the path to success.
This is a unique time in history for change drivers and disruptive thinkers. Your company needs your intrapreneurial skills to help navigate market shifts and meet customer demand for seamless user experiences. Make iterative innovation your new mantra as you work to uncover creative paths that can make your company stand out in a business environment that is both increasingly automated and digital.
Build informal leadership as the resident problem solver.
Companies often end up bringing in outside analysts and consultants to help them figure out answers to their stickiest problems. Yet if you can proactively offer innovative ideas and ways to execute them, you’ll become a go-to resource inside your organization.
No matter what role you’re currently serving, you can take steps to build informal leadership as a person who applies critical creative thinking to come up with out-of-the-box solutions. Take the time to understand your colleagues’ most pressing problems. Your empathy for different business needs will help lead to scalable outcomes and cement your success as an intrapreneur.
Move away from command-and-control leadership.
Many companies still foster a traditional “command and control” leadership style, which relies on establishing and maintaining power over people and organizational processes. This style prevents a more iterative, collaborative and creative experience for both the manager and employees and is the enemy of intrapreneurs because it stifles the chance for real-time feedback and course corrections that can lead to optimal results.
Instead, intrapreneurs favor a more servant-based and human-focused leadership approach that draws on qualities that are generally considered more natural to female leaders. While women are often credited for their leadership roles in relationship-building, collaboration and motivation, research has shown that women also excel (even more so than men) in other areas that intrapreneurs need, such as showing initiative, driving results and being open to change. Both women and men can benefit from incorporating a blend of these attributes to create organizational change and transform their companies from the inside out.
So if you’re an innovator who thrives on an entrepreneurial spirit, there’s no need to found a startup. Try applying that energy within your current organization— and watch the magic happen.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Your Small Business Resource
- Your Career
Become an Intrapreneur with These 5 Easy Tips

Do you have the entrepreneurial spirit but work for someone else and don’t see that changing anytime soon? You can make the most of your entrepreneurial drive by being an intrapreneur.
An intrapreneur thinks and behaves like an owner, even though they’re an employee and don’t take the financial risks that entrepreneurs do. You bring a unique perspective to the company you work for, so as an intrapreneur you’d be able to bring new ideas and solve problems in new ways.
Being intrapreneurial works best if your company encourages you to be innovative and think outside the box . If they do, then you’ll be able to leverage your company’s resources to pursue passion projects.
So, what does it take to become an intrapreneur?
1. Be Persuasive
To explore your ideas, you’ll have to get buy-in from your company and convince your boss that they should take a risk on your plan. When you present your ideas, you’ll have to be able to clearly and fully explain your reasons for wanting to pursue the project.
You can help convince your company to take a risk on your idea by creating a business plan – which will outline how you’ll execute your idea and how it will help the company.
2. Be Creative
As an intrapreneur, the projects you pursue or the problems you try to solve will usually mean you have to think outside the box and try something brand new, which requires you to be creative.
If you’re not sure what project to pursue, look for a problem that everyone’s ignored or worked around, then figure out a solution.
3. Strike a Balance
Even though you’re testing your ideas, you’ll still be expected to handle your normal duties and responsibilities. Carve out time for yourself to test your ideas, without letting your job duties fall through the cracks.
4. Build a Team
An entrepreneur rarely works alone – they usually have advisors and mentors to help them think through their ideas.
Likewise, you don’t have to work alone. Recruit your coworkers and ask them to help you follow through with a project. Look for coworkers who are excited about taking on new projects and passionate about helping the company succeed.
5. Be Prepared to Fail
Just like starting a new company, not every idea you have will be successful. When you encounter a problem, don’t give up. Have a Plan B in place and figure out how to work through the problem.
If an idea fails completely, don’t give up on being an intrapreneur. Learn from the failure so you can build something successful next time.
You may also like...

