
Essays About Creativity: Top 5 Examples and 7 Prompts
Creativity helps us understand and solve problems in different ways. Discover our top essays about creativity examples and use our prompts for your writing.
Albert Einstein defines creativity as “seeing what others see and thinking what others have not thought.” But what makes it such a popular topic to write about? Every person has a creative view and opinion on something, but not everyone knows how to express it. Writing utilizes ideas and imagination to produce written pieces, such as essays.
Creativity reinforces not only new views but also innovation around the world. Because creativity is a broad topic to write about, you’ll need several resources to help you narrow down what you want to discuss in your essay .
| IMAGE | PRODUCT | |
|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | ||
| ProWritingAid |
5 Essay Examples
1. way to foster creativity in young children by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 2. phenomenon of creativity and success by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 3. do schools kill creativity: essay on traditional education by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 4. creativity in dreams essay by writer pete, 5. the importance of creativity in higher education by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 1. what is creativity, 2. how creativity affects our daily lives, 3. the impact of creativity on students, 4. the importance of creativity, 5. creativity: a product of perception, 6. types of creativity, 7. art and creativity.
“There are different ways to foster creativity in young children. They include different approaches to the problem of making children more self-reliant, more creative, and more interested in the process of receiving education, obtaining experience, achieving certain results in the sphere of self-study.”
The essay delves into the importance of promoting creativity by teaching music to young students. The author says music’s intention, rhythm, and organizational features help people understand performance, improve their mood, and educate them about the world they live in, unlike noise. Music is an important area of life, so it is important to teach it correctly and inspire children.
Since music and creativity are both vital, the author notes that music teachers must find ways to facilitate ventures to enhance their students’ creativity. The author also believes that teachers must perform their duties appropriately and focus on shaping their students’ behavior, personality, and worldview. You might be interested in these articles about art .
“Over the past few decades, creativity has evolved from a characteristic normally associated with artistic activities into a quality that is found in people of various professions. However, in the 21st century, creativity has become a rather controversial issue.”
The author discusses that while creativity dramatically contributes to the success of individuals and companies, creativity in the 21st-century workplace still has mixed reception. They mention that creativity leads to new ideas and innovations, helps solve complex problems, and makes great leaders.
However, some still see creative people as irrational, disorganized, and distracting in the workplace. This often results in companies rejecting applicants with this quality. Ultimately, the writer believes creativity is vital in all organizations today. Hiring people with this unique trait is highly beneficial and essential to achieving the company’s goals. For more inspiration, check out these essays about achievement and essays about curiosity .
“… the traditional education system has caused much controversy since the beginning of formal education because traditional education can hurt children’s ability to think creatively, innovate, and develop fascinating minds.”
The essay discusses how school rules and norms affect students’ expression of true individuality. The author mentions that today’s schools focus on students’ test performance, memorization, and compliance more than their aspirations and talents, preventing students from practicing and enhancing their creativity.
The author uses various articles, shows, and situations to elaborate on how schools kill a student’s creativity by forcing them to follow a specific curriculum as a means to succeed in life. It kills the student’s creativity as they become “robots” with the same beliefs, knowledge, and values. According to the writer, killing a child’s creativity leads to a lack of motivation and a wrong career direction.
“Creativity is enhanced whether one chooses to pay attention to it, or not. Each person has the capacity to learn much from their creative dreaming, if they would only think more creatively and openly when awake.”
The essay contains various studies to support claims about people being more creative when asleep. According to the author, the human brain processes more information when dreaming than in the waking state. While the brainstem is inactive, it responds to PGO Waves that trigger the human CMPG, which puts images into the dream to move. The author discusses two main perspectives to discuss how creative dreaming occurs.
First, creativity is enhanced when a person sleeps, not through dreaming but because the mind is free from stress, making the brain more focused on thinking and creating images. The second is that the dreaming mind gathers and processes more information than the human brain unconsciously accumulates daily. The author states that creativity helps express feelings and believes people should not take their creativity in dreams for granted.
“When students have the opportunity to be creative, they’ll have the freedom to express themselves however they want, which satisfies them and drives them to work hard.”
The essay focuses on how the role of creativity is getting slimmer as a student enters higher education. To explain the importance of creativity, the author shares their experience showing how elementary schools focus more on improving and training students’ creativity than higher education. Although rules and restrictions are essential in higher education, students should still practice creativity because it enhances their ability to think and quickly adapt to different situations.
If you want to use the latest grammar software, read our guide to using an AI grammar checker .
7 Prompts for Essays About Creativity
Creativity is an important topic that significantly affects an individual’s development. For this prompt, discuss the meaning of creativity according to experts versus the personal interpretation of creative individuals. Compare these explanations and add your opinion on these similarities and differences. You can even discuss creativity in your life and how you practice creativity in your hobbies, interests, and education.

There are several impacts of creativity in one’s life. It improves mental health, strengthens the immune system, and affects one’s ability to solve problems in school and real life. Sometimes, being creative helps us be more open to various perspectives to reduce our biases.
Use this prompt to write about a specific situation you experienced where creativity made you more innovative, inventive, or imaginative. Discuss these particular moments by pointing out creativity’s impact on your goal and how things would differ without creativity. You may also be interested in learning about the different types of creativity .
Creativity significantly impacts students’ enthusiasm and feeling of belongingness as they share their passion. Additionally, creativity’s effects stretch to students’ career choices and mental health.
Use this prompt to start a discussion of the pros and cons of creativity with students. Give examples where a student’s creativity leads to their success or failure. You can also share your observations as a guardian or a student.
Sometimes, when we lose touch with our creative side, our viewpoint becomes shallow. Creativity not only works for art but also broadens everyone’s perspectives in life.
For this prompt, speak about how creativity matters and prove its importance by providing a situation. Theorize or discuss how creative people and people who fail to increase their creativity respond to the case.
Perception is an underlying characteristic of creativity. It interprets what we observe, while creativity allows us to make sense of them. Use this prompt to define perception to the readers through the lens of creativity.
List your experience proving creativity is a product of perception. For example, people can have vastly different interpretations of a painting or sound depending on how they perceive it.

There are several types of creativity, some people believe creativity is a natural talent, but others say it can be cultivated. In this prompt, briefly define creativity and identify each type, such as musical, artistic, or logical.
Discuss how creativity can be taught and cultivated, and look into how some people are naturally creative. In your essay , use real-life examples; this could be someone you know who has studied a creative subject or a friend who is a naturally creative songwriter.
When people say creativity, they usually think about art because it involves imaginative and expressive actions. Art strongly indicates a person’s ongoing effort and emotional power.
To write this essay effectively, show how art relates to a person’s creativity. Briefly explain creativity and art and incorporate the factors that link these two. Note that art can be anything from contemporary dance and music to sculptures and paintings. For help with your essay , check our round-up of best essay writing apps .
Home — Essay Samples — Arts & Culture — Creativity
Essays on Creativity
Crafting a creativity essay is an exciting journey into exploring and articulating the nuances of creativity, innovation, and original thought. This type of essay offers a unique platform to focus on personal insights, historical analysis, or the impact of creativity across various fields.
Engaging Prompts to Kickstart Your Creativity Essay
Prompt 1: Discuss how a moment of creative insight led to an unexpected outcome or discovery in your personal life or in a historical context.
Prompt 2: Analyze the role of creativity in solving a complex problem in an area of your interest, such as technology, art, or social change.
Prompt 3: Reflect on the process of creative thinking in your own life or in the work of an individual you admire. How does this process defy conventional wisdom?
Brainstorming Techniques for a Captivating Creativity Essay Topic
To unearth a compelling essay topic, immerse yourself in environments that spark your creativity. Reflect on personal experiences where creativity led to meaningful insights or outcomes. Explore historical instances where creativity has reshaped industries or societies. Aim to find a unique angle or a less-trodden path that can provide fresh perspectives on the nature of creativity.
Innovative Creativity Essay Topics to Explore
- The Impact of Digital Technology on Creative Expression in the 21st Century
- Creative Failures: How Mistakes Have Paved the Way for Success
- The Role of Creativity in Environmental Conservation Efforts
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Creativity and Innovation
- The Psychology Behind Creative Blocks and How to Overcome Them
Inspirational Writing Samples for Your Creativity Essay
"In the realm of creativity, every failure is not a dead end but a detour to a new beginning. When I embarked on the journey of creating [Project/Artwork], I encountered numerous setbacks. Yet, it was through these very challenges that the project found its true direction, transforming obstacles into stepping stones toward innovation."
Phrases for Inspiration:
- "The essence of creativity lies not in the arrival but in the journey..."
- "In the tapestry of [Field/Subject], it's the threads of creative thought that weave the most vibrant patterns..."
- "Facing the abyss of the unknown, creativity becomes the bridge to unimaginable discoveries..."
- "Creativity thrives in the interplay between discipline and the freedom to explore..."
- "At the heart of every creative endeavor is a story of resilience, experimentation, and the relentless pursuit of vision..."
Disadvantages of Baskin Paper
Imagination and creativity, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
The Creative Process and Artistic Skills Involved in Cosplay
The importance of creativity in education, creativity is not enough in modern world, the importance of creativity in higher education, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Creativity and Innovation in Our World
The impact of leadership and empowerment on creativity in the workplace, how education kills creativity in students, my style of creative writing, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Digital Creativity in Innovation
The detrimental impact of technology on human creativity, knowledge-based design and design creativity, foods that boost creativity, creative writing: definition, types, essence, a critique of the giant book of creativity for kids, a book by bobbi conner, art spaces in singapore, the link between creativity and psychopathology in salvador dali’s art, nostalgia as a form of escapism in contemporary art and design, technology and creativity in richard louv's "last child in the woods", the reveal of the hypocrisy of the mabo decision within political cartoon, do schools kill creativity speech analysis, honesty perspective: artist or audience, marigolds by eugenia collier summary, the importance of creative intelligence, discussing the relationship between intelligence and creativity, the joy of reading and writing superman and me analysis, the tone of the glass castle, exploring through the lens: my passion for photography, all around me poem analysis, relevant topics.
- Art History
- Frida Kahlo
- Vincent Van Gogh
- Ethnography
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
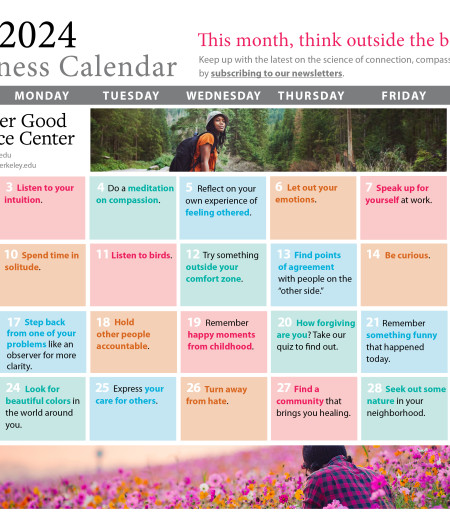
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Eight Lessons From My Research on Creativity
When I was at the beginning of my Ph.D. studies, my advisor at Stanford, Professor Gordon Bower , invited each of his first-year graduate students to his house for dinner. After dinner, he asked each of us what we wanted to study in graduate school.
We all thought we knew what he wanted to hear—“ semantic memory ”—which was what he was studying. There were five guys there, all of us first-year students (and all male). The first one got up and he said, as you would predict, “semantic memory.” The second and third guys said the same. I knew at least two of them were lying and just sucking up. It was like a Solomon Asch experiment, where people hear others lie and then say the same thing so as to be part of the crowd.
Then my turn came. I assure you, I’m no suck-up. I knew what I wanted to study, and it wasn’t semantic memory. But when Gordon asked me what I wanted to study, I said…. “semantic memory”! Like the others, I chickened out. Or to put it another way, I was a coward. What I really wanted to study was human intelligence and creativity. I was just afraid to admit it.
That night, I was humiliated. I thought that if that was the way I was going to run my scholarly career—as a coward—I needed to find something else to do. I told myself I would never sell myself out again. I never have, although I’ve certainly had many opportunities.
In a way, this episode became the beginning of a career as a psychologist studying creativity. Here are eight lessons from my research.
1. Creativity is not so much an innate ability as it is an attitude toward life.
There are lots of people with “creative abilities,” but they lack what the late Professor Roger Schank called the “creative attitude,” so they do not manifest their creativity.
By 1995, I proposed, in collaboration with Professor Todd Lubart (then my graduate student), an “ investment theory of creativity .” The idea was that creativity is, in large part, a decision that one is willing to defy the crowd—exactly what I was unwilling to do that night at Gordon’s house. Creativity requires, more than anything else, the courage to go one’s own way, regardless of what others do.
When I was a teenager, my male peers wore tight pants—all the better, they thought, to attract girls. I wore loose pants. I’m claustrophobic and tight clothes don’t work for me. I’d like to think I was showing a creative attitude. I was also showing myself to be a bit of a dork, but I didn’t care. If you are creative, be prepared to be labeled a “dork,” or worse. Maybe much worse. That’s a price you have to be willing to pay.
2. A key ingredient of creativity is courage.
You can’t be creative unless you are willing to stand up to the crowd. Sometimes, people will dump all over you, and you have to keep going, not fold.
By 2018, I came to a somewhat broader conclusion in a “ triangular theory of creativity ”—that creativity requires not only the courage to defy the crowd, but also the courage to defy oneself and all the ways of thinking that one has always assumed are just “the way things are.”
Often, the hardest thing is not to stand up to others, but to stand up to one’s own entrenched ways of thinking.
3. If you want to be creative, you have to stand up not only to the crowd, but also to yourself.
You have to be willing to let go of ideas that are either wrong or that have served their purpose and now are obsolete. When the time comes, you have to be willing to move past your ideas that have passed their prime.
I have tried to show that courage in my own career and put behind me the mistake I made at Gordon’s house. In my first book , in 1977, I defied the conventional psychometric view of intelligence as just IQ and related abilities. I argued that the problem with this view was that it failed to elucidate the information-processing components that underlie those abilities.

Contemplation and Creativity
A collection of practices that encourage contemplation and creativity
For example, someone could score low on a verbal-analogies test not because they were a poor verbal reasoner, but simply because they did not know what the words meant. If their native language was not that of the test, or if they grew up in a house that was educationally challenged, such knowledge was often not immediately available. I thought I knew all about low IQ scores, because I had had them when I was a child, I liked to think because of test anxiety.
My manuscript was published by Larry Erlbaum; he published it despite a 17.5-page negative, indeed, vitriolic review. The book later became a citation classic . I thought my creative ideas about intelligence would see me through my career.
I was wrong, as we’ll see. If you want to be creative, be prepared to say you were wrong—a lot.
4. Being creative requires you to admit you were wrong or, at least, not quite right.
If you need to be right all the time, you will cut yourself off from the possibility of being creative. You will, at best, be a one-hit wonder.
In my second year as an assistant professor at Yale, I was invited to give a lecture at a big testing company. I thought: “This is great. After all these years doing the wrong thing, they finally are ready to admit the errors of their ways and do the right thing!”
I gave the talk. It bombed. Badly. They hated it. I went from wondering what glory awaited me when I returned to New Haven to wondering whether I still would have a job when I got back. It was yet another humiliation. But then I realized what I had learned, which turned humiliation into a sense of intellectual humility .
5. The more creative your ideas are, the more resistance those ideas will encounter, and the more resilience, perseverance, humility, and sheer courage you will need to keep going in the face of opposition.
Of course, the testers hated the talk. Did I think that a company with zillions of dollars invested in conventional tests, which hired people to work for them who excelled on conventional tests and loved those tests, which showed how smart they were, were going to listen to a 26-year-old upstart? No way!
By 1985, I realized my ideas about intelligence were not as good as I had thought they were. In fact, they were seriously deficient, because although I was studying mental processes, I was studying only the mental processes needed to score high on IQ tests; buts the tests themselves were seriously flawed.
I was director of graduate studies in psychology at Yale at the time, and saw that intelligence required more than the knowledge and abstract-analytical reasoning skills required by IQ tests (and SATs and ACTs and the whole alphabet soup of standardized tests).
I had one student, “Alice,” who was test-smart but not creative; another, “Barbara,” who was highly creative but not nearly as test-smart as Alice; and yet another student, “Celia,” who lacked Alice’s analytical skills and attitudes, and Barbara’s creative skills and attitudes, but who had tremendous practical intelligence (i.e., common sense). So, I had to have the courage to defy myself and propose a new theory of intelligence, which I called triarchic, because it had three parts (analytical, creative, practical).
My work on intelligence and creativity was going well—until it wasn’t. I realized my theories were still incomplete. After a couple of decades of the 21st century, it became clear to me that intelligence and creativity, in themselves, were not nearly as wonderful as I had thought they were.
All those books and papers I had written—and many others had written as well—seemed to be missing a fundamental point. Much of intelligence and creativity were being used for dark purposes. Creative professionals were using their creativity to addict people to nicotine, alcohol, various illegal drugs, and social media that was increasing toxicity in society and even causing people to harm themselves.
As Arthur Cropley and others realized, dark creativity was a serious threat to the future of the world. Narcissistic use of creativity (and, as I have argued in a submitted paper, intelligence) literally can and might destroy the world. Intelligence and creativity without wisdom—the search for a common good—can be dangerous.
6. The world does not need more seriously smart and creative people who are using their talents to advance themselves but also to take down others in the process.
By 2021, I had written a paper on what I called “transformational creativity,” and I now have an edited book in press with Professor Sareh Karami on this topic.
Transformational creativity is wise creativity. It is creativity that makes the world a better place. It is creativity directed toward a common good.
Why is transformational creativity important? Because so much creativity is going toward truly bad ends. How much positive creativity does one see these days in the seat of U.S. government, and how much negative creativity?
7. What the world needs today is not just creativity but, rather, transformational creativity that is oriented toward achieving a common good that will make the world a better place for us all.
Transformational creativity does not seem to be commonplace in the world today. It is so much easier just to look out for one’s own interests.
In a 2022 pape r I wrote with Professor Lubart, we argued for the importance, in creativity, of integrity. Creativity with integrity means that one’s ideas are consistent with each other and that they do not just fly off into outer space. One ensures that the ideas correspond with reality—not a fantasy we imagine, or wish were true. Politicians, please take note!
8. Transformational creativity is so hard not because people lack creativity, but rather because there is so much pressure not to do the right thing—actually to thwart the common good through a lack of integrity.
In other words, courage is hard.
At various points in all our lives, we face the hard decision of whether we will, as a book title once put it, just “look out for #1.” With the serious problems the world faces—pollution, climate change, budding autocrats, weapons of mass destruction, school shootings, racism, xenophobia—we just cannot afford to keep turning out students whose main credentials are their high GPAs, standardized test scores, or preprogrammed extracurricular activities. What we all need most is transformational creativity: the courage to seek a common good in the face of the obstacles the world puts in front of us.

New Course! Courage in Education
Facing Challenges with Strength, Determination, and Hope
About the Author
Robert J. Sternberg
Cornell university.
Robert J. Sternberg is Professor of Psychology in the College of Human Ecology at Cornell University and Honorary Professor of Psychology at Heidelberg University, Germany. Sternberg is a Past President of the American Psychological Association and the Federation of Associations in Brain and Behavioral Sciences. Sternberg’s PhD is from Stanford University, and he holds 13 honorary doctorates. Sternberg has won the Cattell Award and the James Award from the Association for Psychological Science, and the Grawemeyer Award in Psychology. He has been cited over 234,000 times in the scholarly literature. He was cited in 2023 by research.com as the #7 top psychological scientist in the US and #15 in the world.
You May Also Enjoy

How to Foster Group Creativity

How to Combat America’s Creativity Crisis

Ten Habits of Highly Creative People

Five Tips for Reaching Your Creative Potential

Doing Something Creative Can Boost Your Well-Being

Why Your Creative Ideas Get Ignored
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Art
Essay Samples on Creativity
As always, it is easier to say than to do, especially if you have to pen an essay that describes being creative or what forces at play make students succeed, or what kind of secret tricks are used by musicians, artists, or athletes to achieve their great results. It does take hours of hard work, yet being creative is an important factor that is studied by most college professors as they aim to inspire students for thinking outside the box. Just remember about Steve Jobs, Elon Musk, and the other famous personalities that have reached success thanks to their creativity. As a small contribution, we recommend you to look at our creativity essay examples that will guide you through this particular task and will boost your brain as you write.
What Does Creativity Mean to You
Creativity, an intricate tapestry of imagination and innovation, holds a unique significance for each individual. It is a concept that transcends the boundaries of convention, sparking curiosity and igniting the flames of inspiration. In this essay, we embark on a journey to unearth the meaning...
Discussion on the Relationship Between Intelligence and Creativity
The relationship between intelligence and creativity has been subjected to research for many years. Unfortunately, there is yet no consensus on how these constructs are related. The connection between intelligence and creativity is that they are functions of the brain that handle data to determine...
- Intelligence
Do Schools Kill Creativity: the Issues of Music Education
In the TEDx video entitled, 'Do schools kill creativity?' Sir Ken Robinson discusses what he believes to be the main problem with our education system, providing a series of funny anecdotes and facts appropriate for his argument. After watching this video about 'Do schools kill...
Creative and Critical Thinking: Combining the Achievements of Thought
Creative, one word that can be interpreted in many ways whether in thoughts which is include ways of thinking and actions and also in verbal form. Critical, on the other side refers to the ability to analyse information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It...
- Critical Thinking
Culture, Art and Creativity: the Way They Are Related
Art is a reflection of your thinking, your ideas, and your surroundings, the artist adopts his or her surroundings and then by using their imagination, outside thinking and their perspective they present a new face of it in front of the world. Art and creativity...
- Cultural Anthropology
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
The System Of Education: If I Could Change The World
If I could change the world, I would completely change the system of education. It hasn't changed for hundreds of years, and the current system was designed in the Industrial Age. This means, that children in school have to obey every order and do only...
- Importance of Education
The Role of Creative Industries in the United Kingdom
In this essay I will go over and talk about the creative industries and the role they play in the United Kingdom, I will look at the history and the development of the Creative Industries and their sectors. I will then look at the wider...
- Great Britain
Comparing The Pros And Cons Of Books And Movies
In modern America, people are always looking for escapism and entertainment. Two of the most popular forms of entertainment that provide escapism are books and movies. Especially in today’s culture where books are constantly being turned into feature films, it is common practice at this...
- Reading Books
Evolution Of The Concept Of Auteur Theory
Auteur Theory is the concept that the director of a film is seen as the major creative force or author of a film more than what the writer of the screenplay is (The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica 2019). Instead of the plotline conveying the message...
- Film Editing
- Wes Anderson
Comparative Analysis of Spike Lee and Yoky Matsuoka
Shelton Jackson Lee popularly known as Spike Lee was born in Atlanta, Georgia in 1957. Spike Lee came from artistic, education-grounded background; his father- Bill Lee was a jazz composer, and his mother, a schoolteacher. He majored in communications at Atlanta’s Morehouse College, where he...
- Do The Right Thing
The UNESCO's Efforts in the Department of Art Education
This paper was written as a resource document to state and prove that the South African department of education has implemented UNESCO’s recommendations for arts education in the foundation phase curriculum. In this writing there are various sources to state and support why I agree...
- Department of Education
- South Africa
Uses of the Cartoon Illustration Style
Abstract This essay explores beloved and widely used cartoon illustration style. The paper depicts history of drawn cartoon style that is used for book illustrations and further evolution of this art that developed into animated movies using researches of Thomas Milton Kemnitz (1973) and Maureen...
What the Art of Origami Means to Me
“Brandon, don’t destroy paper. If you’re bored, get reading,” My mom frowned at the pile of shredded paper on the floor. I wanted to protest, but I knew, like my friends, she would dismiss my new hobby. At first glance, Origami—an ancient Japanese art form...
The Wisdom of Creating Art: Origami
Art is a skill acquired through experience, study or observation and it can also be the branch of coming up with ideas and gaining knowledge. In addition, art is another way of expressing how a person feels about something through an artwork. Art is not...
The Possibility of Doubling a Cube with Origami
Abstract I was first introduced to origami during a series of art and craft classes in kindergarten. Although I stopped doing it as a hobby as the years passed by, I got back into it during one of my CAS experiences, where I made origami...
The Sister Act and Its Comparison to the Broadway Version
Within the production of ‘Sister Act’ performed by University Centre Weston, I received the secondary role of Assistant Choreographer as well as ‘Sister Mary Lazarus’. Before the rehearsals began, I researched the role of a Choreographer to help with the creative process. On a theoretic...
- Dance Performance Review
The Process of Creation of Logos in Graphic Design
The graphic design pathway project revolves around the creation and rebranding of an existing business’ logo. Firstly, a research study was done various aspects and areas in graphic design, throughout the study a research book was compiled. In chapter one of my studies I explored...
- Graphic Design
Understanding Relationship Between Time-Pressure and Creativity
Introduction The metaphorical lightbulb that illuminates when a person has a break through creative idea, rarely happens under pressure. Take Isaak Newton, one of the most influential scientists of all time, as an example. As a crucial figure in the scientific revolution, Newton had made...
- Isaac Newton
Depiction of Creativity and Innovation in Business Organizations
It is useful to depict creativity in organizations as intricate, social, political and specialized frameworks. To recognize inventive outlets and execution a lot of systems, the administration in business must have what it takes to acknowledge information at the person, group and business levels all...
- Organizational Structure
Innovative Associations and Process of Organizational Creativity
It is useful to depict innovative associations as intricate, social, political and specialized frameworks. To recognize inventive outlets and execution a lot of systems, the administration in associations must have what it takes to acknowledge information at the person, group and association levels all the...
Sewing As A Way To Express My Creativity
Creation twinkles with coolness, sparkling in blues and greens. Innovation sparks in metallic tones, bursting with hues of golds and silvers. Renovation is lit with swirls of a warm palette, some red, some yellow. Since I was a child, I’ve always had a deeply ingrained...
- About Myself
The Theories Of Creativity, Innovation, And Food Entrepreneurship
According to Ward, behind the existed creativity there are several experiments, which include trial and error also from research and observation. To create a big thing we have to put a big effort in the process, therefore, there is no instant result and it goes...
Visual Stimuli And Divergent Thinking In The Mixing Process
Introduction Mixing is an expertly intuitive practice – that activates neural responses that transmit multimodal perceptions, especially audio-visual perception – whereby a mixing engineer is tasked to solve technical disparities surrounding an input signals frequency response, amplitude and spatial image, as well as make creative...
- Engineering
Best topics on Creativity
1. What Does Creativity Mean to You
2. Discussion on the Relationship Between Intelligence and Creativity
3. Do Schools Kill Creativity: the Issues of Music Education
4. Creative and Critical Thinking: Combining the Achievements of Thought
5. Culture, Art and Creativity: the Way They Are Related
6. The System Of Education: If I Could Change The World
7. The Role of Creative Industries in the United Kingdom
8. Comparing The Pros And Cons Of Books And Movies
9. Evolution Of The Concept Of Auteur Theory
10. Comparative Analysis of Spike Lee and Yoky Matsuoka
11. The UNESCO’s Efforts in the Department of Art Education
12. Uses of the Cartoon Illustration Style
13. What the Art of Origami Means to Me
14. The Wisdom of Creating Art: Origami
15. The Possibility of Doubling a Cube with Origami
- Frida Kahlo
- Ansel Adams
- Jean-Michel Basquiat
- Impressionism
- Pablo Picasso
- Interior Design
- Andy Warhol
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
THE big ideas: why does art matter?
Five Theses on Creativity
It permeates life, and, like love, it can break your heart.

By Eric Kaplan
Mr. Kaplan is a television producer and writer.
This essay is part of The Big Ideas , a special section of The Times’s philosophy series, The Stone , in which more than a dozen artists, writers and thinkers answer the question, “Why does art matter?” The entire series can be found here .
The word “art” can seem pretentious: When people hear it, they worry someone will force them to read a novel, or go to a museum, or see a movie without any explosions in it.
To me, art simply refers to those aspects of our lives that can be suffused and transformed by creativity. And having creativity in our lives is important. Without it we’re just going through the motions, stuck in the past. With it we feel alive, even joyous.
But if I say that art is simply life imbued with creativity, isn’t that just a case of obscurum per obscurius — of explaining the murky with the even murkier? After all, what exactly is creativity?
To help unravel this puzzle, here are five theses on creativity:
Thesis No. 1: Creativity makes something new. A different way of talking can suddenly make our world seem new. Here’s an example: In the Middle Ages, a road was something people walked on, the ocean a terrifying expanse of blue. But when the anonymous author of the Old English epic poem “Beowulf” called the ocean a “whale-road,” he made his readers experience the ocean afresh. The ocean may be an obstacle for us land-bound humans, but for whales it’s a road.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

How to Write a Creative Essay: Your Fresh Guide

What Is a Creative Essay
Creative essay is a form of writing that combines elements of fiction, personal experience, and imagination.
Do you ever want to let your imagination loose in your school essays? Creative writing lets you do just that. It allows you to invent characters, places, and stories that might not exist in real life. This type of writing encourages you to play with words, structure, and style to stir emotions, provoke thoughts, or simply entertain your readers.
Unlike more formal writing like journalism or academic essays, creative writing is all about expressing yourself artistically. It gives you the freedom to showcase your personality through characters, stories, and plots that you create.
In this guide, our college essay writer will walk you through everything you need to know, from picking a great topic to putting your ideas down on paper. You'll find examples of creative essays, a template to help you organize your thoughts, and tips on how to make your writing more vivid and impactful.
How to Write a Creative Essay in 6 Steps
Let's go through the key steps for writing a creative essay. By breaking down the process into manageable parts, you'll find it more straightforward to develop engaging ideas and structure your essay effectively.
Meanwhile, check out our special article on how to write in cursive .