Nobody Likes “Fake Work” – Here’s How to Avoid It
March 16, 2018

11 Tips for Celebrating Halloween at Work
October 22, 2018

Should I Be an Employee or an Independent Contractor?
May 4, 2018
- Next story Why Do I Need a SWOT Analysis?
- Previous story Are You Ready for Retirement?
Learn About Workful Payroll
Talk to us: 1.888.200.7038
- Accounting & Finance
- Company Culture
- HR Management
- Start & Grow Your Business
See if Workful is right for your business:
Get Started
Schedule Demo
Let’s Stay In Touch
- Accounting & Finance
- Start & Grow Your Business
Let’s Stay in Touch
Business Advisor
The Business Guide to Intrapreneurship
With the boom of entrepreneurship out there, there has been a distinct separation between corporate work and starting a business of your own. However, most folks are not familiar with what intrapreneurship is, due to it getting far less coverage than it should be.
While entrepreneurship often gets the spotlight, intrapreneurship offers a compelling alternative for those who desire the challenge of building something new but value the stability and resources of a larger company. It’s a chance to be a changemaker from within, leveraging the established infrastructure and support systems of a corporation to bring fresh concepts to life.
What Is An Intrapreneur?
As Murray Newlands shared for Inc. :
The distinction between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs can be seen as a difference in the level of focus. While an entrepreneur should see the company as a vision from starting point to end; the intrapreneur is a facet of this broader vision. The intrapreneur works within the company to solve a specific problem. Thus intraprenuers should have more directly applicable skills for a given task. The intrapreneur will take risks, but within the context of their job in the company. The intrapreneur, unlike the entrepreneur, is not focused on the entire company, but rather processes within it.
Intrapreneurs are creative, motivated, proactive employees. They are eager to handle a specific division of an organization in a leading role without having to venture on their own .
The Difference Between Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
The Intrapreneurial Initiative has prepared a splendid infographic that covers the difference between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs:
The number of intrapreneurs out there is still low. Most hustlers don’t see intrapreneurship as an option for three reasons:
- The media focus on successful startup founders and entrepreneurs for the past 5 years has been overwhelming.
- The actual scope of running a business from the ground is never covered publicly. All of the hustle and 100-hour work weeks is ignored in favor of receiving the next $50M funding by a regular Joe who had started from home.
- Most companies don’t have processes in place to accommodate and nurture intrapreneurs.
And let’s not ignore the obvious reality of business:
Most Startups Don’t Make It
The number of failed startups varies massively depending on the research study you’re looking at. Some optimists claim that nearly 50% of new businesses are successful. I firmly believe that more than 80% fail over the first few years (unless we account for freelancers and solopreneurs with lifestyle businesses).
It’s not uncommon to read about a 90%+ fail rate either:
- 90% Of Startups Fail: Here’s What You Need To Know About The 10% by Neil Patel on Forbes
- Why 95 Percent Of Startups Fail (And How To Be In The Winning 5 Percent) – Wenee Yap on HuffPost
- 90% Of Startups Fail: Here Are 4 Expert Tips to Improve Your Odds – Nitya Timalsina on Startup Grind
- Why 90% of Startups Fail [INFOGRAPHIC] – Samantha Murphy on Mashable
As a business advisor, I’ve worked with 300+ businesses across different industries. The lack of an in-house leadership in a company is a well-known flaw. It prevents scaling a business due to the risks of delegation to hires who wouldn’t take the initiative to head a department or a set of activities themselves.
CB Insights has also done a detailed study on the cause of failure in startups:
Entrepreneurship vs. Intrapreneurship – Lack Of Education
I believe that entrepreneurship should be studied in schools.
Moreover, entrepreneurship should be covered in its entirety – exposing both the good and the bad. The hype in the digital media over the past 5 years has led to a vast number of startups and small businesses that fail (at ~90% rate) over the first years. That’s why I authored a book covering the dark sides of entrepreneurship.
This wouldn’t have been the case if:
- Young entrepreneurs were properly prepared for what a business holds, or
- They have prioritized career growth in existing companies.
I support that rising intrapreneurship trend completely. There’s a major mismatch between the regular workforce and entrepreneurs trying to start a venture simply because they can’t find progression in existing companies.
Having proper training in entrepreneurship from an early age through school and university would be invaluable for motivated, young, determined graduates eager to grow professionally and personally.
Entrepreneurship is Not All Rainbows and Unicorns
It’s exhausting, hard, requires a ton of experience, and hustling 80–100 hours a week for months, if not over a year.
That may impact friendships, health, relationships, and more – and could easily be avoided by working 45–55 hours a week for an organization as a team leader, a manager, or anything else that still includes some responsibilities but offers some help from the organization.
How Are Intrapreneurs Different From Entrepreneurs
So what are intrapreneurs? Intrapreneurs are skilled and sharp experts who can run an entire team, division, department themselves. Similar to entrepreneurs, they have progressive growth thinking, and the ability to influence their team, increasing results over time.
There are no perfect entrepreneurs out there.
All of us excel at a number of skills or traits – such as leadership, management, strategy, marketing, technology, sales, operations, media coverage, etc.
But we don’t cover all grounds equally.
- Oftentimes, big vision thinking results in less productivity when it comes to attention to detail.
- Big extraverted personality isn’t ideal for reading contracts or crunching numbers on billing reports.
- We may be great at selling but suck at reducing operational costs.
Intrapreneurs know their strong suits and can join a strong team in need of additional leadership capacity. They can leverage the extra help in areas that the business provides as assets, and focus 100% of their attention on what they do best.
It’s a powerful combination for every business.
Intrapreneurs Could Leverage Coaching and Mentorship
You can easily outline various areas where a professional coach with business expertise could be of help – restructuring the management processes, coming up with unique product ideas or actionable feedback on improvement, analyzing new monetization opportunities, reflecting on the customer support workflow.
Fresh entrepreneurs may have a hard time figuring these out for themselves. Finding the right mentor isn’t easy either.
But it’s absolutely possible as an intrapreneur working for the right organization. A proactive employee has a network of colleagues, managers, and even the C-Suite of an organization being able to help and share their business experience. That’s massively different than starting a business on your own or even partnering up with one or two co-founders on a new startup.
Based on CB Insights’ study, it’s worth noting that 42% of the startups fail due to the lack of market need .
A coach can hardly help an entrepreneur who has built a product that is not in demand. That’s another sweet spot where an experienced business owner or a senior manager can assist and prevent a disaster from happening in the first place.
Sometimes, they may find an opportunity to restructure the product plan and the marketing strategy in a way that aligns better with the customers’ needs – something that clients want and competitors don’t provide yet.
That’s a major stunt that may or may not work – but it may be worth trying if your business is failing to deliver the right results.
The reason I love working with consultants, coaches, and mentors is their insight into my specific business needs . I use Clarity both for offering and receiving consulting on a regular basis.
Entrepreneurship is like a puzzle – there are tons of actionable tips and strategies – but they are not always applicable, can’t be tested simultaneously, and largely depend on a specific business at a time.
That’s exactly what an established organization does through internal meetings and management/leadership roles.
A professional coach or a mentor working in the management tier can analyze a business plan, identify the weaknesses and optimize the right processes. The specific caveats that require attention are better identified by the entrepreneur or intrapreneur – although they may be unaware of details that could, in fact, be a major obstacle.
How to Be an Intrapreneur
We have been extremely lucky in finding and closing several intrapreneurs across my companies.
The usual profile of how to become an intrapreneur is usually:
- A freelancer who can’t (or doesn’t want to) scale full operations into a running business
- The co-founder of a small team that had a couple of great years, but faced some pressing challenges
- A manager who tried their stunt in the corporate world and gave up on all the bureaucracy
- A small agency rockstar who didn’t have access to growth opportunities to lead their own division
If you fall into this category, intrapreneurship may be your best bet.
- Start with your personal SWOT analysis first. Discover what you do best and memorize it.
- Develop your portfolio or CV to fully outline your strong suits.
- Tap into your network. Look for opportunities in mid-sized to growing organizations that could use your skill set.
- Speak to founders and senior managers. 70%+ of all job opportunities are not available in job sites yet. If you find the right people, you can unlock your own personalized position as well.
- Attend events and career shows. You will be surprised how often showcasing your strong suit can create an opportunity.
- Try with revelant job opportunities on Indeed or Monster. The interview process may unlock a new position tailored to your skills.
Get personalized leadership advice and monthly goal assessment
What does an intrapreneur do.
Intrapreneurs take a leadership position in an organization.
Some intrapreneurs have to prove their worth by starting small first, demonstrating leadership capacities, facilitating their team, assisting in operations and strategy, and earning their supervisor role.
In any case, the end goal is supporting the business with (almost) full autonomy, through activities such as:
- Product marketing or strategy
- Team leadership and growth
- Sales strategy and business development
- Marketing and growth marketing opportunities
- R&D for technical roles
- Ambassador or partnership development gigs
Intrapreneurs take a large problem in the organization and own it. Different businesses face different problems, and I’ve outlined the most common ones in my guide here .
Lack of Explicit Intrapreneurship Opportunities
Again, a lot of intrapreneurship opportunities are not publicly available.
Before growing my own business, I’ve tried to venture as an intrapreneur several times at my previous jobs.
I appreciate the entrepreneurship trend, and I’m glad that I had the opportunity to start at a less conservative time. Baby boomers and Gen X have been raised with a totally different mindset, in a world when many have worked a single job throughout their entire career until retirement .
That’s not necessarily bad – just limiting for people eager to build something on their own.
But the main problem I have with entrepreneurship is the dual contrast that it projects on the younger generation. This creates a context of “ You’re either hustling as an entrepreneur or merely working in a boring cubicle ”.
The critical moment arises when creative, motivated, determined people feel constrained in a corporate environment and feel obliged to venture on their own. After all, the entrepreneurship wave doesn’t nurture any other successful environment, does it?
Which leads to different financial and business bubbles together with the lack of manpower (staff) in the IT industry.
According to different surveys, 35% of the US workforce is now comprised of freelancers . Add that to the percentage of failing startups at scale. Burnouts are a major topic across media outlets. It feels like most business owners have simply started because they see no other alternative – but they aren’t inclined to (or capable of) running an entire business.
Remote working is a good middle ground . But IBM and Yahoo have closed their remote job openings and called everyone at the office.
I firmly believe that many of those failing business owners would be more than happy to work an interesting job for a paycheck . And that’s where intrapreneurship comes in.
The culture of proactiveness and motivation really hasn’t been firmly established in most organizations. I’ve conducted over a thousand interviews over the past few years, and I’m profoundly disappointed, sometimes outright disgusted, by some of the applicants we have been talking to.
We are not a trendy startup, but we still try to do whatever we can in order to keep our team members both efficient and happy, some examples:
- We provide growth opportunities for less experienced members showcasing intrapreneur qualities.
- We hire based on traits and motivation first, skills second.
- We invest in R&D opportunities that enabled DevriX to make it to the top 20 WordPress agencies worldwide.
- We have flexible working hours for the most part.
- Our office offers bean bags or a stand-up desk, a couple hookahs, occasional free lunches, and is dog-friendly.
- We promote an “open door” policy for whatever, whenever.
- We do comply with last-minute university exam notices or taking care of employees’ children (parent-teacher meetings, doctor appointments).
- We invented a new business model in the space called “WordPress retainers” which incorporates a recurring revenue model with consulting and strategy opportunities for everyone in the organization.
There’s a lot more we try to cover despite being a small team of 30 people. But all of our job descriptions and employment-related posts stress proactivity, motivation, self-driven attitude . Not only do we have a nearly impossible time finding that profile, but:
- 35% of applicants don’t even show up for their interview appointments.
- Oven 70% haven’t even browsed our site before an interview (beyond the homepage at best).
- CVs are often sloppy and incomplete.
- The initial interview questions generally revolve around working hours and paycheck, rarely anything about the work or the team.
I could go much further but it gets depressing at a certain point. It gets even worse when dealing with wanna-be developers with absurd payment expectations or teenagers who believe that their time spent on Facebook and Snapchat qualifies as marketing seniority .
Sure, it’s not a rule of thumb – but there’s scarce interest by most applicants/interviewees in a particular job opening . The status quo of traditional, old-school managers doesn’t help a lot. But if people are looking for jobs only for the sake of earning a paycheck and slacking in the meantime, how would that work?
And yes, that’s different for Google, Uber, Amazon, Netflix – any of the top giants that receive tens of thousands of CVs every year. But they represent a tiny portion of the companies operating worldwide, or even in the US alone.
My Hope For Intrapreneurship
Intrapreneurs could be the next best thing for the world of entrepreneurship. Industry experts with practical business expertise. Creative people who get empowered and supported by an organization. Future co-founders or C-level folks at growing startups.
I’d be really excited to see the intrapreneurship trend scaling massively. Small teams can also finally team up and build outstanding solutions together instead of competing for small niche markets.
Have you employed intrapreneurs within your organization yet?
If not, I’d urge you to try. It may drastically change the culture across your organization for good.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What Is an Intrapreneur and Why Does Everyone Want to Hire Them Right Now?