Write Freely
When you start writing, whether it's for essays or stories, it's best to sit down and jot down your first thoughts. Freewriting is a common technique among writers. It helps you start thinking and brainstorming ideas.
Freewriting does two main things:
- It keeps your ideas flowing so you don't forget any good ones.
- It improves your ability to write continuously for longer periods.
For essays, you can begin by writing the topic in the center of a page and then creating a mind map with any relevant ideas that come to mind. This can include different aspects of the topic you want to cover and examples or quotes you've come across.
Remember, this brainstorming session shouldn't take too long. Set a timer for about ten minutes, play your favorite music, and let your ideas flow naturally. This initial step is all about getting your thoughts out there without overthinking it.
Tell the Story in Three Parts
In storytelling, we often use a three-part structure: Setup, Confrontation, and Resolution. This approach is widely used in writing, movies, and TV shows. Unlike the acts in a play, these parts flow into each other seamlessly.
- Setup - Introduces the characters, their relationships, and the world they live in. Early on, there's usually an event called an 'inciting incident' (often around 19 minutes into a film) that sets the story in motion. The main character faces challenges and makes decisions that shape the rest of the narrative.
- Confrontation - The central problem emerges from the inciting incident, and the main character strives to resolve it. They encounter obstacles that test their abilities and resolve. For instance, in a detective story, this phase involves the detective uncovering clues and facing setbacks before reaching a breakthrough.
- Resolution - The story reaches its peak as the main conflict is confronted and resolved. Loose ends are tied up, and the characters' journeys conclude, leaving a sense of closure.
This structure helps writers build engaging narratives that keep audiences invested in the characters' journeys from start to finish.
Start with a Hook
In creative writing, it's often recommended to start with an exciting beginning. One good way is to begin with a 'conversation,' jumping straight into a lively talk to grab the reader's interest right away. For example, in a spy thriller, instead of easing into the story, the writer might open with agents arguing about a secret mission, setting the stage for suspense and excitement. The story could then unfold with more dialogue revealing the characters' motives and actions.
This method also works in essays, especially for certain topics. For instance, if you were writing about the ethical issues of cloning, rather than starting with a slow introduction to different viewpoints, you could begin with a conversation between scientists debating the consequences of cloning animals. Showing different opinions and ethical dilemmas through dialogue could engage readers and lead them into the broader discussion of bioethics and scientific advancements. This approach may not follow the usual essay structure, but it can make your writing more engaging and thought-provoking.
Add Rich Details
To keep your reader engaged, add vivid details about settings and locations, much like creative writers do. Essays can become dull if they only focus on academic concepts, but you can make them more captivating by including descriptive details.
While it can be challenging in essays with strict word limits or those focused on scientific topics, you can certainly incorporate relevant details in subjects like humanities, literature, theater, or history. For example, when analyzing a novel by Jane Austen, you might explore how societal expectations of the time shaped her portrayal of female characters.
By including these extra details and snippets of information, you not only maintain reader interest but also demonstrate your depth of understanding and independent study. This approach can impress your reader and potentially enhance your academic performance.
End Clearly
In creative writing, ambiguity can spark debate, but in essays, clarity is key. Unlike creative writing, in which open endings can be intriguing, essays require a clear conclusion.
Always ensure your essay concludes definitively. This shows your examiner what you've learned and your final answer to the essay question. Unlike creative writing, your goal is to demonstrate understanding and reach a clear conclusion to earn marks.
Make sure your conclusion is straightforward and easy to locate. With many essays to assess, clarity helps your teacher quickly identify your final thoughts. Avoid ambiguity or vague language, which can frustrate readers, including your examiner.
Revise and Improve
Most writers don't nail it on the first try. Editing is crucial, especially when trimming down your word count. It can be tough to cut out sections you've crafted carefully.
After completing your first draft, read through it critically. Consider the order of your points and ensure everything makes sense. With modern technology, editing is easier—you can rearrange sections by copying and pasting and refining your wording for smooth transitions. Once you've made these edits, give your essay a final read-through to polish the wording. Don't overlook proofreading to catch any spelling or grammar mistakes.
Outline for Creative Writing Essay
Here is an outline that will help you structure your creative writing essay, whether it's a poem, a personal essay, a short story, or a speech.
| Introduction 📘 | |
|---|---|
| Briefly introduce the creative writing piece you've chosen (poem, story excerpt, speech introduction, etc.) (Optional) Hint at the main theme or central message you want to convey. | |
| Body: For Poetry & Short Stories ✍️ | Body: For Personal Essays & Speeches 📜 |
| Describe the setting, characters, and central conflict (if applicable). Include vivid details and sensory language to bring your writing to life. | Introduce the personal experience or message you're exploring. Use anecdotes, reflections, or storytelling elements to illustrate your points. |
| Conclusion ✅ | |
| Focus on specific scenes or moments that showcase your writing style and main theme. End with a powerful image or a thought-provoking question. | Connect your personal experience or message to a broader theme or universal truth. Offer a final reflection or call to action. |

Types of Creative Essays
Creative writing comes in many forms, each a great way to tell stories and express yourself. Here are 5 main types:

- Poetry uses short, powerful words to describe feelings, thoughts, and experiences. It can rhyme and have a beat or be more free-flowing. Poets play with language to create strong emotions and ideas, capturing moments in special ways.
- Personal essays mix memories, reflections, and stories to explore a person's experiences and what they learned. Unlike school essays, they focus on the writer's unique voice, using stories and thoughts to tell a narrative. They can be about almost anything, giving readers a glimpse into the writer's mind and feelings with the goal of connecting through shared experiences.
- Short stories can be very short or complete stories, but they have a word limit. This challenges writers to create interesting characters, plots, and settings using concise storytelling. Short stories come in all sorts of genres, like realistic fiction or fantasy, and aim to build suspense and give a satisfying ending in a short space.
- Novels are longer fictional works with complex characters, plots, and settings. They can be literary fiction, science fiction, romance, mysteries, or anything else, offering in-depth stories that unfold over many chapters. Writing novels requires planning and a strong understanding of storytelling to keep readers engaged with vivid worlds and compelling narratives.
- Speeches are written to be spoken aloud, with the goal of informing, inspiring, persuading, or entertaining listeners. They can be formal addresses or informal talks and use special writing techniques along with storytelling elements. Speechwriting is about crafting messages that resonate with listeners' emotions and minds, using stories and anecdotes to capture their attention and hold their interest.
20 Creative Essay Topics
Before putting yourself into creative essay writing, you should pick among the creative writing essay topics that you will be talking about. Here, our paper writer prepared some fresh ideas to make your choice easier:
- Write about a time you overcame a challenge. What did you learn from the experience?
- Imagine you can talk to animals. What would you ask your pet?
- Describe a place that brings back special memories. What makes it so special?
- Create a story about a forgotten object. Where did it come from? Who used it?
- Write a letter to your future self. What are your hopes and dreams?
- If you could have any superpower, what would it be? Why?
- Imagine a world without technology. How would your life be different?
- What is the most important lesson you've learned in life so far?
- Describe a dream you'll never forget. What do you think it means?
- Write a story about a character who is very different from you.
- What historical figure do you find most interesting? Why?
- Create a dialogue between two unlikely characters.
- Imagine you could travel anywhere in the universe. Where would you go? Why?
- Write a story about a robot who wants to be human.
- What does friendship mean to you?
- Describe a work of art that you find moving. Why does it affect you?
- What is your favorite thing about nature? Why?
- Imagine you are invisible for a day. What would you do?
- Write a story about a creature from myth or legend.
- What do you think the future holds for humanity?
Need Some Creative Writing Help?
Choose your personal paper writer on our service and check it out!
Example of a Creative Essay
If you liked these samples, you can buy essays online from us. Our authors will write them flawlessly and deliver them within the specified timeframe. Additionally, you can find helpful information on a book review format in our dedicated article.
Wrapping Up
We hope you now understand what a creative essay is and how to write one. Some people find writing creative essays easier than others. By applying the tips mentioned above, you should be well-equipped to create work that you're proud of.
If you need extra guidance, consider working with our expert coursework writers . They have developed numerous academic essays with professionalism. Place an order today and experience our dedication firsthand!
Are You Short on Creative Writing Topics?
Whether you need a compelling personal statement, a thought-provoking argumentative essay, or a captivating narrative, we've got you covered.
If you feel like some questions were left unanswered, don't you feel disappointed just yet! Our dissertation writers for hire compiled the most frequently asked question on creative essay writing, so take a look for additional information:
What Are the 7 Types of Creative Writing?
What are the 5 c's of creative writing, is creative writing a skill.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

- Added new examples, topics and FAQs
- Added new writing steps and an outline
- 7 Techniques from Creative Writing You Can Use to Improve Your Essays. (2014, June 21). Oxford Royale Academy. https://www.oxford-royale.com/articles/techniques-creative-writing-improve-essays/
- (2023). Oxfordsummercourses.com. https://oxfordsummercourses.com/articles/creative-writing-techniques-to-improve-your-essays/
.webp)

Everyday Creativity and New Views of Human Nature
Available formats, also available from.
- Table of contents
- Contributor bios
- Reviews and awards
- Book details
What is everyday creativity? A capacity, a strategy, a process, all of these. It is an ability that is intimately woven into our daily lives and our personalities, one that we use from hour to hour; yet it remains, for most of us, underdeveloped and, unfortunately, underacknowledged. Writes editor and leading creativity researcher Ruth Richards, "Everyday creativity is about everyone, throughout our lives, and fundamental to our very survival. It is how we find our lost child, get enough to eat, make our way in a new place and culture…With our everyday creativity, we adapt flexibly, we improvise, we try different options, whether we are raising a child, counseling a friend, fixing our home, or planning a fundraising event."
In this provocative collection of essays, an interdisciplinary group of eminent thinkers and writers offer their thoughts on how embracing creativity—tapping into the "originality of everyday life"—can lead to improved physical and mental health, to new ways of thinking, of experiencing the world and ourselves. They show how creativity can refine our views of human nature at an individual and societal level and, ultimately, change our paradigms for survival—and for flourishing—in a world fraught with urgent challenges. Neither a dry treatise nor a manual, this anthology draws upon the latest research in the area to present a lively examination of the phenomenon and process of everyday creativity and its far-reaching ramifications for self, culture, history, society, politics, and humankind's future.
Part I looks at creativity and individuals—our well-being, potential for new and transformative understandings, and openings to richness, immediacy, and profundity of experience. Part II involves social creativity—including issues of complexity, collaboration, contextual relativity, inclusiveness, and creative systems evolving from the ground up (vs. more hierarchical models). Part III presents a detailed and multilayered discussion of 12 potential benefits of living more creatively.
Contributors
Foreword —Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi
Introduction —Ruth Richards
I. Creativity and Our Individual Lives
- Everyday Creativity: Our Hidden Potential —Ruth Richards
- Living Well Creatively: What's Chaos Got to Do With It? —David Schuldberg
- Artist and Audience: Everyday Creativity and Visual Art —Tobi Zausner
- To Understand Is to Create: An Epistemological Perspective on Human Nature and Personal Creativity —Mark A. Runco
- Audience Flow: Creativity in Television Watching With Applications to Teletherapy —Steven R. Pritzker
- Structures of Consciousness and Creativity: Opening the Doors of Perception —Allan Combs and Stanley Krippner
II: Creativity and Society
- Telling the New Story: Darwin, Evolution, and Creativity Versus Conformity in Science —David Loye
- Standing Up for Humanity: Upright Body, Creative Instability, and Spiritual Balance —Mike Arons
- Creativity in the Everyday: Culture, Self and Emotions —Louise Sundararajan and James R. Averill
- A "Knowledge Ecology" View of Creativity: How Integral Science Recasts Collective Creativity as a Basis of Large-Scale Learning —S. J. Goerner
- Cyborgs, Cyberspace, Cybersexuality: The Evolution of Everyday Creativity —Frederick David Abraham
- Our Great Creative Challenge: Rethinking Human Nature—and Recreating Society —Riane Eisler
III: Integration and Conclusions
- Twelve Potential Benefits of Living More Creatively —Ruth Richards
Author Index
Subject Index
About the Editor
Ruth Richards, MD, PhD, is a board certified psychiatrist and educational psychologist. She is a professor of psychology at Saybrook Graduate School in San Francisco, California; a research affiliate at McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts (psychiatric affiliate of Massachusetts General Hospital); and a lecturer in the Department of Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
For many years, Dr. Richards has studied everyday creativity in clinical and educational settings and has published on creativity and social action as well as spiritual development. She is the principal author of The Lifetime Creativity Scales , which broke new ground as a broad-based assessment of real-life everyday creativity in a general population. With Mark A. Runco, Dr. Richards coedited Eminent Creativity, Everyday Creativity, and Health . She served on the executive advisory board for the Encyclopedia of Creativity and is also on the editorial boards of three journals: The Creativity Research Journal ; The Journal of Humanistic Psychology ; and Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts , the journal for APA Division 10 (Society for the Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity and the Arts), where she is also an at-large member of the executive committee.
Personally, Dr. Richards draws, writes, plays three instruments badly, and learns even more about creativity from her teenage daughter.
You may also like
Deliberate Practice in Behavioral Parent Training
Clinical Psychology in Communities of Color
Emotional Processing
Deliberate Practice in Career Counseling
Solution-Focused Brief Therapy With Families

Creativity as a Way of Life
Creativity coach elena greco provides top tips for the creative life..
Posted March 2, 2021 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan

Can you write a novel, paint a painting, or invent a new tech solution if you aren’t open to creative ideas at those times when you aren’t sitting down to write that novel, paint that painting, or invent that solution?
Is creativity something that you turn on and off like a spigot? Or is it an orientation toward life? Are you likely to be blessed with creative ideas if you aren’t open to those ideas all the time? Here’s how professional singer and creativity coach Elena Greco explains the difference between “the creative act” and “living a creative life.”
Elena writes:
Do you want to be more creative? Have you been wanting forever to write a book, or long to paint, or would love to get back to playing an instrument, but can't see how to make the time to fit it in with your challenging career ? Or have you taken a survival job to support you as a creative artist, but now can’t seem to find the time to be creative?
The great news is this: You don’t have to find time in order to be creative. Because being creative has nothing to do with time. You don’t do creativity; you live creativity!
Creativity truly is a way of life, not an activity or a collection of traits. It’s not something to be relegated to certain days or times, comprising only a small portion of our waking hours. It’s about approaching everything in life creatively.
Leonardo da Vinci’s pithy quote says it all: “Never be without your little pad.” He was speaking to his art students, encouraging them to remain artists even while outside the studio, being prepared to capture the sketch of a moment that struck them in their travels through life or to record an idea that occurred to them while walking. He knew that creativity was a way of life, not a time-limited activity.
I am never not creative. I never “turn off” the flow. And as Leonardo admonished, I’m never unprepared for creative ideas which arise. When an idea occurs to me, I use a simple dictation app to record it. I open it, hit the mic button, and speak into my phone, and it transcribes my speech into text for me and automatically saves. I use my phone’s camera app to shoot spontaneous photos and videos. Being creative is easier nowadays!
Being creative means allowing your creativity to always be “on,” rather than relegating it to certain times or days. I am the same creative walking down the street as I am when I’m singing. I’m the same creative taking my morning shower as I am when I’m writing a blog post on my laptop.
In fact, some of my best ideas come to me when I’m in the shower! I leave my phone just outside the shower so that the minute I dry off I can record at the press of a button the ideas that arose in the steam. And creative ideas never fail to flow, prompted by fresh air and beautiful vistas, when I’m walking the trails of Central Park or sitting on a bench there. I always have my phone with me there to take notes and pictures. Never waste an idea!
When I lie down to go to sleep, I envision my next day and ask myself a question related to one of my creative projects, encouraging my mind to present me with a creative solution when I awake. Creativity happens even when you’re asleep! I have a notepad next to me when I sleep so that I don’t lose an idea that presents itself to me when I’m still half asleep.
Being creative means that you look at things with a creative eye, not just when you’re in the art studio painting, or on stage performing, or at your desk writing, or at your job thinking of solutions to a problem, but at every moment of your life.
Once you “turn on” creativity and choose it as your default setting, you’ll begin to notice when your creative ideas flow best. Is it in the shower, in nature, while driving, watching television, performing a certain job function, sitting in meetings, or on your favorite walking trail? Then make sure that you always have simple and easy-to-use tools at hand that accommodate your unique style at those times to capture ideas when they arise. Never miss an opportunity to be creative!
We can choose to live our lives as creative beings. Living life creatively relieves the pressure of having to “turn on” creativity only at the moment you start a rehearsal or begin your writing session. The stream is already flowing! Let it always be flowing.
Elena Greco is a professional singer, writer, and coach.

Eric Maisel, Ph.D. , is the author of more than 50 books, among them Redesign Your Mind.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that could derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face triggers with less reactivity and get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Last updated 27/06/24: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity
- > Creativity’s Role in Everyday Life

Book contents
- The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity
- Copyright page
- Contributors
- Acknowledgments
- An Introduction to the Second Edition
- Part I An Introduction to Creativity
- Part II Underpinnings of Creativity
- Part III Differential Bases for Creativity
- Part IV Creativity in the World
- Collaborative Creativity
- 24 Improving Creativity in Organizational Settings
- 25 Leading for Creativity
- 26 Individual and Group Creativity
- 27 Creativity in Classrooms
- 28 Play and Creativity
- 29 The Creative City
- 30 Creativity’s Role in Everyday Life
- Manifestations of Creativity
30 - Creativity’s Role in Everyday Life
from Collaborative Creativity
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2019
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- Creativity’s Role in Everyday Life
- By Katherine N. Cotter , Alexander P. Christensen , Paul J. Silvia
- Edited by James C. Kaufman , University of Connecticut , Robert J. Sternberg , Cornell University, New York
- Book: The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity
- Online publication: 12 April 2019
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/9781316979839.032
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
- +1.212.203.3252
Subscribe to our News
Special Offers

Using the Tools of Creative Writing, Memoir, Art, Photography, Storytelling and Mindfulness

Creativity in Everyday Life
By Shelley Berc
Why is creativity important in everyday life? Simply put, it is because it makes life infinitely interesting and fulfilling. Creativity is a way of living life that embraces originality and makes unique connections between seemingly disparate ideas. Creativity is about living life as a journey into seeing and communicating the extra-ordinariness of the simplest, most every day acts.
We often think about creativity as making something, but in fact the root meaning of the word means ‘to grow’. When we are creative we feel as if the world and all that is in it is vibrantly alive. Creativity’s by-products are some of the major achievements of civilization-from the invention of the wheel to Mozart’s sonatas.
Human beings are essentially born creative-from infancy on we find innovative ways to negotiate life. The most creative people find ways around obstacles because they see them not just as roadblocks but also as opportunities. Creativity expands our perceptions and along with expanded perceptions come new ways of problem solving-from making an exquisite meal when you don’t know how to cook to painting an extraordinary landscape when you are living in a freezing attic and can’t afford a full box of paints.
15 ideas for expressin creativity in everyday life:
1. Make your immediate surroundings as beautiful or eccentric as you can. Experiment with your sense of color, texture, and line. Add an element of surprise or quirkiness to your home decor. The unexpected can jolt you out of complacency and into inspiration.
2. Go somewhere new-as close as a restaurant you’ve never tried or as far as China. New places excite the mind and senses and when we are excited our creative abilities soar.
3. Spend 10 minutes a day dreaming out the window.
4. Don’t censor yourself.
5. Do something new or something old in a brand new way. As Picasso said “I am always doing that which I can not do, in order that I may learn how to do it.”
6. Slow down your perceptions so you savor them-that means eat slowly and taste your food, look closely at the flowers in the garden, spend time writing down and drawing your perceptions.
7. Believe in and follow your ‘What ifs’-what if I was an amazing writer? What if I could make a revolutionary spaceship? What if when I walk across a room it feels like floating?
When we ‘what if’ ourselves, we start to believe we can achieve our dreams. That is the first step to making them come true.
8. Spend 15 minutes looking around with the eyes of a child. Remember that sense of wonderment, love of color, surprise, curiosity and hunger to explore. It can get your creativity going because you are remembering how you were once very imaginative.
9. Take a notebook and pen everywhere you go and jot down your observations. We often have innovative ideas but we forget them if we don’t record them.
10. Don’t over-criticize yourself. At worst it will kill and at best cripple your creative hopes and dreams.
11. Make up a visualization in which you observe yourself imagining and creating effortlessly. Picture yourself loving the process.
12. Just Do It! Creativity is a muscle: use it or lose it. Dance, draw, brainstorm, change your life. The more you use your creativity, the easier it becomes and the better you get at it.
13. Collaborate creatively with like-minded friends-write a journal together, make a quilt, design a new play space, choreograph a dance piece, start a new business.
14. Dress wildly-revel in color and texture. Buy or make a fabulous hat. Don’t be age appropriate.
15. Remember the words of Samuel Becket, on the secret to life-long creativity: “fail, fail again, fail better”!

UPCOMING WORKSHOPS
| June 25-28 | |
| July 1-4 | |
| July 26-29 | |
| October 4-7 | |
| ........ | |
| 2025 | |
| June 17-20 |

- Writing With Your Eyes Closed By Frank Bruni, The New York Times Continue reading »
- Working With Your Hands Is Good for Your Brain Working With Your Hands Is Good for Your Brain By Marine Buffard Activities like writing, gardening and knitting can improve… Continue reading »
- Why You Should Take A Solo Vacation By BHG Continue reading »
- Why Theater Majors Are Vital in the Digital Age By Tracey Moore, The Chronicle of Higher Education Continue reading »
- What is Creativity? By Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- Use Your Imagination… By Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- Travel and Creativity By AllPsychologyCareers.com Continue reading »
- Time to Nourish our Creativity by Shelley Berc, Boomer Girl Magazine Continue reading »
- Think Less, Think Better by Moshe Bar, The New York Times Continue reading »
- Play, Play, Play by Susie Ellis, The Weekender Continue reading »
- Theatre of the Mind by Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- The Creativity Workshop: My Reflections The Creativity Workshop: My Reflections by K. Renae P., Fund for Teachers fellow Never listen to the naysayers. Smile at… Continue reading »
- Seeing Through the Blur by Alejandro Fogel, Sketchbook Magazine Continue reading »
- The beginning of silent reading changed humans’ interior life By Thu-Huong Ha Continue reading »
- Postcard from Paris by Deborah Murphy, The National Post, Canada Continue reading »
- The Gift of the Amateur by Shelley Berc, Prologue Magazine Continue reading »
- 100 Best Worldwide Vacations to Enrich Your Life by Pam Grout, National Geographic Continue reading »
- My Experience at the Creativity Workshop, NYC My Experience at the Creativity Workshop, NYC By Dan Erickson, on his blog danerickson.net I recently went to New York… Continue reading »
- Why Med Schools Are Requiring Art Classes by Casey Lesser Continue reading »
- La creatività ? Si impara a scuola con il relax e senza tecnologia by Robert Calabro, La Repubblica Continue reading »
- Why Digital Note-Taking will Never Replace the Physical Journal by Bradford Morrow, Literary Hub Continue reading »
- The mistake of seeing only some jobs as creative by Corinne Purtill, Quartz Magazine Continue reading »
- Tap Into Your Inner Artist in a Creativity Workshop Natural Awakenings Magazine Continue reading »
- In Praise of Mediocrity: The pursuit of excellence has infiltrated and corrupted the world of leisure In Praise of Mediocrity: The pursuit of excellence has infiltrated and corrupted the world of leisure By Tim Wu The… Continue reading »
- Hyperphantasia and the quest to understand vivid imaginations Hyperphantasia and the quest to understand vivid imaginations By David Robson William Blake’s imagination is thought to have burned with… Continue reading »
- How to unlock writer’s block How to unlock writer's block By LaDonna Witmer, Creativity Workshop past participant The blank page of paper, staring back at… Continue reading »
- Why Handwriting Is Still Essential in the Keyboard Age The New York Times Continue reading »
- Can You Get More Creative? by A. J. Jacobs, Real Simple Magazine Continue reading »
- For Doctors, Delving Deeper as a Way to Avoid Burnout For Doctors, Delving Deeper as a Way to Avoid Burnout By Siddhartha Mukherjee The New York Times The anatomy laboratory… Continue reading »
- How Fear Chokes Creativity and What to Do About It by Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- How to Cultivate Eureka Moments by Michiko Kakutani Continue reading »
- Doodling for Dollars by Rachel Emma Silverman Continue reading »
- ‘Don’t be afraid to make mistakes’: 11 ways to be more creative 'Don't be afraid to make mistakes': 11 ways to be more creative The Guardian Lauren Child, children's author and illustrator… Continue reading »
- Does Having a Day Job Mean Making Better Art? By Katy Waldman Continue reading »
- 10 Creativity Tips for Teachers: An Inspired Teacher is an Inspiring Teacher by Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- Creativity quotes Creativity Quotes Continue reading »
- Creativity is flying like a bird By Fahri Karakas, Creativity Workshop past participant Continue reading »
- Creativity in Everyday Life by Shelley Berc Continue reading »
- The Creative Academic by Janelle Ward, Inside Higher Ed Continue reading »
- We are born creative geniuses and the education system dumbs us down, according to NASA scientists By Coert Engels Continue reading »
- The Dubai Connection by David Berliner Continue reading »
- Connected Letters, Connected Thinking: How Cursive Writing Helps Us Learn Connected Letters, Connected Thinking: How Cursive Writing Helps Us Learn By Judy Packhem, M. Ed. Landmark 360 Cursive writing is… Continue reading »
- Children need art and stories and poems and music as much as they need love and food and fresh air and play By Philip Pullman Continue reading »
- British Doctors May Soon Prescribe Art, Music, Dance, Singing Lessons By Meilan Solly Continue reading »
- Book of Moments by Shelley Berc, The Paumanok Review Continue reading »
- The Creativity Workshop by Francesca Salidu, Babel Magazine Continue reading »
- Creativity Articles List of Articles Continue reading »
- Take Another Look by Alejandro Fogel, Sketchbook Magazine Continue reading »
- Tapping Creativity by Gary Kuhlmann, In Class, University of Iowa Alumni Magazine Continue reading »
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Social History
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- Ethnic Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Qualitative Political Methodology
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

The Philosophy of Creativity: New Essays

Assistant Professor of Philosophy
Adjunct Assistant Professor of Psychology
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Creativity pervades human life. It is the mark of individuality, the vehicle of self-expression, and the engine of progress in every human endeavor. It also raises a wealth of philosophical questions, but curiously, it hasn’t been a major topic in contemporary philosophy. The Philosophy of Creativity ventures to change that. Illustrating the value of interdisciplinary exchange, this is a series of new essays from some of today’s leading thinkers integrating philosophical insights with empirical research. Join them as they explore such issues as the role of consciousness in the creative process, the role of the audience in the creation of art, the emergence of creativity through childhood pretending, whether great works of literature give us insight into human nature, whether a computer program can really be creative, the definition of creativity, whether creativity is a virtue, the difference between creativity in science and art, and whether creativity can be taught—both in general and within philosophy itself.
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| October 2022 | 21 |
| October 2022 | 6 |
| October 2022 | 18 |
| October 2022 | 9 |
| October 2022 | 11 |
| October 2022 | 42 |
| October 2022 | 11 |
| October 2022 | 10 |
| October 2022 | 16 |
| October 2022 | 11 |
| October 2022 | 21 |
| October 2022 | 46 |
| October 2022 | 11 |
| October 2022 | 39 |
| October 2022 | 8 |
| October 2022 | 15 |
| October 2022 | 6 |
| October 2022 | 89 |
| October 2022 | 42 |
| November 2022 | 6 |
| November 2022 | 8 |
| November 2022 | 31 |
| November 2022 | 11 |
| November 2022 | 2 |
| November 2022 | 28 |
| November 2022 | 16 |
| November 2022 | 2 |
| November 2022 | 52 |
| November 2022 | 8 |
| November 2022 | 1 |
| November 2022 | 5 |
| November 2022 | 10 |
| November 2022 | 8 |
| November 2022 | 3 |
| November 2022 | 3 |
| November 2022 | 8 |
| November 2022 | 6 |
| December 2022 | 7 |
| December 2022 | 4 |
| December 2022 | 4 |
| December 2022 | 6 |
| December 2022 | 13 |
| December 2022 | 24 |
| December 2022 | 4 |
| December 2022 | 3 |
| December 2022 | 9 |
| December 2022 | 4 |
| December 2022 | 5 |
| December 2022 | 1 |
| December 2022 | 2 |
| December 2022 | 1 |
| December 2022 | 2 |
| December 2022 | 10 |
| December 2022 | 1 |
| December 2022 | 7 |
| January 2023 | 5 |
| January 2023 | 6 |
| January 2023 | 8 |
| January 2023 | 11 |
| January 2023 | 14 |
| January 2023 | 10 |
| January 2023 | 14 |
| January 2023 | 6 |
| January 2023 | 12 |
| January 2023 | 13 |
| January 2023 | 8 |
| January 2023 | 8 |
| January 2023 | 34 |
| January 2023 | 2 |
| January 2023 | 1 |
| January 2023 | 5 |
| February 2023 | 14 |
| February 2023 | 7 |
| February 2023 | 7 |
| February 2023 | 12 |
| February 2023 | 12 |
| February 2023 | 129 |
| February 2023 | 2 |
| February 2023 | 7 |
| February 2023 | 3 |
| February 2023 | 10 |
| February 2023 | 1 |
| February 2023 | 65 |
| February 2023 | 4 |
| February 2023 | 4 |
| March 2023 | 7 |
| March 2023 | 2 |
| March 2023 | 3 |
| March 2023 | 12 |
| March 2023 | 3 |
| March 2023 | 16 |
| March 2023 | 275 |
| March 2023 | 12 |
| March 2023 | 21 |
| March 2023 | 6 |
| March 2023 | 8 |
| March 2023 | 13 |
| March 2023 | 5 |
| March 2023 | 7 |
| March 2023 | 8 |
| March 2023 | 33 |
| March 2023 | 7 |
| March 2023 | 1 |
| March 2023 | 11 |
| April 2023 | 3 |
| April 2023 | 10 |
| April 2023 | 6 |
| April 2023 | 23 |
| April 2023 | 9 |
| April 2023 | 9 |
| April 2023 | 14 |
| April 2023 | 99 |
| April 2023 | 1 |
| April 2023 | 2 |
| April 2023 | 1 |
| April 2023 | 1 |
| April 2023 | 7 |
| April 2023 | 1 |
| April 2023 | 11 |
| May 2023 | 17 |
| May 2023 | 2 |
| May 2023 | 4 |
| May 2023 | 10 |
| May 2023 | 5 |
| May 2023 | 26 |
| May 2023 | 5 |
| May 2023 | 5 |
| May 2023 | 4 |
| May 2023 | 3 |
| May 2023 | 2 |
| May 2023 | 3 |
| May 2023 | 3 |
| May 2023 | 5 |
| May 2023 | 6 |
| May 2023 | 9 |
| June 2023 | 12 |
| June 2023 | 3 |
| June 2023 | 3 |
| June 2023 | 5 |
| June 2023 | 2 |
| June 2023 | 6 |
| June 2023 | 9 |
| June 2023 | 6 |
| June 2023 | 15 |
| June 2023 | 11 |
| June 2023 | 10 |
| June 2023 | 5 |
| June 2023 | 2 |
| June 2023 | 2 |
| June 2023 | 5 |
| June 2023 | 6 |
| June 2023 | 1 |
| June 2023 | 8 |
| June 2023 | 6 |
| July 2023 | 11 |
| July 2023 | 7 |
| July 2023 | 1 |
| July 2023 | 20 |
| July 2023 | 5 |
| July 2023 | 5 |
| July 2023 | 11 |
| July 2023 | 6 |
| July 2023 | 2 |
| July 2023 | 21 |
| July 2023 | 10 |
| July 2023 | 3 |
| July 2023 | 3 |
| July 2023 | 9 |
| July 2023 | 2 |
| August 2023 | 7 |
| August 2023 | 5 |
| August 2023 | 5 |
| August 2023 | 7 |
| August 2023 | 21 |
| August 2023 | 4 |
| August 2023 | 4 |
| August 2023 | 5 |
| August 2023 | 4 |
| August 2023 | 1 |
| August 2023 | 4 |
| August 2023 | 3 |
| September 2023 | 24 |
| September 2023 | 9 |
| September 2023 | 6 |
| September 2023 | 11 |
| September 2023 | 15 |
| September 2023 | 25 |
| September 2023 | 8 |
| September 2023 | 8 |
| September 2023 | 16 |
| September 2023 | 10 |
| September 2023 | 5 |
| September 2023 | 2 |
| September 2023 | 6 |
| September 2023 | 1 |
| September 2023 | 9 |
| September 2023 | 5 |
| September 2023 | 3 |
| September 2023 | 3 |
| September 2023 | 5 |
| October 2023 | 8 |
| October 2023 | 16 |
| October 2023 | 10 |
| October 2023 | 2 |
| October 2023 | 18 |
| October 2023 | 1 |
| October 2023 | 19 |
| October 2023 | 56 |
| October 2023 | 4 |
| October 2023 | 13 |
| October 2023 | 10 |
| October 2023 | 41 |
| October 2023 | 3 |
| October 2023 | 3 |
| October 2023 | 11 |
| October 2023 | 12 |
| October 2023 | 9 |
| October 2023 | 15 |
| November 2023 | 103 |
| November 2023 | 1 |
| November 2023 | 5 |
| November 2023 | 19 |
| November 2023 | 8 |
| November 2023 | 10 |
| November 2023 | 12 |
| November 2023 | 18 |
| November 2023 | 63 |
| November 2023 | 2 |
| November 2023 | 5 |
| November 2023 | 8 |
| November 2023 | 5 |
| November 2023 | 28 |
| December 2023 | 16 |
| December 2023 | 3 |
| December 2023 | 1 |
| December 2023 | 8 |
| December 2023 | 8 |
| December 2023 | 1 |
| December 2023 | 22 |
| December 2023 | 2 |
| December 2023 | 21 |
| December 2023 | 1 |
| December 2023 | 1 |
| December 2023 | 10 |
| December 2023 | 7 |
| December 2023 | 5 |
| December 2023 | 3 |
| January 2024 | 21 |
| January 2024 | 6 |
| January 2024 | 18 |
| January 2024 | 23 |
| January 2024 | 2 |
| January 2024 | 18 |
| January 2024 | 2 |
| January 2024 | 22 |
| January 2024 | 6 |
| January 2024 | 5 |
| January 2024 | 3 |
| January 2024 | 31 |
| January 2024 | 5 |
| January 2024 | 25 |
| January 2024 | 1 |
| January 2024 | 13 |
| January 2024 | 42 |
| January 2024 | 4 |
| January 2024 | 13 |
| February 2024 | 13 |
| February 2024 | 4 |
| February 2024 | 6 |
| February 2024 | 7 |
| February 2024 | 19 |
| February 2024 | 61 |
| February 2024 | 14 |
| February 2024 | 6 |
| February 2024 | 41 |
| February 2024 | 4 |
| February 2024 | 2 |
| February 2024 | 8 |
| February 2024 | 9 |
| February 2024 | 1 |
| February 2024 | 1 |
| March 2024 | 14 |
| March 2024 | 6 |
| March 2024 | 2 |
| March 2024 | 28 |
| March 2024 | 19 |
| March 2024 | 65 |
| March 2024 | 4 |
| March 2024 | 21 |
| March 2024 | 11 |
| March 2024 | 122 |
| March 2024 | 21 |
| March 2024 | 2 |
| March 2024 | 10 |
| March 2024 | 1 |
| March 2024 | 7 |
| March 2024 | 8 |
| April 2024 | 12 |
| April 2024 | 6 |
| April 2024 | 5 |
| April 2024 | 16 |
| April 2024 | 2 |
| April 2024 | 23 |
| April 2024 | 58 |
| April 2024 | 23 |
| April 2024 | 20 |
| April 2024 | 10 |
| April 2024 | 137 |
| April 2024 | 6 |
| April 2024 | 23 |
| April 2024 | 22 |
| April 2024 | 6 |
| April 2024 | 2 |
| April 2024 | 8 |
| April 2024 | 1 |
| April 2024 | 6 |
| May 2024 | 3 |
| May 2024 | 10 |
| May 2024 | 9 |
| May 2024 | 30 |
| May 2024 | 14 |
| May 2024 | 50 |
| May 2024 | 39 |
| May 2024 | 13 |
| May 2024 | 11 |
| May 2024 | 6 |
| May 2024 | 25 |
| May 2024 | 1 |
| May 2024 | 5 |
| May 2024 | 7 |
| May 2024 | 2 |
| May 2024 | 15 |
| June 2024 | 13 |
| June 2024 | 5 |
| June 2024 | 1 |
| June 2024 | 6 |
| June 2024 | 1 |
| June 2024 | 14 |
| June 2024 | 13 |
| June 2024 | 14 |
| June 2024 | 42 |
| June 2024 | 4 |
| June 2024 | 3 |
| June 2024 | 9 |
| June 2024 | 4 |
| June 2024 | 3 |
| June 2024 | 6 |
| June 2024 | 3 |
| June 2024 | 1 |
| June 2024 | 10 |
| June 2024 | 7 |
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Creativity is a human quality that exists in every single one of us
Reasercher for Durham Commission on Creativity, Durham University
Head of Department in the School of Education, Durham University
Disclosure statement
The authors do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Durham University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
When you think about creativity, it might be highly creative people like Mozart, da Vinci or Einstein who spring to mind. They were all considered to be “geniuses” for their somewhat unique talents that led to global innovation in their fields. Their type of creativity is what’s known as “ Big C creativity ” (or historical) and is not very common in everyday life. Not all of us can create works of art or music or scientific theories that are new to the world.
But while we can’t all be Mozart, da Vinci or Einstein, many people do enjoy creative activity – through hobbies such as water colour painting or playing the piano. And these types of pursuits are often what people think of when asked what being creative looks like. Our finished pieces may not be comparable with the likes of the great masters, but often the process is therapeutic and the end result can be aesthetically pleasing.
On top of hobbies and interests, we all possess creative attributes that can help as we solve life’s problems and make decisions. It is this type of creativity that enables us to plan different routes to get to the same destination, or how to fit in a trip to the supermarket when our schedule looks full.
It might not sound very creative, but this aspect of creativity relies on our ability to consider options and assess their suitability, as well as how to make decisions based on personal prior experience or what we have learnt formally or informally. These examples are known as “ small c creativity ” or “personal everyday creativity”.
Creative outcomes
While Big C creativity is valued and celebrated, it is often small c creativity that has allowed humans to flourish over thousands of years. It sets us apart from other animals and it is also the type of creativity which can be fostered through our education system and beyond into the workplace.
Traditionally, research tells us that creativity has been largely associated with the arts. Our previous research has shown that teachers are often able to give examples of creative activity in arts subjects, but find it harder to do so when asked to describe creativity in subjects such as science.
But there is a growing realisation that opportunities to be creative are found across a broader range of subjects. For instance, engineering provides opportunities to be creative through problem solving, and history gives the opportunity to think creatively about why events happened, and what motivated those involved.
Research has shown that training teachers to ask particular types of questions can be one way to help support creativity across the curriculum. This is because generating solutions to problems and explanations are creative processes, and these are vital if children are to have a “ complete education ”.
Our research also shows how it can be more helpful to talk about “thinking creatively” rather than “creativity”. This is because people tend to see thinking creatively as independence of thought and a willingness to take risks and seek new perspectives. It is also seen as a way to perceive new relationships, make new connections, and generate new ideas.
Moving creativity forward
The Durham Creativity Commission is a collaboration between Arts Council England and Durham University that aims to identify ways in which creativity, and specifically creative thinking, can play a larger part in our lives.
We are working alongside people in education, as well as businesses and arts and science communities, collecting their views on creativity and creative thinking. We will also be looking across these groups to determine whether or not there is a relationship between creativity and mobility, creativity and identity as well as creativity and well-being. We hope to be able to show that thinking creatively can not only be encouraged and furthered in a variety of contexts, but can also lead to positive outcomes on a personal, social and economic level.

In a rapidly changing world, creativity is important for people and society on many levels – it can help to generate personal satisfaction and be important for economic development. This is why creative thinking must be a key priority in educational environments.
In the same way, creativity must also be recognised and encouraged in the workplace. Because, after all, it’s creative thinking that leads to problem solving and innovation in a range of areas.
- Teaching creativity
- Global creativity index
- Play and creativity

Clinical Trial Manager

PhD Scholarship

Senior Lecturer, HRM or People Analytics

Centre Director, Transformative Media Technologies

Postdoctoral Research Fellowship
Essay Service Examples Art Creativity
Essay on Art and Creativity
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Adolescence
People frequently ask these questions: can one teach or stimulate creativity in an individual? Can...
- Intelligence
Intelligence is a construct that encompasses many ways the mind processes and expands on...
Creativity stands as a cornerstone of human cognition, a dynamic force propelling innovation,...
- Teacher/Teaching
Without creativity to boost our lives and capture our attention, life would be completely...
Since a long time, intelligence and creativity have been seen as two separate abilities and...
What is more important, imagination or knowledge? This is an eternal question. Knowledge is...
- Effects of Technology
The topic of how the internet impacts creativity in people is tentative. It can be presumed to be...
From an extended time, creativity has been a neglected subject in psychological research. This can...
“Creativity is presented in assigning to do a task; creativity must meet be of a quality of a kind...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Understanding the Psychology of Creativity
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Michael H / DigitalVision / Getty Images
What Is Creativity?
When does creativity happen, types of creativity, what does it take to be creative, creativity and the big five, how to increase creativity, frequently asked questions.
What is creativity? Creativity involves the ability to develop new ideas or utilize objects or information in novel ways. It can involve large-scale ideas that have the potential to change the world, such as inventing tools that impact how people live, or smaller acts of creation such as figuring out a new way to accomplish a task in your daily life.
This article explores what creativity is and when it is most likely to happen. It also covers some of the steps that you can take to improve your own creativity.
Studying creativity can be a tricky process. Not only is creativity a complex topic in and of itself, but there is also no clear consensus on how exactly to define creativity. Many of the most common definitions suggest that creativity is the tendency to solve problems or create new things in novel ways.
Two of the primary components of creativity include:
- Originality: The idea should be something new that is not simply an extension of something else that already exists.
- Functionality: The idea needs to actually work or possess some degree of usefulness.
In his book Creativity: Flow and the Psychology of Discovery and Invention , psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi suggested that creativity can often be seen in a few different situations.
- People who seem stimulating, interesting, and have a variety of unusual thoughts.
- People who perceive the world with a fresh perspective, have insightful ideas and make important personal discoveries. These individuals make creative discoveries that are generally known only to them.
- People who make great creative achievements that become known to the entire world. Inventors and artists such as Thomas Edison and Pablo Picasso would fall into this category.
Experts also tend to distinguish between different types of creativity. The “four c” model of creativity suggests that there are four different types:
- “Mini-c” creativity involves personally meaningful ideas and insights that are known only to the self.
- “ Little-c” creativity involves mostly everyday thinking and problem-solving. This type of creativity helps people solve everyday problems they face and adapt to changing environments.
- “Pro-C” creativity takes place among professionals who are skilled and creative in their respective fields. These individuals are creative in their vocation or profession but do not achieve eminence for their works.
- “Big-C” creativity involves creating works and ideas that are considered great in a particular field. This type of creativity leads to eminence and acclaim and often leads to world-changing creations such as medical innovations, technological advances, and artistic achievements.
Csikszentmihalyi suggests that creative people tend to possess are a variety of traits that contribute to their innovative thinking. Some of these key traits include:
- Energy: Creative people tend to possess a great deal of both physical and mental energy. However, they also tend to spend a great deal of time quietly thinking and reflecting.
- Intelligence: Psychologists have long believed that intelligence plays a critical role in creativity. In Terman’s famous longitudinal study of gifted children, researchers found that while high IQ was necessary for great creativity, not all people with high IQs are creative. Csikszentmihalyi believes that creative people must be smart, but they must be capable of looking at things in fresh, even naïve, ways.
- Discipline: Creative people do not just sit around waiting for inspiration to strike. They are playful, yet they are also disciplined in the pursuit of their work and passions.
Certain personality traits are also connected to creativity. According to the big five theory of personality , human personality is made up of five broad dimensions:
- Conscientiousness
- Extroversion
- Agreeableness
- Neuroticism
Each dimension represents a continuum, so for each trait, people can be either high, low, or somewhere between the two.
Openness to experience is a big five trait that is correlated with creativity. People who are high on this trait are more open to new experiences and ideas. They tend to seek novelty and enjoy trying new things, meeting new people, and considering different perspectives.
However, other personality traits and characteristics can also play a role in creativity. For example, intrinsic motivation , curiosity, and persistence can all determine how much people tend to pursue new ideas and look for novel solutions.
While some people seem to come by creativity naturally, there are things that you can do to increase your own creativity .
Some strategies that can be helpful for improving creativity include:
- Being open to new ideas : Openness to experience is the personality trait that is most closely correlated with creativity. Focus on being willing to try new things and explore new ideas.
- Be persistent : Creativity is not just about sitting around waiting for inspiration to strike. Creative people spend time working to produce new things. Their efforts don't always work out, but continued practice builds skills that contribute to creativity.
- Make time for creativity : In addition to being persistent, you also need to devote time specifically toward creative efforts. This might mean setting aside a little time each day or each week specifically to brainstorm, practice, learn, or create.
Csikszentmihalyi has noted that creativity requires both a fresh perspective combined with discipline. As Thomas Edison famously suggested, genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration.
A Word From Verywell
Creativity is a complex subject and researchers are still working to understand exactly what factors contribute to the ability to think creatively. While some people seem to come by creativity naturally, there are also things you can do to build and strengthen this ability.
The late Maya Angelou also suggested that thinking creativity helps foster even greater creativity, "The important thing is to use it. You can’t use up creativity. The more you use it, the more you have," she suggested.
Creativity does not reside in one single area of the brain; many areas are actually involved. The frontal cortex of the brain is responsible for many of the functions that play a part in creativity.
However, other parts of the brain impact creativity as well, including the hippocampus (which is important to memory) and the basal ganglia (which is essential in the memory of how to perform tasks). The white matter of the brain, which keeps the various parts of the brain connected, is also essential for creative thinking.
Research suggests that people can train their brains to be more creative. Engaging in cognitively stimulating tasks, going on a walk, finding sources of inspiration, and meditating are a few strategies that may help boost creative thinking abilities.
The "big five" are the broad categories of traits that make up personality. The five dimensions are openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. Each trait involves a range between two extremes, and people can be either at each end or somewhere in the middle.
American Psychological Association. The science of creativity .
Csikszentmihalyi M. Creativity: Flow and the Psychology of Discovery and Invention . New York: HarperCollins; 2013.
Kaufman J, Beghetto R. Beyond big and little: The four C model of creativity . Review of General Psychology . 2009;13(1):1-12. doi:10.1037/a0013688
Kaufman SB, Quilty LC, Grazioplene RG, et al. Openness to experience and intellect differentially predict creative achievement in the arts and sciences . J Pers . 2016;84(2):248-258. doi:10.1111/jopy.12156
Elliot J. Conversations With Maya Angelou . Jackson, Miss.: University Press of Mississippi; 1998.
Cavdarbasha D, Kurczek J. Connecting the dots: your brain and creativity . Front Young Minds . 2017;5:19. doi:10.3389/frym.2017.00019
Sun J, Chen Q, Zhang Q, Li Y, Li H, Wei D, Yang W, Qiu J. Training your brain to be more creative: brain functional and structural changes induced by divergent thinking training . Hum Brain Mapp . 2016;37(10):3375-87. doi:10.1002/hbm.23246
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Few things shape the human experience as profoundly or as pervasively as creativity does. And creativity raises a wealth of philosophical issues. Since art is such a salient domain of creativity, you might assume, at first, that the philosophy of creativity is the philosophy of art or aesthetics, or a branch thereof. But creativity invites questions of its own that go beyond the purview of those other fields.
Note that the adjective “creative” can be applied to three kinds of things: a person (“Beyoncé is creative”), a process or activity (“Tell us about your creative process”), or a product , where the latter is taken broadly to include an idea in someone’s mind or an observable performance or artifact (“That’s a creative design”).
Now suppose you are looking at a creative product, like a painting or sculpture. The philosophy of art may ask, “What makes this a work of art?” and aesthetics may ask, “What makes this beautiful?”. By contrast, the philosophy of creativity asks, “What makes this creative? Is it just that it’s new, or must it meet further conditions?” We may ask the same question not just of artworks but of any creative product, whether it be a new scientific theory, a technological invention, a philosophical breakthrough, or a novel solution to a mathematical or logical puzzle. Beyond creative products, we can ask about the creative process : Must it proceed without following rules? Is it conscious, unconscious, or both? Must it be an expression of the creator’s agency, and, if so, must that agency be exercised intentionally? Exactly how does the process manage to produce new things? Can it be explained scientifically? Furthermore, we can ask about creative persons, or more generally, creators. What does it mean for a person to be creative? Is it a virtue to be creative? What capacities and characteristics does a being need to have in order to be creative? Could a computer be creative? These are the kinds of questions animating the literature we’ll survey below.
Some of these questions have an empirical dimension, most obviously those which pertain to how the creative process is actually carried out. Thus, much of the research we’ll canvass falls under the inter-disciplinary umbrella of cognitive science, with contributions not only from philosophers but also from researchers in neighboring fields like psychology, neuroscience, and computer science.
1. The Philosophy of Creativity: Past and Present
2.1 challenges to the value condition, 2.2.1 surprise, 2.2.2 originality, 2.2.3 spontaneity, 2.2.4 agency, 2.3 is creativity a virtue, 3. can creativity be learned, 4. can creativity be explained, 5.1 preparation, 5.2.1 blind variation, 5.2.2 the default-mode network, 5.2.3 imagination, 5.2.4 incubation, 5.3 insight, 5.4 evaluation, 5.5 externalization, 5.6 worries and future directions, 6. creativity and artificial intelligence, 7. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries.
Given the significance creativity has in our lives and the deep philosophical questions it raises, one might expect creativity to be a major topic in philosophy. Curiously, it isn’t.
To be sure, some of the most prominent figures in the history of Western philosophy have been fascinated with creativity—or what we now call “creativity”. According to some scholars, the abstract noun for creativity did not appear until the nineteenth century—but the phenomenon certainly existed and many philosophers took an interest in it (McMahon 2013; Nahm 1956; Murray 1989; Tatarkiewicz 1980: chapter 8).
To name just a few examples: Plato (4 th century BCE) had Socrates say, in certain dialogues, that when poets produce truly great poetry, they do it not through knowledge or mastery, but rather by being divinely “inspired” by the Muses, in a state of possession that exhibits a kind of madness ( Ion and Phaedrus ). Aristotle (3 rd century BCE), in contrast, characterized the work of the poet as a rational, goal-directed activity of making ( poeisis ), in which the poet employs various means (such as sympathetic characters and plots involving twists of fate) to achieve an end (of eliciting various emotions in the audience). Margaret Cavendish (1623–1673) and Émilie du Châtelet (1706–1749) championed the creative use of the imagination to pursue freedom, overcome prejudice, and cultivate natural abilities even despite social and political oppression . Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) conceived of artistic genius as an innate capacity to produce original works through the free play of the imagination, a process which does not consist in following rules, can neither be learned nor taught, and is mysterious even to geniuses themselves. Schopenhauer (1788–1860) stressed that the greatest artists are distinguished not only by the technical skill they employ in the production of art, but also by the capacity to “lose themselves” in the experience of what is beautiful and sublime (Schopenhauer 1859: Vol. I: 184–194 and Vol. II: 376–402). Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) argued that the greatest feats of creativity, which he took to be exemplified by the tragic poetry of ancient Greece, was being born out of a rare cooperation between the “Dionysian” spirit of ecstatic intoxication, which imbues the work with vitality and passion, and the “Apollonian” spirit of sober restraint, which tempers chaos with order and form (Nietzsche 1872 [1967]). William James (1842–1910) theorized about creative genius exerts the causal power to change the course of history (Simonton 2018). This is just a glimpse of what each of these philosophers had to say about creativity, and many other figures could be added to their number.
Nevertheless, while some of the topics explored by earlier thinkers have come to occupy a central place in philosophy today—such as freedom, justice, consciousness, and knowledge—creativity is not among them. Indeed, “philosophy of creativity” is still a neologism in most quarters, just as, for example, “philosophy of action” and “philosophy of gender” were not too long ago. However, philosophical work on creativity has been picking up steam over the last two decades (as shown, for example, in a few important collections of essays: B. Gaut & Livingston 2003; Krausz, Dutton, & Bardsley 2009; Paul & Kaufman 2014; B. Gaut & Kieran 2018). We’ll now dive into those contributions, along with earlier work, beginning with what is perhaps the most basic question one can ask in this field.
2. What is Creativity?
As we noted at the outset, the term “creative” can be applied to three kinds of things: a person , a process , or a product (where a product could be an idea, performance, or physical artifact).
Most definitions focus on the product. According to one common approach, persons or processes are creative to the extent that they produce creative products, and a product is creative if it meets two conditions: in addition to being new it must also be valuable . Many theorists argue that novelty is not sufficient, because something can be new but worthless (e.g., a meaningless string of letters), in which case it doesn’t merit the compliment of being called “creative”. Immanuel Kant is often cited as anticipating this definition of creativity in his discussion of (artistic) genius. According to a common interpretation, Kant defines (artistic) genius as the ability to produce works that are not only “original”—since “there can be original nonsense”—but also “exemplary” (Kant 1790: §§43–50 [2000: 182–197]). (Hills & Bird [2018] challenge this reading of Kant.) This definition is so widely accepted among psychologists that it has come to be known as “the standard definition” of creativity in psychology. In practice, “creativity is often not defined” (J.C. Kaufman 2009: 19) in psychological experiments—more on this in §5 below. When psychologists do explicitly adopt a definition, however, they usually say that creative products are not only new, but also valuable in some way, though they variously express the product’s value in terms of its being “useful”, “effective”, “worthwhile”, “fit”, or “appropriate to the task at hand” (Bruner 1962: 18; A. J. Cropley 1967: 67; Jackson & Messick 1965: 313; Kneller 1965: 7; Cattell & Butcher 1968; Heinelt 1974; J.C. Kaufman 2009: 19–20; S.B. Kaufman & Gregoire 2016; Stein 1953; Sternberg & Lubart 1999: 3—for an overview, see Runco & Jaeger 2012). A few psychologists have suggested that the standard definition doesn’t fully capture the concept of creativity (Amabile 1996; Simonton 2012b). As for philosophers, at least one of them defends the standard definition with qualifications (Klausen 2010), but many of them challenge it, as we’ll soon see.
While it is uncontroversial that novelty is required for creativity, philosophers have refined that point. Certain examples may seem, at first, to suggest that novelty isn’t really necessary for creativity. Newton’s discovery of calculus was creative even if, unbeknownst to him at the time, Leibniz got there first—one of many examples of what are called “multiples” in the history of science (Simonton 2004). A beginning student’s idea that freedom is compatible with causal determinism might be creative even if, as she will soon learn, philosophers have been defending such “compatibilist” theories for millennia. However, examples like these do not force us to abandon the novelty requirement, but only to qualify it. Newton’s calculus and the student’s compatibilism were not new in all of history, but they were new to their respective creators, and that is enough for them to count as creative. In the terminology of philosopher Margaret Boden, these ideas are “psychologically creative” (P-creative) even though they are not “historically creative” (H-creative). Notice that P-creativity is more fundamental. Anything that is new in all of history (H-creative) must also be new to its creator (P-creative). Thus, creativity always exhibits psychological novelty, though it doesn’t always exhibit historical novelty.
Again, no one denies that a creative product must be new, at least to its creator. But as we’ll now see, some philosophers depart from the standard definition of creativity by rejecting the value condition ( §2.1 ), or by proposing some further condition(s) ( §2.2 ), or by doing both.
Some theorists have argued that although creative things are valuable, we shouldn’t build value into the definition of creativity, because doing so is not informative or explanatory:
Knowing that something is valuable or to be valued does not by itself reveal why or how that thing is. By analogy, being told that a carburetor is useful provides no explanatory insight into the nature of a carburetor: how it works and what it does. (Stokes 2008: 119; Stokes 2011: 675–76)
Those who maintain that value is required for creativity might reply that it doesn’t need to be informative or explanatory. Being a man is required for being a bachelor even though it’s not informative or explanatory to say that bachelors are men. Stokes notes that “creative” is a term of praise, and uses this point to argue that what is creative must be produced intentionally (since we don’t rightly praise what is unintentional or accidental)—an idea we’ll return to below. But the same point also seems to imply that what is creative must also have value (since we don’t rightly praise what doesn’t have value). And while the concept “carburetor” is value-neutral, as shown by the fact that a carburetor can be worthless or useless (if it’s broken), “creative”, one might argue, is a value-laden concept, like “progress”. Progress necessarily involves novelty or change, but we don’t praise change as progress unless it’s good change. Likewise, defenders of the value condition urge, creativity necessarily involves novelty, but we don’t praise novelty as creative unless it’s good novelty.
Other critics use counterexamples to argue that value isn’t necessary for creativity, the most prominent cases being ones of immoral creativity. (For a collection of essays by psychologists on the phenomenon of immoral or so-called “dark” creativity’, see D. Cropley et al. 2010). Putative cases of immoral creativity include creative accounting to cheat investors or creative testimony to mislead jurors, and the stock example in the literature is creative torture or murder. One can imagine novel and well-designed murders, as Thomas De Quincey once did in a satirical essay:
[S]omething more goes to the composition of a fine murder than two blockheads to kill and be killed—a knife—a purse—and a dark lane. Design, gentlemen, grouping, light and shade, poetry, sentiment, are now deemed indispensable to attempts of this nature. Mr. Williams has exalted the ideal of murder to all of us […] Like Æschylus or Milton in poetry, like Michael Angelo in painting, he has carried his art to a point of colossal sublimity. (De Quincey 1827; see also discussion in Battin et al. 1989)
Innovative ways of inflicting needless agony and craftily designed murders are not good (they have no value), and yet they can be creative. If this is right, then it seems to follow that creativity doesn’t require value.
One way of trying to save the value condition is by flatly denying that torture methods can be creative, and by denying more generally that creative things can be bad (Novitz 1999). But such denial seems ad hoc and implausible—“evil creativity” is not a contradiction in terms—and some have argued that this denial faces other problems besides (Livingston 2018).
Other theorists revise or qualify the value condition in order to accommodate examples of immoral creativity. Paisley Livingston (2018) proposes that a creative product only needs to be instrumentally valuable or “effective” as means to its intended end, regardless of whether that end is morally good, bad, or indifferent. Berys Gaut (2018) distinguishes between something’s being good (or good, period) versus being good of its kind . In his view, a new way of wielding blades and pulleys may be creative if it’s a good of its kind—good as a method of torture—even though it isn’t good. In order for something to count as creative, Gaut says, it doesn’t need to be good; it just needs to be good of its kind.
Alison Hills and Alexander Bird (2018) are unconvinced by such qualifications. They contemplate an elaborate torture device that ends up killing its victims immediately, “without enough suffering on the way”. The device may still be creative, they hold, even though “as a method of torture, it’s no good” (2018: 98). Indeed, they argue, a creative item needn’t be good in any way at all, not even for its creator. The ineffective torture device just described doesn’t satisfy its creator’s preferences, it doesn’t give him pleasure, it isn’t an achievement, it doesn’t contribute at all to his well-being—and yet, they contend, it may be creative, provided that it’s new and was produced in the right way. Exactly what “the right way” amounts to is the topic we turn to next.
2.2 Other proposed conditions
With or without the value condition, some theorists argue that a product must satisfy one or more further conditions, beyond being new, in order to count as creative. The four most prominent proposals are that the product must be (i) surprising, (ii) original (i.e., not copied), (iii) spontaneous, and/or (iv) agential. Each of these is a condition on the process of creativity. To be clear, we are still concerned with what it means for a product to be creative, but the proposals we’ll now consider say that in order for a product to count as creative, it must be brought about in the right way.
Margaret Boden holds that a creative product must be “ new, surprising, and valuable ” (2004: 1; cf. Boden 2010; 2014). It is perhaps most natural to assume that being surprising—like being new and valuable—is a feature of a product. But while Boden does think of creative products as surprising, her interest is more fundamentally in the underlying generative process, in how a creator manages to make something surprising. In her view, there are “three types of creativity”—combinatorial, exploratory, and transformative—“which elicit different forms of surprise, [and] are defined by the different kinds of psychological processes that generate the new structures” (2010: 1, italics added).
Combinatorial creativity occurs when old ideas are combined in new ways. Obvious examples include fictional hybrid creatures or chimeras: add wings to a horse (Pegasus), add the tail of a fish to a woman’s head and upper-body (a mermaid), add a lion’s body to a woman’s head and torso (Sphinx), and so on. Other combinations are found in analogies, such as when Niels Bohr compared an atom to the solar system. The term “combination” can refer either to the product of things combined or to the process of combining them, but Boden’s focus is on the process here, on the fact that one way to generate new ideas is to begin with old ideas and combine them in new ways.
To explain her other two kinds of creativity, Boden invokes the notion of a “conceptual space”, which is roughly a system comprising a set of basic elements (e.g., basic ideas or representations) as well as rules or “constraints” for manipulating or re-combining those elements. A conceptual space is not a painting, song, or poem, for example; it’s a way of creating a painting, song, poem, or theory. The rules or constraints are “the organizing principles that unify and give structure to a given domain of thinking”. And so a conceptual space is
the generative system that underlies that domain and defines a certain range of possibilities: chess moves, or molecular structures, or jazz melodies. (1994: 79)
We could think of a conceptual space as not just a set of thoughts but also a style of thinking defined by rules for generating new thoughts.
“Within a given conceptual space”, Boden observes, “many thoughts are possible, only some of which may have been actually thought” (2004: 4). Some conceptual spaces contain more possibilities than others. Consider different games. Tic-tac-toe is such a simple game that all of its possible moves have already been made many times over. The same is not true in chess, by contrast, which allows for a mind-boggling number of possible moves. The range of possible ideas is also practically inexhaustible in literature, music, the visual and performing arts, as well as the various domains of theoretical inquiry. And within those pursuits, there are various “structured styles of thought”—genres, paradigms, methodological orientations—which Boden thinks of as conceptual spaces.
Boden argues that the elements as well as the operating rules of a conceptual space can be, and in some cases have been, captured in computer programs. She has used this point not only to argue that computers can be creative (a topic we’ll return to below in §5 ), but also to suggest that we should employ the computational model of the mind in order to explain how humans create.
With her notion of conceptual spaces in hand, Boden says that exploratory creativity occurs within a given conceptual space. The new idea that emerges is one that was already possible within that space, because it was permitted by its rules. “When Dickens described Scrooge as ‘a squeezing, wrenching, grasping, scraping, clutching, covetous old sinner,’” Boden writes, “he was exploring the space of English grammar” in which “the rules of grammar allow us to use any number of adjectives before a noun” (Boden 1994: 79). Dickens’s description may strike us somewhat surprising, unexpected, or improbable, but it doesn’t have an air of impossibility about it.
By contrast, Boden argues, another form of creativity does. In this kind of case, the creative result is so surprising that it prompts observers to marvel, “But how could that possibly happen?” (2004: 6). Boden calls this transformational creativity because it cannot happen within a pre-existing conceptual space; the creator has to transform the conceptual space itself, by altering its constitutive rules or constraints. Schoenberg crafted atonal music, Boden says, “by dropping the home-key constraint”, the rule that a piece of music must begin and end in the same key. Lobachevsky and other mathematicians developed non-Euclidean geometry by dropping Euclid’s fifth axiom. Kekulé discovered the ring-structure of the benzene molecule by negating the constraint that a molecule must follow an open curve (Boden 1994: 81–3). In such cases, Boden is fond of saying that the result was “downright impossible” within the previous conceptual space (Boden 2014: 228).
Boden’s definition of creativity has perhaps been most influential among researchers who share her intertest in computer creativity (e.g., Halina 2021; Miller 2019: ch. 3; du Sautoy 2019). In a variation of Boden’s account, one philosopher proposes that what makes a mental process creative is not that it actually involves “the recombination of old ideas or the transformation of one’s conceptual space”, but rather that the creator experiences the process as having one of those features (Nanay 2014).
Maria Kronfeldner (2009; 2018) argues that the process of making something creative must exhibit originality . As she uses the term “original”, it does not simply mean “new”; instead, it has to do with the kind of causal process the creator must employ. She motivates her view by asking why it’s the case that, as we noted earlier, psychological novelty is required for creativity while historical novelty is not. Why is it, for example, that Newton’s invention of calculus was creative even if Leibniz invented it first? The answer, of course, is that it’s because Newton didn’t copy his calculus from Leibniz. Insofar as Newton came up with calculus independently, on his own, then he exhibited originality in his discovery, even though someone else got there first. This originality, Kronfeldner argues, is essential to creativity.
Kronfeldner (2009; 2018) also argues that spontaneity is required for creativity. An idea occurs spontaneously to the extent that it is produced without foresight or intentional control. If you were to foresee the output of the creative process at the beginning of that process, then you wouldn’t need any further process to come up with it. So if an idea is creative, you cannot have fully seen it coming. To that extent, insight comes as a surprise, hence the common phenomenological observation that creative breakthroughs feel like they come unbidden or out of the blue: “Eureka!”, “Aha!”, a lightbulb turns on.
Gaut (2018: 133–137) agrees that creativity requires spontaneity, and he points out, as Kronfeldner does, that it comes in degrees. He explains that you do something spontaneously to the extent that do it without planning it in advance. If you are going to act creatively, he argues, you cannot set out to follow an “exact plan”—a mechanical procedure, routine, or algorithmic rule—which would give you advance knowledge of exactly what the outcome will be and exactly the means you'll take to achieve it. At the outset of a creative act, you have to be to some extent ignorant of the end, or the means, or both. That ignorance opens up room for spontaneity and creativity.
Some philosophers argue that an item does not count as creative unless it has been produced by an agent. Consider a unique snowflake with an intricate shape, a distinctive sunset with stunning layers of red-orange hues, a novel patterning of dunes across a wind-blown desert. All of these things are aesthetically valuable and new. None of them are creative, however, insofar as they all occurred naturally and were not made by an agent. Gaut uses examples like these to argue that creative things must be created by agents (B. Gaut 2018: 129–30; cf. B. Gaut 2010, and B. Gaut 2014b) and several other philosophers agree (Carruthers 2006, 2011; Kieran 2014a, 2014b; Stokes 2008, 2011, 2014; Paul & Stokes 2018).
Of course, many theists would maintain that everything in nature is the handiwork of an agent—namely, God—and so arguably it would make sense for them to regard a natural phenomenon as creative if it is valuable and new. For theists, the unparalleled beauty of nature is a reason to praise the Creator. But this only supports the conceptual point that creativity, by definition, requires agency. We may coherently regard valuable new things as creative if we attribute them to a creative agent, as the theist does with the natural world; otherwise, we can’t. So again, it seems, creativity requires agency.
This leaves open the question of exactly how a creator’s agency must be exercised in order for the result to count as creative. Some philosophers argue that the agent’s act of creation must be intentional . Suppose you are snowboarding on a powder day and, unbeknownst to you, the tracks from your board result in a pleasing new pattern as viewed from high above. The new pattern has aesthetic value, but it isn’t creative. And that is because you didn’t intend to make it. Underlying this intuition, as well as our intuitions about the natural phenomena above, is the fact that “creative” is a term of praise, and we do not extend praise (or blame) for things that are not done by an agent, or for things that an agent doesn’t do in some sense intentionally.
While a number of philosophers endorse some version of the agency requirement for creativity, many theorists make no mention of it, whether to endorse it or reject it, including all of the psychologists cited above. Further, at least two philosophers are willing to attribute creativity to natural phenomena like trees and evolutionary processes: Arnheim (2001) and, in recent work, Boden (2018). These latter theorists don’t discuss agency as such, but insofar as the natural phenomena they call creative are not the result of agency, their view would imply that agency isn’t required for creativity.
The four proposals we’ve just considered all say that a product must arise from a certain kind of process—a process that exhibits surprise, originality, spontaneity, or agency—in order to count as creative. While there is wide agreement among philosophers that creativity requires some special kind of process, not just a special product, there is no consensus on what is required of the process. Of the four process conditions described here, the agency condition seems to be the one that is explicitly endorsed by the greatest number of philosophers thus far, though even they are still just a handful. And as we’ve seen, the other proposed conditions have serious arguments in their favor as well.
Some philosophers argue that if any process requirement is correct, this has an intriguing corollary for judgements about creativity: Even when we are explicitly judging only that a product is creative, we are implicitly assuming something about the process by which it was made. Suppose, for illustration, that the agency requirement is correct—that being generated through an agential process is built into the very concept of a creative product. Suppose further that you are applying that concept competently. It follows that if you come across a captivating arrangement of stones on the beach and you judge it to be creative, you are at least implicitly assuming that it was created through an agential process. If someone later persuades you that the stones happened to be moved into place by the wind and waves, not by any agent but just by chance, then you may still regard the result as aesthetically interesting but you would have to rescind your judgement that it is creative. So if the agency condition is correct, whenever you point to some item and say, “This is creative”, what you are saying, in part is, “This resulted from a creative process”. Furthermore, on this view, analogous implications follow if any other process condition is correct (Paul & Stokes 2018).
Having considered what is required for something to count as a creative product , and whether it must be produced by a certain kind of process , we now turn to analysis of the creative person .
Some theorists suggest that creativity, as an attribute of persons, is an ability to perform creative acts or produce creative things (Boden 2004). Others argue, however, that creativity isn’t merely an ability. An ability is something you can possess without ever putting it to use. You might have the ability to learn Swahili, for example, without ever making the effort to learn that language, despite having ample opportunities to do so. Creativity is different in this regard. If someone has the ability to be creative but never uses that ability when given numerous chances to do so, we would not call that person creative. Creative people are not merely able to act creatively. They are, moreover, disposed to exercise that ability, such that they do act creatively, at least some of the time, when the occasion arises. On this view creativity is a disposition , also referred to as a trait (Grant 2012; cf. B. Gaut 2014b, 2018).
Philosophers have long distinguished virtues as a special subclass of dispositions or traits. In Western philosophy, the tradition of theorizing about virtues goes back to the ancient Greeks, and over the last half-century it has enjoyed a renaissance in ethics (see entry on virtue ethics ) and, more recently, in epistemology (see entry on virtue epistemology ) and aesthetics (Lopes 2008; Roberts 2018; Hills 2018). Traditional examples of virtues include wisdom, justice, temperance, and courage. Should creativity be added to the list?
The answer depends, of course, on what it means for a trait to be a virtue. At the very least, a virtue is a trait that is good or valuable. So whether creativity counts as a virtue in this minimal sense depends on whether creativity is necessarily valuable, a point which is contested, as we saw in the previous section. In fact, those who contend that creativity isn’t necessarily valuable often do so in order to prove that it isn’t a virtue.
But let’s suppose for the sake of argument that creativity is indeed a valuable trait. Is it also a virtue in some more robust sense? Virtue theorists commonly take their cue from Aristotle’s classic discussion in the Nichomachean Ethics . Citing justice and temperance as paradigm virtues, Aristotle asserts that a trait must meet at least three conditions to count as a virtue:
For actions in accord with the virtues to be done temperately or justly it does not suffice that they themselves have the right qualities. Rather, the agent must also be in the right state when he does them. First, he must know [that he is doing virtuous actions]; second he must decide on them, and decide on them for themselves; and thrid, he must also do them from a firm and unchanging state. ( EN II.4, 1105a28–1105a33)
So, for example, if you return something you’ve borrowed, that act exhibits the virtue of justice if and only if (1) you know that you’re returning what you borrowed, (2) you choose to do so because it is the just thing to do, and for no other reason, and (3) you are disposed to do the just thing across the range of circumstances when the opportunity arises. In addition to justice and temperance, Aristotle enumerates other ethical virtues like prudence, generosity, and courage, as well as the intellectual virtue of theoretical wisdom. In his view, each of these traits requires one to meet the three conditions above. While he does not consider whether creativity is a virtue, we may ask whether creativity also has these three criteria. Does one have to meet these three requirements in order to count as creative?
We’ll begin with the third requirement to set it to one side. Does a person’s act count as creative only “if he does it from a fixed and permanent disposition of character”? Examples suggest otherwise. Consider the poet Arthur Rimbaud, who abandoned poetry at the age of 21 to pursue a life of adventure. The fact that he never produced another poem after that does not count against the fact that he was a creative poet in his youth (B. Gaut 2014b). Unlike the Aristotelian virtues, then, creativity does not have to be a permanent disposition.
Even so, it would still be significant if creativity turned out to be like an Aristotelian virtue in meeting the first two requirements. And arguably, creativity does meet the first requirement. A person doesn’t count as doing something creative unless “he knows what he is doing”. This was already implied by the agency condition for creativity discussed earlier.
Where things get interesting is with Aristotle’s second criterion for virtue. In order for your action to count as virtuous, he says, you have to do it “for its own sake”—i.e., you have to do it because you value virtue as an end itself, and not as a means to some external reward like praise, money, status, fame, or winning a competition. Consider the virtue of generosity, for instance. If you give money to someone in need merely because it will make you look good in the eyes of your friends, then you aren’t really being generous. Your act may outwardly look like generosity, but it’s not the real thing. To exhibit real generosity, you have to pursue generosity as an end in itself; you have to help others just for the sake of helping others. Now contrast being generous with being polite. If you compliment your colleague on the good work she’s done, then even if you’re doing this in order to manipulate her, you are being polite to her. You can have an ulterior motive for being polite. So politeness is not a virtue the way generosity is.
Is creativity a virtue in this respect? That is, does being creative require acting creatively for its own sake? Matthew Kieran’s (2014a, 2014b, 2018) answer is a qualified yes. While he grants that you can be motivated by external rewards to exhibit “minimal creativity” in producing valuable new things, he maintains that “exemplary creativity” requires you to be motivated by the value of creativity itself. Thus, in his view, exemplary creativity is a virtue.
To support this claim, Kieran points to a research program in psychology which purports to show that creativity is driven by “intrinsic motivation” rather than “extrinsic motivation”. A classic experiment in this program is “the magic markers study”, in which kids end up producing less creative drawings when they are offered a prize (Lepper et al. 1973). Many other studies have reported similar results, which lead Teresa Amabile to conclude, at first without qualification, that creativity is enhances by intrinsic motivation and hampered by extrinsic motivation (Amabile 1983: 107).
Further research introduced complications. In some studies, subjects were given “immunization techniques” whereby they were first primed or trained to focus on intrinsically motivating factors like the pleasure or aesthetical value of engaging in artistic activities, and it was found that when they engaged in those activities afterward, external rewards actually enhanced their creativity.
As researchers interpreted these findings, offering reward can support one’s intrinsic motivation, provided that the reward works either to boost one’s sense of agency or to provide useful feedback about what’s working and what isn’t. Intrinsic motivation is still what fuels creativity, on this interpretation; rewards help only indirectly, when they reinforce intrinsic motivation. This lead Amabile to revise her hypothesis as the Intrinsic Motivation Principle (IMP):
Intrinsic motivation is conducive to creativity; controlling extrinsic motivation is detrimental to creativity, but informational or enabling extrinsic motivation can be conducive, particularly if initial levels of intrinsic motivation are high. (1996: 107)
Kieran takes this as evidence for his claim that creativity, or at least what he calls exemplary creativity, requires intrinsic motivation and is therefore a virtue in that respect.
Objecting to this proposal, Gaut cites evidence that extrinsic motivation is not always detrimental to creativity. In one study, students in an introductory psychology class came up with more creative short story titles if they were offered a financial reward (Eisenberger & Rhodes 2001). In the studies where immunization techniques were used, proponents of IMP argue that rewards enhance creativity only indirectly, by buttressing intrinsic motivation. But in this case no such techniques were used, and so it seems the prospect of a reward enhanced creativity directly.
Further, Gaut argues that this point coheres with the role that rewards seem to play in so many real-world cases of creative achievement. In their quest to discover the structure of the DNA molecule, Watson and Crick were driven “to imitate Linus Pauling and beat him at his own game” (Watson 1968 [1999: 46]). Picasso and Matisse were both spurred on by their rivalry with each other (Flam 2003: 37). Paul McCready says he was driven to invent his award-winning human-powered glider in 1977 because he needed the prize-money to pay off his debts:
I felt that I didn’t have the time to mess with such things, but I had this strong economic motivation to take an interest in man-powered flight, so I charged around trying to figure out a way to solve it. (quoted in Sternberg & Lubart 1995: 242)
One historian argues that in World War II the Poles beat the French in cracking the Germans’ Enigma Code because they were more terrified of German invasion (Singh 1999: ch. 4). Gaut quips: “Fear of death is a more powerful motivator than the intrinsic satisfactions of code breaking” (Gaut 2014b: 196).
Finally, Gaut points out that even if IMP is true, it is only a causal, probabilistic claim: intrinsic motivation is “conducive” to creativity; extrinsic motivation is “detrimental”. But for a trait to be a virtue, intrinsic motivation must be conceptually necessary for the exercise of that trait. If we learn that someone gave to charity just to enhance his reputation, we conclude that he wasn’t really being generous. By contrast, if we discover that someone created gorgeous artwork just for the fame and glory, we may then lose some of our admiration for her creativity, but we do not deny that she was being creative.
Kieran could remind us that, in his view, intrinsic motivation is not required for all creativity, but only for the special form of it that he calls exemplary creativity. Anticipating this reply, Gaut says that to distinguish between two forms of creativity is just to concede his point. There are not two forms of generosity, one that requires intrinsic motivation and another that does not. If your act of giving isn’t motivated by the right kind of reason, then it doesn’t count as an act of generosity at all. Thus, Gaut argues, to grant the possibility of non-exemplary creativity is to grant that, unlike generosity, creativity isn’t a virtue in the traditional Aristotelian sense.
Another way to examine relations between creativity and virtue is through the lens of virtue epistemology. Linda Zagzebksi defines a virtue
as a deep and enduring acquired excellence of a person, involving a characteristic motivation to produce a certain desired end and reliable success in bringing about that end. (1997: 137, italics added)
While there is a lot packed into this definition, what we’ll pinpoint here is the idea that virtue involves reliable success in achieving a desired end, and that the agent who is epistemically virtuous, in particular, is one who is reliably successful in achieving knowledge. Knowledge requires truth, of course, so an epistemic virtue is a trait that is “truth-conducive”. Epistemologists typically regard a process as truth-conducive to the extent that the beliefs it produces are more often true than false. But Zagzebksi proposes that a process or trait may be truth-conducive in a different sense, insofar as it is necessary for advancing knowledge in some area, even if it produces a very small proportion of true beliefs. Creativity, she claims, is truth-conducive in this sense, and thus it qualifies as an epistemic virtue (1997: 182). Also note the emphasis on agency. In contrast to contemporary western epistemology, virtue epistemology identifies the agent (rather than, say her beliefs) as the essential locus of epistemic valence; it is the agent who is epistemically good (or not). This emphasis comports well with the proposal, discussed above, that the creator’s agency is necessary for genuine creative achievement. A virtue-theoretic approach thus illuminates what may (as we will discuss again later) be essential to creativity, namely, a process that non-trivially involves a responsible agent.