Sure, there’s plenty of talk nowadays about entrepreneurs and freelancers—people who work for themselves, set their own days, and run their own businesses. But there’s another crew in town that’s becoming increasingly popular: intrapreneurs.
If you’re not familiar with this term, you’re not alone.
The first time I heard it was from William Arruda , a global personal branding expert whose clients include many Fortune 100 companies and the author of Career Distinction: Stand Out By Building Your Brand . In it, he describes an intrapreneur as “a person who demonstrates an entrepreneurial spirit within an organization.”
This concept shows just how much the employee-employer relationship has evolved. And when you think about it, it makes a lot of sense in today’s working world. Employees are demanding more freedom and autonomy in order to grow. And employers are understanding the need to create a strong company culture that retains top talent and fosters innovation.
The result? Companies are eager to welcome and embrace people who are creative, proactive, and flexible—in other words, intrapreneurs. I’ll explain what it means to be one and the benefits they bring to employers—and how you can be an intrapreneur, too.
What Is an Intrapreneur?
In many ways, an intrapreneur could be considered an in-house entrepreneur. If we go back to Arruda’s definition, this group of people is classified as having an “entrepreneurial spirit.”
So, what does that mean, exactly?
Well, entrepreneurs are driven by the desire to create new services or products. In doing so, they develop original ideas, think beyond what’s already been done, and are always looking to provide valuable solutions to common problems. They’re personally invested in achieving a successful outcome.
The same thing can be said about intrapreneurs. They’re creative freethinkers who are passionate about sharing new ways to get things done. The difference is, they operate within a company rather than solo. While no one’s job title is likely to be “intrapreneur,” you can adopt the mindset in pretty much any role.
What Are the Characteristics of an Intrapreneur?
You can instantly spot an intrapreneur within a company because they treat their job as if it were their own business. Also, an intrapreneur’s ingenuity makes them a star employee —they’re always coming up with resourceful ways to approach challenging situations.
Here are some more characteristics that make them truly special.
They’re Authentic
An intrapreneur’s greatest trait is being consistently humble and sincere—whether it’s in an email, meeting, or passing conversation. This makes them experts at establishing trust and highly respected and liked throughout a company.
They’re Savvy Collaborators
Ever known someone who can pick up the phone to ask for a favor or information and get an immediate response? Well, that’s a classic intrapreneur move. As masters of building relationships, they never run out of people to contact who are willing to help—because they’d do the same in return.
They’re Highly Confident
It takes a certain level of confidence to express creative ideas and proactively start a project. Intrapreneurs are risk-takers, so they trust their actions and aren’t afraid to try something different or learn from trial and error.

They’re Uber Resilient
Whether it’s about finding an answer to an ongoing problem or hammering out the details of a new plan, an intrapreneur won’t give up. An intrapreneur is not easily deterred and hasn’t met a challenge they’re not willing to tackle head-on.
They Have Strong Personal Brands
Intrapreneurs are highly aware of how they communicate their unique strengths and work hard to maintain a positive external reputation in order to promote their expertise and services. Because their professional image is important to them, they also have just as strong of a presence online as they do in person.
Why Are Intrapreneurs So Valuable to a Company?
You may think, “Hmmm… Wouldn’t these kinds of people be perceived as a threat to a company’s success? And wouldn’t they just take off the second something better came along?”
But it’s actually to a company’s advantage to have employees who take ownership of their work. Employees who feel like their talent and contributions matter (for real) will work smarter, feel more satisfied, and bring forth their best ideas—which will ultimately become the company’s ideas and products.
Some may fear that allowing employees to be too innovative will lead to folks using what they do at work to benefit their own side hustle. However, even if that’s the case, there’s nothing wrong with it, as long as there’s no conflict of interest (for example, working on outside projects during work hours or working on something that’s a direct competitor to the company).
Why Should You Be an Intrapreneur, and How Can You Be One at Any Company?
So as you’re thinking of ways to grow your career , consider how the mindset of an intrapreneur is also an asset to your own brand and success. Sure, your ideas are going toward a company’s vision, but you know where else they’re going? Into your resume and LinkedIn profile—your own portfolio !
Every successful initiative you’re a part of gives you concrete examples of scenarios when you took action and delivered results. This increases your potential to make more money and access more growth opportunities down the road (for example, a promotion, a new role you get to define, or a completely new start somewhere else). Plus, being an intrapreneur allows you to pursue a passion project with the added benefit of having a company’s resources and budget—as opposed to having to start from scratch and launch it all on your own.
As an intrapreneur, your experience is tied to in-demand skills that are transferable anywhere you go, instead of a specific job title.
Here’s how you can start to think and act like an intrapreneur at your company—no matter how formal or traditional it may be:
Be Proactive
Instead of waiting for directions (or for a problem to arise), get the ball rolling to spark the necessary actions to be taken. This can mean sending an email, following up on a discussion, or suggesting a meeting when an idea pops into your head.
Read More: 2 Easy Ways to Expand Your Role (Without Overstepping Your Boundaries)
Adjust to Change (Quickly)
Sometimes unplanned situations come up and you have to immediately drop what you’re working on and switch gears. Be flexible and open to change so that you’re always ready to roll up your sleeves and re-focus your priorities as needed.
Read More: Everything Changes—Here’s How You Can Get Better at Accepting That Fact
Rely on Probing Questions
Gather as many details as possible before making decisions by asking open-ended, probing questions—think questions that begin with “what,” “why,” or “how.” This will instantly help you make smarter and faster choices.
Read More: 4 Questions Smart People Always Ask When They’re Put in Charge of a Project
Challenge the Status Quo
If you think there’s a way to make a process better, don’t be afraid to do something about it if it’s within your control. Start by testing your idea within your own role, and then share your improved process (and results!) with your team.
Read More: 5 Steps for Initiating Change in a “We’ve Always Done it This Way” Office
Track Your Accomplishments
Remember when we talked about how intrapreneurs are always adding experience to their portfolios? Do the same by keeping track of your own accomplishments throughout the year so that you can show exactly what projects you spearheaded, should you ever need to.
Read More: The 10-Minute Weekly Activity That Helps You Get Ahead (Worksheet Included!)
Intrapreneurs are in demand simply because they make companies run better. Employees stay in their roles long-term because they’re challenged and fulfilled by the work they’re doing, and companies thrive because they retain the best people and best ideas—it’s a win-win for everyone.
- View programs
- Take our program quiz
- Online BBA Degree Program
- > Specialization in Artificial Intelligence
- > Specialization in Business Analytics
- > Specialization in Digital Marketing
- > Specialization in Digital Transformation
- > Specialization in Entrepreneurship
- > Specialization in International Business
- > Specialization in Product Management
- > Specialization in Supply Chain Management
- Online BBA Top-Up Program
- Associate of Applied Science in Business (AAS)
- Online MS Degree Programs
- > MS in Data Analytics
- > MS in Digital Transformation
- > MS in Entrepreneurship
- Online MBA Degree Program
- > Specialization in Cybersecurity
- > Specialization in E-Commerce
- > Specialization in Fintech & Blockchain
- > Specialization in Sustainability
- Undergraduate certificates
- Graduate certificates
- Undergraduate courses
- Graduate courses
- Apply to Nexford
- Transfer to Nexford
- Explore Education Partners
- Scholarships
- For organizations
- Career Coalition
- Accreditation
- Our faculty
- Career services
- Academic model
- Learner stories
- Book consultation
- Careers - we're hiring!

What Is Intrapreneurship In Business? (2024)
What is intrapreneurship, and why is it important in business? Learn how fostering innovation within your organization can drive growth and success!
What is intrapreneurship?
Let's talk about the concept of intrapreneurship. In a nutshell, intrapreneurship is simply entrepreneurship within an organization or company. Intrapreneurs are entrepreneurs operating within the structure of a company. They are at the forefront of innovation and are given control of products and services that affect the company’s future growth. Read on to discover how intrapreneurship benefits business, and how it can help your career.
Intrapreneurship is essentially a mechanism within an organizational setting that lets an employee act like that an entrepreneur . These employees are given the task to create and develop new products. They are typically afforded much more leeway, support, and resources than other employees in the company.
Now that we've discussed what is intrapreneurship, let's discuss other aspects around the topic.
History Of Intrapreneurship
The term first appeared in 1979 in “Intrapreneuring: Why You Don’t Have to Leave the Corporation to Become an Entrepreneur” published by Gilford and Elizabeth Pinchot. It later gained mainstream recognition when Time Magazine published the article “Here Come the Intrapreneurs” in 1985. In 1992, the term was added to The American Heritage Dictionary further acknowledging the term’s popularity.
However, the first regarded instance of intrapreneurship happened in 1974. A scientist by the name of Art Fry in 3M developed the iconic Post-it Notes . He partnered with another 3m Scientist named Spencer Silver who developed an adhesive that sticks temporarily and leaves no residue behind. They developed the popular office product and have since seen success to this day.
What is the difference between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship?
Although very similar, entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship have a major fundamental difference that makes them distinct from one another. This difference is what separates an intrapreneur from its more mainstream counterpart.

The major difference
The biggest factor is the setting. Entrepreneurship operates through independent ventures. They are essentially businesses that operate independently from any other companies or organizations. Intrapreneurship, on the other hand, is found within established companies. Because of this major difference, intrapreneurs are afforded perks that are not typically available to entrepreneurs.
Access to a bigger pool of resources
First, and perhaps the biggest, on the list is access to resources. Because an intrapreneur operates within a company, they have access to the company’s resources. This lets the intrapreneur focus on developing and designing new products. This also lets the intrapreneur tap into other non-monetary resources like industry connections, talent, and support along the way. This empowers the innovator to realize their product without much fear of losing funding.
Effective and robust support system
In a company or organization that supports intrapreneurship, support is one of the key factors that help the venture succeed. This mainly comes in the form of allowing the intrapreneur to develop and realize their ideas. After all, no idea takes off without others supporting and adopting it. A good support system empowers the innovator to persevere.
Mitigated risks
Failures and setbacks are inevitable for any innovative pursuit. However, since intrapreneurs are ultimately inside a bigger organization, it isn’t as daunting. Unlike entrepreneurs who bear all the risks in any endeavor, the parent companies of the intrapreneur provide a safety net. This lets the employee with greatly minimized risks.
Get a huge head start in your field
Being an innovator takes a lot of hard work and resources. That is why it helps greatly when you have existing support networks and resources to use. This is essentially what intrapreneurship gives to innovators: a strong chance to succeed in bringing innovation not just to their companies but also to their industry as well.
Learn how to develop the most in-demand skills for your future career!
Discover how you can acquire the most in-demand skills with our free report, and open the doors to a successful career.
Characteristics of intrapreneurs
Intrapreneurs are individuals within an organization who possess an entrepreneurial mindset and drive for innovation. These employees are proactive, creative, and willing to take risks in order to bring about positive change within their company. They are constantly seeking new opportunities for growth and improvement, and are not afraid to challenge the status quo.
Intrapreneurs are also highly motivated, self-starting individuals who are passionate about their work and dedicated to making a difference. They are natural problem-solvers, constantly looking for ways to improve processes and generate new ideas.
In addition, intrapreneurs are adept at building strong relationships and collaborating with others across different departments and levels of the organization. They are also resilient, adaptable, and able to thrive in fast-paced, dynamic environments.
Overall, intrapreneurs are valuable assets to any organization, as they bring a unique blend of creativity, ambition, and determination to drive the company forward.
Who are successful intrapreneurs?
The benefits of being an intrapreneur in a large company can increase your chances of success, but it still boils down to the intrapreneur themselves. It takes a certain combination of traits that makes for a successful intrapreneur.

First—and perhaps the most important—is that successful intrapreneurs are innovators. They are a fountain of ideas that are willing to explore new avenues for improvement and change. They embrace change and thrive in environments that constantly seek growth and improvement. They are always at the forefront of what’s new in their respective fields.
Problem-solvers
Innovators are excellent problem-solvers. After all, innovation is the pursuit to offer an elegant solution to an existing problem. Along the way, there will be various challenges that an intrapreneur must face. With a problem-solving mindset, the intrapreneur rises to these challenges and comes up with effective solutions to address them and innovate.
Risk takers
Innovation is not without risks and pitfalls. A successful intrapreneur acknowledges this fact but welcomes it anyway. They are not afraid to take risks but are smart about them. They understand that innovation entails challenges and that they are but part of the process. They also understand that ultimately growth and progress happen when one takes risks.
Has an eye for opportunity
Risk-taking will not be fruitful if you are not smart about it. Successful intrapreneurs are good at spotting opportunities when they see them. They can recognize situations, good or bad, as opportunities for growth and innovation. This eye for opportunity helps them take steps that are leagues away from their counterparts.
Being at the forefront also means leading others. That is why successful intrapreneurs are born leaders. They inspire others and infect them with their enthusiasm and hunger for innovation. They are doers who lead by example.
Keen collaborators
As leaders, they understand that innovation is a product of different minds coming together. They understand the power of collaboration and actively encourage it. They welcome any and all good ideas, no matter who from. They encourage others to share these with the team. This collaborative mindset helps intrapreneurs have fresh perspectives on their ideas and get valuable insight.
Famous Intrapreneurs - Success Stories
Steve Jobs and Ken Kutaragi are two examples of famous intrapreneurs who have made significant contributions to their respective industries. Steve Jobs was the co-founder and CEO of Apple Inc ., while Ken Kutaragi was the former Chairman and CEO of Sony Computer Entertainment .
Both individuals are known for their exceptional ability to think outside the box and bring innovation to their companies. It was their innovate ideas which led to their companies becoming incredibly successful.
What made them successful intrapreneurs was their visionary mindset and their willingness to take risks. Steve Jobs was known for his relentless pursuit of perfection, leadership skills, innovation efforts and his ability to create products that revolutionized the technology industry. He introduced the iPod, iPhone, and iPad, which changed the way we listen to music, communicate, and consume media. His dedication to creating a cohesive and seamless user experience set Apple apart from its competitors, and this enabled corporate innovation within such an established company.
Similarly, Ken Kutaragi played a crucial role in the development and success of Sony's PlayStation gaming console. He took risks by championing the project within Sony, even when it faced opposition externally and within the existing organization. His new idea and vision for a gaming console that could deliver high-quality graphics and immersive gameplay led to the launch of the original PlayStation, which went on to become one of the most successful gaming platforms of all time.
Both Jobs and Kutaragi were passionate about their work and believed in the potential of their ideas. They were not afraid to challenge the status quo and were relentless in their pursuit of innovation. Their skill and ability to successfully navigate their respective organizations and bring their ideas to life is what made them exceptional intrapreneurs. Their legacies continue to inspire and influence future generations of entrepreneurs in their industries.
How successful intrapreneurship benefits a business
Being an innovator in your company puts you in a very unique position. A position where you get to enjoy many perks and benefits while your company also gets a lot of value from your work. This is what makes intrapreneurship such an extremely rewarding and fulfilling role. Here are a few benefits of being an intrapreneur:
Spearhead innovation
For companies and organizations, having an intrapreneur is a huge advantage. They are the leaders in innovation that drive growth for businesses. Having an entrepreneurial mindset inside the company brings with it a ton of benefits. Intrapreneurs are known to think outside the box and to see things from a different perspective. This brings fresh ideas into the mix.
Draw in brilliant minds
When an organization fosters an intrapreneurial culture, this attracts talents within the industry. When they are given an environment where their talents and skills are appreciated and allowed to flourish, they deliver remarkable results. With an active entrepreneurial environment in place, intrapreneurs feel supported and allowed to flourish while the company reaps the innovation and growth brought on by this. A win-win situation.
Get a good headstart
As an Intrapreneur, you start as a regular employee within the company. During this time you get to meet knowledgable and experienced people in your industry. Some companies have an internal mentoring program designed to help budding intrapreneurs develop the skills they need.
Build your network in the industry easily
Being an industry innovator within an existing company also lets you build your network quickly. This is especially true in big established companies. This can grant you access to an industry-wide event where you get to meet and connect with experts and movers in the industry. This lets you build a pool of intellectual resources that you can tap into.
Training ground for entrepreneurship
The skills you learn as an intrapreneur can help you greatly when you decide to transition to becoming an entrepreneur. A lot of the challenges that an entrepreneur faces are also relevant to intrapreneurs. This lets you learn the ropes without being as risky as any entrepreneurial pursuits.
Looking To Develop Your Intrapreneurship Skills?
Discover how you can acquire the most in-demand skills with our free report, and open the doors to a successful career. Download the free report today!
Looking to potentially take your career even further? Consider how an online BBA , MBA and MS degree can help you develop these skills and increase your earning potential, including our BBA in Entrepreneurship and our MS in Entrepreneurship .
What's an example of intrapreneurship and intrapreneurial spirit?
An example of successful intrapreneurship is when an employee takes the initiative to develop a new product or service that can benefit their company. This could involve researching customer needs, developing prototypes, and testing the market for potential success. The employee would then need to present their idea to management in order for it to be approved and implemented.
Intrapreneurship requires creativity, risk-taking, and dedication in order to be successful. It also requires strong communication skills in order to effectively present ideas and gain support from colleagues and management.
How to encourage intrapreneurship in an organization
Because it is quite contrary to the traditional corporate model, intrapreneurship can be hard to sell to your organization. But if the company sees the benefits of fostering this environment, it will be easy to promote the necessary changes. Here are a few things you can do:
Adopt the mindset
The foremost thing to do is to adopt an entrepreneurial mindset. This means to think like an entrepreneur looking for opportunities. This means looking at things from a problem solver’s point of view and being proactive when addressing challenges. Practicing this daily lets you see things differently than what an employee does.