We’ve seen that even after we fix a specific referent for the term “creative”—whether it be a person, process, or product—there are lively disagreements about what it means. These debates often seem to presuppose that the term always expresses the same concept, for which we can seek necessary and sufficient conditions. But we’ve also seen that some theorists distinguish between different concepts of creativity, corresponding to different senses of the term “creative”. In future work we may see theorists develop such pluralistic approaches in more detail. The trick, though, will be to give principled reasons for multiplying different concepts of creativity so that the analyses do not simply reduce to saying that anything goes.
There is a long tradition of thinkers who answer no to the question above. Two of the most influential are from the eighteenth century—Edward Young and Immanuel Kant—who were concerned specifically with genius , the capacity for achieving the very highest levels of creativity. In Conjectures on Original Composition (1759), Young says,
An Original may be said to be of a vegetable nature; it rises spontaneously from the vital root of genius; it grows , it is not made …. (1759 [1966: 7])
His idea is that originality emerges naturally from something implanted in us by nature, and it can only be hindered by learning. Young seems to think of learning as proceeding either through imitation or through the following of rules, and both, he thinks, are detrimental to originality. Regarding imitation he writes,
Born Originals , how comes it to pass that we die Copies ? That meddling ape Imitation … destroys all mental individuality…. (1759 [1966: 20])
And insofar as learning is “a great lover of rules”, he warns that it “sets rigid bounds to that liberty, to which genius often owes its supreme glory” (1759 [1966: 13]).
Kant makes similar claims in his Critique of Judgment (1790). Like Young, he takes genius to be a natural capacity, though a very rare one:
such a skill cannot be communicated, but is apportioned to each immediately from the hand of nature and dies with him. (1790: §47 5:309 [2000: 188])
It certainly cannot be learned through imitation:
genius is entirely opposed to the spirit of imitation . Now since learning is nothing but imitation, even the greatest aptitude for learning, facility for learning (capacity) as such, still does not count as genius. (1790: §47 5:308 [2000: 187])
Nor can it be learned through rules, Kant holds, for genius is
the talent (natural gift) that gives the rule to art … the inborn predisposition of the mind ( ingenium ) through which nature gives the rule to art. (1790: §46 5:307 [2000: 186])
For Kant, a genius does not follow rules; a genius invents the rules, indirectly, by creating exemplary works from which other artists might extract rules and undertake “a methodical instruction in accordance with rules” (1790: §49 5:318 [2000: 196]).
Young and Kant are concerned with genius, specifically, but if we extend their reasoning to creativity in general, as Berys Gaut (2014a) has noted, we can discern two lines of argument:
The imitation argument All learning is a form of imitation. Imitating someone or something is incompatible with being creative. So, one cannot learn to be creative. The rules argument All learning consists in the following of rules. Following rules is incompatible with being creative. So, one cannot learn to be creative. (2014a: 266)
Gaut points out, first of all, that both arguments are invalid. In both cases, what the premises would entail is that learning cannot be creative, that, in other words, you cannot learn creatively (a claim about how you can learn). But even if that were true, it wouldn’t follow that you cannot learn to be creative (a claim about what you can learn). If you absorb the advice of a creative writing manual then this act of learning may not itself be creative. But if the manual is effective—and we’ll see in a moment how it can be—then what you will learn is how to become more creative.
Gaut also challenges the premises of these arguments. To start with the first premise of the imitation argument, it simply isn’t true that all learning proceeds through imitation, as we learn many things through direct experience, trial and error, and many other means.
The second premise is also suspect. Something superficially close to it is true: mere copying is incompatible with being creative. But to the extent that we learn from others by imitating them, this is not merely a matter of copying them. When a child learns to speak the language of those around her, she doesn’t simply parrot the exact same sentences she hears; she absorbs the vocabulary and underlying grammar in a way that enables her to form new sentences of her own devising.
Now for the rules argument. Contrary to the first premise, it cannot be the case that all learning consists in following rules, Gaut argues, because for any given rule there will be hard cases where it is unclear whether or how the rule applies to them, and so an individual still has to use her own judgment in applying the rule.
The second premise is false too. Recall the distinction from §3 above between two kinds of rules. An algorithm serves as an exact plan, specifying both the outcome and the path for getting to it in exact detail. In contrast, a heuristic is a looser “rule of thumb” that leaves room for an agent to exercise her own judgment, choice, and creativity in determining whether, when, and how to follow the rule. While algorithms, in this sense, may preclude creativity, heuristics do not, which is why, as we’ll see below, the teaching of creativity so often takes the form of heuristics.
There is a sense in which the question at hand can be answered empirically: We can show that creativity can be taught simply by pointing to cases where it has been taught. Gaut himself discusses such examples as they occur in mathematics and fiction writing, which we’ll turn to below. But while such cases may suffice to show that creativity can be taught, Gaut further enriches our understanding by explaining how this is possible . He does so partly by articulating and then debunking the imitation and rules arguments to the contrary. But in addition, he offers the following positive argument to show that creativity can be taught and learned. He calls it “the constitutive argument” because it begins with his view of what constitutes or defines creativity itself.
The constitutive argument
- Creativity is a disposition—involving both the ability and the motivation —to produce things that are new and valuable, and to do so in ways that express one’s agency through “the exercise of choice, evaluation, understanding, and judgment” (Gaut 2014a: 273).
- At least some people can learn to enhance their creative motivation .
- At least some people can learn to enhance their creative abilities .
- So, at least some people can learn to become more creative.
Premise 1 recapitulates the point we’ve already seen Gaut and others defend (in §2.3 above), that creativity is not merely an ability but a disposition or trait, whereby the creative person is disposed or motivated to exercise that ability when given the opportunity.
In support of premise 2, Gaut argues that you can strengthen both your intrinsic motivation to be creative (when you take pleasure in your creative activities), as well as your extrinsic motivation to be creative (when you are rewarded with praise, grades, pay, etc. for your creative efforts).
Defending premise 3, Gaut points out that you can develop your ability to produce valuable new things by practising and strengthening the relevant skills. And this development can be substantially aided by learning certain heuristics.
Heuristics are indeed a staple of education in creative pursuits from mathematics (draw the figure; consider special cases; consider extreme cases; generalize the problem; look for a related problem, etc.—see Pólya 1945; Schoenfeld 1982, 1987a, 1987b) to creative writing (write what you know; be specific and detailed in describing sensory experiences; practice seeing similarities between dissimilar things; show, don’t tell, etc.—see Bell & Magrs 2001; Anderson 2006; Maybury 1967; S. Kaufman & J. Kaufman 2009). Gaut also identifies several heuristics that might be used to foster creativity in philosophy, even among children (cf. M. Gaut 2010; B. Gaut & M. Gaut 2011).
With this last theme, Gaut has a kindred spirit in Alan Hájek (2014, 2016, 2017, 2018), who has independently proposed that by using various heuristics, philosophers can enhance their abilities to make valuable contributions to their field, including ideas that are distinctively creative. It has been said that anyone of average talent can become a strong chess player by learning and internalizing certain chess heuristics: “castle early”, “avoid isolated pawns”, etc. Analogously, Hájek suggests, philosophy has a wealth of heuristics— philosophical heuristics —although they have not been as well documented and studied. Sometimes these take the form of useful heuristics for generating counterexamples, such as “check extreme cases”. Sometimes they suggest ways of generating new arguments out of old ones, as in “arguments involving possibility can often be recast as arguments involving time, or space”. Sometimes they provide templates for positive arguments (e.g., ways of showing that something is possible). Hájek offers a catalogue of such philosophical heuristics to show that, contrary to a common assumption, creativity, even in philosophy, can be compatible with, and enhanced by, following rules.
Upon observing the work of creative people, it is natural to wonder: How do they do that? How do people create? The issue we turn to now is whether we could, at least in principle, answer this question scientifically, using the methods of modern empirical psychology and other cognitive and behavioral sciences. Those who take a negative stance on this matter are not merely saying that, in practice, it would be exceedingly difficult for science to explain creativity. They are saying that it’s altogether impossible that science could ever explain creativity.
Hospers (1985) defends this kind of pessimism based on the variety and complexity of creativity, given that creativity occurs not only in art, but in science, theorizing of any sort, engineering, business, medicine, sport, gaming, and so on. At least two worries may follow. First, given the complexity of any one of these individual domains, one might worry that there are simply too many variables to allow for a clear explanation. Art provides a paradigmatic example. Consider an artwork that you judge to be masterful (a sculpture, a painting, a film). Now imagine attempting to describe or identify all the reasons for which you think it is masterful. Take as much time as you like but, the skeptic will urge, any long description you construct will invariably strike you as woefully incomplete by comparison to the artwork, and the experience thereof. So, if the creative achievements of artists, in all of their complexity, cannot even be adequately described, we have little reason to think that such achievements can be explained.
How can theorists respond to these skeptical worries? Both the complexity and generalizability worries might be partially disarmed by noting analogies between creativity and other phenomena. For instance, consider the range of bodily movement involved in some of the very domains of activities listed above: art, science, engineering, medicine, sport. The kinds of bodily action specific to these domains are complex and vary dramatically: the relevant physical movements of the surgeon are much different from the tennis player. However, it is not plausible that this complexity and variety precludes explanation of bodily action in those domains. It simply implies that some features of the explanation will be context-sensitive, that is, specific to that domain of activity. And further to the analogy: the fact that the long description of, say, the tennis serve is incomplete does not preclude it from being apt and explanatory. If this line of reasoning is sound for bodily action, why not also for creative action?
At this point, one might argue that while complexity and generalizability worries would only show that creativity is difficult to explain in practice, the very nature of creativity implies, more strongly, that it could never be explained, not even in principle. Resources to support this kind of pessimism may be adduced from various past philosophers. We need to tread carefully, however, since most of the figures we are about to consider were writing long before the rise of the relevant sciences, so they could not have made any explicit claim either way as to whether creativity could be explained by those sciences. Nevertheless, some of them did make claims which entail, or seem to entail, that creativity simply isn’t the kind of thing that could be explained through scientific inquiry as we understand it today.
The classic expression of such a view comes from Plato. In his dialogues, Plato features his teacher Socrates as a spokesperson for his own views, and in the Ion he has Socrates argue that poets do not produce poetry through knowledge or skill. When you exercise a skill ( technē ), you apply techniques, rules, or methods to perform a given activity, like charioteering, fishing, or commanding an army. In principle, one could explain these activities by identifying the techniques they involve, and a student or apprentice could learn these activities by applying and practicing those techniques. But poetry is not like that, in Socrates’ view. A poet can only imitate the application of rules or techniques, mimicking the surface appearance of skill. Voicing an idea that was familiar in Ancient Greek culture, Socrates suggests that poetry emerges instead through divine inspiration, whereby a human being is inspired —literally “filled with a spirit”, with a god or goddess, with a muse:
You know, none of the epic [or lyric] poets, if they’re good, are masters of their subject; they are inspired, possessed, and that is how they utter all those beautiful poems. … [They] are not in their right minds when they make those beautiful lyrics, but as soon as they sail into harmony and rhythm they are possessed by Bacchic frenzy. […] For a poet is an airy thing, winged and holy, and he is not able to make poetry until he becomes inspired and goes out of his mind and his intellect is no longer in him. As long as a human being has his intellect in his possession he will always lack the power to make poetry or sing prophecy. […] You see, it’s not mastery [ technē ] that enables them to speak those verses, but a divine power. That’s why the god takes their intellect away from them when he uses them as his servants, as he does prophets and godly diviners, so that we who hear should know that they are not the ones who speak those verses that are of such high value, for their intellect is not in them: the god himself is the one who speaks, and he gives voice through them to us. In this more than anything, then, I think, the god is showing us, so that we should be in no doubt about it, that these beautiful poems are not human, not even from human beings, but are divine and from gods; that poets are nothing but representatives of the gods, possessed by whoever possesses them. ( Ion 534a-d)
Socrates repeats this view in the Phaedrus : “Some of the greatest blessings come by way of madness, indeed madness that is heaven-sent” (244a). He adds that while a poet may have some kind of skill, anyone who aspires to make poetry purely by skill, without the madness or the muse, will fail (245a).
It’s important to note that “madness”, for Plato, is a supernatural affair. From the vantage of contemporary behavioral science, we think of madness—or rather, mental illness—as a pathology arising from some combination of genetic and environmental factors, and those factors can be studied scientifically. So even if creativity is linked to mental illness—a highly controversial proposition—it could still be entirely within the scope of science. However, Plato’s talk of “madness” does not refer to any naturally occurring pathology, but rather to the result of divine intervention: the poet is taken over or “possessed” by the muse and that is precisely why he is “out of his mind”. Plato’s poet suffers divine madness.
According to this story, then, the person we call a poet isn’t really a creator of poetry, but is merely the vessel through which a divine being delivers poetry. If it is literally true that the source of poetry is supernatural, then poetic creativity could never be explained by science, which is limited to the investigation of natural causes. (For more on Plato, see Asmis 1992.)
This kind of supernaturalism has enjoyed a long afterlife in Western thought. In ancient Rome, the Latin term “ genius ” referred to a guiding spirit that was thought to accompany each person throughout their lives. The genius of an artist would occasionally deliver art through that person in the manner of Platonic inspiration.
Conceptions of the artist take a new turn when the idea of genius is transformed in the eighteenth century. As we saw above, Immanuel Kant defines genius as a natural capacity that a certain kind of artist possesses innately and which partly constitutes that artist’s identity. So rather than saying that a gifted artist “has a genius”, Kant says that such a person “is a genius”. What distinguishes the genius is fundamentally an imaginative capacity—an ability to engage in a “free play” of imagination to produce artworks of “exemplary originality”. These works are exemplary not only in the sense that they have artistic or aesthetic value, unlike “original nonsense”; they are also exemplary in the more radical sense of providing an exemplar—a new paradigm and precedent—for lesser artists to follow. A work of genius sets a new standard of artistic value, and, looking to that exemplar, lesser artists may then extract techniques or rules for their own craft. The genius therefore “gives the rule to art”. In creating such works, the genius does not follow any rules or methods. Instead the genius creates art through a “free play of imagination”—where the terms “free” and “play” characterize the nature of an activity unconstrained by any pre-established methods or rules:
[G]enius … is a talent for producing that for which no determinate rule can be given, not a predisposition of skill for that which can be learned in accordance with some rule …. (1790: §46 5:307–8; 2000 trans., 186)
Kant thought that genius, so conceived, is limited to the fine arts, poetry being chief among them. Meanwhile, in Kant’s view, there is no room for genius in science, for example, where good theories and hypotheses must emerge from the careful application of scientific method, and so he said that even Isaac Newton, “that great man of science”, was not a genius. We’ll soon consider why this view might seem to entail that creativity is inexplicable, but first it will be helpful to bring another figure, Arthur Schopenhauer, who was deeply influenced both by Kant and by Plato.
Like Kant, Schopenhauer thought of genius as a natural capacity that is limited to the fine arts. He also echoes Plato’s sentiments about madness, famously stating that “genius and madness have a side where they touch and even pass over into each other” ( The World as Will and Representation , 1859, WWV I: 190), and that “Genius lives only one storey above madness” ( Parerga and Paralipomena , SW 2:53, PP 2:49). In a state of madness, Schopenhauer’s genius is like Plato’s poet in experiencing a momentary loss of self, but what displaces the self is not any divine being but rather a pure Idea which seizes the author’s being and becomes the object of both his fascination and his artistic expression:
We lose ourselves entirely in this object, to use a pregnant expression; in other words, we forget our individuality, our will, and continue to exist only as pure subject, as clear mirror of the object, so that it is as though the object alone existed without anyone to perceive it, and thus we are no longer able to separate the perceiver from the perception, but the two have become one, since the entire consciousness is filled and occupied by a single image of perception. ( World WWV I: 178–179, §34).
With their focus on genius construed as a natural capacity, figures like Kant and Schopenhauer abandon the supernaturalism of the Platonic muse. Nevertheless, they retain the idea that creativity—specifically genius-level creativity in the fine arts—is not a matter of exercising a skill or applying given rules, methods, or techniques.
As we noted earlier, these figures did not and could not have explicitly denied that creativity could be explained by the sciences of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, but they are commonly taken to represent such a denial (Kronfeldner 2018). Why?
Perhaps figures like Kant and Schopenhauer seem to make creativity, or at least creative genius, inexplicable insofar they suppose it to be innate and as they have no story to tell about how one came to acquire an innate capacity except to say that it was either an accident of chance (which is no explanation at all) or a gift from God (which again is not a scientific explanation). But while these figures seemed to think of artistic genius as being endowed entirely by nature with no contribution from nurture, modern genetic theory rejects that dichotomy. Instead of positing all-or-nothing natural abilities, behavioral scientists today think in terms of genetically inherited predispositions. In order for a genetic predisposition to develop into a trait with an observable phenotype, it needs to be triggered and shaped through a complex interaction between an organism’s genes and certain kinds of stimuli or environmental conditions. There are still open questions about exactly how, and how much, genes and environment feed into the development of any given trait, but it’s misguided to pose the binary nature-versus-nurture question as if the two were mutually exclusive (see Tabery 2014). Many researchers agree that some people have a stronger natural predisposition toward creativity than others, and that genius-level creativity partly stems from such a predisposition. Even so, the predisposition itself can be understood scientifically in terms of genetic heritability. (For a sampling of the relevant studies, see the essays collected in S.B. Kaufman 2013.)
Perhaps creativity seems inexplicable according to these accounts because it doesn’t follow rules or methods. In order to explain how to do something—how to build a boat or lead an army etc.—perhaps I need to be able to identify the rules or methods you should follow in order to practice and apply those skills. How-to explanations are instructions. But scientific explanations needn’t be instructions. A lot of good science explains how something happens—e.g., how heat melts ice or how a bat navigates its environment by echolocation—without explaining how to do it yourself.
Perhaps creativity seems inexplicable according to these accounts because creators themselves do not know how they create. But a scientific explanation needn’t be available through introspection. Most people cannot explain how their own digestive, circulatory, or perceptual systems work, but scientists who study those systems can.
Another line of thought is perhaps implicit in Kant but comes to the fore in Schopenhauer, who says that “the nature of genius consists precisely in the preeminent ability” to
consider things independently of the principle of sufficient reason , in contrast to the way of considering which proceeds in exact accordance with this principle, and is the way of science and experience. ( World WWV: I: 192, §36)
The principle of sufficient reason says that for every fact there is a cause which completely explains that fact. So the defining ability of genius is to see things in a way that transcends the causal order and defies all explanation.
A version of this view is defended more recently by Carl Hausman (1975 [1984], 1979, 1985) who frames it in terms of novelty that creativity involves. Hausman asserts that if a product is creative, it must be metaphysically novel (or in his terms, “genuinely novel”) in the sense that it cannot be predicted from, or explained by, prior events—not even in principle. Creativity is therefore incompatible with causal determination and causal explanation: “A causal view of explanation sets a framework for ways of denying that there is anything new under the sun” (Hausman 1984: ix). If something can be explained by prior causes, it is not metaphysically novel, and is therefore, in Hausman’s view, not truly creative.
Against Hausman’s skeptical charge, Maria Kronfeldner (2009) argues that creativity is compatible with causal determination. First, causal determinism does not preclude novelty or change. Determinism says the emergence of new kinds of things can at least in principle be predicted in advance. Importantly, though, when this prediction becomes true, then something new is added to the world. Of course, not all novelty instantiates creativity. The question is whether the kind of novelty involved in creativity must be metaphysical novelty, which is by definition incompatible with causal determination. This is doubtful. Notice that, by definition, metaphysical novelty defies natural laws. The production of something metaphysically novel would therefore require supernatural powers. Traditional Western religions conceive of God as performing the miracle of creation ex nihilo . But are we positing a miracle every time we describe a human artifact or achievement as creative? Surely not. As noted above, human creativity is manifest in things that are novel relative to the agent producing them or new to human history, but both of those kinds of novelty (psychological and historical) are perfectly compatible with causal determination. As Kronfeldner explains, creativity does not preclude causes in general; it only precludes certain kinds of causes. A creative product, she argues, must be original —which means that it cannot be produced through a process of copying something prior. And it must be spontaneous (not produced through a routine or mechanical procedure)—which means that it is to some extent independent of the agent’s intentional control and previously acquired knowledge. (For more on originality and spontaneity, recall §2.2 above). Intuitively, the causes of something creative cannot simply be a matter of copying or following a routine. But it may have causes nonetheless, and cognitive science can investigate those causes, at least in principle. Indeed, as we’ll see next, it is doing so in practice.
5. The Cognitive Science of Creativity
Although creativity has been relatively understudied by contemporary philosophers, as we noted in §1 , it has been receiving a great deal of attention from psychologists over the past few decades. In 1950, J. P. Guilford gave a presidential address at the American Psychological Association calling for research on the topic, and the field soon took off with waves of research investigating the traits and dispositions of creative personalities; the cognitive and neurological mechanisms at play in creative thought; the motivational determinants of creative achievement; the range of institutional, educational, and environmental factors that enhance or inhibit creativity; and more. Today, the blossoming of this field can be seen in the flurry of popular writing on its results; an official division of the American Psychological Association for the psychology of aesthetics, creativity, and the arts (Division 10); numerous academic conferences; dedicated peer-reviewed journals ( Psychology of Aesthetics , Creativity and the Arts ; Creativity Research Journal ; Journal of Creative Behavior ; International Journal of Creativity and Problem Solving ); special issues of journals ( Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , Takeuchi & Jung 2019); literature surveys (Hennessey & Amabile 2010; Runco & Albert 2010; Runco 2017; Glaveanu 2014; Williams et al. 2016); textbooks (J.C. Kaufman 2009; Sawyer 2012; R. W. Weisberg 1986, 2006); and a comprehensive encyclopedia (Runco & Pritzker 2020). According to one overview, creativity has been studied by nearly all of the most eminent psychologists of the twentieth century, and “the field can only be described as explosive” (Albert & Runco 1999: 17). There is also a groundswell of new work on creativity in the fields of computer science, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics.
The present section surveys empirical work in psychology along with some related work in neuroscience, while the next section ( §6 ) covers research in computing, AI, and robotics. Throughout, we’ll see that philosophers are actively in dialogue with these fields under the broad, interdisciplinary umbrella of cognitive science.
The vast body of empirical research of creativity can be seen as addressing a variety of issues, but the central question that concerns us here is the one we identified above as the challenge for explaining creativity: How are people creative? This question is analogous to a number of other questions in cognitive science: How do people perceive through sense modalities such as vision? How do they form concepts? How do they acquire a language? How do they make inferences? Just as psychologists investigate the psychological and neurological processes, systems, and mechanisms at work in these other mental operations, as well as the internal and external factors that either enhance or hinder these operations, they are doing the same for creativity. There is no pretension to achieving a complete explanation which would include each and every causal factor, and provide the basis for perfectly predicting creative outcomes in advance. But to the extent that we identify some of the relevant causal factors involved in creativity we thereby make progress in explaining creativity, just as we do with other features of the mind.
As we noted in §2 , the standard definition of creativity in psychology says that a product (idea or artefact) is creative to the extent that it is both new and valuable (“effective”, “useful” or “appropriate”), and, in turn, people and processes are creative to the extent that they produce new and valuable things. As we also noted, many psychologists do not actually employ this, or any, definition of creativity in conducting their research. In one sampling of studies of creativity published in peer-reviewed psychology journals, only 38% of them included an explicit definition of creativity (Plucker, Beghetto, & Dow 2004), as they rely in one way or another on the assumption that we know it when we see it. For example, many studies use the Consensual Assessment Technique (CAT), whereby experimental subjects produce things that are then rated for how creative they are by a panel of experts in the relevant field; so paintings are rated by professional painters, stories by published authors, etc. Many other research methodologies are used, as we’ll see below.
Empirical research on creativity departs in several ways from the traditional approaches that seemed to place creativity outside the scope of science. For starters, in stark contrast to Plato’s supernaturalism, empirical psychologists take creativity to be a completely natural phenomenon. Creative people may of course be “inspired” in the sense of feeling energized or filled with ideas, but rather than being literally “breathed into” by some god or muse, their thoughts and behaviors are presumed to have causes that are perfectly natural. While it is difficult in practice to identify these causes, they are not in principle beyond the reach of science.
Further, the range of phenomena that contemporary researchers countenance within the ambit of creativity is far broader and more diverse than the traditional focus on poetry and the fine arts, as creativity can be manifest in any kind of art or craft, as well as in the sciences, technology, entrepreneurship, cooking, humor, or indeed in any domain where people come up with ideas or things that are novel and valuable in some way or another. Departing from Kant, genius, the highest echelon of creativity, may be acknowledged in virtually any of these domains, not just in the fine arts. And while a few researchers (e.g., Simonton 1984, 1994, 1997, 2009; Root-Bernstein & Root-Bernstein 1999) venture to examine genius (so-called “Big-C” creativity), most of them focus instead on relatively ordinary creative feats (“little-c” creativity) including the kinds of story-making, drawing, and problem-solving that can be elicited on command from regular people in experimental settings. Some researchers propose that in order to understand how the mind generates new ideas, we should begin with even more rudimentary phenomena. For example, philosopher Jesse Prinz and psychologist Lawrence Barsalou focus on how we form new concepts to categorize the things we perceive, a process which they claim is creative, albeit in a “mundane” rather than “exceptional” way (Prinz & Barsalou 2002; Barsalou & Prinz 1997; cf. Child 2018).
Of course, many feats of human creativity, and the ones that are most interesting, go far beyond the basic formation of concepts. A major step toward explaining those feats is to recognize that what we call “the creative process”, as if it were a single, homogenous phenomenon, is in fact an assembly of multiple stages or operations. The simplest recognition of this fact is the Geneplore model which distinguishes just two stages: generating ideas and exploring ideas (Finke 1996; Smith, Ward, & Finke 1995). This distinction may be seen as echoing one made by philosophers of science in the early twentieth century, between the context of discovery and the context of justification (Popper 1934). Other theorists posit up to eight stages of creativity (for a summary of proposals, see Sawyer 2012: 89). But the most influential stage-theory traces back to Henri Poincaré’s lecture, “Mathematical Creation” (1908 [1913: 383–394]), in which he identifies four phases in his own innovative work as a mathematician:
- conscious hard work or preparation ,
- unconscious incubation ,
- illumination , and
- verification .
In his book, The Art of Thought (1926), the psychologist Graham Wallas endorses Poincaré’s four stages with corroborating evidence from the personal reports of other eminent scientists like Hermann von Helmholtz. Wallas’s scheme, as a development of Poincaré’s, is still the one that is most widely cited, and we employ a version of it here with some slightly different terminology and with two more substantive alterations: instead of “incubation”, we identify the second operation more generally as the “generation” of ideas, which may include unconscious incubation but may also occur in conscious, deliberate thought; and we add “externalization” for a total of five operations:
- Preparation —You invest a great deal of effort learning and practicing in order to acquire the knowledge, skills, and expertise required for work in a given domain.
- Generation —You produce new ideas, whether through conscious reflection or unconscious incubation.
- Insight —You consciously experience the emergence of a new idea, which would strike you with a feeling of surprise: “Aha!”, “Eureka!”
- Evaluation – You assess the idea to determine whether it should be discarded, retained, revised, or amended.
- Externalization —You express your idea in a concrete, observable form.
Artists provide compelling examples (though not the only ones) of each of these five operations. Such examples can be especially illustrative since they come straight from the artists’ mouths, as they reflect upon, and share, their creative process. The twentieth century painter Jacob Lawrence was known for painting in the style of visual narratives. Lawrence developed a system, much like a filmmaker’s storyboard, for the preparation of these paintings. He would lay as many as 60 wood panels on the studio floor, each with individual scenes and sometimes with captions. From these storyboards, Lawrence would generate and evaluate ideas and insights for a visual narrative, culminating in the paintings such as those in his Migration Series (see Whitney Museum, 2002, in Other Internet Resources ). Toni Morrison, the Nobel prize winning novelist, remarks on the labors and sustained effort required at the preparation, generation, evaluation, and externalization stages of a creative writing process. Commenting on her novel Jazz , she says,
I thought of myself as like the jazz musician—someone who practices and practices and practices in order to be able to invent and to make his art look effortless and graceful. I was always conscious of the constructed aspect of the writing process, and that art appears natural and elegant only as a result of constant practice and awareness of its formal structures.
She further notes that insight does not always come in a flash,
[I]t’s a sustained thing I have to play with. I always start out with an idea, even a boring idea, that becomes a question I don’t have any answers to. (T. Morrison 1993)
Writer Ishmael Reed claims that insight can come unexpectedly and in various contexts:
One can find inspiration from many sources. The idea of Japanese by Spring originated in a news item that claimed the endowment to a major university was traced to Japanese mob, the Yakuza. Flight to Canada began as a poem. The Terrible series began when I heard someone at party mention that there was a black figure, Black Peter, in the Dutch Christmas, and by coincidence I was invited to the Netherlands shortly afterwards, where I witnessed the arrival of Saint Nicholas and Peter on a barge that floated into Amsterdam with crowds looking on. I took photos of the ceremony …. (Howell 2020: 91)
And with signature profundity, James Baldwin suggested that all elements of the creative artistic process, from preparation to externalization, require a basic enabling condition: being (and willing to be) alone (Baldwin 1962).
As Wallas recognized (1926: 81), and as the above examples suggest, the “stages” of the creative process are not necessarily discrete steps that follow one another in a tidy sequence. Creative work is messy: over time you have numerous ideas, keeping some and abandoning others in multiple rounds of trial-and-error; you incubate new ideas for one problem while you’re busy externalizing your ideas for another; and your moments of insight, evaluation, and externalization trigger further generative processes that send you cycling through these operations many times over. It’s still important to distinguish these operations, however, because, as researchers are confirming, they are enabled and influenced by different causal factors.
Among the additional stages that researchers have posited, one of the most widely discussed is known as problem-finding. Psychologists often conceptualize creative thought in terms of problem-solving: the ideas generated within the creative process are seen as candidate solutions to a given problem—where “problems” are broadly construed to include any creative aim, like that of producing a particular kind of artwork or proving a particular theorem, etc. (Flavell & Draguns 1957: 201; Newell, Shaw, & Simon 1962). But following some early work by Mihalyi Csikszentmihalyi (1965), many researchers came to appreciate that a lot of creative work is done not just in solving problems but in finding the right problem to begin with (Abdulla et al. 2020; Csikszentmihalyi & Getzels 1970; Getzels 1965; Getzels & Csikszentmihalyi 1975). While we agree that problem-finding often plays a key role in creativity, we have not assigned it to a separate stage, for the following reasons. Consider that you might settle on a problem to work on in either of two ways. On one hand, you might choose a problem to work on from a pre-existing menu of options. In that case, your choice would fall under the evaluation phase; it’s just that the idea you select is a problem that calls for the pursuit of further ideas. If, on the other hand, you develop a new problem, you would thereby be engaging in the generation of a new idea—the new problem—which may emerge in a moment of insight . Einstein and his colleague celebrated the novelty in such problem-finding:
The formulation of a problem is often more essential than its solution, which may be merely a matter of mathematical or experimental skill. To raise new questions, new possibilities, to regard old problems from a new angle, requires creative imagination and marks real advance in science. (Einstein & Infeld 1938: 92)
Either way—whether you “find” a problem by picking a pre-existing one or by coming up with a new one yourself—problem-finding, though important, does not need to be seen as an additional operation beyond the five listed above; it’s just a special case of generation, insight, or evaluation.
The next five sub-sections will respectively examine the five operations of creative work. Notice that three of them—preparation, evaluation, and externalization—are uncontroversially ordinary activities that involve no apparent mystery; it’s a challenge to explain them but no one is tempted to regard them as inexplicable or as violating the laws of nature. As we saw in §4 , traditional skepticism about the possibility of explaining creativity is really focused on the two remaining phenomena: the generation of new ideas ( §5.2 ) and the experience of insight whereby an idea seems to come out of the blue, as if from a god ( §5.3 ).
It’s myth that outsiders are more creative. To put yourself in a position to create anything of value, you have to spend a great deal of time and effort acquiring the relevant knowledge, skills, and expertise. In what has come to be called “the ten-year rule”, Howard Gardner (1993) found that, on average, people spend about 10 years learning and being immersed in a domain before they make any significant creative contribution to it.
Though a certain amount of rote learning is required, gaining mastery in a field is not simply a matter of passively absorbing information. Much of it involves what Anders Ericsson calls deliberate practice, where you focus on tasks which are a little beyond your current abilities, but which you eventually conquer through feedback and repetition. Across a variety of domains—including physics, medicine, programming, dance, and music—Ericsson found that, on average, world-class performance becomes possible for people only after 10,000 hours of deliberate practice in their chosen activity. This finding also converges on the ten-year rule, because if you engage in deliberate practice four hours a day, five days a week, that would add up to 10,000 hours in ten years (Ericsson, Krampe, & Tesch-Römer 1993; Ericsson et al. 2006).
However, there seems to be a point at which too much formal training can dampen creativity. Simonton (1984: 70–73) has reported that the relationship between creativity and education level is an inverted-U, as too much schooling can reinforce familiar, pre-established styles of thought. Even so, the point remains that, before you run into diminishing returns, years of preparatory learning and practice are required for exceptional creativity.
5.2 Generation
In this section we discuss four kinds of mental capacities or processes that researchers have posited for generating new ideas.
Psychologist Donald T. Campbell (1960, 1965) proposed that creative thought proceeds through “blind variation and selective retention (BVSR)”. The “variations” he refers to are the various ideas that might occur to a creator, and the process of generating them is “blind” to the extent that it is not guided or directed by prior knowledge of how valuable or useful they will be: “Real gains must have been the products of explorations going beyond the limits of foresight or prescience , and in this sense blind” (Campbell 1960: 92, emphasis added). Once ideas have been generated, however, there is a subsequent stage where the creator selectively retains some of those ideas while discarding others, and Campbell says this stage is “sighted” rather than blind since it is guided by the creator’s judgments as to which ideas are valuable. While there is little debate that selective retention is sighted in this sense, there has been more controversy over whether the initial production of ideas is, by contrast, blind.
In his prolific body of work, Dean Keith Simonton has extended and refined Campbell’s proposal. His work nicely illustrates the interdisciplinary nature of creativity research as he, like Campbell, is a psychologist who engages with philosophers, some of whom are broadly sympathetic to the BVSR theory (Briskman, 2009; Nickles, 2003), while others are skeptical (Kronfeldner 2010, 2011, 2018). In earlier writings Simonton suggested, in a way Campbell did not, that BVSR is to be understood on the model of Darwinian evolution (Simonton 1999a, 1999b). But Simonton (forthcoming: 2–3) has come to rescind the Darwinian framing of BVSR, conceding that it is misleading. Reprising Campbell’s core idea, he says that a process of generating an idea is blind to the extent that it is not guided by “the creator’s prior knowledge of the variation’s utility” (Simonton forthcoming: 5; cf. Simonton 2011, 2012a, 2012b, 2018). He stresses that blindness is not all-or-nothing; it comes in degrees. An example of a highly sighted process is that of using the quadratic formula to find the roots of a quadratic equation: you know in advance that if you apply the formula correctly, it will yield the correct answer. Examples of relatively blind processes include remote association and mind wandering.
Despite the foregoing criticism of BVSR, recent neuroscientific studies suggest a network of brain activity that may serve the blind variation role. Brain activity doesn’t cease when one is not focusing on a task, when one is at rest, daydreaming, and so on. Following this insight, researchers have used neuroimaging methods to identify what is now called the default mode network (DMN). The precise anatomy of this network is still a matter of investigation, but it is supposed to be less active when one is focused on an external task (say a problem in the real world or in the lab) and more active when one is not so focused (Raichle et al. 2001; Buckner & DiNicola 2019). Notice then, that while this network is not creativity-specific—it is supposed to be active during memory recall, imagining future events, daydreaming, and so on—it does seem especially well-suited for creativity, and particularly for the random idea generation hypothesized by the BVSR (Jung et al. 2013). Creativity researchers in these fields often refer to this more “free” production of ideas as “divergent thinking”, and some argue on the basis of neuroimaging studies that creative thought requires cooperation between this mode of thought as well as that under “executive control”. As one team puts the point,
In general, we contend that the default network influences the generation of candidate ideas, but that the control network can constrain and direct this process to meet task-specific goals via top-down monitoring and executive control.. (Beaty, Benedek, et al. 2016; see also Mayseless, Eran, & Shamay-Tsoory 2015; Beaty, Seli, & Schacter 2019; Chrysikou 2019)
Notice how well this comports with both the Geneplore and the BVSR frameworks, perhaps identifying a way to keep some of the insights of both without commitment to a special creativity mechanism after all.
At least since Kant, theorists have identified an important link between creativity and imagination; indeed, the two are sometimes unfortunately conflated. Construed broadly, imagination can take various forms: sensory imagery, propositional imagination, supposition, free association. Berys Gaut (2003, 2009, 2010) and Stokes (2014, 2016) have both recently argued that, although imagination and creativity are distinct, imagination is especially well-suited to creative thought because of its characteristic flexibility. They both agree that imagination is decoupled from action (Gaut 2003) and “non-truthbound” (Stokes 2014) in the sense that, unlike belief, imagination is not limited by the proper function of accurately representing (some part of) the world. This freedom or playfulness of imagination is crucial to generating new ideas, since it allows one to safely “try out” hypotheses, conceptual combinations, strategies for solutions, and so on, without epistemic or behavioral commitment.
A series of studies illustrates both the need for non-truthbound capacities in creative thought, as well as the difficulty of employing them. When people—children and adults alike—are asked to imagine and draw non-existent houses, people, or animals, they depict things that are strikingly similar to their familiar counterparts in the real world: imagined people, for example, were generally drawn with some version of a head, limbs, eyes, and so forth. (Karmiloff-Smith 1990, 1992: 155–61; Cacciari et. al 1997; Ward 1994, 1995). This suggests that we are highly constrained in our creativity by the concepts we already have. Concepts of existing things are truth-bound: your concept of an animal, for example, has the proper function of accurately representing the range of things that are in fact animals. When you try to envision a new, fictional kind of animal, you begin with a mental image that exemplifies your existing concept of animal, which is why you are constrained by that concept. You then have to manipulate your initial image, varying its features in ways that abandon the aim of accuracy, using a capacity that isn’t truthbound. Generalizing this point yields the cognitive manipulation thesis , according to which creative thought requires cognitive manipulation, which involves thinking in ways that are not bound to the truth (Stokes 2014: 167). Plausibly, imagination is the mental capacity which is best suited to serve in this cognitive manipulation role. In the studies just cited, subjects must use their imagination to manipulate their existing concepts so as to form new ideas.
Recent empirical research on visual imagery seems to corroborate this claim. Various studies have identified positive correlations between creative problem solving and visual image generation, image transformation, and vividness of imagery (Finke 1990, 1996; Zemore 1995; R. Morrison & Wallace 2001; Pérez-Fabello and Campos 2007). A more recent study highlights the importance of image transformation ability—the ability to mentally manipulate a given image—and the ability to achieve high degrees of visual creativity. Further, the results of this study suggest that although vividness negatively correlates with the practicality of images created, vividness positively correlates with novel idea generation (Palmiero et al. 2015). The novelty involved is minimal, but again it appears that imagination, here in the form of imagery, well serves the role of cognitive manipulation.