Adopt the mindset The foremost thing to do is to adopt an entrepreneurial mindset. This means to think like an entrepreneur looking for opportunities. This means looking at things from a problem solver’s point of view and being proactive when addressing challenges. Practicing this daily lets you see things differently than what an employee does.
Always think of ways to improve and adapt
To be an intrapreneur is to be an innovator. As an innovator, you should always be on the lookout for things to improve. You identify current existing problems and you create creative ways to solve them. Get in the habit of thinking about improvement and growth when developing any product.
Embrace new innovative ideas
Another good way to promote intrapreneurship within an organization is to embrace and encourage innovative ideas. A good intrapreneur understands that ideas are integral to innovation and should be highly encouraged. As an intrapreneur, you should also welcome ideas, especially those that are not from you. This encourages others to adopt the mindset as well.
Encourage collaboration
Collaboration is at the heart of any intrapreneurial pursuit. Minds working together to design and develop can accomplish a whole lot more than a single mind can. That is why fostering a healthy collaborative environment also encourages intrapreneurship as a whole. You can do this by starting brainstorming meetings where you let other members of the team showcase their creativity and expertise.
How to become an intrapreneur
Becoming an intrapreneur doesn’t happen overnight. It requires key changes in how you think as well as adopting the right habits and practices along the way. However, with enough effort and hard work, you too can become the force of innovation in your organization. Here are some things you can do to start this transition now:
Learn the ins and outs of the innovation process
Innovation isn’t simply having an idea and working on it. For innovation to be truly impactful, one must know the proper steps in the ideation process. From ideation and research up to development and implementation. Understanding this process is key to being successful in any venture.
Learn how to foster and manage a team of like-minded individuals
Innovators thrive with other innovators around them. That is why it is important to understand how to manage a team of talents. This includes improving collaboration, learning conflict resolution, and balancing interests among others. Knowing this lets you understand and leverage the team’s dynamics and properly channel their strengths while addressing their weaknesses.
Be passionate about improvement
There is always something to be improved upon and made better. An innovator is always passionate about finding these things. Be proactive in suggesting ways to bring positive changes into your department. Be consistent and always look for opportunities to improve.
Understand the business side of things
Though things are a little easier since you are operating within a company, it wouldn’t hurt to know the business side of things. This includes looking at financial statements, understanding basic accounting, learning to do cost estimates, and creating business proposals. Understanding this lets you balance the interests of your company and your own.
Learn through online courses
Another great way to learn the ropes is to have knowledgeable teachers show you how it is done. You can get this through education such as in universities. Fortunately, in this hyperconnected world, you can learn right from the comfort of your home. Nexford’s Introduction to Intrapreneurship and Innovation is a great resource for people wanting to dip their toes.
Benefits of being an intrapreneur
Being an intrapreneur within an organization can offer several benefits from the individual’s perspective. Some of the key advantages include:
Autonomy and control
Intrapreneurs have the freedom to control their work, goals, and methods, which can boost motivation, satisfaction, and productivity[3]. They can explore new ideas and approaches, allowing them to take ownership of their work and make a meaningful impact.
Opportunities for growth and development
Intrapreneurship enables individuals to develop key skills such as leadership, problem-solving, and innovation, which can lead to more opportunities for career progression within the organization. This can also provide a platform for individuals to test their entrepreneurial skills and see if entrepreneurship is the right fit for them, without the risks of leaving their current job.
Innovation and creativity
Intrapreneurs are encouraged to take an innovative and creative approach to their work, allowing them to explore new ideas, processes, and strategies that can benefit the organization. This can be intellectually stimulating and rewarding for individuals who thrive on finding unique solutions to challenges.
Sense of purpose and fulfillment
Intrapreneurship enables individuals to focus on areas they are passionate about, creating more meaning in their jobs. This sense of purpose and fulfillment can lead to higher job satisfaction and overall well-being.
Recognition and rewards
Intrapreneurs who successfully implement innovative ideas and drive positive change within the organization are often recognized and rewarded for their contributions. This can include promotions, bonuses, and other forms of recognition, which can further motivate and incentivize individuals to continue their intrapreneurial efforts.
Networking and collaboration
Intrapreneurs often have the opportunity to work with a diverse range of colleagues, including executives, managers, and other intrapreneurs, which can expand their professional network and provide valuable learning and growth opportunities. This collaborative environment can foster the exchange of ideas and knowledge, leading to even more innovative and impactful solutions.

Known for strategy and attention to detail
Joe has more than 10 years of marketing experience, working within the public sector, client-side, and agency side.
He is passionate about using data and customer insights to improve marketing performance.
Join our newsletter and be the first to receive news about our programs, events and articles.
- Random Read
- Digital Book
- Founder Insights
20 Tips To Succeed As A Successful Intrapreneur
Do you have an idea, want to scale it but lack the resources or confidence to go for it with…
- Author towardsbusiness
- Published March 23, 2022
- 0 comments Join the Conversation
Do you have an idea, want to scale it but lack the resources or confidence to go for it with your own money on the line? Do you have an entrepreneurial mindset and want to lead a company’s team whose vision motivates you? If “Yes,” intrapreneurship may be your way to go.
Intrapreneur can be a crucial element to success for a business. The creative freedom provided to intrapreneurs motivates them to take experimental initiative and propel the industry with new innovations and ideas.
An intrapreneur fits somewhere between an employee and an entrepreneur where they have the mindset of an entrepreneur and take the initiative and responsibility as an entrepreneur but work on salary.
Simply put, an intrapreneur is someone who works as an entrepreneur in an already established company that they do not own . They are given the freedom to build the company or develop a project and lead the team.
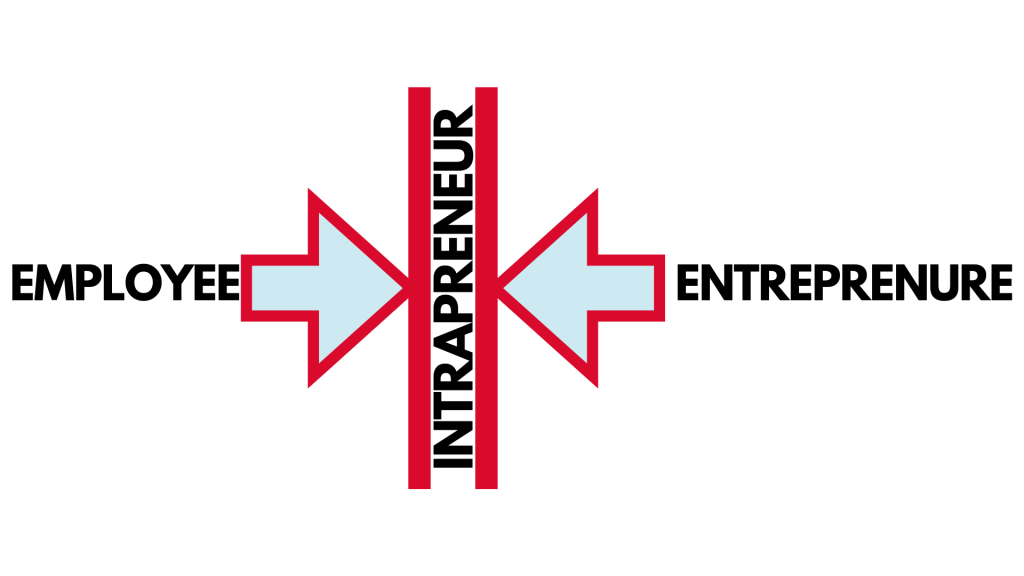
Confident, committed, passionate, and responsible are the qualities that describe an intrapreneur and set them apart from an employee.
How to Succeed as an Intrapreneur?
Here is the highly-curated list of 20 tips to help you grow and succeed as an intrapreneur:
1. Know Your Stuff
“Knowledge is love and light and vision.” Helen Keller

Intrapreneurs should be well aware of the goings-on and have a firm knowledge about the project or company they are working for. In addition, you should know your idea and vision front and back. Remember, a research-backed idea is always taken more solemnly than a vague idea.
2. Know What Is Going On In The Company

Knowing the company better can help you become a thriving intrapreneur. The projects that are going on, the company’s goals, and marketing strategy. Having this knowledge will help you better formulate your plans and strategies.
3. Create A Plan

A properly written plan shows the clarity of your thoughts. Planning enables you to avoid future uncertainties and has steady progress. A proper program helps Intrapreneurs achieve short-term and long-term goals and communicate their ideas with owners.
4. Align Your Of Ideas

Your ideas must align with the company’s strategic goals and vision. For example, say you are an intrapreneur at a cake shop, but you have a great idea about creating custom shoes for players. Does the objective of the company align with your vision? Unfortunately, no. The shop owner will probably not back you up for the idea. Instead, coming up with a creative marketing campaign that targets the young demographic and executing it would bring value to the business. Hence your thesis should go hand in hand with the company’s objectives.
5. Stay Passionate
“You have to be burning with an idea, or a problem, or a wrong that you want to right. If you’re not passionate enough from the start, you’ll never stick it out.” Steve Jobs

The small hurdles come up, and working on the same thing becomes monotonous. The fire that you started with begins to dwindle. Ask yourself, why did you start this in the first place? What problem were you trying to solve?
Stay passionate and hungry. This way, you can motivate and lead your team and make your ideas come to life.
6. Develop Your Entrepreneurial Leadership Skill
“Becoming a leader is synonymous with becoming yourself. It is precisely that simple and it is also that difficult.” Warren Bennis

An intrapreneur has the power to bring exponential growth to a company. But only if they have the skills to influence and motivate their team towards a common purpose.
Entrepreneurial leadership skill enables an intrapreneur to manage a group of people behind them and achieve the business objectives through innovation and creativity.
7. Share your idea