Stokes observes further that we can voluntarily control imaginative states (in contrast with other non-truthbound states, like desires and wishes). And because imagination connects in important ways with inferential systems, as well as affective systems, the thoughts it produces can often be integrated with knowledge and skills to formulate an innovative strategy or solution to a problem. Finally, this role for imagination in creativity is not exclusive to the rich creativity of artists and scientists, but indeed seems to characterize the minimally creative behavior that we all enjoy. This claim is partly motivated by the empirical research just discussed. Here, as in the more radical cases, instances of novel achievement or learning by subjects requires more than rote memorization; it requires cognitive manipulation of the information in the relevant conceptual space (e.g., combining concepts about houses and persons). This kind of cognitive activity is best done by using the imagination.
Peter Carruthers has argued that imagination is important to creativity on evolutionary grounds (2002, 2006; see also Picciuto & Carruthers 2014). Like the above analyses, he focuses on the playfulness of imagination. Pretend play typically develops early in childhood in humans. And imagination in adults provides the right mechanisms for generating and exploring ideas (just as required by the Geneplore model). Carruthers argues that imagination evolves under adaptive advantage as a kind of practice for adult creativity—and may have been accordingly selected for, aligning with the putative creativity explosion of 40,000 years ago (Mithen 1996, 1998; Harris 2000). This, he argues, is the most parsimonious explanation of both the emergence and the ubiquity of creativity in the human species. See B. Gaut (2009) for a critique of Carruthers’ analysis.
While we may generate ideas consciously in imagination, we may also do so during a period of unconscious incubation, when we are focused on something else. This point is illustrated by any number of famous stories, though some are probably embellished after years of retelling. Isaac Newton witnessed an apple fall from a tree (on some accounts, falling upon Newton’s head) and thereby found the insight for his laws of gravity. August Kekulé is reported to have discovered the structure of the benzene molecule while daydreaming of a serpent circling upon and seizing its own tail. Henri Poincaré alleged that, while boarding a bus, he enjoyed a needed flash of insight that led to his discovery of non-Euclidian geometry. Richard Feynman, the Nobel prize winning physicist, claimed to find inspiration while sipping soda and doodling at adult clubs. And Einstein reported:
I was sitting in a chair in the patent office at Bern when all of a sudden a thought occurred to me. “If a person falls freely he will not feel his own weight”. I was startled. This simple thought made a deep impression on me. It impelled me toward a theory of gravitation. (Einstein, “Kyoto Lecture”, translated and quoted in Pais 1982: 179)
In each case, someone is suddenly struck with a flash of insight about one thing while engaged with something else entirely. The empirically-minded theorist rejects the notion that such ideas arise ex nihilo or through divine possession. So how are they explained in terms of natural mental phenomena?
Arthur Koestler, partly inspired by the work of Henri Poincaré (1908 [1913]), hypothesized that during creative thought processing, ideas are combined in novel ways, and this combination is performed largely unconsciously , by what Poincaré called the subliminal self (Koestler 1964: 164–5). For Poincaré there are only two ways we might think of the unconscious. One, we might think of the unconscious in Freudian terms, as a self capable of careful and fine discernment and, importantly, distinctions and combinations that the conscious self fails to make. Alternatively (and this is the option favored by both Poincaré and Koestler), we can think of the unconscious as a sub-personal automaton that mechanically runs through various combinations of ideas. Importantly, this unconscious process (or, if one likes, automaton) generates random conceptual associations and ideas. And these can then be further considered, examined, explored, and revised.
In the context of creativity in particular, there is precedent, or at least overlap, in Colin Martindale’s cortical arousal theory. This theory centers around the nature of focuses of attention (Martindale 1977, 1981, 1995, 1999; Martindale & Armstrong 1974; Martindale & Hines 1975). Martindale proposes a multi-stage model of problem solving, which if the right mechanism is possessed, leads to creative thought. In the initial stages, information is gathered, various approaches are taken to the problem, and there is a high level of cortical arousal with a narrow focus of attention. As information increases and the problem remains unsolved, two kinds of responses may occur. The first kind of response is to keep attempting the same solutions to the problem such that the arousal and attention focus stay high and narrow, respectively. Alternatively, some persons experience a decrease in cortical arousal coupled with a wider range of attention focus. Information then enters what Martindale calls primary processing: a kind of subconscious cognition not under the complete control of the agent. It is this kind of processing, and the arousal mechanisms that enable it, that distinguish creative insight or achievement from non-creative ones. The first kind of response typically results in frustration and failure (fixation), while the second often results in creative insight.
Some early studies on these phenomena centered around a familiar observation. Consider the tip-of the-tongue phenomenon, when you know that you know some bit of information (an actor’s name or the title of a song) but, try as you may, you just can’t recall it. It often helps to give up for a moment and allow the memory to surface without effort. Researchers found that the same approach—forgetting about a problem—works well to overcome fixation on ineffective ideas so as to allow the actual solution to pop up. Smith and Blankenship primed two groups of subjects with inappropriate or misleading solutions to problems. They left one group to continue struggling with the same problem, while they distracted the second group with a distinct but cognitively demanding task. The second group thereby overcame fixation and outperformed the first group when returning attention to the original target problem (Smith & Blankenship 1989, 1991; see also Smith, Ward, & Finke 1995).
These behavioral methods can be combined with contemporary understanding of neural plasticity and the effects of cognitive effort and attention. Neuroscientists have long recognized that the human brain is plastic —stable in genetic material but constantly undergoing functional change and development in neural networking in response to external stimuli, with the work of Donald Hebb in the middle of the twentieth century being one important early precedent. As Hebb put it, neural cells that “fire together, wire together”. Cell assemblies thus form as a result of the synchrony and proximity of the firing of individual cells.
[A]ny two cells or systems of cells that are repeatedly active at the same time will tend to become “associated”, so that activity in one facilitates activity in the other. (Hebb 1949 [2002: 70])
And continued attention to a problem, what some have called cerebral effort , causes changes in the networking of the brain’s cortex (Donald 2001: 175–8). Importantly, these changes can continue to take place, to “reverberate” even after one has removed attention from that problem. This motivates a simple (and somewhat unsurprising) hypothesis: attending to and performing cognitive tasks affects neural networking (Posner et al. 1997; Posner & Raichle 1994; see also Kami et al. 1995), and those changes can involve strengthening of synaptic connectivity (which correlate with conceptual connections and associations). These changes, again, can occur both when one is attending to a task and after one has diverted attention elsewhere. And, finally, the latter goes some way to explain a moment of insight after incubation (the so-called incubation effect): when one returns attention to the target problem, new or newly strengthened neural connectivity (as a result of previous cognitive effort) can give rise to a new idea. And because that neural process is not in any sense done by you, the emergence of the new idea can feel like a burst of insight (see Stokes 2007; Thagard & Stewart 2011; Ritter & Dijksterhuis 2014; and Heilman 2016).
There are also various recent studies on closely related topics: on mindwandering and spontaneous thought (Christoff et al. 2016; Irving & Thompson 2018; Murray et al. forthcoming), on so-called “divergent thinking” (Mekern et al. 2019), and more on the neural basis of insight (Jung-Beeman et al. 2004; Bowden et al. 2005; Limb & Braun 2008; Dietrich & Kanso 2010; Kounios & Beeman 2014).
It should be intuitive that creativity often involves solving problems and doing so in interesting or surprising ways. In exceptional cases, the individual identifies a problem solution that perhaps no one (including the creator) anticipated. But there are countless examples of more mundane instances of problem solving, where the solution may be surprising (or especially interesting) to only a few individuals, perhaps even only to the problem solver. One broad, standard experimental method used by researchers thus focuses on insight in problem solving. Some problems (thankfully!) can be solved by straightforward appeal to memory, or by applying some technique or method of calculation in a mechanical way. Solving the problem may still take time and effort, but the solution will come so long as one executes the appropriate strategy or applies the relevant knowledge from memory. An insight problem, by contrast, typically requires something new on the part of the individual, and one must often “change views” of the structure of the very problem. Predictably, there are a variety of definitions or characterizations of “insight” in the literature. Here are two recent, representative examples. Bowden et al. suggest that insight occurs
when a solver breaks free of unwarranted assumptions, or forms novel, task-related connections between existing concepts or skills. (Bowden et al. 2005: 322)
More recently, Kounios and Beeman write,
we define insight as any sudden comprehension, realization, or problem solution that involves a reorganization of the elements of a person’s mental representation of a stimulus, situation, or event to yield a nonobvious or nondominant interpretation. (2014: 74)
There are at least two, separable components of insight thus understood. First, an insight problem requires non-mechanical or non-algorithmic solution, and this in turn requires some kind of conceptual reorganization. A hackneyed phrase may come to mind here: one has to “think outside the box”.
The second element of insight as understood here is subjective or phenomenological. An insightful problem solution is often described as occurring suddenly and with little or no apparent effort. It is an aha moment, even if less dramatic than the traditionally romanticized Eureka moment. One way researchers have tested for this subjective feature is to ask subjects to report nearness or “warmth” relative to solving a problem. They find that for insight problems, by contrast to non-insight problems, subjects report that as they near solution they experience abrupt changes in the sense of warmth for solving the problem (Metcalfe & Wiebe 1987; see also Dominowski 1995; Laukkonen & Tangen 2018). More recently, researchers have begun to employ neuroimaging techniques to study insight and insightful problem solving (Luo & Niki 2003; Mai et al. 2004).
First, researchers have developed methods for using subjective report, where subjects rate whether they felt that they used insight in solving a designated problem (Bowden et al. 2005). And second, and coupled with those report methods, researchers have developed simple problems that can be solved with insight. One such example is the “Compound remote associates problem” (CRA). Here is an example of a CRA problem:
Each of the three words in (a) and (b) below can form a compound word or two-word phrase with the solution word. The solution word can come before or after any of the problem words. french, car, shoe boot, summer, ground [ 1 ] (Bowden et al. 2005: 324)
Because of their simplicity, these problems can be solved unambiguously and quickly, and with this speed comes better potential for neuroimaging study. In instances where subjects report insight solutions to these kinds of problems,
EEG shows a burst of high-frequency (gamma-band) EEG activity over the right temporal lobe, and fMRI shows a corresponding change in blood flow in the medial aspect of the right anterior superior temporal gyrus (Jung-Beeman et al. 2004). (Kounios & Beeman 2014: 78)
The question for neuroscientists is whether this convergence of evidence is sufficient to establish neural correlates of insight.
A moment of “insight” can be misleading, as what initially strikes you as a promising idea may ultimately turn out to be a dead end. You may have countless ideas in the course of undertaking a complex creative project, while only a few of them will make the final cut. A crucial part of your creative work therefore consists in evaluating your ideas. For any idea that occurs to you, you might have to ask: Will this work? Is it new? How does it fit in with other parts of your project? Do you have the resources and abilities to bring it to fruition? Is it worth the time and effort?
Much of the research on this phase of the creative process is concerned to identify and categorize the range of factors that people take into consider as they evaluate their ideas (Blair & Mumford 2007; Dailey & Mumford, 2006). Unsurprisingly, those factors vary from one domain to another. New culinary dishes are judged by factors like aroma, taste, texture, color, presentation (Horng & Lin 2009), whereas improved musical performances are judged according to their complexity, originality, and technical virtuosity (Eisenberg & Thompson 2003), and so on. Your understanding of the relevant factors is part of your internalized model of the domain (Bink & Marsh, 2000; Csikszentmihalyi & Sawyer 1995). And since you acquired and refined that model through years of preparation, your capacity for evaluation is largely a consequence of your efforts from that initial stage.
Somewhat more surprisingly, there is some evidence that people who are good at evaluating ideas are also good at generating them (Runco 1991; Runco & Dow 2004; Runco & Chand 1994; Runco & Vega 1990).
Other studies support what Sawyer calls Sawyer (2012: 131) calls the productivity theory, which says that the best way to get good ideas is to have lots of ideas and just throw away the bad ones. In historiometric studies, Simonton found that creators who yielded the greatest number of works over their lifetimes were mostly likely to produce works that were significant and stood the test of time. Even more striking, he discovered that, from year to year, the periods when creators were most productive were also the ones in which they were most likely to do exceptional work (Simonton 1988a, 1988b). Linus Pauling, who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954 as well as the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962, summed up the productivity theory in a famous remark:
If you want to have good ideas you must have many ideas. Most of them will be wrong, and what you have to learn is which ones to throw away. (quoted by Crick 1995 [time 34:57])
The final operation of the creative process—externalizing ideas—may involve any number of disparate activities, which Keith Sawyer sums up as follows:
Creativity research has tended to focus on the early stages of the eight-stage creative process—particularly on the idea-generating stage. But a lot has to happen to make any idea a reality. Successful creators are skilled at executing their ideas, predicting how others might react to them and being prepared to respond, identifying the necessary resources to make them successful, forming plans for implementing the ideas, and improvising to adjust their plans as new information arrives. These activities are important in all creativity, but are likely to be even more important in practical domains such as technological invention and entrepreneurship (Mumford, 2003; Policastro & Gardner, 1999). (Sawyer 2012: 133–4)
It may be tempting to assume that the real creative work is finished once a new idea emerges in the moment of insight, and that externalization is just the uncreative, mechanical chore of making the idea public. But a closer look at the phenomenon reveals that externalization is often integral to creativity itself.
Vera John-Steiner (1985) interviewed, and examined the notebooks of, over 70 exceptional creators (ranging from author Anaïs Nin to composer Aaron Copland), and consulted the notebook of another 50 eminent historical creators such as Leo Tolstoy and Marie Curie. A recurring theme throughout was that at the beginning of each creative endeavor and continually throughout its development, creators manipulate and build upon their impressions, inklings, and tentative hunches using sketches, outlines, and other external representations.
Perkins (1981) corroborated this finding by analyzing the 61 sketches Picasso made en route to painting his famous work, Guernica , as well as Beethoven’s musical drafts and Darwin’s notebooks. In each case, the artist progressed by engaging with external representations.
Other studies found that people discovered and solved more problem when they used sketches during a task (Verstijnen 1997), and that people come up with better ideas for improving inventions when they work with visual diagrams (Mayer 1989).
One reason externalization is so vital to substantial creative work is because of our limited capacity to consciously hold and manipulate information in our minds. It helps to offload ideas and store them in the form of physical symbols and expressions in order to free up space for the mind to examine those ideas at arm’s length while entertaining new ones. Thus research shows that internal strategies like mental visualization can help with relatively simple tasks, but for more complex projects externalization is key (Finke et al. 1992: 60).
We close our survey of the cognitive science of creativity with a brief discussion of some general worries about current work, and some prescriptions for future research.
Some have worried about the validity of the psychometric measures employed in neuroimaging studies. One such concern regards the confidence that we should have that the tests employed are really tracking creative behavior. This is of course a general problem, partly symptomatic of the challenges that come with defining creativity (like other phenomena) and with the special challenges that attach to features such as insight and incubation. But there are particular challenges that come with using neuroimaging technologies such as fMRI scanning to attempt to study naturally occurring phenomena. Use of this technology is almost invariably ecologically invalid—one cannot run an fMRI in the artist’s studio. And because of the cost and sensitivity of these imaging systems, the correlative behavioral tests are often significantly abbreviated. This may impose constraints on space for occurrence of the target phenomena—novel thinking and insight—during the imaging session. As one researcher worries,
Too often single tests are used—or even single items! This is contrary of psychometric theory in general (where longer tests allow errors to cancel themselves out and are thus more reliable) and true of the research on creativity assessment in particular, where differences among items and even tests are common (Richards, 1976; Runco, Mohamad, & Paek, 2016 [sic should be Runco, Abdulla et al. 2016). Results from any one test will not generalize to other tests. Results from a single item of course have even less generalizability. (Runco 2017: 309–310; see also Abraham 2013)
Another empirical researcher criticizes what he sees as “the wild goose chase” in the neuroscience of creativity. Arne Dietrich (2019) recapitulates the above worries about validity of psychometric measures and their abbreviated and piecemeal application. He further worries about the now dominant emphasis on divergent thinking, and the default mode network (as well as the now mostly abandoned emphasis on notions such as madness, the right brain, and REM sleep). Dietrich’s concern in each case is that the research emphasis is unhelpfully myopic, and that while the imaging methods are sound and state of the art, the characterization of creativity is not. He decries the temptation to identify what may be a feature of creativity with the whole of the phenomenon. Divergent thinking, he suggests, is likely a cluster of various mental phenomena rather than a singular one, and
there is no effort underway to dissect divergent thinking and link it to the kinds of cognitive processes we use to operationalize all other psychological phenomena, such as working memory, cognitive control, semantic memory, perceptual processes, or executive attention. (2019: 37)
Notice, then, that the “wild goose” for Dietrich is to hastily conclude and then center studies around a singular, special creativity mechanism.
Dietrich also offers various prescriptions for remedy. To combat myopia, he suggests (as some have in other disciplines, e.g., Boden 2004) a plurality of types of creativity (and/or features of creativity). He cautions,
Since different types of creativity contain opposing brain mechanisms—focused versus defocused attention, for instance—any all-encompassing claim about creativity in the brain will almost certainly qualify as phrenology. (2019: 39)
He pairs this with a prescription for a more interdisciplinary approach to the topic. Others in the field have made the same prescription, advocating a “systems” approach sensitive both to the multi-faceted nature of creativity and the value of theorizing at multiple levels of explanation (Hennessy & Amabile 2010).
These directives for future research seem hard to resist. At the very least, it would seem advantageous to ensure that the full range of empirical method across the behavioral and brain sciences is communicated across the relevant sub-disciplines. This would ideally lead to better collaboration amongst such researchers. What’s interesting is that a cousin to this prescription is not well heeded by the same researchers advancing it here. However little crossover there is between, say, behavioral psychologists and neuroscientists in studies of creativity, there is comparatively even less crossover (almost none) between the psychological sciences and computational approaches to creativity. The next section thus begins by highlighting this “gap”, and identifying some of the potentially fruitful areas for interdisciplinary work on that front. It then continues with a discussion, generally, of research on creativity in the fields of computing science, artificial intelligence, and robotics.
Just as we find in psychology and neuroscience, there is a rich research literature on creativity in artificial intelligence and computer science, with devoted journals, special issues, and conferences ( The Journal of Artificial Creativity , The Journal of Creative Music Systems , Digital Creativity , Minds and Machines special issue on Computational Creativity [Gervás et al. 2010], The International Conference on Computational Creativity ). The question we focus on here is whether a computer could be creative . As background, it is worth considering how theorists approached the analogous question as to whether a computer could think .
Although theorists of various kinds have asked whether machines can think since at least the early modern period, the most important conceptual innovations on the topic came from Alan Turing, centering around his 1950 paper “Computing machinery and intelligence”. Here Turing provided a number of groundbreaking insights. Perhaps most familiar is Turing’s “imitation game”, now commonly known as “the Turing Test”. In brief, the test involved an unknowing interrogator who could ask an open-ended series of questions of both a human and a computer. If the interrogator could not distinguish computer from human, Turing postulated that this would suffice to illustrate genuine intelligence. There is no shortage of controversy regarding the aptness of the test for intelligence, and arguably no computer has yet passed it. (For more thorough discussion of Turing and the Turing test see entries on Alan Turing , Turing machines , and the Turing test ).
Successful performance in Turing’s game would require remarkable behavioral flexibility. And it is highly operational: specify a threshold for imitation, and then simply allow the interrogator to ask questions, then assess performance. If the behavior is sufficiently flexible to fool the interrogator, Turing claimed, the behavior was intelligent and, therefore, the computer intelligent.
With this background in mind, what are some of the cases in AI research lauded as success cases, and how do they align with some of Turing’s criteria?
Many of the familiar success cases are highly specialized. Deep Blue defeated chess master Garry Kasparov (Kasparov & Greengard 2017); some language processing systems managed to navigate social contexts such as ordering from a menu at a restaurant (Schank & Abelson 1977); AlphaGo more recently defeated the world champion Go player. This specialization is both a virtue and a limitation. On the one hand, achievement in such a specialized domain implies an exceptional amount of detailed memory and skill. On the other hand, this knowledge and skill does not generalize. Neither Deep Blue nor Alpha Go could successfully order from a menu, along with countless other basic human tasks. Put in terms of Turing’s imitation game, these systems would fail miserably to fool a human, or even remotely imitate one (except for their performance in a very narrow domain). What about systems such as IBM’s Watson , which famously won (against humans) on the television game show Jeopardy! This performance is more general, since topics on the show vary widely, and seemed to require both language comprehension and some minimal reasoning skills (see entry on artificial intelligence for extended discussion). Even so, Watson’s capabilities are still quite limited: it cannot make fluid conversation “in real time” and is largely insensitive to temporal and other factors that come with context.
There are many, many more examples of computational systems that display sophisticated behavior, from the highly specialized to the more general. On the language processing front, very recent AI systems such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s LaMDA significantly outperform the systems described above. To be clear, these are remarkable achievements that display substantial complexity and, it appears in some cases, significant flexibility—features Turing highlighted in characteristically human behaviors. But this also underscores a distinction, often invoked by critics of artificial intelligence research. There is a difference between a computer’s displaying or merely imitating an intelligent behavior, and a computer’s instantiating intelligence through such behavior. And the critic will say, even if a computer behaves as if it is intelligent, this is just modeling or simulating intelligence. The greater ambition, though, is “genuine artificial intelligence”, a system that actually thinks. John Searle refers to this as the distinction between “weak AI” and “strong AI”, respectively.
- Weak AI : Could a computer behave as if it thinks?
- Strong AI: Could a computer genuinely think?
The general worry here is that however sophisticated a system’s behavior may appear “from the outside”, for all we know it may just be a “hollow shell” (Haugeland 1981 [1997]; Clark 2001). The worry has then been fleshed out in various ways by specifying what is missing from the shell, as it were. Here are three standard such candidates. And, again, in each case however sophisticated the computer’s behavior may appear it still may be lacking in any or all of the following. First, the computer may lack consciousness . Second, the computer may lack any understanding of the symbols over which it computes (Searle 1980). Finally, the computer may operate without caring about its own behavior or, as John Haugeland colorfully puts it, without “giving a damn”. In each case, any kind of response from the ambitious AI researcher encounters the substantial challenges that come with theorizing mental phenomena such as consciousness, understanding, linguistic competence, and emotion. (Turing 1950, for instance, recognized but largely eschewed these kinds of topics).
It’s one thing to ask whether computers could think, and another to ask whether they could be creative. And just as the prospect of artificial intelligence or thinking divides into two questions—of weak AI and strong AI—we may distinguish two analogous questions about artificial creativity, which we’ll refer to as the questions of “weak AC” and “strong AC”, respectively. To begin with the former:
- Weak AC : Could a computer behave as if it’s creative?
Something behaves as if it’s creative if it produces things which are psychologically new (new to that thing) and valuable . Arguably, a number of computers have already done that.
In the 1970s, Harold Cohen began using computational technologies to produce new drawings and paintings. The work of his computer painter, Aaron, has exhibited at galleries such as the Tate and the Victoria and Albert Museum in London. David Cope’s “EMI” (Experiments in Musical Intelligence) has composed musical works in the style of various known composers and styles, even a full-length opera. Some of these works have been recorded and produced by bona fide record labels. Just search “Emily Howell” on Spotify or Apple Music and give it a listen (Cope 1996, 2006). Simon Colton’s The Painting Fool is an ongoing project, involving a software that abstracts phrases, images, and other items from newspaper articles and creates collage-style pieces. It has also produced portraits, based on images of film characters, of the same individual in different emotional states (see Painting Fool in Other Internet Resources ; see Colton 2012 for theoretical discussion). Even more recently, there have been explosive developments in generative art systems like DALL•E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, VQGAN+CLIP. (For discussion see Paul & Stokes 2021). In all of these cases, the relevant outputs of the computer program are new relative to its past productions—so they are psychologically (or behaviorally) novel, which again is all the novelty that creativity requires. And although historical novelty isn’t required for creativity, it’s worth noting that these products appear to be to be new in all of history as well.
What about value? As noted above in §2.1 , some theorists reject the value condition, but even if value is required for creativity, that too is a condition these computer artworks seem to meet. Assessments of value can be controversial, but that is no less true for the outputs of human creativity. The fact that these works are critically acclaimed, showcased in prestigious galleries, and commissioned by selective record labels testifies to their artistic merit, and viewers find them pleasing, interesting, and appealing, even before being apprised of their unusual origin. So it is reasonable to conclude computer programs like the ones just described exhibit at least weak AC insofar as they produce works of valuable novelty, and one could cite many more examples in the same vein.
Some theorists have noted that, whether or not the original Turing test is a good test for intelligence or thinking, we might adopt an analogous test for creativity: If a computer can fool human observers into thinking that it is a human creator, then it is in fact creative (Pease & Colton 2011; see also Chen 2020 for useful discussion of artificial creativity, including many additional examples of particular cases, and so-called Dartmouth-based Turing tests). If we employ this test, we might find ourselves with an unexpected conclusion: computers can be creative; in fact, some of them already are. But one might reasonably worry that the test is inadequate and the conclusion is too quick (Berrar & Schuster 2014; Bringsjord et al. 2001). From the fact that a computer operates as if it’s creative, one might argue, it doesn’t follow that it really is. Which brings us to our next question:
- Strong AC : Could a computer genuinely be creative?
This obviously returns us to the question of what conditions something must meet in order to count as being genuinely creative. And here we need go beyond the outwardly observable product-features of novelty and value to consider the underlying processes of genuine creativity. As we saw in §2.2 , theorists have variously proposed that in order for a process to count as creative, it must be surprising, original, spontaneous, and/or agential. There is no consensus to appeal to here, but if any one of these conditions is indeed required for genuine creativity, then a computer could be genuinely creative only to the extent that it executes processes which satisfy that condition.
The classic statement of skepticism regarding the possibility of computer creativity is due to Lady Ada Lovelace who had this to say while remarking on “the Analytical Engine” designed by her friend Charles Babbage:
It is desirable to guard against the possibility of exaggerated ideas that might arise as to the powers of the Analytical Engine. The Analytical Engine has no pretensions whatever to originate anything. (Lovelace 1843, italics added)
Though Lovelace does not frame her comments in terms of “creativity” as such, she explicitly denied that a computer could satisfy at least one condition that is plausibly required for creativity, namely originality . A computer cannot be the originator, the author, or the creator of anything new, she contends; it can only do what it is programmed to do. We cannot get anything out of a computer that has not already been programmed into it. Further, Lovelace may also be interpreted as expressing or implying doubt about whether a computer could satisfy the three other proposed requirements for genuine creativity. Insofar as a computer’s outputs cannot be original, one might also suspect that they cannot be surprising . The image of a machine strictly following rules invokes precisely the kind of mechanical procedure that is the antithesis of spontaneity . And it may seem that such a machine could not be a genuine agent either. The problem isn’t just that a computer can’t produce anything original; it’s that it deserves no credit for whatever it does produce. Any praise or blame for the outputs of a computer rightly go to the engineers and programmers who made the machine, not to the machine itself. While these points may be intuitive, at least some of them are being challenged by modern technologies, which have come a long way since Babbage’s invention.
Consider AlphaGo again. This is a “deep learning” system, which involves two neural networks: a Policy network and a Value network. Very briefly: The system is trained using a vast number of legitimate moves made in actual games of Go played by professional human players (28.4 million moves from 160,000 games, to be precise; see Silver et al. 2016 and Halina 2021). The network is further trained, again using learning algorithms, by playing many games (some 100 million) against previous versions of itself (in the sense of a differently weighted neural network). The weights of nodes in the network are then adjusted by a learning algorithm that favors moves made in winning games. The value network is trained over a subset of these many games, with node weighting adjustments resulting in reliable probability assignments to moves vis-à-vis their potential to contribute to a win. Finally, the system employs a Monte Carlo search tree (MCT). Generally, this kind of algorithm is designed to simulate a decision process to optimize success given chosen parameters. In this case, the search algorithm selects a given path of moves, then adds some valid moves to this path, and then if this process does not terminate (end in win/loss), the system performs a “rollout”. A rollout essentially plays the game out for both players (using samples of possible moves) to its conclusion. The information that results from the MCT and processing by the value network are then fed back (back propagated) into the system. This entire process (once the system is trained) is rapid and determines how AlphaGo “decides” to move in any given game.
Here are some things to note. AlphaGo’s style of play is surprising . As commentators have noted, it is starkly unconventional relative to standards of human play (Halina cites Baker and Hui 2017 [ Other Internet Resources ]). Indeed, Lee Sodol, the world champion Go player defeated by AlphaGo in 2016, remarked that AlphaGo’s play revealed that much of human play is, contrary to prior common opinion, not creative after all—intimating that at least some of the play of AlphaGo is . Note further that this system is flexible. While there are learning algorithms and rules that adjust network weights, the system is not mechanical or predictable in the same fashion as earlier, classical systems (including Deep Blue , for example). In a recent paper, Marta Halina has made this argument (Halina 2021). She explicitly invokes Boden’s characterization, which requires novelty, value, and surprise of creativity. Again, the novelty and value should be plausibly attributed in this case. Regarding surprise, Halina suggests that it is AlphaGo’s employment of MCT that enables a kind of “insight”, flexibility, and unpredictable results. She writes,
It is the exploration parameter that allows AlphaGo to go beyond its training, encouraging it to simulate moves outside of those recommended by the policy network. As the search tree is constructed, the system starts choosing moves with the highest “action value” to simulate, where the action value indicates how good a move is based on the outcome of rollouts and value-network evaluations. (Halina 2021: 324)
Halina grants that given its domain-specificity, as we have already noted, this system’s particular abilities do not generalize in a way that may be required to properly attribute genuine intelligence. But she suggests that the complex use of the MCT search may amount to “mental scenario building” or, we might say, a kind of imagination. And insofar as this search algorithm technology can be applied to other systems in other domains, and imagination is a general component of intelligence, perhaps here lies space for generalizability. AlphaGo also affords at least some reply to the traditional Lovelace worry.
Artificial systems do not act only according to preprogrammed rules hand-coded by engineers. Moreover, current deep-learning methods are capable of producing systems that are superhuman in their abilities to discover novel and valuable solutions to problems within specific domains. (Halina 2021: 327)
If this is right, then AlphaGo exhibits originality . Finally, the flexibility with which this system operates may also satisfy Kronfeldner’s spontaneity requirement.
Some of these same features are found in a related approach in AI, namely research in evolutionary robotics. These systems also involve various forms of machine learning but in this case the learning is distributed, as it were, across a population of individuals rather than one individual. This approach can be understood, albeit imperfectly, as analogous to natural evolution. One begins, typically in computer simulation, with a population of agents. These agents are typically identified with individual neural networks, the connections and weightings of which are random to start. Relative to some task—for instance, avoiding obstacles, collecting objects, performing photo or phonotaxis—a genetic algorithm assigns a fitness value to each individual agent after a certain period of time or number of trials. Fitter agents are typically favored and used to generate the next population of agents. Also included in this generation are random mutation and genetic crossover (digital breeding!). Although it can take hundreds of generations, this is a discovery approach to engineering or constructing a system that successfully performs a task; it is “gradient descent learning” (Clark 1996). In this bottom-up approach, no single individual, nor even an entire population, are in any strict sense programmed. Rather, successful agents have “learned” as a result of generations of randomness, crossover, and small fitness improvements (and lots and lots of failures). Early success cases evolved robots that can follow trails (Koza 1992), locomote in insect-fashion (Beer & Gallagher 1992), guide themselves visually (Cliff, Husbands, & Harvey 1993), and collect garbage (Nolfi & Floreana 2000). See Bird and Stokes (2006, 2007) and Stokes and Bird (2008) for analysis and study of creativity in the context of evolutionary robotics.
These systems most certainly produce novelty. Later, fit individuals achieve novelty at their aimed task relative to whole generations and populations of previous agents. And this novelty is often surprising to the engineers and programmers that build them, indeed sometimes even unpredictably independent of any relevant task for individuals in the population. There are many examples in the literature. Indeed Lehman and others (2020) catalog a large range of cases where digital evolution surprises its creators, categorizing them in four representative groups: “mis-specified fitness functions”, “unintended debugging”, “exceeded experimenter expectations”, and “convergence with biology”. Here is one now relatively famous example of the first type of case. In early research in artificial life (A-Life), Karl Sims (1994) designed virtual creatures that were supposed to learn to walk (as well as swim and jump) in a simulated environment. The fitness function assessed individual agents on their average ground velocity across 10 seconds. Some of the fittest individuals to evolve were surprising: they grew tall and rigid and when they would fall over they would achieve high ground velocity, thus maximizing fitness given the (mis)specified parameters in unpredicted ways.
This is but one example of how systems like these can evolve in unpredictable or surprising ways. This unpredictability has occurred not just in simulated robotics, but in embodied robotics as well. In using a genetic algorithm to attempt to evolve oscillating sensors, researchers unintentionally evolved a radio antenna (Bird & Layzell 2002). This unexpected result arose from a combination of the particular algorithm used (which was intended) and various physical features of the space such as proximity to a PC monitor (which the researchers had presumably deemed irrelevant but which the evolved system, in a sense, did not). And one might be further inclined to describe some of these achievements as creative (and not just in the trivial sense that they are original instances of robotic success), since they also produce value, at least insofar as they are useful at performing a task, whether it is locomoting or locating a source of light or sensing radio waves.
Some theorists in this domain might argue that these systems achieve spontaneity as well. Given the substantial inclusion of randomness in the system’s development—both at the outset when the individual’s neural networks are randomized and more importantly with random mutation across populations—it is intuitive to describe the system’s as not following a mechanical procedure. Indeed, the way in which systems exploit fitness functions and data patterns further underscores this point. (Again, see the rich catalog of cases offered by Lehman et al. 2020).
On the face of it, then, recent technologies in AI, evolutionary robotics, and artificial life, seem to fulfill many of the conditions proposed for genuine creativity. These systems produce things that are novel and valuable, and do so through computational processes that are plausibly surprising, original, and spontaneous. The one requirement we have yet to address, however, is agency . Recall the suggestion, implicit in Lovelace’s remarks, that whatever a computer produces is to the credit of the programmer, not the computer. Notice that as sophisticated as current technologies in artificial creativity may be, presumably they are still not subject to praise or blame for what they do. If any beings are responsible for the work of these programs, it still seems to be the programmers and engineers who make them, not the programs themselves. The programs themselves do not seem to “give a damn”. So, if the creative process requires agency, arguably we have not yet created, programmed, or evolved a computational system that is really creative, however much they might appear to be. In the pursuit of strong AC, agency might be the final frontier (Paul & Stokes 2021).
It should be clear from the above discussions that there are rich and lively research programs, across a range of scientific disciplines, studying human creativity. These approaches substantiate the view that, contrary to the romantic tradition, creativity can be explained. Psychological functions and neural correlates have been identified, and remarkable advances are being made with computational and robotics technologies. What may be less clear is that, despite these advances, the distinct research programs in question are largely disjoint or siloed.
In a recent paper, Geraint Wiggins and Joydeep Bhattacharya (2014) highlight this “gap” between scientific studies of creativity. Their particular emphasis is on the gaps between research in neuroscience and research in computer science, and they advocate a bridge in the form of a neurocomputational approach. This kind of bridging may be called for even beyond what these authors prescribe, since there are gaps not just between these disciplines, but also between these and behavioral psychology, AI and A-Life research, and philosophical analysis. Creativity is a deeply complex and deeply important phenomenon. Fully understanding it will require us to integrate a variety of theoretical perspectives, and, as this survey reveals, philosophy has a vital role to play in that endeavor.
- Abdulla, Ahmed M., Sue Hyeon Paek, Bonnie Cramond, and Mark A. Runco, 2020, “Problem Finding and Creativity: A Meta-Analytic Review”, Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts , 14(1): 3–14. doi:10.1037/aca0000194
- Abraham, Anna, 2013, “The Promises and Perils of the Neuroscience of Creativity”, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , 7. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2013.00246
- Albert, Robert S. and Mark A. Runco, 1999, “A History of Research on Creativity”, in Sternberg 1999: 16–32. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511807916.004
- Amabile, Teresa, 1983, The Social Psychology of Creativity , (Springer Series in Social Psychology), New York: Springer-Verlag.
- –––, 1996, Creativity in Context: Update to the Social Psychology of Creativity , Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Anderson, Linda, 2006, Creative Writing: A Workbook with Readings , Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781315811932
- Aristotle, The Complete Works of Aristotle: The Revised Oxford Translation , Jonathan Barnes (ed.), Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1984.
- Aristotle, [EN], Nicomachean Ethics , Terrence Irwin (trans.), Indianapolis, IN: Hackett Publishing, 2019.
- Arnheim, R., 2001, “What It Means to Be Creative.” British Journal of Aesthetics 41(1): 24–25. doi:10.1093/bjaesthetics/41.1.24
- Asmis, Elizabeth, 1992, “Plato on Poetic Creativity”, in The Cambridge Companion to Plato , Richard Kraut (ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 338–364. doi:10.1017/CCOL0521430186.011
- Baldwin, James, 1962, “The Creative Process”, in Creative America, New York, NY: Ridge Press.
- Barsalou, Lawrence W. and Jesse J. Prinz, 1997, “Mundane Creativity in Perceptual Symbol Systems”, in Creative Thought: An Investigation of Conceptual Structures and Processes. , Thomas B. Ward, Steven M. Smith, and Jyotsna Vaid (eds.), Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 267–307. doi:10.1037/10227-011
- Battin, Margaret P., John Fisher, Ronald Moore, and Anita Silvers, 1989, Puzzles about Art: An Aesthetics Casebook , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- Beaty, Roger E., Mathias Benedek, Paul J. Silvia, and Daniel L. Schacter, 2016, “Creative Cognition and Brain Network Dynamics”, Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 20(2): 87–95. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2015.10.004
- Beaty, Roger E., Paul Seli, and Daniel L Schacter, 2019, “Network Neuroscience of Creative Cognition: Mapping Cognitive Mechanisms and Individual Differences in the Creative Brain”, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 27(June): 22–30. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.08.013
- Beer, Randall D. and John C. Gallagher, 1992, “Evolving Dynamical Neural Networks for Adaptive Behavior”, Adaptive Behavior , 1(1): 91–122. doi:10.1177/105971239200100105
- Bell, Julia and Paul Magrs (eds), 2001, The Creative Writing Coursebook: Forty Authors Share Advice and Exercises for Fiction and Poetry , London: Macmillan UK.
- Berrar, Daniel Peter and Alfons Schuster, 2014, “Computing Machinery and Creativity: Lessons Learned from the Turing Test”, Kybernetes , 43(1): 82–91. doi:10.1108/K-08-2013-0175
- Bink, Martin L. and Richard L. Marsh, 2000, “Cognitive Regularities in Creative Activity”, Review of General Psychology , 4(1): 59–78. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.4.1.59
- Bird, Jon and P. Layzell, 2002, “The Evolved Radio and Its Implications for Modelling the Evolution of Novel Sensors”, in Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC’02 (Cat. No.02TH8600) , Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2:1836–1841. doi:10.1109/CEC.2002.1004522
- Bird, Jon and Dustin Stokes, 2006, “Evolving Minimally Creative Robots”, in Proceedings of the Third Joint Workshop on Computational Creativity, 17th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence , Simon Colton and Alison Pease (eds), 1–5. [ Bird and Stokes 2006 available online ]
- –––, 2007, “Minimal Creativity, Evaluation and Fractal Pattern Discrimination”, in Proceedings of the Fourth International Joint Workshop on Computational Creativity , Amílcar Cardosa and Geraint A. Wiggins (eds), 121–128. [ Bird and Stokes 2007 available online ]
- Blair, Cassie S. and Michael D. Mumford, 2007, “Errors in Idea Evaluation: Preference for the Unoriginal?”, The Journal of Creative Behavior , 41(3): 197–222. doi:10.1002/j.2162-6057.2007.tb01288.x
- Boden, Margaret A., 1994, “What Is Creativity?”, in Dimensions of Creativity , Margaret A. Boden (ed.), Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 75–117. doi:10.7551/mitpress/2437.003.0006
- –––, 1998, “Creativity and Artificial Intelligence”, Artificial Intelligence , 103(1–2): 347–356. doi:10.1016/S0004-3702(98)00055-1
- –––, 2004, The Creative Mind: Myths and Mechanisms , second edition, London/New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203508527
- –––, 2010, Creativity and Art: Three Roads to Surprise , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2014, “Creativity and Artificial Intelligence: : A Contradiction in Terms?”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 224–244. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0012
- –––, 2018, “The Value of Creativity”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 173–193.
- Borcherding, Julia, unpublished, “Fancies and Illusions: Cavendish and du Châtelet on the Liberating Powers of the Imagination”, Philosophy, Cambridge University.
- Bowden, Edward M., Mark Jung-Beeman, Jessica Fleck, and John Kounios, 2005, “New Approaches to Demystifying Insight”, Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 9(7): 322–328. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2005.05.012
- Bringsjord, Selmer, 1994, “Lady Lovelace Had It Right: Computers Originate Nothing”, Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 17(3): 532–533. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00035718
- Bringsjord, Selmer, Paul Bello, and David Ferrucci, 2001, “Creativity, the Turing Test, and the (Better) Lovelace Test”, Minds and Machines , 11(1): 3–27. doi:10.1023/A:1011206622741
- Briskman, Larry, 1980, “Creative Product and Creative Process in Science and Art.” Inquiry: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Philosophy 23(1): 83–106. doi.org/10.1080/00201748008601892
- Bruner, Jerome S., 1962, “The Conditions of Creativity”, in Contemporary Approaches to Creative Thinking , H. Gruber, G. Terrell, and M. Wertheimer (eds), New York: Atherton, 1–30.
- Buckner, Randy L. and Lauren M. DiNicola, 2019, “The Brain’s Default Network: Updated Anatomy, Physiology and Evolving Insights”, Nature Reviews Neuroscience , 20(10): 593–608. doi:10.1038/s41583-019-0212-7
- Cacciari, Cristina, Maria Chiara Levorato, and Piercarla Cicogna, 1997, “Imagination at Work: Conceptual and Linguistic Creativity in Children”, in Creative Thought: An Investigation of Conceptual Structures and Processes. , Thomas B. Ward, Steven M. Smith, and Jyotsna Vaid (eds.), Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 145–177. doi:10.1037/10227-007
- Campbell, Donald T., 1960, “Blind Variation and Selective Retentions in Creative Thought as in Other Knowledge Processes”, Psychological Review , 67(6): 380–400. doi:10.1037/h0040373
- –––, 1965, “Variation and Selective Retention in Socio-Cultural Evolution”, in Social Change in Developing Areas : A Reinterpretation of Evolutionary Theory , H.R. Barringer, G.I. Blanksten, and R.W. Mack (eds), Cambridge, MA: Schenkman, 19–49.
- Carruthers, Peter, 2002, “Human Creativity: Its Cognitive Basis, Its Evolution, and Its Connections with Childhood Pretence”, The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 53(2): 225–249. doi:10.1093/bjps/53.2.225
- –––, 2006, The Architecture of the Mind: Massive Modularity and the Flexibility of Thought , Oxford: Clarendon Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199207077.001.0001
- –––, 2011, “Creative Action in Mind”, Philosophical Psychology , 24(4): 437–461. doi:10.1080/09515089.2011.556609
- –––, 2020, “Mechanisms for Constrained Stochasticity”, Synthese , 197(10): 4455–4473. doi:10.1007/s11229-018-01933-9
- Cattell, Raymond B. and Harold John Butcher, 1968, The Prediction of Achievement and Creativity , Indianapolis, IN: Bobbs-Merrill.
- Chen, Melvin, 2020, “Imagination Machines, Dartmouth-Based Turing Tests, & a Potted History of Responses”, AI and Society , 35(1): 283–287. doi:10.1007/s00146-018-0855-3
- Child, William, 2018, “Wittgenstein, Seeing-As, and Novelty”, in Aspect Perception After Wittgenstein: Seeing-As and Novelty , Michael Beaney, Dominic Shaw, and Brendan Harrington (eds), New York: Routledge, 29–48.
- Christoff, Kalina, Zachary C. Irving, Kieran C. R. Fox, R. Nathan Spreng, and Jessica R. Andrews-Hanna, 2016, “Mind-Wandering as Spontaneous Thought: A Dynamic Framework”, Nature Reviews Neuroscience , 17(11): 718–731. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.113
- Chrysikou, Evangelia G, 2019, “Creativity in and out of (Cognitive) Control”, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 27(June): 94–99. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.09.014
- Clark, Andy, 1996, Being There: Putting Brain, Body, and World Together Again , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- –––, 2001, Mindware , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Cliff, Dave, Phil Husbands, and Inman Harvey, 1993, “Explorations in Evolutionary Robotics”, Adaptive Behavior , 2(1): 73–110. doi:10.1177/105971239300200104
- Colton, Simon, 2012, “The Painting Fool: Stories from Building an Automated Painter”, in Computers and Creativity , Jon McCormack and Mark d’Inverno (eds.), Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 3–38. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-31727-9_1
- Cope, David, 1996, Experiments in Musical Intelligence , (Computer Music and Digital Audio Series 12), Madison, WI: A-R Editions.
- –––, 2006, Computer Models of Musical Creativity , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Crick, Francis, 1995, “The Impact of Linus Pauling on Molecular Biology”, video (with transcript), part of a conference, “The Life and Work of Linus Pauling (1901–1994): A Discourse on the Art of Biography”, 28 February – 2 March 1995, Oregon State University, Special Collections & Archives Research Center, Oregon State University Libraries. [ Crick 1995 available online .
- Cropley, A. J., 1967, Creativity (Education Today), London: Longmans.
- Cropley, David H., Arthur J. Cropley, James C. Kaufman, and Mark A. Runco (eds.), 2010, The Dark Side of Creativity , New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511761225
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly, 1965, “Artistic Problems and Their Solutions: An Exploration of Creativity in the Arts”, PhD thesis, University of Chicago. [ Csikszentmihalyi 1965 available online ]
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly and J. W. Getzels, 1970, “Concern for Discovery: An Attitudinal Component of Creative Production 1”, Journal of Personality , 38(1): 91–105. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.1970.tb00639.x
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly and Keith Sawyer, 1995, “Creative Insight: The Social Dimension of a Solitary Moment”, in The Nature of Insight , R. J. Steinberg and J. E. Davidson (eds.), Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 329–363. Reprinted in Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi’s The Systems Model of Creativity: The Collected Works of Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi , Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2014, 73–98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
- Dailey, Lesley and Michael D. Mumford, 2006, “Evaluative Aspects of Creative Thought: Errors in Appraising the Implications of New Ideas”, Creativity Research Journal , 18(3): 385–390. doi:10.1207/s15326934crj1803_11
- De Quincey, Thomas, 1827, “On Murder Considered as One of the Fine Arts”, Blackwood’s Magazine , 21(122/February): 199–213.
- Dietrich, Arne, 2019, “Where in the Brain Is Creativity: A Brief Account of a Wild-Goose Chase”, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 27(June): 36–39. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.09.001
- Dietrich, Arne and Riam Kanso, 2010, “A Review of EEG, ERP, and Neuroimaging Studies of Creativity and Insight”, Psychological Bulletin , 136(5): 822–848. doi:10.1037/a0019749
- Dominowski, Roger L., 1995, “Productive Problem Solving”, in Smith, Ward, and Finke 1995: 73–95.
- Donald, Merlin, 2001, A Mind so Rare: The Evolution of Human Consciousness , New York: W.W. Norton.
- du Sautoy, Marcus, 2019, The Creativity Code: Art and Innovation in the Age of AI , Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press.
- Einstein, Albert, “Kyoto Lecture”, 14 December 1922, from notes in Japanese taken by Jun Ishiwara and published as Einstein Koen-Roku , Tokyo: Tokyo-Tosho, 1977.
- Einstein, Albert and Leopold Infeld, 1938, The Evolution of Physics: The Growth of Ideas from Early Concepts to Relativity and Quanta , New York: Simon and Schuster.
- Eisenberger, Robert and Linda Rhoades, 2001, “Incremental Effects of Reward on Creativity”, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 81(4): 728–741. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.81.4.728
- Eisenberg, Jacob and William Forde Thompson, 2003, “A Matter of Taste: Evaluating Improvised Music”, Creativity Research Journal , 15(2–3): 287–296. doi:10.1080/10400419.2003.9651421
- Ericsson, K. Anders, Neil Charness, Paul J. Feltovich, and Robert R. Hoffman (eds.), 2006, The Cambridge Handbook of Expertise and Expert Performance , New York/Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511816796
- Ericsson, K. Anders, Ralf T. Krampe, and Clemens Tesch-Römer, 1993, “The Role of Deliberate Practice in the Acquisition of Expert Performance”, Psychological Review , 100(3): 363–406. doi:10.1037/0033-295X.100.3.363
- Essinger, James, 2014, Ada’s Algorithm: How Lord Byron’s Daughter Ada Lovelace Launched the Digital Age , Brooklyn: Melville House.
- Finke, Ronald A., 1990, Creative Imagery: Discoveries and Inventions in Visualization , Hillsdale, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates.
- –––, 1996, “Imagery, Creativity, and Emergent Structure”, Consciousness and Cognition , 5(3): 381–393. doi:10.1006/ccog.1996.0024
- Finke, Ronald A., Ward, Thomas B., Smith, Steven M., 1992, Creative Cognition: Theory, Research, and Applications , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Flam, Jack D., 2003, Matisse and Picasso: The Story of Their Rivalry and Friendship , Cambridge, MA: Icon Edition/Westview Press.
- Flavell, John H. and Juris Draguns, 1957, “A Microgenetic Approach to Perception and Thought”, Psychological Bulletin , 54(3): 197–217. doi:10.1037/h0041350
- Gardner, Howard, 1993, Creating Minds: An Anatomy of Creativity Seen through the Lives of Freud, Einstein, Picasso, Stravinsky, Eliot, Graham, and Gandhi , New York: BasicBooks.
- Gaut, Berys, 2003, “Creativity and Imagination”, in Gaut and Livingston 2003: 148–173 (ch. 6).
- –––, 2009, “Creativity and Skill”, in Krausz, Dutton, and Bardsley 2009: 83–104.
- –––, 2010, “The Philosophy of Creativity”, Philosophy Compass , 5(12): 1034–1046. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2010.00351.x
- –––, 2012, “Creativity and Rationality”, Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 70(3): 259–270. doi: 10.1111/jaac.2012.70.issue-3
- –––, 2014a, “Educating for Creativity”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 265–287. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0014
- –––, 2014b, “Mixed Motivations: Creativity as a Virtue”, Royal Institute of Philosophy Supplement , 75: 183–202. doi:10.1017/S1358246114000198
- –––, 2018, “The Value of Creativity”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 124–39.
- Gaut, Berys and Morag Gaut, 2011, Philosophy for Young Children: A Practical Guide , London: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203818428
- Gaut, Berys and Matthew Kieran (eds.), 2018, Creativity and Philosophy , New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781351199797
- Gaut, Berys Nigel and Paisley Livingston (eds.), 2003, The Creation of Art: New Essays in Philosophical Aesthetics , New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Gaut, Morag, 2010, “Can Children Engage in Philosophical Enquiry?” in Exploring Interdisciplinary Trends in Creativity and Engagement , Barbara McKenzie and Phil Fitzsimmons (eds), Oxford, U.K.: Oxford Inter-Disciplinary Press, 195–203.
- Gervás, Pablo, Rafael Pérez y Pérez, and Tony Veale, 2010, Computational Creativity , special issue of Minds and Machines , 20(4).
- Getzels, Jacob W., 1965, “Creative Thinking, Problem Solving, and Instruction”, in Theories of Learning and Instruction. Sixty-Third Year Book of the National Society for the Study of Education , E.R. Hilgard (ed.), Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 240–67.
- Getzels, Jacob W. and Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, 1975, “From Problem Solving to Problem Finding”, in Perspectives in Creativity , Irving A. Taylor and Jacob W. Getzels (eds.), Chicago: Aldine, chap. 4.
- Glaveanu, Vlad Petre, 2014, “The Psychology of Creativity: A Critical Reading”, Creativity. Theories—Research—Applications , 1(1): 10–32.
- Grant, James, 2012, “The Value of Imaginativeness”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 90(2): 275–289. doi:10.1080/00048402.2011.574143
- Guilford, J. P., 1950, “Creativity”, American Psychologist , 5(9): 444–454. doi:10.1037/h0063487
- Guyer, Paul, 2003, “Exemplary Originality: Genius, Universality, and Individuality”, in Gaut and Livingston 2003: 116–137.
- Hájek, Alan, 2014, “Philosophical Heuristics and Philosophical Creativity”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 288–318. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0015
- –––, 2016, “Philosophical Heuristics and Philosophical Methodology”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophical Methodology , Herman Cappelen, Tamar Szabó Gendler, and John Hawthorne (eds), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ch. 19.
- –––, 2017, “The Philosophy Toolkit”, AEON , 3 April 2017. [ Hájek 2017 available online ]
- –––, 2018, “Creating Heuristics for Philosophical Creativity”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 292–312.
- Halina, Marta, 2021, “Insightful Artificial Intelligence”, Mind & Language , 36(2): 315–329. doi:10.1111/mila.12321
- Harris, Paul L., 2000, The Work of the Imagination , (Understanding Children’s Worlds), Oxford/Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
- Haugeland, John (ed.), 1981 [1997], Mind Design , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Second and enlarged edition as Mind Design II: Philosophy, Psychology, and Artificial Intelligence , Cambridge, MA: A Bradford Book. First edition, 1997. doi:10.7551/mitpress/4626.001.0001
- Hausman, Carl R., 1975 [1984], A Discourse on Novelty and Creation , The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. New edition Albany, NY: SUNY Press, 1984.
- –––, 1979, “Criteria of Creativity”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 40(2): 237–249. doi:10.2307/2106319
- –––, 1984, “Second Preface”, in the 1984 edition of Hausman 1975.
- –––, 1985, “Originality as a Criterion of Creativity”, in Creativity in Art, Religion, and Culture , Michael H. Mitias (ed.), Amsterdam: Rodopoi, 26–41.
- Hebb, D. O., 1949 [2002], The Organization of Behavior: A Neuropsychological Theory , New York: Wiley, Reprinted Mahwah, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates, 2002.
- Heilman, Kenneth M., 2016, “Possible Brain Mechanisms of Creativity”, Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology , 31(4): 285–296. doi:10.1093/arclin/acw009
- Heinelt, Gottfried, 1974, Kreative Lehrer = Kreative Schüler , Freiburg: Herder.
- Hennessey, Beth A. and Teresa M. Amabile, 2010, “Creativity”, Annual Review of Psychology , 61(1): 569–598. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.093008.100416
- Hills, Alison, 2018, “Moral and Aesthetic Virtue”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 118(3): 255–274. doi:10.1093/arisoc/aoy015
- Hills, Alison and Alexander Bird, 2018, “Creativity Without Value”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 95–107.
- Hofstadter, Douglas, 2001, “Staring EMI Straight in the Eye—and Doing My Best Not to Flinch”, in Virtual Music: Computer Synthesis of Musical Style , David Cope (ed.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 33–82.
- Horng, Jeou-Shyan and Lin Lin, 2009, “The Development of a Scale for Evaluating Creative Culinary Products”, Creativity Research Journal , 21(1): 54–63. doi:10.1080/10400410802633491
- Hospers, John, 1985, “Artistic Creativity”, The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 43(3): 243–255. doi:10.2307/430638
- Howell, Patrick A., 2020, Dispatches from the Vanguard: The Global International African Arts Movement versus Donald J. Trump , London: Repeater Books.
- Irving, Zachary and Evan Thompson, 2018, “The Philosophy of Mind-Wandering”, in Oxford Handbook of Spontaneous Thought: Mind-Wandering, Creativity, and Dreaming , Christoff Kalina and Fox Kieran, Oxford University Press, ch. 8.
- Jackson, Philip W. and Samuel Messick, 1965, “The Person, the Product, and the Response: Conceptual Problems in the Assessment of Creativity1”, Journal of Personality , 33(3): 309–329. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.1965.tb01389.x
- John-Steiner, Vera, 1985, Notebooks of the Mind: Explorations of Thinking . 1st ed. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press.
- Jung, Rex Eugene, Brittany S. Mead, Jessica Carrasco, and Ranee A. Flores, 2013, “The Structure of Creative Cognition in the Human Brain”, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , 7. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2013.00330
- Jung-Beeman, Mark, Edward M Bowden, Jason Haberman, Jennifer L Frymiare, Stella Arambel-Liu, Richard Greenblatt, Paul J Reber, and John Kounios, 2004, “Neural Activity When People Solve Verbal Problems with Insight”, PLoS Biology , 2(4): e97. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020097
- Kami, Avi, Gundela Meyer, Peter Jezzard, Michelle M. Adams, Robert Turner, and Leslie G. Ungerleider, 1995, “Functional MRI Evidence for Adult Motor Cortex Plasticity during Motor Skill Learning”, Nature , 377(6545): 155–158. doi:10.1038/377155a0
- Kant, Immanuel, 1790 [2000], Kritik der Urteilskraft , Berlin und Libau : Lagarde und Friedrich. Translated as Critique of the Power of Judgment , Paul Guyer (ed.), Eric Matthews (trans.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000. Citations include the section of the Critique , the volume and page number of the Akademie edition, and page number of this translation. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511804656
- Karmiloff-Smith, Annette, 1990, “Constraints on Representational Change: Evidence from Children’s Drawing”, Cognition , 34(1): 57–83. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(90)90031-E
- –––, 1992, Beyond Modularity: A Developmental Perspective on Cognitive Science , (Learning, Development, and Conceptual Change), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Kasparov, Garry K. and Mig Greengard, 2017, Deep Thinking: Where Machine Intelligence Ends and Human Creativity Begins , New York: PublicAffairs, an imprint of Perseus Books.
- Kaufman, James C., 2009, Creativity 101 , (The Psych 101 Series), New York: Springer Publishing.
- Kaufman, Scott Barry (ed.), 2013, The Complexity of Greatness: Beyond Talent or Practice , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199794003.001.0001
- Kaufman, Scott Barry and Carolyn Gregoire, 2016, Wired to Create: Discover the 10 Things Great Artists, Writers and Innovators Do Differently , Perigee/Penguin.
- Kaufman, Scott Barry and James C. Kaufman (eds.), 2009, The Psychology of Creative Writing , Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0007
- Kieran, Matthew, 2014a, “Creativity as a Virtue of Character”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 125–144. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0007
- –––, 2014b, “Creativity, Virtue and the Challenges from Natural Talent, Ill-Being and Immorality”, Royal Institute of Philosophy Supplement , 75: 203–230. doi:10.1017/S1358246114000241
- –––, 2018, “Creativity, Vanity and Narcissism” in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 74–92.
- Kivy, Peter, 2001, The Possessor and the Possessed: Handel, Mozart, Beethoven, and the Idea of Musical Genius , (Yale Series in the Philosophy and Theory of Art), New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Klausen, Søren Harnow, 2010, “The Notion of Creativity Revisited: A Philosophical Perspective on Creativity Research” Creativity Research Journal , 22(4):347–360. doi:10.1080/10400419.2010.523390
- Kneller, George F., 1965, The Art and Science of Creativity , New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Koestler, Arthur, 1964, The Act of Creation , New York: Macmillan.
- Kounios, John and Mark Beeman, 2014, “The Cognitive Neuroscience of Insight”, Annual Review of Psychology , 65(1): 71–93. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115154
- Koza, John R., 1992, Genetic Programming: On the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection , (Complex Adaptive Systems), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Krausz, Michael, Denis Dutton, and Karen Bardsley (eds.), 2009, The Idea of Creativity , Leiden/Boston: Brill. doi:10.1163/ej.9789004174443.i-348
- Kronfeldner, Maria E., 2009, “Creativity Naturalized”, The Philosophical Quarterly , 59(237): 577–592. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9213.2009.637.x
- –––, 2010, “Darwinian ‘Blind’ Hypothesis Formation Revisited”, Synthese , 175(2): 193–218. doi:10.1007/s11229-009-9498-8
- –––, 2011, Darwinian Creativity and Memetics , (Acumen Research Editions), Durham, UK: Acumen Publishing.
- –––, 2018, “Explaining Creativity”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 213–229.
- Laukkonen, Ruben E. and Jason M. Tangen, 2018, “How to Detect Insight Moments in Problem Solving Experiments”, Frontiers in Psychology , 9(March): article 282. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00282
- Lehman, Joel, Jeff Clune, Dusan Misevic, Christoph Adami, Lee Altenberg, Julie Beaulieu, Peter J. Bentley, Samuel Bernard, Guillaume Beslon, David M. Bryson, et al., 2020, “The Surprising Creativity of Digital Evolution: A Collection of Anecdotes from the Evolutionary Computation and Artificial Life Research Communities”, Artificial Life , 26(2): 274–306. doi:10.1162/artl_a_00319
- Lepper, Mark R., David Greene, and Richard E. Nisbett, 1973, “Undermining Children’s Intrinsic Interest with Extrinsic Reward: A Test of the ‘Overjustification’ Hypothesis”, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 28(1): 129–137. doi:10.1037/h0035519
- Limb, Charles J. and Allen R. Braun, 2008, “Neural Substrates of Spontaneous Musical Performance: An FMRI Study of Jazz Improvisation”, PLoS ONE , 3(2): e1679. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001679
- Livingston, Paisley, 2018, “Explicating ‘Creativity’”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 108–123.
- Lopes, Dominic McIver, 2008, “Virtues of Art: Good Taste”, Aristotelian Society Supplementary Volume , 82(1): 197–211. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8349.2008.00169.x
- Lovelace, Ada Augusta, 1843, “Translation of, and Notes to, Luigi F. Menabrea’s Sketch of the Analytical Engine Invented by Charles Babbage”, in Scientific Memoirs, Volume 3 , Richard Taylor (ed.), London: Richard and John E. Taylor, 691–731.
- Luo, Jing and Kazuhisa Niki, 2003, “Function of Hippocampus in ‘Insight’ of Problem Solving”, Hippocampus , 13(3): 316–323. doi:10.1002/hipo.10069
- Mai, Xiao-Qin, Jing Luo, Jian-Hui Wu, and Yue-Jia Luo, 2004, “‘Aha!’ Effects in a Guessing Riddle Task: An Event-Related Potential Study”, Human Brain Mapping , 22(4): 261–270. doi:10.1002/hbm.20030
- Martindale, Colin, 1977, “Creativity, Consciousness, and Cortical Arousal”, Journal of Altered States of Consciousness , 3(1): 69–87.
- –––, 1981, Cognition and Consciousness , (Dorsey Series in Psychology), Homewood, IL: Dorsey Press.
- –––, 1995, “Creativity and Connectionism”, in Smith, Ward, and Finke 1995 :249–68.
- –––, 1999, “Biological Bases of Creativity”, in Sternberg 1999: 137–152. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511807916.009
- Martindale, Colin and James Armstrong, 1974, “The Relationship of Creativity to Cortical Activation and Its Operant Control”, The Journal of Genetic Psychology , 124(2): 311–320. doi:10.1080/00221325.1974.10532293
- Martindale, Colin and Dwight Hines, 1975, “Creativity and Cortical Activation during Creative, Intellectual and Eeg Feedback Tasks”, Biological Psychology , 3(2): 91–100. doi:10.1016/0301-0511(75)90011-3
- Maybury, Barry, 1967, Creative Writing for Juniors , London: B. T. Batsford.
- Mayer, Richard E., 1989, “Systematic Thinking Fostered by Illustrations in Scientific Text”, Journal of Educational Psychology , 81(2): 240–246. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.81.2.240
- Mayseless, Naama, Ayelet Eran, and Simone G. Shamay-Tsoory, 2015, “Generating Original Ideas: The Neural Underpinning of Originality”, NeuroImage , 116(August): 232–239. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.030
- McMahon, Darrin M., 2013, Divine Fury: A History of Genius , New York: Basic Books.
- Mekern, Vera, Bernhard Hommel, and Zsuzsika Sjoerds, 2019, “Computational Models of Creativity: A Review of Single-Process and Multi-Process Recent Approaches to Demystify Creative Cognition”, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 27(June): 47–54. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.09.008
- Metcalfe, Janet and David Wiebe, 1987, “Intuition in Insight and Noninsight Problem Solving”, Memory & Cognition , 15(3): 238–246. doi:10.3758/BF03197722
- Miller, Arthur I., 2019, The artist in the machine: The world of AI-powered creativity , Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. doi:10.7551/mitpress/11585.001.0001
- Mithen, Steven J., 1996, The Prehistory of the Mind: The Cognitive Origins of Art, Religion and Science , New York: Thames and Hudson.
- –––, 1998, “A Creative Explosion? Theory of Mind, Language, and the Disembodied Mind of the Upper Paleolithic”, in Creativity in Human Evolution and Prehistory , Steven Mithen (ed.) , London: Routledge, 97–106.
- Morrison, Robert G. and Benjamin Wallace, 2001, “Imagery Vividness, Creativity and the Visual Arts”, Journal of Mental Imagery , 25(3–4): 135–152.
- Morrison, Toni, 1993, “The of of Fiction No. 134”, interview by Elissa Schappell and Calaudia Brodsky Lacour, The Paris Review , 128(Fall 1993). [ Morrison 1993 available online ]
- Mumford, Michael D., 2003, “Where Have We Been, Where Are We Going? Taking Stock in Creativity Research”, Creativity Research Journal , 15(2–3): 107–120. doi:10.1080/10400419.2003.9651403
- Murray, Penelope, 1989, Genius: The History of an Idea , Oxford/New York: B. Blackwell.
- Murray, Samuel, Nathan Liang, Nicholaus Brosowsky, and Paul Seli, forthcoming, “What Are the Benefits of Mind Wandering to Creativity?”, Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts , early online: September 2021. doi:10.1037/aca0000420
- Nahm, Milton Charles, 1956, Genius and Creativity: An Essay in the History of Ideas , New York: Harper Torchbooks.
- Nanay, Bence, 2014, “An Experiential Account of Creativity”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 17–36. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0002
- Newell, Allen, J. C. Shaw, and Herbert A. Simon, 1962, “The Processes of Creative Thinking”, in Contemporary Approaches to Creative Thinking: A Symposium Held at the University of Colorado. , Howard E. Gruber, Glenn Terrell, and Michael Wertheimer (eds.), New York: Atherton Press, 63–119. doi:10.1037/13117-003
- Nickles, Thomas, 2003, “Evolutionary Models of Innovation and the Meno Problem”, in L. V. Shavinina (ed.), The International Handbook on Innovation, 54–78. New York, NY: Elsevier Science.
- Nietzsche, Friedrich, 1872 [1967], The Birth of Tragedy out of the Spirit of Music , Walter Kaufmann (trans.), New York: Vintage.
- Nolfi, Stefano and Dario Floreano, 2000, Evolutionary Robotics: The Biology, Intelligence, and Technology of Self-Organizing Machines , Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. doi:10.7551/mitpress/2889.001.0001
- Novitz, David, 1999, “Creativity and Constraint”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 77(1): 67–82. doi:10.1080/00048409912348811
- Pais, Abraham, 1982, Subtle Is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press.
- Palmiero, Massimiliano, Raffaella Nori, Vincenzo Aloisi, Martina Ferrara, and Laura Piccardi, 2015, “Domain-Specificity of Creativity: A Study on the Relationship Between Visual Creativity and Visual Mental Imagery”, Frontiers in Psychology , 6(December). doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01870
- Paul, Elliot Samuel and Scott Barry Kaufman (eds.), 2014, The Philosophy of Creativity: New Essays , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.001.0001
- Paul, Elliot Samuel and Dustin Stokes, 2018, “Attributing Creativity”, in Gaut and Kieran 2018: 193–210.
- –––, 2021, “Computer Creativity is a Matter of Agency”, Institute of Arts and Ideas News , 11 November 2021, [ Paul and Stokes 2021 available online ]
- Pease, Alison and Simon Colton, 2011, “On Impact and Evaluation in Computational Creativity: A Discussion of the Turing Test and an Alternative Proposal”, in Proceedings of AISB ’11: Computing and Philosophy , Dimitar Kazakov and George Tsoulas (eds.), York: Society for the Study of Artificial Intelligence and Simulation of Behaviour, 15–22.
- Pérez-Fabello, María José and Alfredo Campos, 2007, “Influence of Training in Artistic Skills on Mental Imaging Capacity”, Creativity Research Journal , 19(2–3): 227–232. doi:10.1080/10400410701397495
- Perkins, David N., 1981, The Mind’s Best Work , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Picciuto, Elizabeth and Peter Carruthers, 2014, “The Origins of Creativity”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 199–223. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0011
- Plato, Plato: Complete Works , John M. Cooper and D.S. Hutchinson (eds), Indianapolis, IN: Hackett Publishing, 1997.
- Plucker, Jonathan A., Ronald A. Beghetto, and Gayle T. Dow, 2004, “Why Isn’t Creativity More Important to Educational Psychologists? Potentials, Pitfalls, and Future Directions in Creativity Research”, Educational Psychologist , 39(2): 83–96. doi:10.1207/s15326985ep3902_1
- Poincaré, Henri, 1908 [1913], Science et Méthode , Paris: Flammarion. Translated as “Science and Method” in The Foundations of Science: Science and Hypothesis, The Value of Science, Science and Method , George Bruce Halsted (trans.), (Science and Education 1), New York: The Science Press, 1913. [ Poincaré 1913 available online ]
- Policastro, Emma and Howard Gardner, 1999, “From Case Studies to Robust Generalizations: An Approach to the Study of Creativity”, in Sternberg 1999: 213–225. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511807916.013
- Pólya, George, 1945, How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Popper, Karl Raimund, 1934 [1959], Logik der forschung: zur erkenntnistheorie der modernen naturwissenschaft , (Schriften zur wissenschaftlichen weltauffassung, Bd. 9), Wien: J. Springer. Translated as The Logic of Scientific Discovery , London: Hutchinson, 1959.
- Posner, Micheal I., and Raichle, Marcus E., 1994, Images of Mind , New York, NY: WH Freeman and Co.
- Posner, Michael I., DiGirolamo, Gregory, J., Fernandez-Duque, Diego, 1997, “Brain mechanisms of cognitive skills”, Consciousness and Cognition 1997, 6(2-3):267-90. doi: 10.1006/ccog.1997.0301. PMID: 9262412.
- Prinz, Jesse and Laurence Barsalou, 2002, “Acquisition and Productivity in Perceptual Symbol Systems: An Account of Mundane Creativity”, in Creativity, Cognition, and Knowledge: An Interaction , Terry Dartnall (ed.), Westport, CT: Praeger, ch. 2.
- Raichle, Marcus E., Ann Mary MacLeod, Abraham Z. Snyder, William J. Powers, Debra A. Gusnard, and Gordon L. Shulman, 2001, “A Default Mode of Brain Function”, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 98(2): 676–682. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.2.676
- Richards, Ruth L., 1976, “A Comparison of Selected Guilford and Wallach-Kogan Creative Thinking Tests in Conjunction With Measures of Intelligence*”, The Journal of Creative Behavior , 10(3): 151–164. doi:10.1002/j.2162-6057.1976.tb01018.x
- Ritter, Simone M. and Ap Dijksterhuis, 2014, “Creativity: The Unconscious Foundations of the Incubation Period”, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , 8(April). doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00215
- Roberts, Tom, 2018, “Aesthetic Virtues: Traits and Faculties”, Philosophical Studies , 175(2): 429–447. doi:10.1007/s11098-017-0875-8
- Root-Bernstein, Robert Scott and Michèle Root-Bernstein, 1999, Sparks of Genius: The Thirteen Thinking Tools of Creative People , Boston, MA: Houghton, Mifflin and Company.
- Runco, Mark A., 1991, “The Evaluative, Valuative, and Divergent Thinking of Children*”, The Journal of Creative Behavior , 25(4): 311–319. doi:10.1002/j.2162-6057.1991.tb01143.x
- –––, 2017, “Comments on Where the Creativity Research Has Been and Where Is It Going”, The Journal of Creative Behavior , 51(4): 308–313. doi:10.1002/jocb.189
- Runco, Mark A., Ahmed M. Abdulla, Sue Hyeon Paek, Fatima A. Al-Jasim, and Hanadi N. Alsuwaidi, 2016, “Which Test of Divergent Thinking Is Best?”, Creativity. Theories—Research—Applications , 3(1): 4–18. doi:10.1515/ctra-2016-0001
- Runco, Mark A. and Robert S. Albert, 2010, “Creativity Research: A Historical View”, in The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity , James C. Kaufman and Robert J. Sternberg (eds.), New York: Cambridge University Press, 3–19. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511763205.003
- Runco, Mark A. and Ivonne Chand, 1994, “Problem Finding, Evaluative Thinking, and Creativity”, in Problem Finding, Problem Solving, and Creativity , Mark A. Runco (ed.), (Creativity Research), Westport, CT: Ablex Publishing, 40–76.
- Runco, Mark A. and Gayle T. Dow, 2004, “Assessing the Accuracy of Judgments of Originality on Three Divergent Thinking Tests”, Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving , 14(2): 5–14.
- Runco, Mark A. and Garrett J. Jaeger, 2012, “The Standard Definition of Creativity”, Creativity Research Journal , 24(1): 92–96. doi:10.1080/10400419.2012.650092
- Runco, Mark A. and Steven R. Pritzker (eds.), 2020, Encyclopedia of Creativity , third edition, Amsterdam: Academic Press.
- Runco, Mark A. and Luiz Vega, 1990, “Evaluating the Creativity of Children’s Ideas”, Journal of Social Behavior & Personality , 5(5): 439–452.
- Sawyer, R. Keith, 2012, Explaining Creativity: The Science of Human Innovation , second edition, New York: Oxford University Press.
- Schank, Roger A. and Abelson, Robert P., 1977, Scripts, Plans, Goals, and Understanding: An Inquiry Into Human Knowledge Structures , London: Psychology Press.
- Schoenfeld, Alan H., 1982, “Measures of Problem-Solving Performance and of Problem-Solving Instruction”, Journal for Research in Mathematics Education , 13(1): 31–49. doi:10.2307/748435
- –––, 1987a, “Pólya, Problem Solving, and Education”, Mathematics Magazine , 60(5): 283–291. doi:10.2307/2690409
- –––, 1987b, “What’s All the Fuss about Metacognition?”, in Cognitive Science and Mathematics Education , Alan H. Schoenfeld (ed.), Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 189–215.
- Schopenhauer, Arthur, 1859 [WWV], Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung , third edition, Leipzig. First edition in 1811 and expanded in 1844. Translated as The World as Will and Representation , two volumes, E. F. J. Payne (trans.), Indian Hills, CO: The Falcon’s Wing Press, 1958. Reprinted New York: Dover Publications, 1966. Citations, WWV, with volume and page are to the 1966 edition.
- –––, 1851 [SW/PP], Parerga und Paralipomena: kleine philosophische Schriften , two volumes, Berlin. Collected in his Sämtliche Werke [SW], Arthur Hübscher (ed.), Mannheim: F. A. Brockhaus, 1988, volumes 5 and 6. Translated as Arthur Schopenhauer: Parerga and Paralipomena Short Philosophical Essays , 2 volumes, Christopher Janaway, Sabine Roehr, and Adrian Del Caro (eds.), Adrian Del Caro (trans.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 and 2015. Page numbers are given both to the SW edition with volume and page and to the Cambridge University edition [PP] with volume and page.
- Searle, John R., 1980, “Minds, Brains, and Programs”, Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 3(3): 417–424. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00005756
- Shevlin, Henry, Karina Vold, Matthew Crosby, and Marta Halina, 2019, “The Limits of Machine Intelligence: Despite Progress in Machine Intelligence, Artificial General Intelligence Is Still a Major Challenge”, EMBO Reports , 20(10). doi:10.15252/embr.201949177
- Silver, David, Aja Huang, Chris J. Maddison, Arthur Guez, Laurent Sifre, George van den Driessche, Julian Schrittwieser, Ioannis Antonoglou, Veda Panneershelvam, Marc Lanctot, et al., 2016, “Mastering the Game of Go with Deep Neural Networks and Tree Search”, Nature , 529(7587): 484–489. doi:10.1038/nature16961
- Simonton, Dean Keith, 1984, Genius, Creativity, and Leadership: Historiometric Inquiries , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1988a, “Creativity, Leadership, and Chance”, in R. J. Sternberg (ed.), The Nature of Creativity , 386-426. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1988b, Scientific genius: A psychology of science . New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1994, Greatness: Who Makes History and Why , New York: Guilford.
- –––, 1997, Genius and Creativity: Selected Papers , Westport, CT: Ablex Publishing.
- –––, 1999a, “Creativity as Blind Variation and Selective Retention: Is the Creative Process Darwinian?”, Psychological Inquiry , 10(4): 309–328.
- –––, 1999b, Origins of Genius: Darwinian Perspectives on Creativity , New York/Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2004, Creativity in Science: Chance, Logic, Genius, and Zeitgeist , Cambridge, UK/New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2009, Genius 101 , (The Psych 101 Series), New York: Springer.
- –––, 2011, “Creativity and Discovery as Blind Variation: Campbell’s (1960) BVSR Model after the Half-Century Mark”, Review of General Psychology , 15(2): 158–174. doi:10.1037/a0022912
- –––, 2012a, “Creativity, Problem Solving, and Solution Set Sightedness: Radically Reformulating BVSR”, The Journal of Creative Behavior , 46(1): 48–65. doi:10.1002/jocb.004
- –––, 2012b, “Taking the U.S. Patent Office Criteria Seriously: A Quantitative Three-Criterion Creativity Definition and Its Implications”, Creativity Research Journal , 24(2–3): 97–106. doi:10.1080/10400419.2012.676974
- –––, 2018, “Creative Genius as Causal Agent in History: William James’s 1880 Theory Revisited and Revitalized”, Review of General Psychology , 22(4): 406–421. doi:10.1037/gpr0000165
- –––, forthcoming, “The Blind-Variation and Selective-Retention Theory of Creativity: Recent Developments and Current Status of BVSR”, Creativity Research Journal , early online: 14 April 2022 (20 pages). doi:10.1080/10400419.2022.2059919
- Sims, Karl, 1994, “Evolving 3D Morphology and Behavior by Competition”, Artificial Life , 1(4): 353–372. doi:10.1162/artl.1994.1.4.353
- Singh, Simon, 1999, The Code Book: The Secret History of Codes and Codebreaking , London: Fourth Estate.
- Smith, Steven M. and Steven E. Blankenship, 1989, “Incubation Effects”, Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society , 27(4): 311–314. doi:10.3758/BF03334612
- –––, 1991, “Incubation and the Persistence of Fixation in Problem Solving”, The American Journal of Psychology , 104(1): 61–87. doi:10.2307/1422851
- Smith, Steven M., Thomas B. Ward, and Ronald A. Finke (eds.), 1995, The Creative Cognition Approach , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Stein, Morris I., 1953, “Creativity and Culture”, The Journal of Psychology , 36(2): 311–322. doi:10.1080/00223980.1953.9712897
- Sternberg, Robert J. (ed.), 1999, Handbook of Creativity , Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511807916
- Sternberg, Robert J. and Todd I. Lubart, 1995, Defying the Crowd: Cultivating Creativity in a Culture of Conformity , New York, NY: Free Press.
- –––, 1999, “The Concept of Creativity: Prospects and Paradigms”, in Sternberg 1999: 3–15. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511807916.003
- Stokes, Dustin R., 2007, “Incubated Cognition and Creativity”, Journal of Consciousness Studies , 14(3): 83–100.
- –––, 2008, “A Metaphysics of Creativity”, in New Waves in Aesthetics , Kathleen Stock and Katherine Thomson-Jones (eds.), New York: Palgrave-Macmillan, 105–124.
- –––, 2011, “Minimally Creative Thought: Minimally Creative Thought”, Metaphilosophy , 42(5): 658–681. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9973.2011.01716.x
- –––, 2014, “The Role of Imagination in Creativity”, in Paul and Kaufman 2014: 157–184. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199836963.003.0009
- –––, 2016, “Imagination and Creativity”, in The Routledge Handbook of the Philosophy of Imagination , Amy Kind (ed.), London/New York: Routledge, chapter 18.
- Stokes, Dustin R. and Jon Bird, 2008, “Evolutionary Robotics and Creative Constraints”, in Beyond the Brain: Embodied, Situated, and Distributed Cognition , Benoit Hardy-Vallée and Nicolas Payette (eds.), Newcastle: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 227–245.
- Tabery, James, 2014, Beyond versus: The Struggle to Understand the Interaction of Nature and Nurture , (Life and Mind: Philosophical Issues in Biology and Psychology), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Takeuchi, Hikaru and Rex Jung (eds), 2019, Creativity , special issue of Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 27: 1–174.
- Tatarkiewicz, Władysław, 1980, A History of Six Ideas: An Essay in Aesthetics , Dordrecht: Springer Science & Business Media.
- Thagard, Paul and Terrence C. Stewart, 2011, “The AHA! Experience: Creativity Through Emergent Binding in Neural Networks”, Cognitive Science , 35(1): 1–33. doi:10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01142.x
- Turing, Alan M., 1950, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”, Mind , 59(236): 433–460. doi:10.1093/mind/LIX.236.433
- Verstijnen, Ilse Marieke, 1997, “Sketches of Creative Discovery: A Psycological Inquiry into the Role of Imagery and Sketching in Creative Discovery”, Doctoral thesis, Technische Universiteit, Delft, The Netherlands. [ Verstijnen 1997 available online ]
- Wallas, Graham, 1926, The Art of Thought , London: J. Cape.
- Ward, Thomas B., 1994, “Structured Imagination: The Role of Category Structure in Exemplar Generation”, Cognitive Psychology , 27(1): 1–40. doi:10.1006/cogp.1994.1010
- –––, 1995, “What’s Old about New Ideas?” in Smith, Ward, and Finke 1995: 157–178.
- Watson, James D., 1968 [1999], The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA , New York: Atheneum. First Touchstone edition, London: Penguin, 1999.
- Weisberg, Robert W., 1986, Creativity: Genius and Other Myths , New York: W.H. Freeman.
- –––, 2006, Creativity: Understanding Innovation in Problem Solving, Science, Invention, and the Arts , Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Wiggins, Geraint A. and Joydeep Bhattacharya, 2014, “Mind the Gap: An Attempt to Bridge Computational and Neuroscientific Approaches to Study Creativity”, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , 8(July). doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00540
- Williams, Rich, Mark A. Runco, and Eric Berlow, 2016, “Mapping the Themes, Impact, and Cohesion of Creativity Research over the Last 25 Years”, Creativity Research Journal , 28(4): 385–394. doi:10.1080/10400419.2016.1230358
- Young, Edward, 1759 [1966], Conjectures on Original Composition: In a Letter to the Author of Sir Charles Grandison , London: A. Millar. Reprinted Leeds: Scolar Press, 1966.
- Zagzebski, Linda Trinkaus, 1997, Virtues of the Mind: An Inquiry into the Nature of Virtue and the Ethical Foundations of Knowledge , Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Zemore, Sarah E., 1995, “Ability to Generate Mental Images in Students of Art”, Current Psychology , 14(1): 83–88. doi:10.1007/BF02686876
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Baker, Lucas and Fan Hui, 2017, “ Innovations of AlphaGo ”, on the DeepMind blog, 10 April 2017. Accessed 9 July 2021.
- Whitney Museum, 2002, The Migration Series: His Painting Method .
artificial intelligence | epistemology: virtue | ethics: virtue | imagination | Turing, Alan | Turing machines | Turing test
Copyright © 2023 by Elliot Samuel Paul < elliotspaul @ gmail . com > Dustin Stokes < dustin . stokes @ utah . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Psychology Discussion
Essay on creativity (910 words).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Creativity!
Creativity is a constructive process which results in the production of essentially a new product. Creativity is seeing or expressing new relationships. Creativity is not limited to the objects of everyday use, but it is an instrument for increasing knowledge. Creativity is possible in all areas of life like thinking, working, playing or social interaction.
In almost everything we do, we can change old relationships into new arrangements, add new items or forms to the old structure.
It is used in connection with Guilford’s divergent thinking.
Creativity involves at least three conditions:
(1) Production of a novel idea or a response, (2) this idea must solve a problem or accomplish some goal and (3) the original insights must be sustained and developed to the full. Creativity is extended over a period of time than limited to a brief episode. It is characterised by originality, adaptiveness and realisation.
Creativity is not equivalent to intelligence. A highly intelligent individual need not necessarily be creative.
Studies show that there is no significant correlation between the two. Creativity is more governed by the mode of thinking, rather than the amount of intelligence. However, creativity needs some amount of intelligence.
Fostering creativity: Educationists always emphasise the importance of developing creativity in children.
They are of the opinion that, the necessary steps must be taken by the concerned to foster creativity among them. It is found that development of creativity involves genetic as well as environmental factors.
Though we cannot alter genetic factors, we can alter behaviour through manipulation of the environment in which the individual lives. It is found that the culture, family atmosphere and education play significant roles in the development of creative talent. “Creativity flourishes when creative behaviour is encouraged.
It is also observed that by proper training creative thinking can be improved. Recognition of the creativeness of the child by the family members and teachers and encouraging the child to develop creative thinking yields good results as found by studies.
Gold (1965) has suggested the following guidelines for school personnel to foster creativity among pupils.
1. Rich environment which stimulates creative thinking is essential
2. Freedom from completely structured situation allows the child for free expression in art, science, etc. instead of assigning endless task to perform
3- Recognizing the creative child and reinforcing his creative abilities
4- Teachers should put emphasis on helping children see relationships, contrasts and sequences
5- Group contributions and interpersonal stimulation to be encouraged
6- Teachers must help children for creative play, dramas, drawings, paintings, music, dance, etc.
7. Role of self-discovery in creative activities must be recognized
8. Recognition of readiness for creativity
9. The importance of the whole community as a stimulus to creative effort has to be realized
10. Good and stimulating environment is necessary so that the child develops self-confidence
11. The teacher instead of expecting mere obedience, encourage for free expression, originality and variety.
Related Articles:
- Creative Thinking: 4 Stages of Creativity Thinking
- Essay on Creativity: Meaning, Nature and Stimulation
- Aptitude: Short Essay on Aptitude (450 Words)
- Intelligence: Essay on Intelligence (940 Words)
- Explore Majors
- Explore Careers
- Become Career Ready: Skills Employers Seek
- Write a Resume, CV, or Cover Letter
- Network with Professionals
- Prepare for an Interview
- Gain Experience
- Find an Internship or Co-op
- Prepare for Graduate School
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
- Career Champions
- Agriculture, Animals, Food, and the Environment
- Arts, Media, and Communication
- Business, Finance, Sales, and Marketing
- Doctoral Degree
- Education and Sports
- Government, Public Administration, and Law
- Healthcare and Wellness
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Let’s Explore
- Non-profit, Social Service, and other Careers for the Common Good
- Science, Data, and Technology
- Sustainability, Conservation, and Energy
- What are Affinity Communities
- Asian and Asian American Community
- Black Community
- First-Generation Students
- International Students
- Latine Community
- Middle Eastern and North African Community
- Native and Indigenous Community
- Neurodiverse Community
- Religiously Affiliated
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented and DACAmented Students
- Veterans and Service Members
- Request a Workshop
- Request a Class Assignment
- Career Events
- Career Fairs
- On-Demand Webinars
- Special Events & Series
- Events for Graduate Students
- Outcomes Data Collection
- Undergraduate Student Outcomes
- Our Vision, Mission, and Values
- Awards, Presentations & Memberships
- Professional Staff
- Graduate Assistants
- Student Interns
- Student Ambassadors
- Work at the Center
How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity
- Share This: Share How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity on Facebook Share How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity on LinkedIn Share How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity on X