Make your idea spread like a virus. The more people you reach out to and discuss your opinion, the more feedback you get to refine your idea and build a more substantial supporter base for your idea.
Present your ideas confidently and boldly. This grabs people’s attention and gets them excited about your idea.
8. Be Open To Changes
The feedback and suggestion from people are valuable. Openness to change will help you improve your idea and, over time get a filtered idea that is more likely to succeed.
9. Be Confident
“Confidence is contagious. So is lack of confidence” Vince Lominbardi

If you believe in your idea, everyone will. With confidence in yourself and your idea, you can cut through the stormy seas. Light is at the end of the tunnel but sometimes the tunnel can be longer and confidence will help you survive through it.
10. Don’t Work For A Salary, Work To Add Value

With your skillset and unique ideas, you can bring real value to the company. Employees are those who work for a salary. An intrapreneur works to bring value to the company and its customers. Bringing impact on people’s lives is the purpose of an intrapreneur
11. Prepare A Killer Presentation

The way you present your ideas is sometimes more important than the idea itself. For example, although you have a million-dollar idea without a powerful presentation that resonates with people, no one will trust you.
If you cannot hook your audience within 10 minutes of your presentation, most likely, they will not listen to the rest of it. On the other hand, your presentation can make people as excited about the idea as you are or make you throw your idea into a trash can. So, be prepared with a killer presentation ahead of time.
12. Surround Yourself With Like-Minded Individuals

You are the product of the environment and culture you grew up with. Being around people with an entrepreneurial mindset helps you develop a similar thought process. Rather than sitting folks at a coffee shop and criticizing the government, spend your time with self-motivated, enthusiastic individuals who strive to achieve higher standards.
13. Be Responsible

Avoiding responsibility for the failure of ideas is the most common mistake entrepreneur and intrapreneurs make. It is always easy to blame someone. Successful intrapreneurs have a sense of ownership of the company even though they do not own the company.
14. Go Beyond What You Are Expected

Doing what you are expected to do is the job of an employee. As an intrapreneur, you have to go beyond what is expected from you. Generate new ideas, execute them and add value to the company. Be the reason for the success of the company and let your presence matter.
15. Master The Art Of Execution
“People may doubt what you say, but they will believe what you do.” Lewis Cass
Firstly, have a crystal clear image of your plan in your mind and then execute the plan but it is way easier said than done.

Rather than getting stuck on developing new strategies, executing existing strategies should be prioritized. Learn to proactively plan and execute strategy and get the business to new heights.
16. Build Trust

An organization can only foster if the workers and leader trust each other. Trust is pivotal for the free flow of ideas and creativity. It is burdensome to communicated and coordinate with untrustworthy individuals. Building trust is important in any relationship. So, be honest, admit your mistakes, be helpful and build a trustworthy community at work.
17. Ask For Help

Seek help from the experts in other departments like the marketing department, IT department and ask for advice from the entrepreneur. Often, they will be delighted to help you out. With their help, you can develop and execute strategies in a structured and systematic manner to skyrocket the business.
18. Practice Delayed Gratification
It takes years to make an overnight success. Eddie Cantor

The marshmallow test perfectly demonstrates the connection between delayed gratification and success in life. Delayed gratification is overcoming the temptation of instant rewards to get more valuable and precious rewards in the future. The instant gratification we get from social media is addictive. Patience and consistency is the key to a company’s success and you can excel in intrapreneurship and life by practicing delayed gratification.
19. Be Proactive, Not Reactive

Great leaders are proactive. Being reactive is reacting to the problems as they occur whereas proactive is being prepared to solve a problem before it occurs. Aim high, think long-term, pre-plan, and develop problem-solving skills to have a smooth sailing journey as an intrapreneur.
20. Expedite The Process

All businesses desire to save money, save time and get the work done effectually and if you can help them do that, you will bring value to the company. Identify the customers’ problems and find a better way to solve them and help the company stay ahead of its competitors.
Bottom Line
There is no such thing as overnight success. It takes time, persistence, and dedication. We hope these 20 tips will help you harness your skills and provide you with the guidance to grow your company and reach new heights.
10 Killer Digital Marketing Tips To Promote Your E-commerce Store
Post a comment click here to cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is an Intrapreneur?
History of intrapreneurship, characteristics of an intrapreneur.
- Intrapreneur FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Leaders
- Entrepreneurs
What Are Intrapreneurs? History, Role, and Benefits for a Company
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Investopedia / Julie Bang
An intrapreneur is an employee who is tasked with developing an innovative idea or project within a company. The intrapreneur may not face the outsized risks or reap the outsized rewards of an entrepreneur; however, the intrapreneur has access to the resources and capabilities of an established company.
Key Takeaways
- An intrapreneur works inside a company to develop an innovative idea or project that will enhance the company's future.
- The term "intrapreneur" is a portmanteau of the two words "internal" and "entrepreneur." It was first coined by Gifford Pinchot III and Elizabeth S. Pinchot in a 1978 white paper.
- The intrapreneur is generally given autonomy to work on a project that may have a considerable impact on the company.
- Over time, an intrapreneur may turn into an entrepreneur and start their own venture outside of the established organization.
- Intrapreneurs are typically highly motivated individuals who have specific skill sets—as well as leadership abilities and an innovative vision that others in the corporation can get behind.
Roles of Intrapreneurs
Intrapreneurs are employees of a company who are assigned to work on a special idea or project. They are given the time and freedom to develop the project as an entrepreneur would.
However, they are not working solo. Intrapreneurs have the resources and capabilities of the firm at their disposal.
An entrepreneur starts a company as a means of providing a good or service. An intrapreneur seeks to improve an existing company.
Intrapreneurs and entrepreneurs have different objectives. An entrepreneur envisions creating a company from the ground up. An intrapreneur has a broader vision for an established company. This vision may involve radical changes to company traditions, processes, or products. The intrapreneur typically has direct applicable skills and experience to bring to the job.
The term "intrapreneur" is a portmanteau of the two words "internal" (or the prefix "intra" to mean internal) and "entrepreneur." It was first coined by the couple Gifford Pinchot III and Elizabeth S. Pinchot in a 1978 white paper titled "Intra-Corporate Entrepreneurship" for the Tarrytown School for Entrepreneurs. After this white paper was released, the term began to gain traction in various academic studies. In February 1985, Time magazine had an article "Here Come the Intrapreneurs" which popularized the term even further.
Benefits of Intrapreneurship
An entrepreneur starts a company as a means of providing a good or service. An intrapreneur explores policies, technologies, or applications that will help improve the performance of an existing company. Inevitably, as an intrapreneur develops the skills needed to recognize and solve important problems, that intrapreneur may turn into an entrepreneur.
An intrapreneur can expect to be given the freedom and autonomy needed for such a project. Day-to-day deliverables are generally not demanded. The intrapreneur is expected to analyze and understand the trends necessary for planning the company’s future. Intrapreneurs synthesize their findings and make proposals for staying ahead of their competitors.
An intrapreneur is usually given the freedom and autonomy needed to explore new projects, but sometimes they have to do this in addition to their regular day job.
Intrapreneurs often become a company’s executive leaders over time. They move the business forward and rise to the top with a deep understanding of the business from all levels. When intrapreneurs work at solving problems, they foster the growth of other talented intrapreneurs and integrate more new ideas for the good of the entire company.
In the original "Intra-Corporate Entrepreneurship" whitepaper, Pinchot outlines that intrapreneurs are people who follow some of the following principles, including:
- Risk something of value to themselves; such as time or financial sacrifice.
- Share the reward of an intrapreneurial project between a corporation and the intrapreneur in a defined and equitable way.
- Give the intrapreneur the ability to build something akin to capital.
- Are given independence by the corporation, after it is earned.
- Become their own "venture capitalist" within a corporation
Intrapreneurs are typically highly motivated individuals who have specific skill sets—as well as leadership abilities and an innovative vision that others in the corporation can get behind. Although intrapreneurs may have their "day job" and usual assignments on top of their new venture, they are willing to take certain risks and interpret trends in the marketplace to visualize the next steps that a company may need to innovate or stay ahead of the competition.
Example of an Intrapreneur
In less than a year on the job as eBay’s chief of staff of global product management, Healey Cypher realized the company was missing out on a major business opportunity.
At the time, eBay offered only e-commerce services to its clients. Despite the growth of Internet retail, the majority of consumer purchases are still made within 15 miles of a consumer’s home. Many eBay retailers told Cypher they wanted a physical retail presence as well.
After consulting with eBay’s chief executive officer (CEO), Cypher assembled a team of engineers to develop tools that could be used to create an eBay presence in physical stores. The engineers created an interactive storefront that Toys"R"Us eventually installed. Over the following two years, the engineers did the same for TOMS, Sony, and Rebecca Minkoff.
Cypher’s success became a new division of eBay, giving workers autonomy for solving problems and moving the company forward. Cypher became eBay's Head of Retail Innovation.
What Is the Difference Between an Entrepreneur and an Intrapreneur?
An entrepreneur envisions creating a company from the ground up. An intrapreneur works within an established corporation to develop an innovative idea or project.
Who Is Called an Intrapreneur?
What is the role of an intrapreneur.
An intrapreneur explores policies, technologies, or applications that will help improve the performance of an existing company.
What Is the Intrapreneurial Mindset?
An intrapreneur has a broader vision for an established company. This vision may involve radical changes to company traditions, processes, or products. The intrapreneur typically has direct applicable skills and experience to bring to the job.
How Do You Become an Intrapreneur?
Intrapreneurs are high-performing employees who are typically assigned to explore new ways for a company to innovate, improve its existing products, or stay ahead of the competition; however, intrapreneurs are not always assigned this role and individuals with innovative ideas can also surface them or work on these projects on the side, before introducing them to senior leadership.
Intrapreneurs are often overlooked within the realm of entrepreneurship, but innovation with already established corporations can also be world-changing. In many senses, intrapreneurs get the best of both worlds: the autonomy to pursue innovative projects and the financial backing of a company that has resources and attention to devote to these strides.
MIT Management Sloan School. " Intrapreneurship, Explained ."
Google Drive. " Intra-Corporate Entrepreneurship ."
Time. " Here Come the Intrapreneurs ."
eBay. " eBay Inc.'s Healey Cypher Named to SVBJ's 40 Under 40 List ."
LinkedIn. " Healey Cypher ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/intrapreneurship.asp-final-145a12d7892a450da49ad1290ebeec87.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Intrapreneurship Mastery
Why Intrapreneurs Don’t Need a Business Plan (And What You Should Use Instead)
Business Model
minute reAD
Business plans are usually thought of as crucial to any project that aims to bring a new product or service to market. They’re seen as the “roadmap to success”. But in reality, they are actually detrimental to innovation projects and a LONG way from being the best tool for intrapreneurship.
In this article we’ll look at why they fail and provide you with a better alternative to use instead.
The Problem with Business Plans
If you’ve ever worked on a project, led a business unit, or proposed any new piece of work at your company, then you’ll likely have created an outline planning document to set out the costs, the intended benefits and a plan of action.
Depending on your company processes and the size of the project you are proposing, this planning document might have been called a Business Plan , a Business Case , or possibly a PID (Project Initiation Document).
You might even have called it something else in your company, but regardless of the name, it will likely include the same basic content:
- An explanation of the scope of the work
- An estimate of costs, effort and resources
- A timeline, possibly including a Gantt Chart
- Some milestones along the way
- An estimate of the benefits / results expected
- A revenue forecast for the next 2-3 years
- A justification of the costs of the project based on the expected benefits.
That’s a heck of a lot of planning effort. And a heck of a lot of GUESSWORK.
Yes, guesswork! Let’s be honest about what’s happening here. When we work on innovation projects, we genuinely don’t know whether our innovation will be successful.
We don’t know if people want it, we don’t know if they’ll buy it, and we don’t know if they’ll use it. We can’t even be confident that the solution we end up with will resemble the same one we started out with! In a project where there are so many uncertainties and ANYTHING could change, any plan we create at the start is no more than a work of fiction. In other words, everything about an innovation project plan is guesswork. It’s a plan based on what we HOPE will happen, rather than a plan based on any kind of EVIDENCE of what will happen.
Eric Reis put it well when he wrote “Planning and forecasting are only accurate when based on a long, stable operating history and a relatively static environment.”
Innovation projects have neither.
And yet companies cling to the business plan, because they lack any kind of credible alternative.
The Challenge of Planning Innovation Projects
Unlike a plan for an existing business unit, innovation projects have no operating history; we are often striving to enter a new market where we have little experience; and (because companies are seeking to manage the financial risk) we usually have modest funding.
Putting it all together we have:
- An incomplete Business plan,
- Untested Market Demand, and
- Inadequate Funding.
When we put it like that the challenge for intrapreneurs and companies alike is clear.
Instead of a “fantasy plan”, what we need is a way for us to document our strategy, and a process through which to evolve it: A new kind of plan that can adapt and change as we learn more about the market, about our own capabilities, and about what really brings us success.
The Tools to Use Instead
Okay, we’re all agreed. Business Plans are useless for intrapreneurs. But the learning we get from the act planning is essential.
How can we do some planning and document our learnings without the onerous and ineffective process of writing a business plan?
As intrapreneurs we do two things instead:
- Create a “best-guess” Business Model to use as a starting point for our exploration
- Use a structured and systematic process to help us decide exactly what to do next, as events unfold
Let’s look at both of those in a bit more detail.
The Business Model
For early stage exploration, we love using the Lean Canvas . It’s our tool of choice and we teach it in all our courses .
If you’re familiar with the Business Model Canvas and it’s companion, the Value Proposition Canvas, you’ll find that that the Lean Canvas omits some of the boxes that aren’t so important for early-stage innovation projects. By doing so it provides wonderfully succinct one-page summary of all the key things you need to think about on a day-to-day basis.
When we use the Lean Canvas, instead of spending days or weeks researching and writing a business plan, we can often brainstorm a business model in a few hours. The business model captures all our assumptions about the customer, our offering, how we will enter the market, how we will make money… and much more.
Then it’s time to move rapidly on to testing our ideas in the real world. That’s when we need a process…
Running Growth Experiments
Launching a new product or service is an iterative journey. At the heart of that journey are Growth Experiments. These are experiments that are performed by intrapreneurs who want to test out parts of their business model and validate (or invalidate) their assumptions.
Growth Experiments provide the structure through which intrapreneurs can deliver new value to customers and drive growth.
Growth Experiments work like this:
- Review your business model and identify the assumptions
- Prioritize the risks
- Formulate a hypothesis. Like a scientist, make a prediction about what will happen if you perform a specific, repeatable action
- Plan an experiment to test your hypothesis
- Build your experiment and collect the data
- Analyse, learn and make a decision about what to do next
To learn more about how to develop a business model for your internal startup, and how to plan, build and learn from growth experiments, the best place to start is our Intrapreneurship Mastery Programme . Or, if you want to read some more first, we’ve got a free intrapreneurship guide that goes into more detail too.
We hope this article has provided some insight into why business plans should be avoided by intrapreneurs. If you have any questions about business plans, business models or growth experiments feel free to message us .
You may also like
The vital role of a vision statement in innovation projects, the subtle art of crafting a vision statement: 3 big mistakes and how to avoid them, 30 best intrapreneurship books to read in 2024, how to read and evaluate a business model using the lean canvas, join the intrapreneur nation global community of intrapreneurs.
Subscribe to our newsletter and we'll send you the complete "Corporate Entrepreneurship Roadmap" guide. Your FREE blueprint to effective corporate innovation.
By signing up you agree that we may contact you regarding intrapreneurship resources and offers. Your details will be processed in accordance with our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time. If you prefer not to be contacted, simply email us and we'll send you the Blueprint directly.
Privacy Overview
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
How to Identify Intrapreneurs Within Your Company Intrapreneurs are indispensable investments for your organization. Here's how you can identify them early.
By John McGrath Edited by Dan Bova Apr 4, 2016
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
An intrapreneur is the manager or employee who recognizes problems as opportunities to advance and improve the company from the inside out. They function as leaders who challenge processes and invigorate ideas. Intrapreneurs often drive progress within a company's infrastructure without direct guidance from management. With an entrepreneur's spirit, an inventor's capacity to solve complex problems, and a passion for adjusting operational systems, intrapreneurs are most likely working for you, but would you know how to identify them?
Intrapreneurs are indispensable investments for your organization. Identify them early and ensure they have the room and resources to thrive and help your company grow.
You can identify successful intrapreneurs in your company using these common traits:
Total commitment
Being a highly successful intrapreneur is a full-time responsibility. The intrapreneur's mind is constantly working and challenging the status quo. They are architects of new ideas, new plans and better methods. The intrapreneur sees the world through the lens of the administrative and financial operations of the business and relates everyday decisions into growing and improving the company. They often listen and learn from entrepreneurs, typically the CEO and/or president, incorporating their knowledge to create plans for internal improvement.
Related: Intrapreneurship is the New Entrepreneurship
Adaptability
Intrapreneurs function well in a start-up industry because of their ability to thrive in a changing environment. They are excellent at observing, reflecting, accepting, and then adapting. They often create solutions from a new starting point. They welcome growing pains. It's often said that the squeaky wheel gets the grease; intrapreneurs are those who grease the wheels without always looking for praise.
Internally motivated
Though intrapreneurs appreciate the value and importance of return on investment, they generally are not solely driven by profit. They typically are motivated by how they can contribute to further the overall success of their company. Intrapreneurs typically initiate meaningful innovations within their departments before expecting or requesting a raise.
One of the most, if not the most, important element in business is the possession of confidence. Self doubt weighs heavily on an individual's confidence and ability to creatively perform, think and act -- which progressively deteriorates corporate profitability. Having a high level of confidence is critically important. Confidence is a state of mind and a state of being. Positive thinking and engagement with like-minded people is central to the dynamic creation and execution of successful business plans which promotes attractive returns on investment.
Related: 6 Steps for Converting Employees Into Intrapreneurs
Intrapreneurs are generally even-tempered. When a company is in change, intrapreneurs keep a level head. Employees tend to follow an executive with a consistent and balanced temperament compared to an inconsistent or negative attitude. Effective management encourages creative minds to seek solutions during tough organizational challenges.
The straight shooter
Honesty and transparency are central to creating and maintaining a successful intrapreneurial corporate culture. Intrapreneurial chief executive officers should:
- Create a culture of innovation and dynamic leadership.
- Create a culture of integrity and compliance.
- Advocate for a culture of shared vision and teamwork.
- Advocate a core value system to have courage, determination and a contagious spirit to do what is right, regardless of the difficulties or consequences.
The mirror effect
The best way to ensure your company will attract the intrapreneurial spirit is to foster creativity in your company culture. Many entrepreneurs are (or were) intrapreneurs. Entrepreneurs often have the ability to identify mirror images of themselves and make room for advancing those employees to help the company succeed. The creation of intrapreneurial spirit could be exactly what it takes for your business to achieve the best possible results while fostering loyal, career-minded individuals that share your determination for success.
Related: 5 Must-Have Skills of Intrapreneurs Inside Their Grown-Up Startups
Closing note
Chairman, CEO and President of American Collegiate Acquisitions, Inc.
Dr. John J. McGrath is the Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and President of American Collegiate Acquisitions, Inc. (ACA) . He is a higher educational expert and business executive with experience in academic administration including being the chairman of the board, CEO, president, assistant vice president, campus dean, department chairman, distinguished professor and professor at multiple colleges.
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock The Average American Can't Afford a House in 99% of the U.S. — Here's a State-By-State Breakdown of the Mortgage Rates That Tip the Scale
- Richard Branson Shares His Extremely Active Morning Routine : 'I've Got to Look After Myself'
- Lock This Flexible, AI-Powered Side Hustle Lets a Dad of Four Make $32 an Hour , Plus Tips: 'You Can Make a Substantial Amount of Money'
- Tennis Champion Coco Gauff Reveals the Daily Habits That Help Her Win On and Off the Court — Plus a 'No Brainer' Business Move
- Lock 3 Essential Skills I Learned By Growing My Business From the Ground Up
- 50 Cent Once Sued Taco Bell for $4 Million. Here's How the Fast-Food Giant Got on the Rapper's Bad Side .
Most Popular Red Arrow
One of america's oldest companies just laid off 600 workers as it shifts focus to production in mexico.
Over 600 John Deere employees in Iowa and Illinois were laid off effective August 30.
Here's How Much Investing $10,000 in Nvidia When It Went Public Would Be Worth Now
Nvidia was founded in 1993 and went public in January 1999, first trading at $12 per share.
How Entrepreneurs Can Apply the 7 Laws of Success to Their Business and Personal Life
Most folks have a hard line between work and life. "It's just business," "I am a different person at work," etc. But what if we brought some of the beauty of the personal into the professional?
How to Text Customers Without Getting Sued — Your SMS Marketing Compliance Guide
SMS marketing is a growing channel, but you've got to stay compliant with regulations. Here's what to know and do.
The Best Funding Resources for Entrepreneurs With Disabilities
There are numerous options to assist those in need.
"It Was Horrifying and Scary": Bar Rescue's Jon Taffer Describes the First Time He Screamed at Someone on Camera
Here's why Jon Taffer first started yelling on TV — and what it can teach every new manager.
Successfully copied link