Developing a consistent writing habit is helpful for success in content creation. Public or personal, you can develop a writing habit and bolster your creativity in different areas of your life. Read the full article How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity for practical strategies and insights to help build and maintain an effective writing practice.
Office Hours: 8AM – 5PM Career Coaching Hours: 8AM – 5PM * Evening appointments vary by semester. * If you require an accommodation to utilize any resource or to participate in any event, please contact our office.
(860) 486-3013 career@uconn.edu
Center for Career Development Wilbur Cross Building, Rm 202 233 Glenbrook Road U-4051 Storrs, CT 06269
Troy students show creativity in Juneteenth arts & essay contest
Troy students create juneteenth artwork.
Although Juneteenth is part of our country’s history, you won’t find it in every classroom’s curriculum.
So teachers in the Troy City School District got creative and made it fun for students with an arts & essay contest.
The winner was a fourth grader who wrote “Inside A Life of a Slave.”
The following is an excerpt from that poem.
Imagine this, you’re at your house, the people come, they chain you up, you try to resist but then you realize they have the will to you.
They put you on a boat, you make a mental note. You see people falling out, people are already withering out. You think I’m going to make it?
But there’s no doubt about it because in your heart, you know, it’s gonna shout it that you are making it. That’s the only thing keeping your soul alive.
This is one of the more than 75 projects submitted this year for Troy school districts’ 2024 Juneteenth Arts & Essay Contest.
There were 18 winners.
Another one of those winners, Atiqah Umarmukhtar, is working with her teachers on these dolls that are covered in Juneteenth freedom colors.
They are also selling two Juneteenth T-shirts. All the funds from the sales are split and given to the children in the contest.
The contest is one of the initiatives to come from the Troy Teachers Association’s Together We Rise program. Fourth-grade teacher Tina Wilcox and sixth-grade teacher Carrie Dwyer said the district needed this program.
Learn more how the program came together and what it does by watching video of Faith King’s story.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews honors local students for creative achievements
More than 70 students representing private and public schools throughout the county were honored for their creativity Thursday by the Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews.
During its annual meeting at the Wells Fargo branch on South County Road, the nonprofit organization recognized elementary, middle and high school students for their excellence in art, music, writing and speaking as part of its annual Essay and Creative Arts Competition.
Awards were distributed in seven different categories: art (painting and drawing); art (poster); essay; music performance; poetry; spoken word; and video.
Related: Palm Beach nonprofits hand out college scholarships to children of town employees
Students were recognized as first, second and third-place finishers and honorable mention awardees. Winners received cash prizes ranging from $25 to $100, said Sherri Gilbert, Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews executive director.
Teachers also were honored at Thursday's event, with each receiving a cash prize to show appreciation for their efforts in the classroom, Gilbert added.
This year's theme was "Impact: The Power of our Words and Actions."
"It's an interesting theme," Gilbert said. "I feel like I've been surrounded by that in the world at large, with cyberbullying and things like that."
The Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews has been handing out student awards for nearly three decades, Gilbert said, and this year's competition drew more than 300 submissions.
A handful of students collected their awards in person Thursday, Gilbert said, and they had the opportunity to mingle with Fellowship members and supporters and learn about the organization.
"It's nice, because people in the community, all the parents and families and the kids, get to see what we do, especially for young people," Gilbert said. "And then our board members and members of the community get to meet these teachers and honor the educators. It's a real nice mix."
First-place finishers were:
Art (painting and drawing) — Isabella Abalo, grade 7, Bak Middle School of the Arts; art (poster) — Colette Conde, grade 6, Bak Middle School of the Arts; essay (grade 6), Mae Havlicek, The Benjamin School; essay (grade 7), Annabel Brown (The Benjamin School); essay (grade 8), Liv Heurich, The Benjamin School, and Tara Huynh, Western Pines Middle School; essay (high school), Cabo Kujawa, The Benjamin School); music performance, Celeste Campos, Gabriela Chavez and Bryan Hernandez, grade 7, St. Luke Catholic School; poetry (haiku), Finn Martin, The Benjamin School); poetry (high school), Michael Louis, grade 12, The Benjamin School; poetry (middle school), Brody Dunhill, grade 6, Rosarian Academy, Tessa Brown, grade 8, Rosarian Academy, Beatrice George, grade 8, Rosarian Academy, Caroline Yohe, grade 8, Rosarian Academy; spoken word, Nick Ferik, grade 7, Rosarian Academy, Santino Merchan, grade 7, Rosarian Academy, Andrew Sevald, grade 7, Rosarian Academy, Cerina Deitz, grade 6, Rosarian Academy, Brynn Saleeby-Russell, grade 6, Rosarian Academy, Khloe Ugarte, grade 6, Rosarian Academy; video, Cameron Lencheski, grade 8, Rosarian Academy.
The Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews is a nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting fellowship, understanding, and respect among all religions and cultures, and bringing the community together through education, dialogue, and interaction. For information, visit www.palmbeachfellowship.net/ .
Jodie Wagner is a journalist at the Palm Beach Daily News , part of the USA TODAY Florida Network. You can reach her at [email protected] . Help support our journalism. Subscribe today .
This article originally appeared on Palm Beach Daily News: Palm Beach nonprofit honors local students for creative achievements
More From Forbes
How ai boosts your creative potential.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Creativity is a vital soft skill that enhances our interactions with AI and is equally enhanced by ... [+] AI tools.
Creativity is one of the traits that makes us uniquely human. Creativity enables humans to express their individuality. It allows humans to express a wide range of emotions. It involves a willingness to consider new ideas, experiences, and perspectives. Individuals can use their imagination to think about new ideas, concepts, and scenarios.
As AI, and generative AI, continues to touch many aspects of our personal and professional lives, we are able to do things such as writing, generating reports, creating images and presentations with ease. What once required years of experience and certain skills to create, now can be done fairly simply with the help of AI.
The transformative power of AI lies in its ability to unlock new creative potentials and augment human ingenuity. Creativity enhances our interactions with AI systems, particularly genAI and prompt engineering. But AI also has the ability to enhance human creativity. As you look at it from both sides, it becomes evident that creativity is an indispensable soft skill in the age of AI, driving innovation and collaboration.
The Role Creativity plays with Generative AI
Creativity plays a crucial role in effectively interacting with AI, particularly genAI. Innovative thinking is essential for crafting unique and effective prompts, which directly influences the quality and relevance of AI outputs. For example, when using genAI to create images or write stories, the specificity and creativity of the prompts can lead to diverse and compelling results. Instead of a simple prompt like "create an image of a tree," a more creative prompt such as "Create a surreal forest scene with glowing trees and mystical creatures. Have the mood of the scene be peaceful and the lighting of the scene be dim." can inspire the AI to generate more imaginative and engaging content and images.
Creative prompt engineering has led to some remarkable results. AI-generated and AI-assisted artworks have won awards and competitions . AI-assisted writing tools are helping authors develop unique narratives, brainstorm ideas, and help develop outlines. AI is helping marketers write better promo, create personalized ad content, and social media posts. AI is helping casual musicians and composers create new music in a variety of different styles and genres. AI is helping filmmakers and video producers to automate editing processes, generate special effects, and overall enhance visual storytelling. These examples highlight how creative inputs can significantly enhance AI outputs, demonstrating the importance of creativity in the interaction with generative AI systems.
Dana White Says Former Champion Just Had ‘His Last Fight’
Ufc 303 results: ufc rising star scores amazing 19-second ko, black people’s responses to trump’s notion of ‘black jobs’, being more creative will help you with generative ai.
On the flip side, being more creative is going to help you be better with genAI and prompting. Increasingly, the necessity and enhancement of creativity with AI is being understood as is expressed in this AI Today podcast episode. The beauty of prompt engineering lies in its low stakes for failure. This encourages you to embrace your creative side, try “out of the box” ideas, and experiment with different prompt patterns and tools. Don't hesitate to test various approaches, even those outside your comfort zone.
Study successful prompts used by others, and try them out yourself. Foster creativity within your organization by sharing your own successful prompts. This transparency helps everyone see prompts, prompt patterns, and techniques work well for different situations. Drawing inspiration from others is crucial, as creativity thrives on diverse inputs. Observing how different prompts are structured can spark innovative ideas and different viewpoints and ways of thinking or approaching problems. Explore the diverse features of LLMs, such as uploading files to extract information and outputting results into tables or other formats.
Most importantly, don’t let fear or intimidation hold you back. You might hesitate to try prompt engineering due to fear of mistakes, judgment, or feeling overshadowed by more experienced peers. Instead, view each prompt as a learning opportunity to refine your technique and expand your possibilities. Get creative, experiment, and consider using LLMs in ways you might not have thought of, such as document analysis, sentiment analysis, translation, or automating routine customer interactions.
The Synergy Between Human Creativity and AI
Creativity is a vital soft skill that enhances our interactions with AI and is equally enhanced by AI tools. The mutual enhancement of creativity and AI interaction can lead to innovative thinking and remarkable outcomes. As we continue to integrate AI into various aspects of life and work, developing creativity, alongside other soft skills such as communication and critical thinking, is crucial for maximizing the potential of these powerful technologies. By embracing and cultivating these skills, we not only stay ahead in an AI-driven world but also unlock the full potential of human-AI collaboration. Together, human creativity and AI capabilities can truly create some remarkable outcomes.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- DOI: 10.5861/ijrsll.2024.022
- Corpus ID: 270340931
A study of life skills, learning abilities, and career planning of Chinese college students
- Published in International Journal of… 15 June 2024
- Education, Linguistics
4 References
The correlation of metacognitive ability, self‐directed learning ability and critical thinking in nursing students: a cross‐sectional study, a qualitative research study on the importance of life skills on undergraduate students’ personal and social competencies, development of higher education students’ creative abilities in learning and research activity., developing career vision roadmap for student career planning, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

COMMENTS
7. Art and Creativity. When people say creativity, they usually think about art because it involves imaginative and expressive actions. Art strongly indicates a person's ongoing effort and emotional power. To write this essay effectively, show how art relates to a person's creativity.
This type of essay offers a unique platform to focus on personal insights, historical analysis, or the impact of creativity across various fields. Engaging Prompts to Kickstart Your Creativity Essay. Prompt 1: Discuss how a moment of creative insight led to an unexpected outcome or discovery in your personal life or in a historical context.
Here are eight lessons from my research. 1. Creativity is not so much an innate ability as it is an attitude toward life. There are lots of people with "creative abilities," but they lack what the late Professor Roger Schank called the "creative attitude," so they do not manifest their creativity. By 1995, I proposed, in collaboration ...
4. Go outside: Spending time in nature and wide-open spaces can expand your attention, enhance beneficial mind-wandering, and boost creativity. 5. Revisit your creative ideas: Aha moments can give you a high—but that rush might make you overestimate the merit of a creative idea.
It's usually defined in terms of imagination and innovation and especially related to the production of artwork. Yet creativity isn't necessarily about art per se but is a quality of being ...
What Does Creativity Mean to You. Creativity, an intricate tapestry of imagination and innovation, holds a unique significance for each individual. It is a concept that transcends the boundaries of convention, sparking curiosity and igniting the flames of inspiration. In this essay, we embark on a journey to unearth the meaning...
Thesis No. 3: Creativity permeates life. Creativity fills our lives like ocean water fills the grains of a sand castle — saturating the spaces between this moment and the next, this action and ...
Here is an outline that will help you structure your creative writing essay, whether it's a poem, a personal essay, a short story, or a speech. Introduction 📘. Briefly introduce the creative writing piece you've chosen (poem, story excerpt, speech introduction, etc.) (Optional) Hint at the main theme or central message you want to convey.
In this provocative collection of essays, an interdisciplinary group of eminent thinkers and writers offer their thoughts on how embracing creativity—tapping into the "originality of everyday life"—can lead to improved physical and mental health, to new ways of thinking, of experiencing the world and ourselves.
Creativity truly is a way of life, not an activity or a collection of traits. It's not something to be relegated to certain days or times, comprising only a small portion of our waking hours. It ...
Summary. The growing field of scholarship on "everyday creativity" sorts into two strands: (1) studies of "little-c" and "mini-c" creativity - the many products and ideas people create in their everyday lives and (2) studies of the natural ecology of creativity - how creative products, both eminent and humble, come about in ...
Creativity is about living life as a journey into seeing and communicating the extra-ordinariness of the simplest, most every day acts. It is also a way of living life that embraces originality and makes unique connections between seemingly disparate ideas. Essentially, creativity is a tool that can make work fun, life easier, save you from ...
Effective creativity training and workshops emphasize that creativity is a way of living and leads to pleasure in life-long learning. Developing creativity through play. The basic components of the creative process are involved in play. It generates new experimentation, possibilities, and exploration of unlimited fantasy and reality.
15 ideas for expressin creativity in everyday life: 1. Make your immediate surroundings as beautiful or eccentric as you can. Experiment with your sense of color, texture, and line. Add an element of surprise or quirkiness to your home decor. The unexpected can jolt you out of complacency and into inspiration. 2.
Abstract. Creativity pervades human life. It is the mark of individuality, the vehicle of self-expression, and the engine of progress in every human endeavor. It also raises a wealth of philosophical questions, but curiously, it hasn't been a major topic in contemporary philosophy. The Philosophy of Creativity ventures to change that.
In a rapidly changing world, creativity is important for people and society on many levels - it can help to generate personal satisfaction and be important for economic development. This is why ...
Essay on Art and Creativity. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Children deserve an education rich in arts opportunities. There is a direct correlation between exposure to the arts and creating successful, well-rounded students as well ...
1184 Words5 Pages. Creativity is important in everyday life. It can be used to describe an attitude, a process, a product, a skill, a set of personality traits, and a set of environmental conditions. Everyone is born with the potential to be creative. There are different ways to help enhance creativity at different stages throughout life.
Energy: Creative people tend to possess a great deal of both physical and mental energy. However, they also tend to spend a great deal of time quietly thinking and reflecting. Intelligence: Psychologists have long believed that intelligence plays a critical role in creativity. In Terman's famous longitudinal study of gifted children, researchers found that while high IQ was necessary for ...
The constitutive argument. Creativity is a disposition—involving both the ability and the motivation—to produce things that are new and valuable, and to do so in ways that express one's agency through "the exercise of choice, evaluation, understanding, and judgment" (Gaut 2014a: 273). At least some people can learn to enhance their creative motivation.
Well-being and creativity. Creativity contributes to well-being not only through its relationship with positive emotions, but it can enhance one's sense of flourishing or eudemonic well-being, an additional component of overall psychological welfare concerned with having meaning and purpose in one's life, feeling competent, and having positive relationships (Diener et al., Citation 2010).
ADVERTISEMENTS: Essay on Creativity! Creativity is a constructive process which results in the production of essentially a new product. Creativity is seeing or expressing new relationships. Creativity is not limited to the objects of everyday use, but it is an instrument for increasing knowledge. Creativity is possible in all areas of life like thinking, working, […]
Public or personal, you can develop a writing habit and bolster your creativity in different areas of your life. Read the full article How Writing Regularly Can Improve Your Creativity and Clarity for practical strategies and insights to help build and maintain an effective writing practice. ...
So teachers in the Troy City School District got creative and made it fun for students with an arts & essay contest. The winner was a fourth grader who wrote "Inside A Life of a Slave ...
For Your Essay: To infuse humor and self-reflection into your essay, start by identifying an ordinary experience or object and think about how it relates to your life. Write down funny or ...
The Palm Beach Fellowship of Christians and Jews honored local students Thursday as part of its annual Essay and Creative Arts Competition.
Creativity in the Gorge is a monthly feature in Columbia Gorge News that features creative works from readers of all ages. Send your submissions of artwork, short prose pieces and poetry to [email protected], subject: Creativity in the Gorge.
Creative prompt engineering has led to some remarkable results. AI-generated and AI-assisted artworks have won awards and competitions.AI-assisted writing tools are helping authors develop unique ...
Social media has become an integral part of daily life in the digital age, especially for the younger generation. Platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, TikTok, and Facebook provide endless content streams, encouraging connectivity and creativity, but they also present significant mental health challenges, especially for their younger users.
DOI: 10.5861/ijrsll.2024.022 Corpus ID: 270340931; A study of life skills, learning abilities, and career planning of Chinese college students @article{Xue2024ASO, title={A study of life skills, learning abilities, and career planning of Chinese college students}, author={Hai Xue}, journal={International Journal of Research Studies in Language Learning}, year={2024}, url={https://api ...