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 4. Sketch. After taking the time to choose a target market for your corporate startup, and then performing first-party research to get a full understanding of the problem, Step 4 of the Corporate Entrepreneurship Roadmap is to focus on solutions. But you won't be building anything yet.
Definition of Intrapreneurship. Intrapreneurship is the secret weapon of successful companies, where employees with an intrapreneurial mindset work within the existing framework to create innovations that secure the company's future. These employees, known as intrapreneurs, apply entrepreneurial skills to develop new ideas and projects that ...
5 Best LinkedIn Profile Writing Services in 2024; ... As always, a business plan lays out how you're going to get from where you are now to where you want to be, based on solid research and analysis of things like markets, competitors, pricing, marketing, and credible financial projections, along with an innovation strategy — how to work ...
In order to be an intrapreneur, do the following six things: 1. Have ideas, and write them down. Keep your eyes and ears open, and constantly think of ways that can help your company. Write your ...
Conclusion: What You Can Learn From These Intrapreneur Examples. Intrapreneurship is all about harnessing the entrepreneurial spirit within an established organization. The examples of intrapreneurs we have explored demonstrate that innovation and creativity can come from anyone, regardless of their position or title within a company.
To create intrapreneurs, reverse the job description process. Match an employee's gifts with your company's needs. This ensures your company's needs are addressed by a person with the ...
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here's what Cobello recommends: 1. Conduct your research. Before writing your business plan, you'll want to do a thorough investigation of what's out ...
Entrepreneurship is the process that turns those ideas into actual innovations, and when it occurs in large corporations we tend to refer to it as intra preneurship or corporate innovation. In ...
A business plan is of significant importance when it comes to guiding entrepreneurs in succession planning, which involves preparing for the future transition of leadership and ownership within a business. To effectively use a business plan for succession planning, assess current leadership and ownership, identify potential successors, define ...
Conclusion. Intrapreneurship, the practice of applying entrepreneurial principles within established organizations, fosters innovation and growth. It plays a significant role in empowering employees to drive innovation from within. Intrapreneurship isn't just a concept; it's a catalyst for innovation, adaptability, and sustainable growth.
Both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs apply qualities like passion, empathy, critical thinking and collaboration to help their organizations compete and evolve. Yet although they use similar ...
1. Be Persuasive. To explore your ideas, you'll have to get buy-in from your company and convince your boss that they should take a risk on your plan. When you present your ideas, you'll have to be able to clearly and fully explain your reasons for wanting to pursue the project. You can help convince your company to take a risk on your idea ...
The Complete Guide to Intrapreneurship is full of insights and strategy for product managers, business leaders, innovation managers and anyone else looking to refine their current skills and get up to speed on how to take new ideas and innovations to market. Read it now to build and refine your new product development plan without the false ...
A professional coach or a mentor working in the management tier can analyze a business plan, identify the weaknesses and optimize the right processes. The specific caveats that require attention are better identified by the entrepreneur or intrapreneur - although they may be unaware of details that could, in fact, be a major obstacle.
Essentially, an intrapreneur is an employer-sponsored entrepreneur. Some key characteristics of intrapreneurs are: They risk something of value, like time or effort. They innovate and create. They work independently within their company. They locate necessary resources within their company. They share the reward of their risk with their company.
from an existing business who can share technical, human and financial resources R N N R N N to help drive the project forward and develop it into a successful new business! Who can be an INTRAPRENEUR? Someone with an entrepreneurial spirit who has an innovative idea that they would like to launch with the support of a mentor from their network ...
7. Be Conscientious and Disciplined: The Foundation of Achievement. Organization, dependability, and hard work are essential traits for intrapreneurs. They follow through on their commitments and keep their projects on track, ensuring that their ideas come to fruition.
Plus, being an intrapreneur allows you to pursue a passion project with the added benefit of having a company's resources and budget—as opposed to having to start from scratch and launch it all on your own. As an intrapreneur, your experience is tied to in-demand skills that are transferable anywhere you go, instead of a specific job title.
In a nutshell, intrapreneurship is simply entrepreneurship within an organization or company. Intrapreneurs are entrepreneurs operating within the structure of a company. They are at the forefront of innovation and are given control of products and services that affect the company's future growth. Read on to discover how intrapreneurship ...
Here is the highly-curated list of 20 tips to help you grow and succeed as an intrapreneur: 1. Know Your Stuff. "Knowledge is love and light and vision.". Helen Keller. Intrapreneurs should be well aware of the goings-on and have a firm knowledge about the project or company they are working for. In addition, you should know your idea and ...
You can use these six steps to help create better pitches to potential clients. Just reframe the language a little, and you'll be well on your way to more sophisticated proposals.) Step one ...
Intrapreneur: An intrapreneur is an inside entrepreneur, or an entrepreneur within a large firm, who uses entrepreneurial skills without incurring the risks associated with those activities ...
When we use the Lean Canvas, instead of spending days or weeks researching and writing a business plan, we can often brainstorm a business model in a few hours. The business model captures all our assumptions about the customer, our offering, how we will enter the market, how we will make money… and much more.
Entrepreneur India. An intrapreneur is the manager or employee who recognizes problems as opportunities to advance and improve the company from the inside out. They function as leaders who ...